Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
REVIEWS
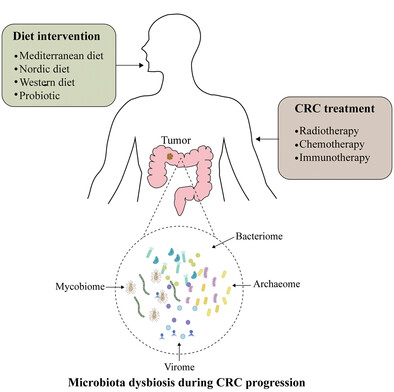
Development and treatment of colorectal cancer: Insights from multi-kingdom microbiota
- First Published: 12 April 2023
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Studying host genetic background effects on multimorbidity of intestinal cancer development, type 2 diabetes and obesity in response to oral bacterial infection and high-fat diet using the collaborative cross (CC) lines
- First Published: 14 February 2021
REGULAR ARTICLES
SHORT COMMUNICATION
A rare case of giant panda cancer: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- First Published: 11 November 2022
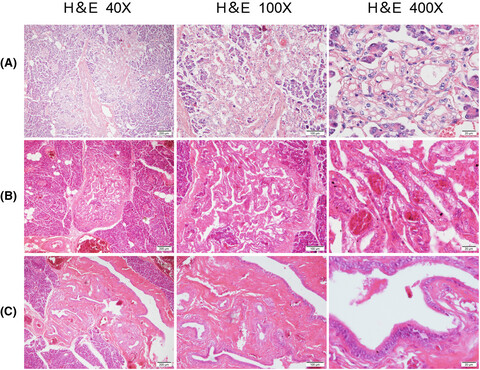
Pancreatic tissues' tumors exhibited three different situations. (A) Several glandular tubular adenocarcinoma structures could be seen in pancreatic tissue. (B) Tubular area could be seen in the pancreas, exhibiting papillary growth in the area. (C) The ductal epithelium in the pancreas was replaced by high columnar mucous cells, which showed pseudostratified columnar epithelial cells.
COLORECTAL SURGERY
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on colorectal cancer diagnosis and management: a Binational Colorectal Cancer Audit study
- First Published: 07 July 2021
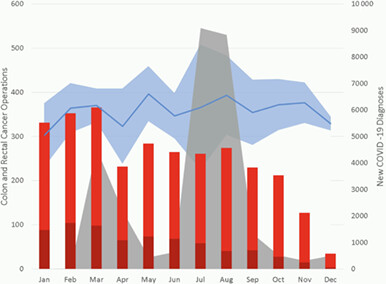
This paper examines the impact of COVID-19 on colorectal cancer diagnosis and management in Australia and New Zealand by comparing patients receiving colorectal cancer surgery during the pandemic against averages from the same period over the preceding three years. The key findings are a significant reduction in total colorectal cancer operations, particularly in rectal cancers, cancers presented at a more advanced stage and operations were more likely to be emergencies. The response to COVID-19 has had measurably negative effects on the diagnosis and management of colorectal cancer in two countries that have had significantly fewer COVID-19 cases than many other countries.
Sarcopenia is a strong predictive factor of clinical and oncological outcomes following curative colorectal cancer resection
- First Published: 07 March 2021
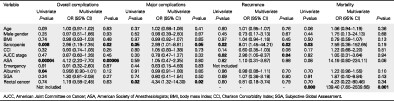
Sarcopenia as assessed on computed tomography was investigated as a predictor of outcomes following colorectal cancer resection. Associations were found with length of stay, complications and recurrence at 1 year. Sarcopenia was found to be a better predictive factor for recurrence and morbidity than other traditional measures of nutrition.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
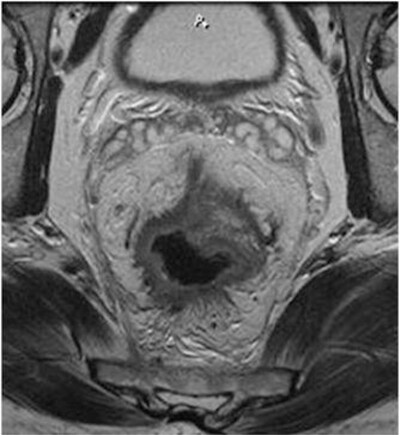
Pictorial essay on MRI local staging of rectal carcinoma: An easy approach
- First Published: 18 April 2022
REVIEWS
The therapeutic effects of berberine for gastrointestinal cancers
- First Published: 13 March 2023
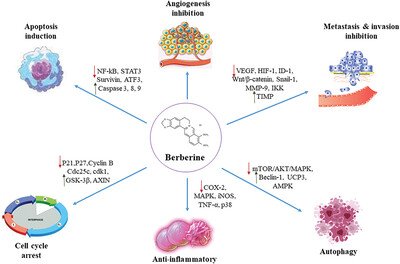
Multiple effects of berberine (BBR) as a gastrointestinal (GI) cancer therapeutic agent. BBR acts as a potential anti-GI cancer agent by inducing apoptosis, autophagy, and cell-cycle arrest, as well as metastasis and angiogenesis inhibition. It plays an important role in suppressing GI cancer cells.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
A global assessment of recent trends in gastrointestinal cancer and lifestyle-associated risk factors
- First Published: 25 September 2021
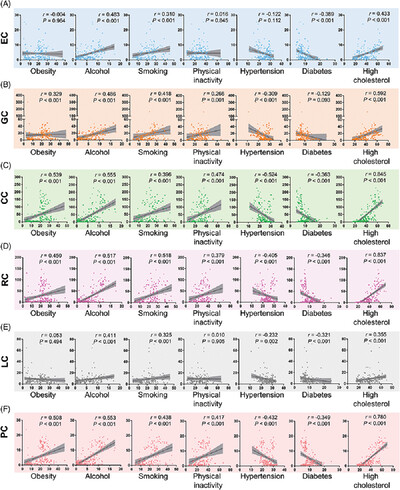
Prevalence of gastrointestinal cancers was positively correlated with national human development index levels, but negatively with hypertension and diabetes rates. Age-specific trends were observed in stomach cancer and esophagus cancer for incidence and in liver cancer and pancreatic cancer for mortality, as well as sex-specific trends for stomach cancer and pancreatic cancer in the elder.These findings suggest that future research has to focus on the specific etiology of gastrointestinal cancers behind these epidemiologic transitions and improve therapeutic strategies for patients with comorbid metabolic diseases.
Survival trends of patients with non-metastatic gastric adenocarcinoma in the US and European countries: the impact of decreasing resection rates
- First Published: 06 June 2022
Carcinogenesis
Frequent loss of metastatic ability in subclones of Apc, Kras, Tgfbr2, and Trp53 mutant intestinal tumor organoids
- First Published: 28 December 2022
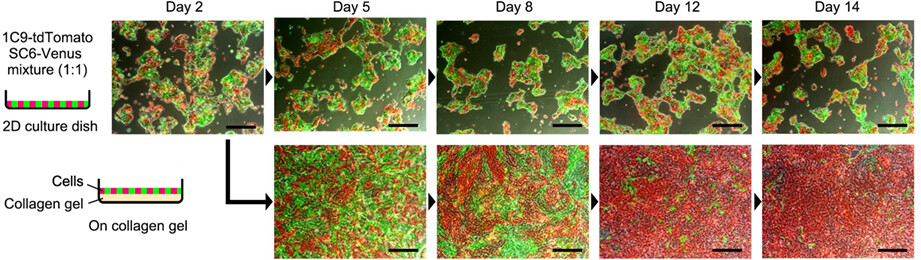
We have performed subcloning of metastatic intestinal tumor-derived organoids from single cells. Notably, approximately 30% of subclones showed loss of metastatic ability associated with growth suppression, although driver mutations were not affected. The results suggest that cancer evolution is regulated not only by positive selection but also by negative selection.
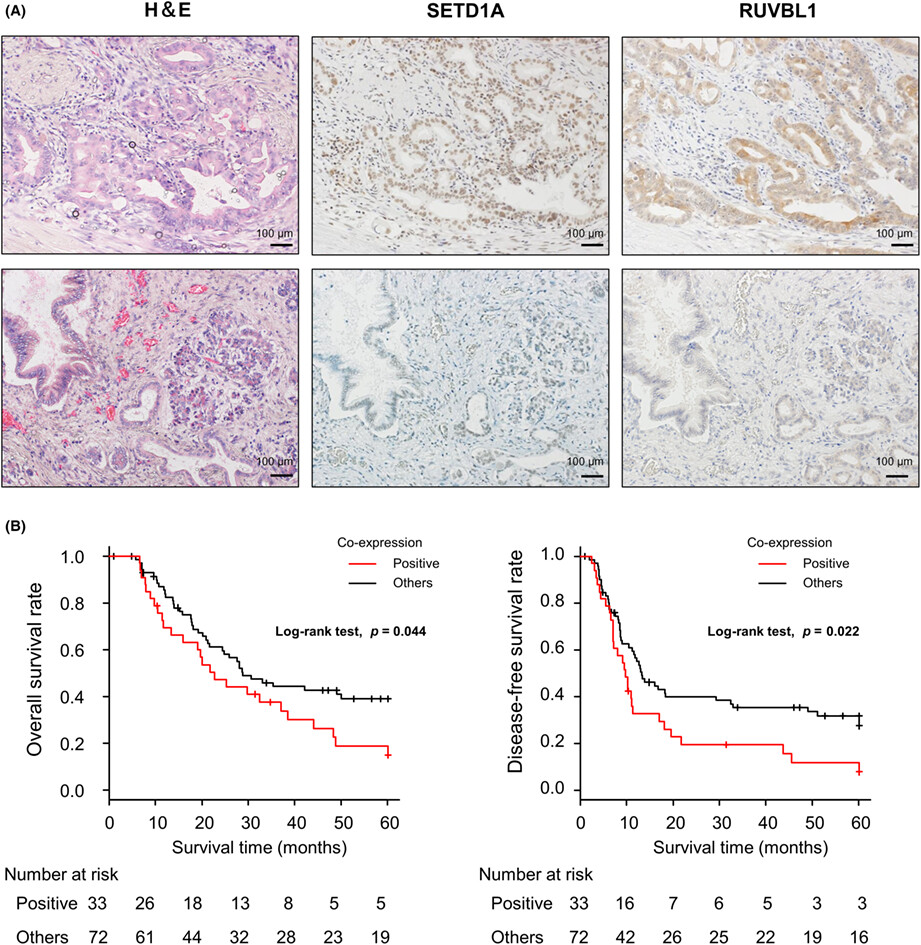
Identification of a novel target of SETD1A histone methyltransferase and the clinical significance in pancreatic cancer
- First Published: 22 October 2022
Determinants of survival outcomes among esophageal cancer patients at a national referral hospital in Kenya
- First Published: 20 November 2022
REVIEW ARTICLES
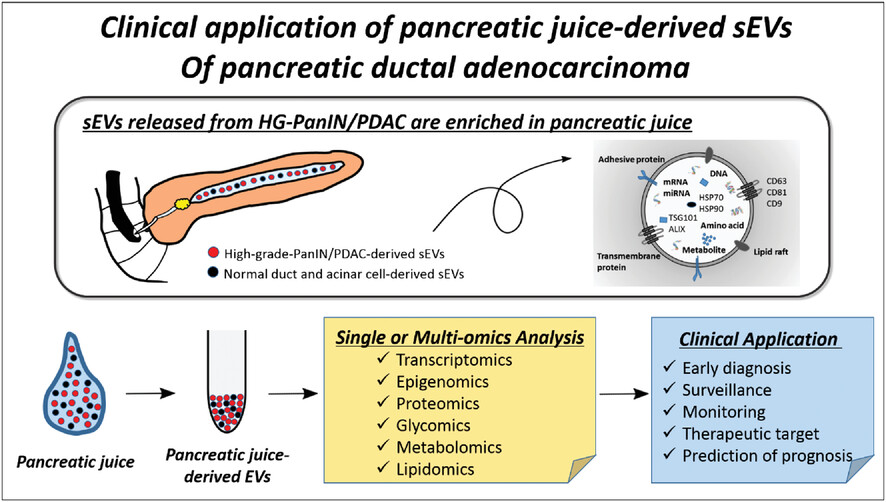
Clinical application of pancreatic juice-derived small extracellular vesicles of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- First Published: 28 March 2023
COMMENTARY
The crosstalk between the RNA demethylase, non-coding RNAs, and transcription factors in gastric cancer: An ALKBH5 perspective
- First Published: 11 April 2023
RESEARCH ARTICLES
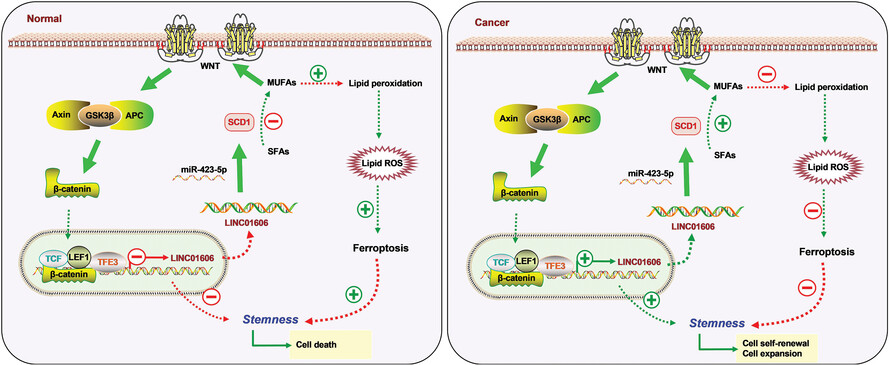
Long noncoding RNA LINC01606 protects colon cancer cells from ferroptotic cell death and promotes stemness by SCD1–Wnt/β-catenin–TFE3 feedback loop signalling
- First Published: 29 April 2022
-
LINC01606 functions as an oncogene to facilitate malignant phenotypes of colon cancer cells by enhancing tumour cell stemness and anti-ferroptosis by Wnt/β-catenin signalling;
-
LINC01606 protects colon cancer cells from ferroptotic cell death by increasing the formation of monounsaturated fatty acids;
-
LINC01606–Wnt/β-catenin–TFE3 positive feedback regulatory loop signalling blocks ferroptosis and promotes stemness.
Phosphoproteomic analysis of metformin signaling in colorectal cancer cells elucidates mechanism of action and potential therapeutic opportunities
- First Published: 13 February 2023
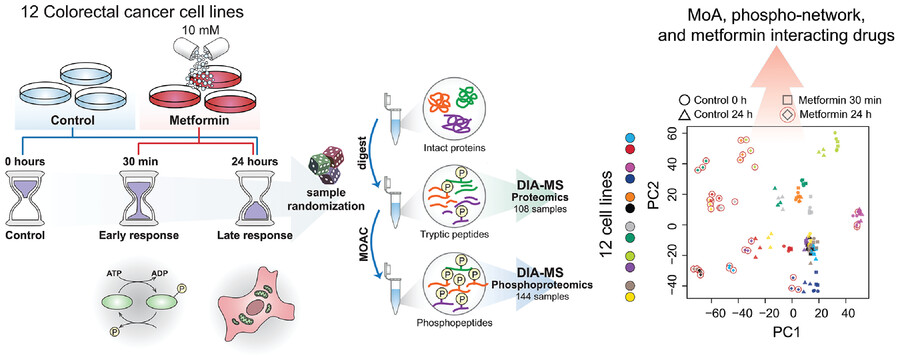
- An in-depth proteomic and phosphoproteomic resource on metformin signaling in colorectal cancer (CRC).
- The phosphoproteomic response to metformin was highly heterogeneous in CRC cell lines.
- Establishing a phosphorylation site-specific MetScore, which identified 55 most significant metformin signature sites.
- Leveraging the phosphoproteomics to discover potential metformin∼drug interactions in CRC, e.g., navitoclax.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Effect of hospital-based case management on psychosocial wellbeing and treatment outcomes in colorectal cancer patients: A quasi-experimental study
- First Published: 06 September 2022
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Localized stomach cancer: Perioperative or postoperative approach? A meta-analysis of phase III studies
- First Published: 18 March 2022
The burden of gastrointestinal diseases in Japan, 1990–2019, and projections for 2035
- First Published: 07 March 2023
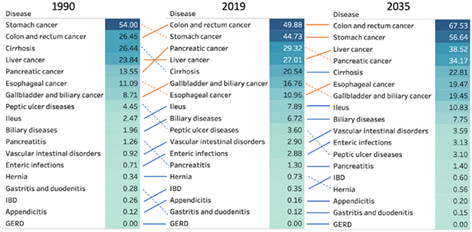
Disease burden estimation allows clinicians and policymakers to plan for future healthcare needs. Our study provides comprehensive estimates of the burden of gastrointestinal diseases in a super-aging society focusing on cancers and other chronic gastrointestinal diseases. Currently, colorectal, gastric, pancreatic, and liver cancers are the focus of early detection and treatment.