Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Articles
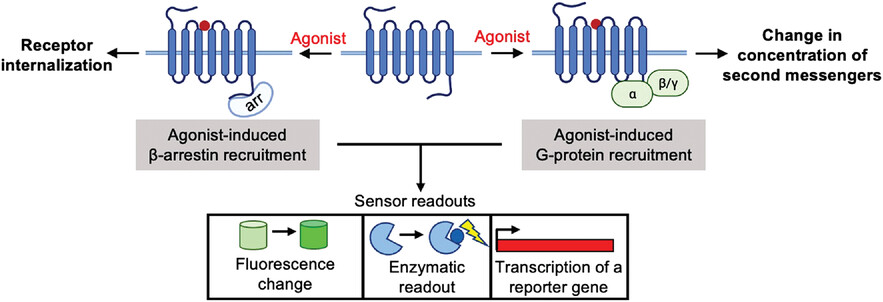
Genetically encoded tools for in vivo G-protein-coupled receptor agonist detection at cellular resolution
- First Published: 29 November 2022
The clinical potential of optogenetic interrogation of pathogenesis
- First Published: 02 May 2023
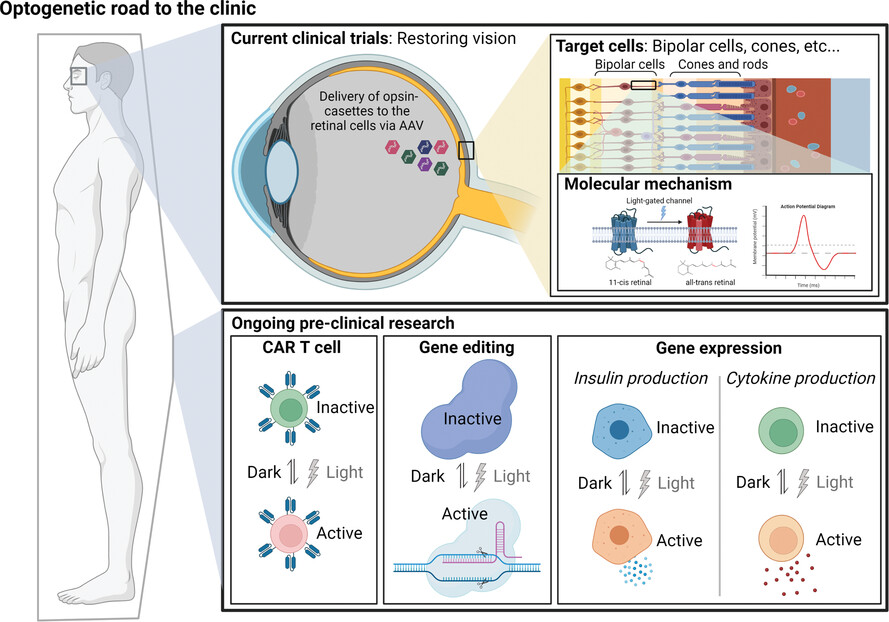
- Opsin-based and opsin-free optogenetics employs light to modulate membrane conductance and protein-protein interaction.
- Clinical trials focus on treating blindness due to the easy delivery of light.
- Protein engineering improves the photophysics and biocompatibility of photoactivatable proteins.
- Opsin-free optogenetics expands clinical applications such as the chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) and clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)-based genomic engineering and transcriptional regulation.
Boolean logic in synthetic biology and biomaterials: Towards living materials in mammalian cell therapeutics
- First Published: 29 June 2023
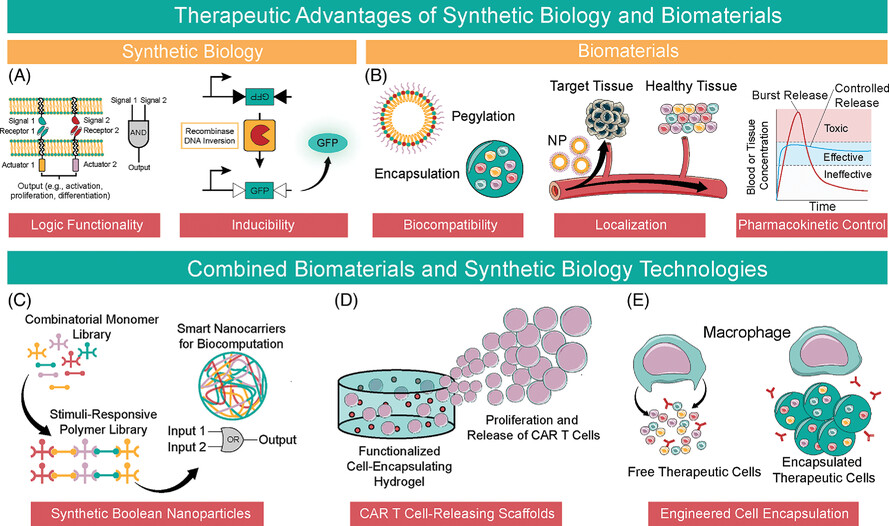
The intersection of synthetic biology and biomaterials promises to enhance safety and efficacy in novel therapeutics. By using Boolean logic in both cellular therapy and drug delivery devices, researchers have achieved better safety and efficacy outcomes. We expect that these collaborations will continue to grow and realize the next generation of living biomaterial therapeutics.
Development of immune-related cell-based machine learning for disease progression and prognosis of alcoholic liver disease
- First Published: 28 June 2023
Split-Cas9-based targeted gene editing and nanobody-mediated proteolysis-targeting chimeras optogenetically coordinated regulation of Survivin to control the fate of cancer cells
- First Published: 24 August 2023
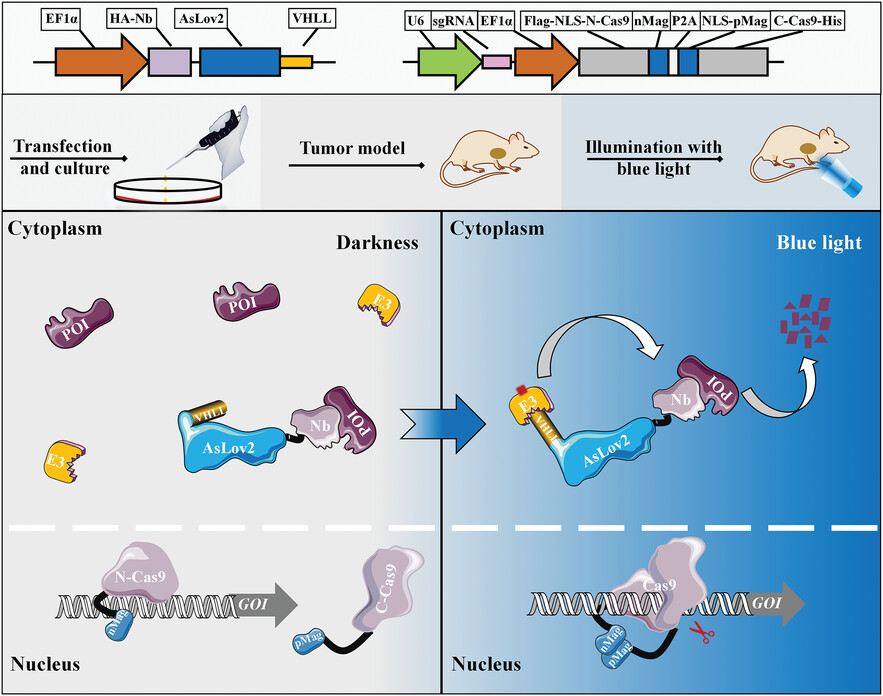
-
The photoactivatable PROTACs-Like (paProtacL) target protein via nanobodies and can controllably induce degradation of POI (protein of interest) under blue light.
-
The photoactivatable Cas9 (paCas9) system can edit GOI (gene of interest) in the nucleus in a controlled manner under blue light irradiation.
-
When paProtacL is combined with the paCas9 system, it can minimize the expression of the target protein.
RNA interference therapy for targeting ANGPTL3 and atherogenic lipoproteins: Findings and implications of a recent phase I study
- First Published: 27 November 2023
Optimization strategies and advances in the research and development of AAV-based gene therapy to deliver large transgenes
- First Published: 15 March 2024
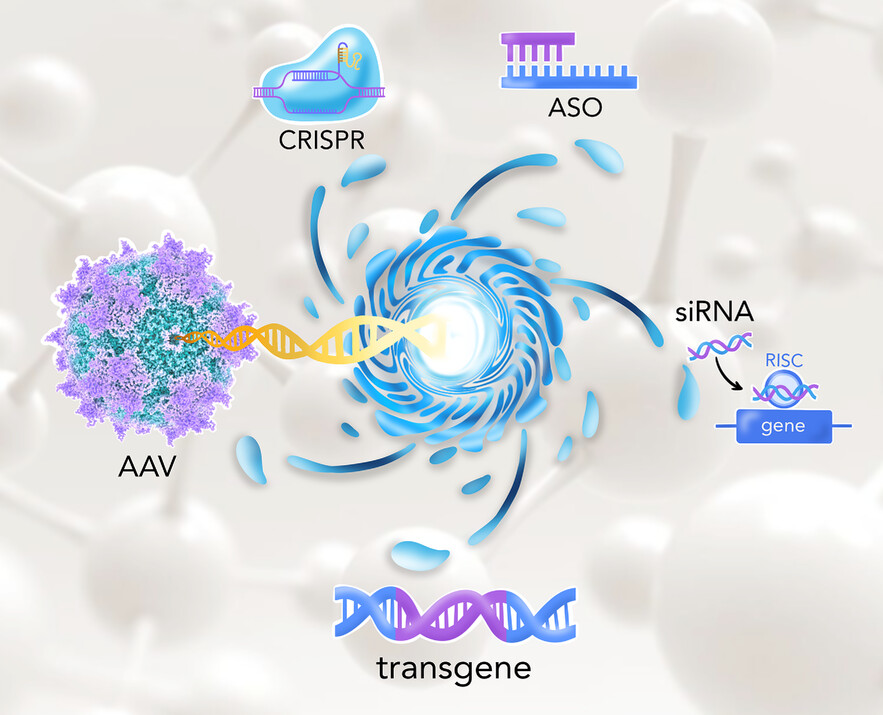
- AAV-based gene therapy are on increasing demand to cover the needs in the patient communities with inherited genetic disorders.
- Single AAV vectors delivering functional gene copy are the most popular approach in RnD pipeline.
- Multiple split vectors, inteins and trans-splicing strategy so far underperform monovector AAV-delivery.
- Neural networks guided by protein fitness data facilitate de novo protein design to fit into AAV capsid.
Single-cell and spatial alterations of neural cells and circuits in clinical and translational medicine
- First Published: 22 May 2024
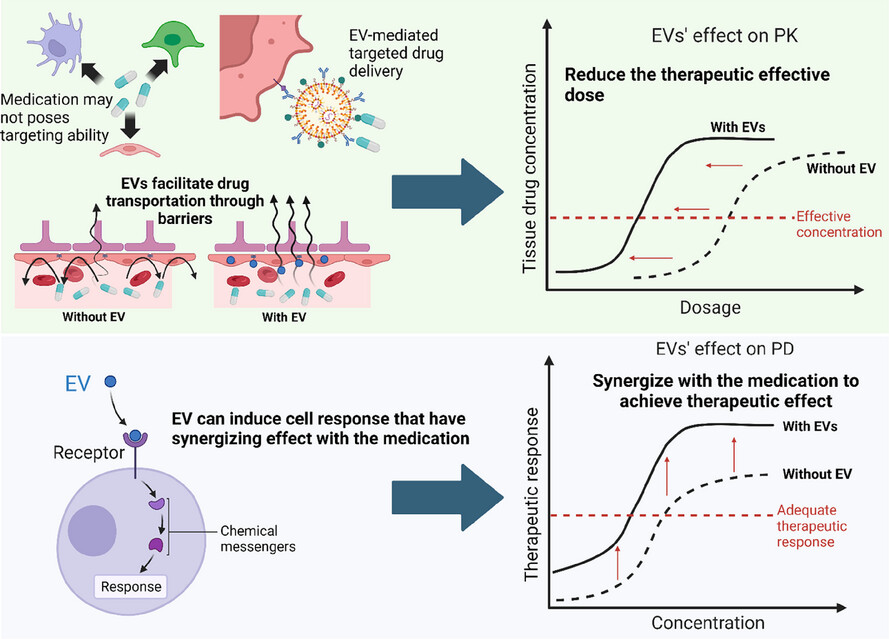
Extracellular vesicles as the next-generation modulators of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of medications and their potential as adjuvant therapeutics
- First Published: 21 August 2024
Insight into prostate cancer osteolytic metastasis by RelB coordination of IL-8 and S100A4
- First Published: 16 October 2024
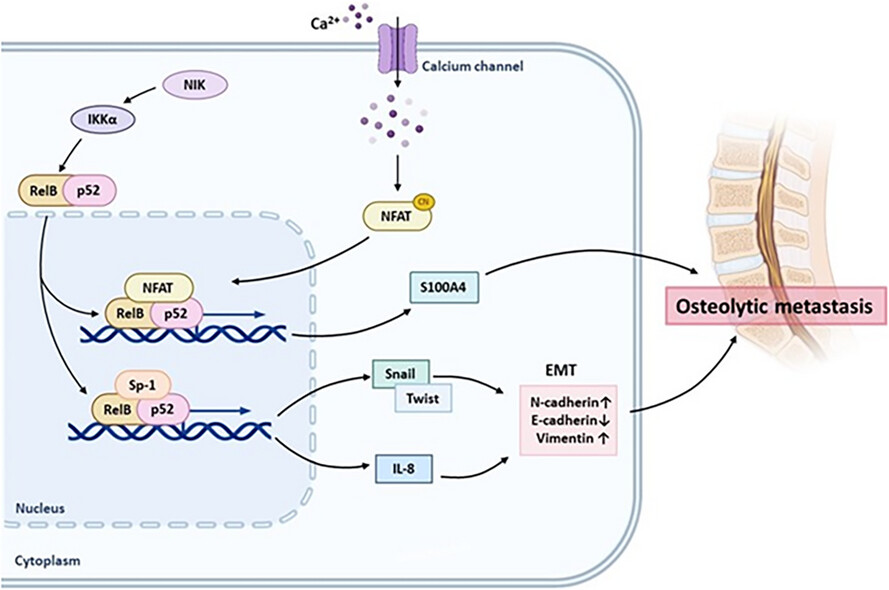
- RelB activates inflammatory signalling by upregulating IL-8 and suppressing AR.
- RelB upregulates S100A4 by cooperating with NFATC1.
- IL-8 boosts EMT by activating Snail 1 and Twist 1, and S100A4 exacerbates osteolytic metastasis via calcium consumption.
- RelB harnesses IL-8 and S100A4 to drive PCa osteolytic metastasis.