Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW
EMT-associated microRNAs and their roles in cancer stemness and drug resistance
- Pages: 199-217
- First Published: 27 January 2021
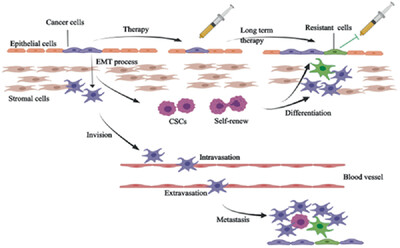
In this review, we preliminarily looked into the various roles that the EMT-associated miRNAs play in the stem-like nature of malignant cells. Then we reviewed the interaction between drug resistance and EMT-associated miRNAs with elaborated signal pathways, especially the opposite roles in various cancer types. We finally arrived at a conclusion concerning the relationship between EMT, stemness and drug resistance and discussed the potential application of miRNA therapy for malignant tumors.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Co-occurrence of germline pathogenic variants for different hereditary cancer syndromes in patients with Lynch syndrome
- Pages: 218-228
- First Published: 25 February 2021
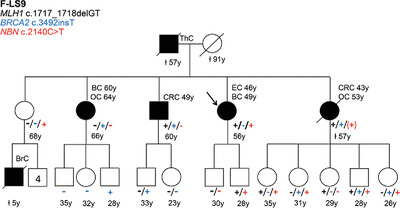
We aimed to explore whether other pathogenic variants for hereditary cancer genes are present in Lynch syndrome patients, to have a more comprehensive view of the genetic architecture for cancer risk. We found five families (6%) with at least two pathogenic variant in high- and/or moderate-risk-associated cancer genes. However, in most cases, no clinical manifestations associated with the secondary pathogenic variants were evidenced.
Outcomes in refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: results from a multicenter real-world study in China
- Pages: 229-239
- First Published: 22 January 2021
BAALC-AS1/G3BP2/c-Myc feedback loop promotes cell proliferation in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- Pages: 240-257
- First Published: 21 January 2021
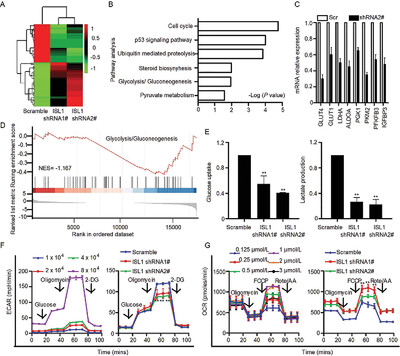
Insulin gene enhancer protein 1 mediates glycolysis and tumorigenesis of gastric cancer through regulating glucose transporter 4
- Pages: 258-272
- First Published: 11 February 2021
RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT
Intensive chemotherapy and sequential hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: Is it necessary for high-risk T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma?
- Pages: 273-274
- First Published: 19 February 2021
LETTERS TO THE EDITOR
Real-world outcomes of ibrutinib therapy in Korean patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma: a multicenter, retrospective analysis
- Pages: 275-278
- First Published: 24 February 2021
Phase III trial of docetaxel cisplatin 5-fluorouracil induction chemotherapy for resectable oral cancer suggests favorable pathological response as a surrogate endpoint for good therapeutic outcome
- Pages: 279-283
- First Published: 20 January 2021