Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW
TRIP13: A promising cancer immunotherapy target
- First Published: 11 October 2024
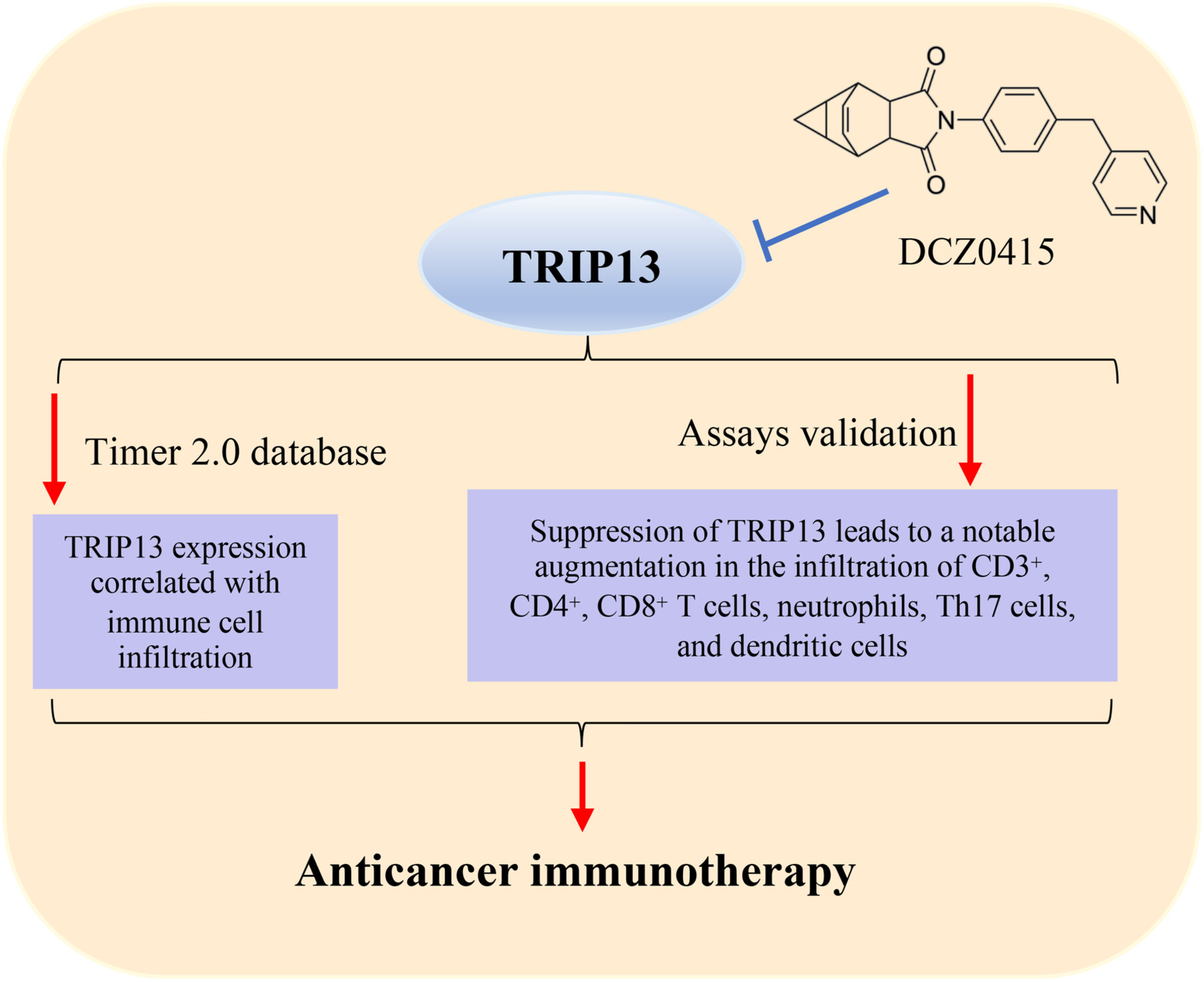
Thyroid hormone receptor interactor 13 (TRIP13) inhibition presents a promising avenue for immunotherapy against tumors. Administration of DCZ0415 to immunocompetent myeloma models resulted in an upregulation of immune cells infiltrated in the tumor microenvironment, suggesting the immunotherapeutic potential of TRIP13 inhibition. Using the TIMER 2.0 database, we also explored the association between TRIP13 expression and immune infiltration levels across various types of cancer.
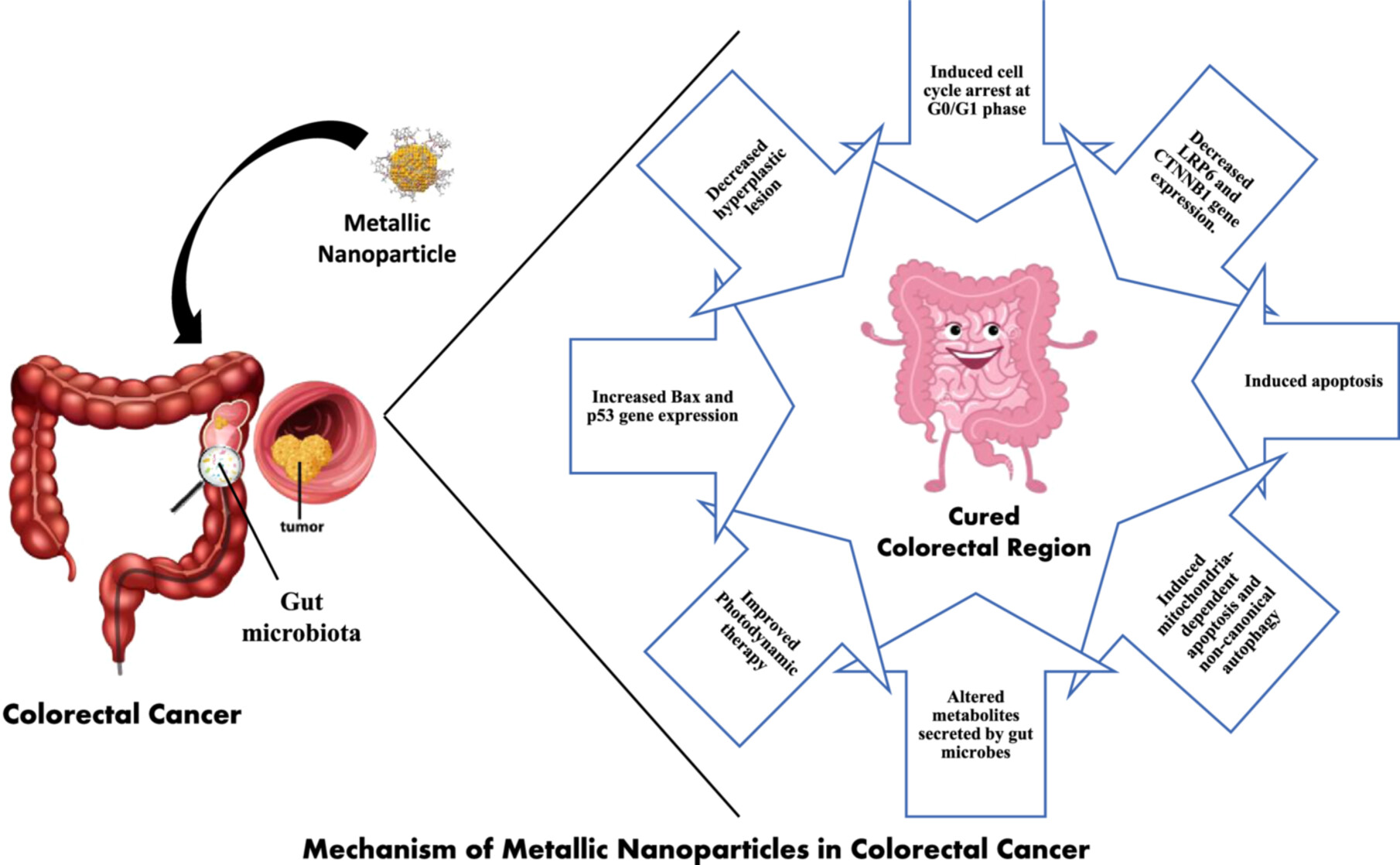
Impact of metallic nanoparticles on gut microbiota modulation in colorectal cancer: A review
- First Published: 11 October 2024
Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor B4: A keystone in immune modulation and therapeutic target in cancer and beyond
- First Published: 22 October 2024
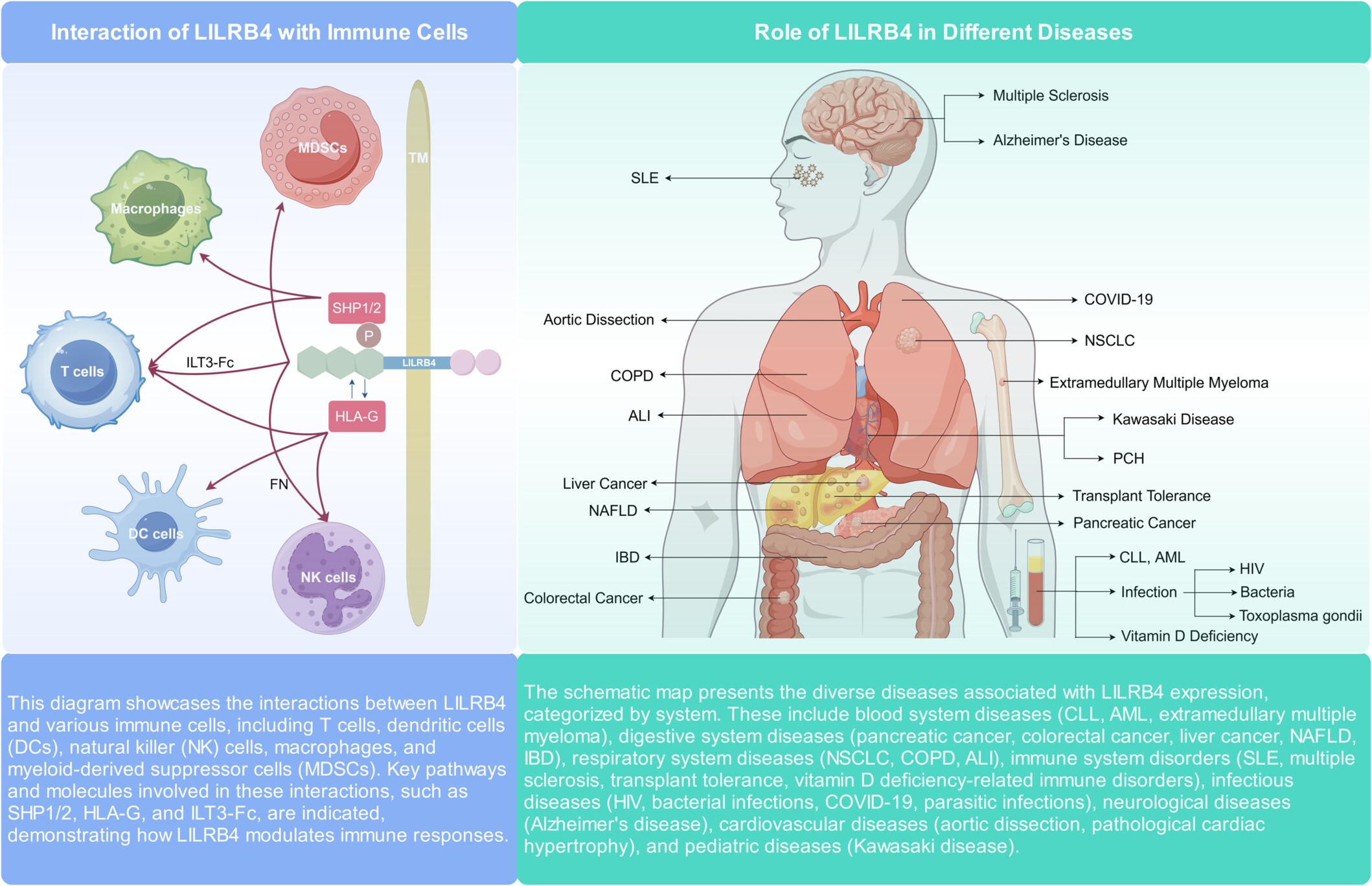
Interaction of LILRB4 with Immune Cells: This diagram showcases the interactions between LILRB4 and various immune cells, including T cells, dendritic cells (DCs), natural killer (NK) cells, macrophages, and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs). Key pathways and molecules involved in these interactions, such as SHP1/2, HLA-G, and ILT3-Fc, are indicated, demonstrating how LILRB4 modulates immune responses. Role of LILRB4 in Different Diseases: The schematic map presents the diverse diseases associated with LILRB4 expression, categorized by the system. These include blood system diseases (CLL, AML, extramedullary multiple myeloma), digestive system diseases (pancreatic cancer, colorectal cancer, liver cancer, NAFLD, and IBD), respiratory system diseases (NSCLC, COPD, and ALI), immune system disorders (SLE, multiple sclerosis, transplant tolerance, and vitamin D deficiency-related immune disorders), infectious diseases (HIV, bacterial infections, COVID-19, and parasitic infections), neurological diseases (Alzheimer's disease), cardiovascular diseases (aortic dissection, pathological cardiac hypertrophy), and pediatric diseases (Kawasaki disease).
COMMENTARY
Retinoic acid receptor responder 2 and lipid metabolic reprogramming: A new insight into brain metastasis
- First Published: 24 October 2024
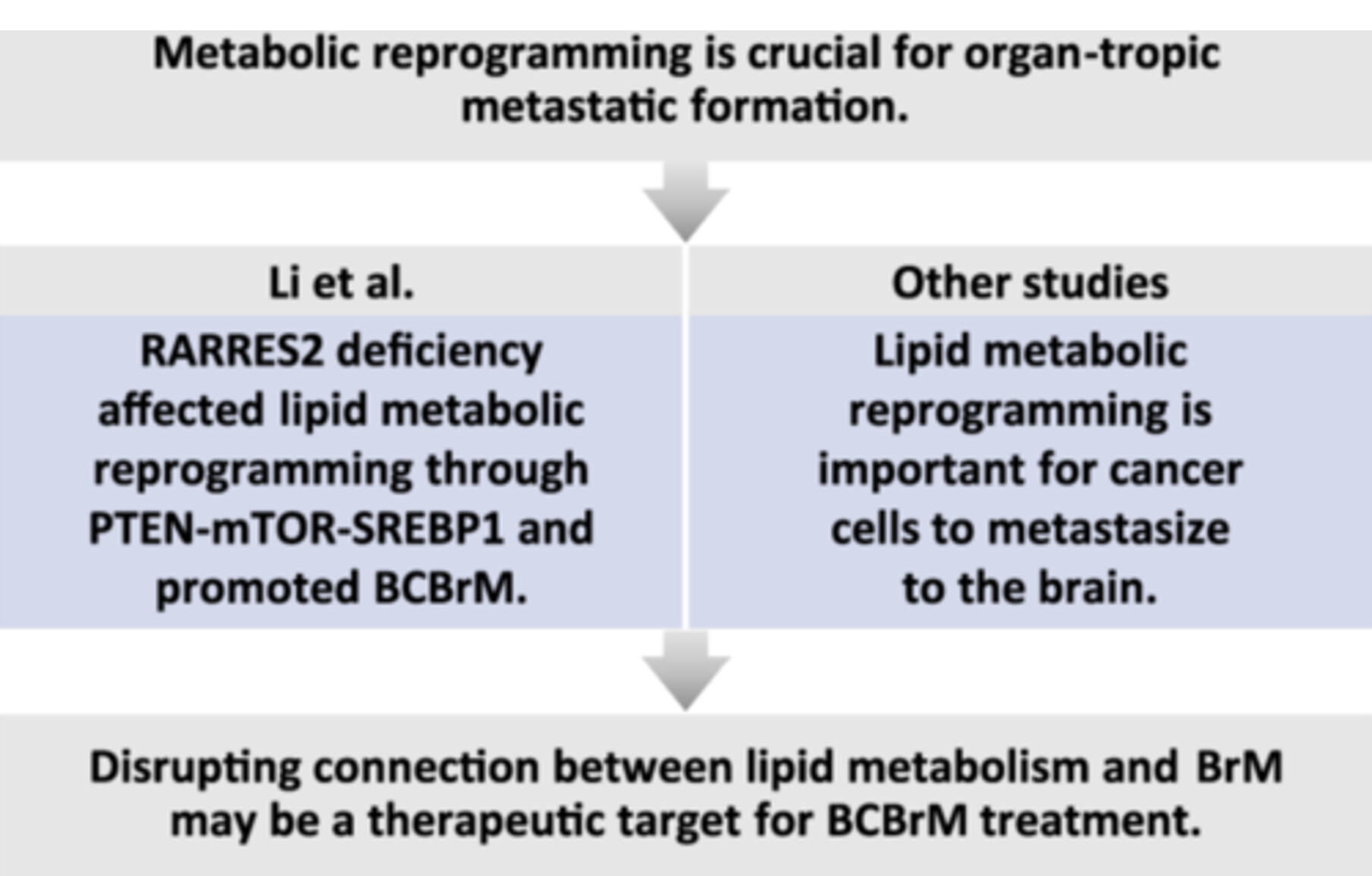
The brain is a common metastatic site for carcinoma, and metabolic reprogramming is crucial for organ-tropic metastatic formation. Li et al. found RARRES2 deficiency affected lipid metabolic reprogramming through PTEN-mTOR-SREBP1 pathway and promoted BCBrM. Other studies revealed that lipid metabolic reprogramming is part of metabolic adaptation to central nervous system. Overall, there is an intricate connection between lipid metabolism and brain metastases, and disrupting this connection may be a potential therapeutic target for BCBrM treatment.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Development and validation of the NCC-BC-A scale to assess patient-reported outcomes for breast cancer patients in China
- First Published: 18 October 2024
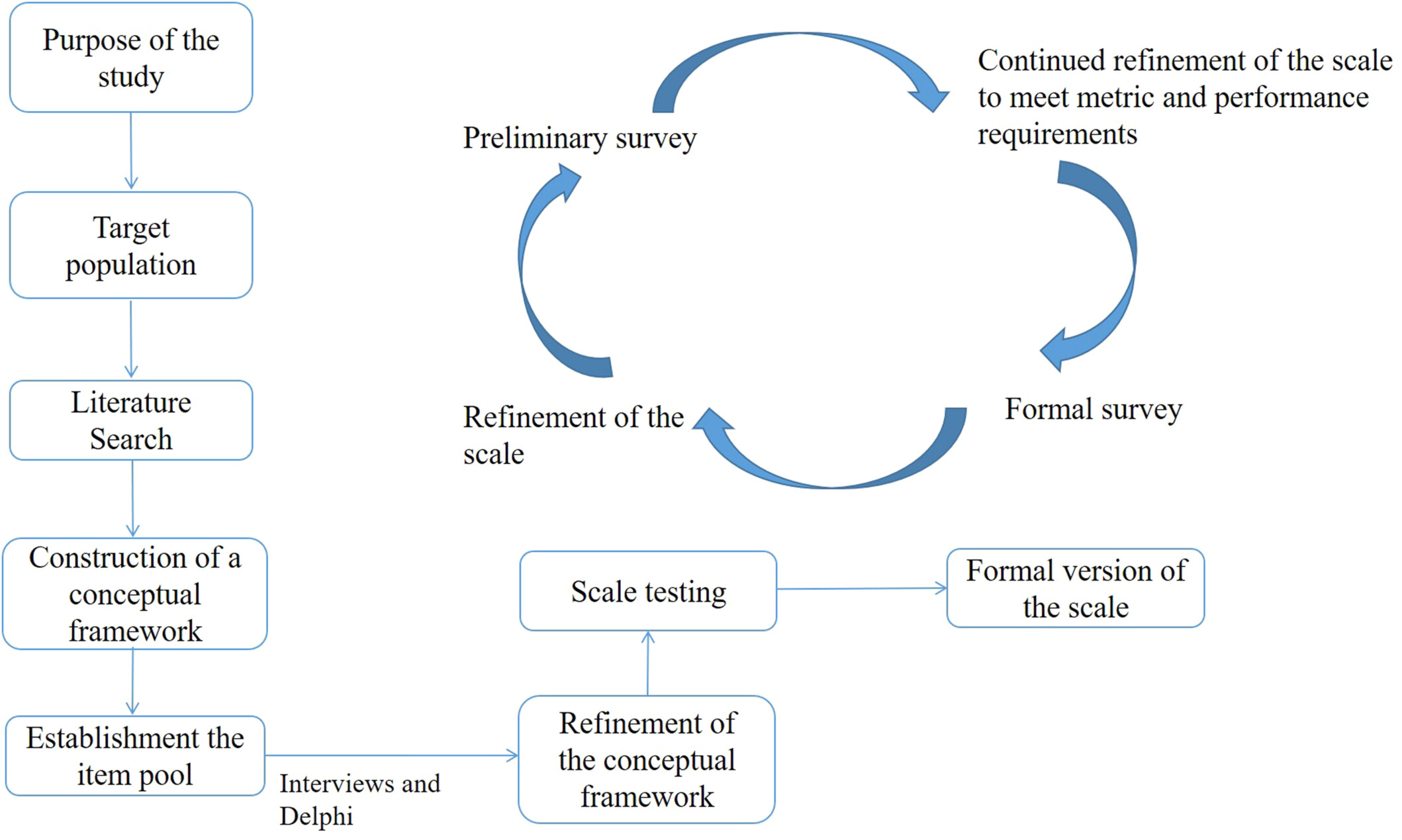
This study developed a NCC-BC-A scale with relatively high validity and reliability for breast cancer (BC) patients. NCC-BC-A scale fully considered the characteristics of systemic treatment status for BC and the realistic situation in China, which may help clinicians to pay more attention to QOL of BC patients and to optimize management system for BC.
Beyond clinical trials: CDK4/6 inhibitor efficacy predictors and nomogram model from real-world evidence in metastatic breast cancer
- First Published: 25 October 2024
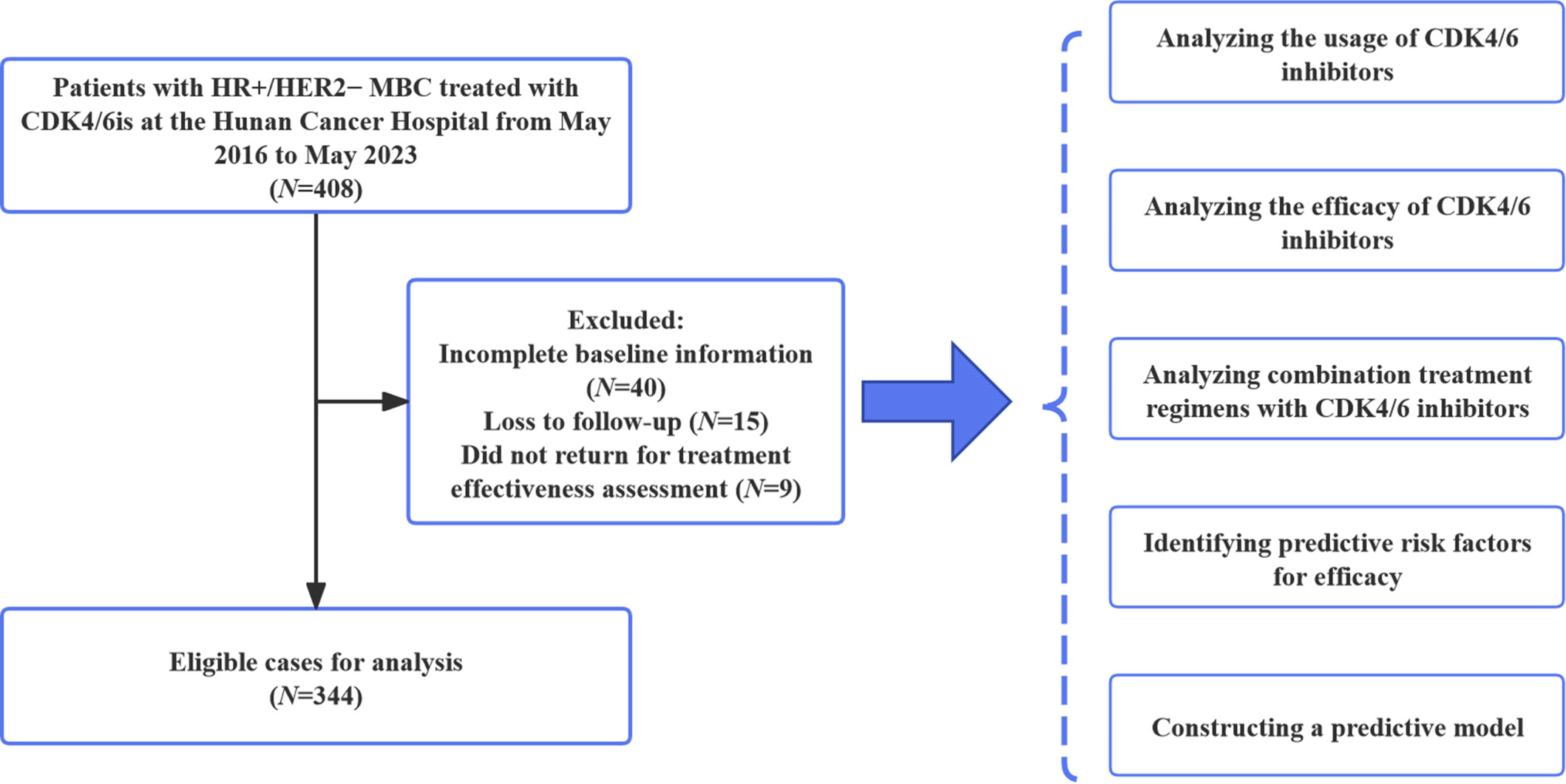
The graphical abstract summarizes a study evaluating CDK4/6 inhibitors (CDK4/6i) combined with endocrine therapy in hormone receptorr-positive (HR+/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 metastatic breast cancer patients. It highlights a median progression-free survival (PFS) of 12.8 months, with significant factors reducing PFS including visceral metastasis, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status ≥ 1, low estrogen receptor/progesterone receptor levels, high Ki-67, and later-stage treatment. Adverse reactions such as neutropenia (29.1%), leukopenia (13.7%), and anemia (4.1%) were manageable. A prognostic nomogram showed good predictive performance (C-index 0.714), and a rechallenge of CDK4/6i demonstrated median PFS of 7.7 months, extending to 11.4 months for nonprogression discontinuation.
Combination therapy using low-dose anlotinib and immune checkpoint inhibitors for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer
- First Published: 28 October 2024
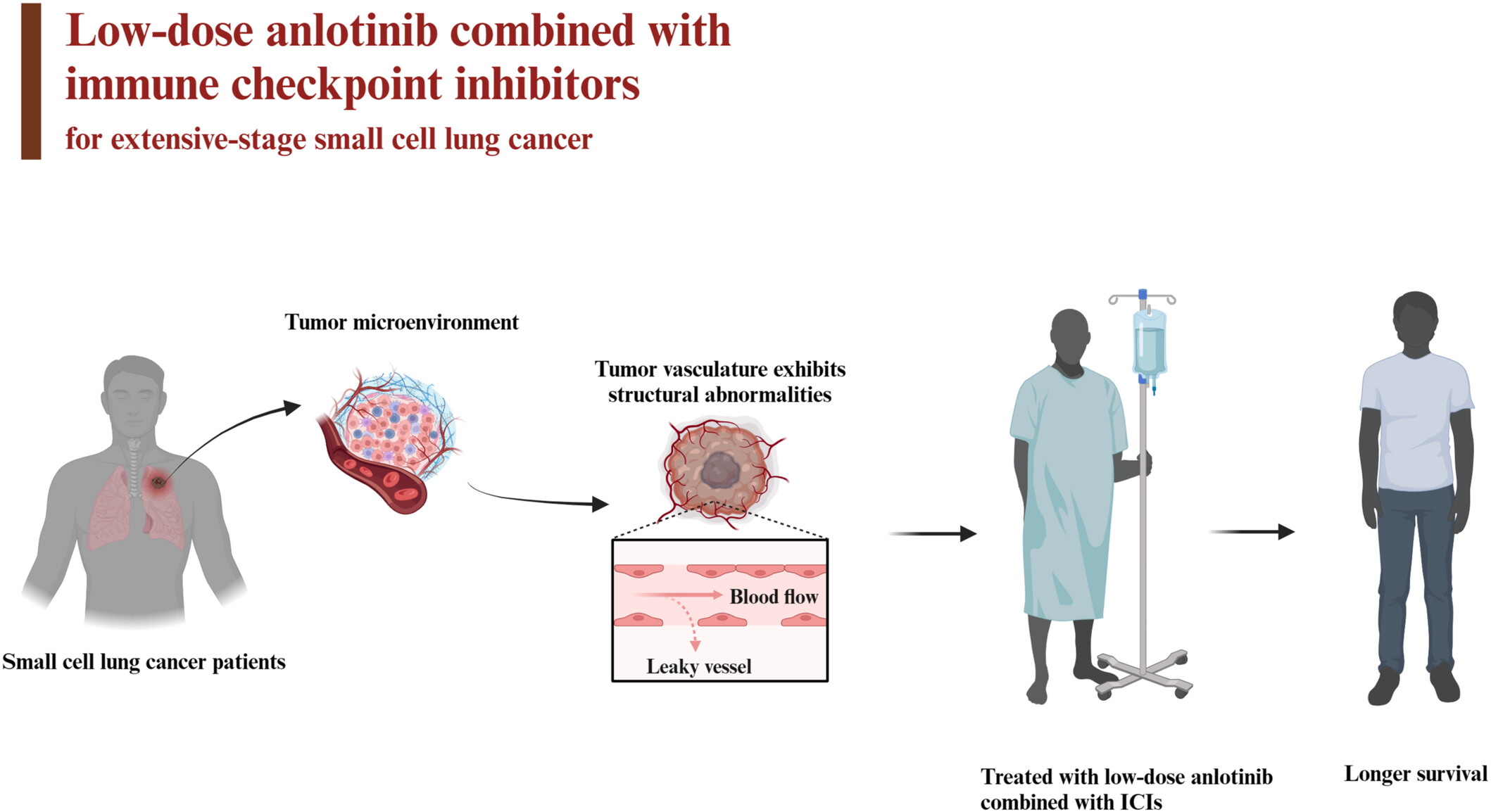
In this retrospective study, we evaluated the efficacy and safety of low-dose anlotinib combined with immune checkpoint inhibitors as a second-line or subsequent therapy for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer. It demonstrated that this combination improves survival and confers tolerable adverse. However, additional work is needed to identify more patients who may benefit from this treatment as a second-line or subsequent therapy to improve survival outcomes.
Prognostic nomograms for young breast cancer: A retrospective study based on the SEER and METABRIC databases
- First Published: 25 October 2024
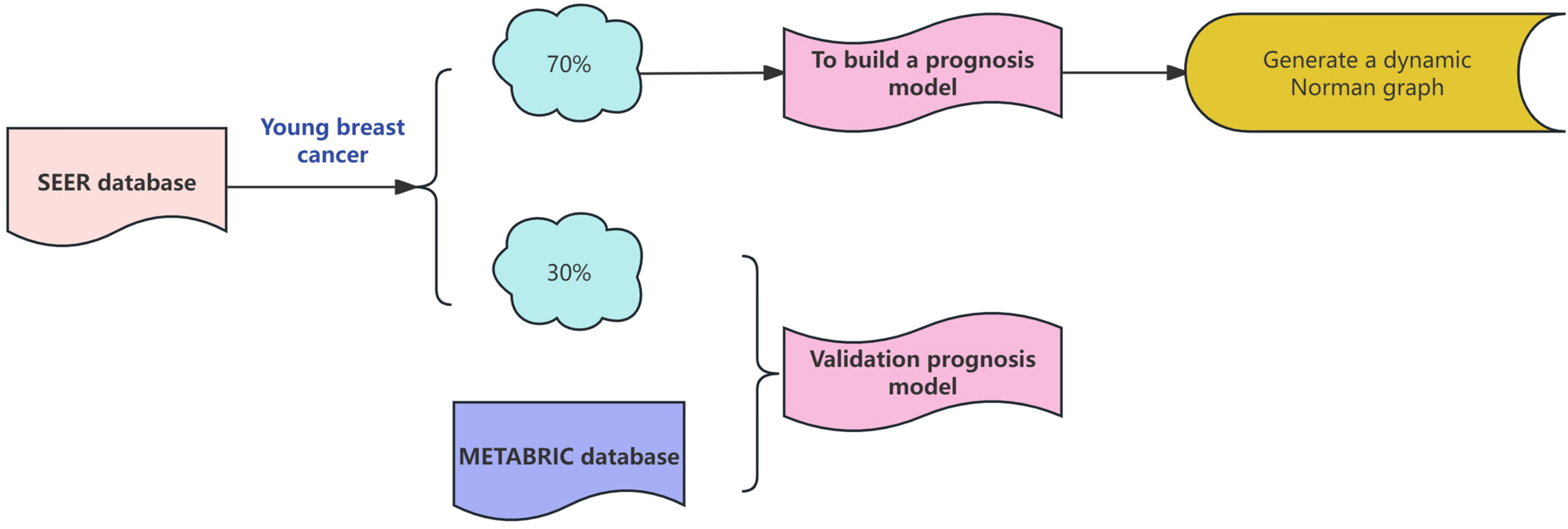
This study focuses on developing and validating prognostic nomograms for young breast cancer patients, integrating multiple clinical factors such as TNM stage, HER2 status, and pathological differentiation to predict overall survival and breast cancer-specific survival. Using data from the SEER and METABRIC databases, the nomograms provide accurate 3-, 5-, and 10-year survival estimates. Dynamic versions of these nomograms offer personalized, user-friendly tools to guide clinical decision-making, with the goal of improving prognosis and treatment outcomes for breast cancer with young patients.