Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Dynamic and Uncertainty Analysis of RC Frame–Wall Structures Against Progressive Collapse Under Various Column Removal Scenarios
- Pages: 5-23
- First Published: 26 March 2025
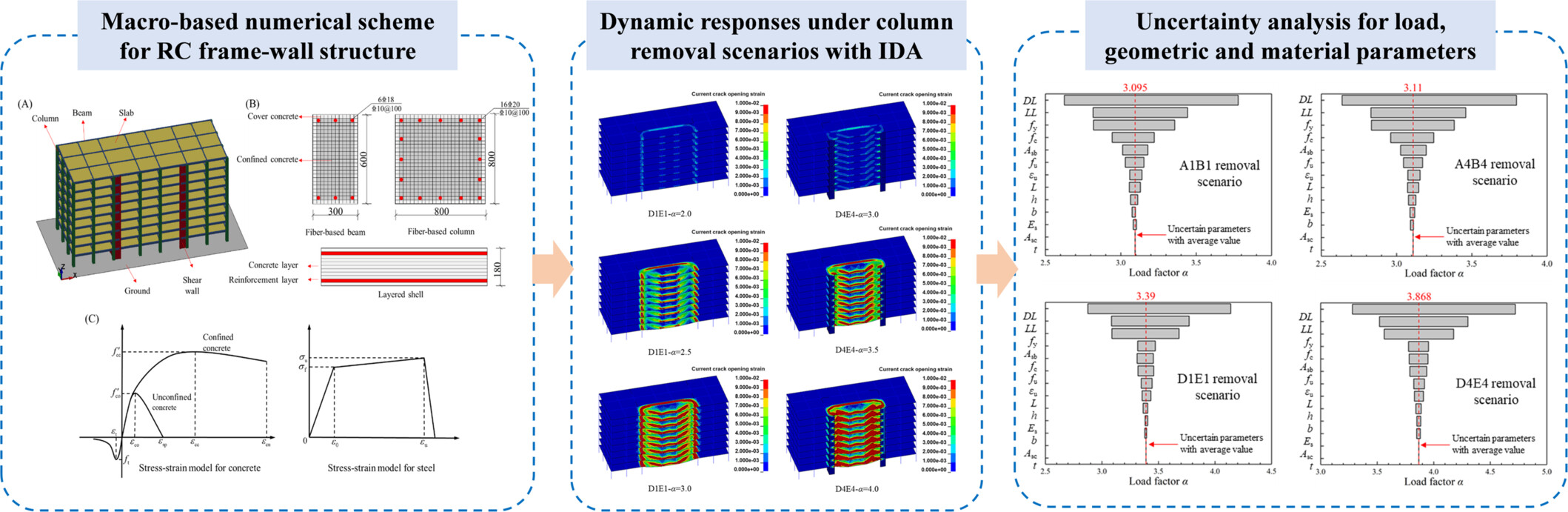
Macro-based numerical scheme is adopted for reinforced concrete (RC) frame–wall structures, and dynamic responses of the structures under different column removal scenarios are obtained through incremental dynamic analysis. The results can be used to illustrate the effect of the shear walls on the progressive collapse resistance of RC frame–wall structures. Finally, uncertainty analyses are conducted for the structure considering the probability distribution of load, geometrical, and material parameters.
Tensile Performance of Occlusive Bolt Connection in Load-Bearing Support and Hanger System
- Pages: 24-40
- First Published: 26 March 2025
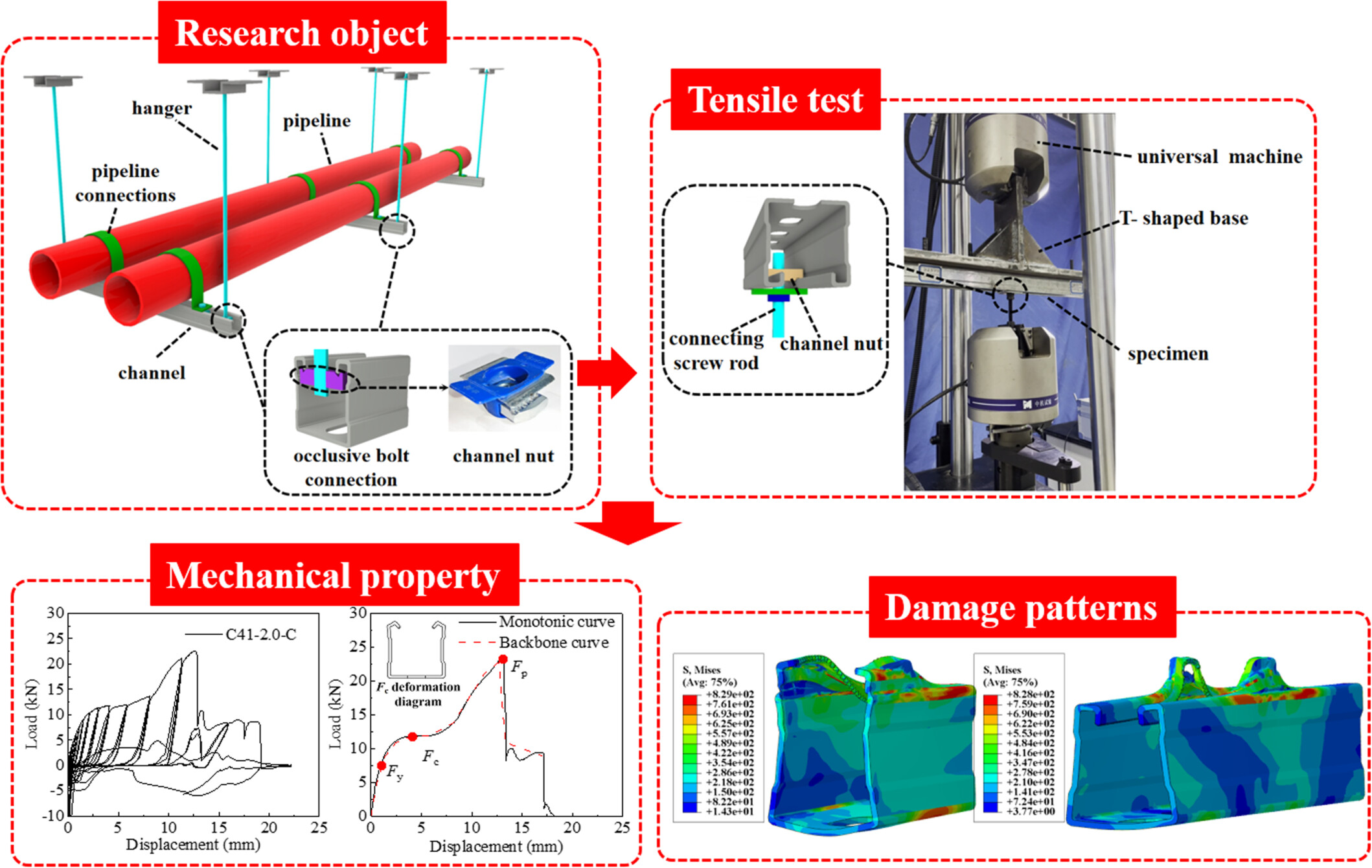
The monotonic and cyclic tests were carried out on the occlusive bolt connections in load-bearing support and hanger systems using cold-formed thin-walled channels. Additionally, the finite element validation and parametric analysis were conducted on the edge distance of channel nut and steel grade of channels.
Seismic Reliability Evaluation of Interdependent Water and Power Supply Networks
- Pages: 41-60
- First Published: 28 March 2025
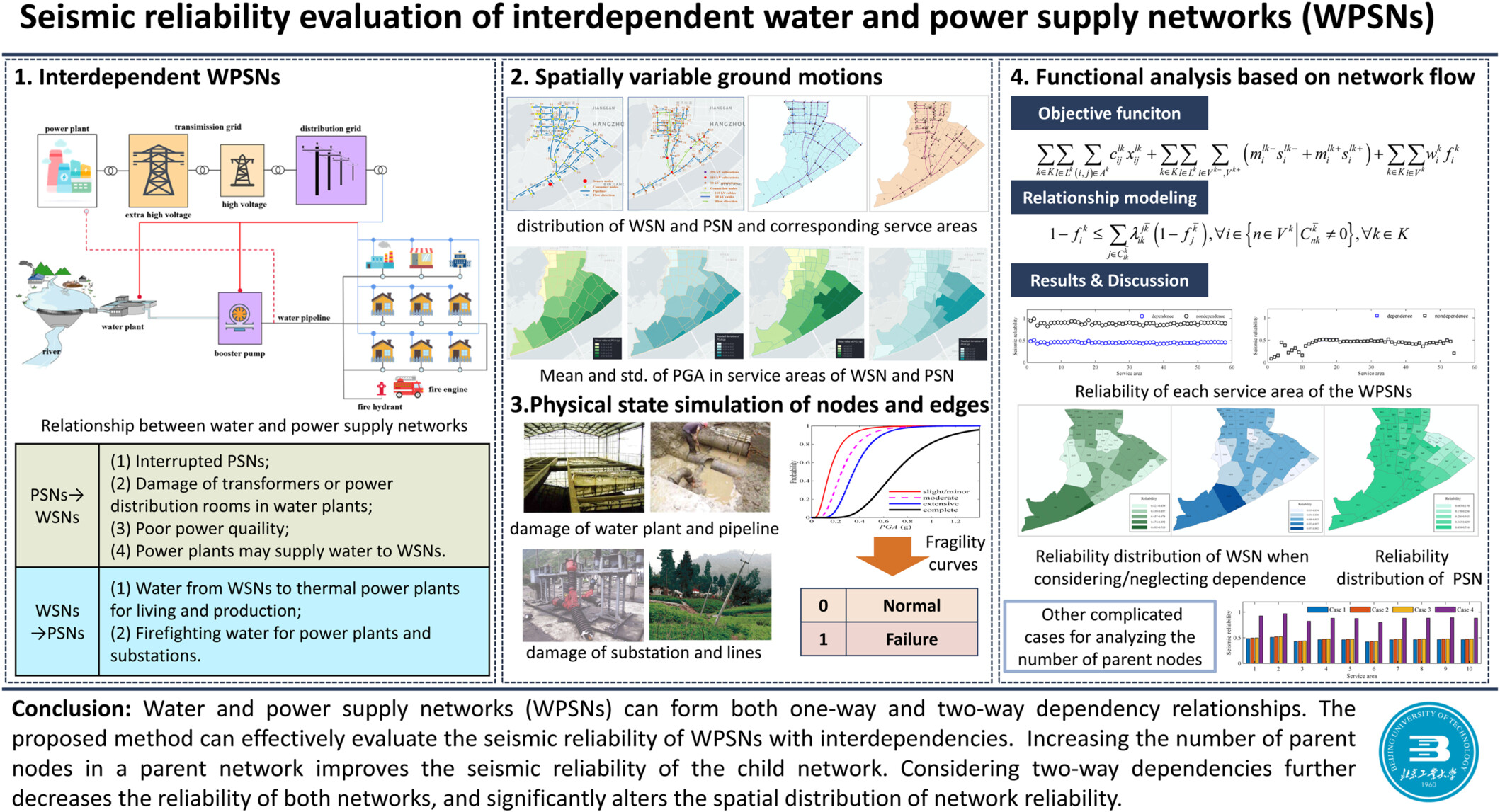
(1) Build a model to present the spatially variable ground motions, and then, based on the spatial distribution of the water and power supply networks, generate ground motion samples; (2) analyze the physical states of the nodes and edges based on empirical models or physical models; and (3) analyze the functional states of different nodes while considering the interdependence among networks, and count the number of nodes in the normal state among all samples.
Integrated Redundancy Assessment of Highway Bridge Network Systems Subjected to Emergencies
- Pages: 61-75
- First Published: 26 March 2025
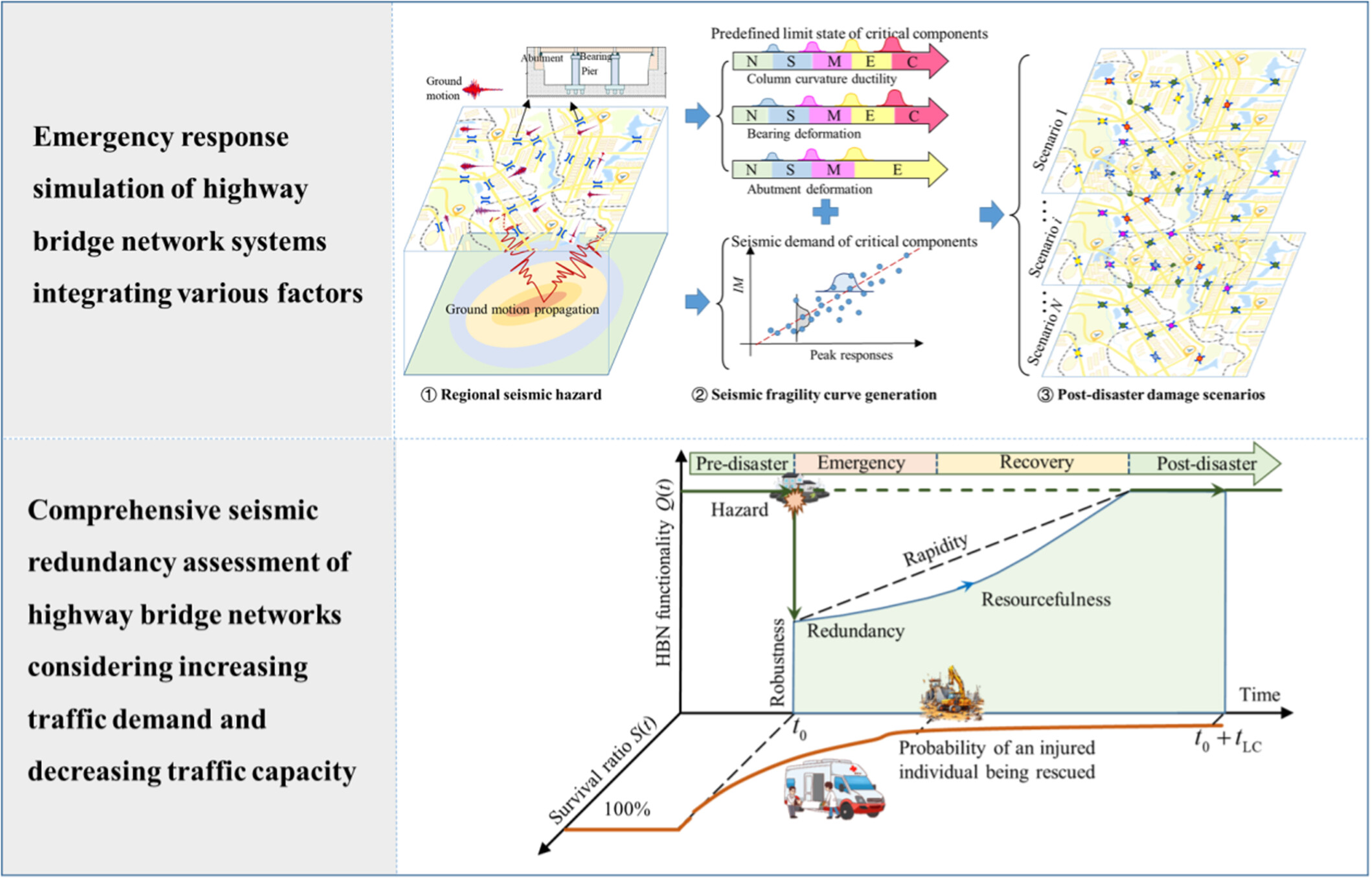
As arteries of transportation infrastructure, highway bridge networks (HBNs) are essential for normal residential and commercial activities yet are susceptible to natural or man-made disasters. Their redundancy during emergencies is crucial for effective disaster mitigation and management. To address that, this study explores the ability of HBNs to independently withstand and recover from emergency events. A system-level emergency response simulation method is proposed, integrating seismic hazard analysis, network configurations, traffic data, physical damage to regional bridges, and other factors while accounting for various sources of uncertainty. The potential increase in traffic demand and decrease in bridge capacity in emergency scenarios is also analyzed. Further, a set of comprehensive multi-criteria indicators is introduced to evaluate the redundancy of HBNs. The proposed methodologies are expected to provide a preliminarily but effective improvement of resilience assessment for HBNs, facilitating the inspection and recovery processes.
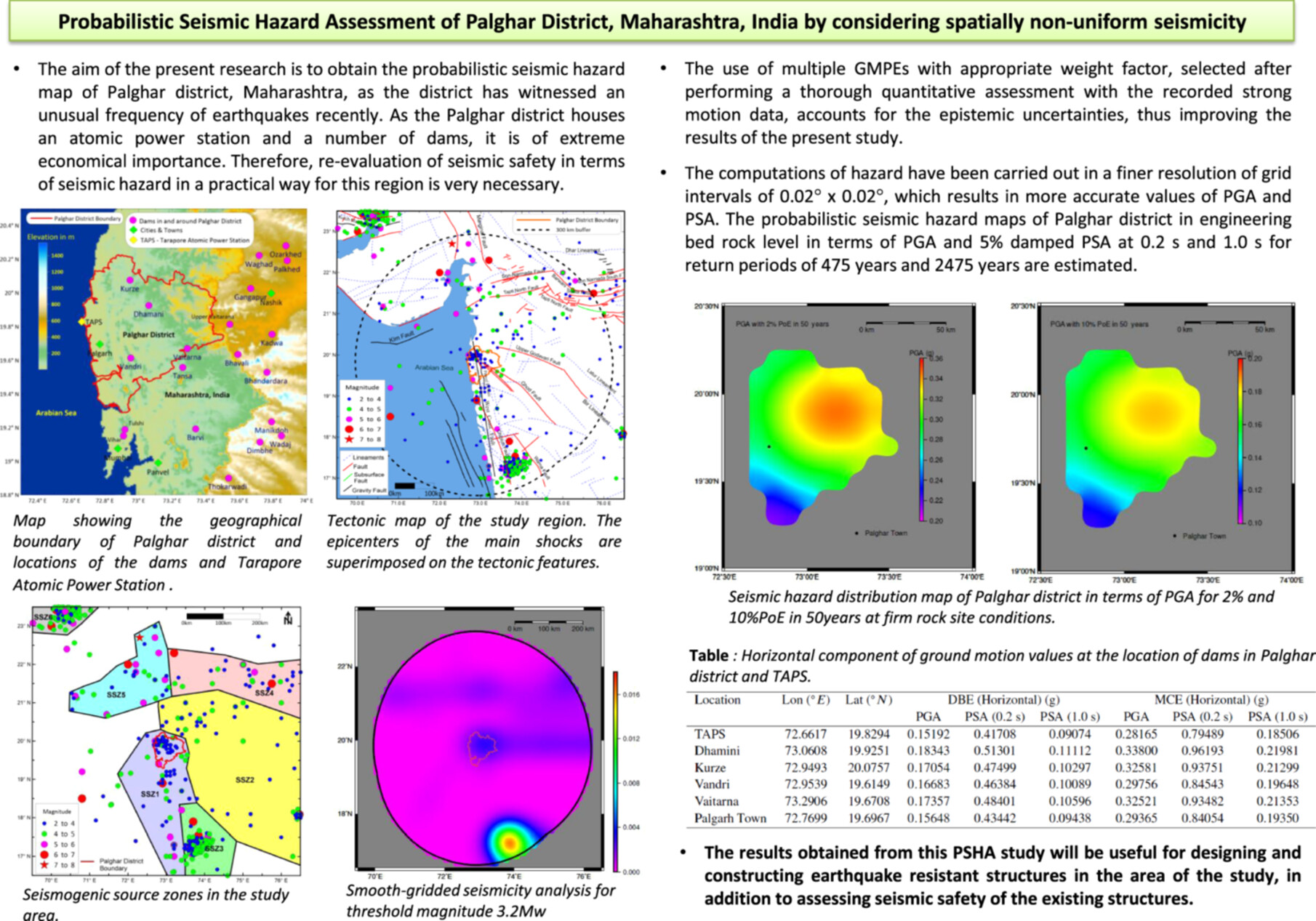
Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Assessment of Palghar District, Maharashtra, India by Considering Spatially Nonuniform Seismicity
- Pages: 76-96
- First Published: 31 March 2025
Evaluating the Seismic Risk of FRP Retrofitting Schemes for Corroded RC Frame Structures Based on Benefit-Cost Assessment
- Pages: 97-115
- First Published: 31 March 2025
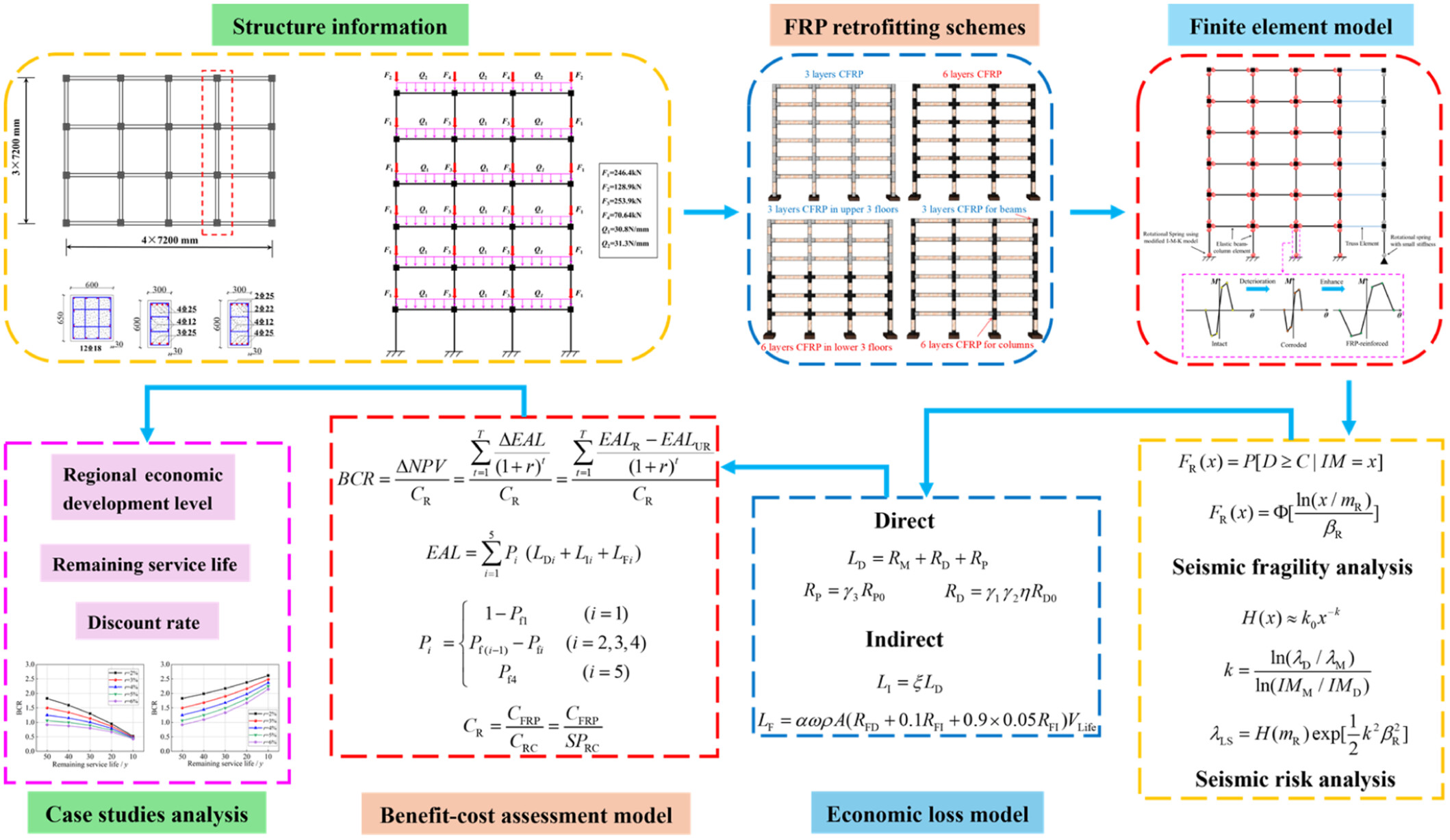
Corrosion of reinforced concrete structures can lead to a decrease in load-bearing capacity and increase the risk of collapse during earthquakes. To solve this problem, fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP) is widely used to enhance the ductility and seismic performance of structures. Experimental studies have shown that FRP is capable of improving strength and reducing crack formation. However, the current analysis of FRP effects at different corrosion levels is still insufficient, and the change of life cycle risk after modification is not considered enough. Therefore, the finite element model is used to analyze three states: intact state, corrosion state, and FRP reconstruction state, and the seismic vulnerability and risk modeling are carried out, as well as the benefit and cost analysis of different reconstruction schemes. The case study also explores the economic factors affecting the retrofit benefits, including site development level, service life, and hazard accumulation. Ultimately, the findings will provide guidance for future seismic retrofitting strategies for corroded structures.
On Seismic Response and Hazard of Girder Falling for High-Speed Railway Bridge Considering Constrain Effects of Rail
- Pages: 116-131
- First Published: 31 March 2025
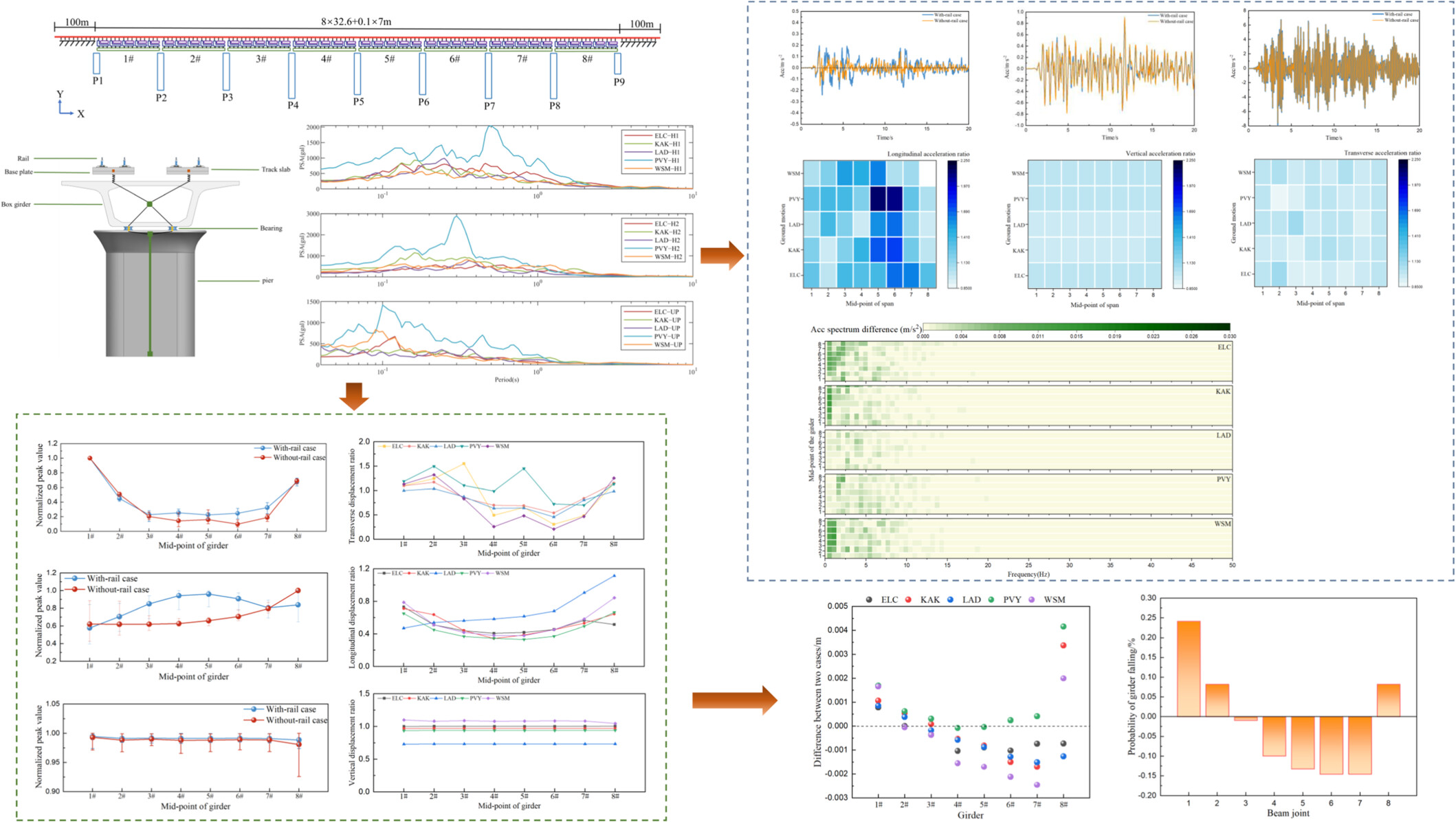
Seismic responses of the high-speed railway bridge for selected near-fault ground motions are calculated. The constraint effects of the rail are revealed through comparisons of seismic responses of a bridge with and without the rail. The influence of the existence of the rail on the risk of the girder falling for the bridge is discussed.
A Robust Compensation Strategy Combining H∞ Loop Shaping and Polynomial Extrapolation for Multi-Axial Real-Time Hybrid Simulations
- Pages: 132-148
- First Published: 31 March 2025
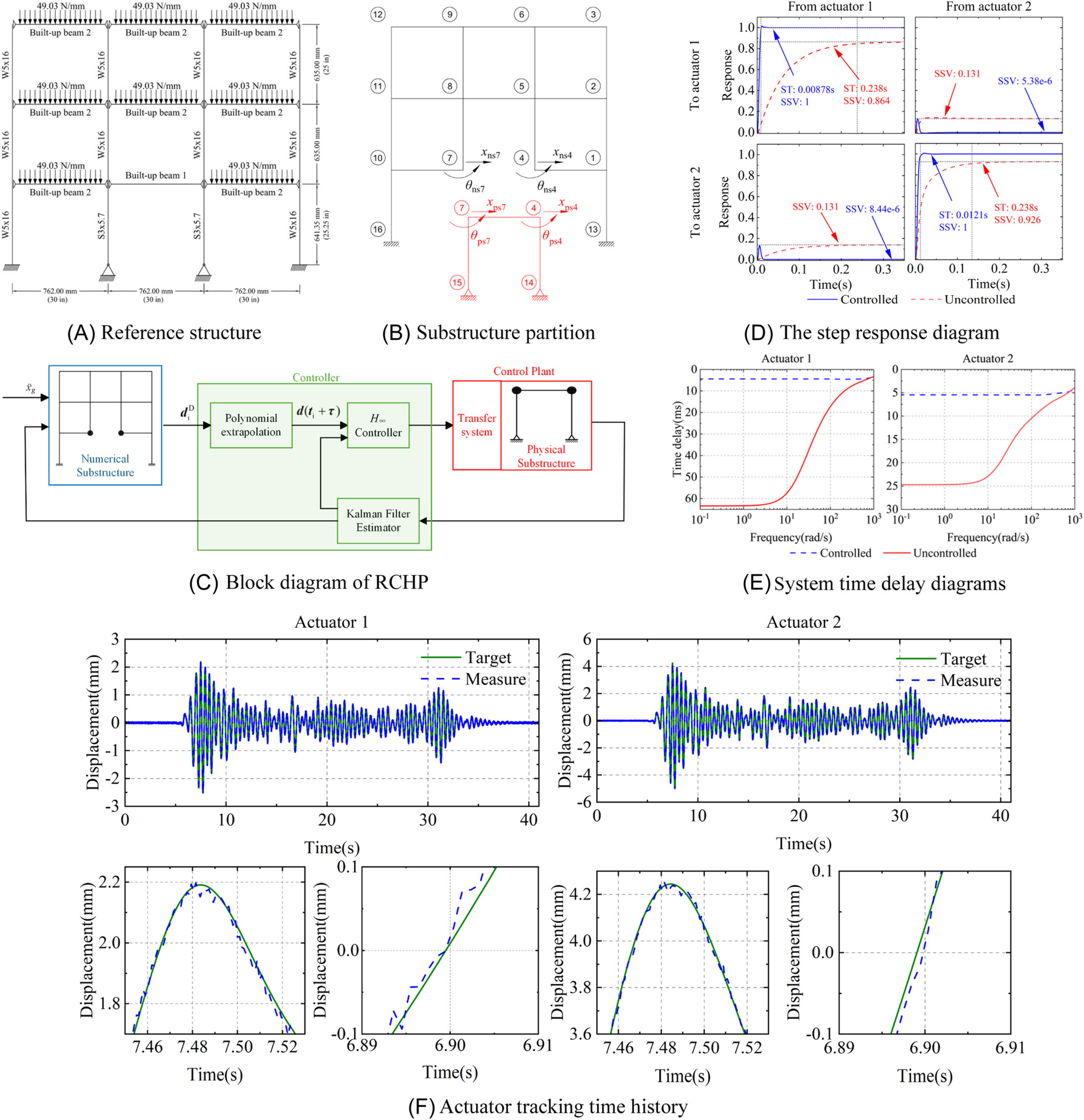
Aiming at the multi-axial real-time hybrid simulation (RTHS) (maRTHS) benchmark problem, we propose a robust compensation strategy, combining H∞ loop shaping theory and polynomial extrapolation, to tackle servo-hydraulic dynamics issues for maRTHS problems. The proposed method consists of an H∞ loop shaping feedback controller and polynomial extrapolation. As can be seen in the figure, the H∞ loop shaping controller stabilize the servo-hydraulic actuator and physical substructure (PS) dynamics and achieves approximate decoupling among the actuators. Polynomial extrapolation can further reduce the time delay as well as amplitude discrepancies. The results show that the proposed method has significant potential for high-precision experiment synchronization.
Seismic Fragility of Medium-Rise Soft Story SMRF Building Under Near Field, Fling Step, and Far Field Excitations
- Pages: 149-162
- First Published: 31 March 2025