Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW
Explainable artificial intelligence in breast cancer detection and risk prediction: A systematic scoping review
- First Published: 03 July 2024
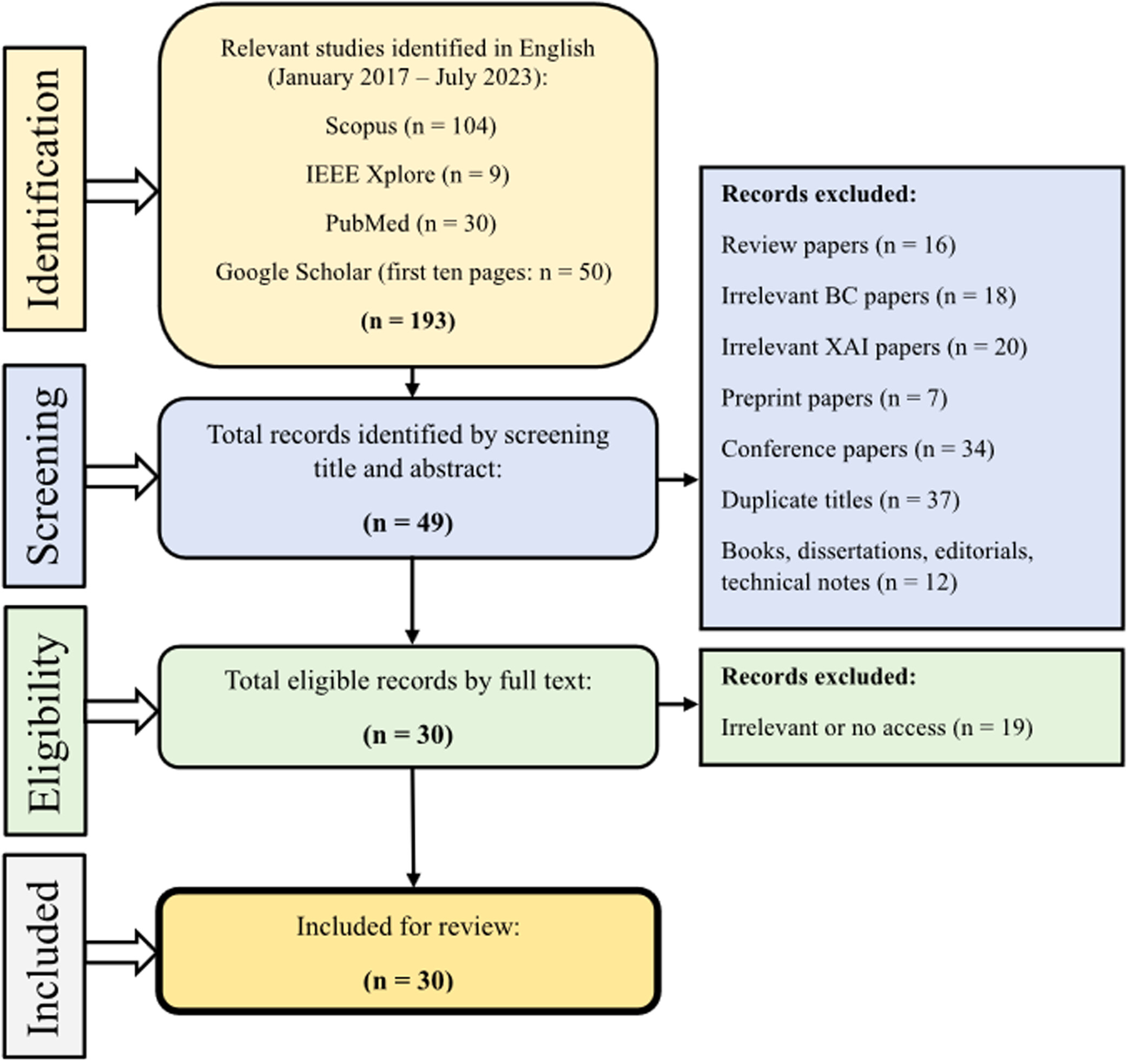
This systematic review is carried out using the preferred reporting items on systematic reviews and meta-analysis (PRISMA) guideline in three steps as follows:
- Step 1:
Identifying studies (total of 193 studies were initially included).
- Step 2:
Selecting the studies (total of 30 articles met the inclusion criteria for our comprehensive review).
- Step 3:
Data extraction and summarization (A data extraction form was developed in Google Sheets, consisting of eight variables, including Authors, Year, the aim of the study (Objective), Data set(s), Data type, Important features, type of artificial intelligence (machine learning or deep learning), and the Explained model. Two reviewers (Amirehsan Ghasemi and Soheil Hashtarkhani) extracted data from all included articles, and any disagreement was resolved by consensus.
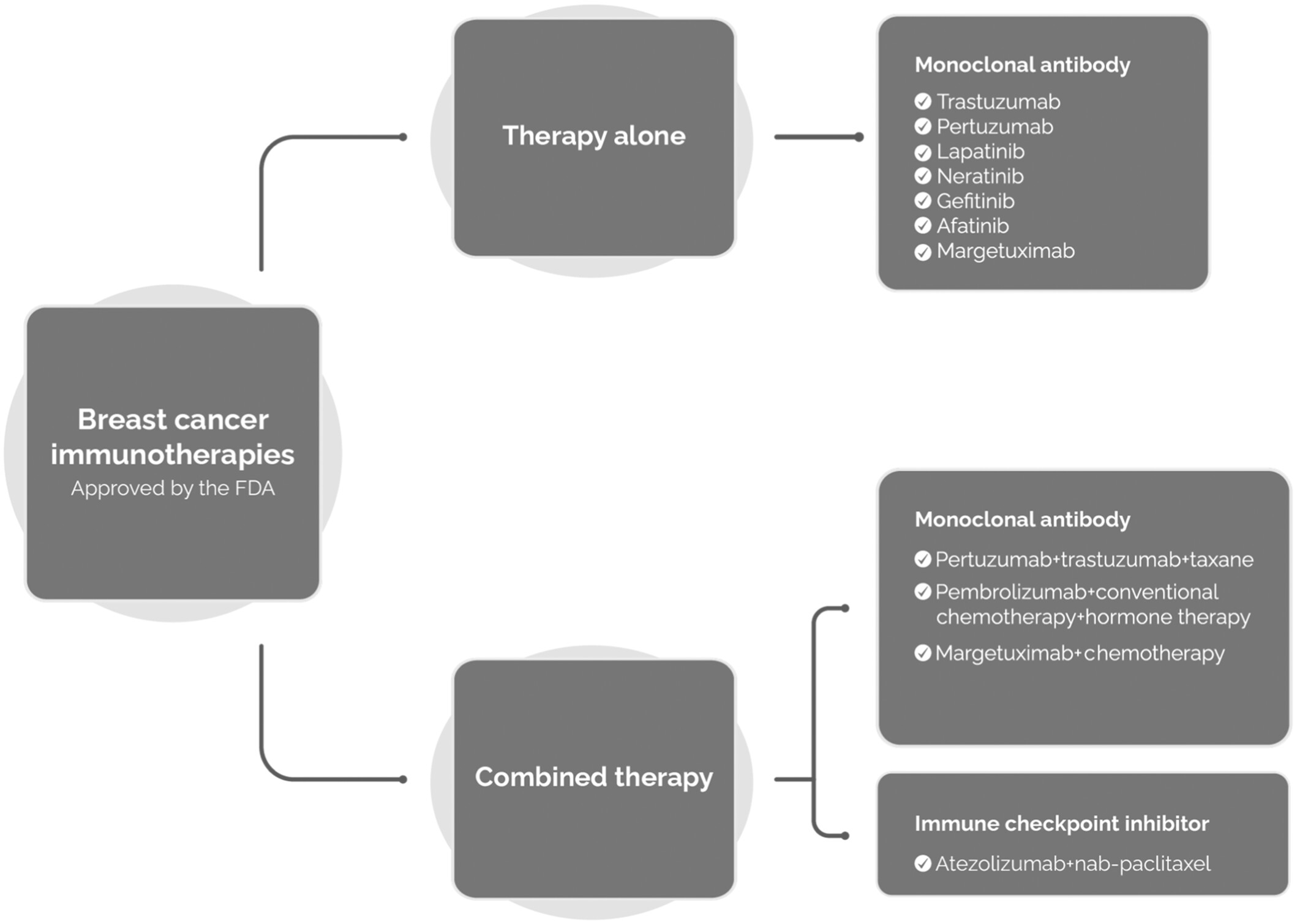
Breast cancer immunotherapy: Realities and advances
- First Published: 22 September 2024
Role of liquid–liquid phase separation in cancer: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications
- First Published: 17 September 2024
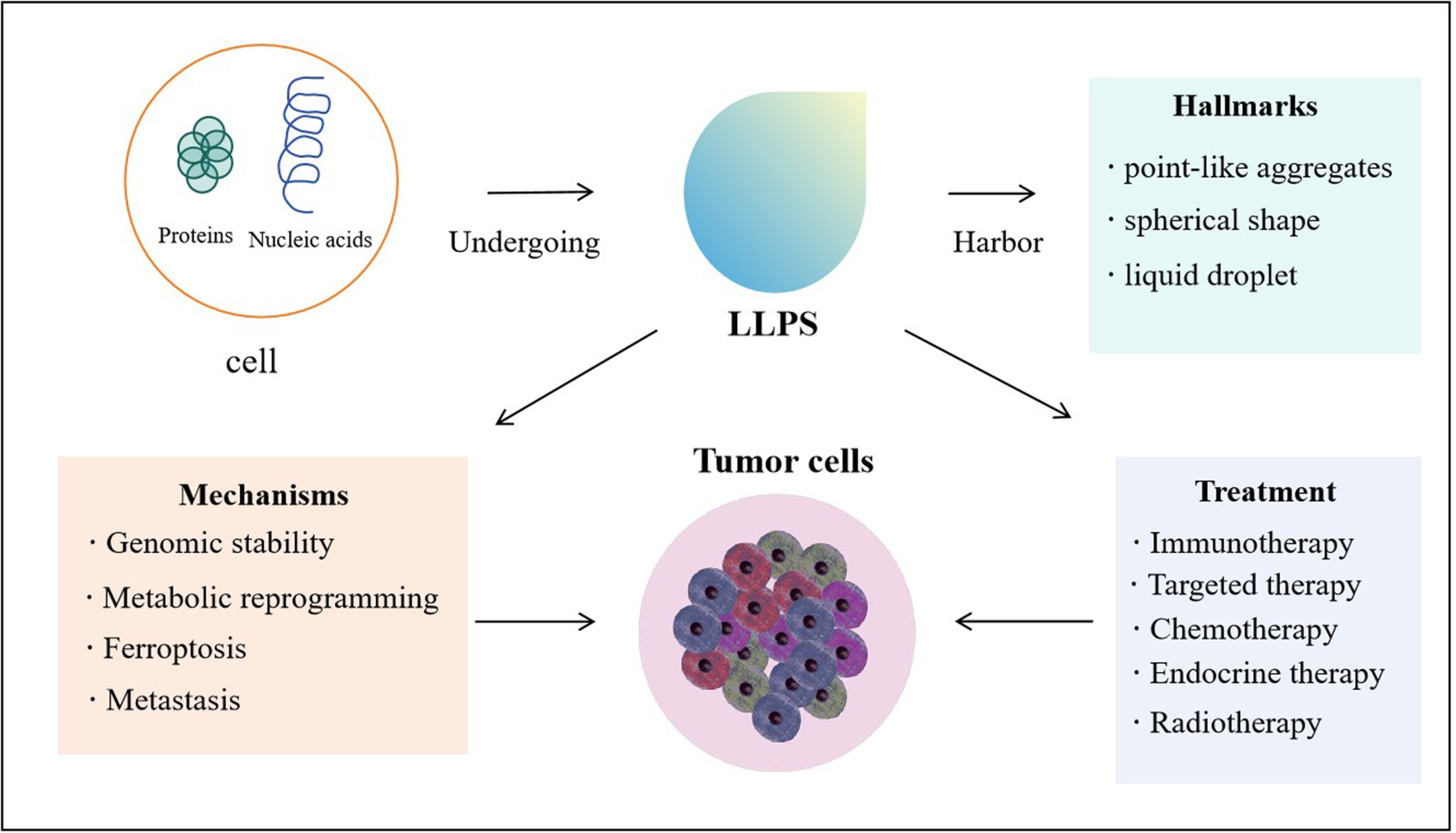
Mechanisms and clinical implications of liquid–liquid phase separation (LLPS) in cancer. LLPS is involved in genomic stability, metabolic reprogramming, ferroptosis, and metastasis of cancer. The potential implications of LLPS in cancer treatment include immunotherapy, targeted therapy, chemotherapy, endocrine therapy, and radiotherapy.
CLINICAL GUIDELINE
Chinese expert consensus on an innovative patient-centered approach to diagnosis and treatment of cancer
- First Published: 30 July 2024
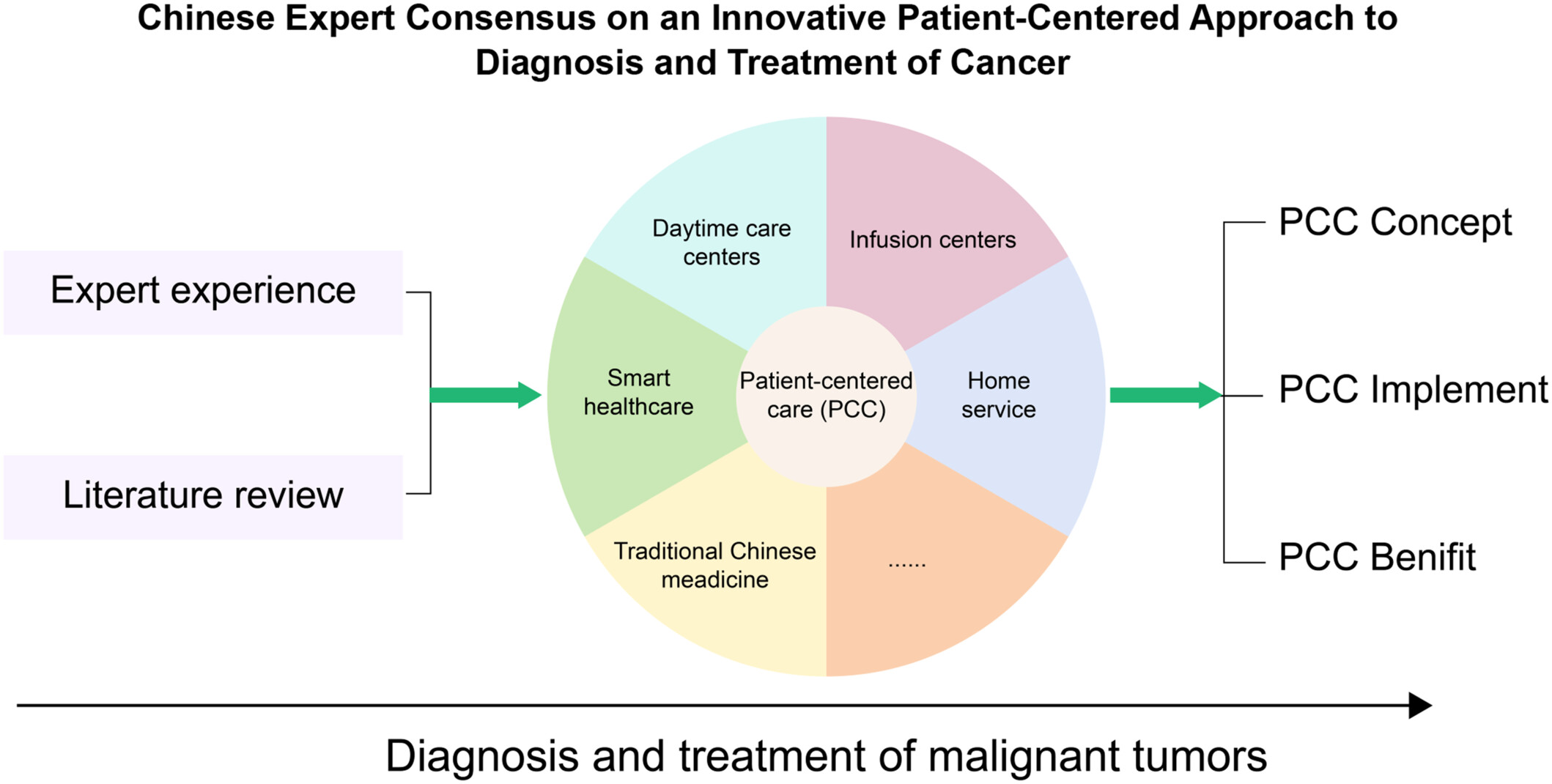
Patient-centered care (PCC) is a developing and innovative approach to the diagnosis and treatment of malignant tumors, aiming to improve the experience of cancer patients throughout their disease management. This consensus provides a clear definition of PCC, outlines its main components as observed in real-world practice, delves into the implementation of PCC, and explores its potential benefits.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Radiomics models to predict bone marrow metastasis of neuroblastoma using CT
- First Published: 28 June 2024
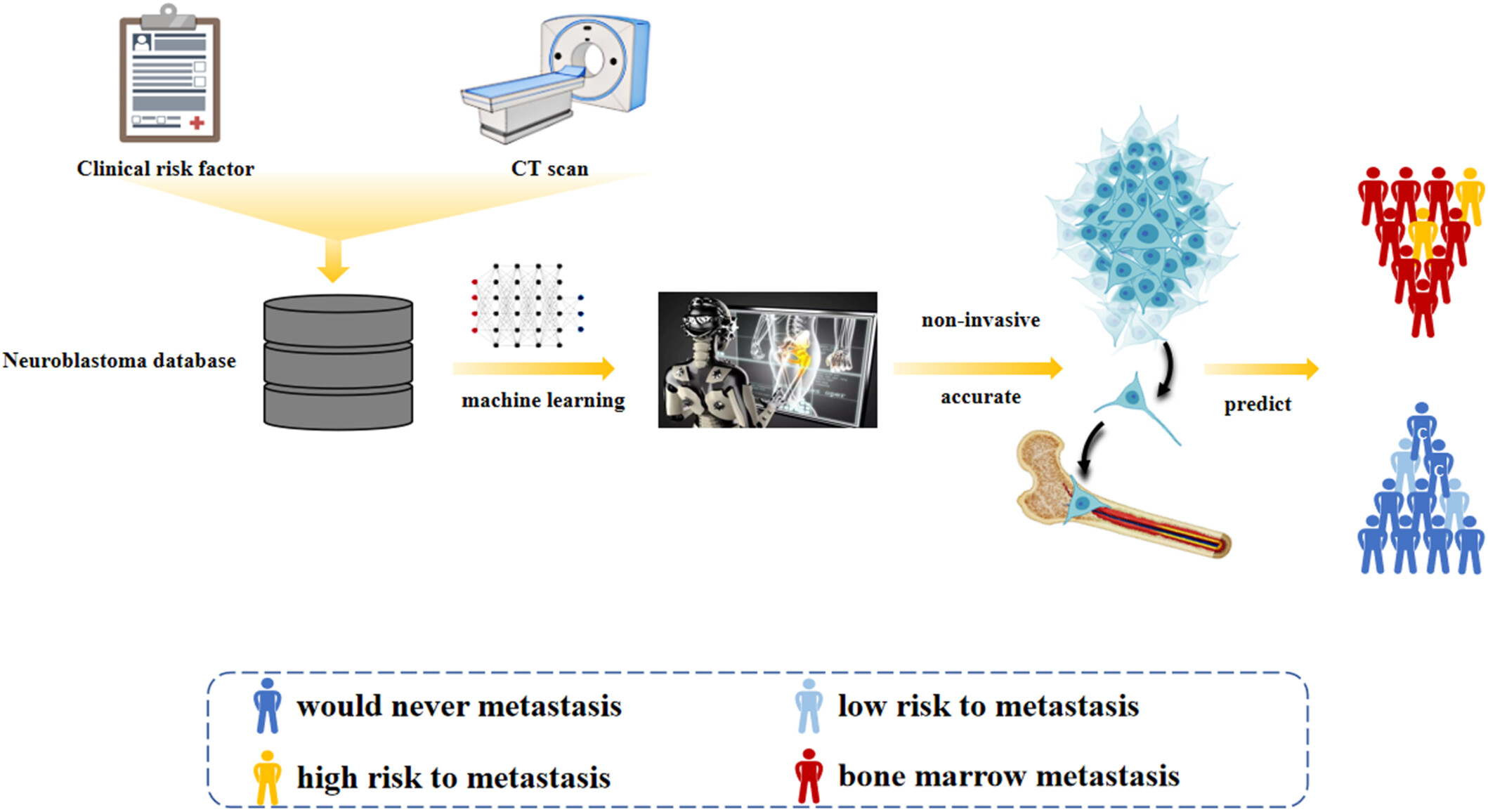
Information from 187 patients with neuroblastoma were retrospectively collected and randomly divided into the training and validation sets. Radiomics features were extracted from computed tomography to build noninvasive radiomics models. We attempted 13 machine learning algorithms and eventually chose three best-performed models.
A pan-cancer analysis of Wnt family member 7B in human cancers
- First Published: 09 September 2024
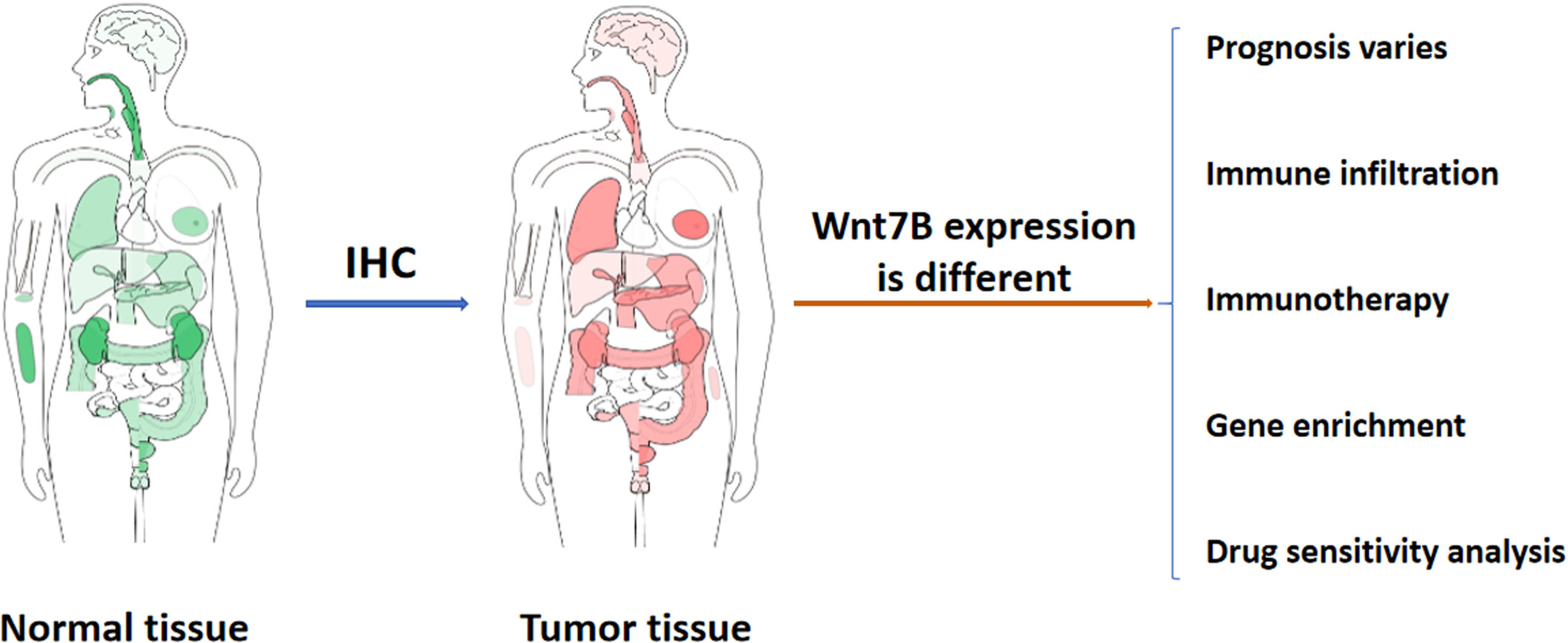
Previous studies have confirmed the important role of Wnt family member 7B (Wnt7B) in the formation of various cancers such as breast, pancreatic, and gastric cancers; however, studies on the specificity of Wnt7B in tumors are limited to certain specific cancers, and systematic pan-cancer studies are lacking, and whether it can be used as a potential biomarker for cancer diagnosis and prognosis remains to be determined. We used bioinformatics techniques and immunohistochemistry (IHC) to observe its expression and function in cancerous and paracancerous tissues of various tumors. Finally, we found that Wnt7B exhibited significant upregulation in the majority of cancer cases,at the same time,Wnt7B affects cancer prognosis through regulating tumor microenvironment,immune infiltration, tumor stemness, and other aspects, which suggests that Wnt7B can be a new cancer prognostic indicator and therapeutic target, and also the pharmacosensitivity analysis related to Wnt7B and cancer therapy can provide some help for clinical precision treatment.
Inetetamab combined with sirolimus and chemotherapy for the treatment of HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer patients with abnormal activation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway after trastuzumab treatment
- First Published: 19 September 2024
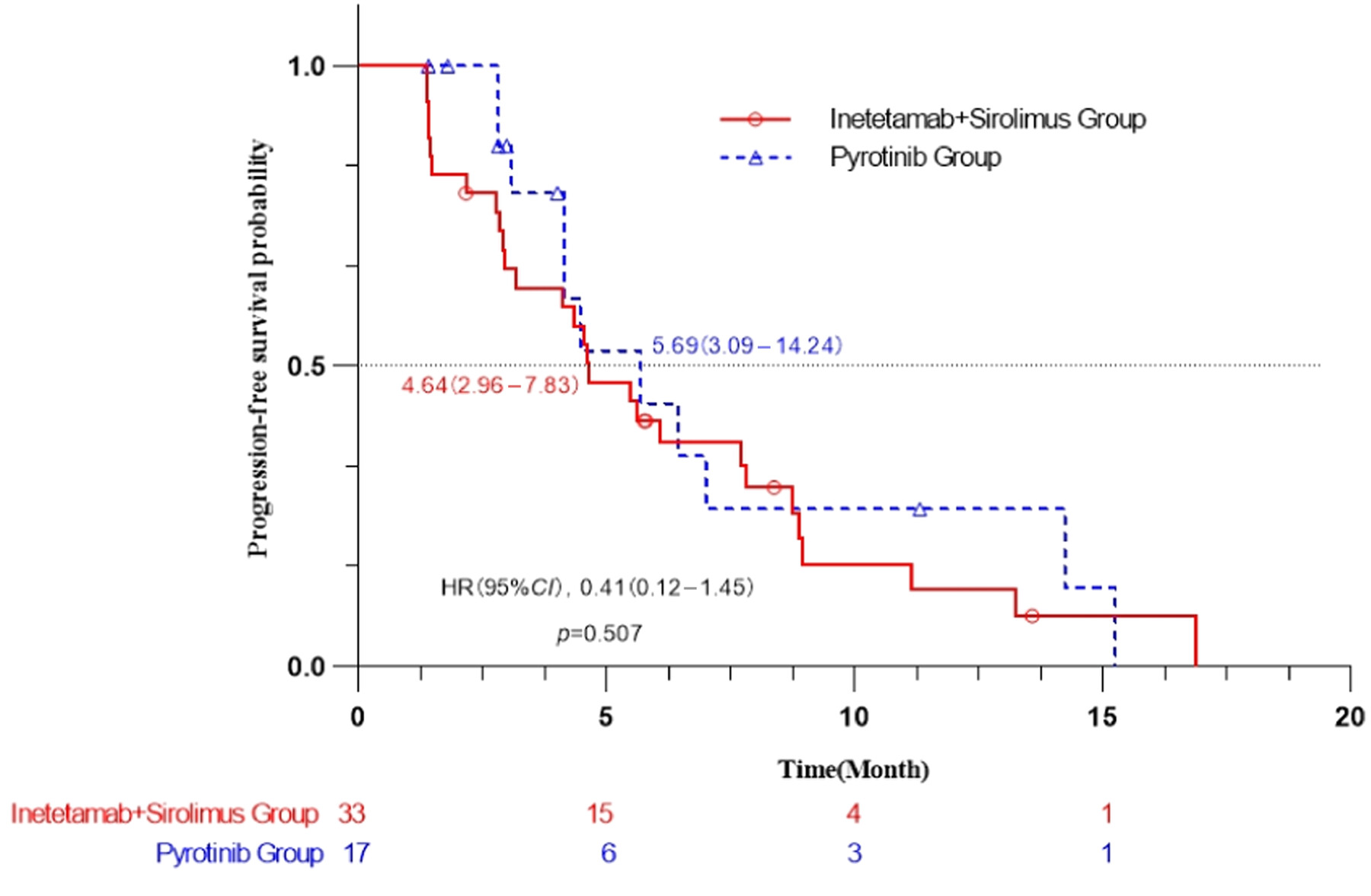
This prospective multicenter clinical study revealed that for metastatic Human epidermal factor receptor 2 (HER2)-positive breast cancer patients with abnormal activation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR (PAM) pathway and previous trastuzumab treatment, the combination of inetetamab with sirolimus and chemotherapy is equivalent to the combination of pyrotinib and chemotherapy, and this regimen could be one of the treatment options for PAM pathway activated metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer patients.
Multiomics and single-cell sequencings reveal the specific biological characteristics of low Ki-67 triple-negative breast cancer
- First Published: 19 September 2024
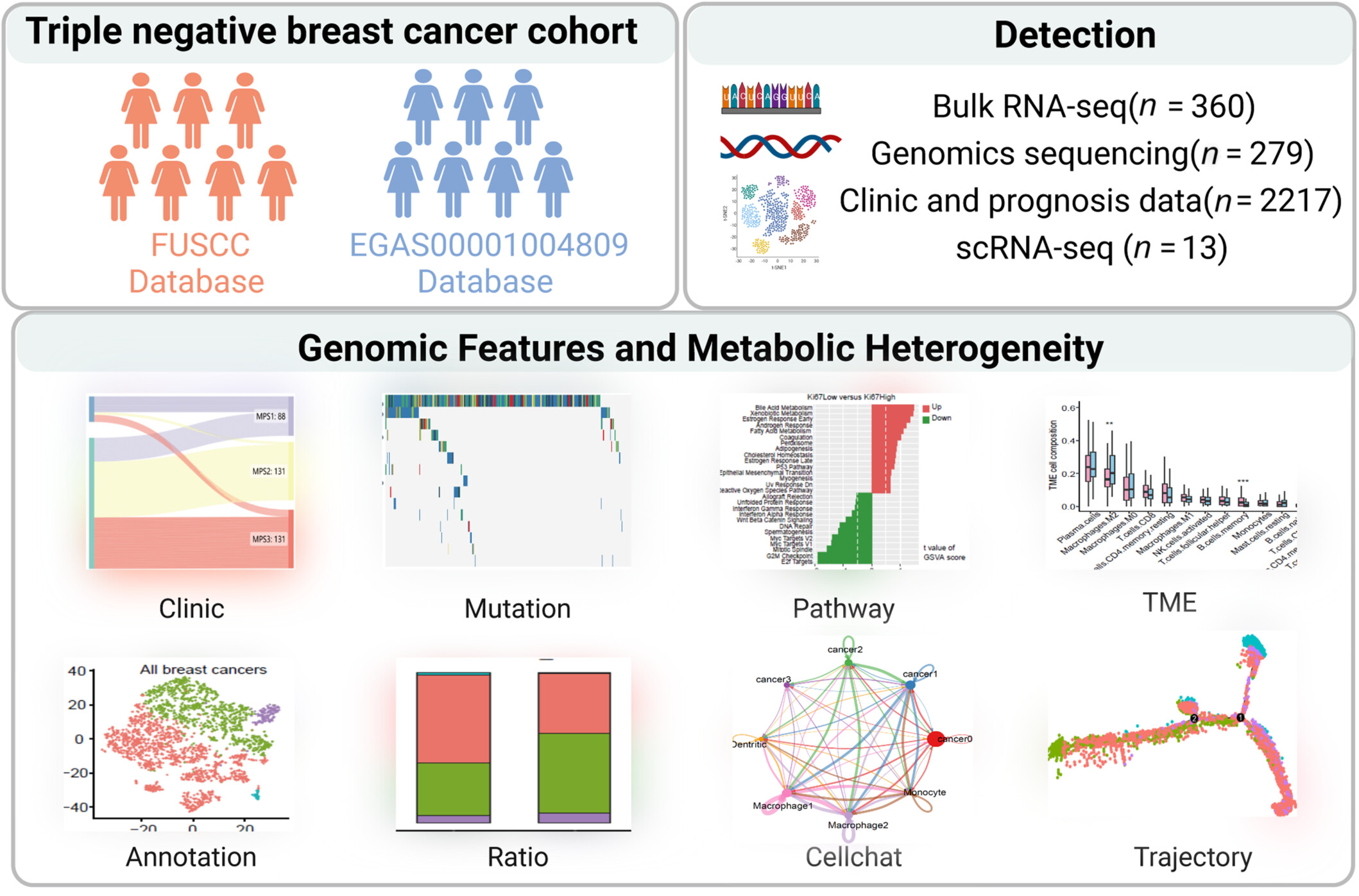
The cohort in this study was the largest single-center multiomics cohort of low Ki-67 triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) patients, enabling the systematic elucidation of the characteristics of low Ki-67 TNBC at the genomic, transcriptomic, and single-cell levels. Low Ki-67 TNBC is characterized by an elevated age at diagnosis, a reduced proportion of invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC), increased alterations in the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway, upregulated lipid metabolism pathways. The PI3K pathway mutation frequency reached 50% in the low Ki-67 TNBC, accompanied by an increase in M2 macrophage infiltration. This suggested a broad scope for the combined application of PI3Kγ inhibitors and immune checkpoint inhibitors in the treatment of low Ki-67 TNBC.