Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Evaporation Performance of Wood-Based Evaporator for Solar Interfacial Vapor Generation
- First Published: 07 April 2022

Inspired by the transpiration of plants, an interfacial evaporator based on wood is designed. The evaporation efficiency can reach 93.35% under 3.5 sun. Considering its low cost and high efficiency, the wood-based evaporator provides the possibility for the popularization and application of solar interfacial evaporation. More details can be found in article number 2101020, Huiling Duan and co-workers.
Back Cover
Rechargeable Aluminum-Air Batteries Based on Aqueous Solid-State Electrolytes
- First Published: 07 April 2022
Al-air batteries assembled with water-based solid electrolytes can be recharged. As illustrated on the cover, this is possible thanks to the combined use of two solid electrolytes containing a different amount of water and contacted with anode and cathode without separators. A valuable feature of these electrolytes is that they are prepared with biodegradable polymers. More details can be found in article number 2101046, Maria F. Gaele and Tonia M. Di Palma.
Masthead
Review
Inverted Perovskite Solar Cells: The Emergence of a Highly Stable and Efficient Architecture
- First Published: 29 December 2021
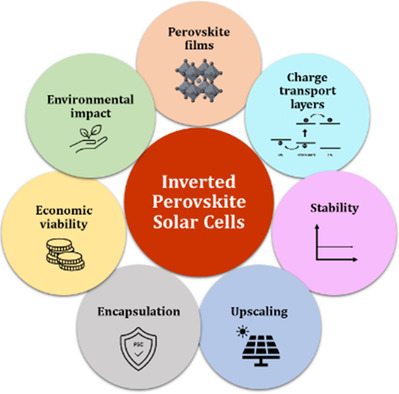
This state-of-the-art brings together the recent developments concerning perovskite structures, deposition methods, charge transport materials, and electrode contacts in inverted perovskite solar cells. Strategies to reach simultaneously high stability and efficiency are also forecast. Additionally, environmental opportunities, stability issues, fabrication methods for large-area inverted perovskite solar cells, encapsulation techniques, and economic evaluation are also discussed.
Research Articles
Evaporation Performance of Wood-Based Evaporator for Solar Interfacial Vapor Generation
- First Published: 22 January 2022
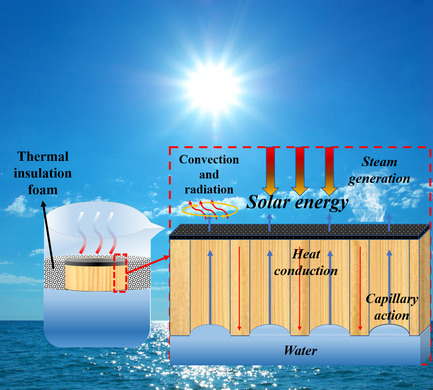
Inspired by the natural transpiration of plants, an interfacial evaporator based on natural wood and a carbon black film is designed. The evaporation efficiency of this wood-based evaporator can reach 93.35% under 3.5 sun. Considering its simplicity, low cost, and high efficiency, the wood-based evaporator prepared in this article provides the possibility for the popularization and application of solar interfacial evaporation.
Rechargeable Aluminum-Air Batteries Based on Aqueous Solid-State Electrolytes
- First Published: 25 January 2022

A dual solid electrolyte, prepared frombiodegradable materials and aqueous solutions, is used in aluminum-air batteries to verify the possibility of recharging, by maintaining minimum water content on the anode and increasing it on the cathode side. The three-electrode cycling demonstrates that the batteries can be recharged through suitable water management inside the electrolytes.
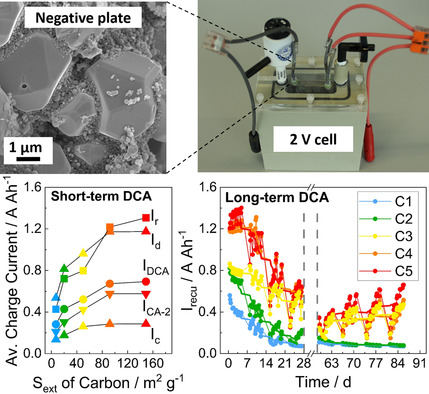
Comparison of Dynamic Charge Acceptance Tests on Lead–Acid Cells for Carbon Additive Screening
- First Published: 25 January 2022
Drying of NCM Cathode Electrodes with Porous, Nanostructured Particles Versus Compact Solid Particles: Comparative Study of Binder Migration as a Function of Drying Conditions
- First Published: 19 January 2022
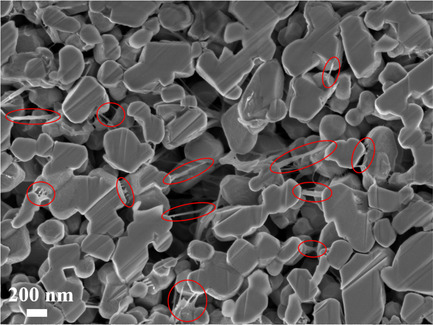
Herein, the properties of electrodes made of two different active materials at increasing drying rates and the binder distribution are comparatively investigated. When using porous nanostructured particles instead of solid particles, a significantly lower binder migration and a very low dependence of the discharge capacity at higher C rates on the drying rate are observed.
Fabrication of Coral-Shaped MoS2@Ni(Mn)VO X Electrocatalyst for Efficient Alkaline Hydrogen Evolution
- First Published: 19 January 2022
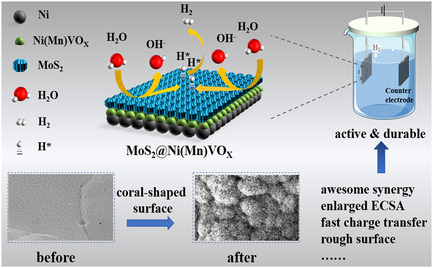
MoS2@Ni(Mn)VO X is successfully synthesized using a two-step electrodeposition method. Benefiting from a rapid charge transfer rate, abundant active sites, and a large effective surface area, it shows excellent activity and maintains prominent durability for 20 h. Herein, a novel catalyst and a new view for the design of multimetal cooperative electrocatalysts for highly efficient hydrogen evolution reactions in alkaline media are provided.
Preparation of MC–CuS–PGr/PPy Nanocomposite Films via Strong Interfacial Interactions as a Battery-Type Electrode
- First Published: 12 January 2022
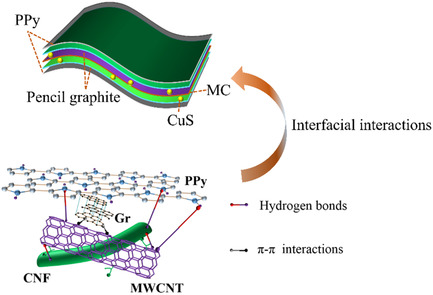
A battery-type nanocomposite film driven by different intermolecular interactions is designed. Hydrogen bonds and π–π interactions interact synergistically to achieve a rapid combination of various materials and improve the structural stability, mechanical properties, and electrochemical performance of electrodes.
Tailoring Conductive 3D Porous Hard Carbon for Supercapacitors
- First Published: 25 January 2022
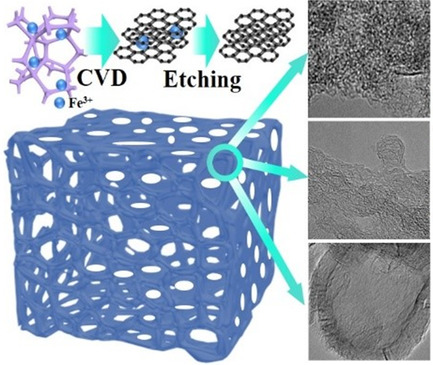
Space-confined nanographite domains with enhanced conductivity are formed via in situ iron-catalyzed graphitization with the Si–O–Si network under 1000 °C. A rational strategy to obtain three-dimensional porous hard carbon with high electrical conductivity (12 S cm−1), high specific surface area (2075 m2 g−1), and high capacitance (315 F g−1) via adjusting the Fe content is presented.
Flexible Bielectrode-Based Highly Sensitive Triboelectric Motion Sensor: A Sustainable and Smart Electronic Material
- First Published: 19 January 2022

A cost-effective touchless triboelectric sensor is fabricated using commercially available latex rubber and copper for human motion sensing and monitoring. The device is tested with specimens of different areas and height in motion. The device precisely provided significant output signals for each movement of the human body showing prospects for tracking human motion in the fields of security, energy, and medicine.
Hybrid Energy-Harvesting System by a Coupling of Triboelectric and Thermoelectric Generator
- First Published: 21 January 2022
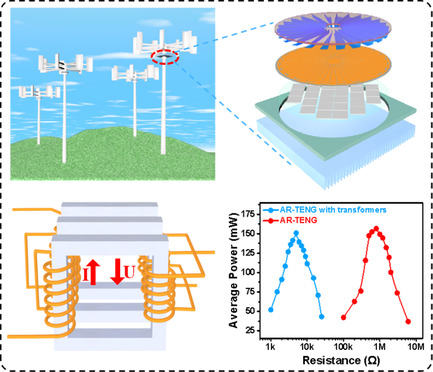
The hybrid energy-harvesting device of an adaptive rotating triboelectric nanogenerator (AR-TENG) and thermoelectric generator with good output performance can harvest wind energy to drive electronics. Moreover, the output conversion efficiency of the transformers circuit for AR-TENG is enhanced up to 96.4%. Therefore, the energy storage velocity of the whole device is improved by 28 times than that of alone AR-TENG.
Evaluation of Deformation Behavior and Fast Elastic Recovery of Lithium-Ion Battery Cathodes via Direct Roll-Gap Detection During Calendering
- First Published: 21 January 2022
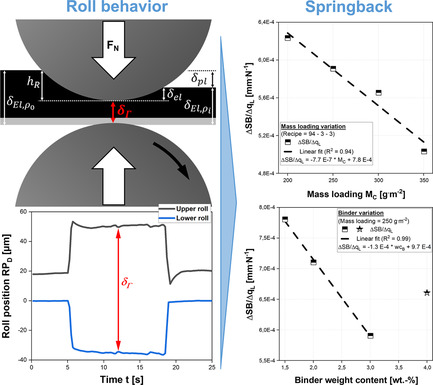
Herein, a novel method for gap detection is presented, allowing insights into electrode and machine behavior during calendering. Using this method, electrode springback (SB) of cathodes with various mass loadings and binder weight contents is investigated, showing linear correlation of the SB with applied line load. Based on these results, a first empirical model for SB is provided.
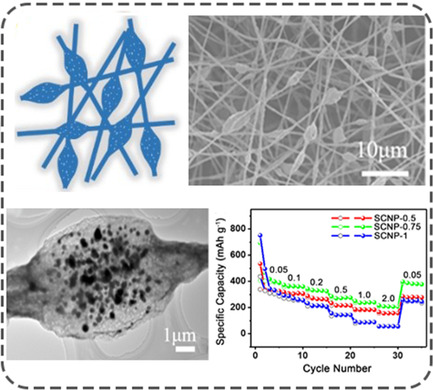
Necklace-Like Sn@C Fiber Self-Supporting Electrode for High-Performance Sodium-Ion Battery
- First Published: 22 January 2022
Improving Hole Transport and Extraction by Interface Engineering in Perovskite Solar Cells
- First Published: 09 February 2022
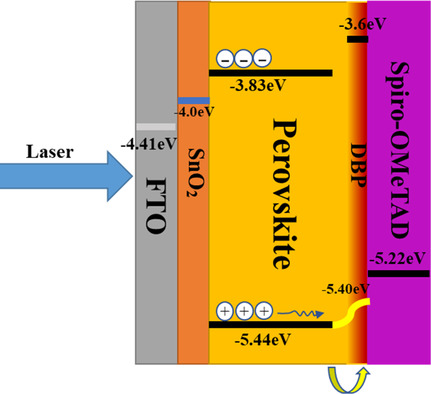
Significantly improved perovskite solar cell is demonstrated by spin-coating an ultrathin tetraphenyldibenzoperiflanthene layer between perovskite and Spiro-OMeTAD. Dynamic analysis of photogenerated carriers by time-resolved photoluminescence reveals the intermediate layer leads to faster hole transport and hole extraction due to smoothing the energy alignment and passivation in the interface, this eventually achieves a much improved conversion efficiency and stability.
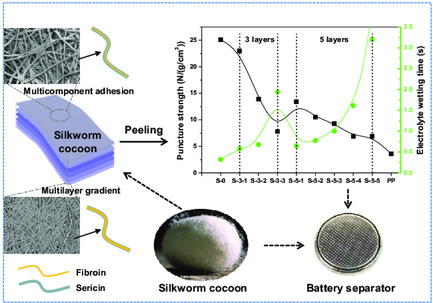
Silkworm Cocoon Layer with Gradient Structure as Separator for Lithium-Ion Battery
- First Published: 28 January 2022
High-Temperature Solid-State Synthesis and Electrochemical Properties of Transition Metal Sulfides for Thermal Batteries
- First Published: 01 February 2022
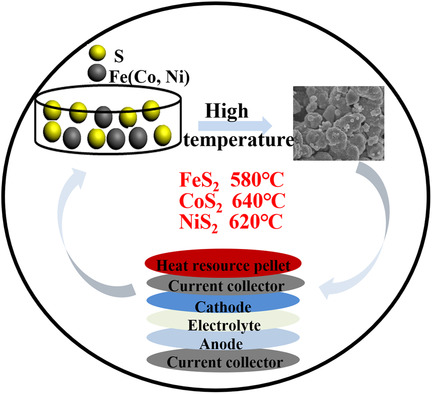
Transition metal sulfides with single-phase and good crystalline structure are prepared by a high-temperature solid-state method via controlling the synthesis temperature. The optimum synthesis temperatures of FeS2, CoS2, and NiS2 are 580, 640, and 620 °C, respectively. The simple method is suitable for the large-scale industrialization of transition metal sulfides, and provides matching cathode materials for a thermal battery system.
Electrochemical Performance and Mechanism of Surface-Fluorinated Fe3O4 as Stable Anode for Lithium-Ion Batteries
- First Published: 01 February 2022
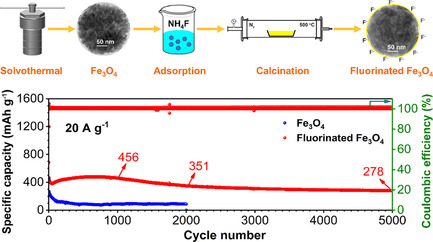
A simple surface fluorination strategy is developed to significantly improve the electrochemical properties of Fe3O4 anodes. The fluorinated layer stabilizes the electrode/electrolyte interface, shortens the Li+ diffusion pathway, and enhances the charge storage capability. Accordingly, the fluorinated electrode has a high specific capacity and impressive high-rate performance (802/456 mAh g−1 after 1000 cycles at 10/20 A g−1).
Performance of a Lever-Gear Type Piezoelectric Energy Harvester for Collecting Pedestrian Energy
- First Published: 01 February 2022
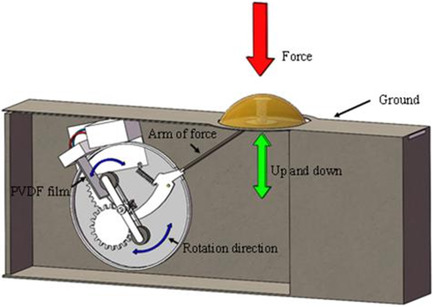
A piezoelectric energy harvester is proposed to collect the kinetic energy of pedestrians. The harvester involves a gear–lever mechanism, which is used to amplify the amplitude and frequency of the input vibration source. Both indoor and outdoor experiments are carried out to examine the working performance of the device.
Morphology Control of Free-Standing LiFePO4-Based Composite Membranes for Advanced Lithium-Ion Battery Cathodes
- First Published: 08 February 2022
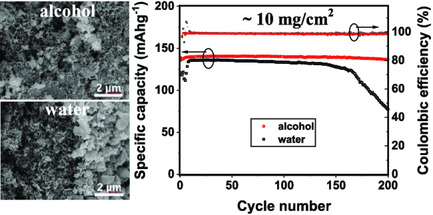
Free-standing LiFePO4-based composite membranes with a high conductivity of 2.55 S cm−1 are obtained by adding alcohol in the aqueous slurry. The composite membranes have a specific capacity of about 105 mAhg−1 at 5 C for a LiFePO4 mass loading of about 10 mg cm−2. Furthermore, a specific capacity is retained as 137.2 mAhg−1 after 300 cycles at 1 C.
Controllable Coaxial Coating of Boehmite on the Surface of Polyimide Nanofiber Membrane and Its Application as a Separator for Lithium-Ion Batteries
- First Published: 08 February 2022
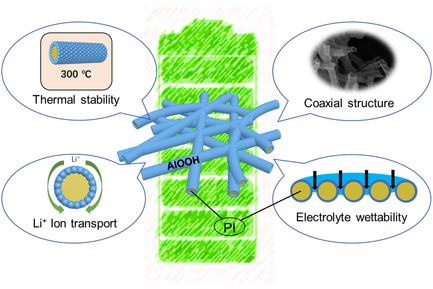
Herein, a PI@AlOOH composite nanofiber membrane with a coaxial structure is prepared by an innovative adsorption complexation alkaline hydrolysis method. The effects of the types of base membranes and preparation conditions on the macroscopic and electrochemical properties of the PI@AlOOH composite nanofiber membrane are studied. Finally, the performance of the PI@AlOOH composite nanofiber membrane as a lithium battery diaphragm is explored.
Monolithically Integrated Sensing, Communication, and Energy Harvester
- First Published: 08 February 2022
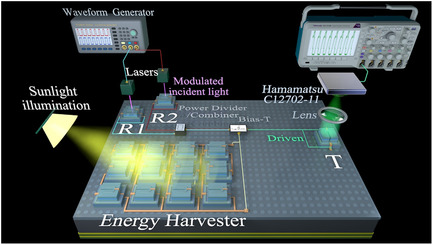
Both energy and information are different manifestations of light. Using light to offer the coexistence of sensing, communication, and energy harvesting functionalities, monolithically integrated III-nitride diode system toward the Internet of Things is dealt with. Self-powered III-nitride system is a paradigm change where the previously competing sensing, communication, and energy harvesting operations can be implemented on a single chip.
Operation of a Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Reactor with Multiple Stacks in a Pressured System with Fuel Gas Recirculation
- First Published: 01 February 2022
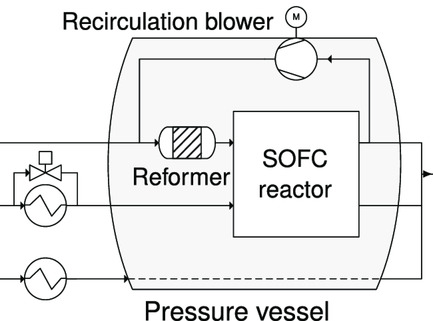
In this work, the behavior of a 30 kW solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) reactor with multiple stacks in a pressured system with fuel gas recirculation is investigated. The main results are the analysis of the SOFC reactor operation behavior with respect to the individual stacks and the influence of the system components on the SOFC reactor.
Enhanced Storage and Interface Structure Stability of NCM811 Cathodes for Lithium-Ion Batteries by Hydrophobic Fluoroalkylsilanes Modification
- First Published: 12 February 2022
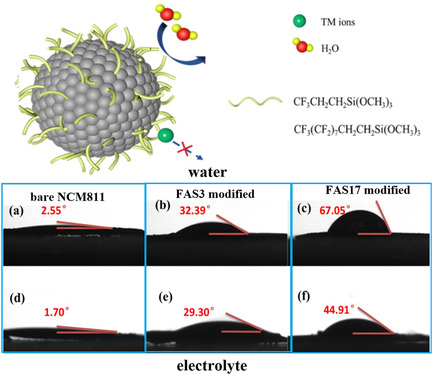
The construction of hydrophobic fluoroalkylsilanes as a stable surface coating on NCM811 cathode materials is an effective strategy to suppress the formation of residual lithium and inhibit transition metal dissolution. As a result, FAS17-modified NCM811 cathode materials after 30-day humid air exposure (humidity 70%) exhibit the greatest overall capacity retention of 74.2% after 200 charge/discharge cycles.
Battery Health Diagnosis Approach Integrating Physics-Based Modeling with Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
- First Published: 11 February 2022
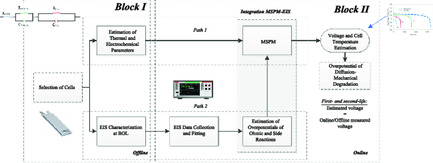
Herein, a battery health diagnosis approach that combines electrochemical performance aging and lumped thermal models with electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and voltage monitoring is proposed, allowing the segregation and quantification of ohmic, chemical, and diffusion-mechanical-related losses. This approach accurately identifies battery lifetime thresholds combining the use of a capacity indicator and overpotentials as battery health indicators.
Investigation of Self-Discharge Behavior on Electrical Double-Layer Capacitors by Hybrid Mechanism Simulation
- First Published: 09 February 2022
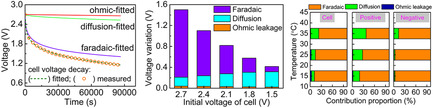
The self-discharge (SD) behavior of electrical double-layer capacitors (EDLCs) in organic electrolyte can be analyzed by the hybrid mechanism simulation. The hybrid mechanism simulation can distinguish the contribution of each mechanism of the positive and negative electrodes, and research the SD mechanism influenced by the initial voltage (1.5–2.7 V) and the temperature (15–35 °C).
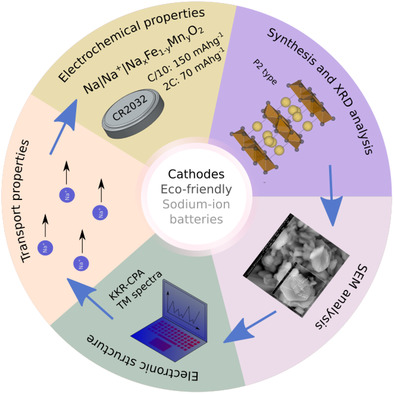
Transport and Electrochemical Properties of Na x Fe1–y Mn y O2-Cathode Materials for Na-Ion batteries. Experimental and Theoretical Studies
- First Published: 15 February 2022
Effect of Hydrogen Peroxide on the Recovery of Valuable Metals from Spent LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 Batteries
- First Published: 23 February 2022
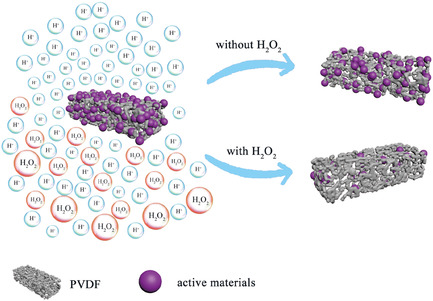
Herein, DL-malic acid and H2O2 are used as the leaching system to conduct efficient green leaching of spent LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 batteries. The kinetic analysis indicates that the leaching process is controlled by chemical reaction in the absence of H2O2, and the leaching process after the addition of H2O2 is controlled by the chemical reaction process and the diffusion process.
State-of-Health Prediction for Lithium-Ion Batteries Based on Complete Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition with Adaptive Noise-Gate Recurrent Unit Fusion Model
- First Published: 28 January 2022
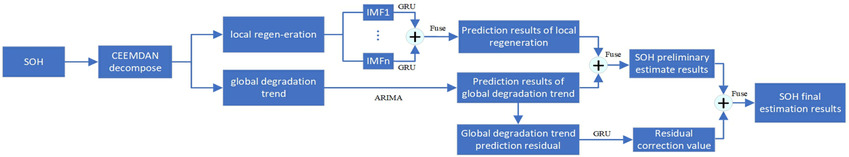
State-of-health (SOH) estimation is one of the most critical battery management system tasks. A new complete ensemble empirical mode decomposition with adaptive noise (CEEMDAN) and gate recurrent unit (GRU) based fusion prediction model for SOH estimation is proposed to solve the problem effectively. The proposed method is verified by experimental battery data with high estimation accuracy and strong robustness.
Electrochemical Properties of Layered Na x Ni x/2Mn1−x/2O2 (0.5 ≤ x ≤ 1.1) with P3 Structure as Cathode for Sodium-Ion Batteries
- First Published: 17 February 2022
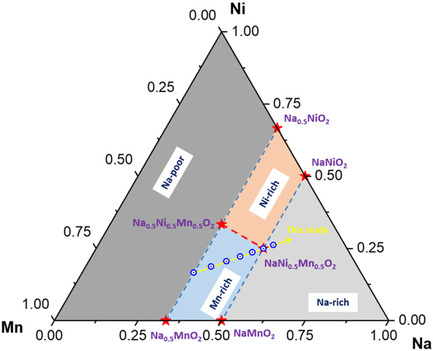
Layered transition metal oxides are the most promising cathode materials for sodium-ion batteries as their composition can be varied over a wide range. In this study, the properties of P3-Na x Ni x/2Mn1−x/2O2 with 0.5≤x≤1.1 is studied. While capacity fade is observed for all materials, the most favorable composition is Na0.6Ni0.3Mn0.7O2 providing an initial capacity of 209 mAh g−1.
Interface Evolution of Solid Oxide Cells between the Electrode and the Interconnect Rib Induced with Applied Current
- First Published: 15 February 2022
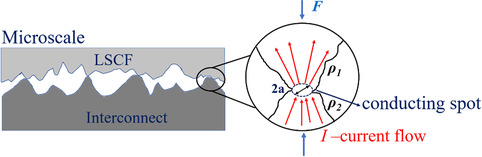
Herein, the interface evolution of solid oxide cells on the interfacial contact resistance (ICR) at different current densities is quantitatively studied using a SUS430/(La,Sr) (Co,Fe)O3 (LSCF)/SUS430 sandwich structure. The ICR between the SUS430 interconnect rib and the LSCF electrode slowly increases in the long term with current passing through the interface.
Theoretical and Experimental Investigation about the Influence of Peltier Effect on the Temperature Loss and Performance Loss of Thermoelectric Generator
- First Published: 15 February 2022
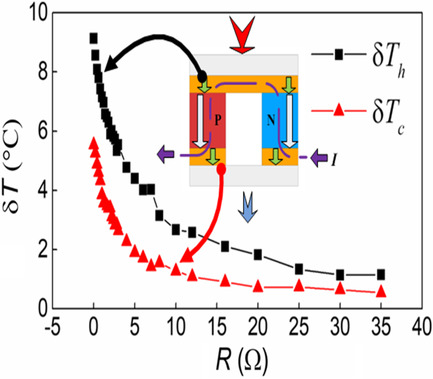
Influences of the Peltier effect on temperature loss at both sides of the thermoelectric generator (TEG) are studied. The temperature loss at the cold side of the TEG is less than that of the hot side. The maximum loss of power, energy, and exergy efficiency occurs at a particular load range, where power, energy, and exergy efficiency reach the maximum, respectively.