Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Editors’ Collection 2022
Combination therapy with chitosan/siRNA nanoplexes targeting PDGF-D and PDGFR-β reveals anticancer effect in breast cancer
- First Published: 22 November 2022
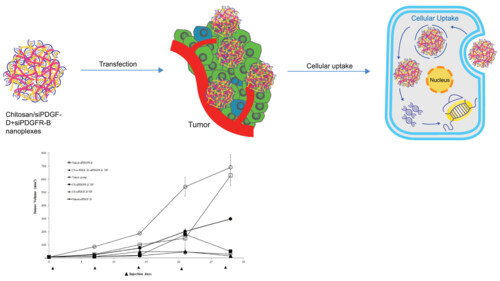
The suppression of Platelet derived growth factors (PDGF)-D signaling pathway with small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) targeting both PDGF-D and PDGF receptor (PDGFR)-β is a promising strategy for anticancer therapy. The downregulation of PDGF-D and PDGFR-β with chitosan/siRNA nanoplex formulations reduced proliferation and invasion in breast cancer cells and markedly decreased in tumor volume in the in vivo breast tumor model.
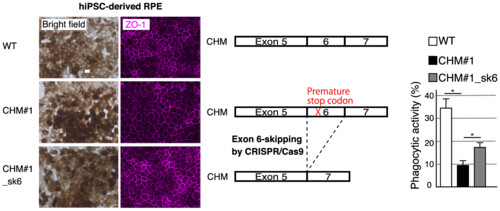
Evaluation of CRISPR/Cas9 exon-skipping vector for choroideremia using human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived RPE
- First Published: 22 November 2022
Impact of ABCB1, ABCC1, ABCC2, and ABCG2 variants in predicting prognosis and clinical outcomes of north Indian lung cancer patients undergoing platinum-based doublet chemotherapy
- First Published: 31 October 2022
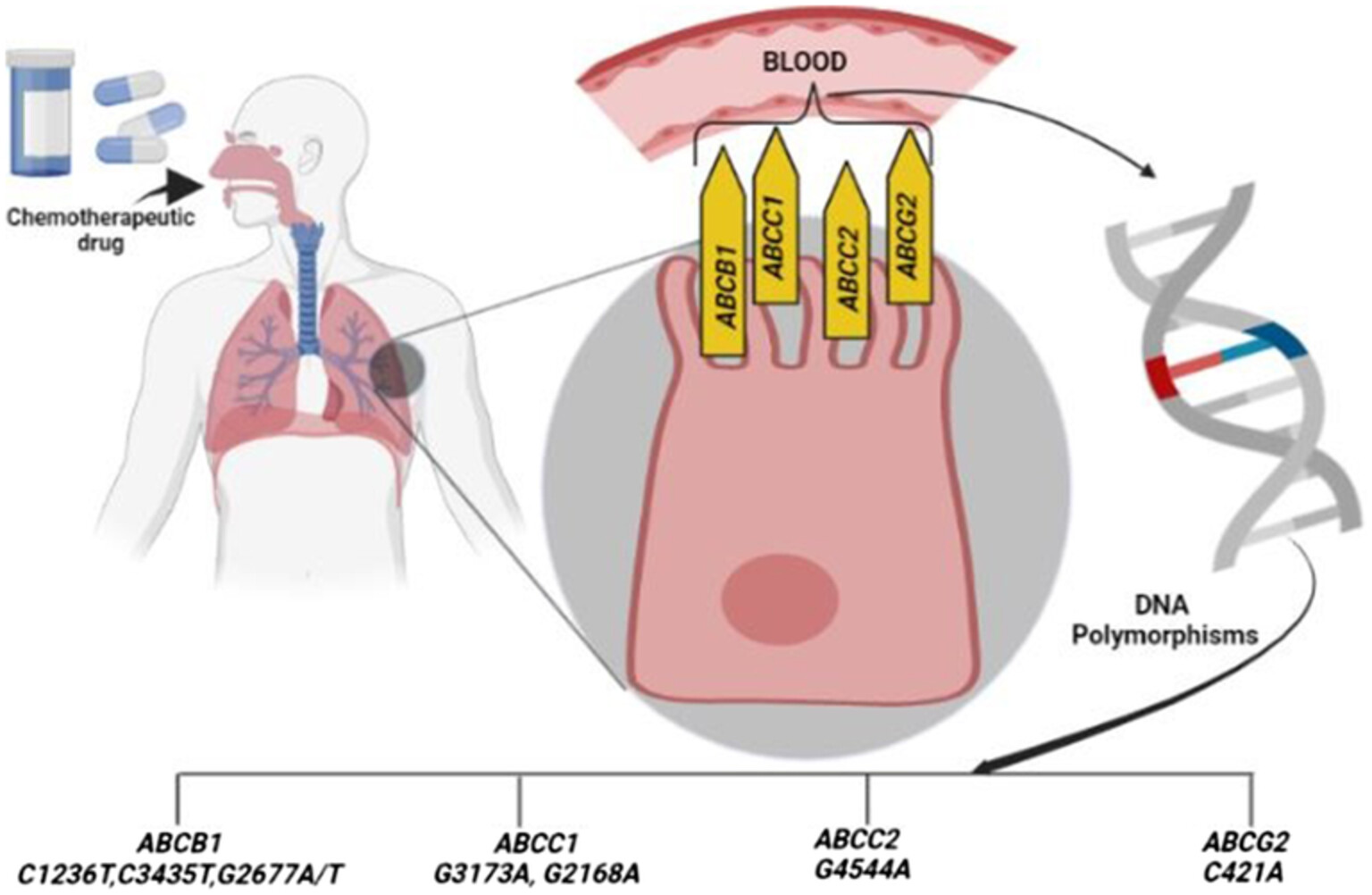
ABC transporters are actively involved in transporting chemotherapeutic agents through biological membranes. The ABCB1, ABCC1, ABCC2, and ABCG2 genes are expressed in human lungs and gene mutations influence drug efflux. The polymorphisms of ABC genes play a crucial role in predicting the overall survival and clinicopathological outcomes in lung cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy treatment.
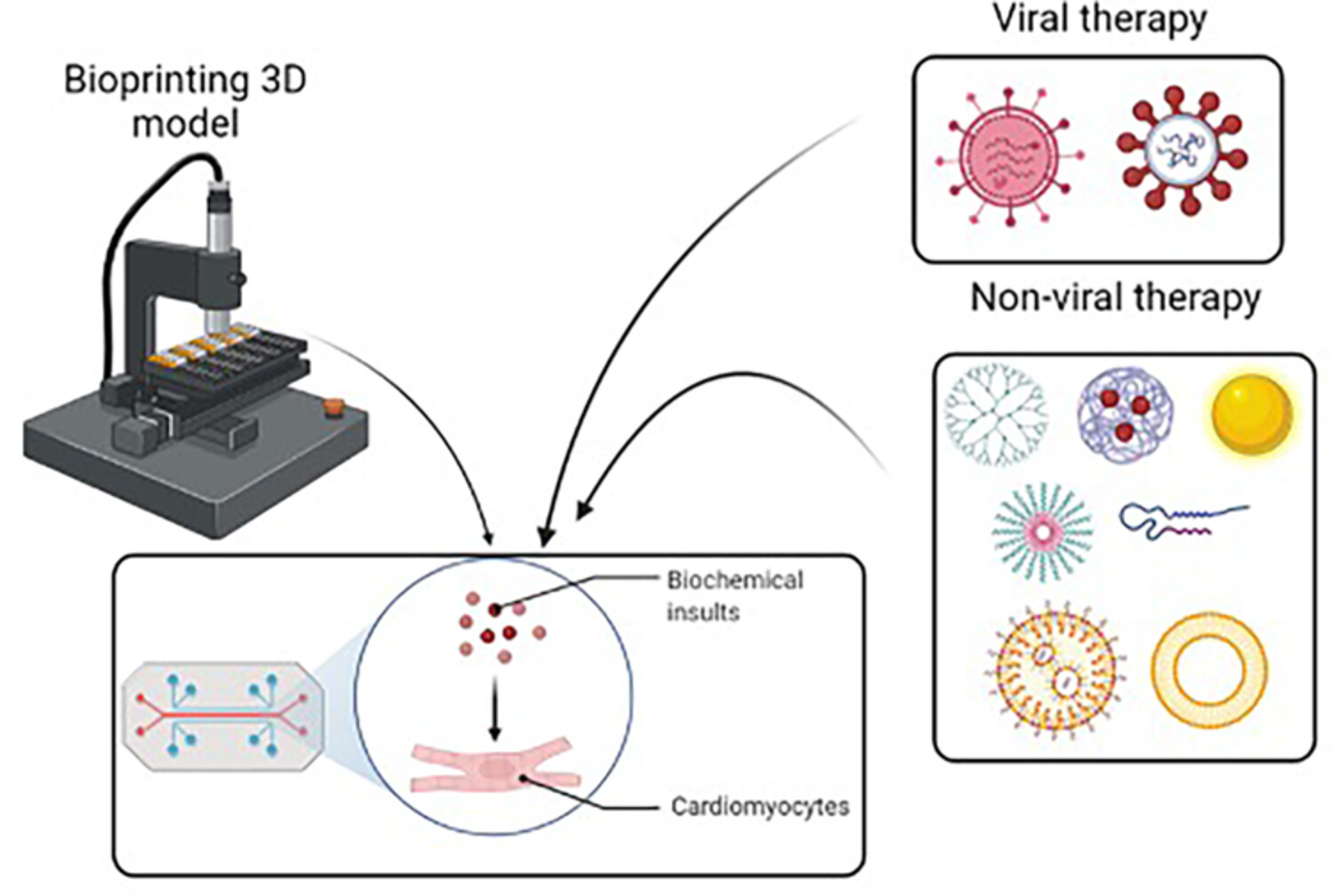
Viral and non-viral gene therapy using 3D (bio)printing
- First Published: 24 October 2022
Early distribution of18 F-labeled AAV9 vectors in the cerebrospinal fluid after intracerebroventricular or intracisternal magna infusion in non-human primates
- First Published: 24 October 2022
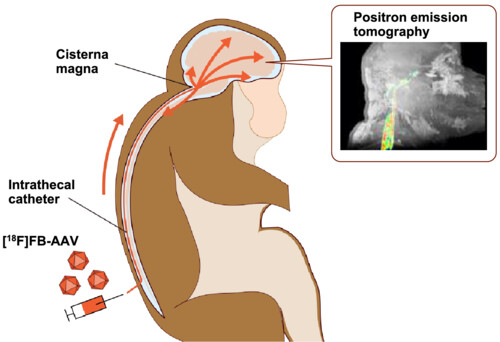
Early distribution of [18F]fluorobenzoate-labeled AAV9 vectors infused into the cisterna magna of non-human primates was evaluated using positron emission tomography. The vectors diffused into the broad arachnoid space around the brain stem and cervical spinal cord. The cisterna magna infusion would be an effective administration method for gene therapy.
Characterization of the evolution trajectory and immune profiling of new histologic patterns in lung adenocarcinoma
- First Published: 04 October 2022
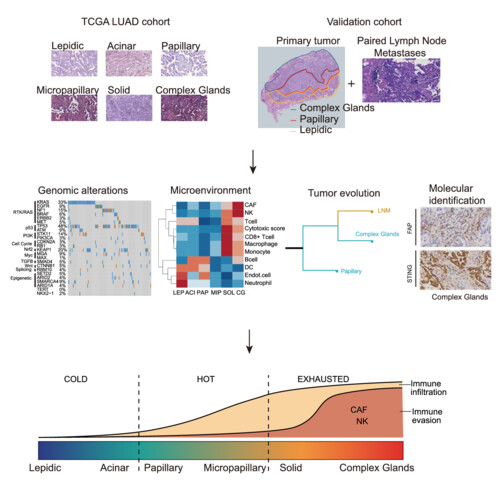
Combining TCGA-LUAD and our own validation data, we systematically revealed the heterogeneity of genomic alterations profiles and tumor microenvironment across the histological patterns in lung adenocarcinoma. We found the most aggressive complex glands were enriched cancer-associated fibroblasts exhibiting a higher possibility of lymph node metastasis.
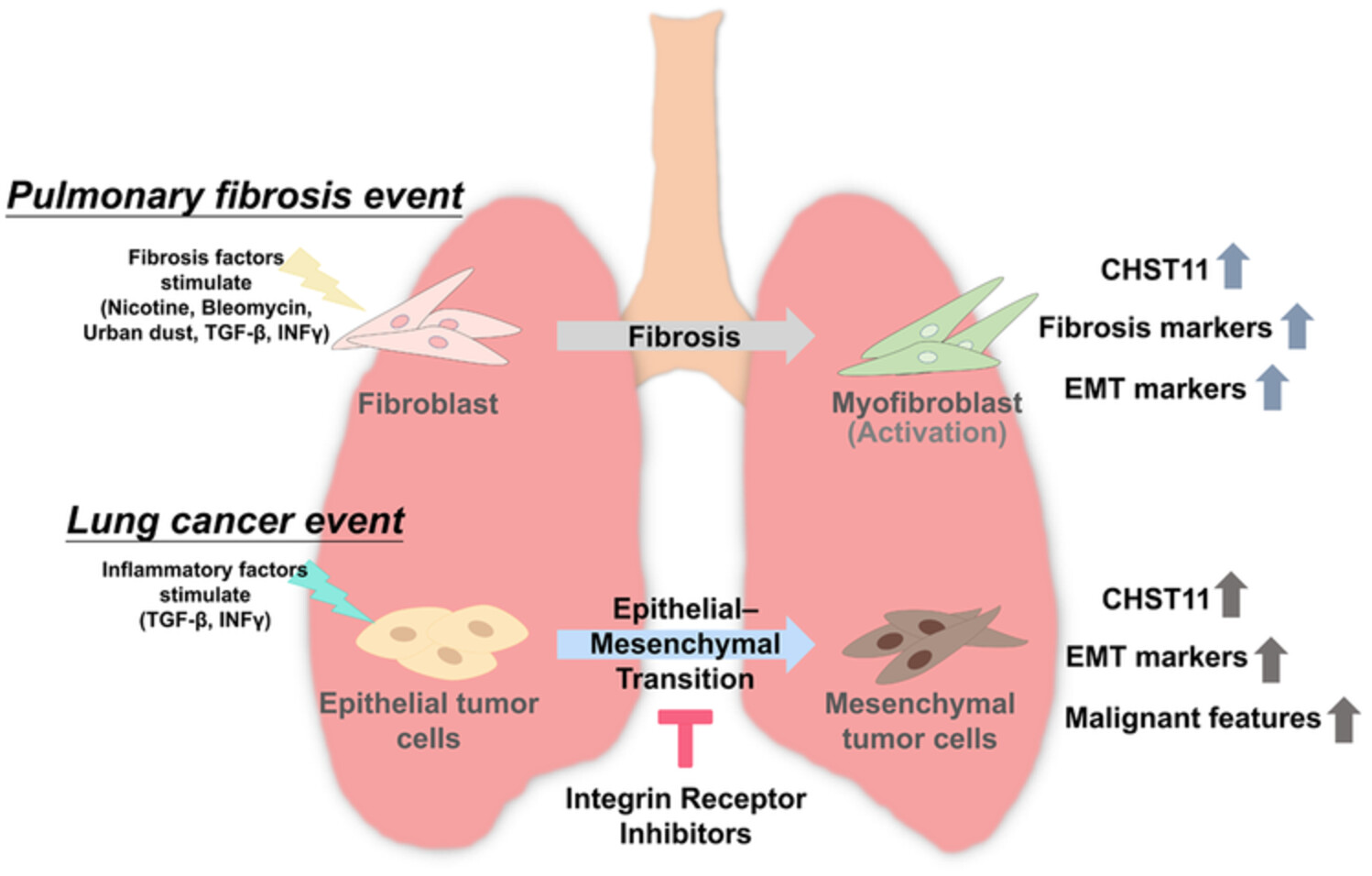
The CHST11 gene is linked to lung cancer and pulmonary fibrosis
- First Published: 30 September 2022
RNA sequencing and bioinformatics analysis revealed PACSIN3 as a potential novel biomarker for platinum resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer
- First Published: 28 September 2022
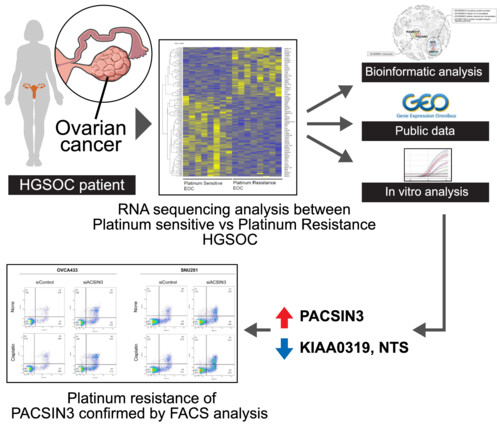
RNA sequencing was performed by using tissues obtained from high grade serous ovarian cancer (HGSOC) patients. After performing RNA sequencing, we analyzed data between platinum sensitive and platinum resistance HGSOC by spatial analysis of functional enrichment software analysis and validated with public database and in vitro analysis. The result showed that protein kinase C and casein kinase substrate in neurons 3 (PACSIN3) was upregulated in platinum resistance HGSOC and KIAA0319 and neurotensin were downregulated. Finally, we selected PACSIN3 because it was the only upregulate gene and cisplatin-induced apoptosis was measured in PACSIN3 knockout OVCA433 and BRCA-mutated epithelial ovarian cancer cell line, SNU251, by a fluorescence-activated cell sorting-based Annexin-V/propium iodide double staining assay, which revealed a significant increase in apoptosis.
Extracellular vesicle-packaged miR-181c-5p from epithelial ovarian cancer cells promotes M2 polarization of tumor-associated macrophages via the KAT2B/HOXA10 axis
- First Published: 26 August 2022
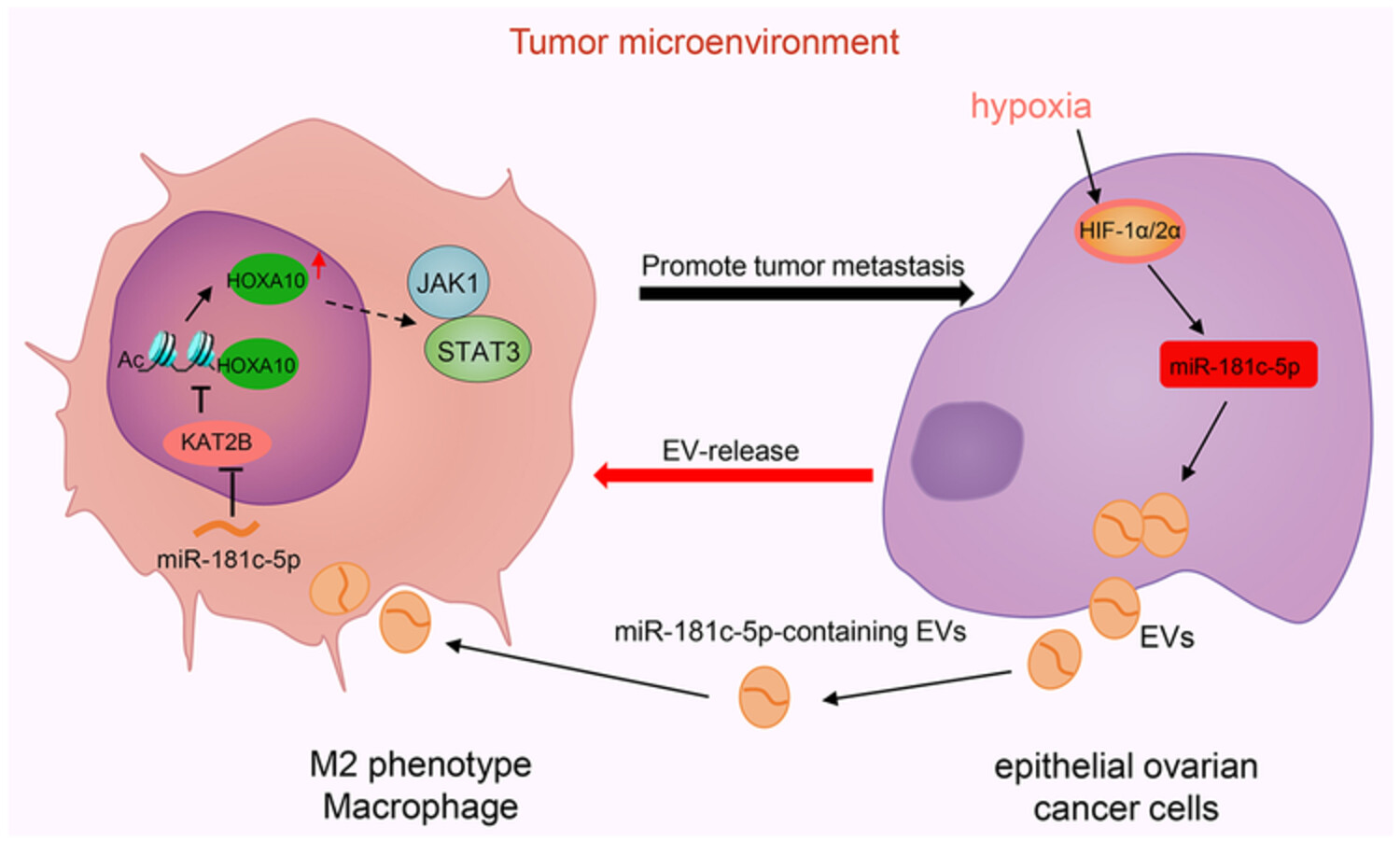
Schematic illustration of molecular mechanism of miR-181c-5p loaded by EVs in hypoxic epithelial ovarian cancer. miR-181c-5p delivered by hypoxic epithelial ovarian cancer cell-derived EVs targets KAT2B to upregulate HOXA10 and activate the JAK1/STAT3 pathway, thereby promoting the M2 polarization of TAMs and thus stimulating the growth and metastasis of epithelial ovarian cancer.
Inhibition of AHNAK nucleoprotein 2 alleviates pulmonary fibrosis by downregulating the TGF-β1/Smad3 signaling pathway
- First Published: 26 July 2022
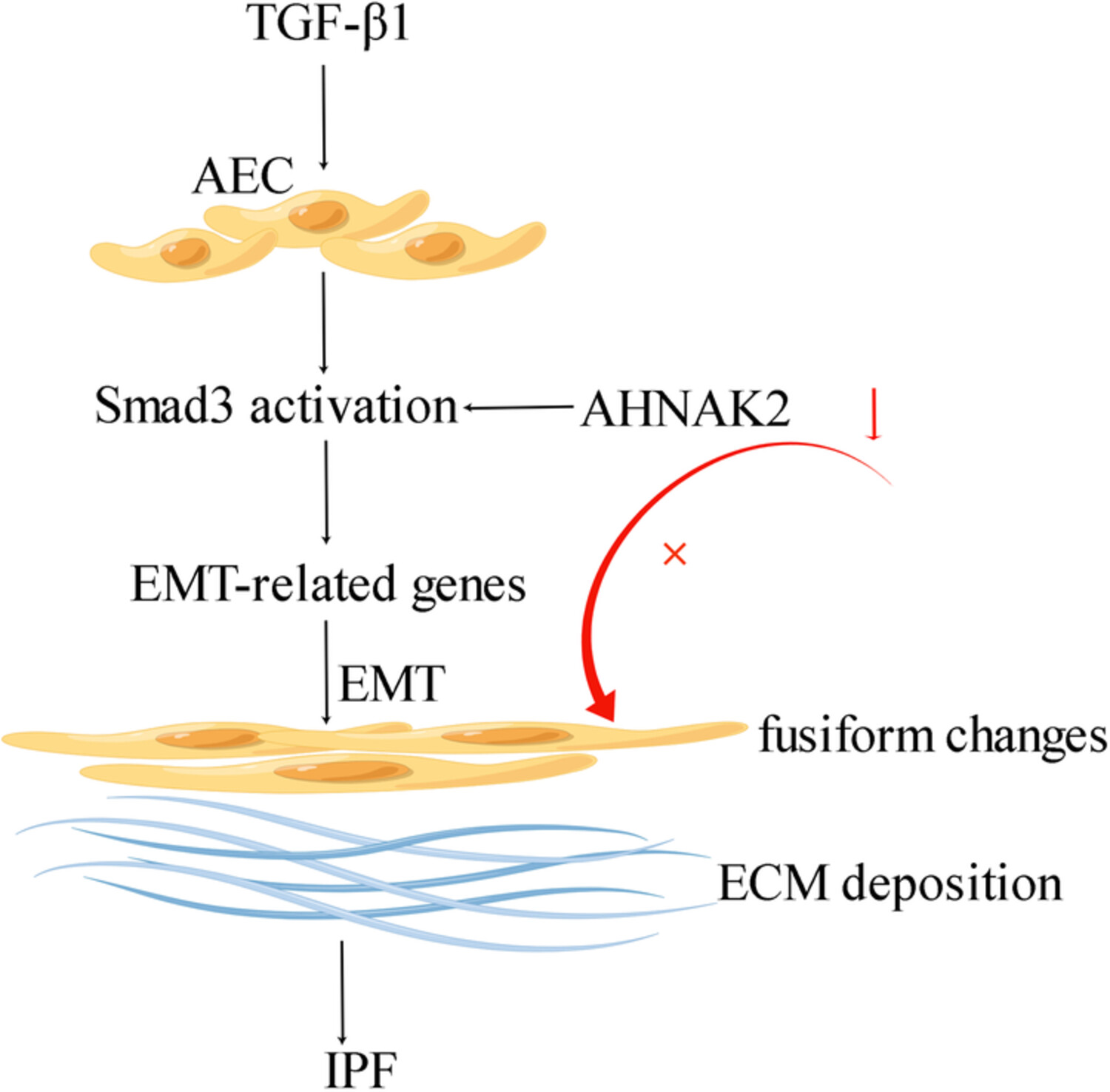
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a chronic and advanced interstitial lung disease with poor prognosis. AHNAK nucleoprotein 2 (AHNAK2) is a macromolecular protein and highly expressed in IPF. Inhibition of AHNAK2 alleviates pulmonary fibrosis by downregulating the TGF-β1/Smad3 signaling pathway.
SYNGR2 serves as a prognostic biomarker and correlates with immune infiltrates in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- First Published: 15 July 2022
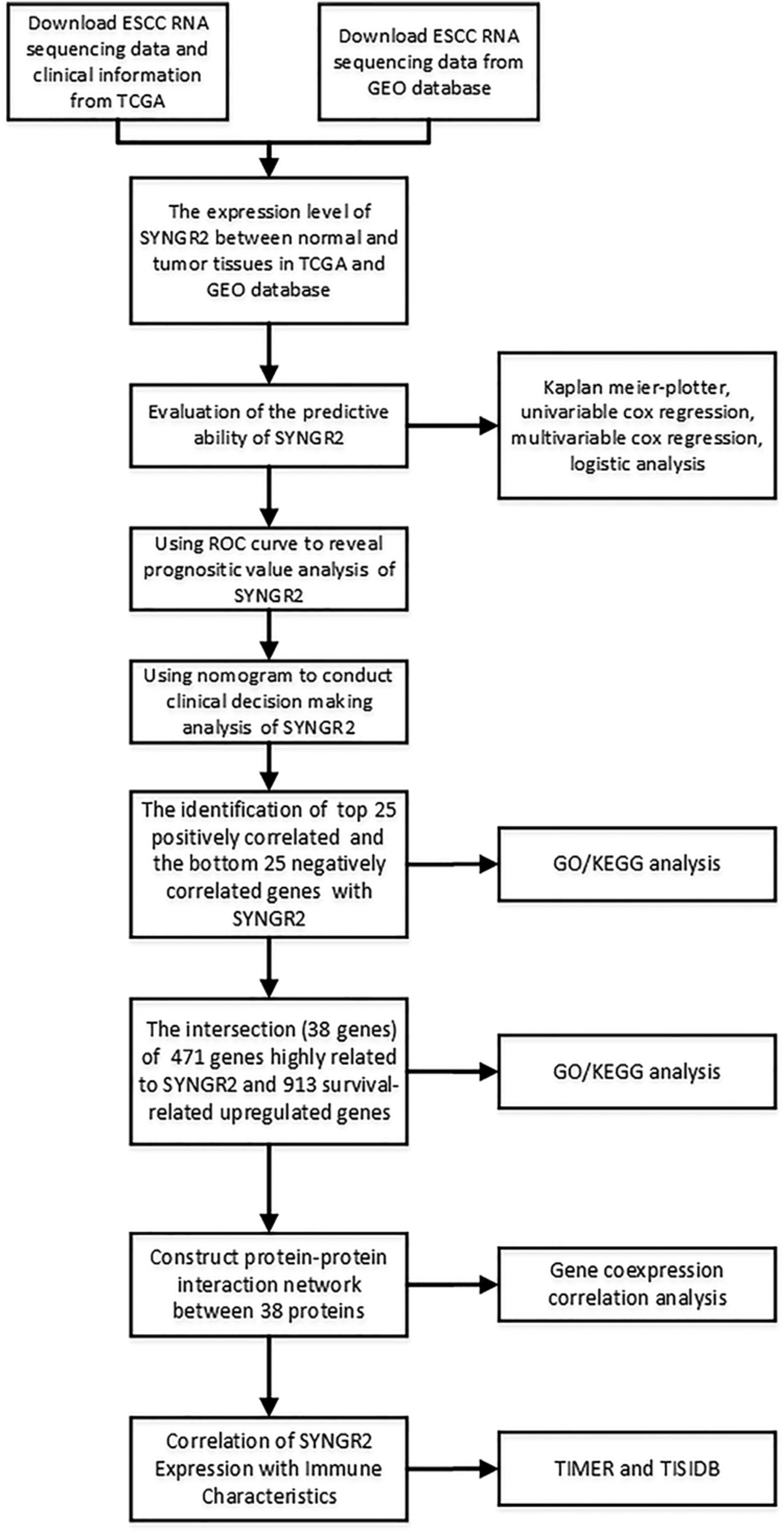
First, the sequencing data and clinical data of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) were downloaded from TCGA and GEO databases to further analyze the expression of SYNGR2 in cancer cells and adjacent tissues. Then the prognostic value of SYNGR2 in ESCC patients was evaluated, and the diagnostic value of SYNGR2 was evaluated via the receiver operating characteristic curve and nomogram. The genes closely related to SYNGR2 and the prognosis of ESCC were further screened and analyzed using enrichment analysis, protein–protein interaction analysis and correlation analysis. Finally, SYNGR2 and immune infiltrating cells in tumor microenvironment were analyzed using the TIMER and TISIDB databases.
Long non-coding RNA SNHG1 activates glycolysis to promote hepatocellular cancer progression through the miR-326/PKM2 axis
- First Published: 11 July 2022
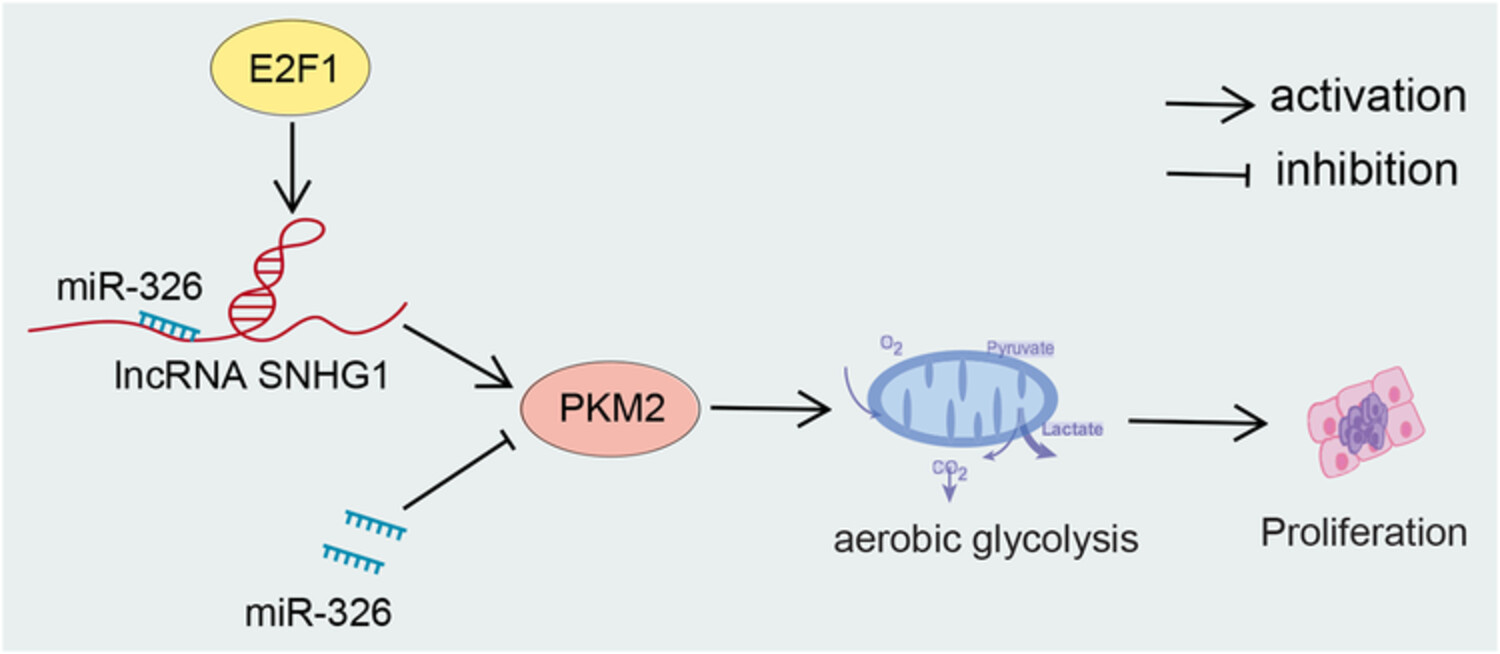
In hepatocellular cancer cells, elevated E2F1 activates SNHG1 transcription and thus upregulates SNHG1 expression. E2F1-activated SNHG1 binds to miR-326 and sequesters the interaction of miR-326 and PKM2, resulting in upregulation of PKM2 expression, thus facilitating glycolysis and promoting the proliferation of hepatocellular cancer cells.
Intramyocardial adenoviral vascular endothelial growth factor-D∆N∆C gene therapy does not induce ventricular arrhythmias
- First Published: 24 June 2022
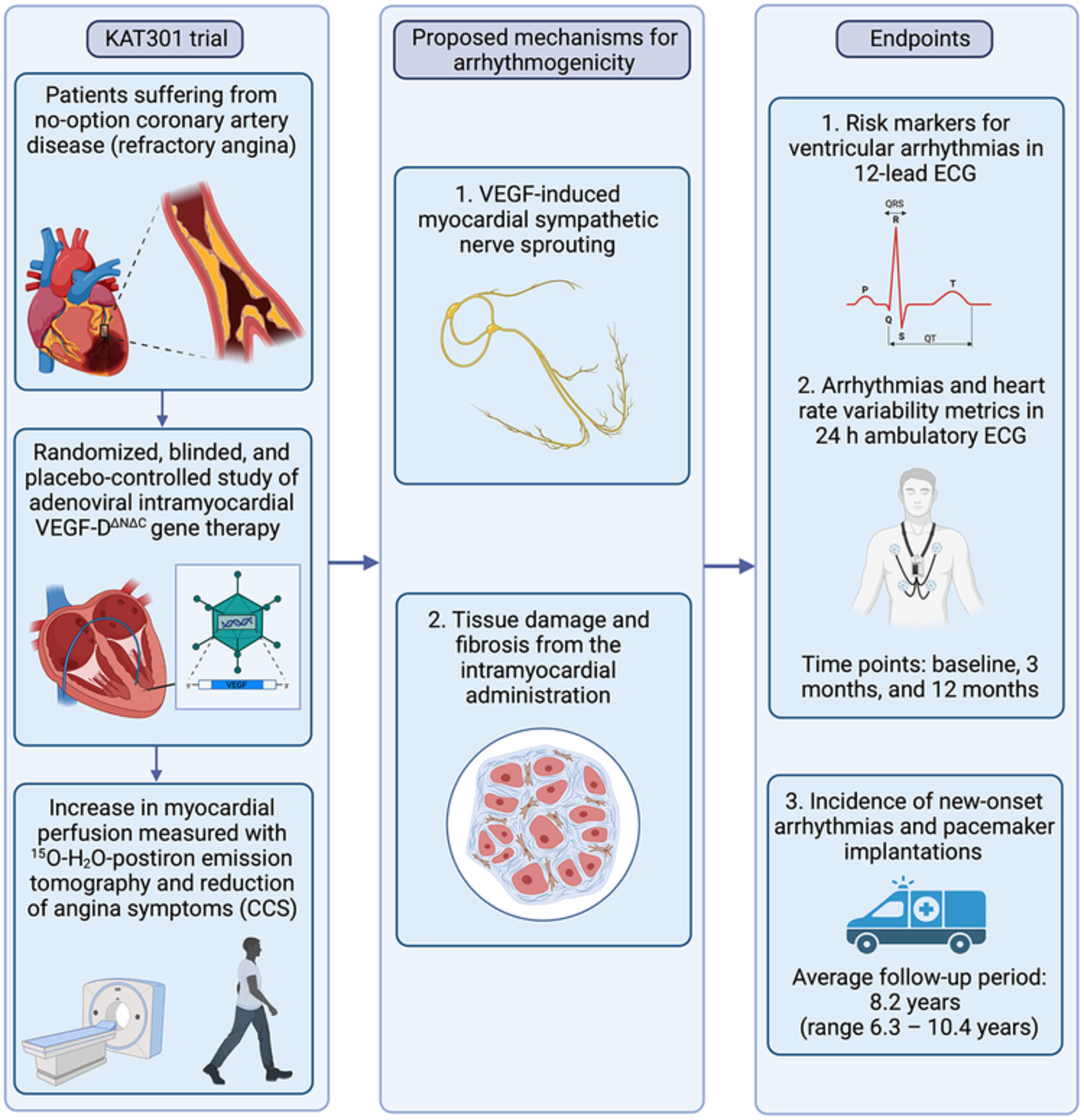
There is some evidence suggesting that overexpression of vascular endothelial growth factors, as well as their intramyocardial delivery, might induce ventricular arrhythmias. In the present study, we show that intramyocardial adenoviral vascular endothelial growth factor-D∆N∆C is not associated with an increased risk of arrhythmias but might instead improve cardiac autonomic regulation when using heart rate variability metrics as reference. Created using BIORENDER (https://biorender.com).
OMICRON: Virology, immunopathogenesis, and laboratory diagnosis
- First Published: 21 June 2022

Several mutations in SARS-CoV-2, especially deletion mutations in the spike (S) protein, have led to the development of a new variant of concern, named Omicron. Omicron has higher transmissibility and infectivity but milder symptoms compared with other SARS-CoV-2 variants. Currently, five subvariants of Omicron have been identified, including BA.1 and BA.1.1, BA.2, BA.3, BA.4 and BA.5. Laboratory diagnosis of Omicron includes genetic testing using reverse transcriptase PCR and next-generation sequencing, serology testing for neutralizing IgM/IgG and imaging studies.
Targeted gene next-generation sequencing reveals genomic profile in a cohort of 46 Chinese patients with breast cancer
- First Published: 25 April 2022
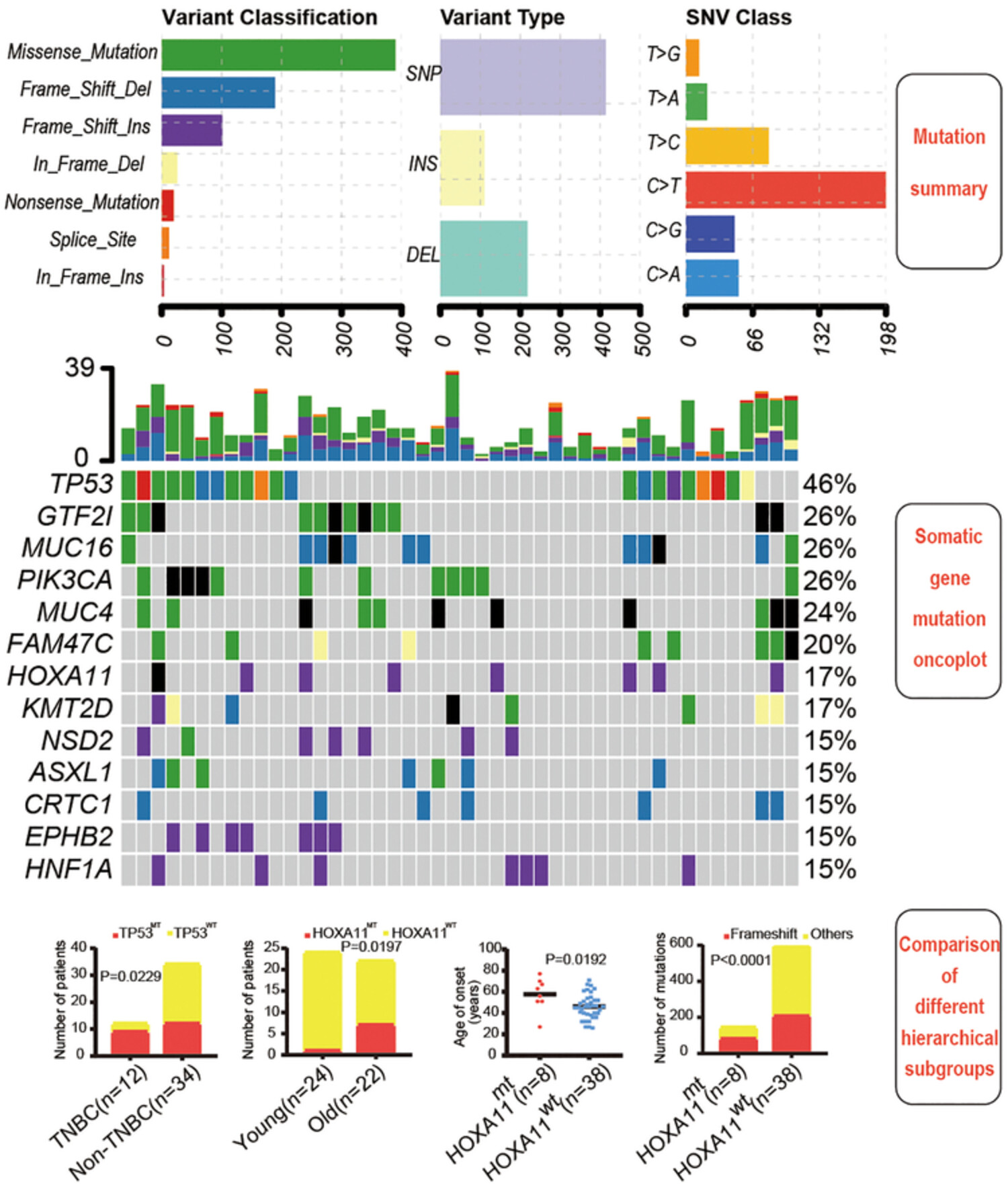
Next-generation sequencing of Chinese patients with breast cancer (BC) revealed the somatic gene variants, frequently mutated genes and the heterogeneity of somatic mutations between different hierarchical subgroups. These distinct mutation profiles might be potentially relevant in the development of treatment strategies for specific subset of BC patients.
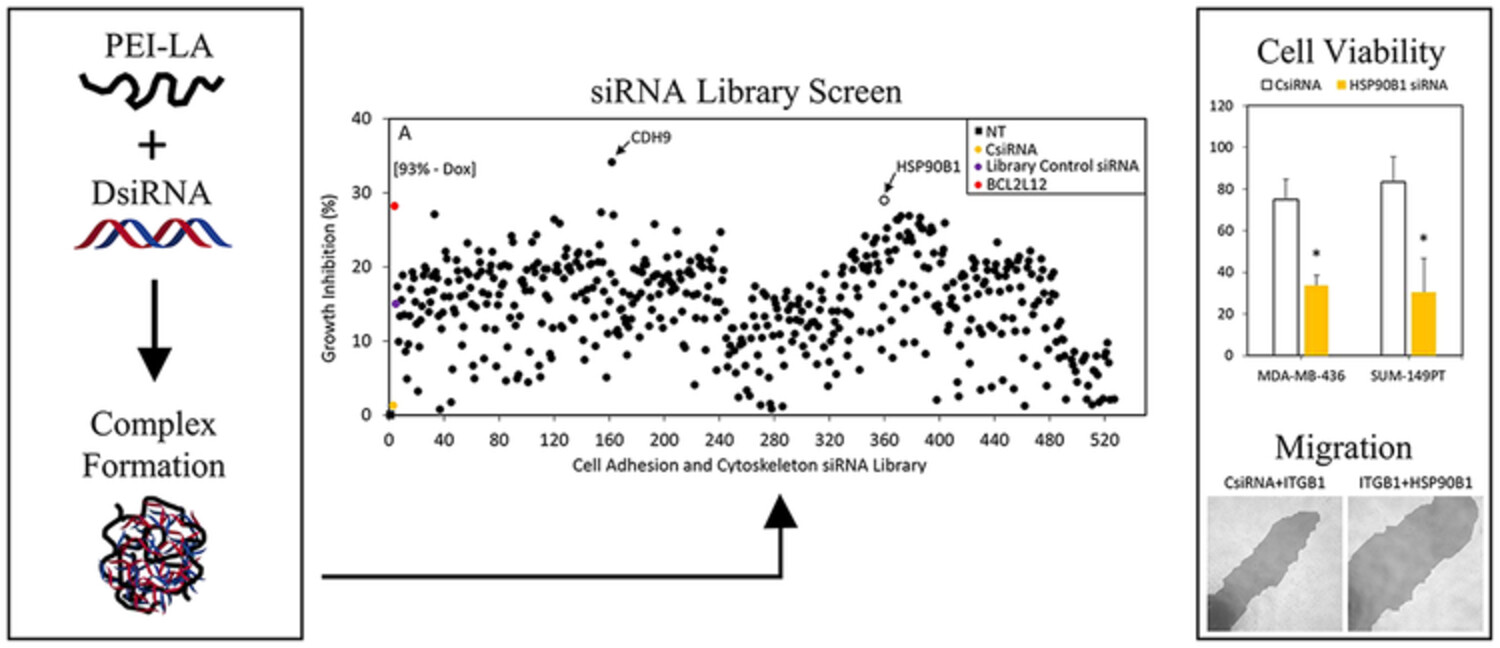
Linoleic-acid-substituted polyethylenimine to silence heat shock protein 90B1 (HSP90B1) to inhibit migration of breast cancer cells
- First Published: 04 April 2022
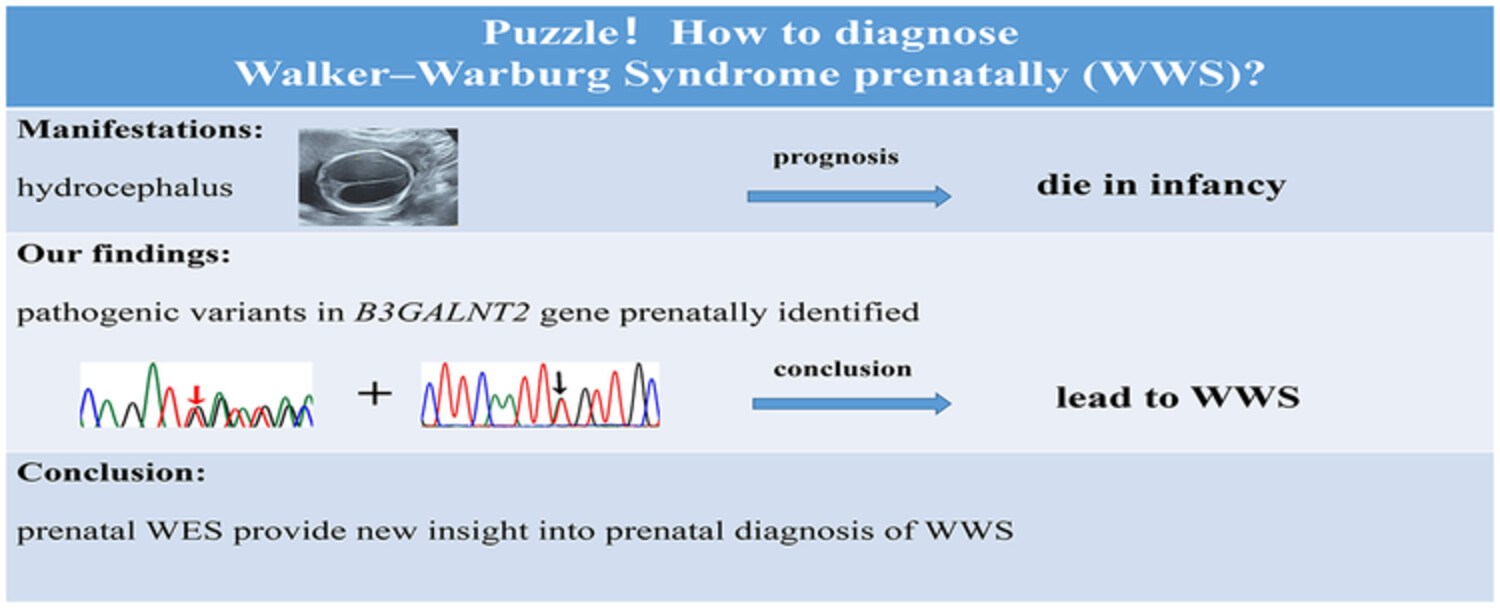
Prenatal diagnosis of Walker–Warburg syndrome due to compound mutations in the B3GALNT2 gene
- First Published: 25 March 2022
ANKRD37 inhibits trophoblast migration and invasion by regulating the NF-κB pathway in preeclampsia
- First Published: 26 February 2022
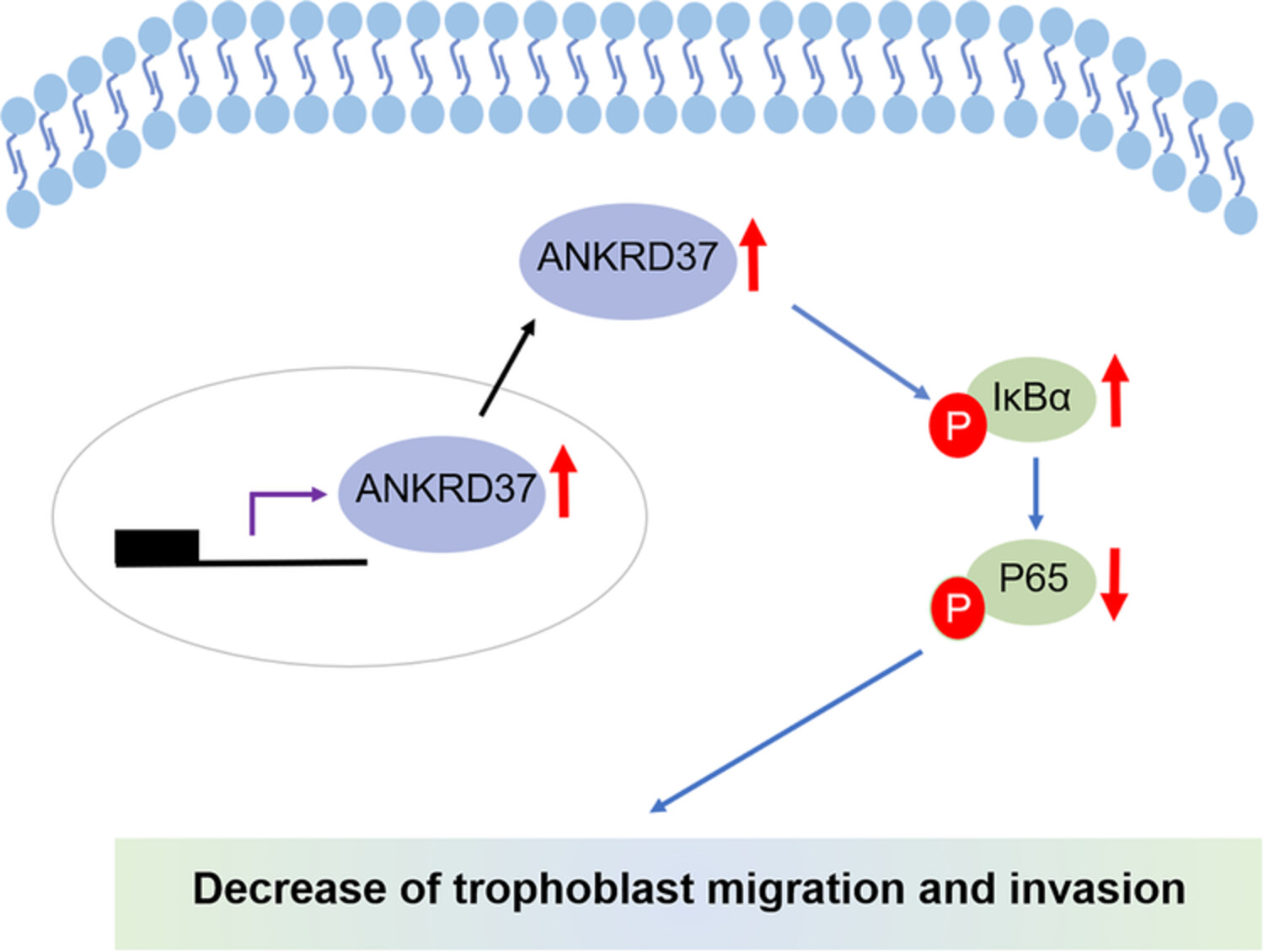
Preeclampsia (PE) is one of the most feared complications of pregnancy and inadequate trophoblast invasion plays an important role in the pathogenesis of PE. The present study found that ankyrin repeat domain protein 37 (ANKRD37) inhibited trophoblast migration and invasion via the NF-ĸB pathway possibly. The study is the first to investigate the biological function of ANKRD37 and provides new targets for PE therapy.
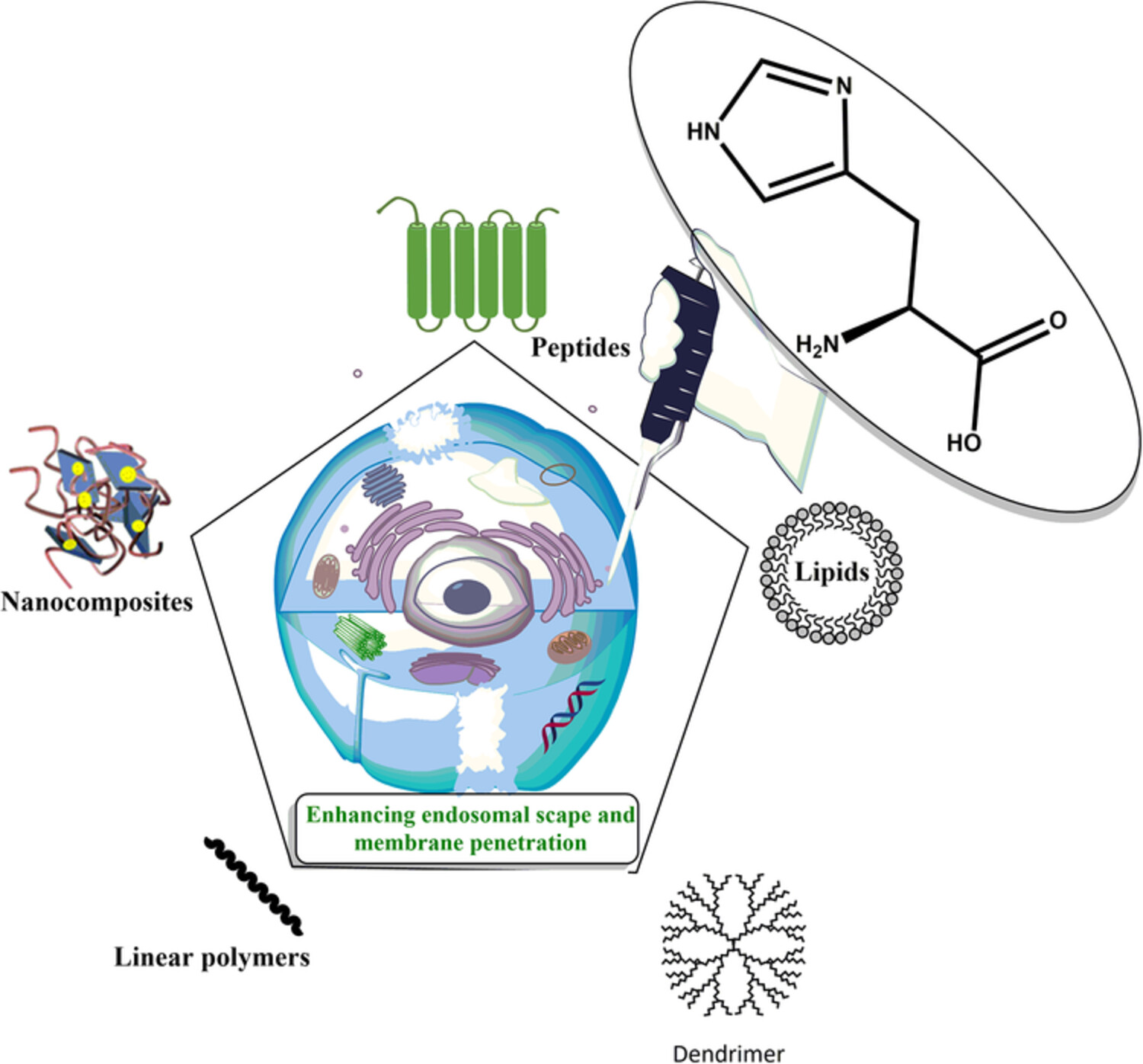
Histidine-enhanced gene delivery systems: The state of the art
- First Published: 07 February 2022
Circ_0072088 knockdown contributes to cisplatin sensitivity and inhibits tumor progression by miR-944/LASP1 axis in non-small cell lung cancer
- First Published: 01 February 2022
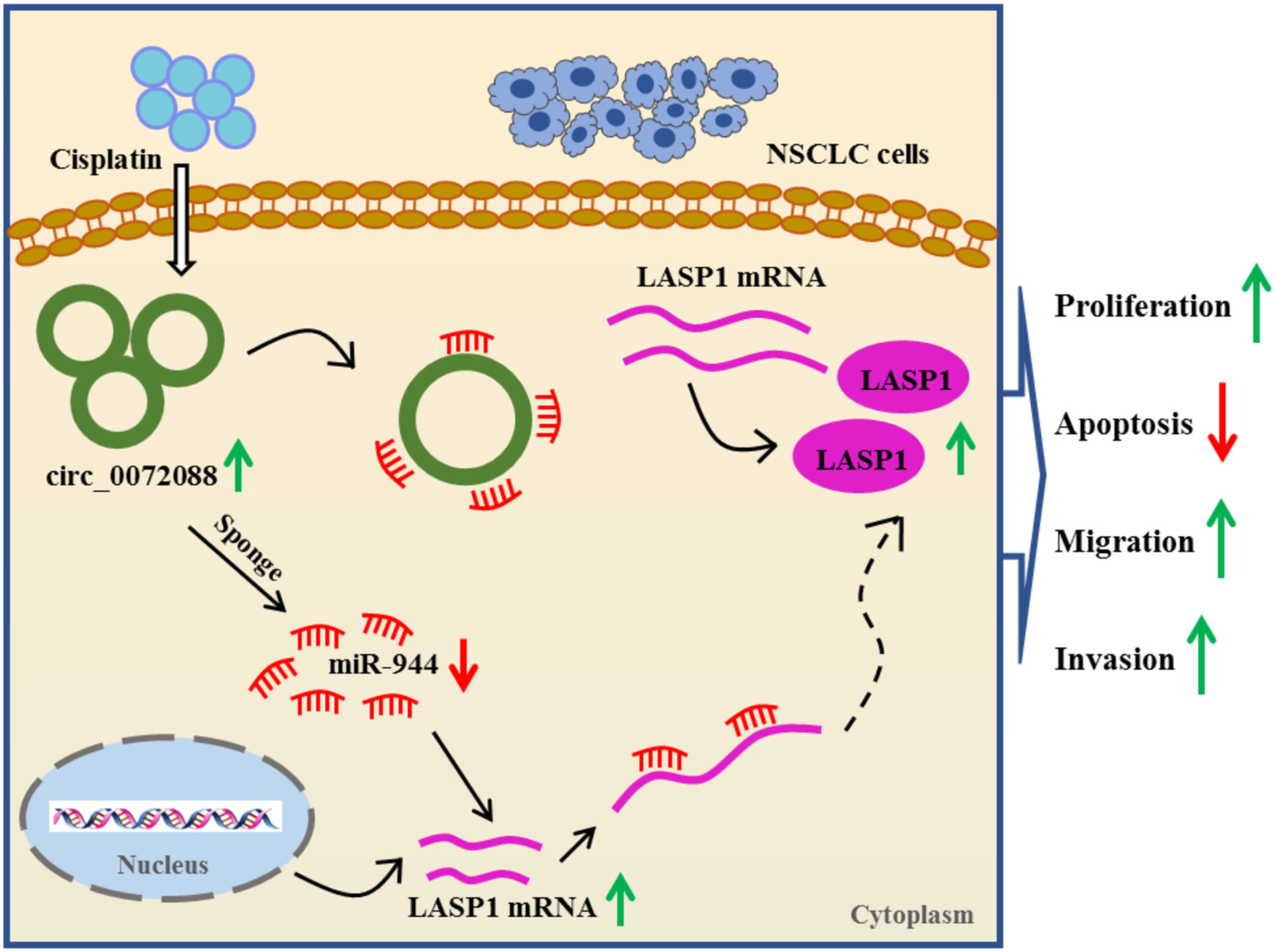
Schematic diagram showing the molecular mechanism of circ_0072088 in regulating the sensitivity of CDDP-resistant NSCLC cells to CDDP. Cisplatin treatment leads to upregulation of circ_0072088 in CDDP-resistant NSCLC cells, and increased expression of circ_0072088 induces LASP1 production by binding to miR-944, to promote NSCLC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion and inhibit cell apoptosis.




1521-2254.editors-collection-2022.cover.gif)