Edited By: Prof Yang Yang
Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology is a broad scope pharmacology journal aiming to advance the translation of basic research to clinical practice. The journal covers clinical and experimental pharmacology and physiology, blood pressure, cardiovascular disease, heart failure, pharmacokinetics, toxicology, and more.
Journal Metrics
- 5.5CiteScore
- 2.5Journal Impact Factor
- 12%Acceptance rate
- 5 days Submission to first decision
Articles
Sinomenine Suppresses Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Migration and Invasion by Inhibiting O-GlcNAcylation of SP1
- 17 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
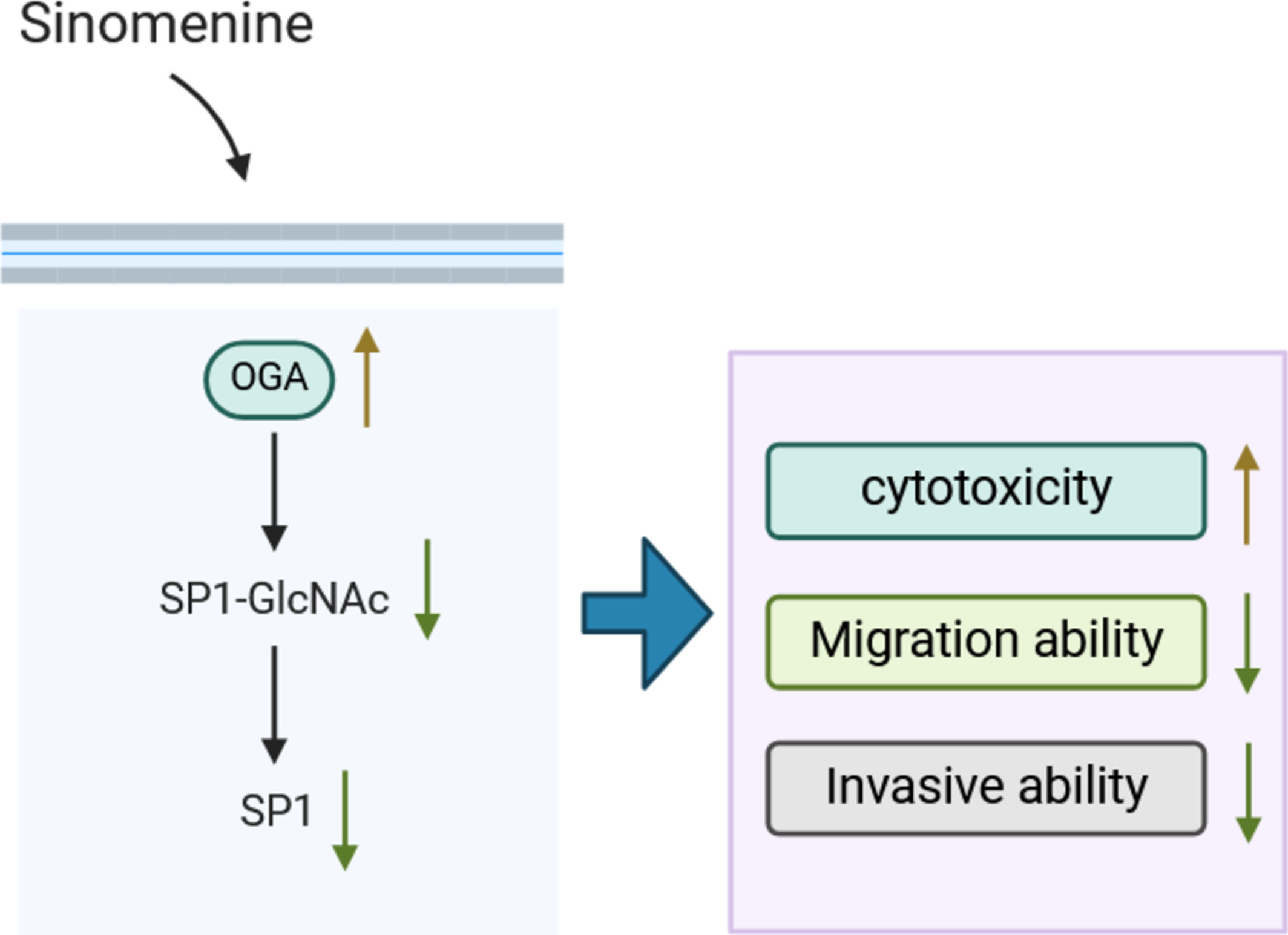
The anti-tumour efficacy of SIN in HCC by suppressing the malignant processes of HCC cells. Mechanistically, SIN upregulated OGA expression to block the O-GlcNAcylation of SP1 and thus decrease the protein stability of SP1. All these findings reveal a novel potential therapeutic target of SIN for HCC patients.
M2 Macrophages-Derived Exosomes Inhibited Podocyte Pyroptosis via lncRNA AFAP1-AS1/EZH2 Axis
- 15 July 2025
Graphical Abstract

This study revealed that exosomes derived from M2 macrophages inhibited podocyte pyroptosis via transferring AFAP1-AS1 to podocytes. Mechanistically, AFAP1-AS1 interacted with EZH2 to transcriptionally regulate H3K27me3 level in the NLRP3 promoter region, thus epigenetically repressing NLRP3 expression to inhibit podocyte pyroptosis. Our findings provided a potential molecular target for the therapeutic interventions of diabetic nephropathy.
Potential Kidney Risks Associated With Clinical Doses of Omeprazole: In Vivo and In Vitro Studies
- 7 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
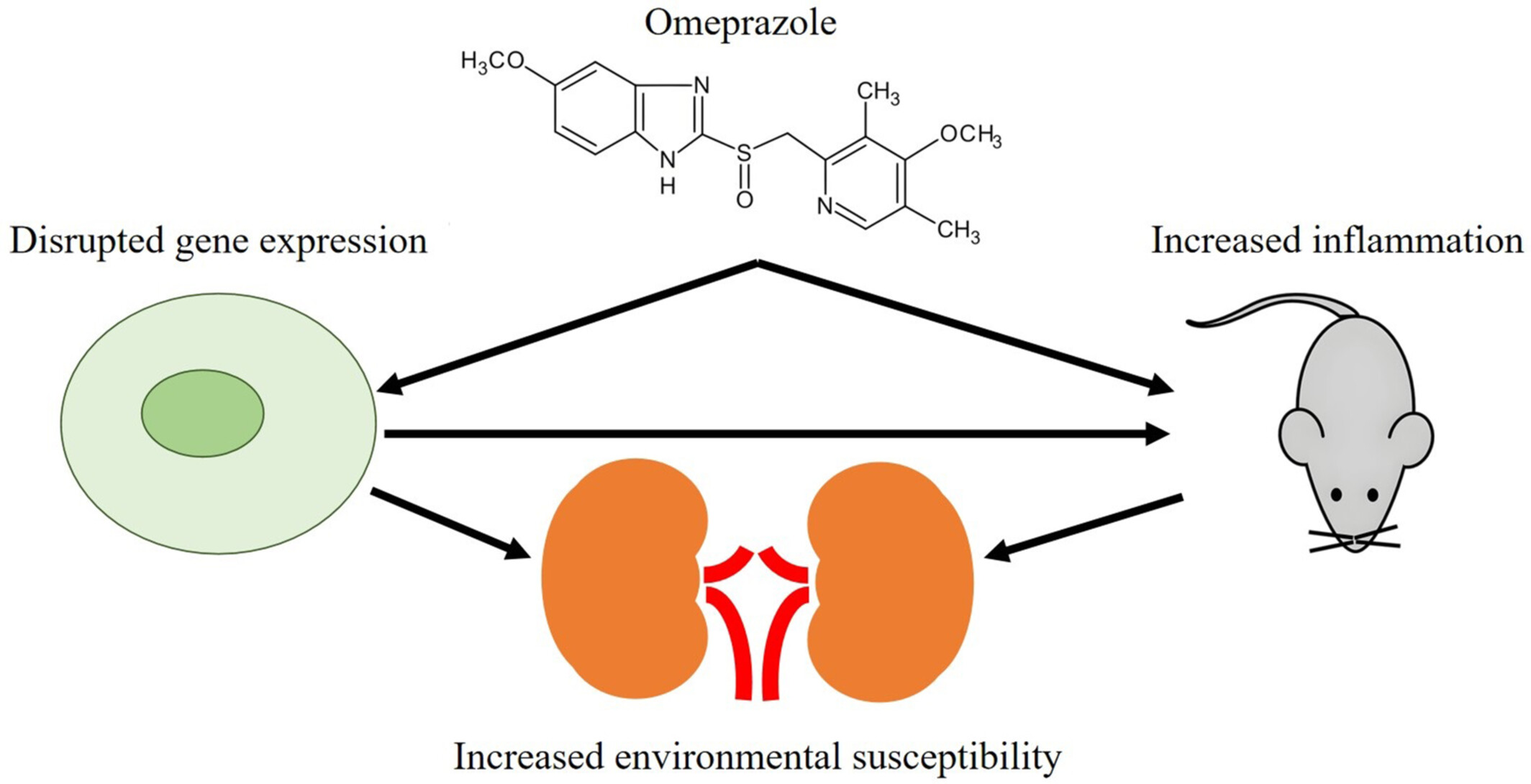
Omeprazole decreases cell proliferation and viability by disrupting gene expression; thus, the long-term use of omeprazole may increase inflammation and environmental susceptibility. These findings provide valuable insights for the clinical use of omeprazole, highlighting the need for careful consideration of its effects in the kidney.
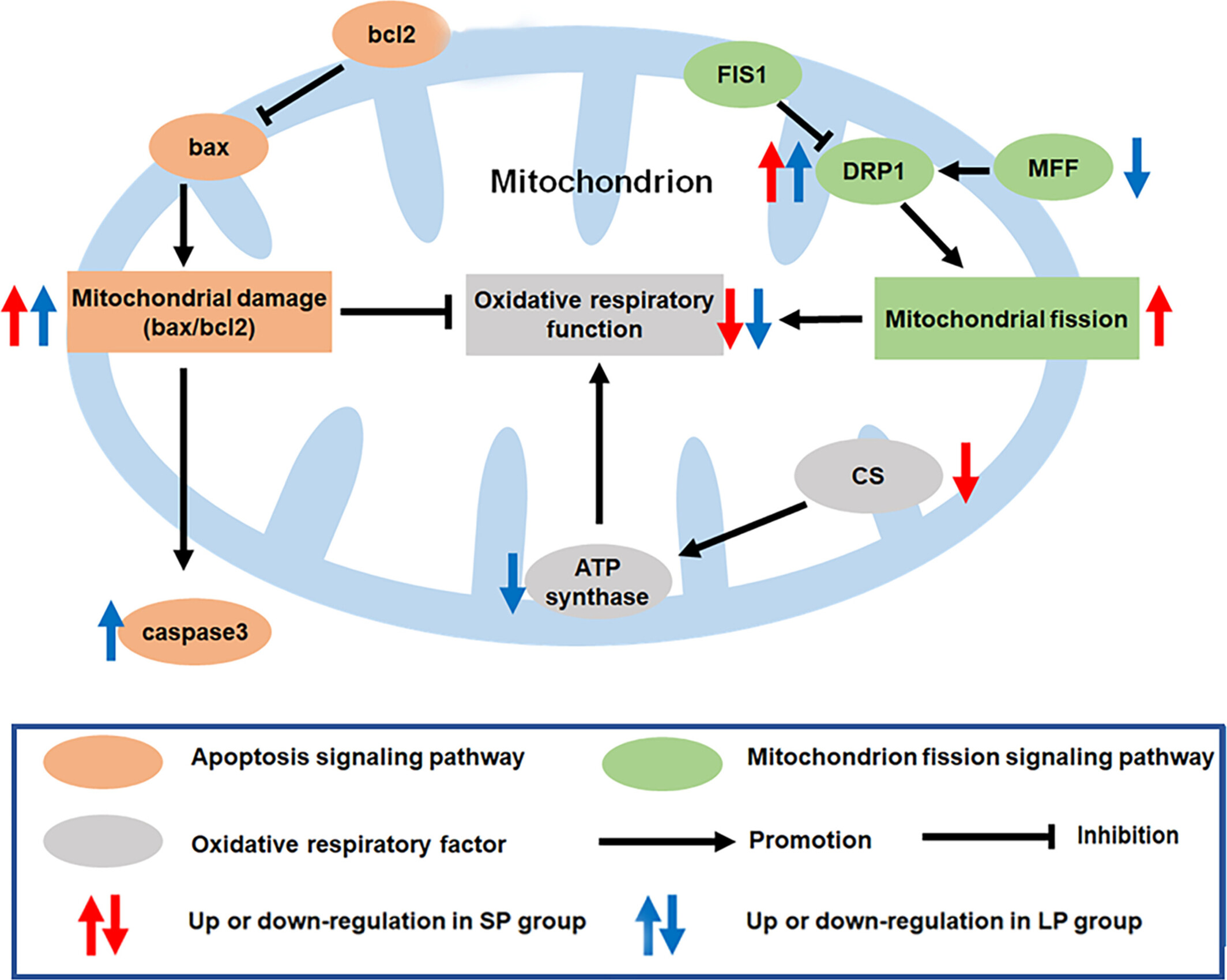
Decrease in Mitochondrial Oxidative Respiratory Function in Liver of Cricetulus barabensis Under Long and Short Photoperiods: The Role of Mitochondrial Fission and Apoptosis
- 30 June 2025
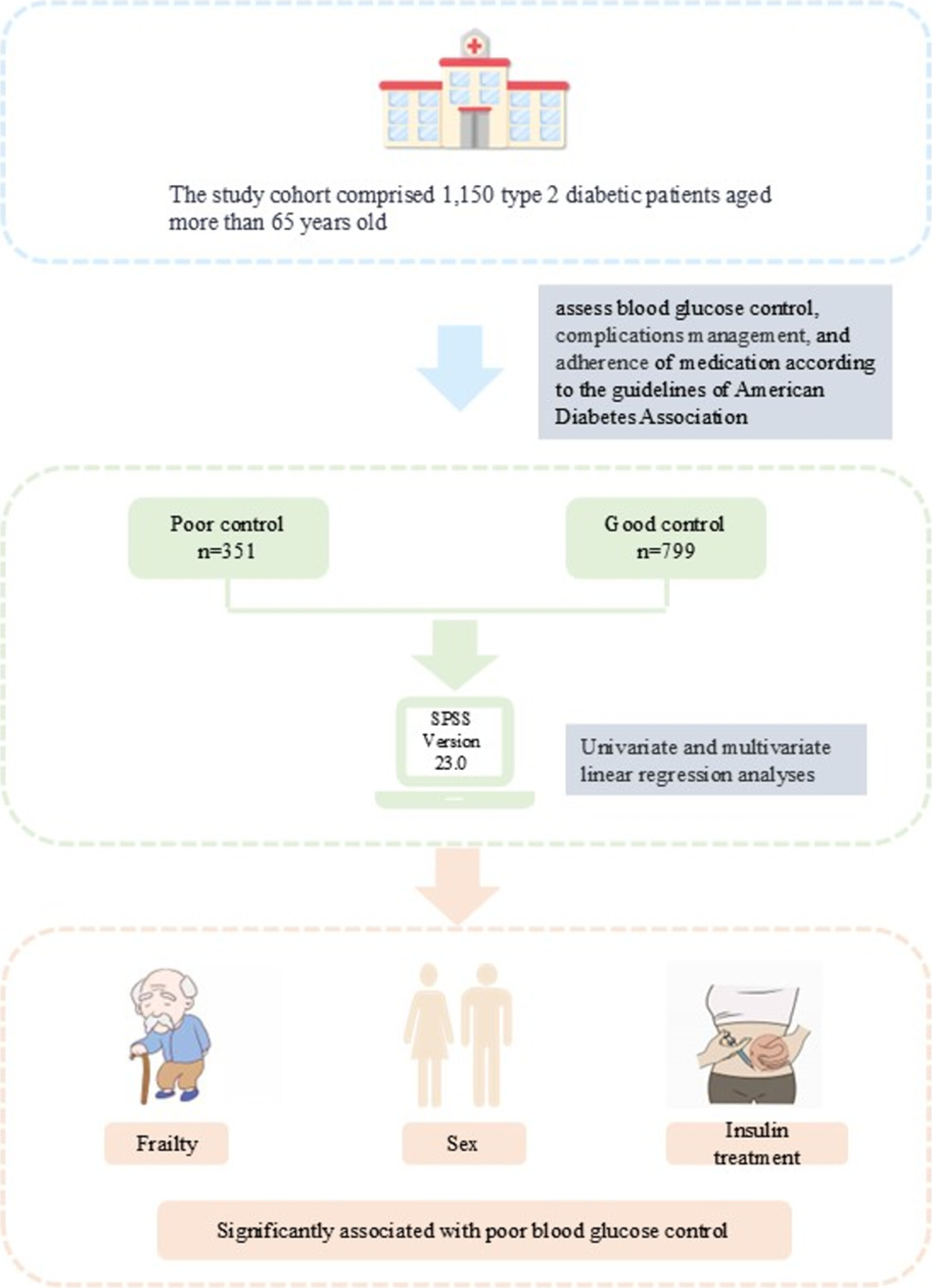
Frailty: An Important Determinant Influencing Glycaemic Control in Elderly Chinese Patients Diagnosed With Type 2 Diabetes
- 29 June 2025
GPR39 Activation Attenuates AngII-Induced Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm by Suppressing ETS-1 Mediated VEGF-A/VEGFR2 Signalling
- 29 June 2025
Graphical Abstract
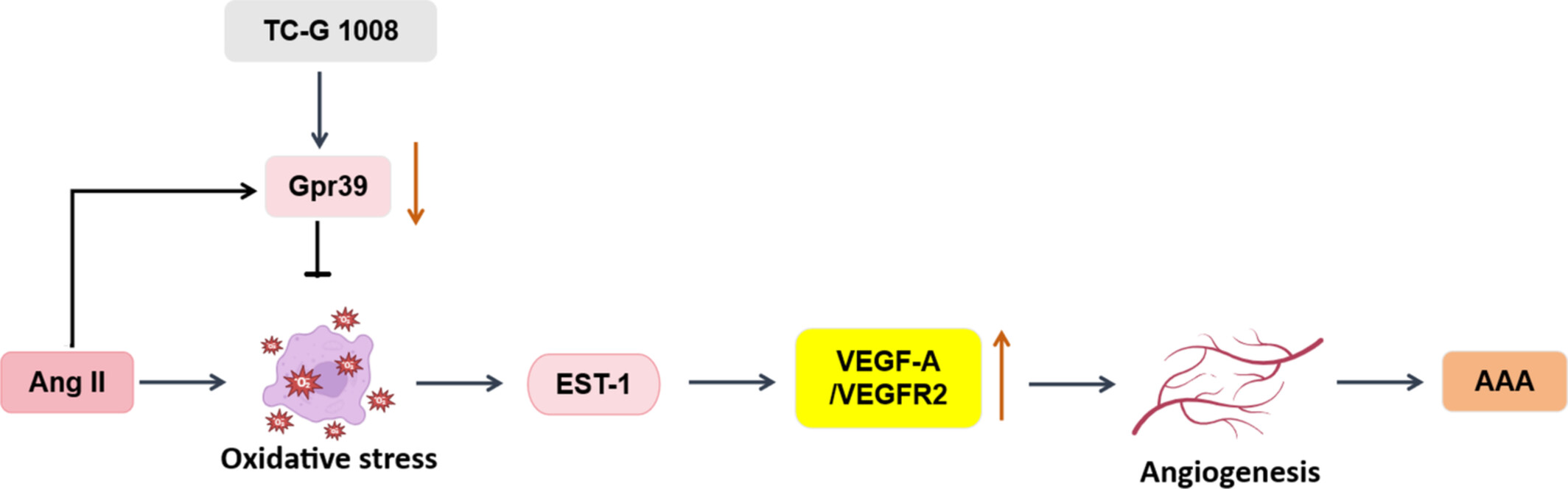
GPR39 activation by TC-G 1008 attenuates AngII-induced AAA in ApoE−/− mice by reducing oxidative stress (lowering MDA, increasing SOD/GSH) and suppressing VEGF-A/VEGFR2 signalling. The protective mechanism involves downregulation of the transcription factor ETS-1, which mediates VEGF-A/VEGFR2 expression and angiogenic tube formation in HUVECs. ETS-1 overexpression reverses TC-G 1008's effects, confirming its pivotal role in GPR39-mediated protection against AAA.
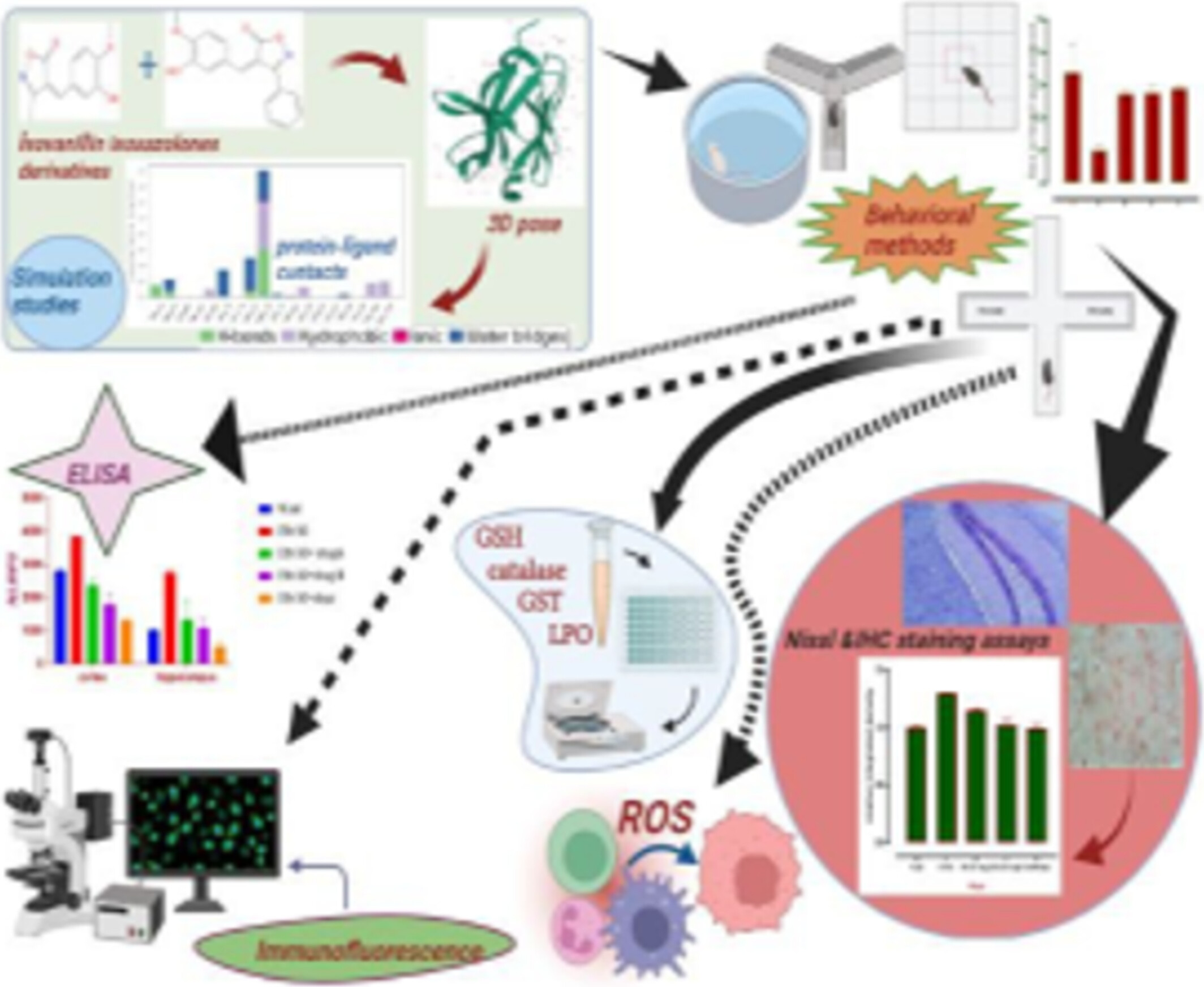
Synthesis, Characterization, Molecular Dynamic Simulation and Neuroprotective Effects of Synthetic Isoxazolone Derivatives in Ethanol‐Induced Neurodegeneration
- 22 June 2025
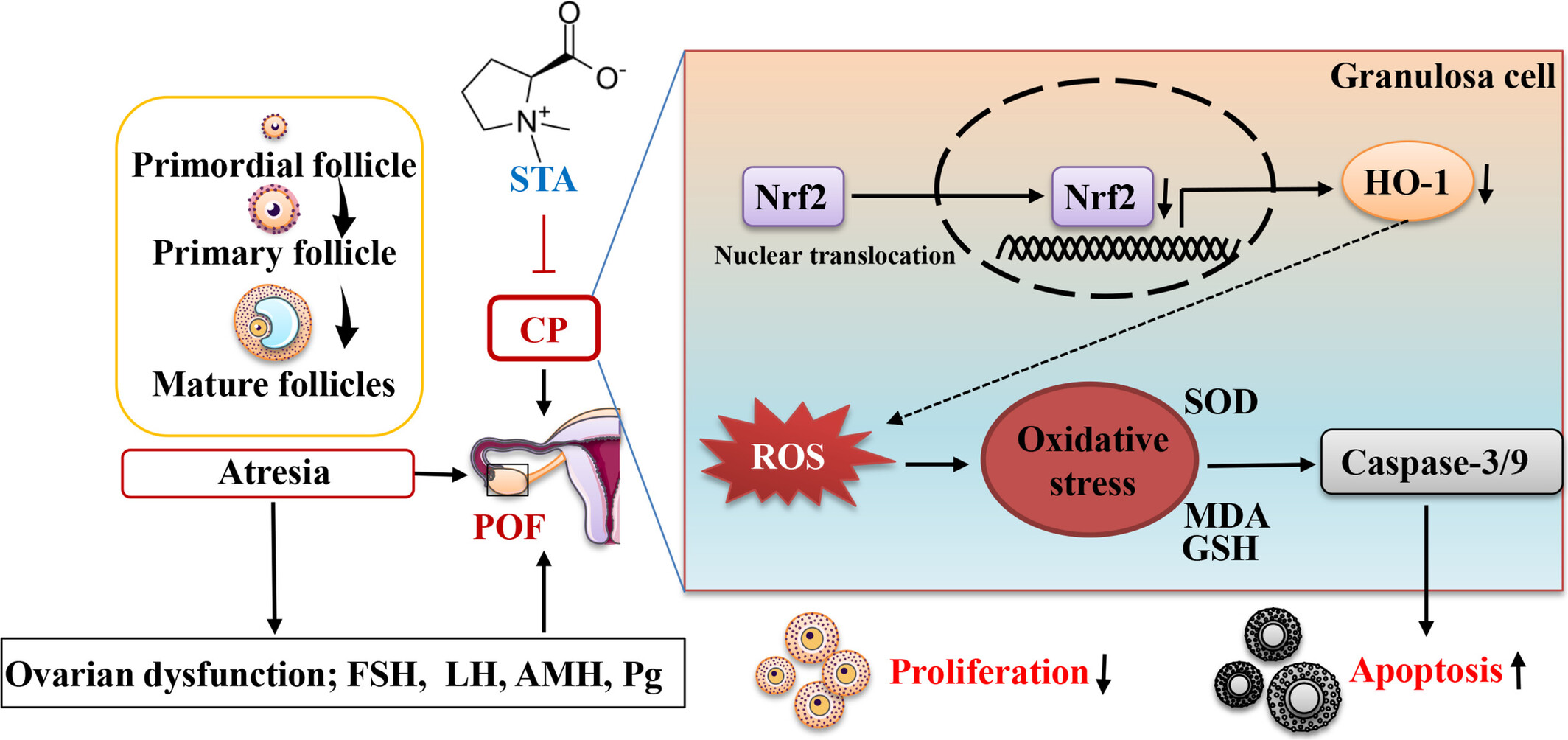
Stachydrine Protects Against Cyclophosphamide-Induced Premature Ovarian Insufficiency in Wistar Rats by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis via the Activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 Signalling Pathway
- 22 June 2025
Graphical Abstract
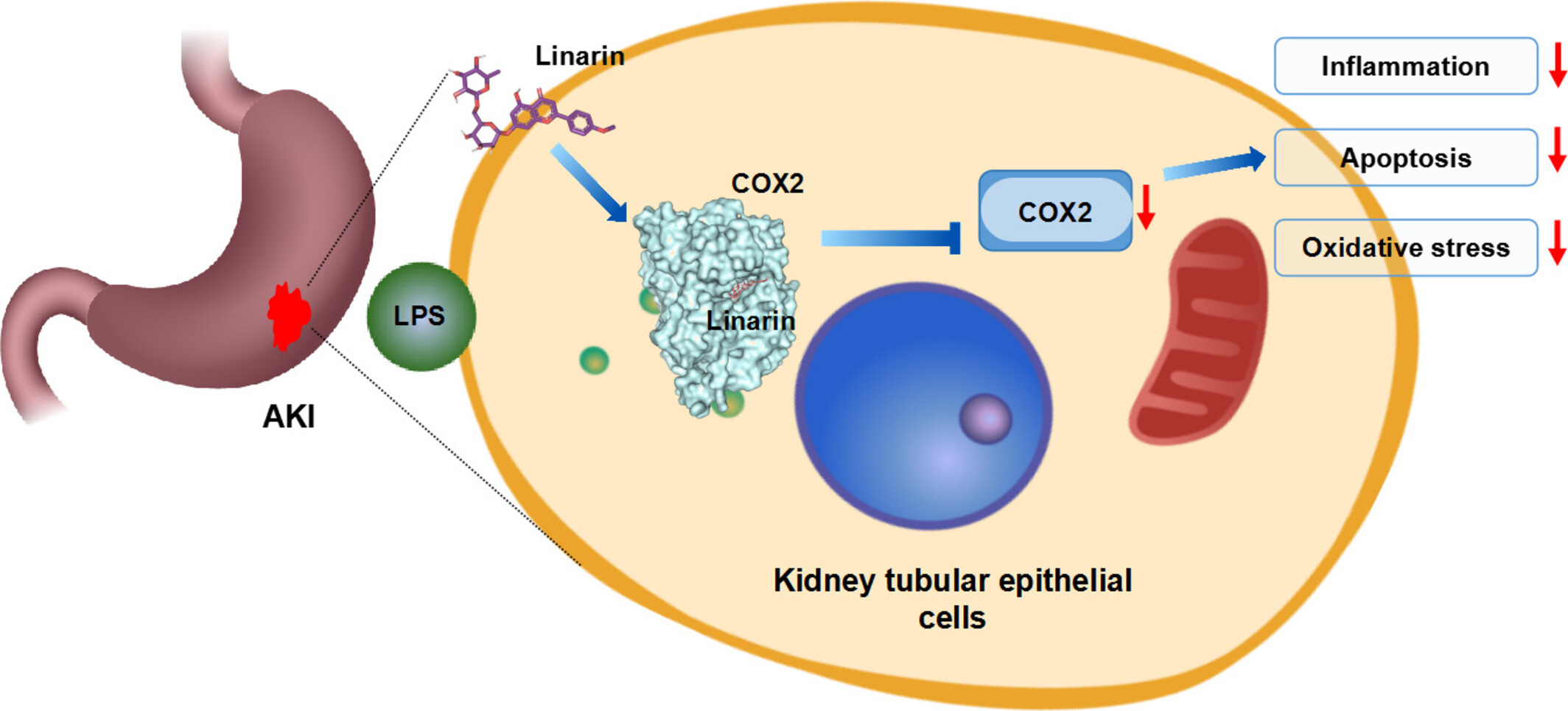
Linarin Relieves Apoptosis, Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in LPS-Induced Acute Kidney Injury by Modulating COX2
- 9 June 2025
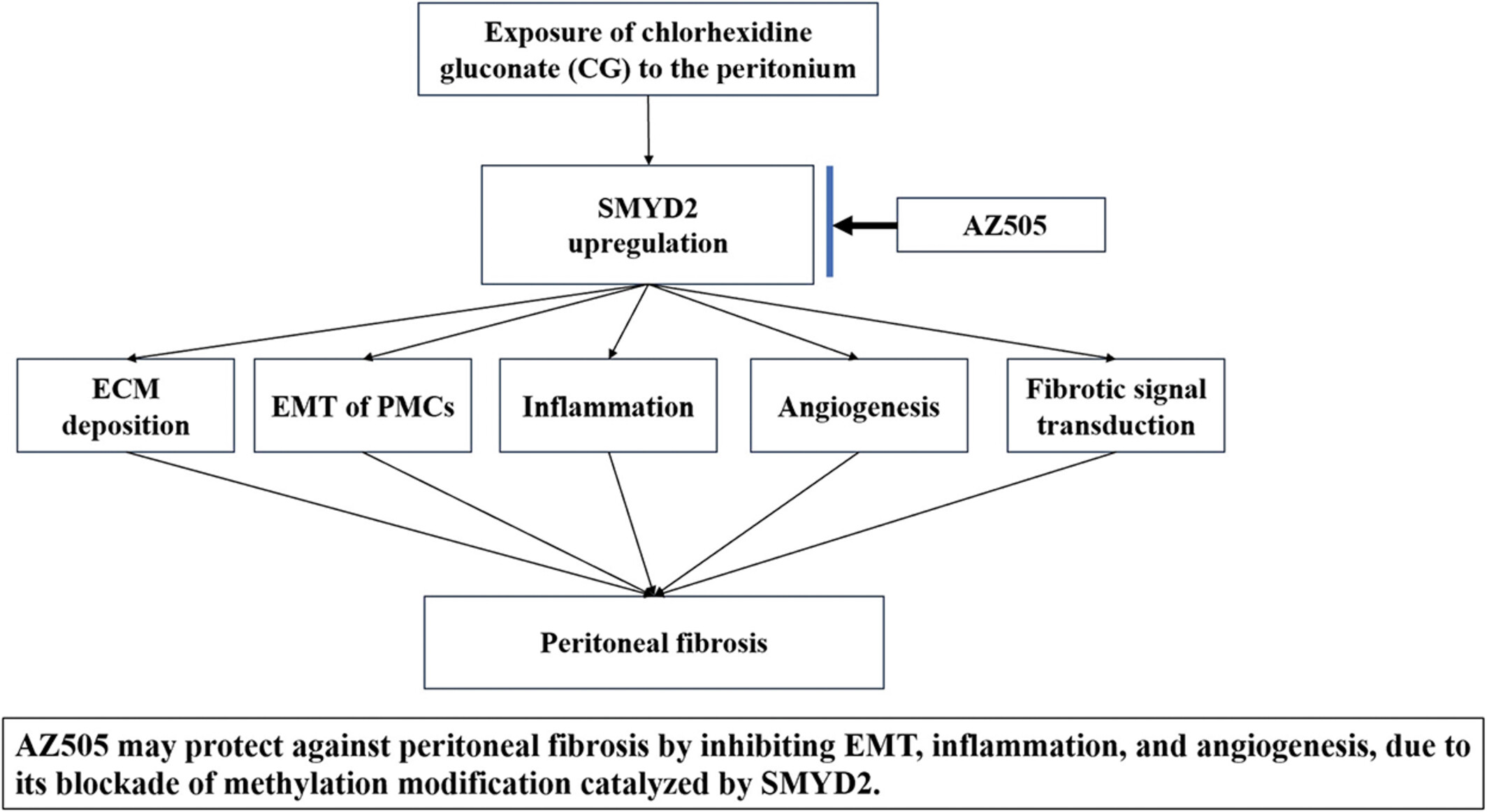
A Novel Inhibitor of Methyltransferase SMYD2, AZ505 Protects Against Peritoneal Fibrosis in Mice
- 25 May 2025
Ellagic acid improves osteoarthritis by inhibiting PGE2 production in M1 macrophages via targeting PTGS2
- Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology
- 26 August 2024
AEBP1 restores osteoblastic differentiation under dexamethasone treatment by activating PI3K/AKT signalling
- Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology
- 2 October 2024
Cancer-associated fibroblast-derived circFARP1 modulates non–small cell lung cancer invasion and metastasis through the circFARP1/miR-338-3p/SOX4 axis
- Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology
- 13 August 2024
Agomelatine-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers alleviate neuropathic pain in rats by Nrf2/HO-1 signalling pathway
- Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology
- 30 September 2024
Regulatory mechanism of TRIM21 in sepsis-induced acute lung injury by promoting IRF1 ubiquitination
- Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology
- 3 October 2024
Down-regulation of CYTL1 attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice by inhibiting M2 macrophage polarization via the TGF-β/CCN2 axis
- Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology
- 5 August 2024
High‐sensitivity C‐reactive protein to high‐density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio predicts long‐term adverse outcomes in patients who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention: A prospective cohort study
- Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology
- 15 September 2024
Gross saponins of Tribulus terrestris attenuate rheumatoid arthritis by promoting apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes and reducing inflammation by inhibiting MAPK signalling pathway
- Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology
- 24 October 2024
Caffeic acid phenethyl ester ameliorates colistin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats via modulation of FOXO1/Nrf2/Sirt1 axis
- Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology
- 24 October 2024
Latest news
Recent issues
- Volume 52, Issue 9September 2025
- Volume 52, Issue 8August 2025
- Volume 52, Issue 7July 2025
- Volume 52, Issue 6June 2025