Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW
Materials and structures at cold-region and Arctic low temperatures: A state-of-the-art review
- Pages: 519-547
- First Published: 24 December 2024
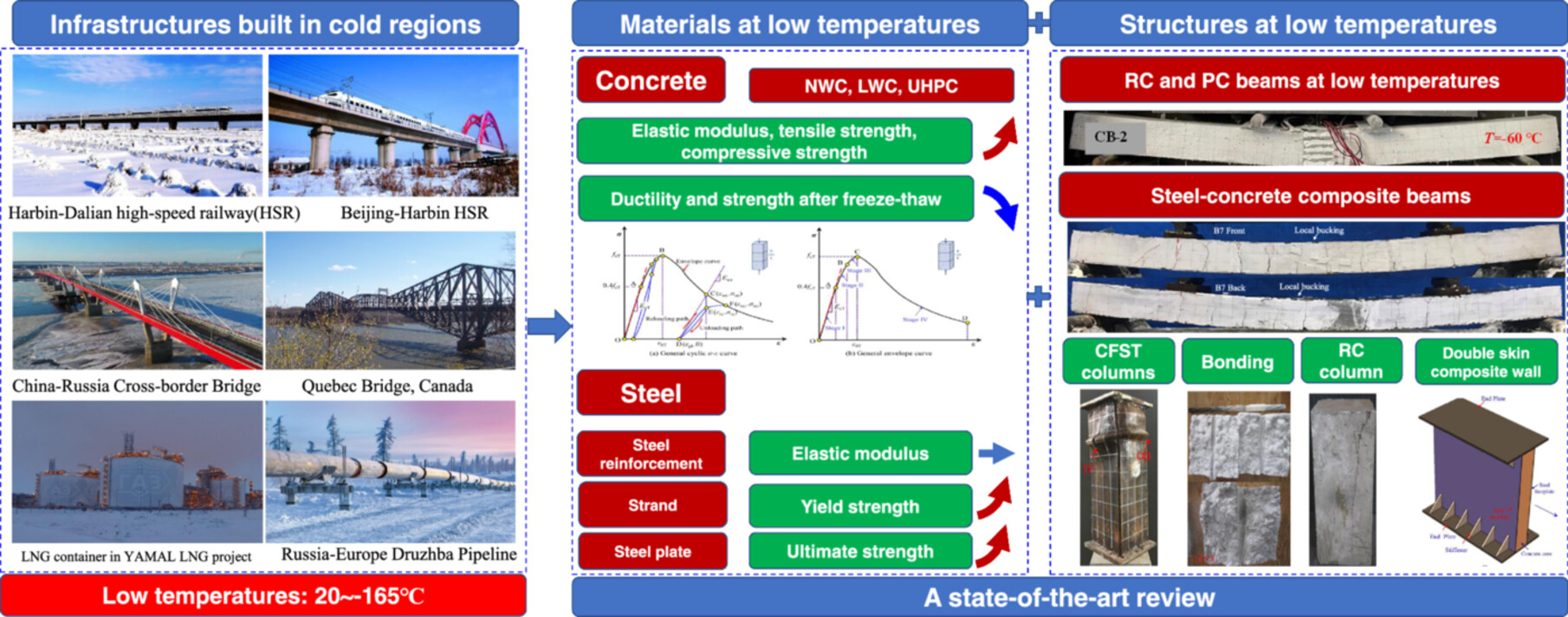
Constructions of infrastructures in the cold region and Arctic exhibit a rapid growth after the 2000s, for example, railway, oil and gas exploration platform, bridges, roads, and pipelines. However, the harsh cold-region or Arctic low temperatures significantly influence the mechanical behaviors of construction materials in these infrastructures, and bring safety and durability challenges to these engineering structures in cold regions. This study made a state-of-the-art review of materials and structures exposed to low temperatures. This review includes mechanical properties of construction materials, including concrete, steel reinforcements, mild/high-strength steel plate, and steel strands at low temperatures. This paper also made a review on steel–concrete bonding behaviors, reinforced concrete, prestressed concrete structures, concrete-filled steel tubes, steel–concrete composite beams at low temperatures.
Mainshock–aftershock seismic fragility assessment of civil structures: A state-of-the-art review
- Pages: 548-573
- First Published: 28 December 2024
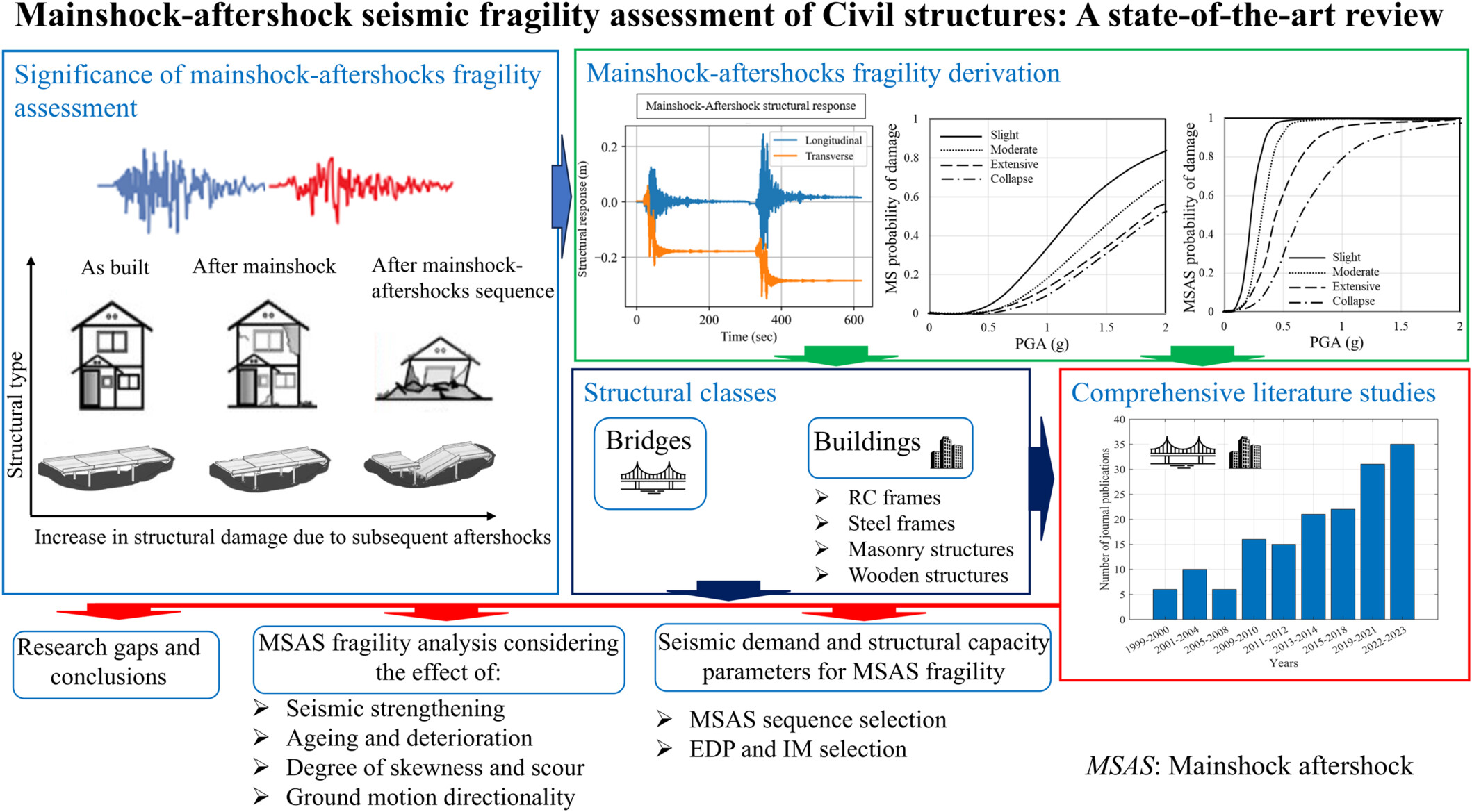
This article provides a state-of-the-art review of seismic fragility assessment for civil structures under mainshock-aftershock sequences. It highlights methodologies, key factors affecting the fragility of bridges and buildings, and identifies critical research gaps essential for advancing resilience assessment under sequential seismic hazards.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Experimental study on mechanical behavior of bolted steel-neosinocalamus affinis-based bamboo scrimber and steel connections
- Pages: 574-593
- First Published: 24 December 2024
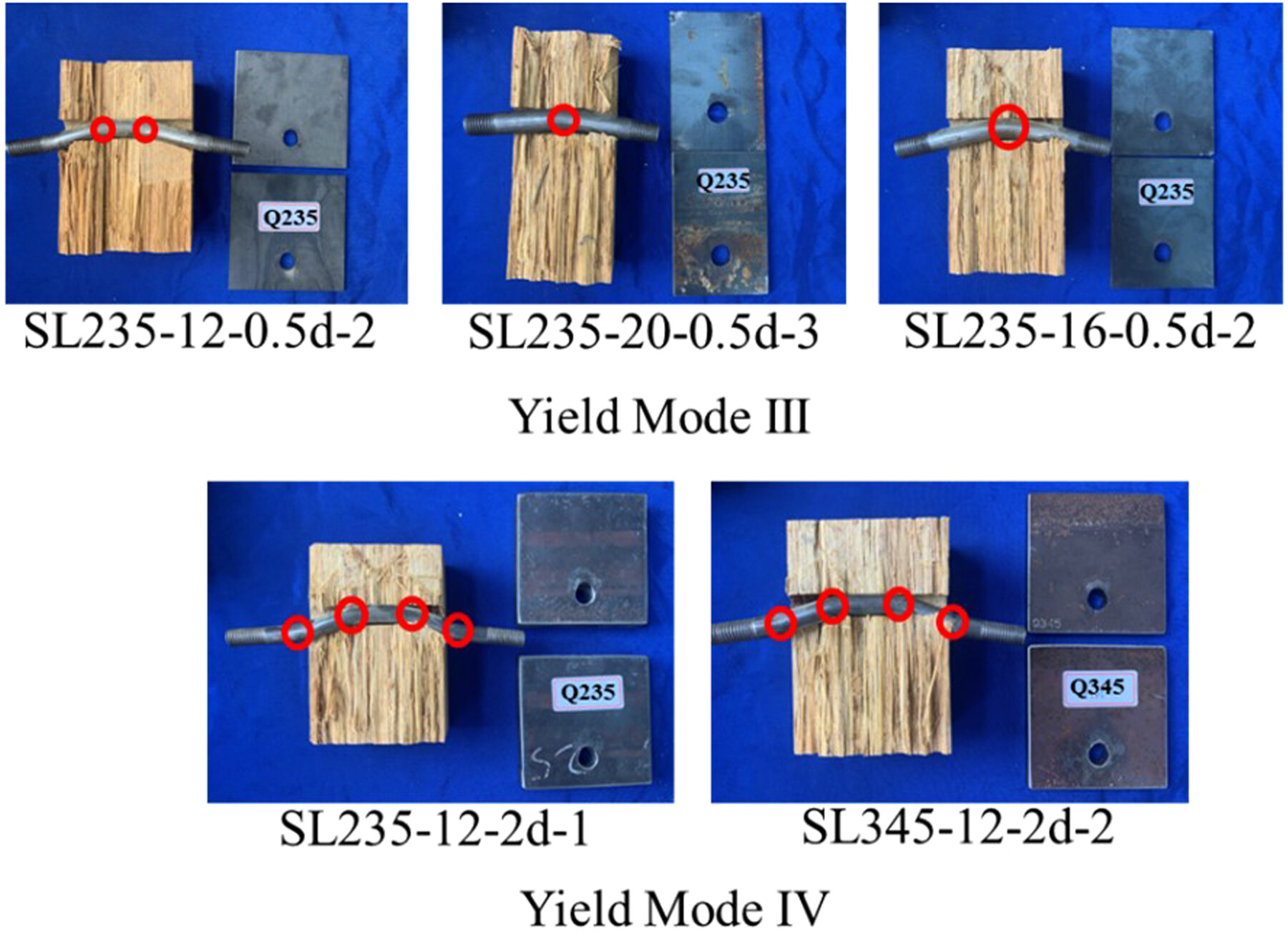

The results demonstrate that for thick steel plates (t = 2d) in bolted steel-based bamboo scrimber and steel connections, a double-hinge failure mode near each shear plane alongside the local carrying yield of the bamboo indicates Yield Mode IV. In contrast, connections with relatively thinner steel plates (0.5d − 1d) exhibited a single hinge and local carrying yield. This aligns with Johansen findings in timber structures, though distinctions in steel plate thickness between Yield Modes III and IV differ. Specifically, a steel plate thickness of 1d does not mark the boundary between thin and thick plates, suggesting a critical point between 1d and 2d. Despite adherence to Eurocode 5 design requirements for end, spacing, and edge distances, all connections avoided failure in Yield Mode I, with no definitive preyield deformation in steel plates observed before bolt deformation. Previous studies and literature also confirm that connections meeting the thickness requirements of GB50005 and Eurocode 5 (a ≥ 4d) fail in Mode III or IV, not Mode I. This indicates that, under certain construction standards, bolted steel-based bamboo scrimber and steel connections effectively utilize the mechanical properties of their components, particularly the bending capacity of bolts.
Seismic fragility and life-cycle loss analyses of high-speed railway bridges supported by segmentally assembled round-end hollow piers
- Pages: 594-611
- First Published: 24 December 2024
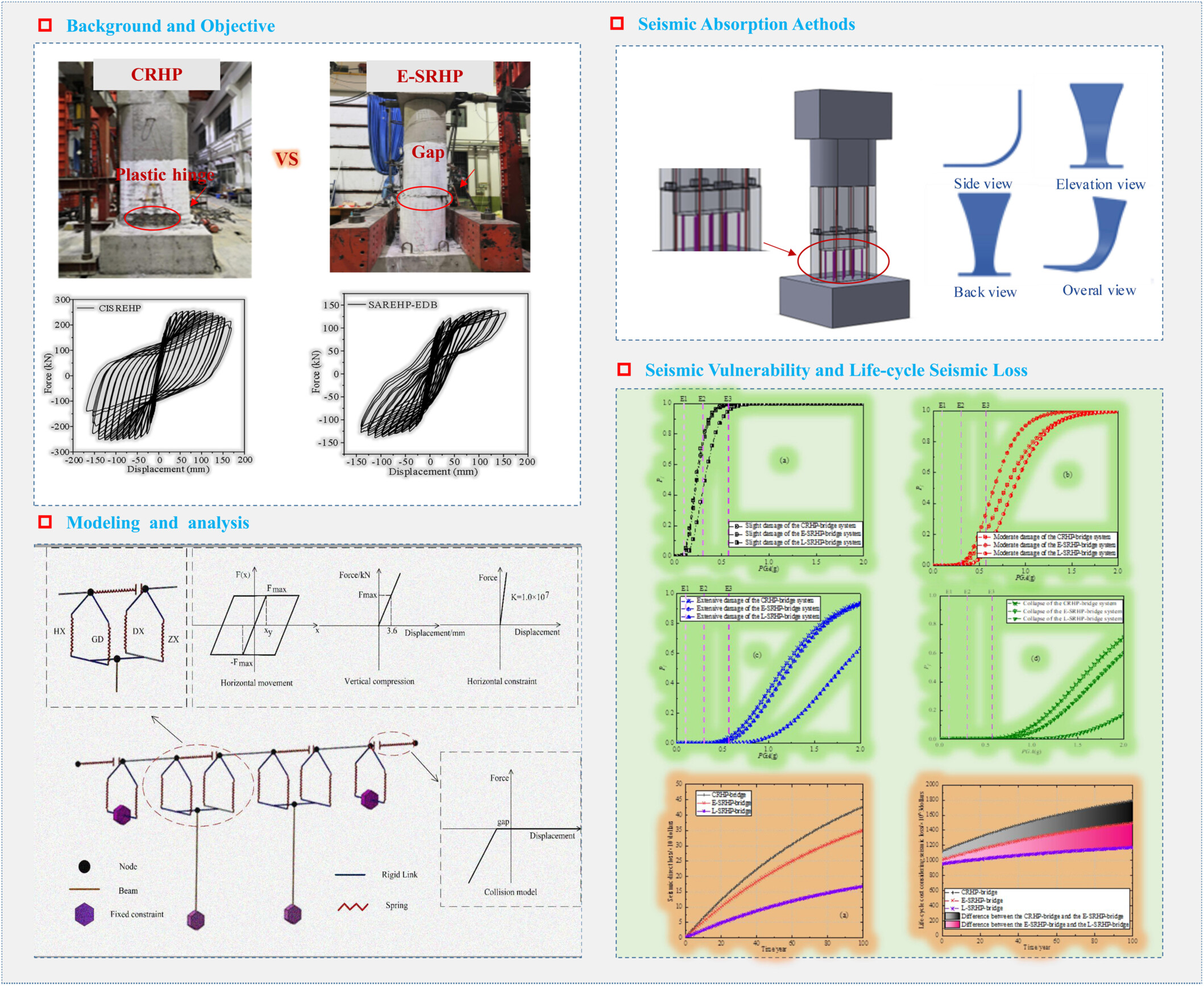
Seismic design and absorption measures for assembled piers were provided. The numerical simulation method for bridges with assembled piers was studied. Seismic vulnerability curves for bridges with assembled piers were established. The life-cycle seismic loss of bridges with different types of piers was assessed. Bridges with assembled piers using connection buckles show good seismic safety.
Component-level seismic fragility database of suspended piping systems in buildings
- Pages: 612-636
- First Published: 24 December 2024
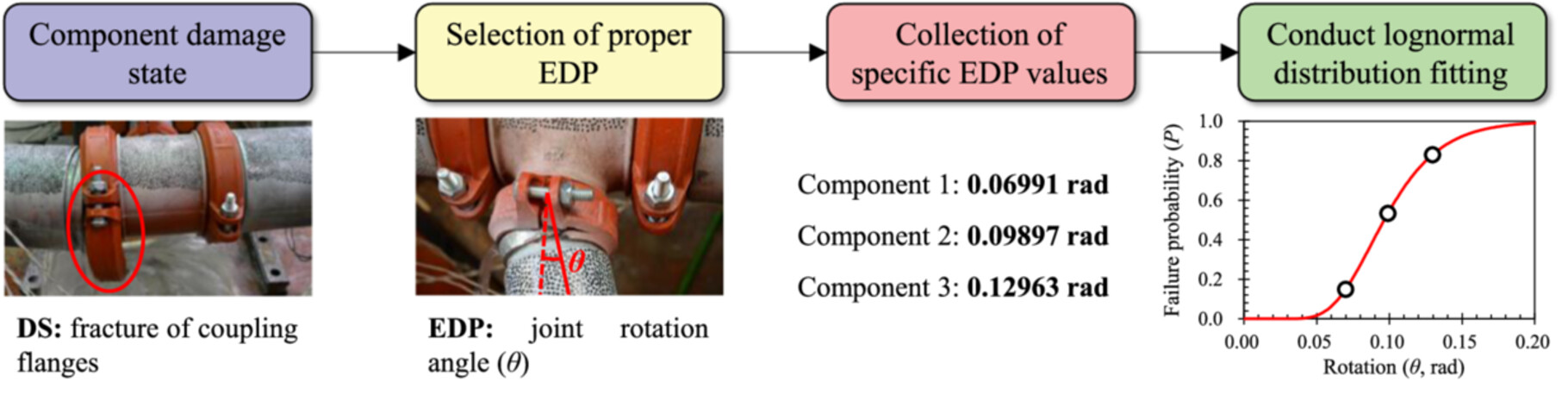
To achieve more accurate seismic fragility analysis of suspended piping systems in buildings, a component-level seismic fragility database of piping components including pipes, piping joints, and piping braces through quasi-static tests are developed based on the fragility analysis method. Specific hysteretic curves of these components are also presented, which are used for the calibration of numerical models. The developed component-level fragility database can be used to help understand the seismic performance of the piping system.
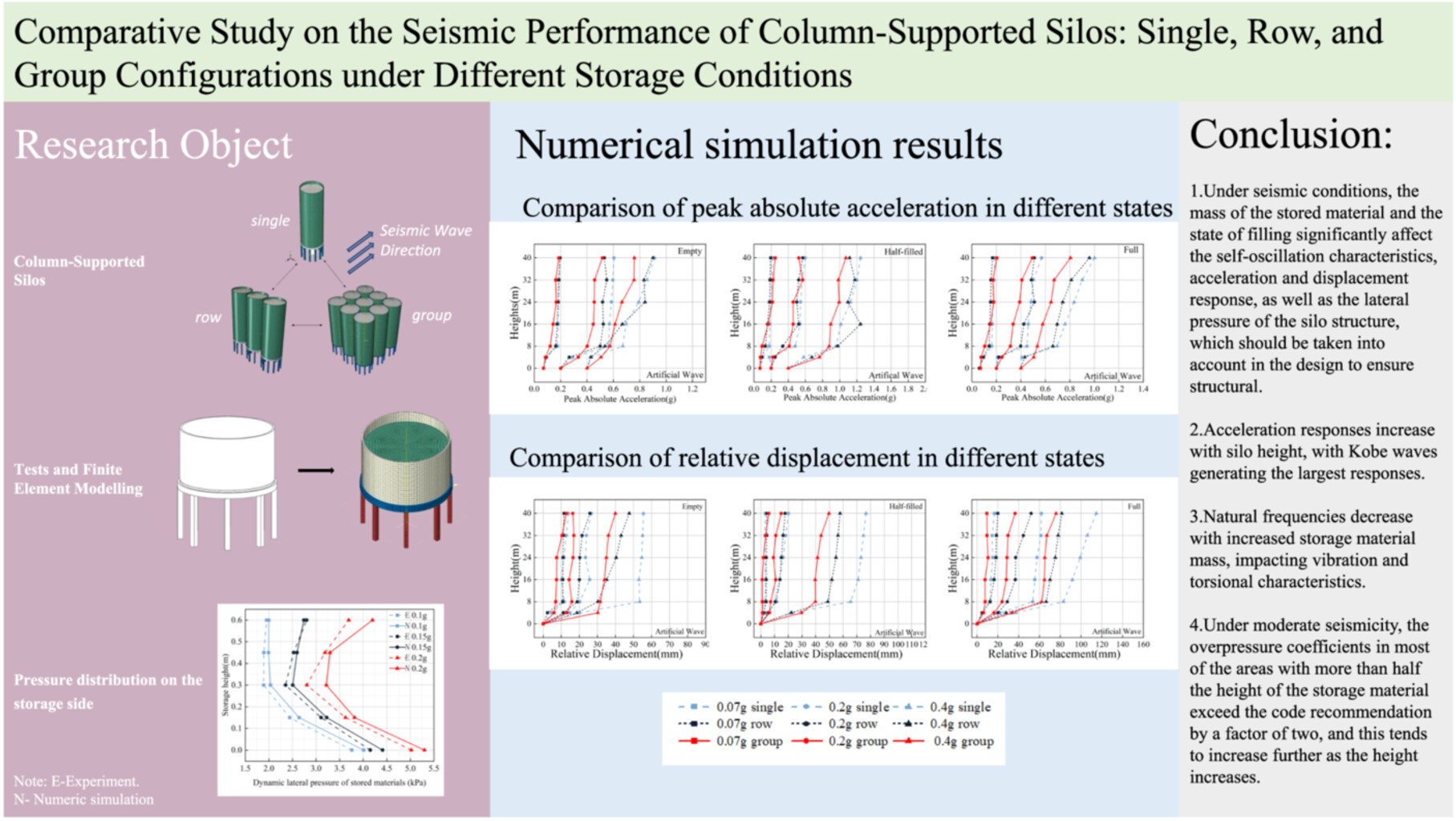
Comparative study on the seismic performance of column-supported silos: Single, row, and group configurations under different storage conditions
- Pages: 637-660
- First Published: 26 December 2024
Numerical model and effect of site condition on the coupled dynamic characteristics of water storage tank of AP1000 shield building
- Pages: 661-679
- First Published: 26 December 2024
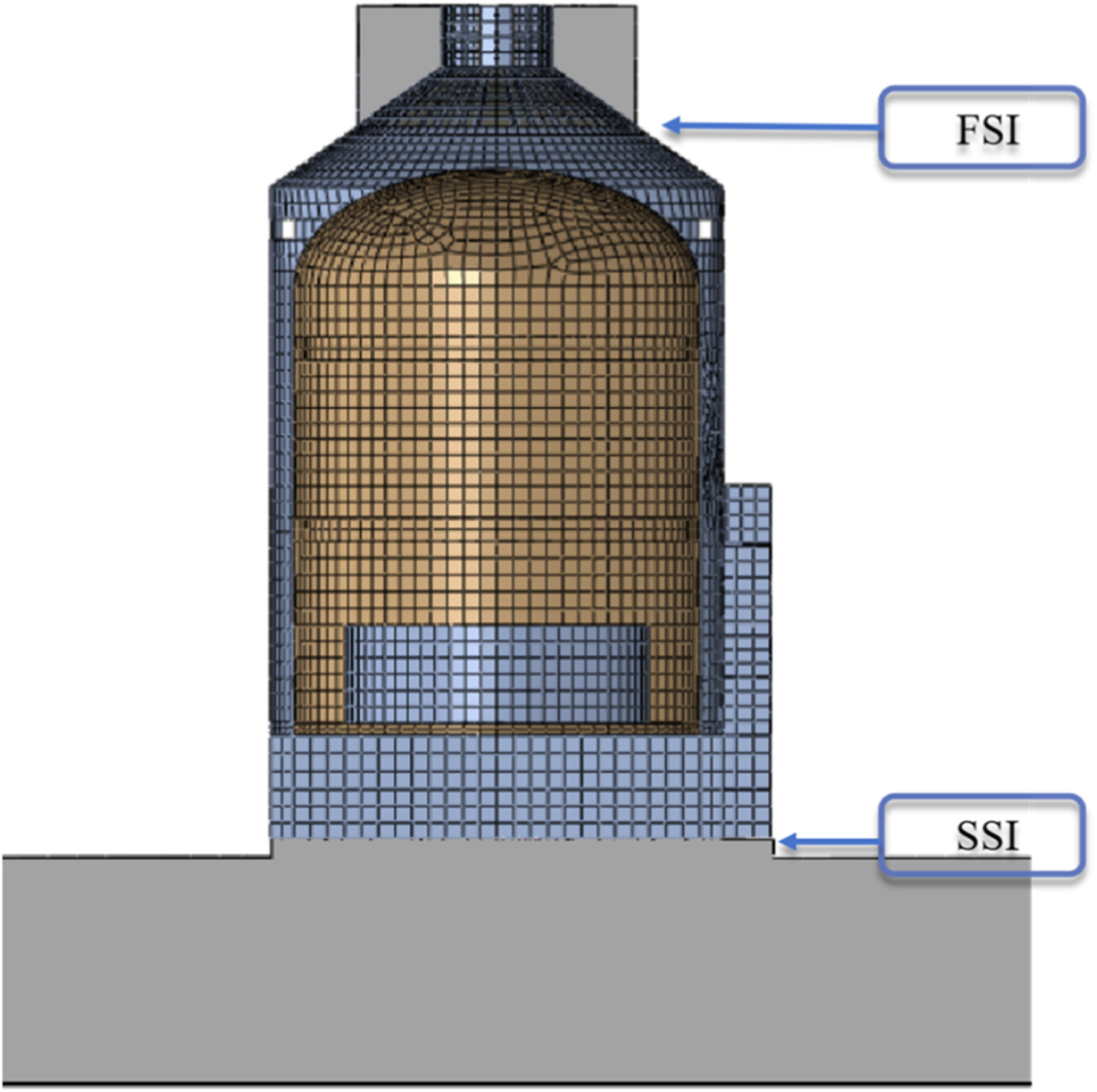
Since the Fukushima nuclear incident in 2011, the focus on nuclear safety has intensified significantly, leading to heightened demands for nuclear power plant modeling to go beyond the mere dynamic analysis of soil–structure interaction (SSI) or fluid–structure interaction (FSI). This study is based on a sophisticated liquid-structure foundation model validated using a comparative case analysis. Simulations were conducted using the parameters of five different types of nuclear power engineering sites for both homogeneous and layered foundations. In this study, we developed a refined FSI-SSI effects model in nuclear engineering, addressing the deficiencies of the traditional Housner model in the detailed simulation of irregularly shaped water tanks. The results indicated that the hydrodynamic pressure response and acceleration amplification of layered foundations significantly exceeded those of homogeneous foundations, underscoring the importance of considering layered sites in the comprehensive complex modeling of nuclear power projects.
Effect of the change of foundation stiffness on the dynamic characteristics of base-isolated structure
- Pages: 680-696
- First Published: 24 December 2024
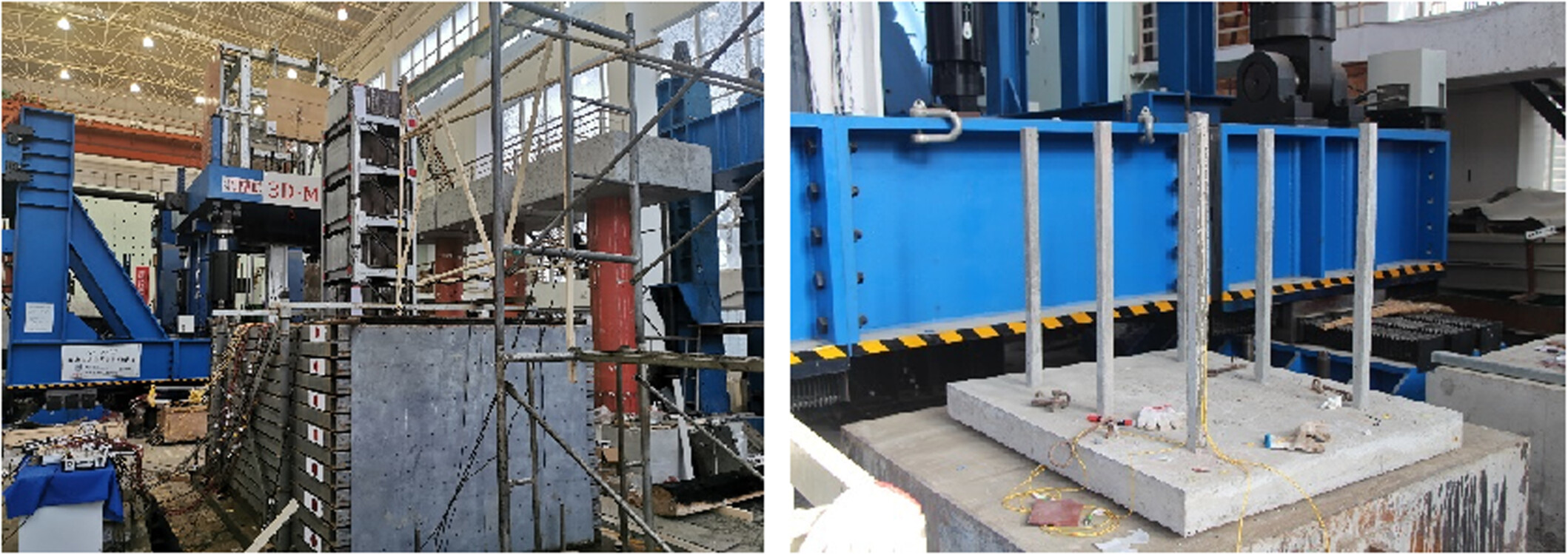

A shaking-table test method for base-isolated structures on variable-stiffness soil foundations was proposed and implemented. The influence laws of foundation stiffness on the dynamic characteristics of base-isolated structures were analyzed. The research results provide a certain scientific basis and reference for the seismic design of base-isolated structures on soft soil foundation.
Experimental study on the load-carrying capacity of steel-mesh-reinforced rubber bearings under axial compression
- Pages: 697-713
- First Published: 26 December 2024
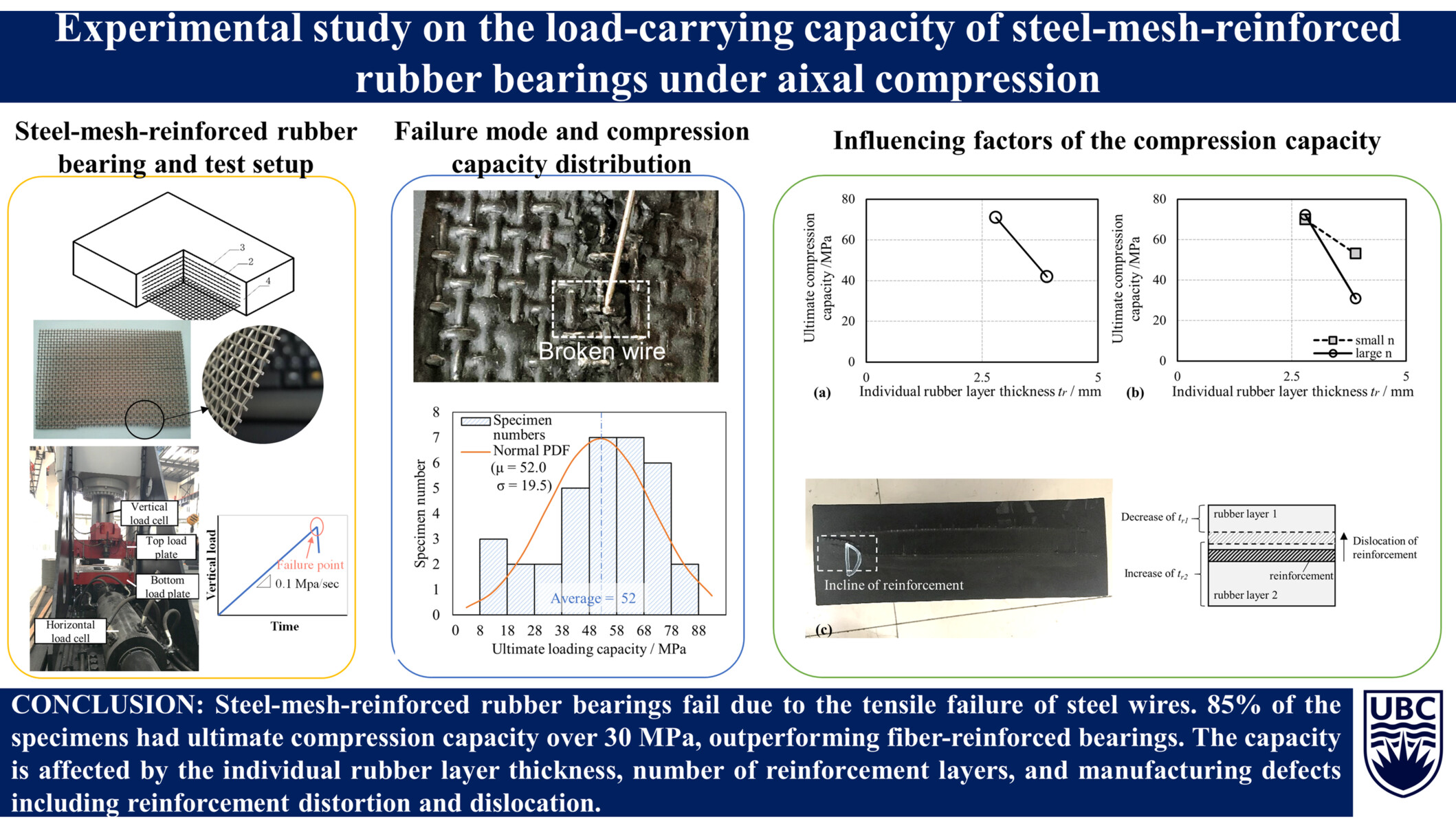
The newly issued Chinese seismic design code for highway bridges has increased the vertical design load requirement for isolation bearings to 30 MPa. To meet this standard, we introduced high-strength steel wire woven mesh as reinforcement for fiber-reinforced bearings. The ultimate compression capacity of steel-mesh-reinforced rubber bearings was experimentally investigated, along with the factors influencing their performance. The results show that steel-mesh reinforcement ensures that 85% of the specimens achieve a compression capacity exceeding 30 MPa. This capacity can be further improved by reducing the individual rubber layer thickness, decreasing the number of reinforcement layers, and minimizing reinforcement distortion or dislocation.
PERSPECTIVE
The two- and three-dimensional response spectra: Orientation-independent intensity measures more suitable for seismic structural design
- Pages: 714-727
- First Published: 24 December 2024
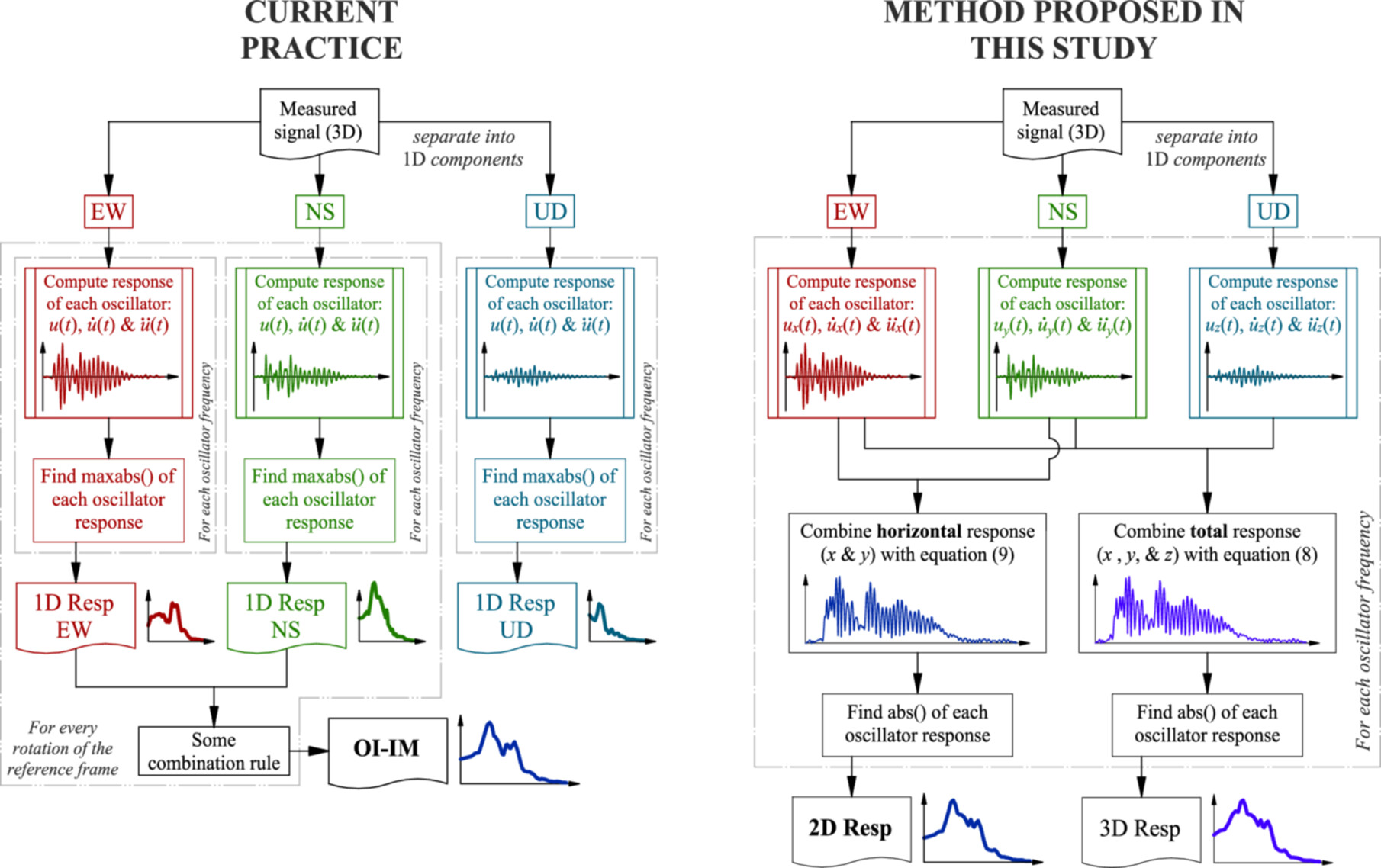
A novel orientation-independent measurement that captures the true spectral acceleration of an orthogonal array of accelerometers is presented here. In this measure, all three components of the recording are processed simultaneously, rather than combining the isolated processing of each component and evaluating the response in a large number of directions. By comparison with other commonly accepted orientation-independent intensity measures, it was found that the horizontal seismic demand can be systematically underestimated by as much as 29% in the worst case. As well as, with this new measure, the processing of seismic records can be optimized, and the uncertainty of the design seismic acceleration estimate can be reduced.