Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT
Identification of immune-activating metabolite for enhancing T cell therapy of cancer
- Pages: 535-537
- First Published: 18 May 2021
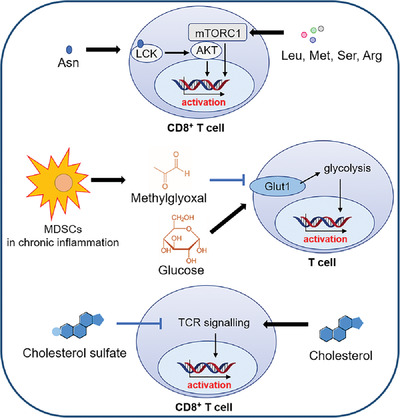
In this Research Highlight, we summarized the results from a study by Wu et al. published in Nature Cell Biology which uncovered that asparagine (Asn), a non-essential amino acid in mammalians, is able to enhance the TCR-mediated activation and efficacy of CD8+ T cells towards tumour through lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase (LCK) signalling. This study provides insights into the physiological function of Asn in T cell activation and effector functions, showing the encouraging possibility of key metabolites for empowering cancer immunotherapy.
REVIEW
N6-methyladenosine Steers RNA Metabolism and Regulation in Cancer
- Pages: 538-559
- First Published: 06 May 2021
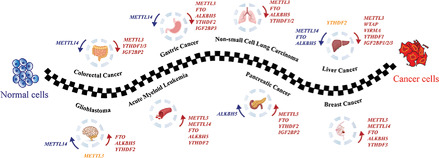
As one of the best studied ribonucleic acid (RNA) modifications in eukaryotes, N6-methyladenosine (m6A) plays a predominant role in controlling gene expression and further influences physiological and pathological processes, including oncogenesis and tumor progression. Here we review the functions of m6A and its regulators in RNA metabolism control, their oncogenic or tumor suppressive roles in diverse malignancies, as well as the application of m6A methylation in cancer diagnosis and therapeutics.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
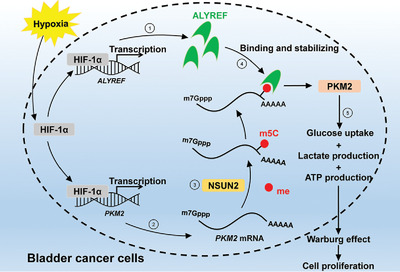
The role of the HIF-1α/ALYREF/PKM2 axis in glycolysis and tumorigenesis of bladder cancer
- Pages: 560-575
- First Published: 15 May 2021
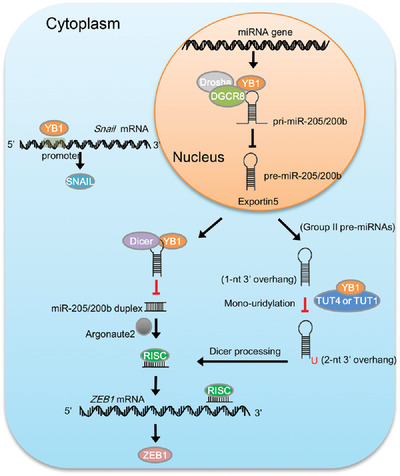
YB1 regulates miR-205/200b-ZEB1 axis by inhibiting microRNA maturation in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Pages: 576-595
- First Published: 10 June 2021
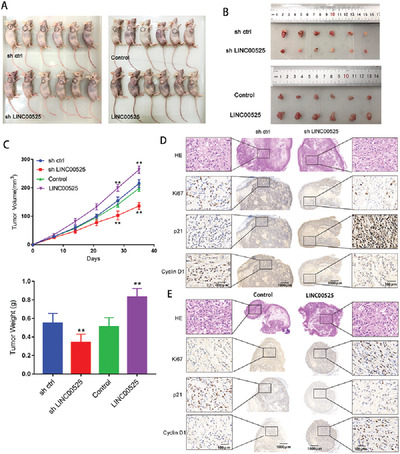
LncRNA LINC00525 suppresses p21 expression via mRNA decay and triplex-mediated changes in chromatin structure in lung adenocarcinoma
- Pages: 596-614
- First Published: 09 June 2021
Structural and functional characterization of multiple myeloma associated cytoplasmic poly(A) polymerase FAM46C
- Pages: 615-630
- First Published: 28 May 2021
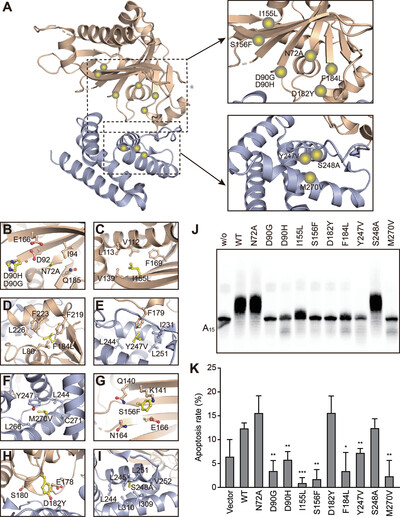
- Mammalian FAM46C is a unique non-canonical poly(A) polymerase (PAP) with a bacterial-like protein fold.
- FAM46C differs from its homolog FAM46B in PAP activity due to the divergence of amino acid residues at several critical sites.
- The structural-functional characterization of MM-related FAM46C mutations that may be used for prognosis in the future.
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Establishment of an orthotopic perirenal space xenograft mouse model of retroperitoneal sarcoma
- Pages: 631-634
- First Published: 13 May 2021