Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER IMAGE
Cover Image
- Page: i
- First Published: 19 February 2023

The cover image is based on the Research Article Clinical spectrum of rectal cancer identifies hallmarks of early-onset patients and next-generation treatment strategies by Dingcheng Shen et al., https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.5120.
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEWS
Clinical Cancer Research
Immune checkpoint inhibitors as first line in advanced melanoma: Evaluating progression-free survival based on reconstructed individual patient data
- Pages: 2155-2165
- First Published: 03 August 2022
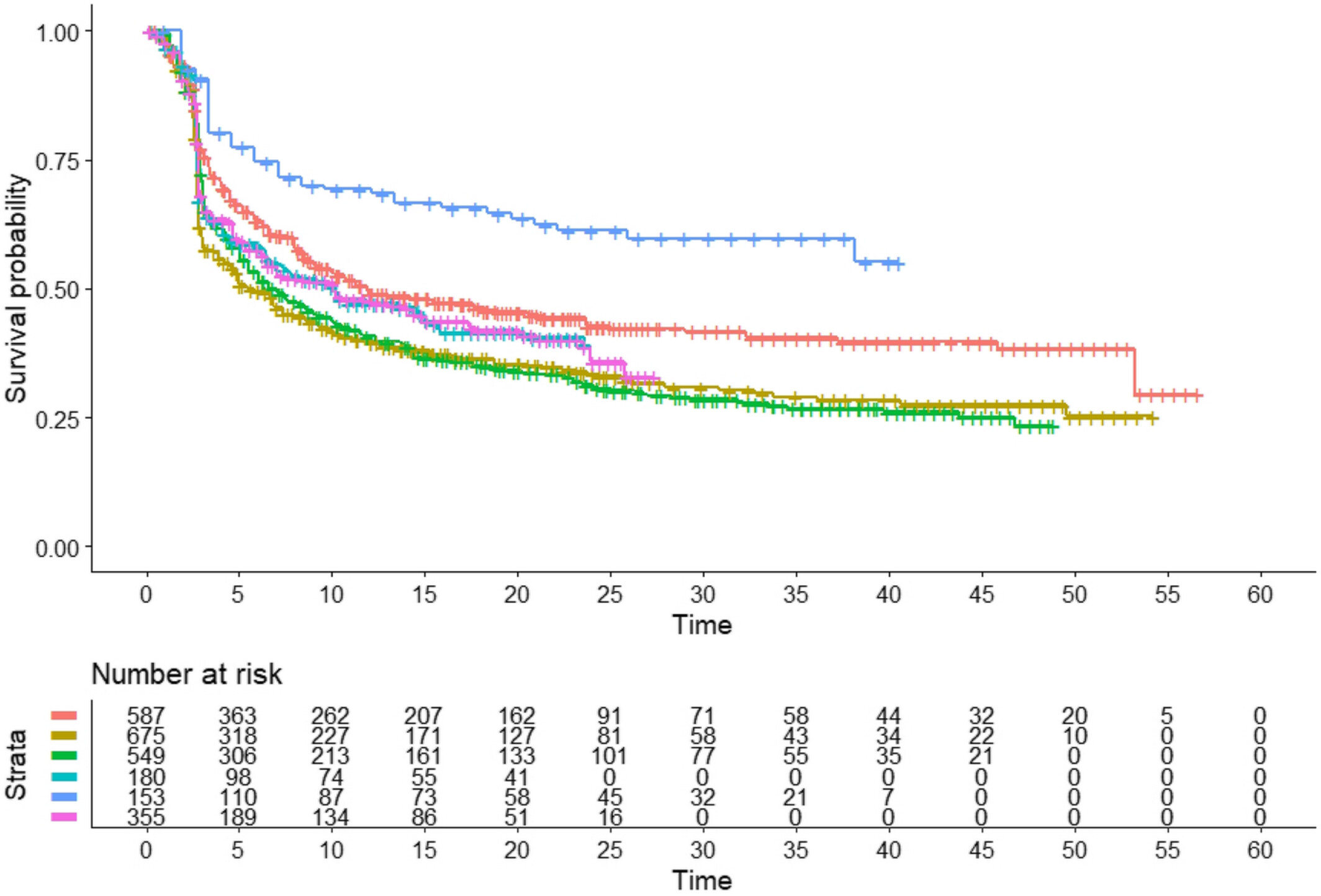
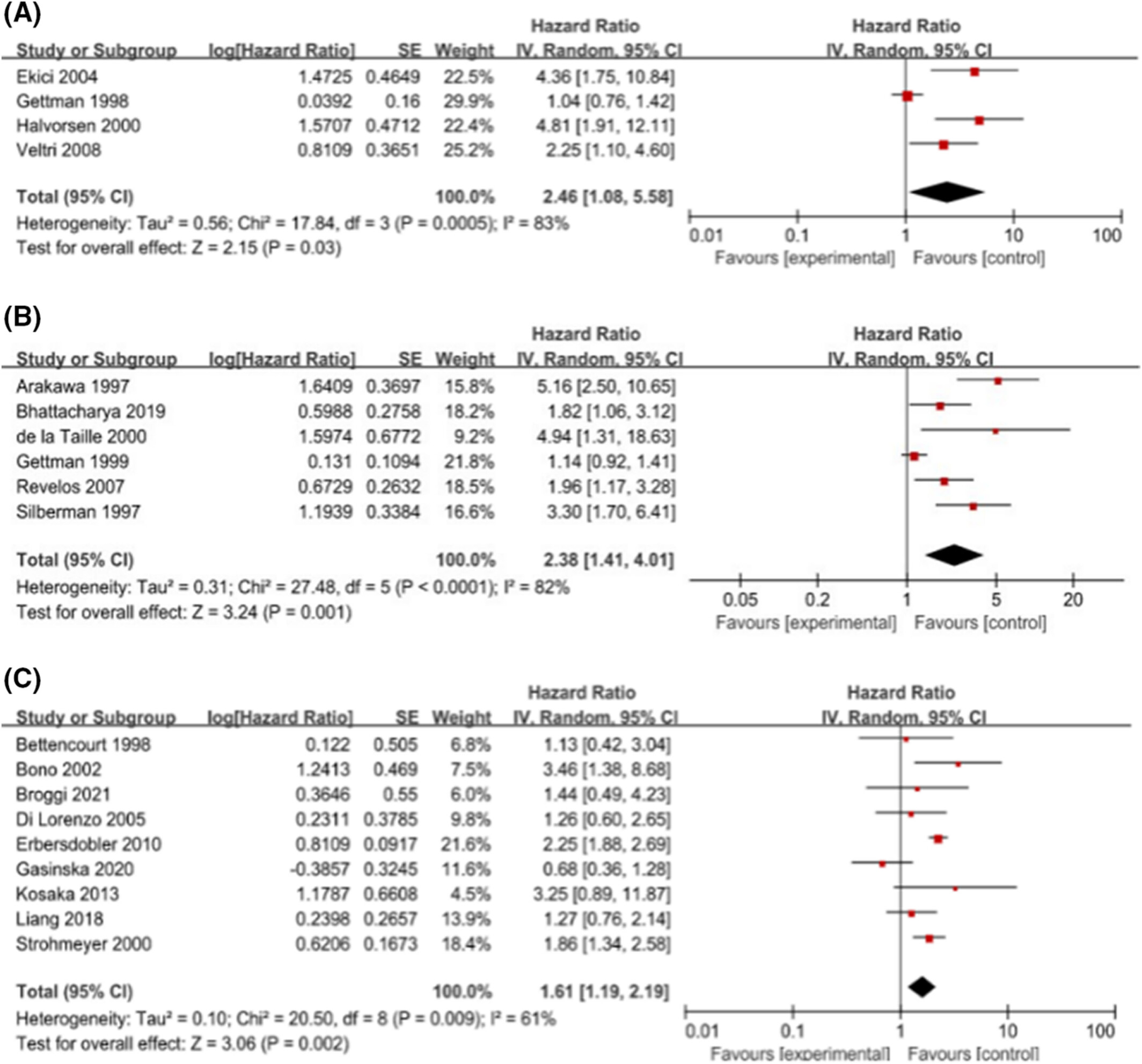
Different predictive values of microvessel density for biochemical recurrence among different PCa populations: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 2166-2178
- First Published: 07 August 2022
Competing risk analysis of cardiovascular death in patients with primary gallbladder cancer
- Pages: 2179-2186
- First Published: 03 August 2022
Using patient data from the SEER database to assess risk factors for cardiovascular death in Primary gallbladder carcinoma patients, the article adopts a competing risk model approach that can provide a clearer understanding of the link between Primary gallbladder carcinoma and cardiovascular disease. It can better help clinicians make relevant clinical decisions.
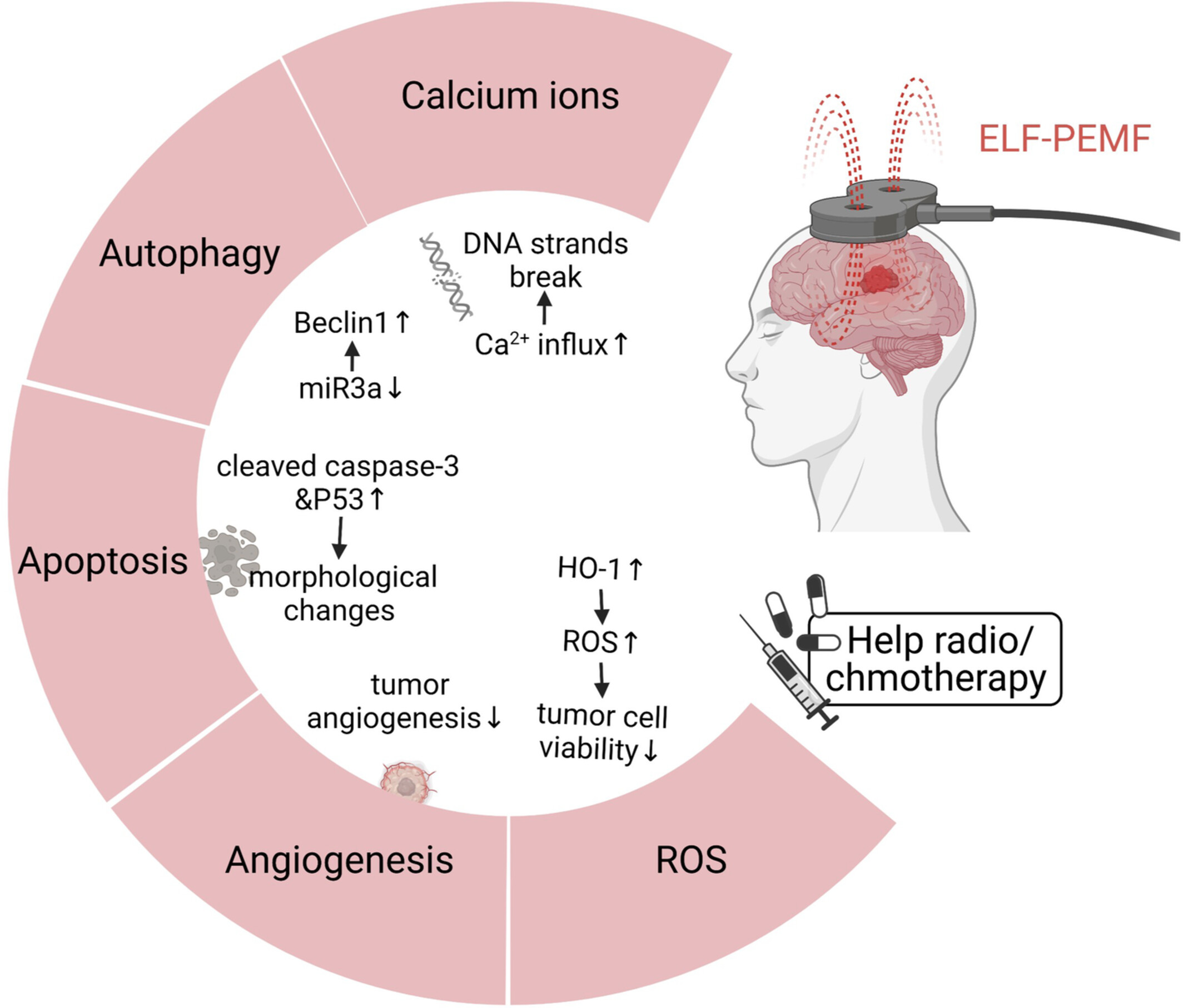
Is extremely low frequency pulsed electromagnetic fields applicable to gliomas? A literature review of the underlying mechanisms and application of extremely low frequency pulsed electromagnetic fields
- Pages: 2187-2198
- First Published: 05 August 2022
Aberrantly expressed long noncoding RNAs as potential prognostic biomarkers in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma: A systemic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 2199-2218
- First Published: 04 September 2022
Increasing patient participation in oncology clinical trials
- Pages: 2219-2226
- First Published: 31 August 2022
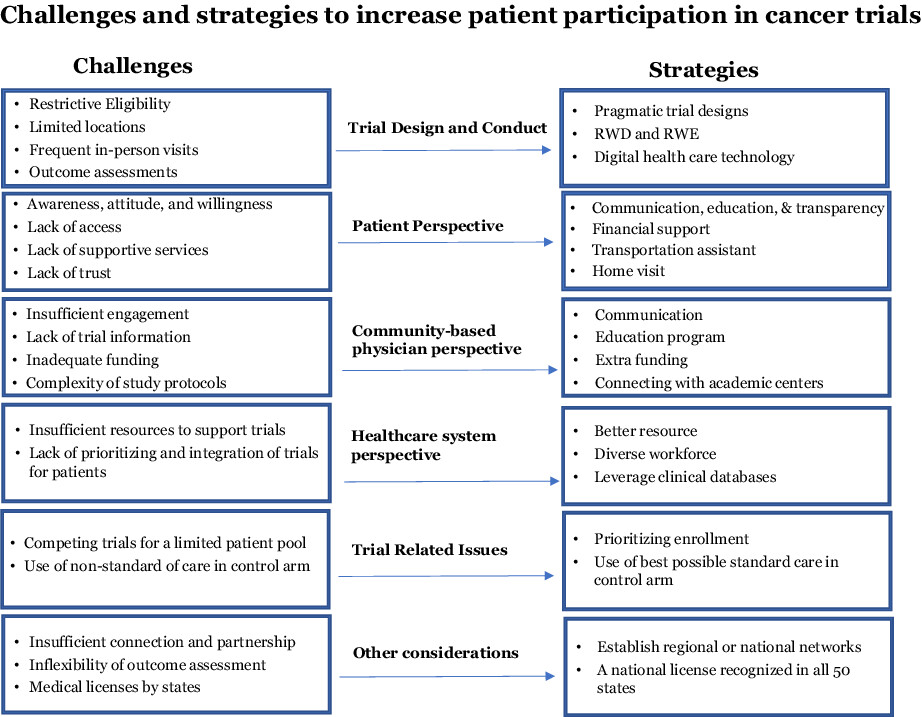
Timely recruitment of eligible participants is essential for the success of clinical trials, with insufficient accrual being the leading cause for premature termination of both oncology and non-oncology trials. In this paper we further elaborate on the challenges for patient participation in oncology trials from physician, patient, healthcare system, and some trial-related perspectives and present strategies such as use of digital healthcare technologies, real-world data and real-world evidence, decentralized clinical trials, pragmatic trial designs, and supportive services to increase patient participation.
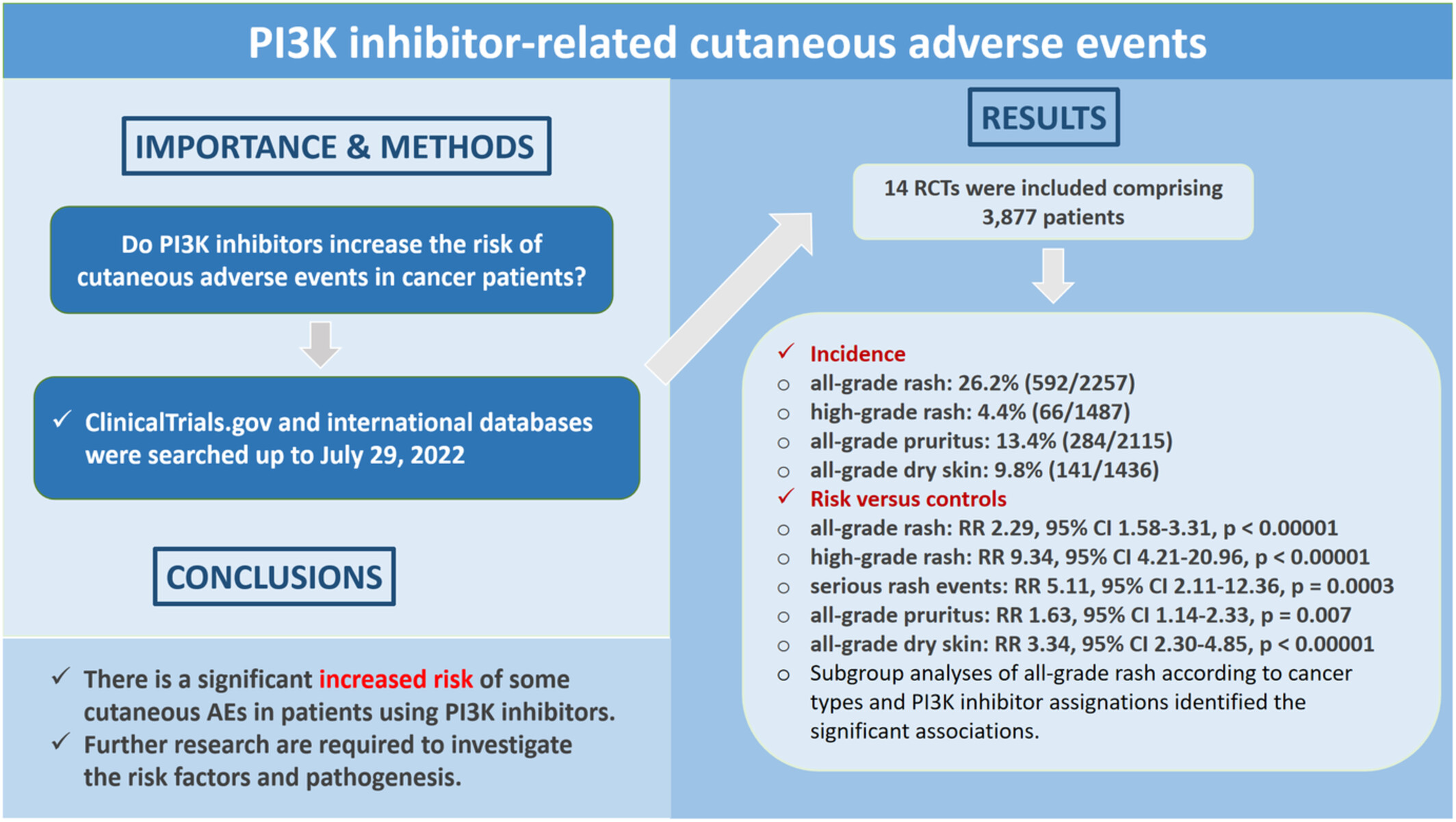
Risk of cutaneous adverse events in cancer patients treated with phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase inhibitors: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- Pages: 2227-2237
- First Published: 19 August 2022
Efficacy of various adjuvant chemotherapy methods in preventing liver metastasis from potentially curative colorectal cancer: A systematic review network meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials
- Pages: 2238-2247
- First Published: 22 August 2022
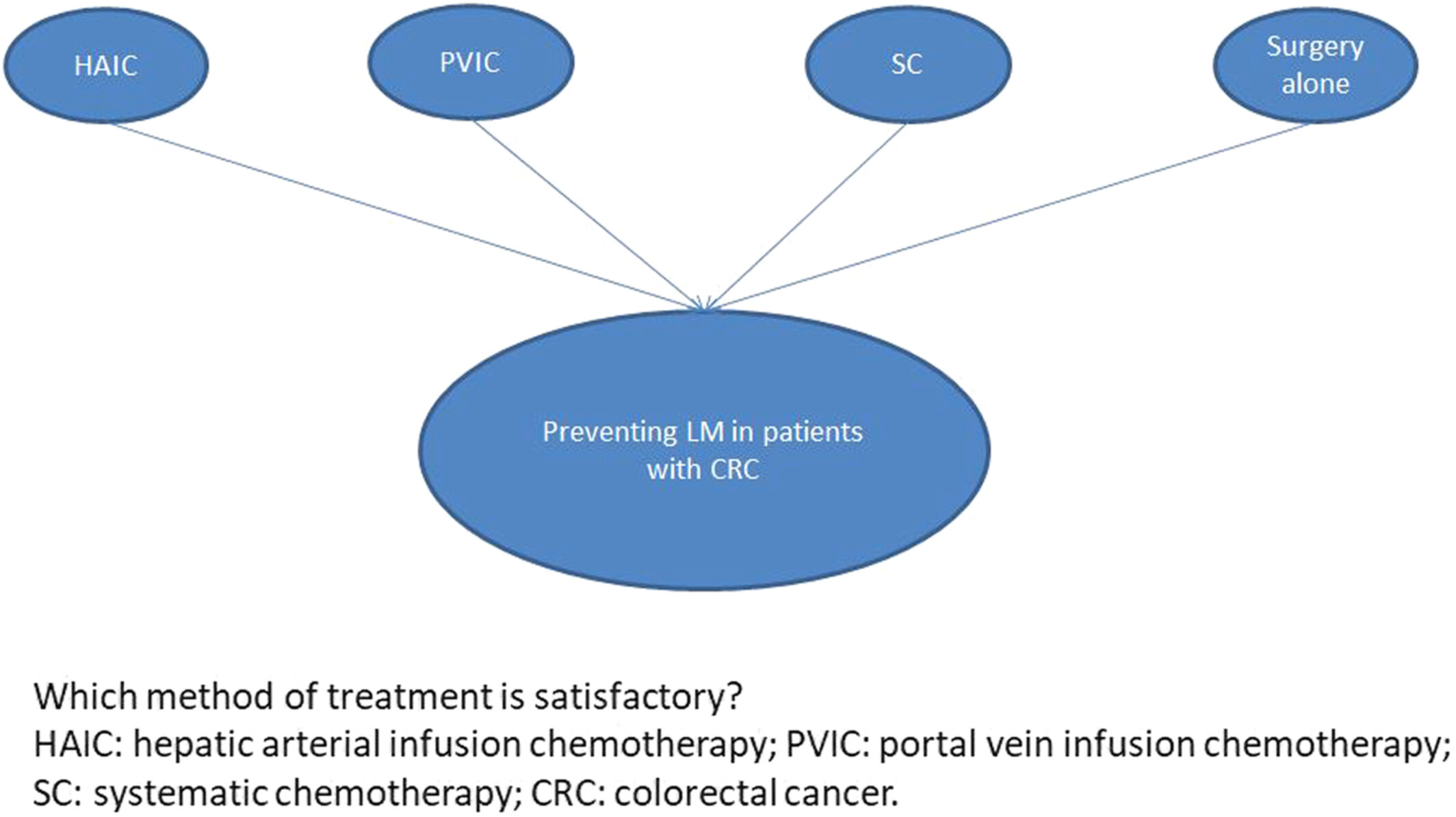
We compared four different methods (portal vein infusion chemotherapy, hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy, systematic chemotherapy, and surgery alone) for preventing liver metastasis in patients with colorectal cancer undergoing curative surgery by means of a network meta-analysis and concluded that hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy might be a satisfactory method.
Sequencing of cerebrospinal fluid in non-small-cell lung cancer patients with leptomeningeal metastasis: A systematic review
- Pages: 2248-2261
- First Published: 24 August 2022
Health-related quality of life in stage III-IV melanoma treated with targeted therapy or immunotherapy: A systematic review on the adequacy of reporting and clinical issues in phase III randomized controlled trials
- Pages: 2262-2280
- First Published: 28 August 2022
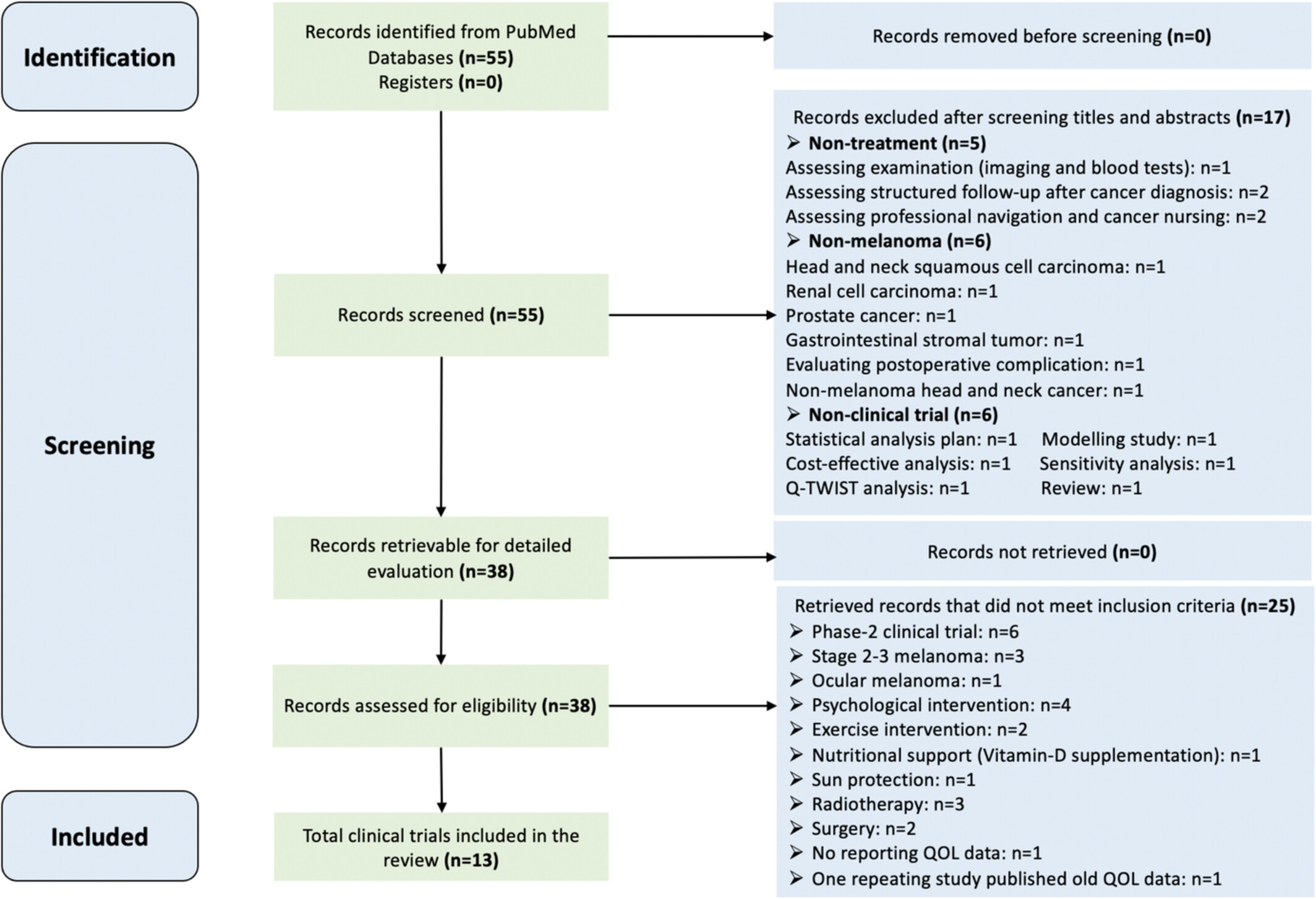
In this systematic review, we appraise the adequacy of health-related quality of life reporting in phase-III randomized controlled trials of stage III-IV cutaneous melanoma, and the clinical issues of immunotherapy and small-molecular targeted therapy on health-related quality of life. The potential effect of reporting might yield new insights into clinical decision making.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Clinical Cancer Research
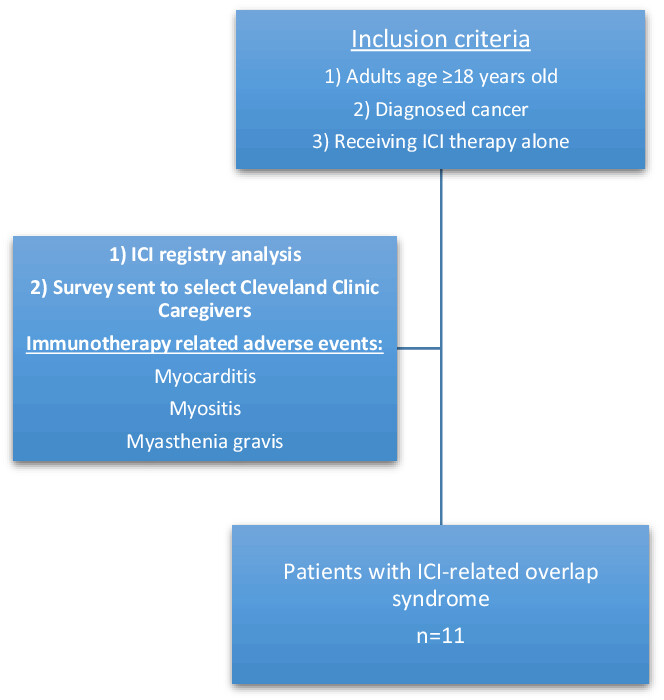
Immune checkpoint inhibitor induced myocarditis, myasthenia gravis, and myositis: A single-center case series
- Pages: 2281-2289
- First Published: 21 September 2022
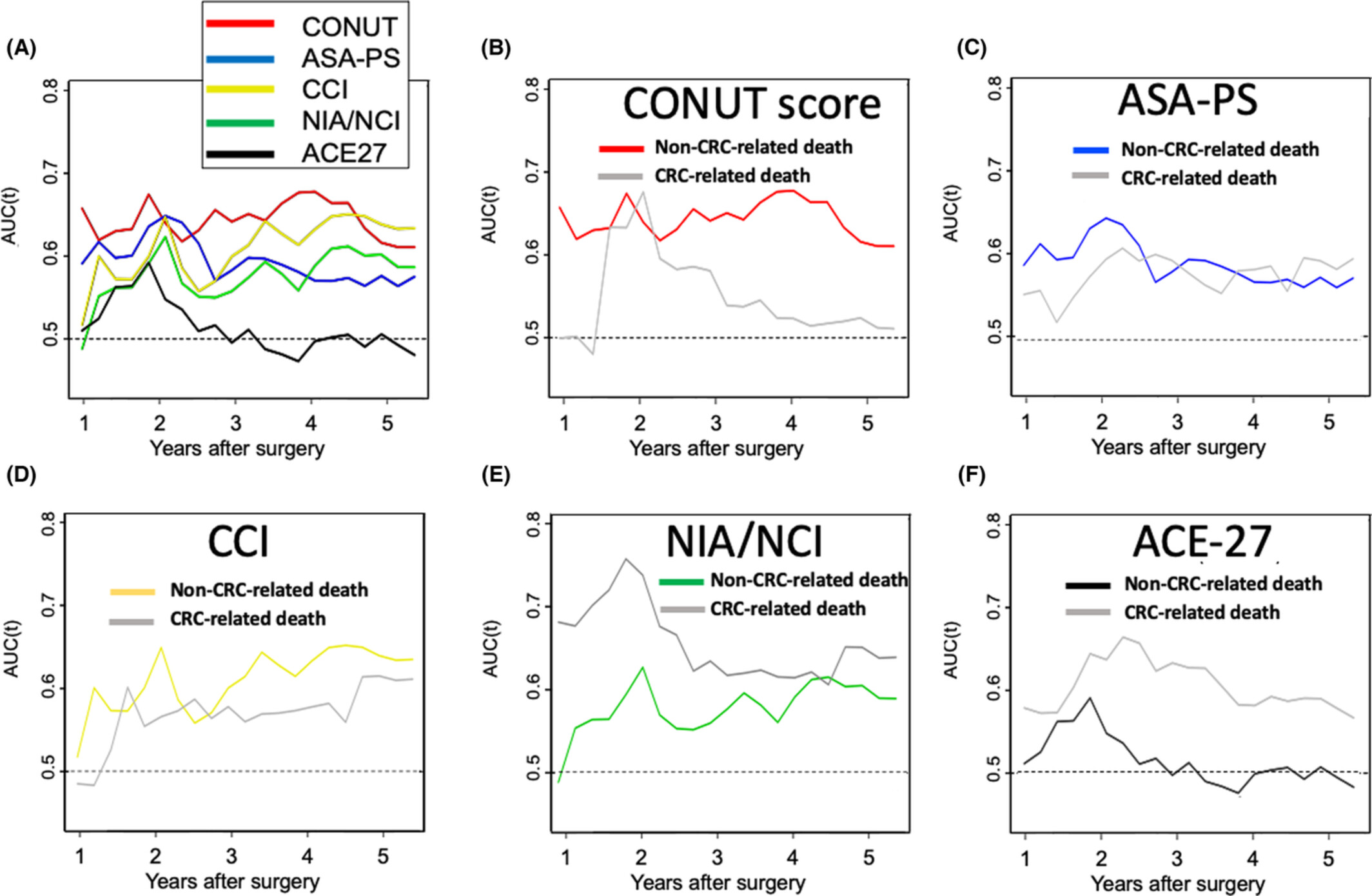
Risk of non-colorectal cancer-related death in elderly patients with the disease: A comparison of five preoperative risk assessment indices
- Pages: 2290-2302
- First Published: 24 July 2022
Second-line treatment options in advanced thymic carcinoma after failure of platinum-based chemotherapy: A multicenter retrospective study
- Pages: 2303-2311
- First Published: 04 August 2022
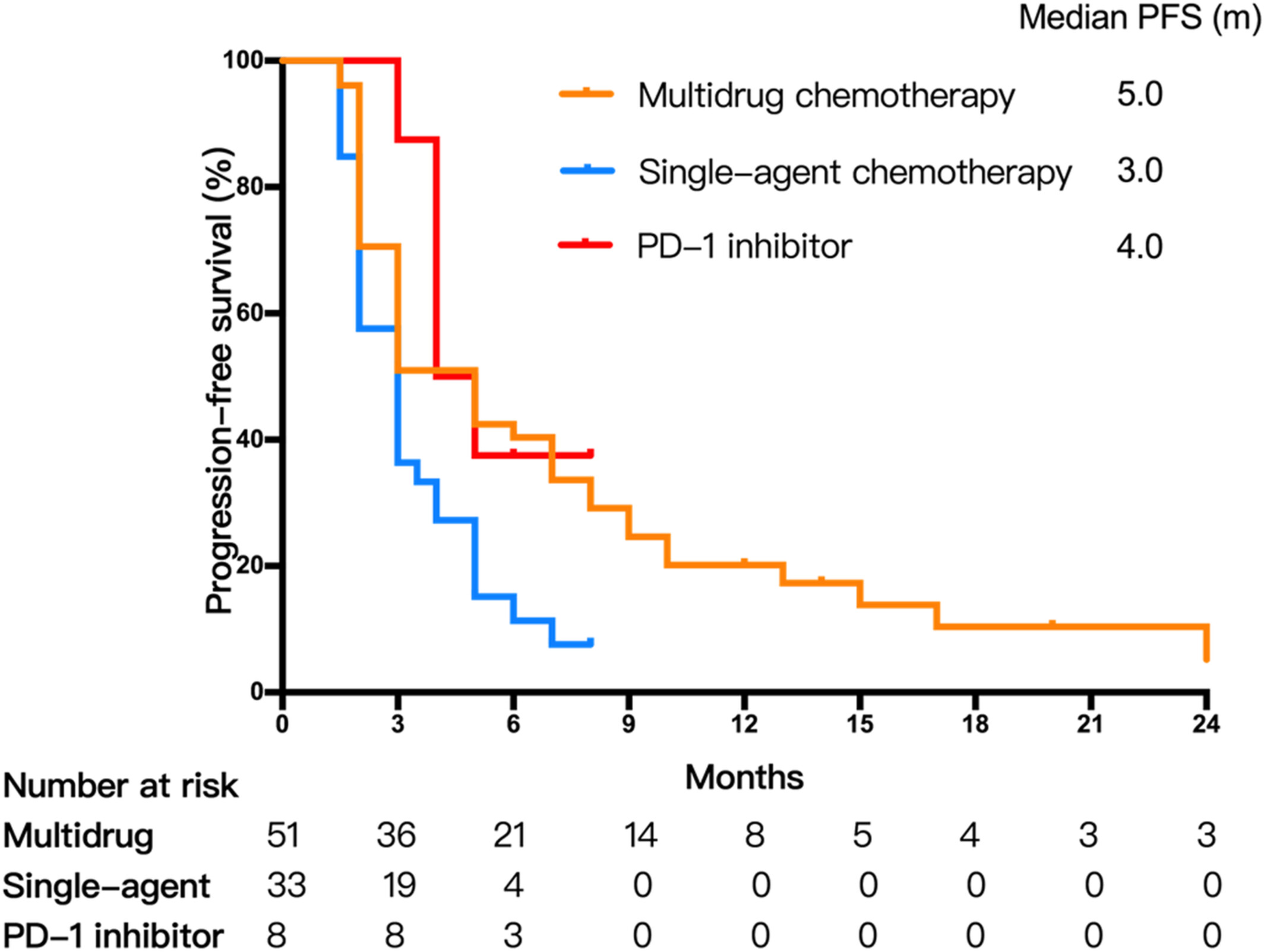
(1) In 92 patients, the multidrug chemotherapy group showed better efficacy than the single-agent chemotherapy group and the PD-1 inhibitors group, with an ORR of 35.3%, 6.0%, and 12.5%, respectively (p = 0.006). (2) In second-line therapy, the median PFS was 5.0 months for multidrug chemotherapy, 3.0 months for monotherapy and 4.0 months for PD-1 inhibitors (p = 0.008). (3) The multidrug chemotherapy group had an advantage over the other groups in OS (p = 0.045), with median OS of 30.4 months.
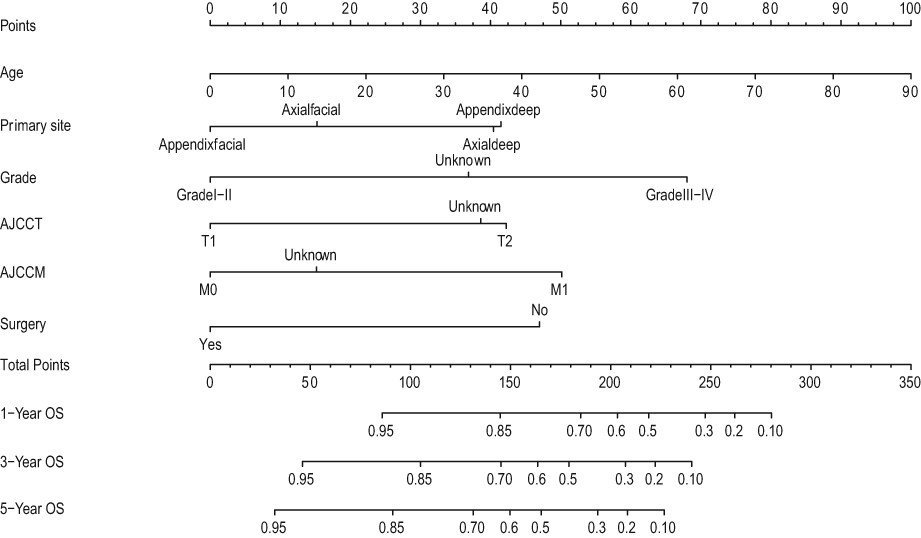
Comparison of the long-term outcomes of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma within the Milan criteria treated by ablation, resection, or transplantation
- Pages: 2312-2324
- First Published: 25 August 2022
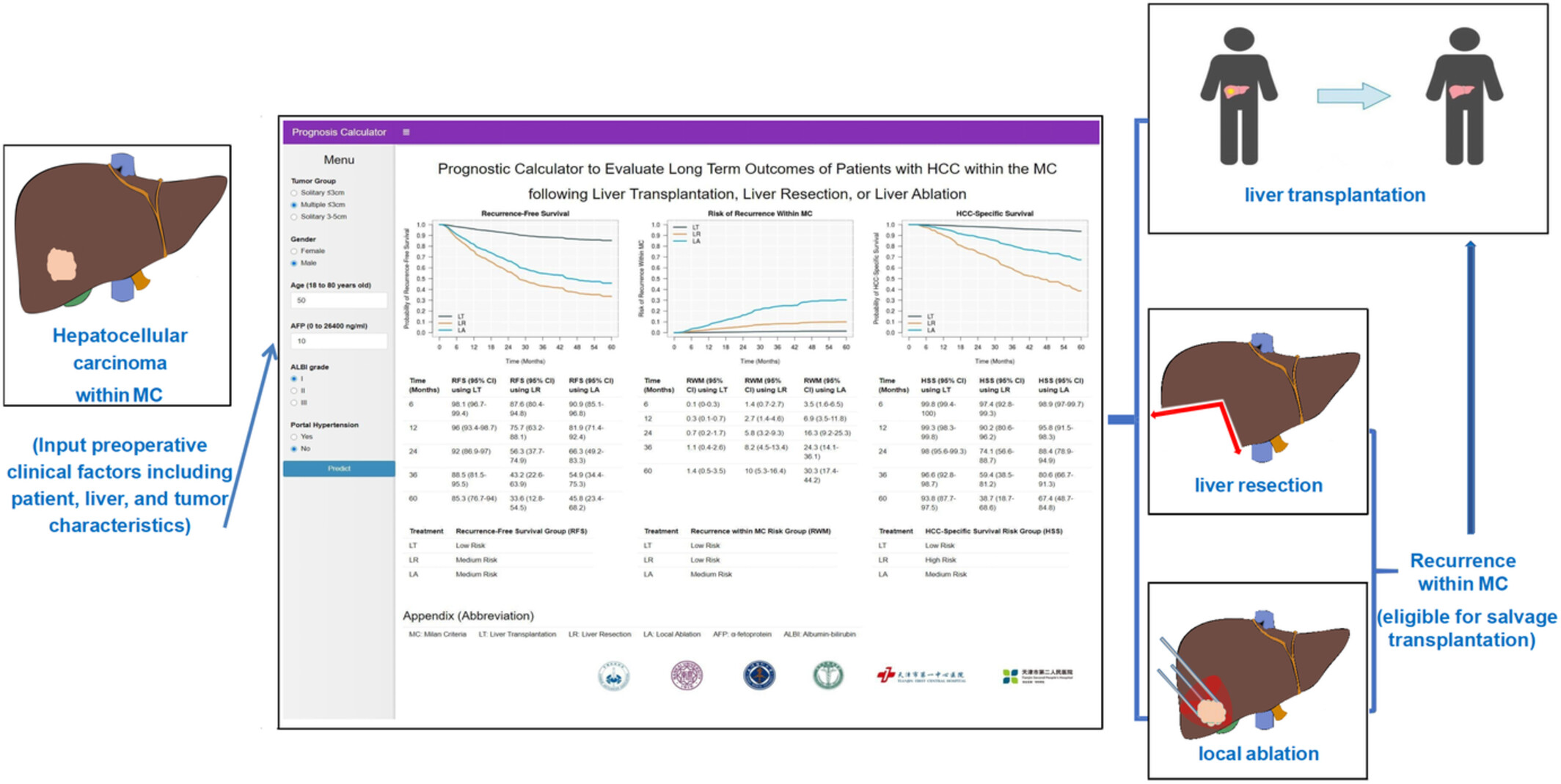
For patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) within the Milan Criteria (MC), three curative-intent treatment options are liver transplantation (LT), resection (LR) and ablation (LA). This online prognostic calculator was developed based on the preoperative clinical factors that were independently associated with outcomes to evaluate and compare recurrence-free survival (RFS), recurrence within the Milan criteria (RWM), and HCC-specific survival (HSS) at different time intervals for all three treatment options. Patients who recurred within the MC are potentially eligible for salvage transplantation.
Discontinuation of pembrolizumab for advanced urothelial carcinoma without disease progression: Nationwide cohort study
- Pages: 2325-2332
- First Published: 21 July 2022
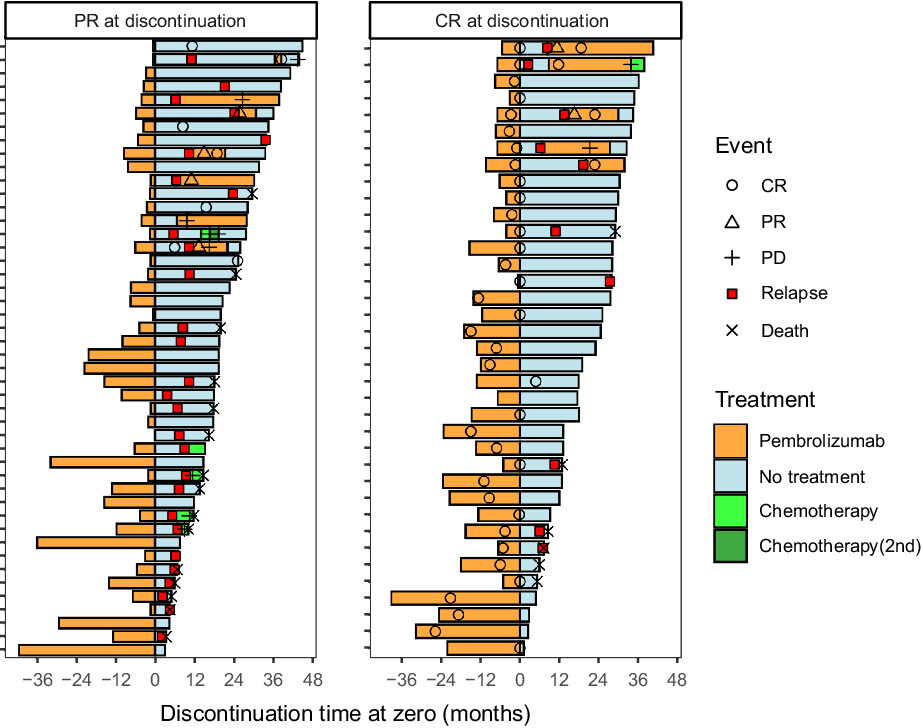
Favorable relapse-free survival was observed after pembrolizumab discontinuation in patients with urothelial carcinoma, especially in those with complete responses, higher hemoglobin levels, and better ECOG-PS at the time of discontinuation. Re-administration upon progression was effective in 90.9% of the patients, and no difference in overall survival was observed between the patients who continued or discontinued treatment after complete or partial responses.
Efficacy and safety of pyrotinib-containing regimen in the patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer: A multicenter real-world study
- Pages: 2333-2344
- First Published: 27 July 2022

Pyrotinib, a novel irreversible epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (EGFR)/HER2 dual tyrosine kinase inhibitor, has shown promising antitumor efficacy and tolerable toxicity in HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer (MBC) in several clinical trials. Whereas, the clinical trials do not usually well reflect the condition of patients in real clinical settings. Our study showed that the pyrotinib-based regimen can effectively treat HER2-positive MBC in real world, including patients, who progressed after lapatinib treatment and with brain metastasis, and drug-related toxicity are acceptable.
Impact of comprehensive family history and genetic analysis in the multidisciplinary pancreatic tumor clinic setting
- Pages: 2345-2355
- First Published: 30 July 2022
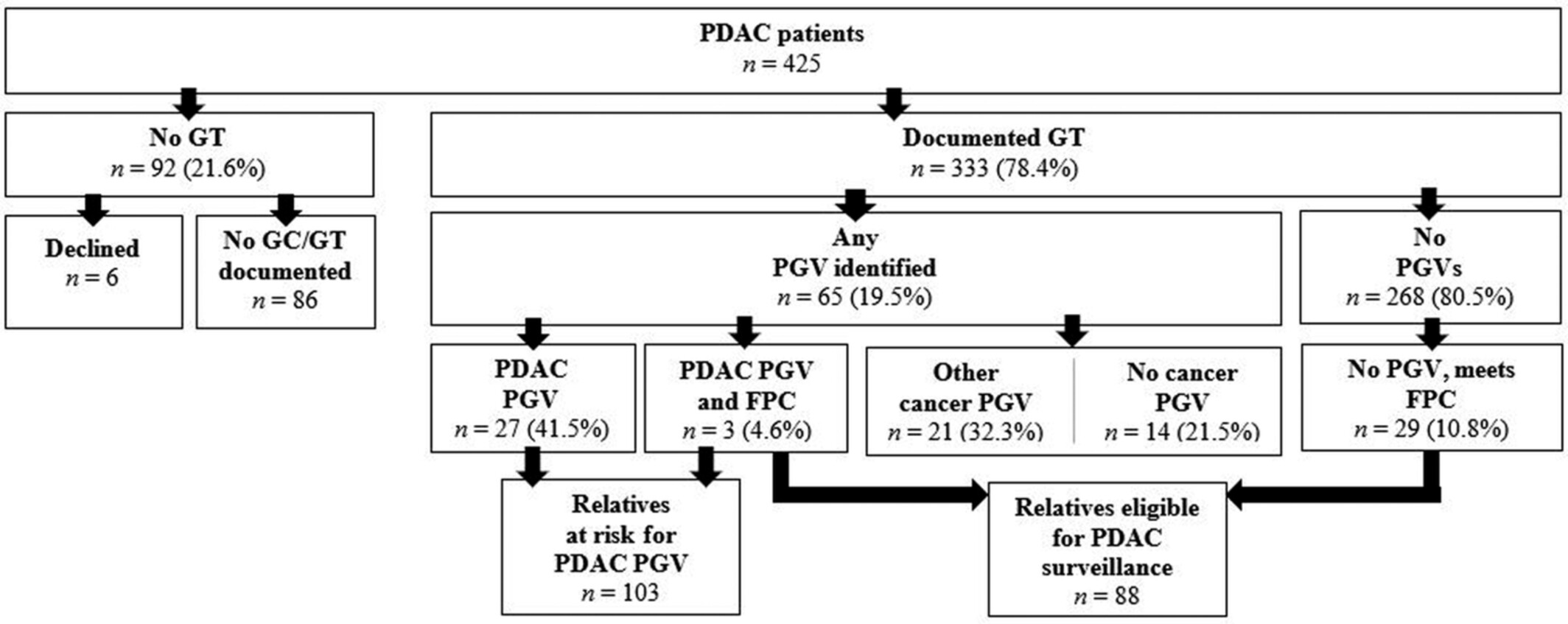
Genetic testing is recommended for all pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) patients. Limited information exists regarding the utility of integrated genetics in the multidisciplinary pancreatic cancer clinic setting. We found that integrating genetics into the multidisciplinary setting significantly improved genetic testing compliance by reducing logistical barriers for PDAC patients, and clarified cancer risks for their relatives while conserving clinical resources.
Metastatic melanoma of the heart: Retrospective cohort study and systematic review of prevalence, clinical characteristics, and outcomes
- Pages: 2356-2367
- First Published: 27 July 2022
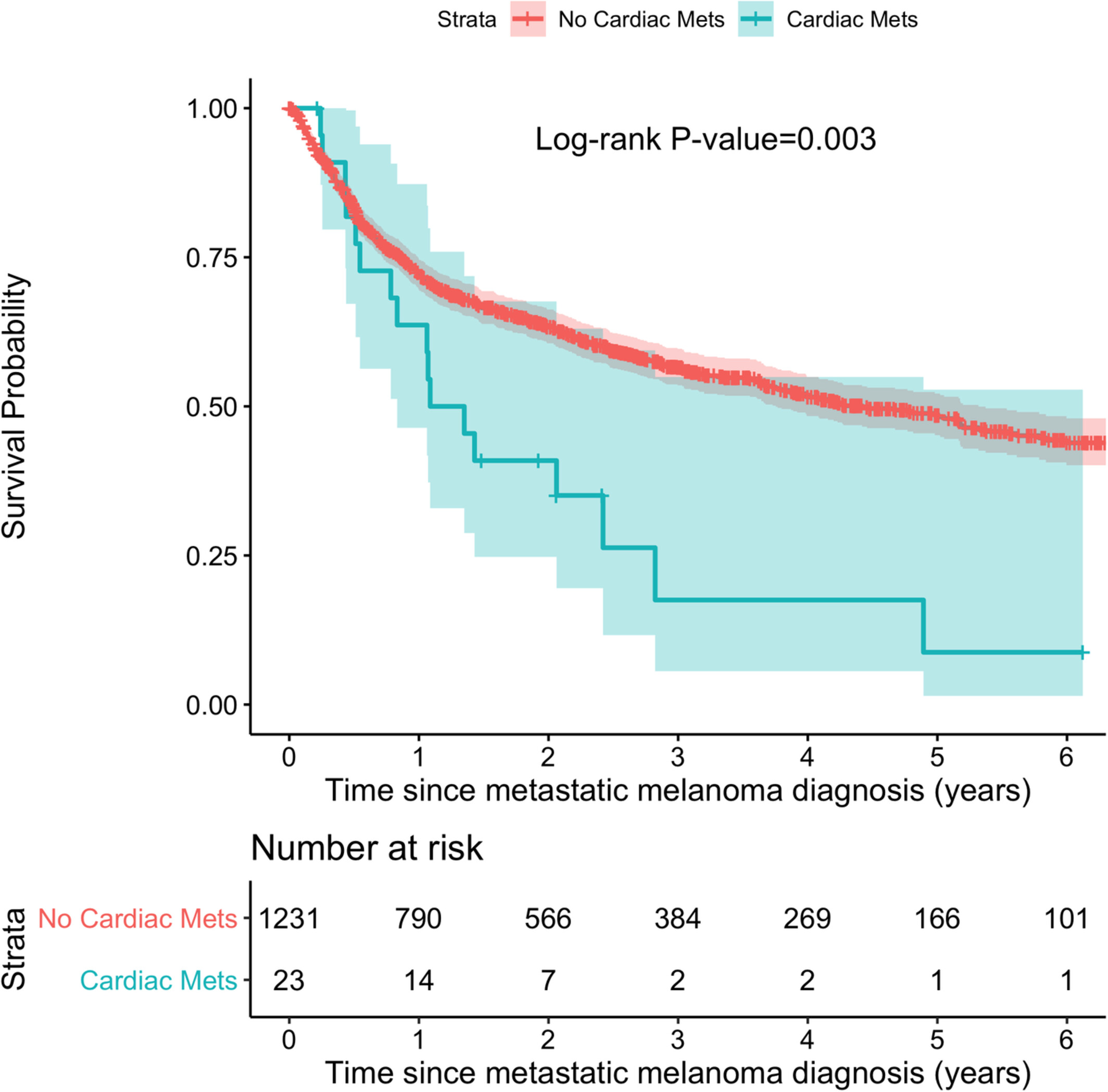
Cardiac metastasis occurs in 2% of patients with metastatic melanoma, can affect all cardiac structures, and is associated with high mortality. Cardiovascular complications may occur after the diagnosis of cardiac metastasis of melanoma, however with limited impact on mortality, which is predominantly due to progression of malignancy.
Prognosis of adenoid cystic carcinoma in head and neck region treated with different regimens—A single-centre study
- Pages: 2368-2377
- First Published: 07 August 2022
Real-World nivolumab dosing patterns and safety outcomes in patients receiving adjuvant therapy for melanoma
- Pages: 2378-2388
- First Published: 25 July 2022

Real-word data on use of the flat-dose nivolumab 480 mg Q4W regimen for the adjuvant treatment of melanoma are limited. Findings from the current study suggest that the real-world safety and tolerability profiles of nivolumab 240 mg Q2W and 480 mg Q4W are similar and that both are comparable to weight-based dosing (3 mg/kg Q2W), adding to existing data supporting their approval and use as adjuvant treatments for melanoma.
Adjuvant 5-Fluorouracil/leucovorin, capecitabine, and oxaliplatin-related regimens for stage II/III colon cancer patients 66 years or older
- Pages: 2389-2406
- First Published: 13 October 2022
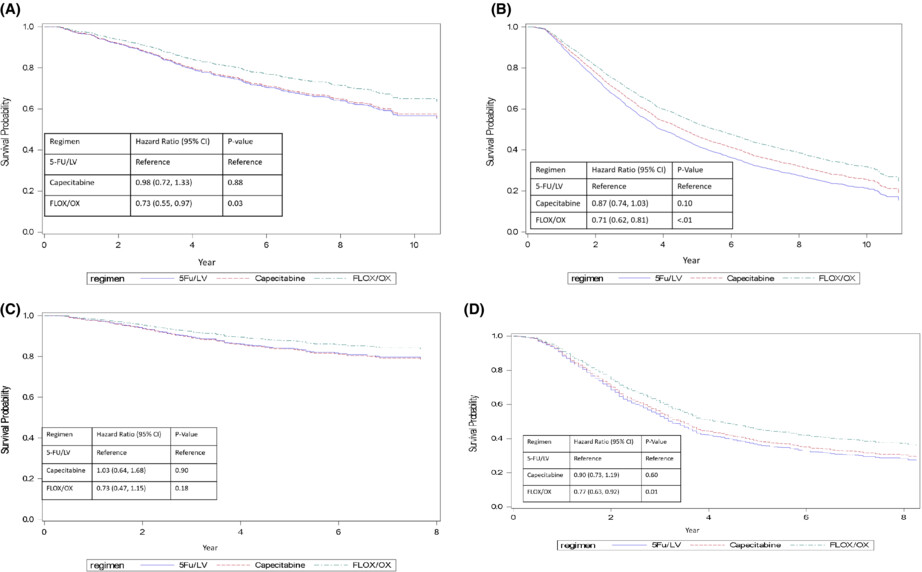
FLOX/OX treatment was associated with improved overall survival (OS) and improved cancer specific survival in stage III patients compared with 5-FU/LV and the survival benefit of FLOX/OX was sustained in stage III patients aged 70 years. Capecitabine had the lowest emergency room visit/hospitalization among the three regimens with 19.2% in stage II and 28.9% in stage III patients.
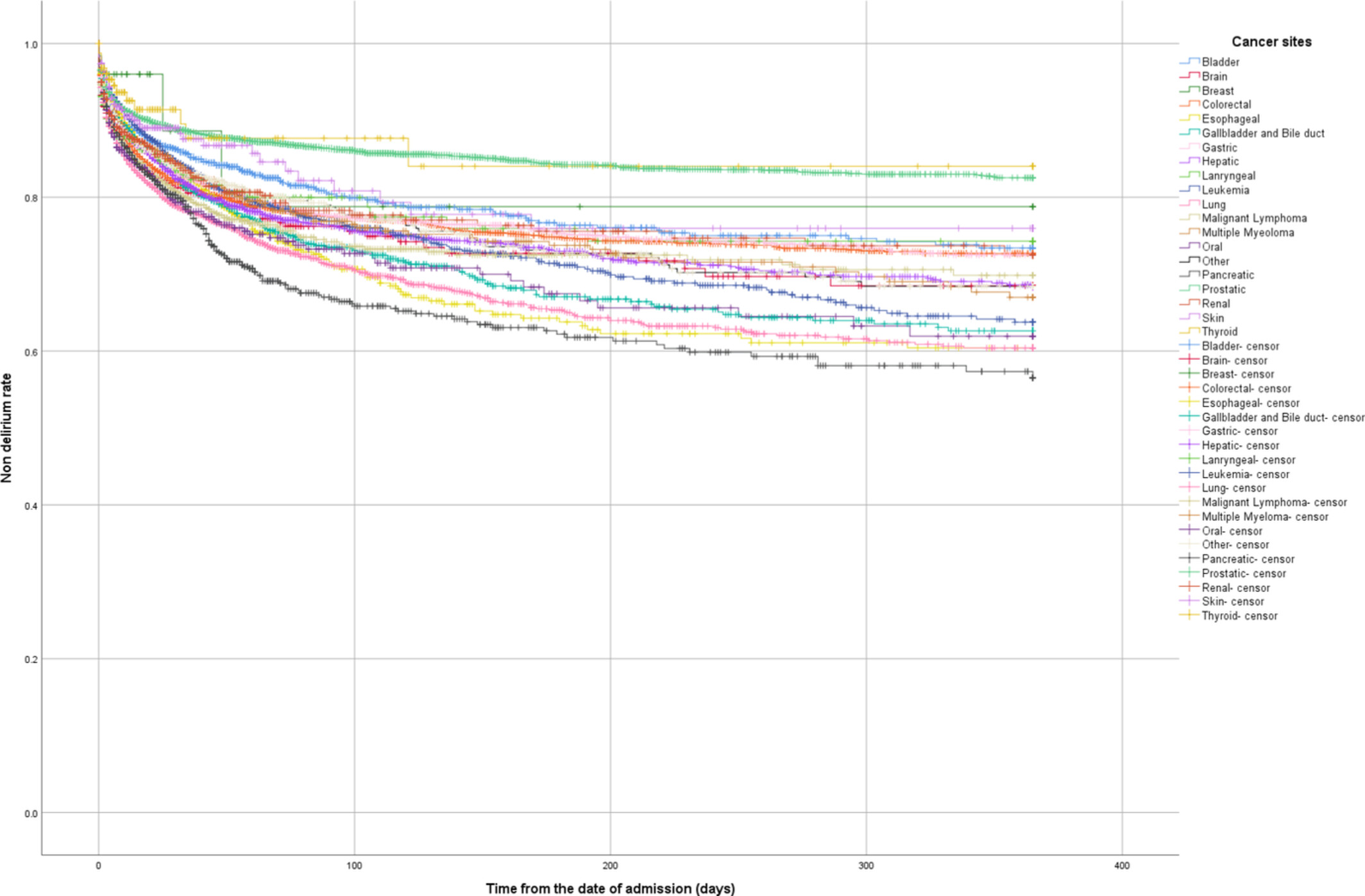
An association between cancer type and delirium incidence in Japanese elderly patients: A retrospective longitudinal study
- Pages: 2407-2416
- First Published: 26 July 2022
Assessment of neoadjuvant chemotherapy with docetaxel, cisplatin, and fluorouracil in patients with oral cavity cancer
- Pages: 2417-2426
- First Published: 26 July 2022
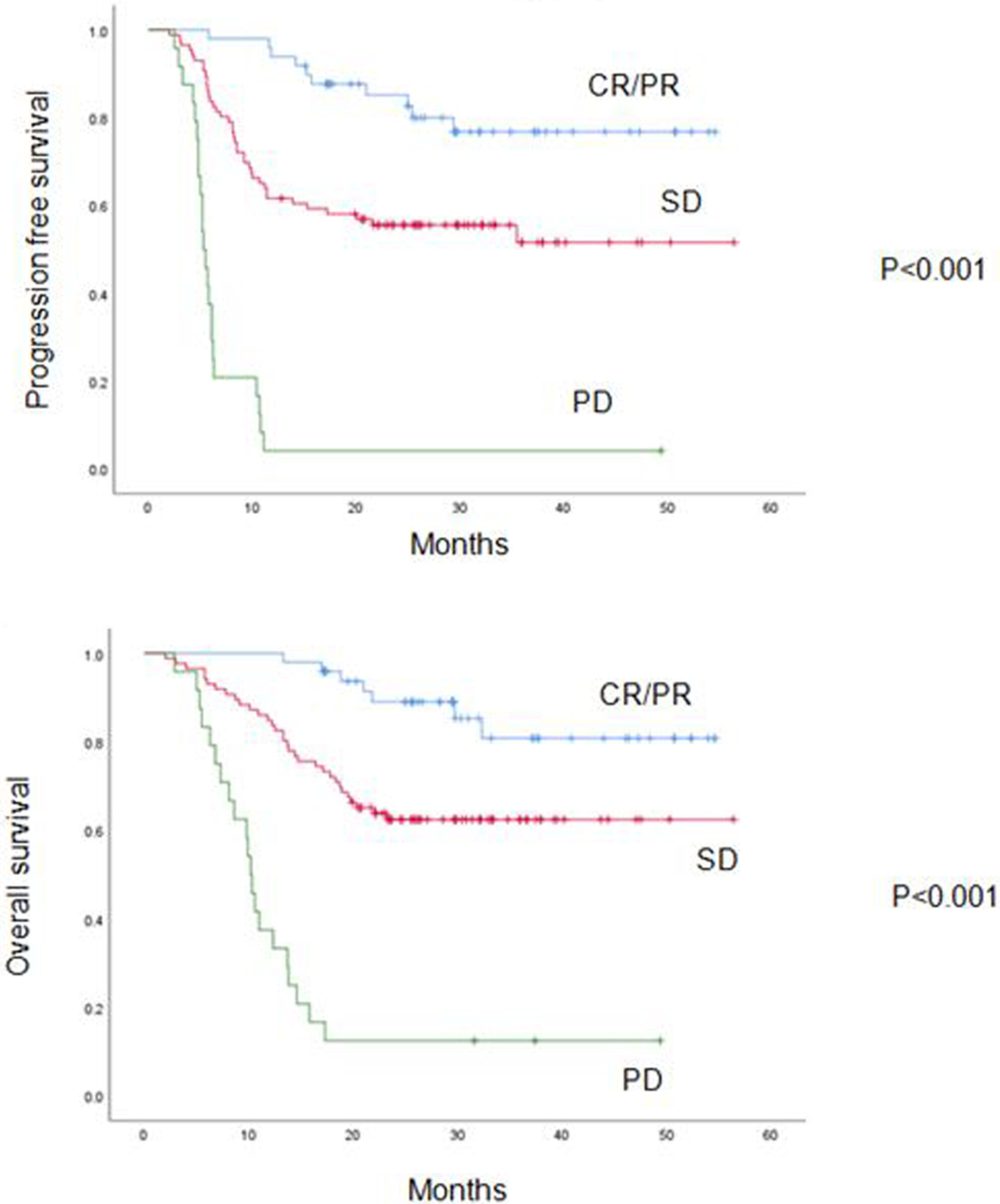
The response of neoadjuvant TPF chemotherapy in patients with oral cavity cancer was related to the disease stage, especially the nodal stage. Patients with bulky nodes or lymph node with obvious necrosis may have low response. Patients with complete or partial response developed less progression events and better survival.
Comparing the associations between host and tumor factors with survival outcomes with anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in metastatic melanoma
- Pages: 2427-2439
- First Published: 04 August 2022
The efficiency of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in colon cancer with mismatch repair deficiency
- Pages: 2440-2452
- First Published: 29 July 2022
Clinical evaluation of urine laminin-γ2 monomer as a potent biomarker for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer
- Pages: 2453-2462
- First Published: 04 August 2022
CT radiomics identifying non-responders to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy among patients with locally advanced rectal cancer
- Pages: 2463-2473
- First Published: 01 August 2022
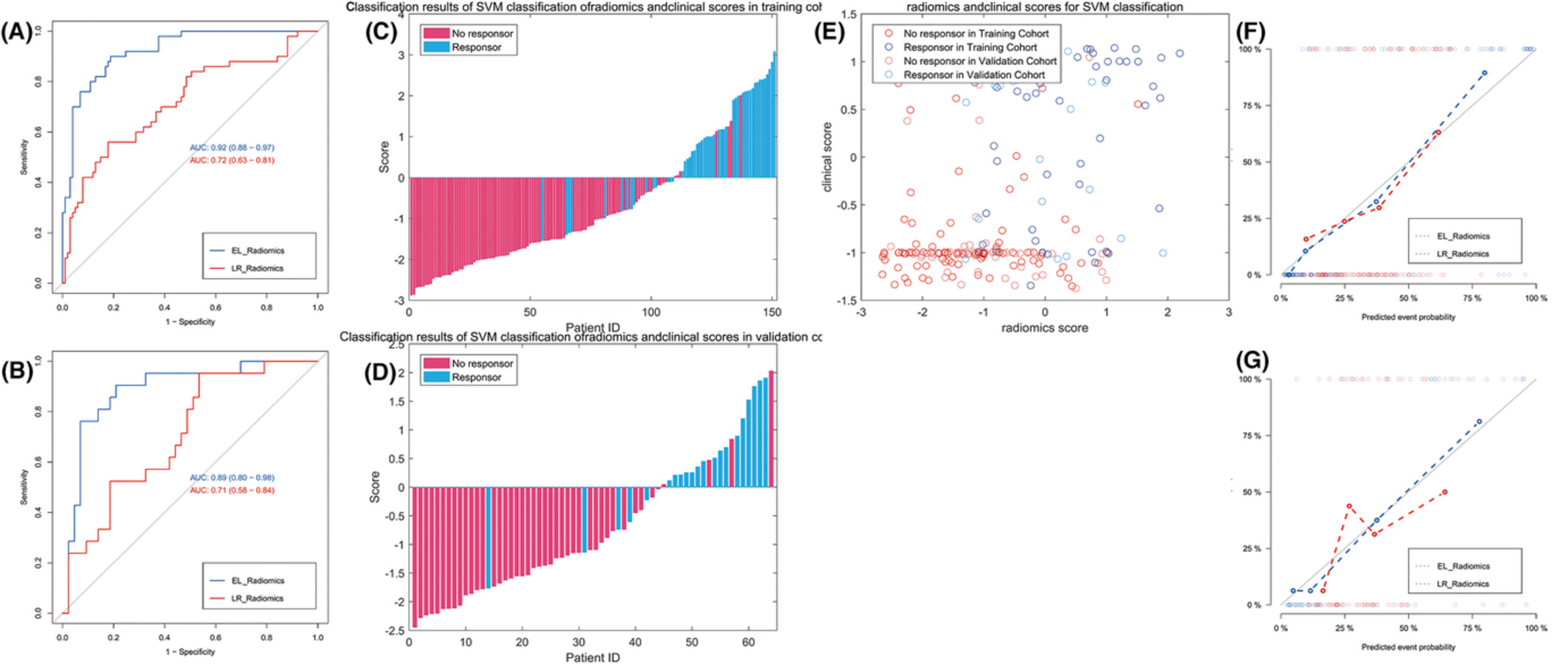
Non-invasive methods to predict the response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer could help clinicians develop individualized treatment strategies. In this work, we retrospectively enrolled 215 patients with locally advanced rectal cancer who received neoadjuvant chemoradiation therapy, and we analyzed their pretreatment radiotherapy planning CT images for both radiomic and traditional radiological features. A machine learning model built with the selected radiomics and clinicopathological features. achieved satisfying performance for predicting non-response to neoadjuvant chemoradiation therapy with an area under the curve (AUC) value of 0.92 for the training cohort and 0.89 for the validation cohort. The machine learning model outperformed a traditional logistic regression model. These findings support the use of radiomics for clinical decision-making in locally advanced rectal cancer.
Multiple primary melanoma in association with other personal and familial cancers
- Pages: 2474-2483
- First Published: 05 August 2022
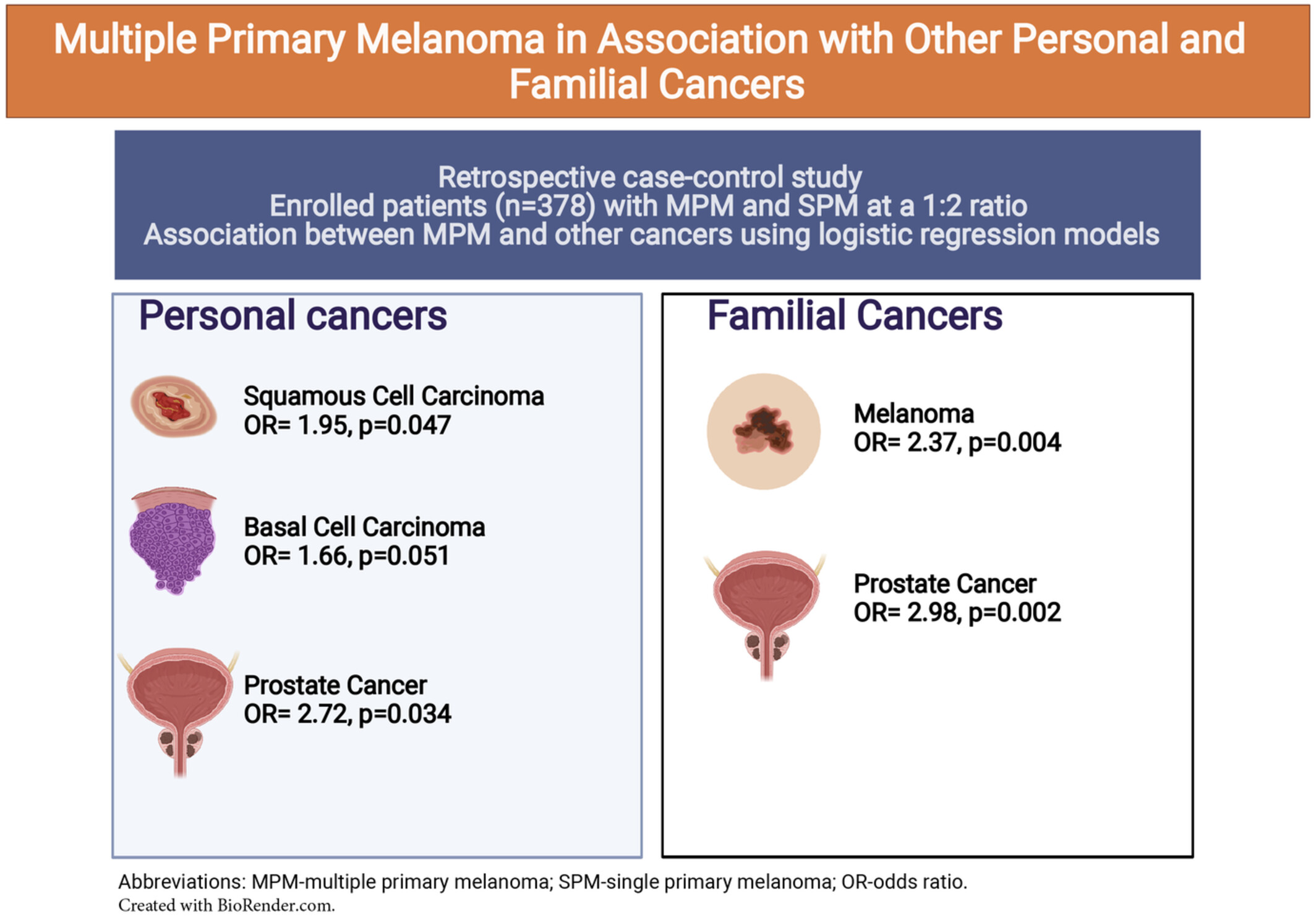
This retrospective case–control study enrolled patients (n = 378) with multiple primary melanoma (MPM) and single primary melanoma (SPM) at a 1:2 ratio and evaluated the association between MPM and other cancers using logistic regression models. Compared with patients with SPM, patients with MPM were more likely to have squamous cell carcinoma (OR 1.95, 95% CI 1.001–3.79, p = 0.047), basal cell carcinoma (OR 1.66, 95% CI 0.99–2.74, p = 0.051), and prostate cancer (OR 2.72, 95% CI 1.07–7.01, p = 0.034).
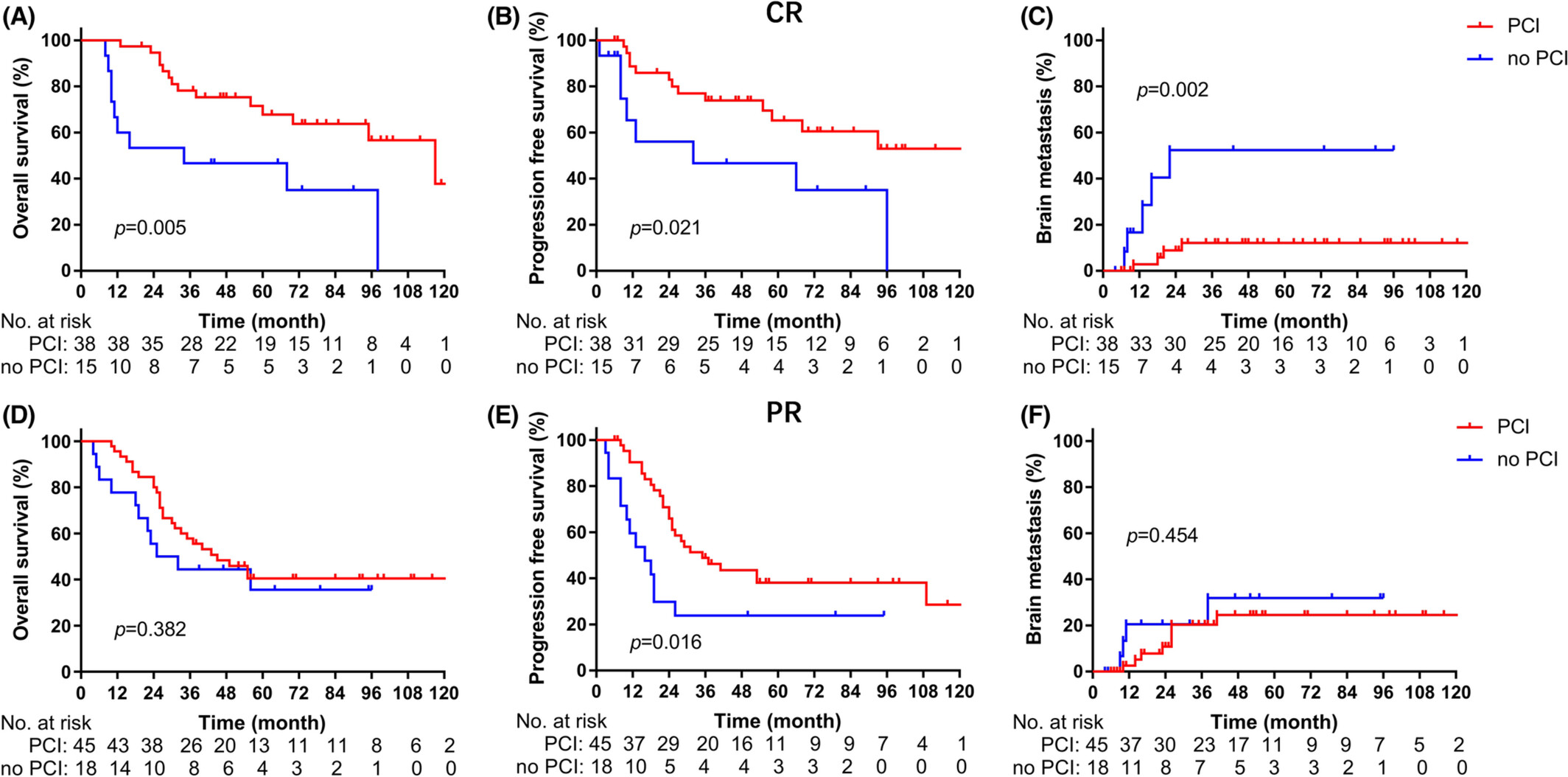
Prophylactic cranial irradiation for limited-stage small-cell lung cancer in the magnetic resonance imaging era
- Pages: 2484-2492
- First Published: 27 July 2022
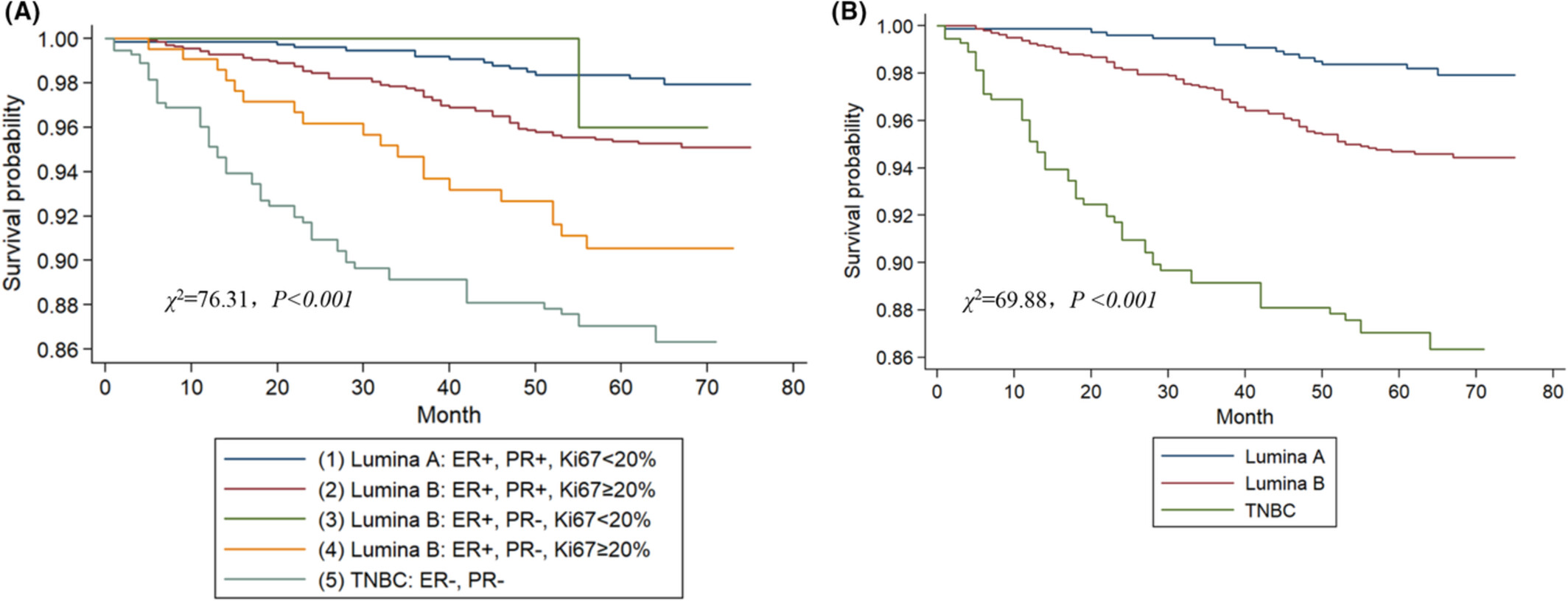
The regrouping of Luminal B (HER2 negative), a better discriminator of outcome and recurrence score
- Pages: 2493-2504
- First Published: 31 July 2022
Does acute pancreatitis herald pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma? A multicenter electronic health research network study
- Pages: 2505-2513
- First Published: 31 July 2022

Understanding the risk of pancreatic cancer following an acute pancreatitis diagnosis is a critical component to early intervention for pancreatic cancer in this high-risk population as multiple data sets have demonstrated that early detection can lead to an increased percentage of patients diagnosed with stage I disease, and hence an improved chance for cure.
Long-term survival outcomes of patients with primary ocular adnexal MALT lymphoma: A large single-center cohort study
- Pages: 2514-2523
- First Published: 30 July 2022
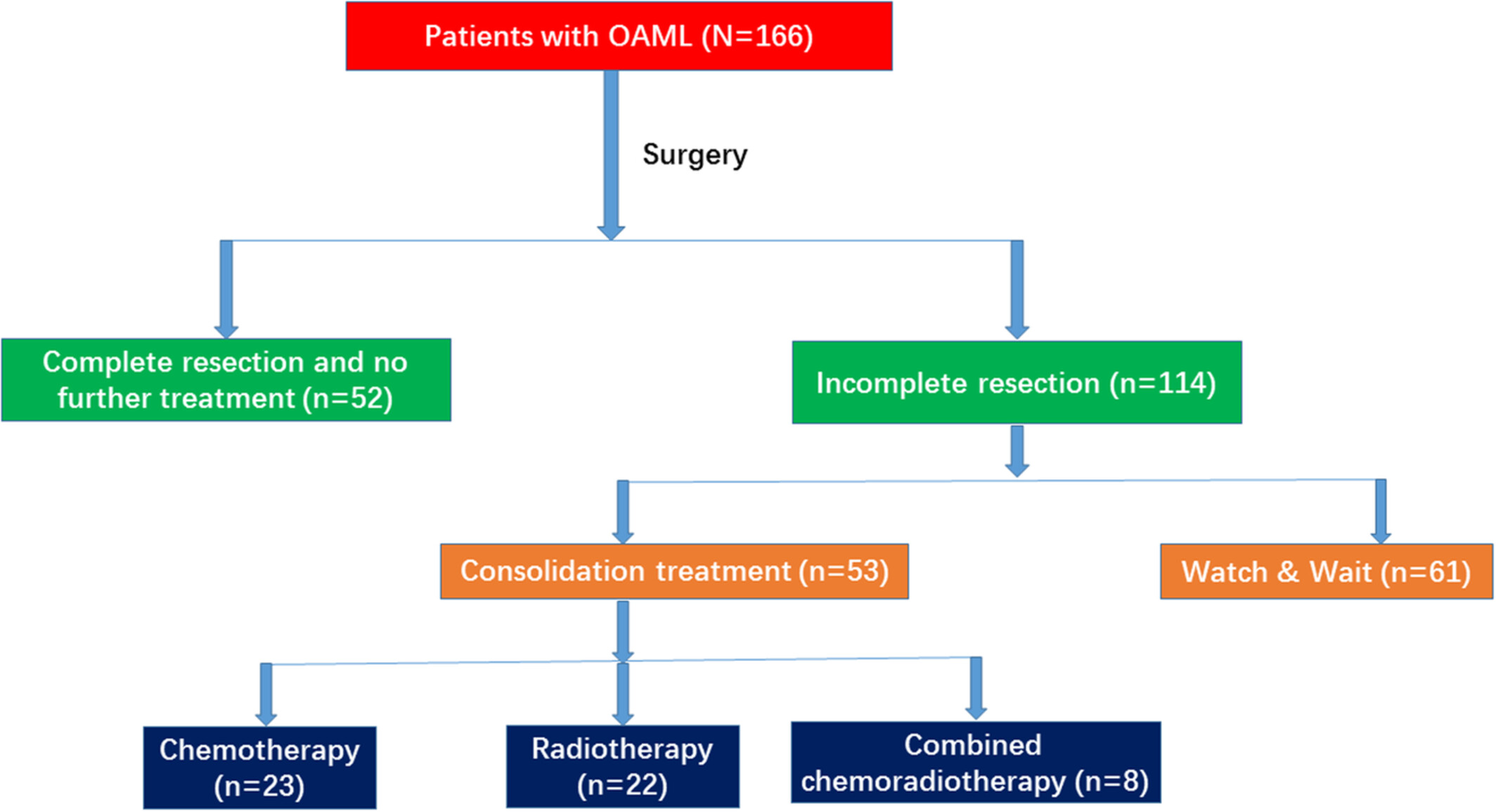
Bilateral involvement was associated with a poor prognosis of OAML and call for extended surveillance of disease progression for patients with bilateral involvement. Among patients with residual lesions after surgical treatment, further consolidation treatment could lead to improved survival, compared with watchful waiting. Systemic treatment might be considered as a treatment candidate, given the noted rare adverse event.
Radiomic study on preoperative multi-modal magnetic resonance images identifies IDH-mutant TERT promoter-mutant gliomas
- Pages: 2524-2537
- First Published: 29 September 2022
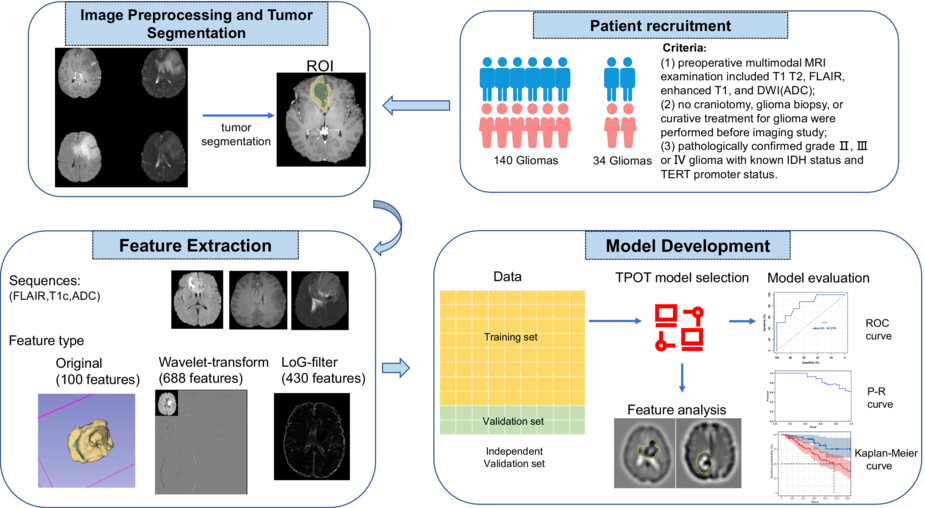
Preoperative multi-modal magnetic resonance imaging radiomic study could distinguish IDH-mutant TERT promoter-mutant gliomas from other gliomas. Contrast-enhanced T1, FLAIR, and ADC maps played an important role in detecting IDH-mutant TERT promoter-mutant gliomas. MR imaging of IDHmut pTERTmut gliomas showed homogenous low-complexity texture in three modalities.
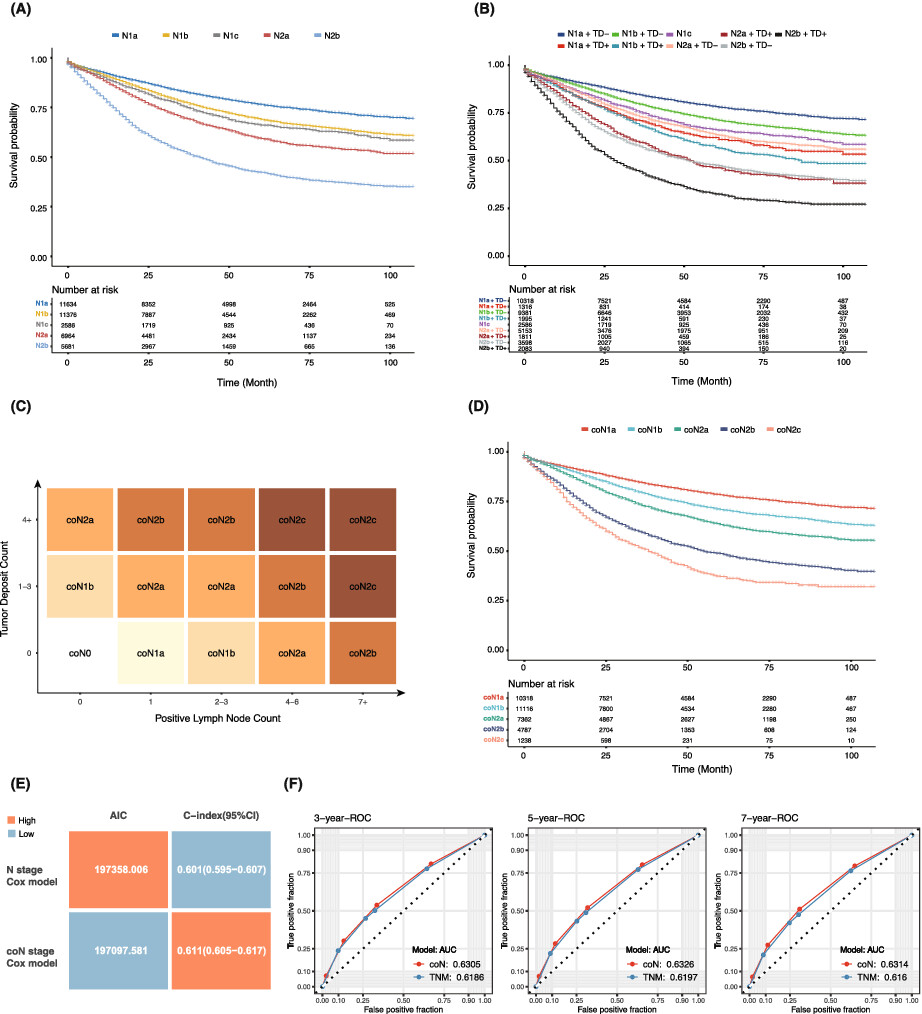
The new ‘coN’ staging system combining lymph node metastasis and tumour deposit provides a more accurate prognosis for TNM stage III colon cancer
- Pages: 2538-2550
- First Published: 01 August 2022
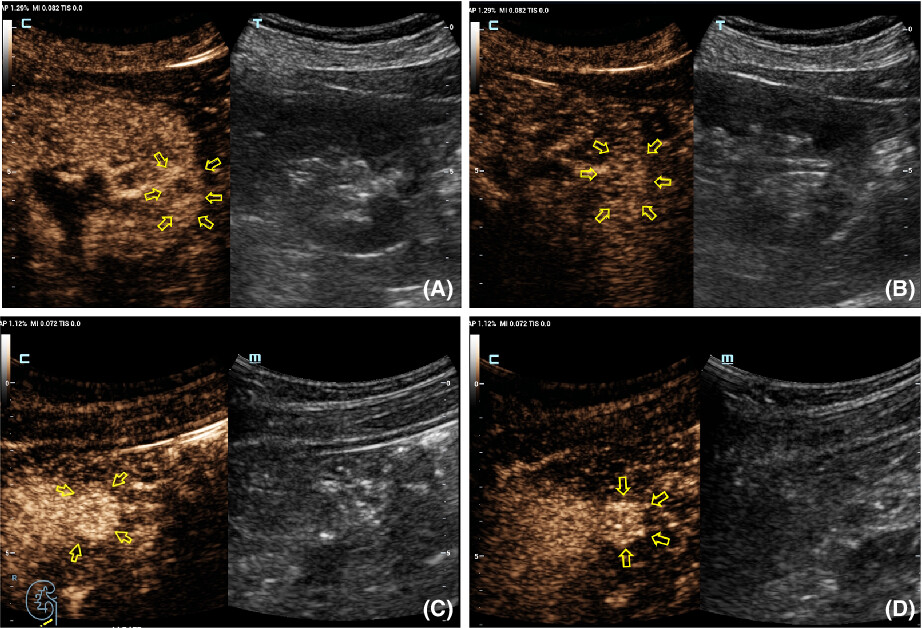
Contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) of benign and malignant renal tumors: Distinguishing CEUS features differ with tumor size
- Pages: 2551-2559
- First Published: 04 September 2022
Development and external validation of a novel nomogram to predict prostate cancer in biopsy-naïve patients with PSA <10 ng/ml and PI-RADS v2.1 = 3 lesions
- Pages: 2560-2571
- First Published: 03 August 2022
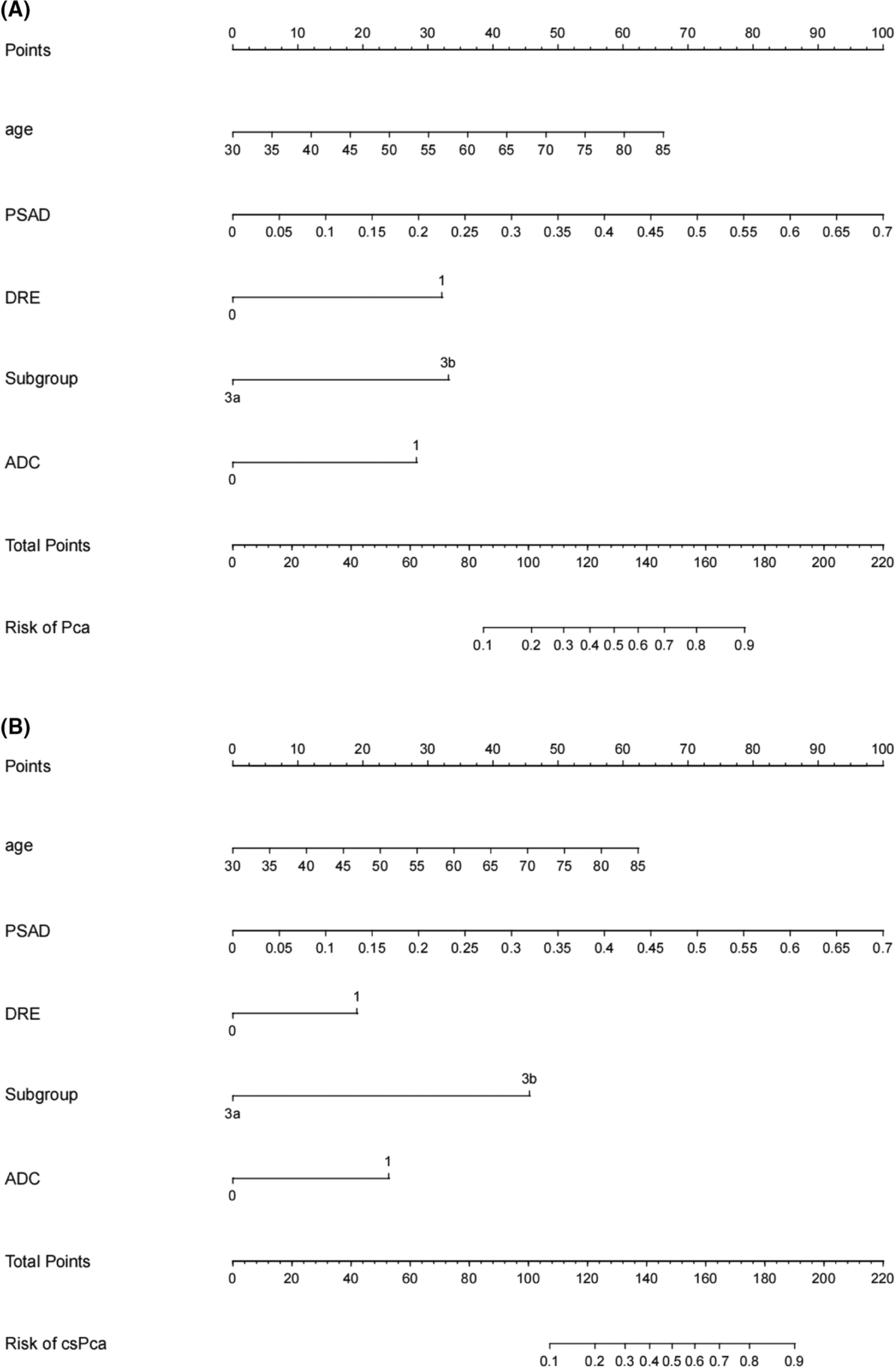
To our knowledge, this is the first study that applied PI-RADS 3 subgroup into nomogram. Overall, the nomogram is a promising tool for predicting prostate cancer and clinically significant prostate cancer in biopsy-naïve patients with PSA <10 ng/ml and PI-RADS v2.1 = 3 lesions due to the good calibration and net benefit. Our model may assist urologists in biopsy decision making for the “double gray zone” patients.
Efficacy and safety of lenvatinib in patients with recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after liver transplantation
- Pages: 2572-2579
- First Published: 05 August 2022
Influence of the skeletal muscle index on pharmacokinetics and toxicity of fluorouracil
- Pages: 2580-2589
- First Published: 08 August 2022
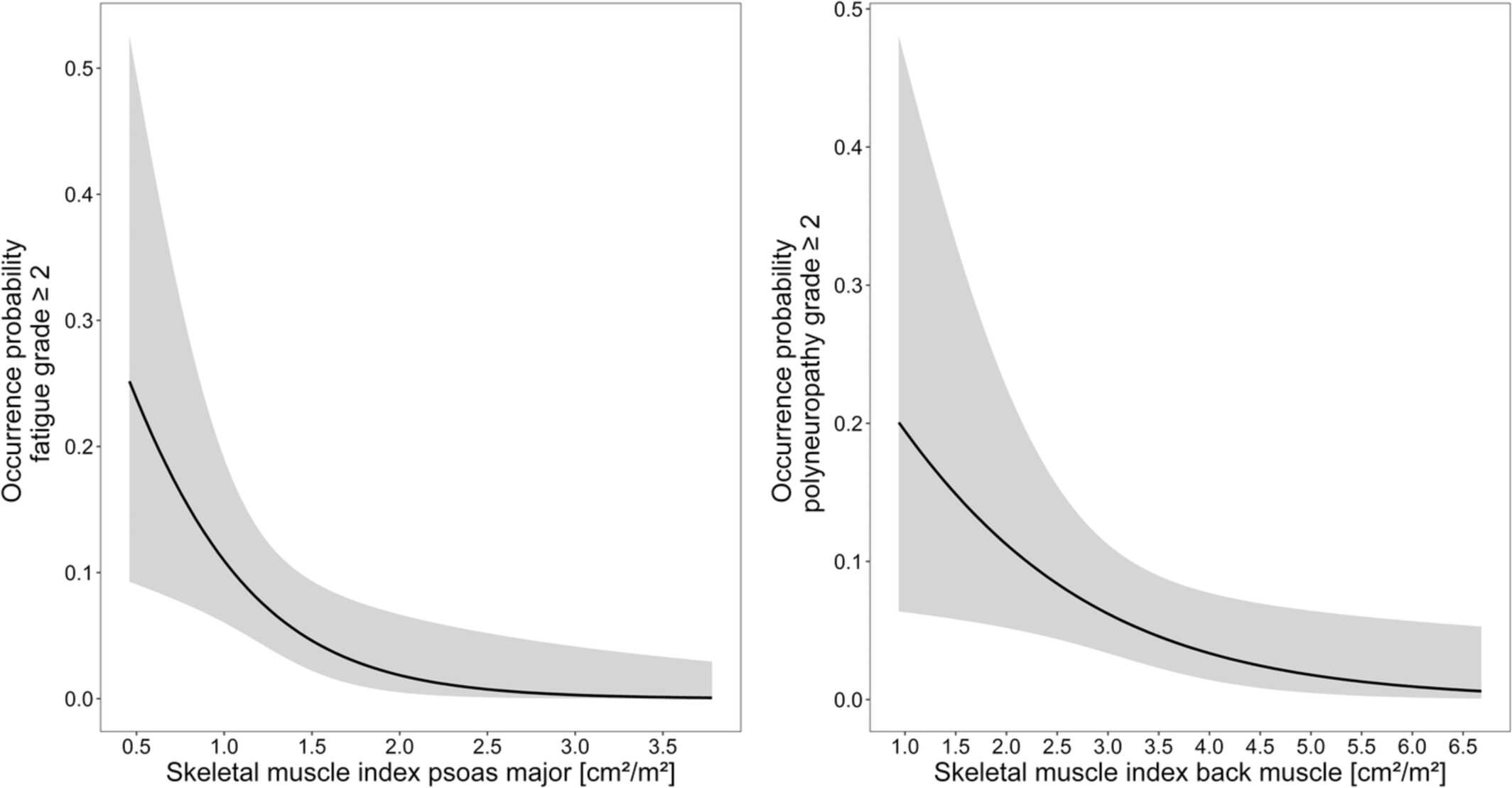
In sarcopenic cancer patients, the influence of altered body composition on clinical outcome of anticancer drug therapy is still not completely understood. Results from population pharmacokinetic modeling and logistic regression suggest that skeletal muscle index (SMI) measures may be associated with clearance of fluorouracil (5FU) and the occurrence of fatigue and polyneuropathy, respectively. These relationships deserve further investigation.
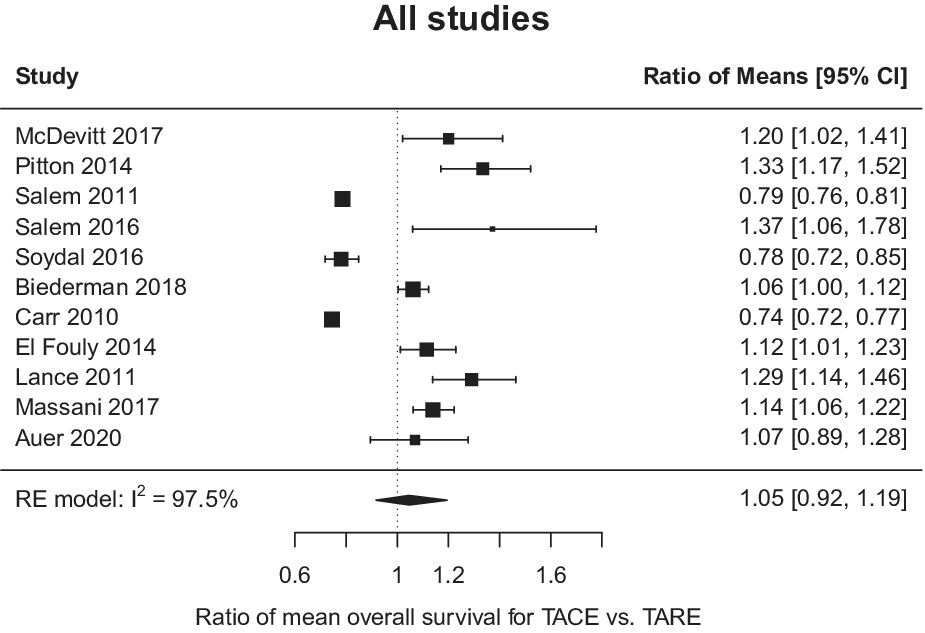
TACE versus TARE for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: Overall and individual patient level meta analysis
- Pages: 2590-2599
- First Published: 09 August 2022
Nomograms and scoring system for forecasting overall and cancer-specific survival of patients with prostate cancer
- Pages: 2600-2613
- First Published: 22 August 2022
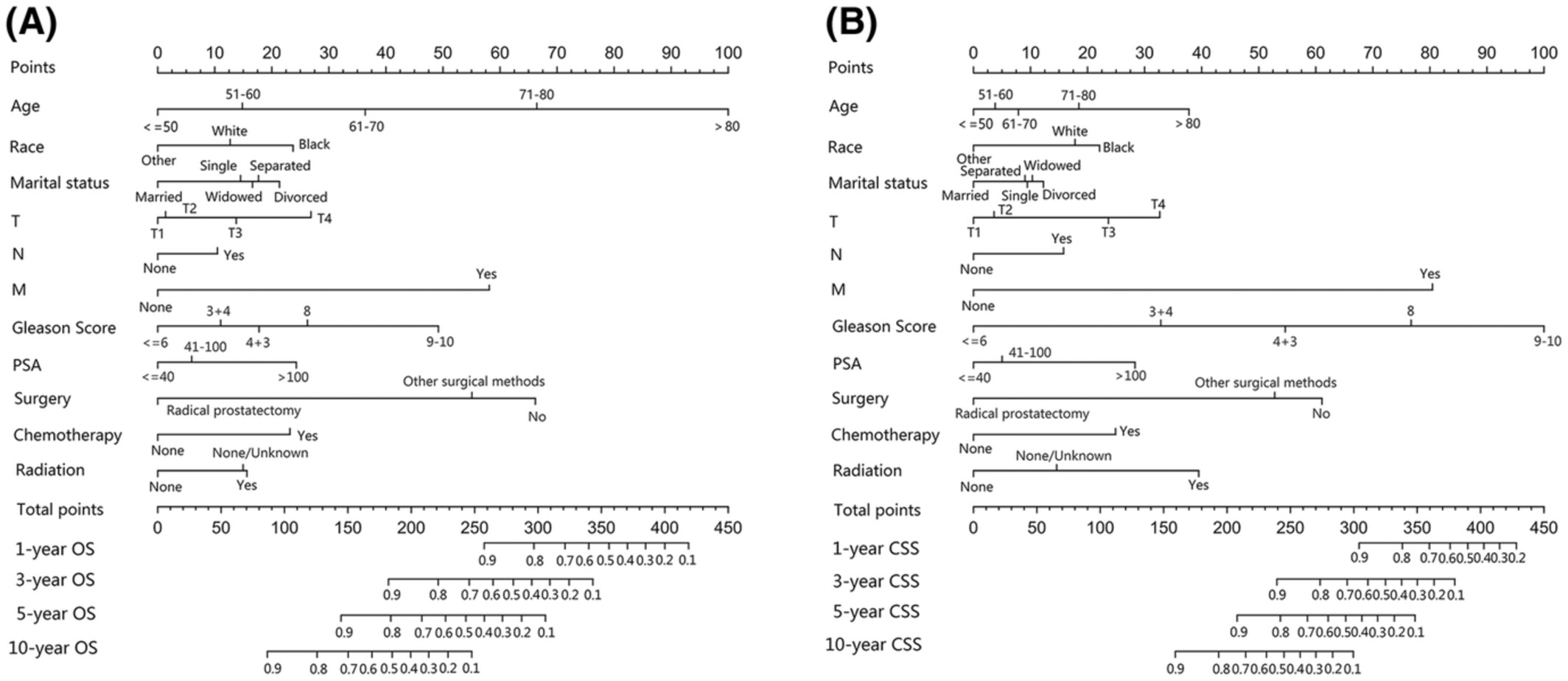
Based on a large data set of prostate cancer patients, we developed and valdated prognostic nomograms and demonstrated their favourable ability in predicting 1-, 3-, 5-, and 10-year overall and cancer-specific survival for prostate cancer patients. We further proposed the prognostic scoring system for the first time to more intuitively present the influence of clinical pathological factors on overall and cancer-specific survival of prostate cancer. The proposed survival model of prostate cancer can help clinicians select individualized and effective treatment.
Real-World clinical features and survival outcomes associated with primary gastrointestinal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma from 1999 to 2020
- Pages: 2614-2623
- First Published: 17 September 2022

This article investigated the clinical characteristics and survival outcomes of a rare lymphoma subtype, primary gastrointestinal natural killer (NK)/T-cell lymphoma. To date, this is the largest series of cases reported at a single medical center. The median OS was 4.0 months and a 2-year OS rate of 30.7%. Moreover, we observed that perforation, serum LDH ≥ULN and EOCG PS score ≥2 were markedly associated with worse OS.
Secondary malignancies in non-Hodgkin lymphoma survivors: 40 years of follow-up assessed by treatment modality
- Pages: 2624-2636
- First Published: 17 August 2022
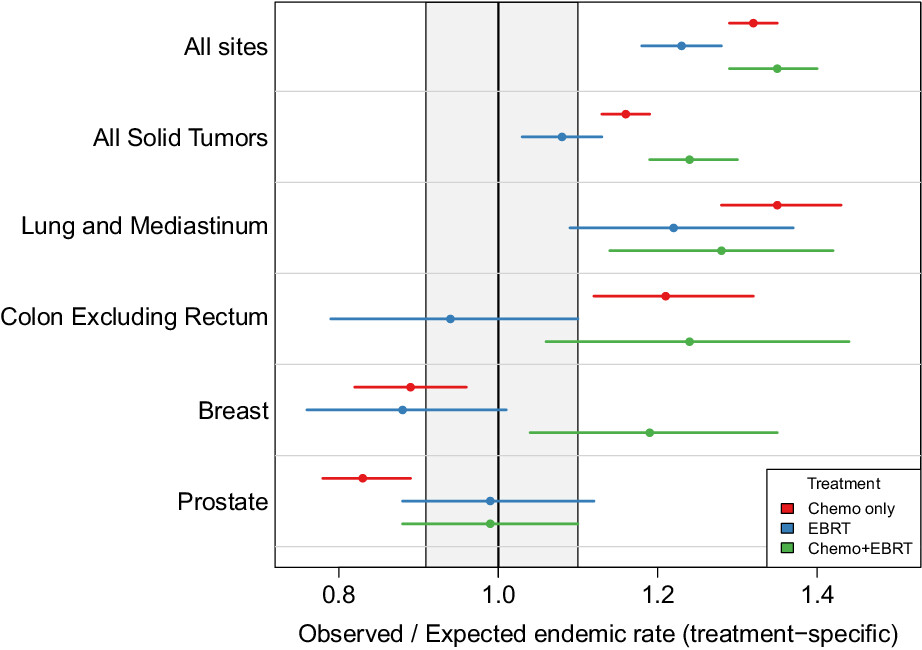
Survivors of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) have increased secondary malignancy (SM) risk. Treatment with radiotherapy did not increase overall SM risk, while chemotherapy was associated with a higher overall risk. However, certain sub-sites were associated with higher risk of SM, and they varied by treatment, age group, race and time since treatment." cd_value_code="text
Survival prediction by Bayesian network modeling for pseudomyxoma peritonei after cytoreductive surgery plus hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy
- Pages: 2637-2645
- First Published: 21 August 2022
Initial therapeutic results of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab for unresectable advanced hepatocellular carcinoma and the importance of hepatic functional reserve
- Pages: 2646-2657
- First Published: 14 August 2022
Real-life second-line epirubicin–paclitaxel regimen as treatment of relapsed small-cell lung cancer: EpiTax study
- Pages: 2658-2665
- First Published: 24 August 2022
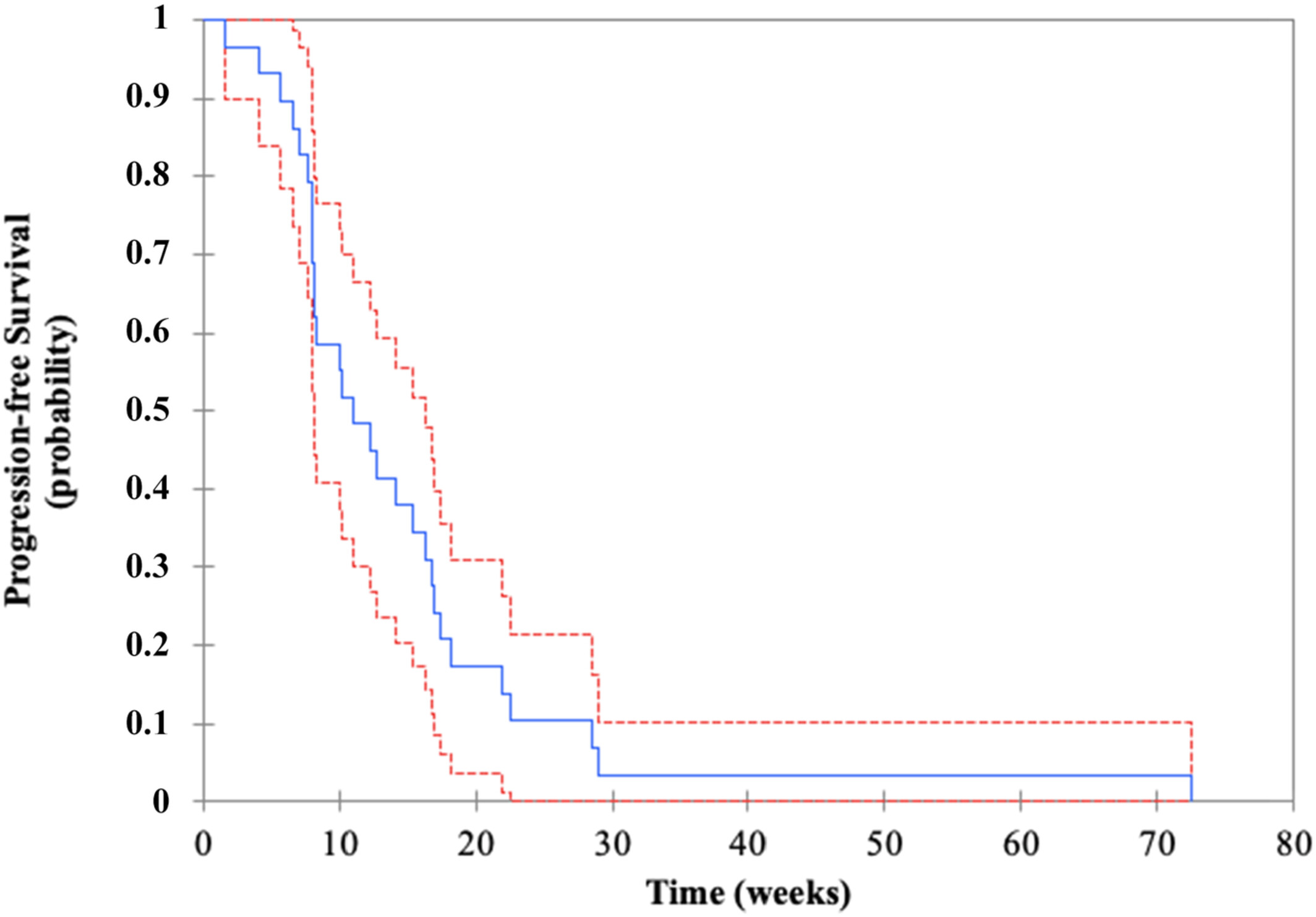
In this real-life study, we investigate the efficacy and safety of second-line epirubicin-paclitaxel regimen in 29 extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC) patients. Our results highlight promising survival outcomes, significative systemic activity and favorable toxicity profile. This association seemed to be effective and could represent another valuable therapeutic option in a pre-treated ES-SCLC population.
Results from the IMpower132 China cohort: Atezolizumab plus platinum-based chemotherapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 2666-2676
- First Published: 02 September 2022
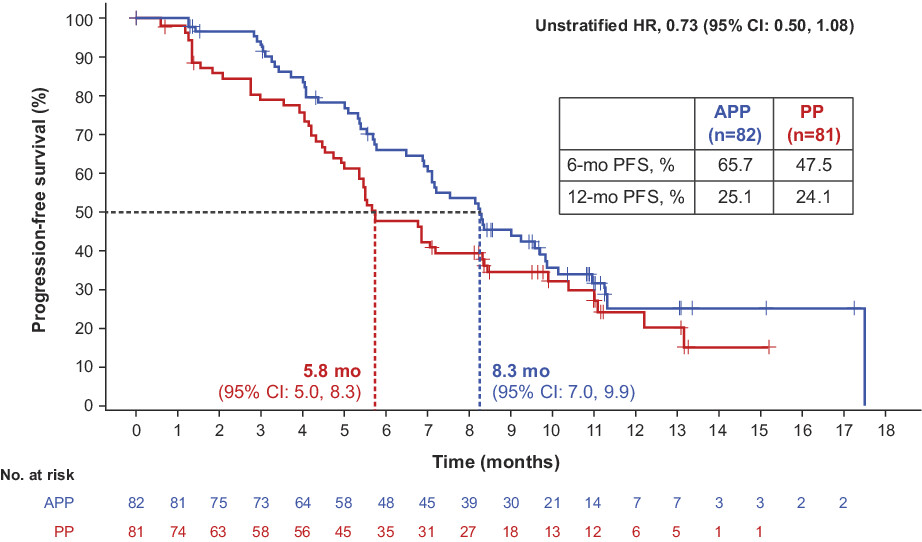
Atezolizumab plus pemetrexed and cisplatin (APP) versus pemetrexed plus cisplatin (PP) was studied in Chinese patients with non-squamous advanced non-small cell lung cancer in IMpower132. Progression-free survival benefit was seen with APP versus PP; there was a trend toward overall survival benefit favoring APP versus PP, though interim overall survival data were immature at this analysis. No new safety signals were seen with APP in Chinese patients.
Survival benefits of primary tumor surgery for synchronous brain metastases: A SEER-based population study with propensity-matched comparative analysis
- Pages: 2677-2690
- First Published: 14 August 2022
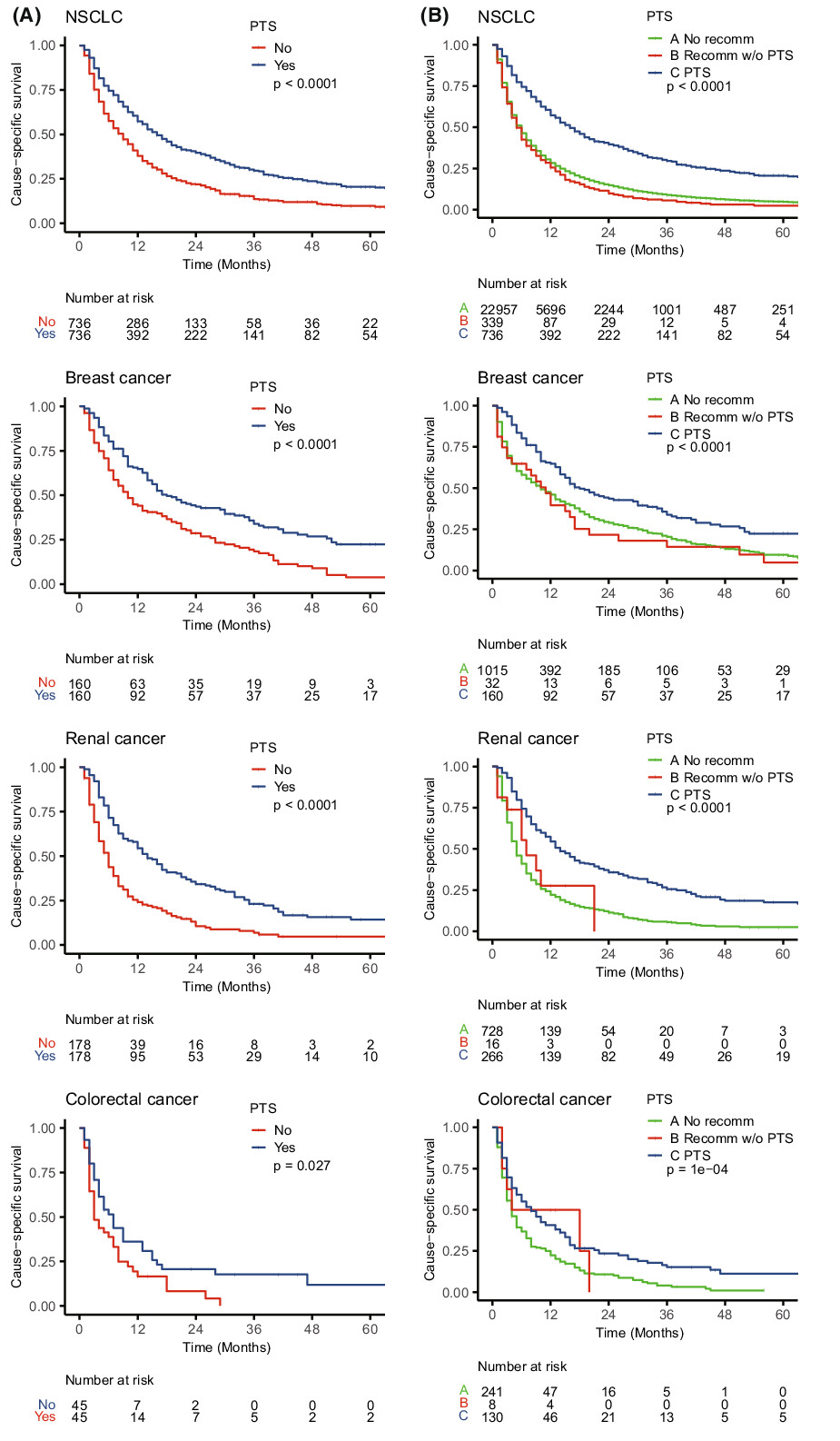
This SEER-based study assessed the survival benefits of primary tumor surgery (PTS) in patients with brain metastases (BMs). PTS appeared to significantly prolong cause-specific survival (CSS) time for patients with BMs secondary to non-small cell lung cancer, breast cancer, renal cancer, and colorectal cancer, rather than BMs from small cell lung cancer, melanoma, and liver cancer.
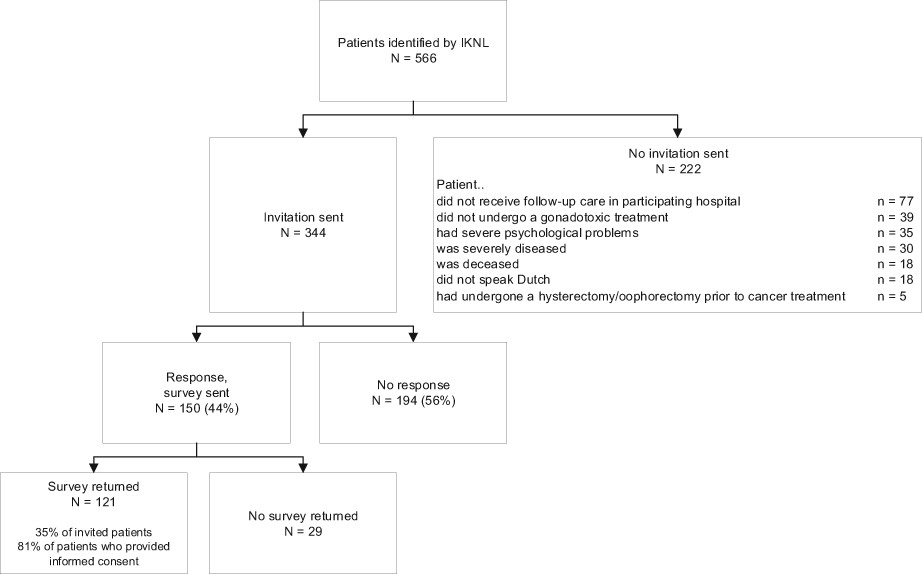
Quality of integrated female oncofertility care is suboptimal: A patient-reported measurement
- Pages: 2691-2701
- First Published: 29 August 2022
The association between body mass index and efficacy of pembrolizumab as second-line therapy in patients with recurrent/metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- Pages: 2702-2712
- First Published: 17 August 2022
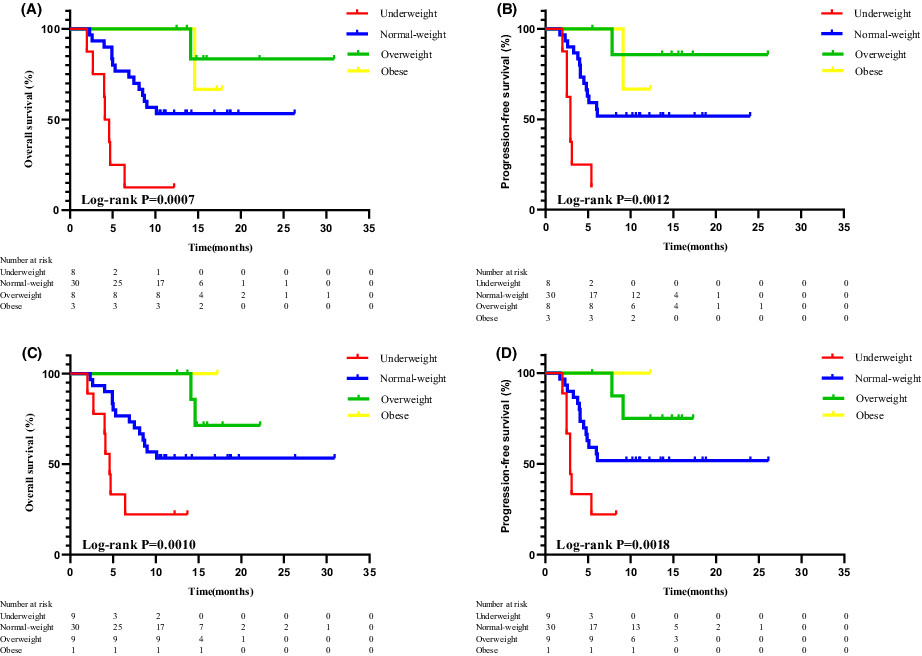
BMI is independently associated with clinical outcomes in patients with R/M HNSCC. Compared to normal patients, underweight patients tend to mean higher risk of death. In survival analysis, overweight and obese patients have better OS and PFS than normal weight patients, and underweight patients had poorer prognosis.
Pylorus-preserving versus Pylorus-resecting: Impact on dynamic changes of nutrition and body composition in pancreatic cancer patients before and after pancreatoduodenectomy
- Pages: 2713-2721
- First Published: 26 August 2022
The preoperative value of fine-needle aspiration in adult soft tissue lesions: An analysis of 514 cases at Shanghai Cancer Center
- Pages: 2722-2730
- First Published: 19 August 2022
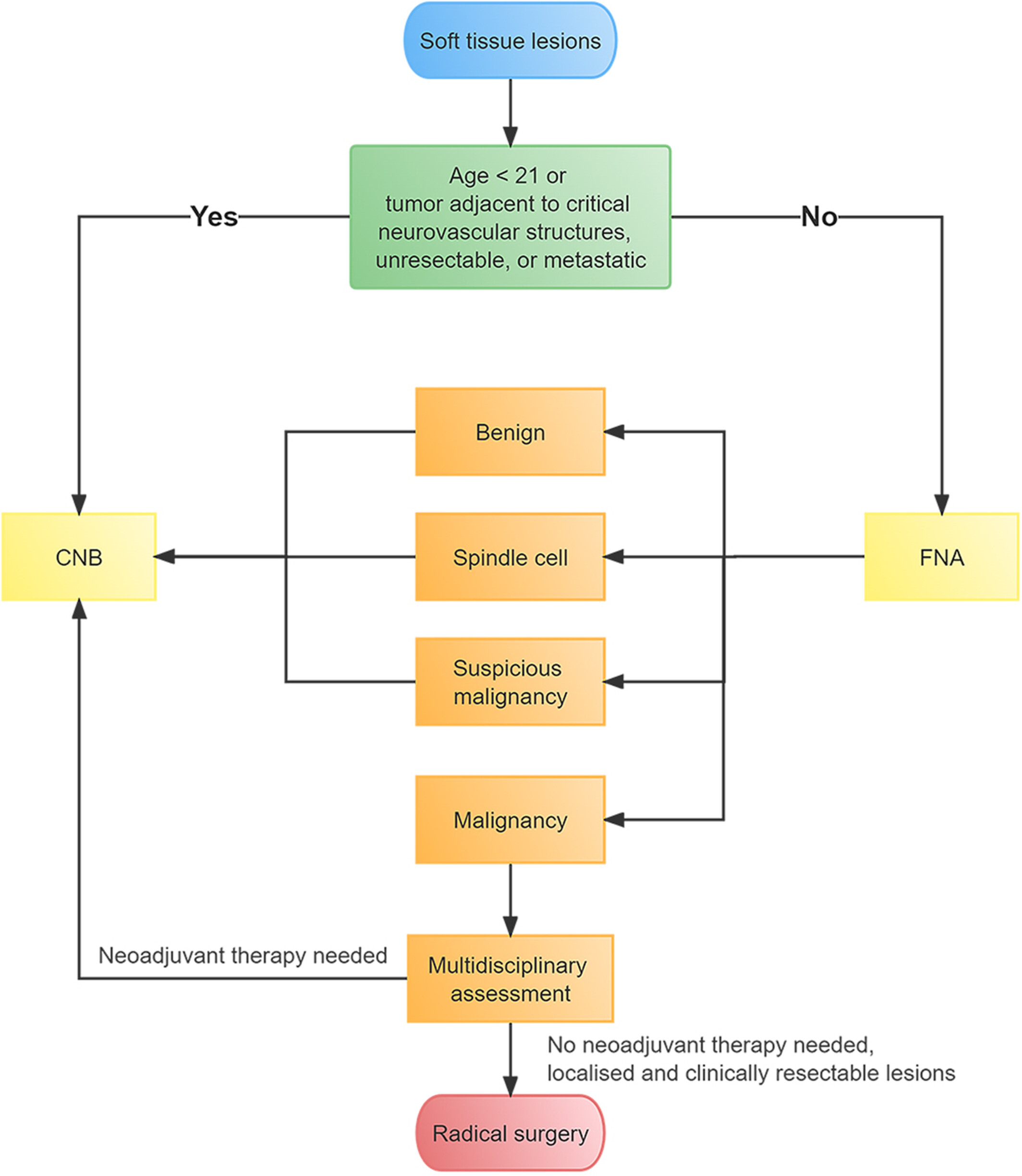
Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) has a high positive predictive value (PPV) for detecting malignancy in the soft tissue lesions. For patients with resectable lesions and malignant FNA, the core needle biopsy (CNB) step can be omitted with multidisciplinary evaluation, and subsequent radical surgery can be performed.
Predictive biomarkers of survival in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma receiving atezolizumab plus bevacizumab treatment
- Pages: 2731-2738
- First Published: 23 August 2022
Subcutaneous rituximab in patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma and follicular lymphoma: Final results of the non-interventional study MabSCale
- Pages: 2739-2751
- First Published: 26 August 2022
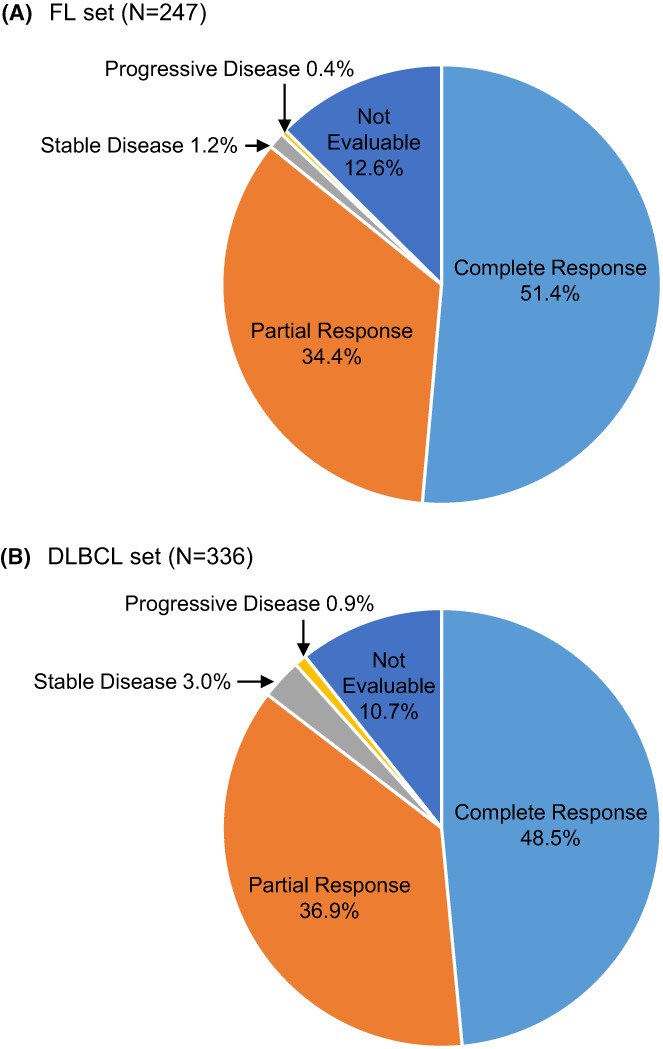
The non-interventional study MabSCale assessed the effectiveness and safety of subcutaneous rituximab for the treatment of follicular lymphoma (FL) and diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL). The results confirm the effectiveness and safety of subcutaneous rituximab in both the FL and the DLBCL group. Furthermore, patient and nurse satisfaction with subcutaneous administration was high.
Urachal carcinoma: A novel staging system utilizing the National Cancer Database
- Pages: 2752-2760
- First Published: 07 September 2022
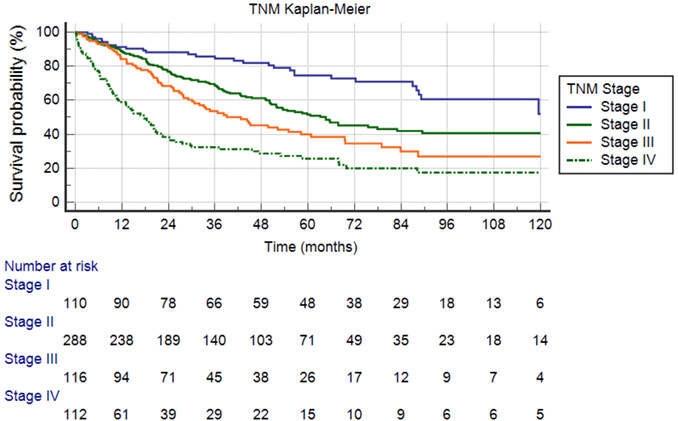
This study proposed a novel TNM staging system for urachal carcinoma based a large number of patients in NCDB. It provides a more balanced sample distribution and a more accurate stage-survival correlation than the traditional Sheldon, Mayo, and Ontario staging systems. It is clinically applicable and enables better risk stratification, prognosis, and therapeutic decision-making.
Japanese subgroup analysis of EV-301: An open-label, randomized phase 3 study to evaluate enfortumab vedotin versus chemotherapy in subjects with previously treated locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma
- Pages: 2761-2771
- First Published: 02 September 2022
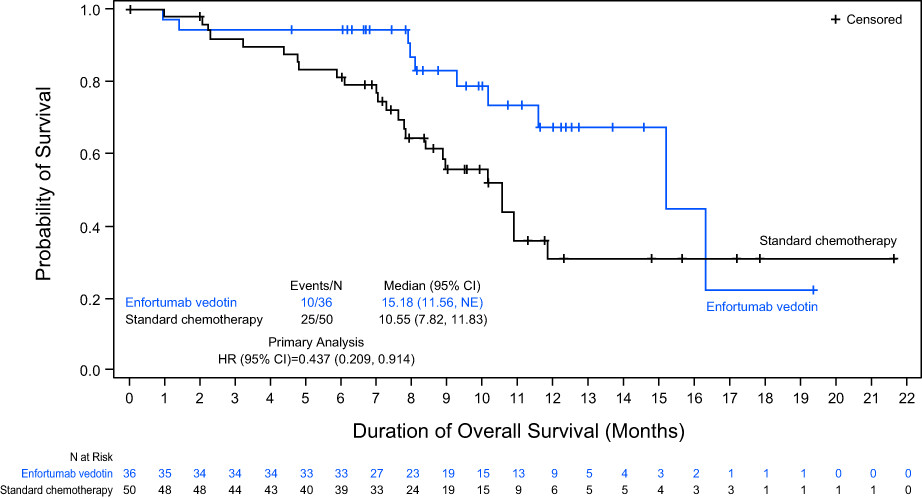
In the global, open-label, phase 3 EV-301 trial, enfortumab vedotin (EV) demonstrated clinically significant overall survival (OS) benefit compared with standard chemotherapy in patients with previously treated locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma. This subgroup analysis of EV-301 Japanese patients confirmed that EV demonstrated an OS benefit and no new safety signals identified in the Japanese subpopulation, consistent with the efficacy and safety/tolerability in the EV-301 overall study population.
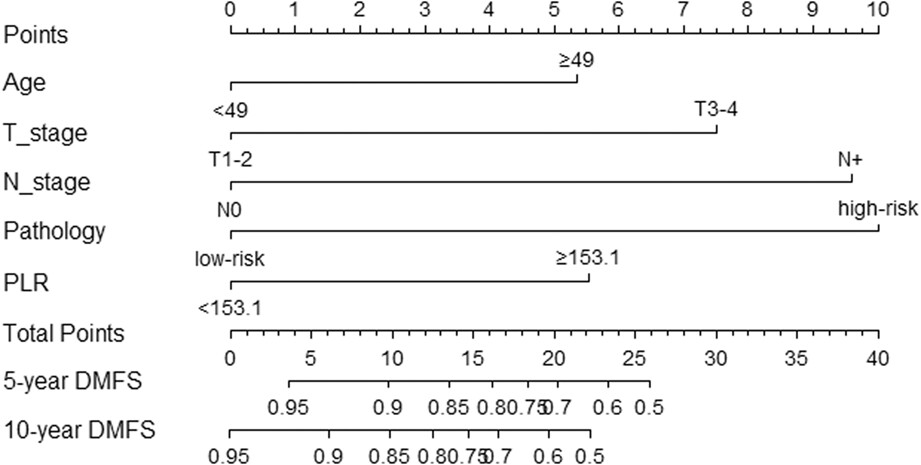
A nomogram involving immune-inflammation index for predicting distant metastasis-free survival of major salivary gland carcinoma following postoperative radiotherapy
- Pages: 2772-2781
- First Published: 01 September 2022
The relationship between immediate postmastectomy reconstruction modalities and survival benefits in patients with triple negative breast cancer
- Pages: 2782-2794
- First Published: 15 September 2022
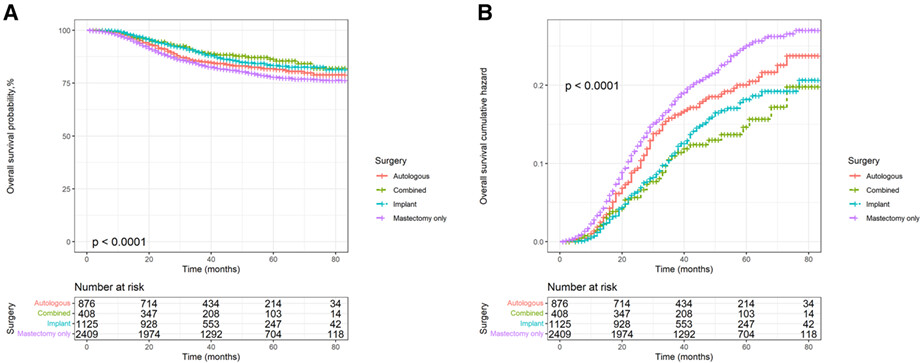
Kaplan–Meier survival curves and log-rank tests were used to evaluate the effect of different reconstruction methods (implant, autologous, implant and autologous combined reconstruction) on the overall survival (OS) of triple negative breast cancer patients. All three reconstruction methods had higher OS and lower risk than mastectomy alone (p < 0.0001). Among the three reconstruction methods, autologous reconstruction has the lowest survival rate and the highest risk.
PHF6 mutation is associated with poor outcome in acute myeloid leukaemia
- Pages: 2795-2804
- First Published: 29 September 2022
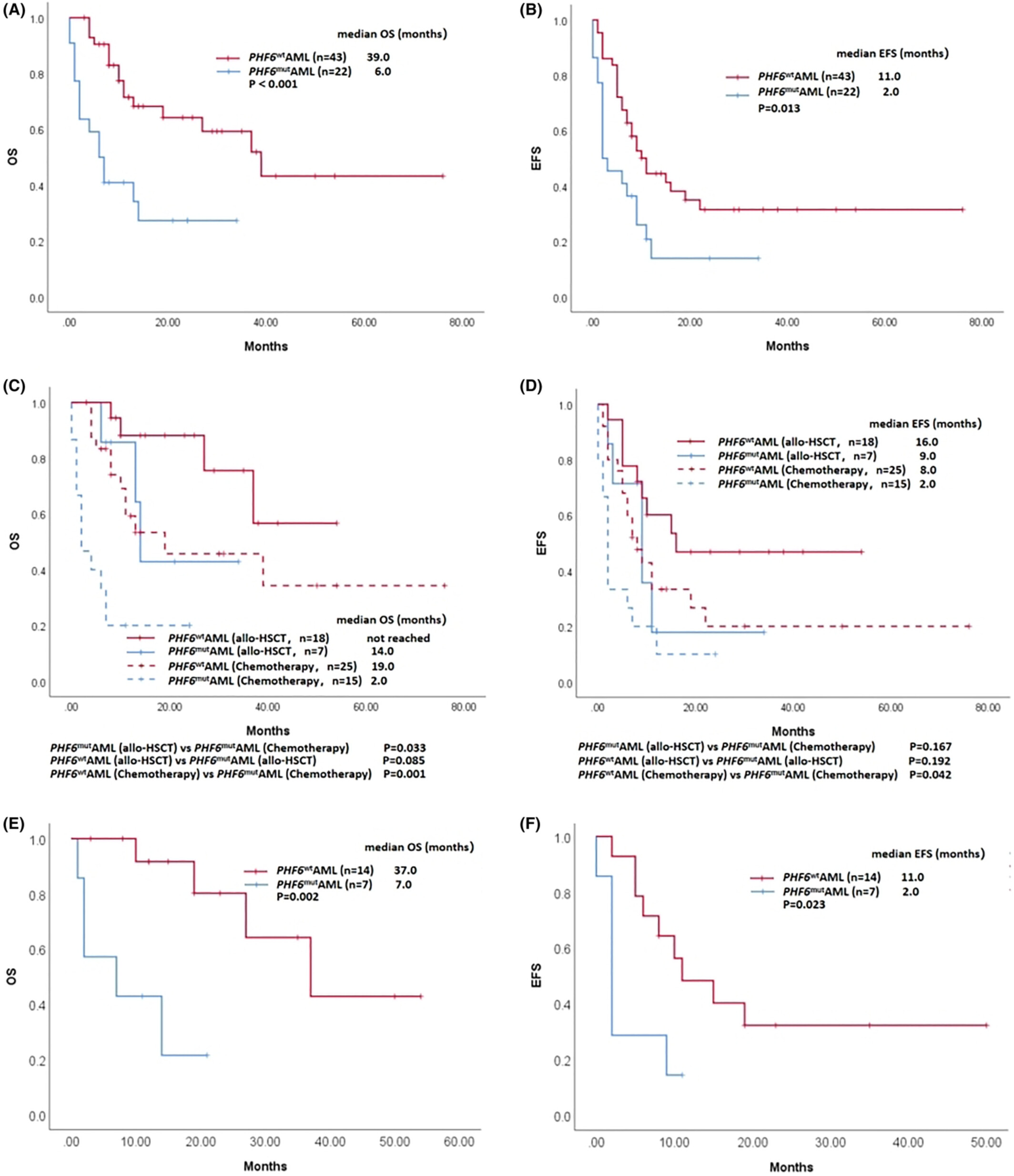
We performed a retrospective propensity score-matched cohort study to assess the therapeutic responses and survival outcomes of AML patients with PHF6 mutation compared with those without PHF6 mutation after balancing age, sex and risk categories. Our data revealed that PHF6 mutation was associated with a lower chemotherapy response and shorter survival, suggesting that PHF6 mutation is a predictor of poor prognosis in AML.
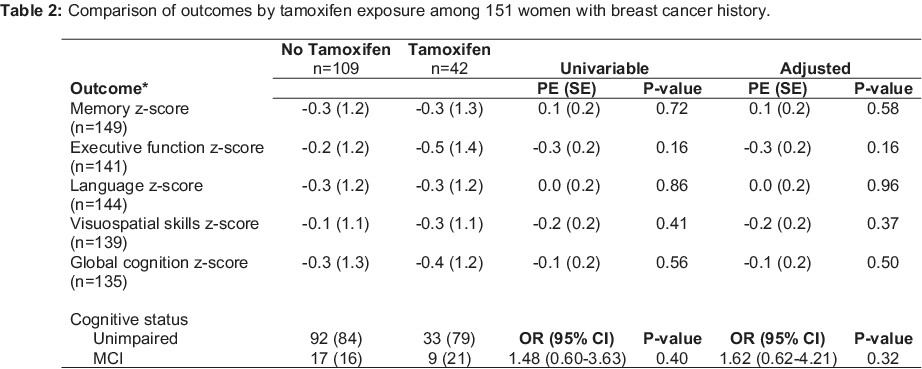
Association of raloxifene and tamoxifen therapy with cognitive performance, odds of mild cognitive impairment, and brain MRI markers of neurodegeneration
- Pages: 2805-2817
- First Published: 30 August 2022
Handgrip weakness, systemic inflammation indicators, and overall survival in lung cancer patients with well performance status: A large multicenter observational study
- Pages: 2818-2830
- First Published: 08 September 2022
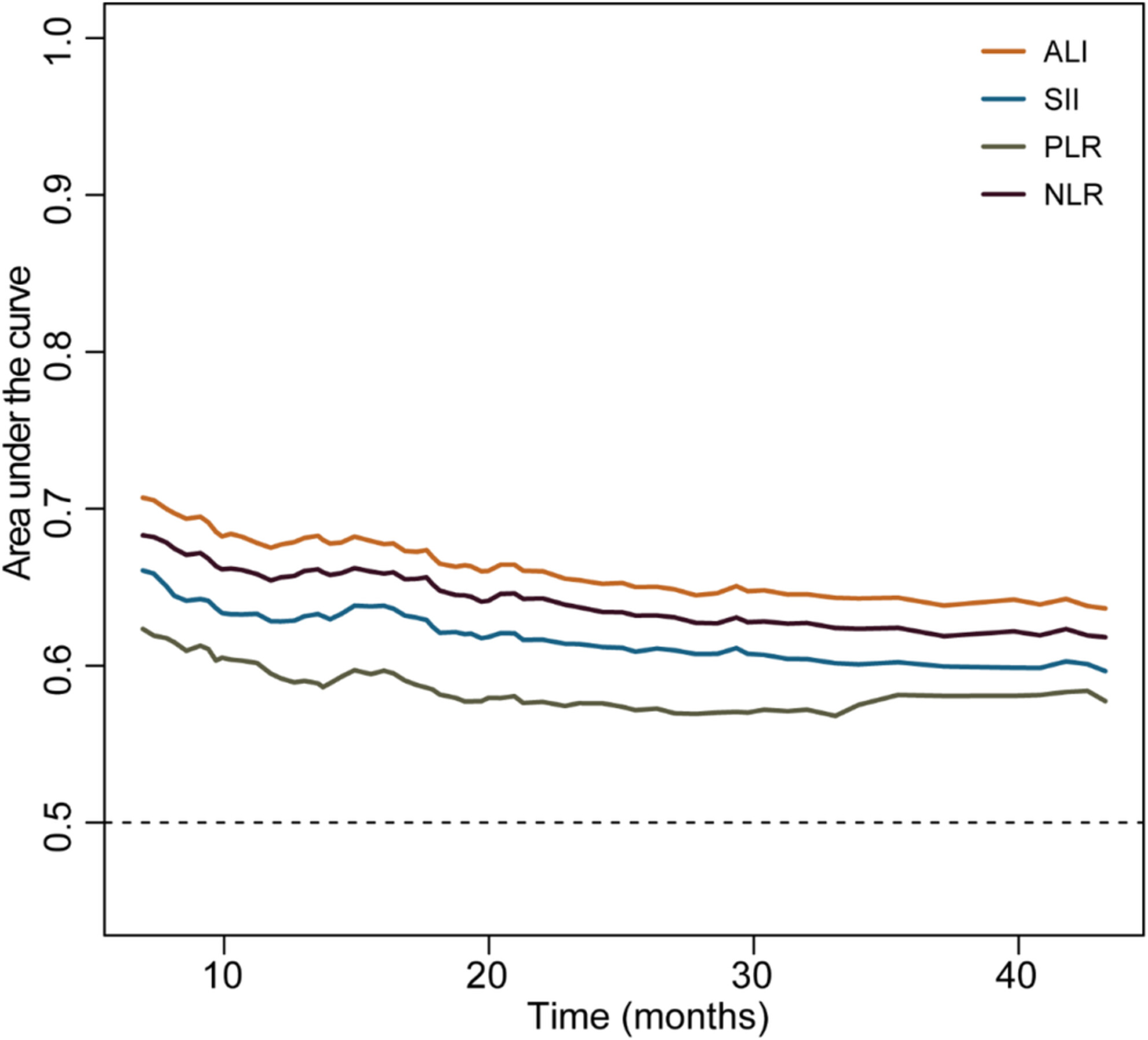
HGS, ALI, SII, NLR, and PLR were independent risk factors for overall survival of lung cancer patients. Co-occurrence of low HGS and systemic inflammation significantly elevated the risk of death. The predictive ability of handgrip weakness combined with low ALI for OS was better than the other three combinations.
Incorporation of liver chemistry score in predicting survival of liver-involved advanced gastric cancer patients who received palliative chemotherapy
- Pages: 2831-2841
- First Published: 04 September 2022
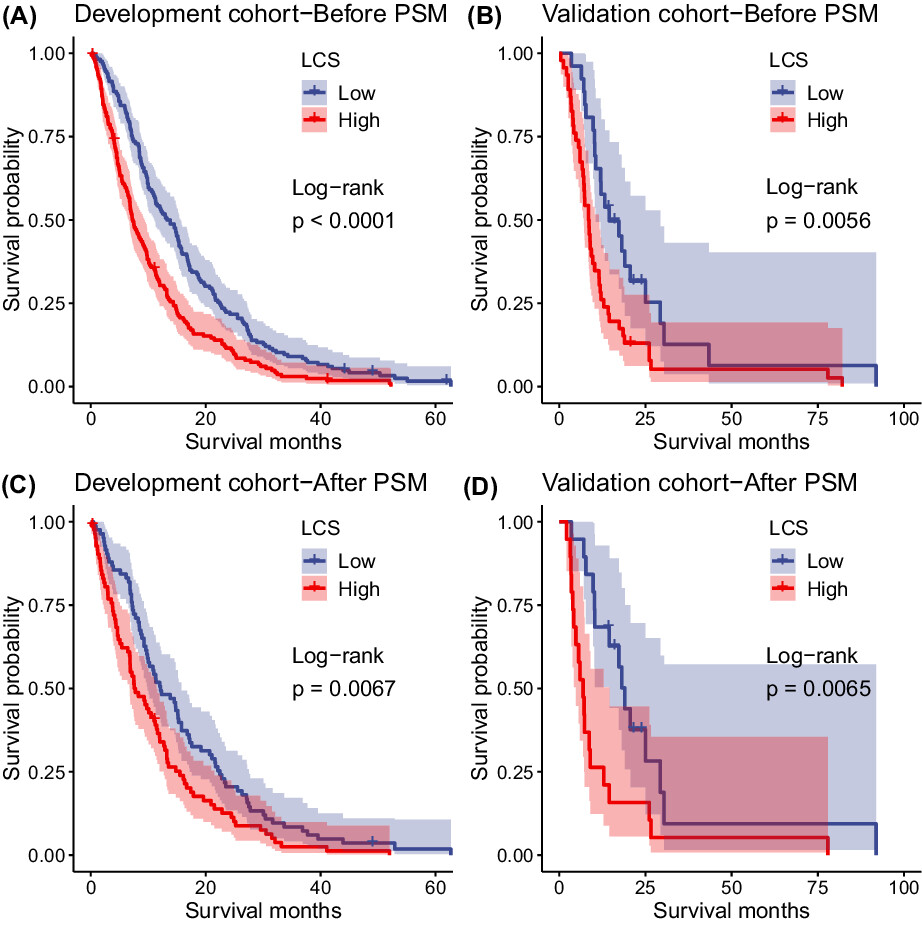
In this study, serum parameters of liver function tests in patient with gastric cancer liver metastasis (GCLM) were analyzed by lasso regression; a liver chemistry score (LCS) was generated as 0.03343515 × ln (AST, U/L) + 0.02687997 × ln (ALP, U/L). Patients in low (LCS < 0.232) or high (LCS = 0.232) score group experienced different survival times. The score was also demonstrated as an independent prognostic factor for GCLM patients and incorporated into predictive nomogram model.
Increasing equitable access to telehealth oncology care in the COVID-19 National Emergency: Creation of a telehealth task force
- Pages: 2842-2849
- First Published: 10 October 2022
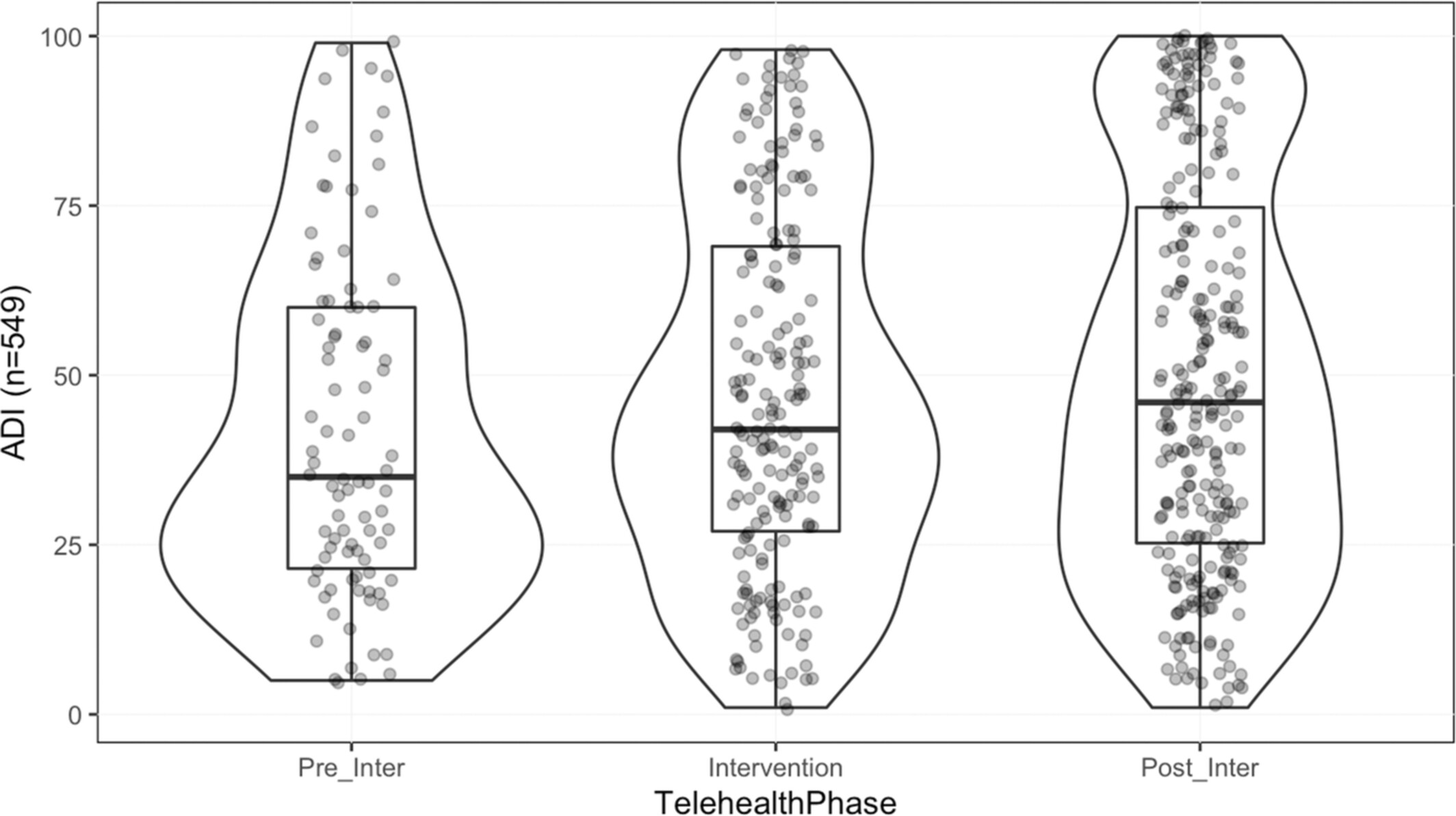
In response to COVID-19 and disparities in access determined by socioeconomic factors, we assessed the impact of a personalized digital support structure, the Telehealth Task Force (TTF), to reduce disparities in TH. Implementation of the TTF helped close the digital divide; increasing TH access for vulnerable patients. Attention to digital readiness can mitigate disparities in access to care.
Association between body mass index at diagnosis and outcomes in Chinese children with newly diagnosed acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Pages: 2850-2860
- First Published: 27 September 2022
We found that overweight/obese children were at higher risk of treatment-related mortality and developing severe toxicities than underweight or health-weight children. Our findings reinforce the importance of the normalizing weight during the treatment period to improve survival and treatment outcomes.
Clinical outcomes of curative surgical resection of peritoneal metastasis in patients with colorectal cancer: A long-term follow-up study
- Pages: 2861-2868
- First Published: 07 September 2022
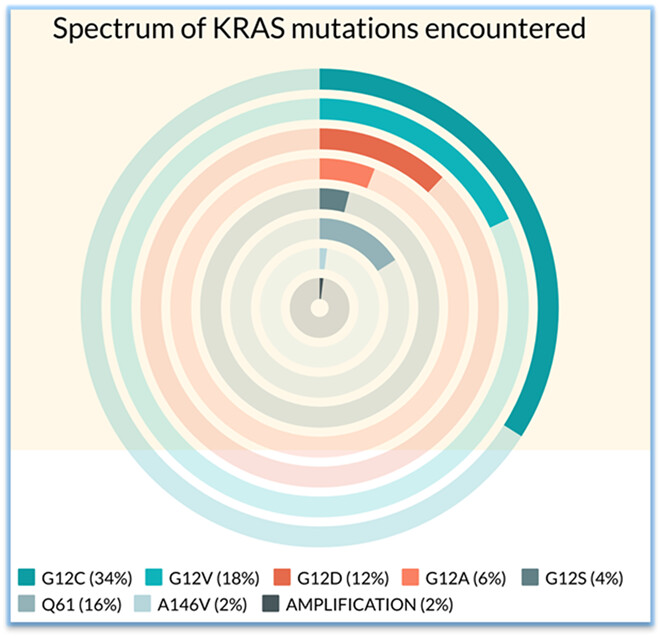
KRAS mutated Non-Small Lung Carcinoma: A Real World Context from the Indian subcontinent
- Pages: 2869-2874
- First Published: 07 September 2022
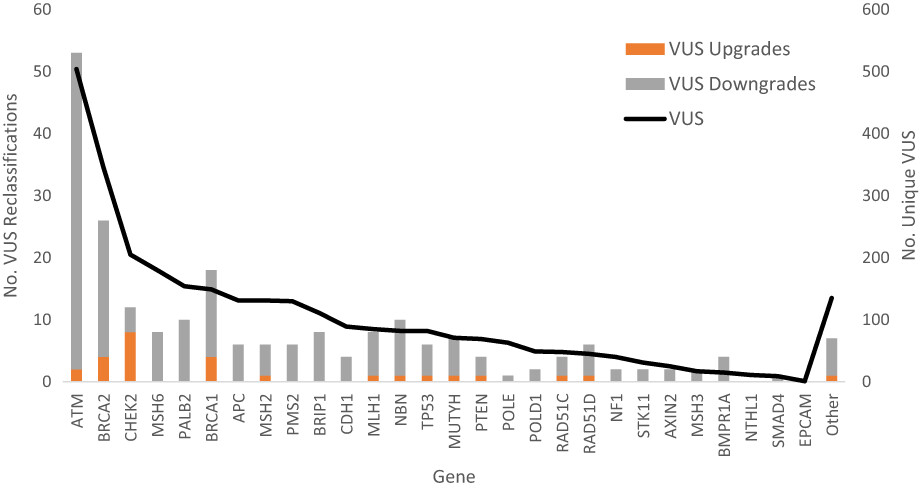
A multicenter study of clinical impact of variant of uncertain significance reclassification in breast, ovarian and colorectal cancer susceptibility genes
- Pages: 2875-2884
- First Published: 24 November 2022
Characteristics and in-hospital outcomes of elderly patients with cancer in a top-ranked hospital in China, 2016–2020: Real-world study
- Pages: 2885-2905
- First Published: 26 September 2022
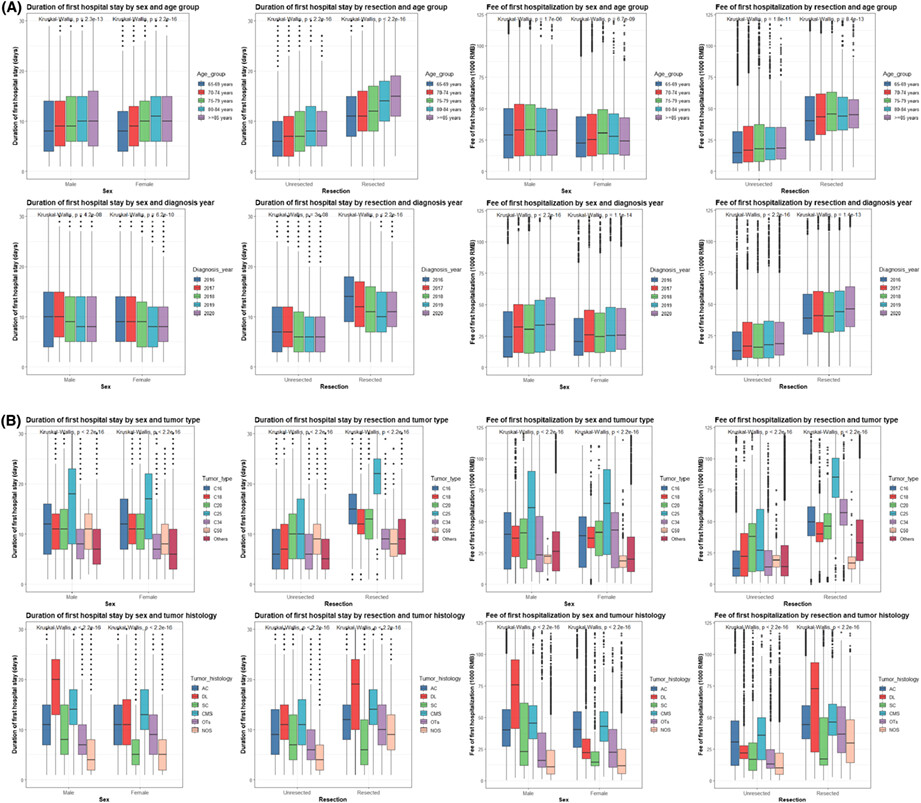
This real-world study identified certain baseline patient and tumor characteristics, medical and medication histories, changes of weight and food intake, diet, and self-care ability which were independently associated with in-hospital outcomes among 20,650 older patients (≥65 years) with cancer admitted to a top-ranked hospital in China during 2016-2020, and which should be paid special attention to. Our study can help to identify patients at higher risks of inferior in-hospital outcomes.
Comparison of the tumor immune microenvironment phenotypes in different breast cancers after neoadjuvant therapy
- Pages: 2906-2917
- First Published: 08 September 2022
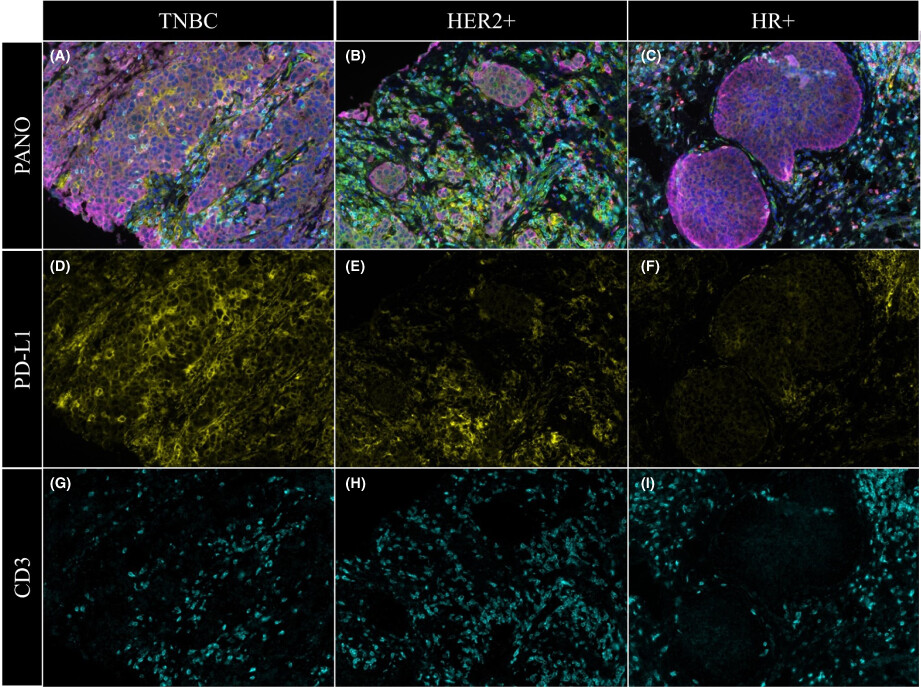
We analyzed pre-NAT tumor biopsies from TNBC, HR+, and HER2+ breast cancer patients who received NAT and compared the different immune makers (PD-1, PD-L1, CD3, and CD8) of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs). We found PD-L1+ cells were significantly higher in TNBC patients than others, and PD-L1+ cells were higher in pathologic complete response (pCR) than in no-pCR TNBC patients. Our results demonstrated that TNBC patients had significantly different TME, suggesting a potential role for immunotherapy in these patients.
Efficacy and safety of anamorelin in patients with cancer cachexia: Post-hoc subgroup analyses of a placebo-controlled study
- Pages: 2918-2928
- First Published: 16 November 2022
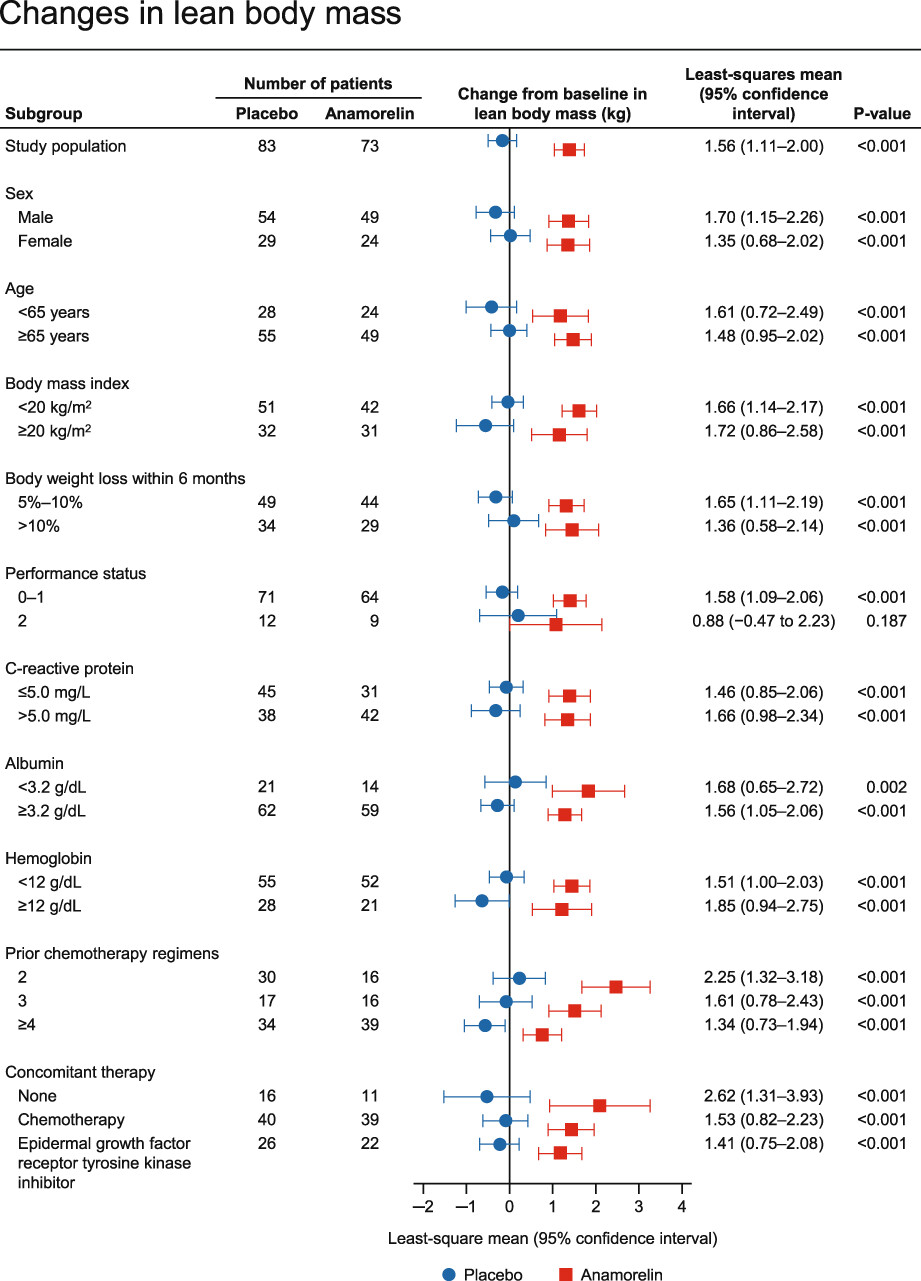
We performed post-hoc analyses of the ONO-7643-04 study to investigate the efficacy and safety of anamorelin in subgroups of Japanese patients with non-small cell lung cancer. This study revealed consistent improvements in lean body mass, body weight, and appetite score using QOL-ACD item 8 across most subgroups of anamorelin-treated patients versus placebo. This study also demonstrated the tolerability of anamorelin regardless of age and performance status, with a low incidence of serious adverse drug reactions in each subgroup.
Impact of prior cancer history on survival of patients with hypopharyngeal cancer
- Pages: 2929-2936
- First Published: 04 September 2022
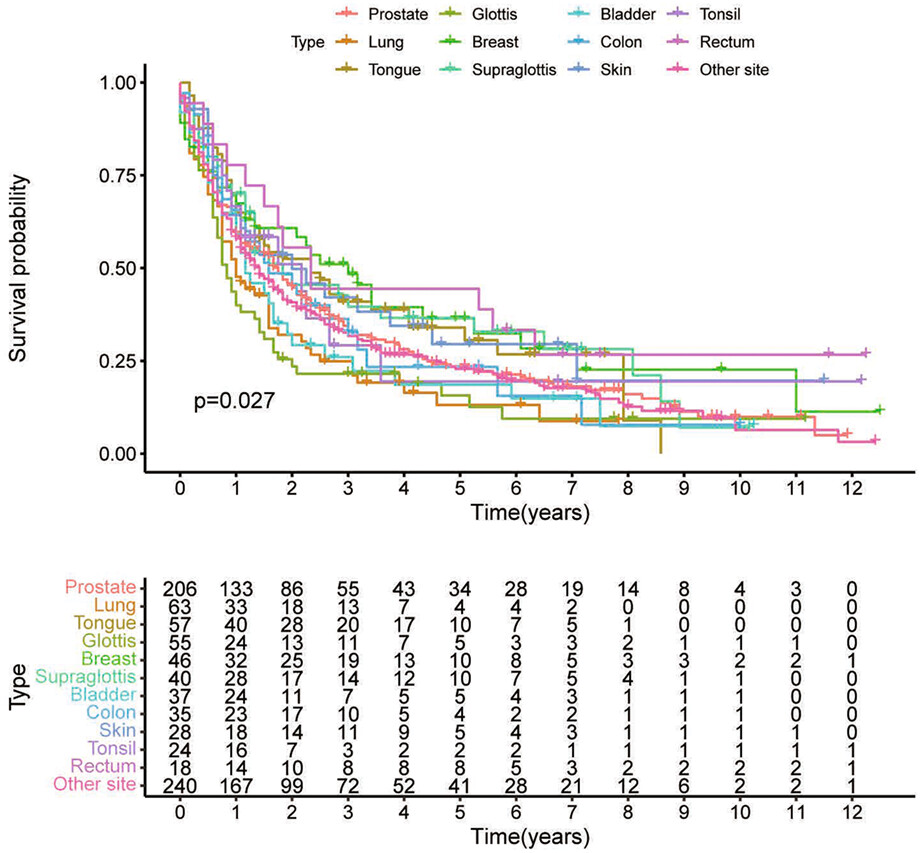
In this paper, we assessed the impact of prior cancer history on survival of patients with hypopharyngeal cancer. The results showed that the previous cancer diagnoses did not significantly impact the hypopharyngeal carcinoma patients' overall survival, which means maybe more hypopharyngeal cancer patients with prior cancer should be considered for clinical trials.
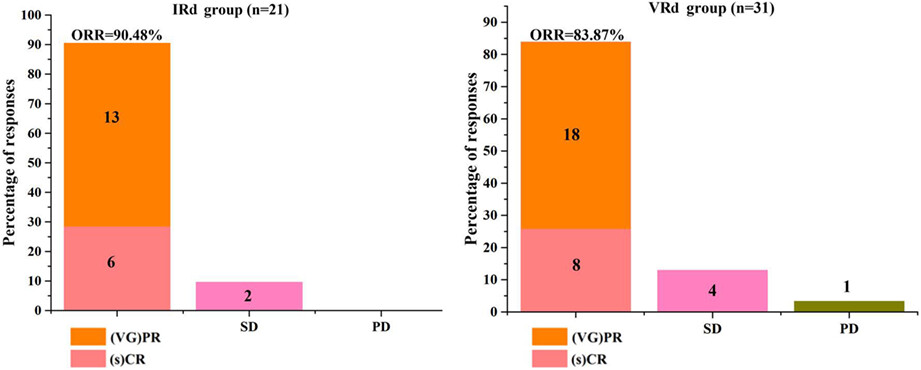
Ixazomib combined with lenalidomide and dexamethasone chemotherapy for newly diagnosed multiple myeloma in China—Compared with bortezomib/lenalidomide/dexamethasone
- Pages: 2937-2944
- First Published: 02 September 2022
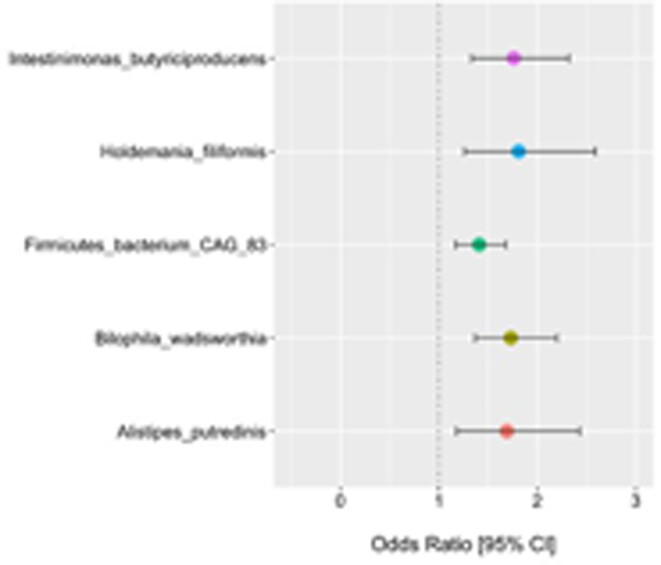
Metagenomic analysis of the fecal microbiome in colorectal cancer patients compared to healthy controls as a function of age
- Pages: 2945-2957
- First Published: 03 September 2022
Sex disparities in the association between acute myocardial infarction and colon cancer risk
- Pages: 2958-2969
- First Published: 07 September 2022
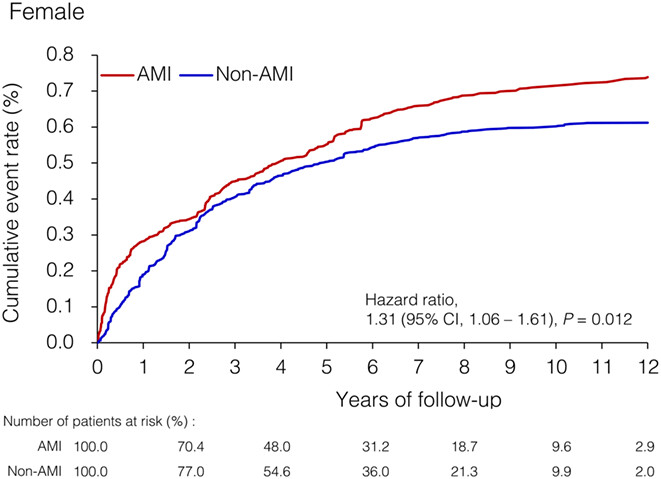
This study is one of the largest studies to examined the risk of colon cancers in patients with AMI. The results showed that AMI was associated with a significantly higher risk of colon cancer in the female patients, but not in the male patients. Cardiologists who treat patients with acute myocardial infarction should be aware of colon cancer risk, especially in women.
The impairment of induction chemotherapy for stage II nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated with intensity-modulated radiotherapy with or without concurrent chemotherapy: A propensity score-matched analysis
- Pages: 2970-2978
- First Published: 17 September 2022
A phase II study of antiangiogenic therapy (Apatinib) plus chemotherapy as second-line treatment in advanced small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 2979-2989
- First Published: 09 September 2022
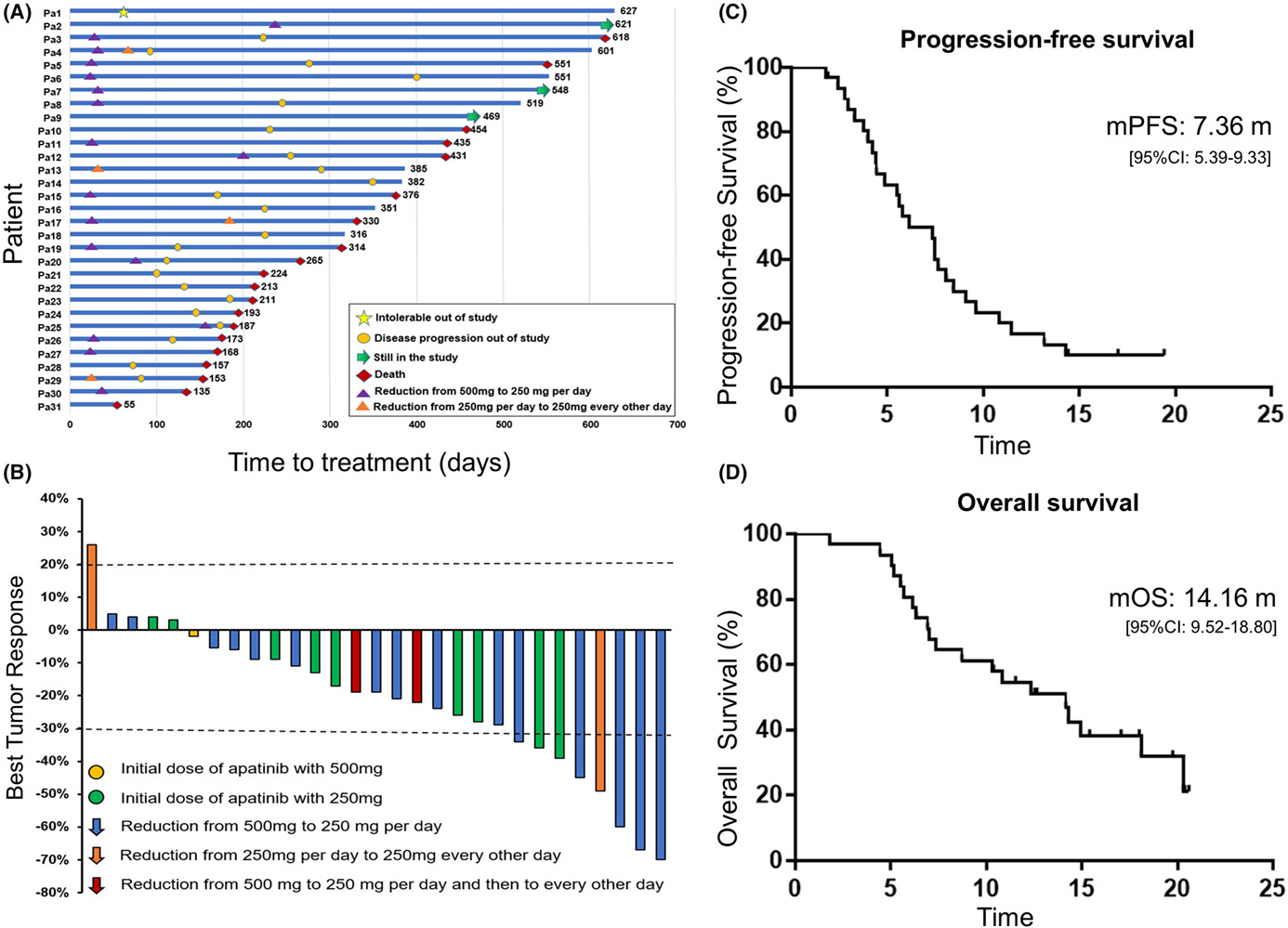
Antiangiogenic therapy (Apatinib) plus chemotherapy had better efficacy compared with standard second-line chemotherapies for advanced SCLC patients. No more intolerable toxicities were observed for this new regimen, which should provide a highlight view on the current status of second-line therapy in SCLC.
Asciminib vs bosutinib in CML patients pretreated with ≥2 tyrosine kinase inhibitors: Results from the Japanese subgroup analysis of ASCEMBL study
- Pages: 2990-2998
- First Published: 27 September 2022
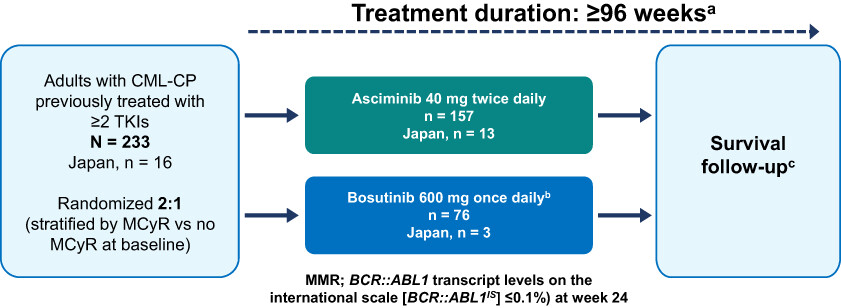
Asciminib, a first-in-class, allosteric inhibitor of BCR-ABL1 that acts by STAMP (Specifically Targeting the ABL Myristoyl Pocket), is a novel therapeutic option for patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). In the global, phase 3, open-label ASCEMBL study in patients with CML in chronic phase (CML-CP) pretreated with = 2 tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), asciminib (40 mg twice-daily) demonstrated statistically significant superiority over the ATP-competitive TKI bosutinib (500 mg once daily) for the primary endpoint of major molecular response (MMR; BCR-ABL1 transcript levels on the international scale [BCR-ABL1IS] = 0.1%) at week 24. Here, we present a descriptive subgroup analysis results of Japanese patients enrolled in the ASCEMBL study.
Comprehensive association analysis of speech recognition thresholds after cisplatin-based chemotherapy in survivors of adult-onset cancer
- Pages: 2999-3012
- First Published: 12 September 2022
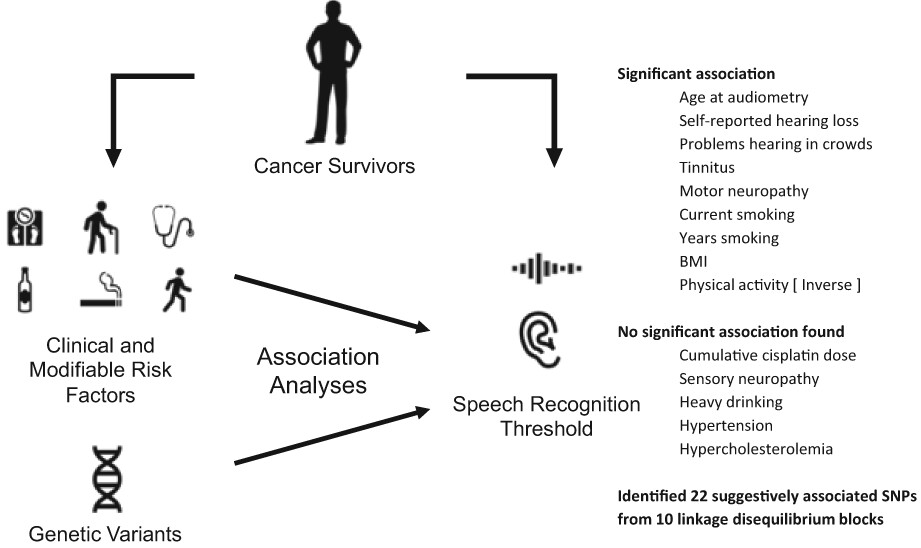
We investigated the risk factors associated with decline in understanding speech as measured by speech recognition threshold among testicular cancer survivors. Associated factors were higher BMI, lower physical activity and smoking, and peripheral motor neuropathy alongside genetic variants with suggestive associations including those related to three genes involved in neuronal development.
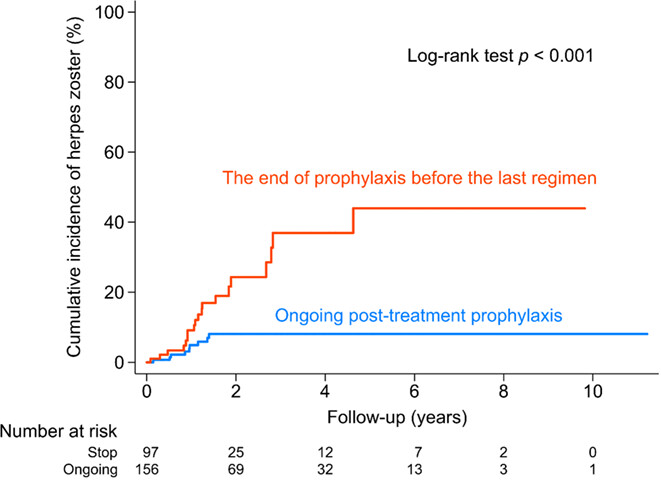
Herpes zoster prophylaxis: Essential for treating newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients
- Pages: 3013-3026
- First Published: 20 September 2022
Response to neoadjuvant paclitaxel predicts survival in anaplastic thyroid carcinoma
- Pages: 3027-3035
- First Published: 02 September 2022
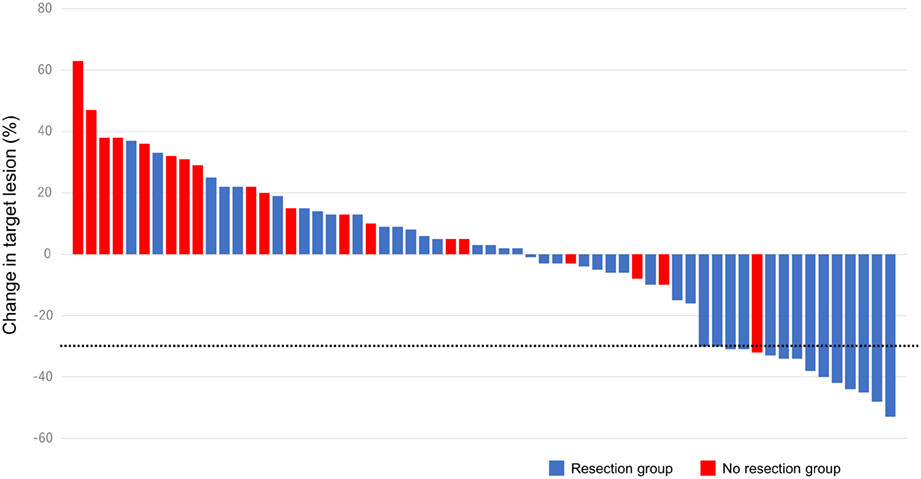
The current study investigated the outcomes in anaplastic thyroid carcinoma (ATC) patients treated by paclitaxel as neoadjuvant setting. Prognostic index ≥2, response to paclitaxel, resection, and radiotherapy were independent prognostic factors in ATC patients treated with paclitaxel as neoadjuvant setting.
A survey across orbital lymphoma in Poland: Multicenter retrospective study of polish lymphoma research group (PLRG)
- Pages: 3036-3045
- First Published: 26 September 2022
The advanced clinical stage of the disease (non-IE according to the Ann Arbor) concerns two thirds of the overall population of patients with ocular adnexal lymphoma and one third of MALT lymphoma patients. Due to the high prevalence of advanced stages of ocular adnexal lymphoma, treatment with combined therapies is warranted. Combined treatment tends to improve PFS compared to chemotherapy alone in the overall population of patients with ocular adnexal lymphoma.
Treatment outcomes of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma in real-life practice: Chemotherapy versus multikinase inhibitors
- Pages: 3046-3053
- First Published: 09 September 2022
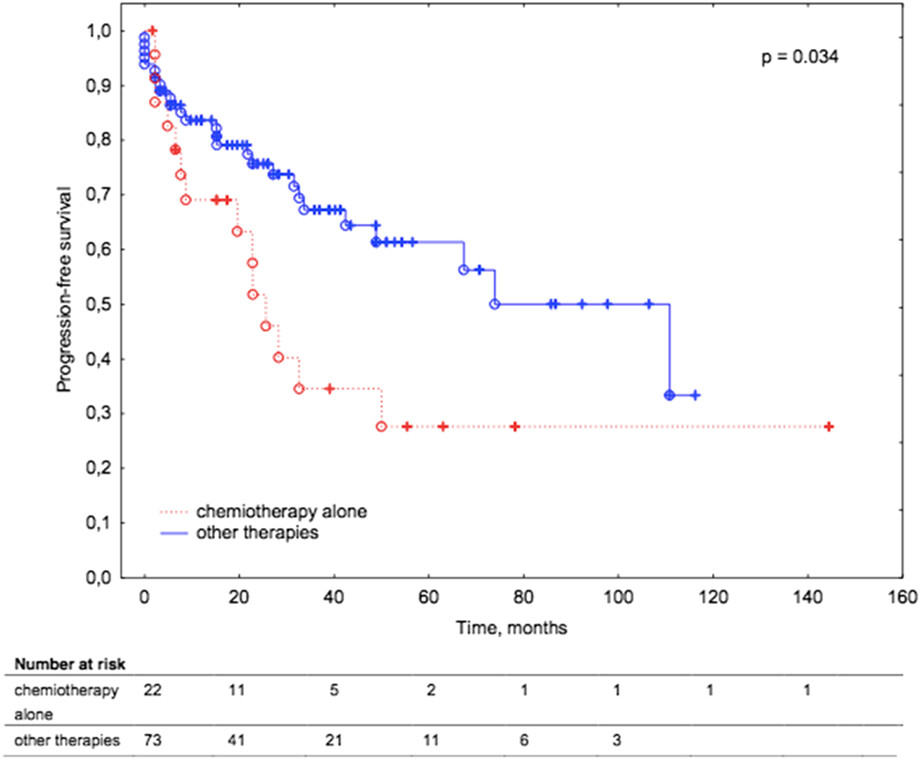
A stratified therapeutic model incorporated with studies on regulatory B cells for elderly patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma
- Pages: 3054-3067
- First Published: 20 September 2022
The management of elderly patients with MM remains challenging due to the heterogeneity of disease conditions, especially immune deficiency. In order to provide more evidence-based practice for the elderly MM, the study established and assessed a stratified therapeutic model with studies on Regulatory B cells for Chinese Elderly Multiple Myeloma in 2021 (CEMM2021).
Peritumor tertiary lymphoid structures are associated with infiltrating neutrophils and inferior prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Pages: 3068-3078
- First Published: 09 September 2022
Prognostic nomogram in patients with epithelioid sarcoma: A SEER-based study
- Pages: 3079-3088
- First Published: 08 September 2022
Identification of nine mutant genes and establishment of three prediction models of organ tropism metastases of non-small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 3089-3100
- First Published: 26 September 2022
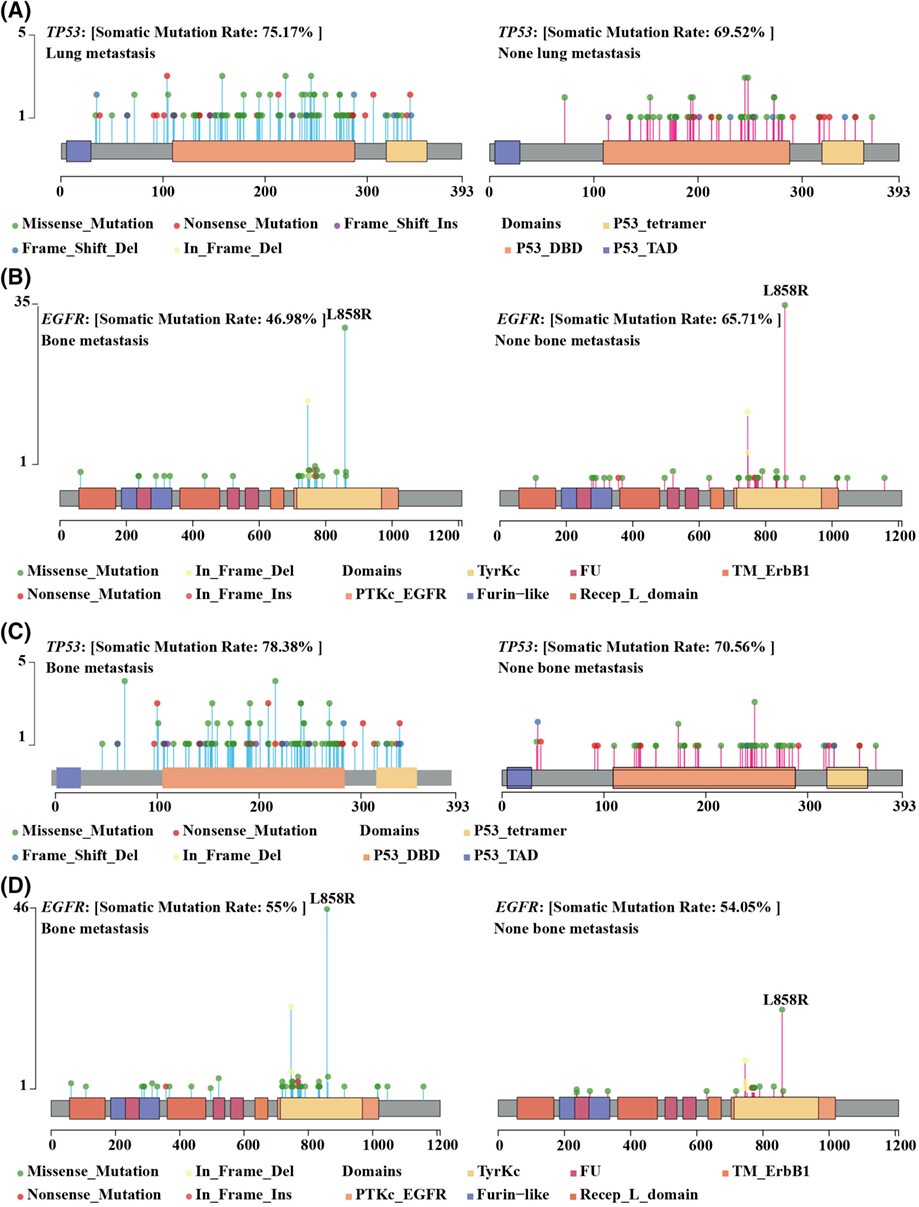
This study identified ten factors including nine gene mutations and smoking history as predictors for the organ tropism metastasis of NSCLC through analyses of NGS data and other clinical factors. Then three models were established to predict lung metastasis, brain metastasis, and pleura dissemination of NSCLC using these factors.
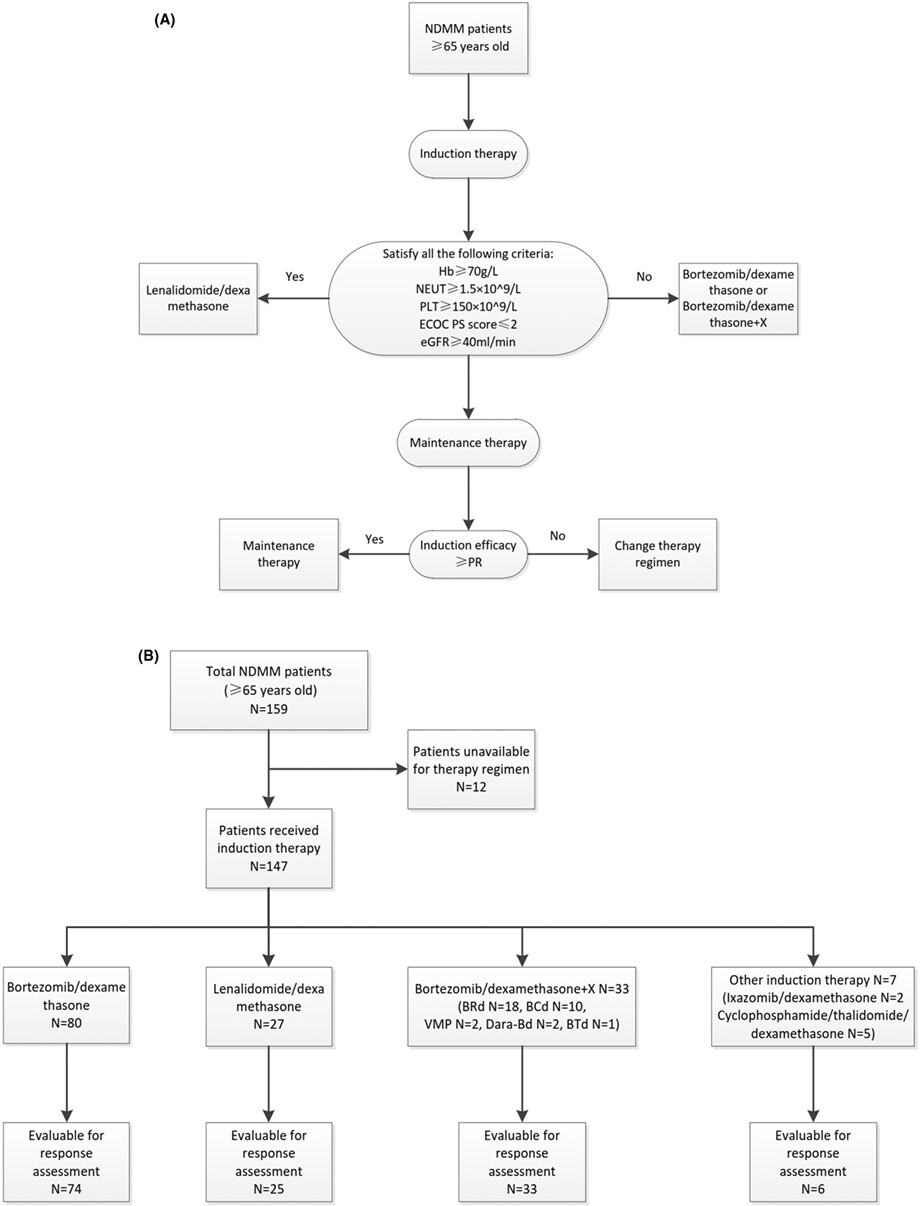
Front-line treatment efficacy and clinical outcomes of elderly patients with multiple myeloma in a real-world setting: A multicenter retrospective study in China
- Pages: 3101-3111
- First Published: 21 October 2022
Differences in sensitivity to new therapies between primary and metastatic breast cancer: A need to stratify the tumor response?
- Pages: 3112-3122
- First Published: 13 September 2022
Risk of metachronous contralateral breast cancer in patients with primary invasive lobular breast cancer: Results from a nationwide cohort
- Pages: 3123-3133
- First Published: 20 September 2022
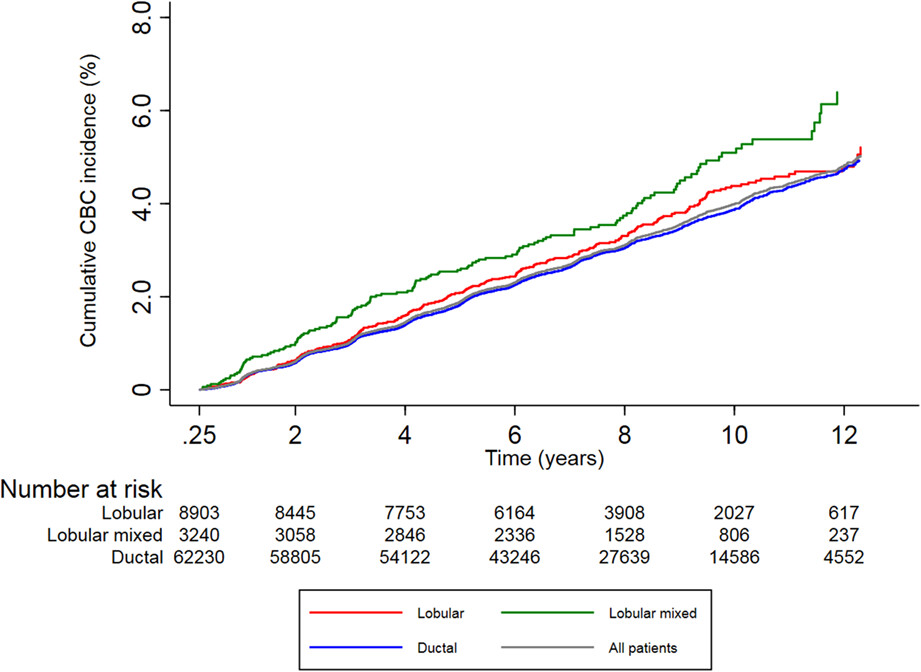
In a nationwide cohort of 74,373 primary breast cancer (PBC) patients, patients with lobular and especially those with lobular mixed histology had higher contralateral breast cancer (CBC) risks as compared to patients with ductal histology. Systemic treatment was associated with decreased CBC risk in all patients. The results of this study contribute to personalized risk assessment, with potential impact on treatment and follow-up decisions for PBC.
Watchful waiting is an acceptable treatment option for asymptomatic primary ocular adnexal mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma: A retrospective study
- Pages: 3134-3144
- First Published: 12 September 2022
Duration of frontline therapy and impact on clinical outcomes in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients not receiving frontline stem cell transplant
- Pages: 3145-3159
- First Published: 24 September 2022
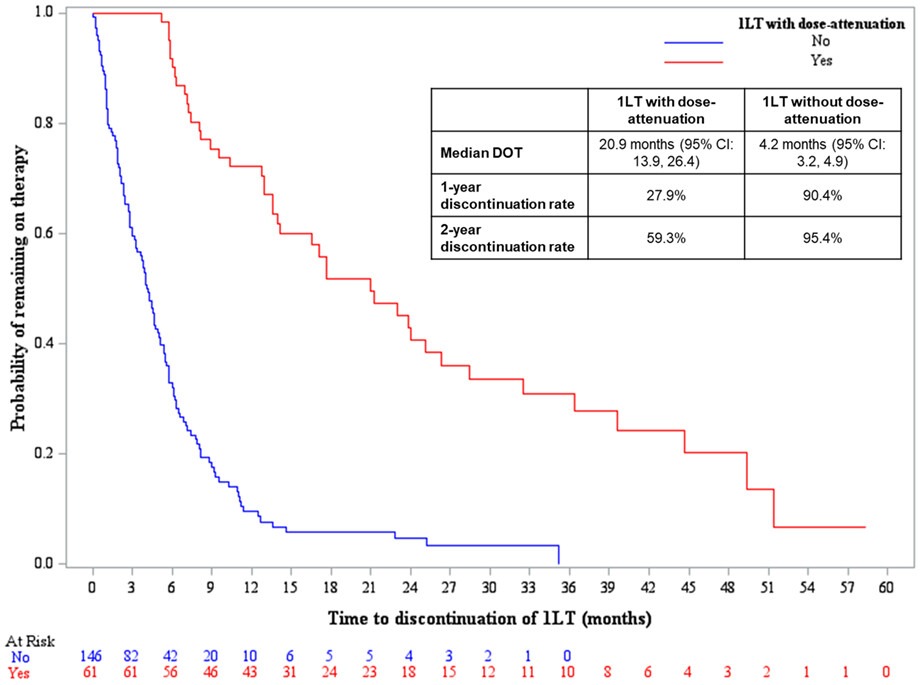
Frequently, transplant-ineligible patients are those who are frail and/or elderly, highlighting an unmet medical need for tolerable therapies; one approach to sustaining response balanced with tolerability is the use of maintenance or dose-attenuated therapies. Among newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients who did not receive stem cell transplant, dose-attenuated first-line therapy was associated with longer duration of therapy vs first-line therapy without dose-attenuation. Each additional month of first-line therapy was associated with a reduced adjusted likelihood of disease progression and death at 2 years.
BRIEF COMMUNICATION
Clinical Cancer Research
Single-agent gemcitabine in patients with advanced, pre-treated angiosarcoma: A multicenter, retrospective study
- Pages: 3160-3166
- First Published: 15 August 2022
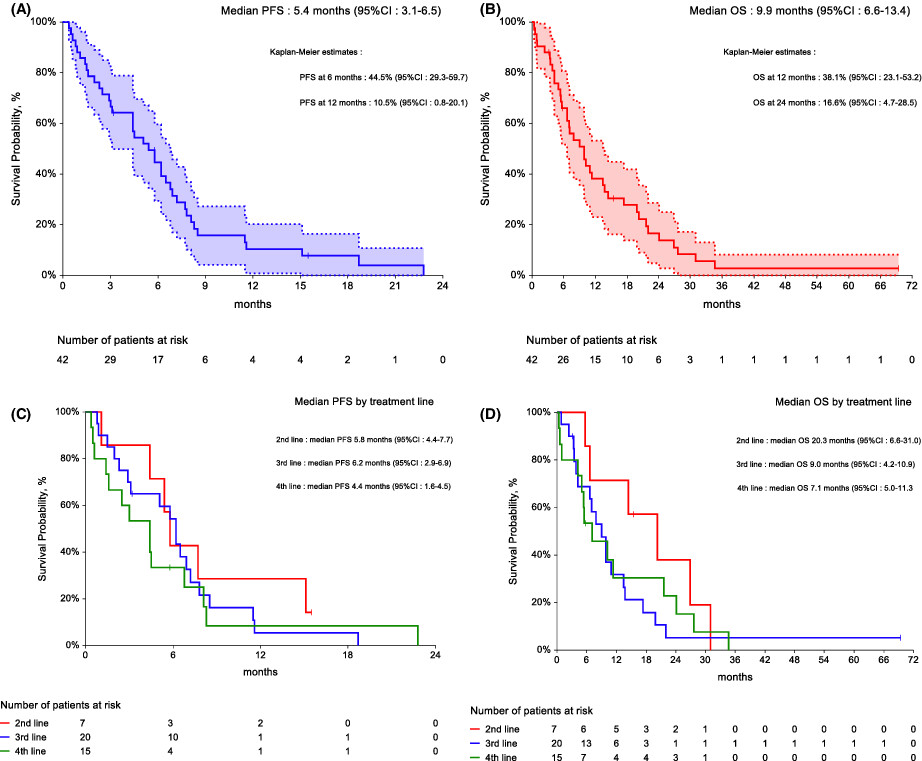
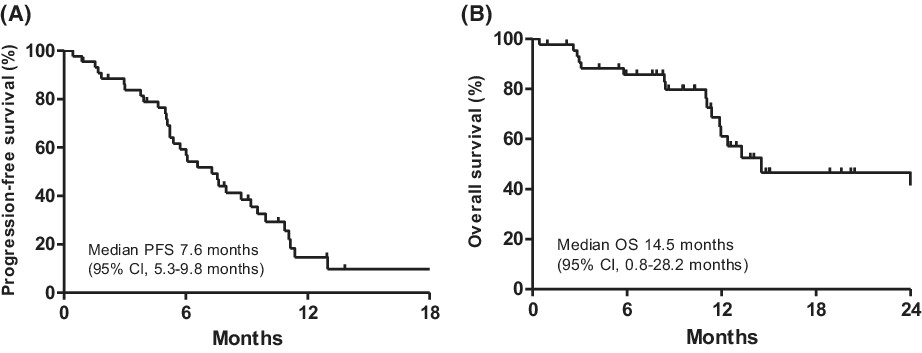
We aimed to evaluate the activity of single-agent gemcitabine in the largest series of 42 patients with advanced angiosarcoma. The best tumor response was partial response (PR) in 16 patients (38%), or stable disease (10 patients, 24%), median PFS was 5.4 months, and median OS was 9.9 months. Single-agent gemcitabine has clinically meaningful activity in advanced, heavily pre-treated angiosarcoma.
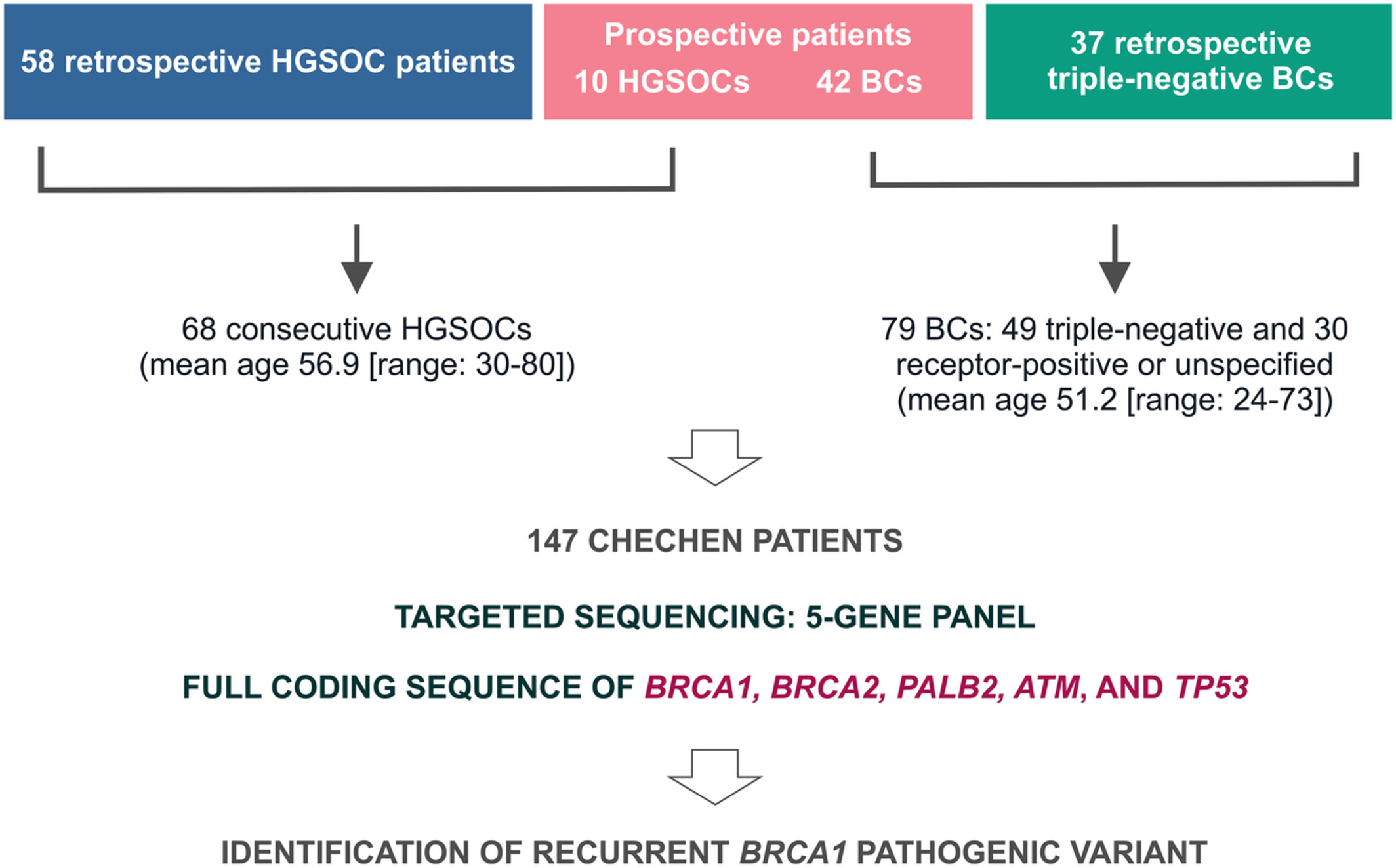
Strong founder effect for BRCA1 c.3629_3630delAG pathogenic variant in Chechen patients with breast or ovarian cancer
- Pages: 3167-3171
- First Published: 23 August 2022
Inclusion of patients with chronic kidney disease in randomized phase 3 clinical trials in patients with prostate, breast, lung, and colorectal cancer
- Pages: 3172-3175
- First Published: 26 September 2022
The majority of clinical trials restrict enrollment of patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and the exclusion criterion is undefined in most trials. Patients with CKD have therefore little access to innovation in oncology but solutions can be proposed to allow their inclusion in clinical trials.
Sequential therapy with darolutamide in patients with non-metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer resistant to enzalutamide or apalutamide
- Pages: 3176-3179
- First Published: 31 August 2022
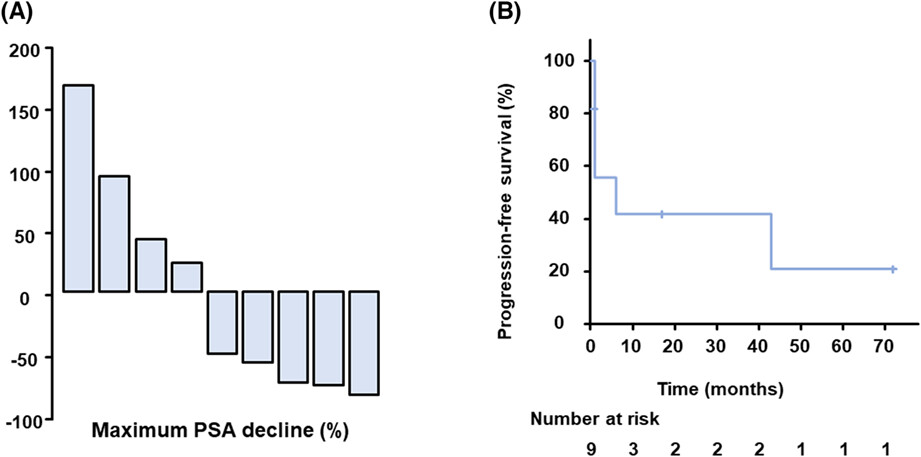
In this study, we retrospectively evaluated the efficacy of an androgen receptor-axis-targeted therapies (ARAT) switch from apalutamide or enzalutamide to darolutamide for non-metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (nmCRPC). More than half of the patients had a PSA response of more than 50% decline after starting darolutamide. Darolutamide could be the option of sequential therapy in patients with nmCRPC resistant to other ARAT.
LETTERS TO THE EDITOR
Clinical Cancer Research
BCR::ABL1 levels at first month after TKI discontinuation predict subsequent maintenance of treatment-free remission: A study from the “GRUPPO TRIVENETO LMC”
- Pages: 3180-3184
- First Published: 08 October 2022

We analyzed BCR::ABL1 expression at stop and in the first month after discontinuation in 168 CML patients stopping imatinib or 2G-TKIs, dividing patients who maintained response (1, n = 123) and those who lost MMR (group 2, n = 45). Mean BCR::ABL1 RNA levels at 1 and 2 months after discontinuation was higher in group 2 than in group 1, with a similar trend for imatinib and 2G-TKIs. A BCR::ABL1 value <0.0051% at 1 month after discontinuation was the stronger predictor of treatment-free remission (92.2% specificity).
REVIEWS
Cancer Biology
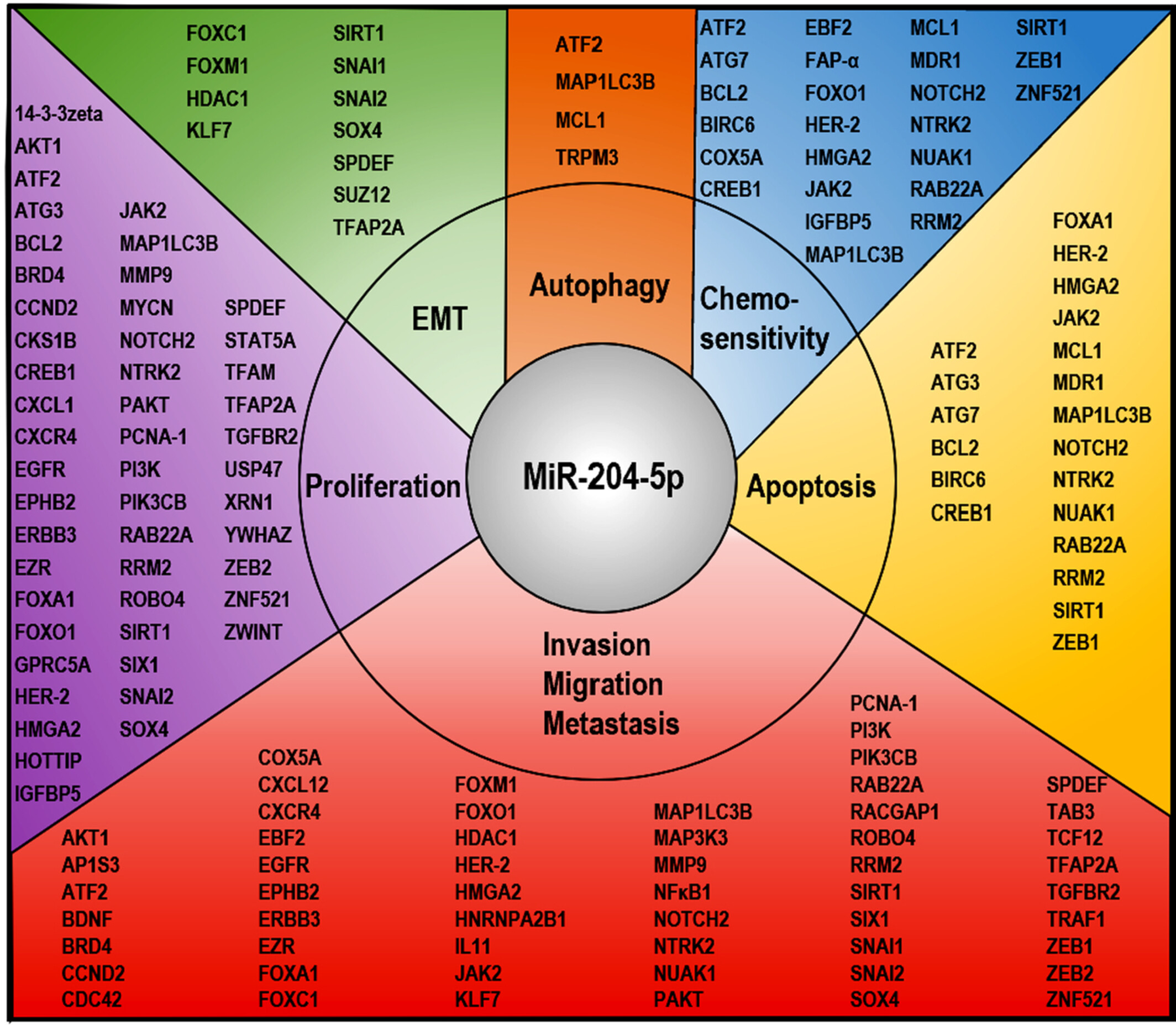
MicroRNA-204-5p: A pivotal tumor suppressor
- Pages: 3185-3200
- First Published: 31 July 2022
Hyperthermia combined with immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy: Synergistic sensitization and clinical outcomes
- Pages: 3201-3221
- First Published: 31 July 2022
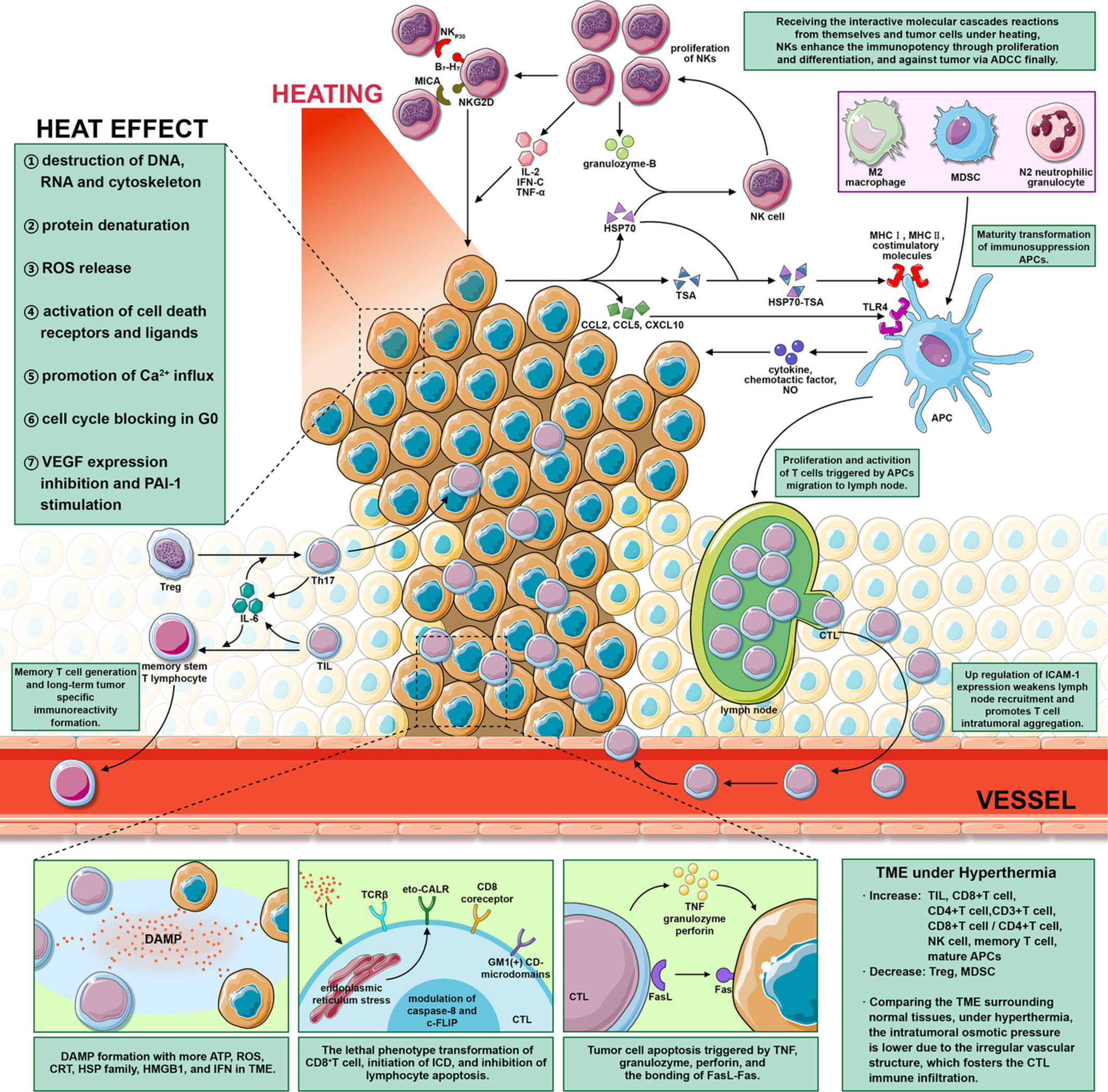
Our review analyses and discusses the recent basic research and clinical application of hyperthermia combined with immune checkpoint inhibitors for malignant tumors treatment. And the development tendency of this therapy is set forth constructively, which aims to provide a helpful guide to follow-up practice.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Cancer Biology
Tumor-derived endomucin promotes colorectal cancer proliferation and metastasis
- Pages: 3222-3236
- First Published: 15 August 2022
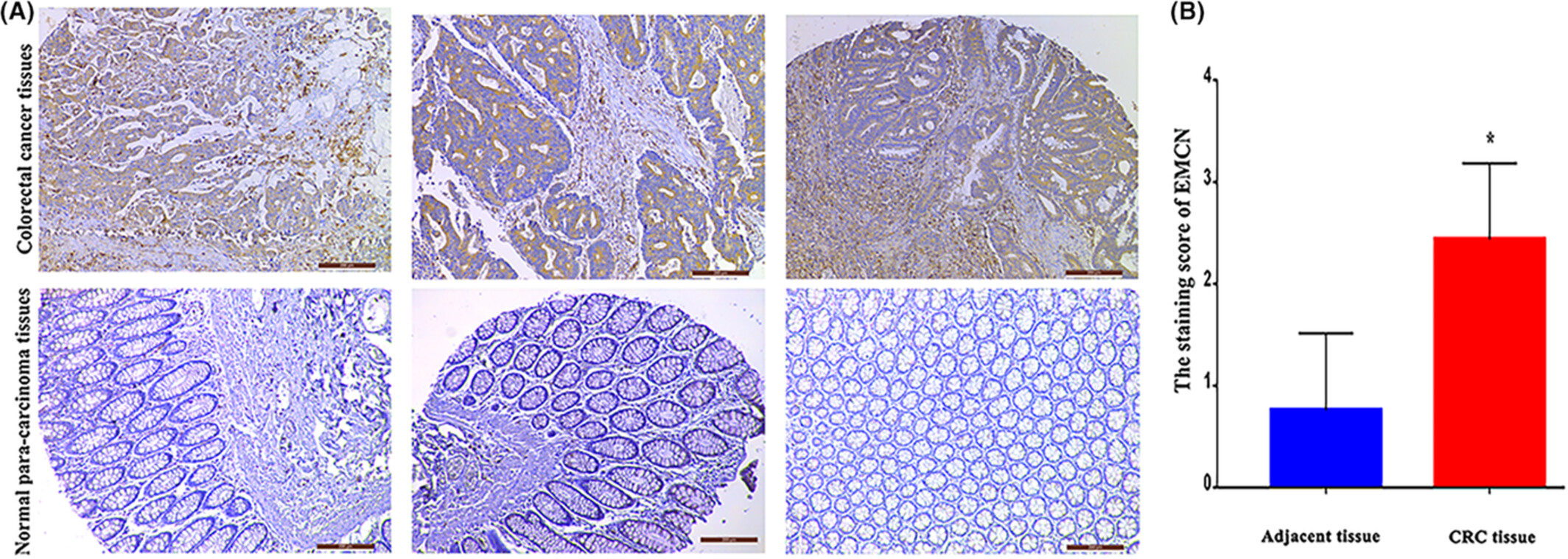
Endomucin (EMCN) was overexpressed in tumor tissues compared to normal para-carcinoma tissues. overexpression of EMCN induced colorectal cancer proliferation and metastasis both in vitro and in vivo experiments. identified EMCN-binding proteins were significantly enriched in carcinogenesis related functions and pathways.
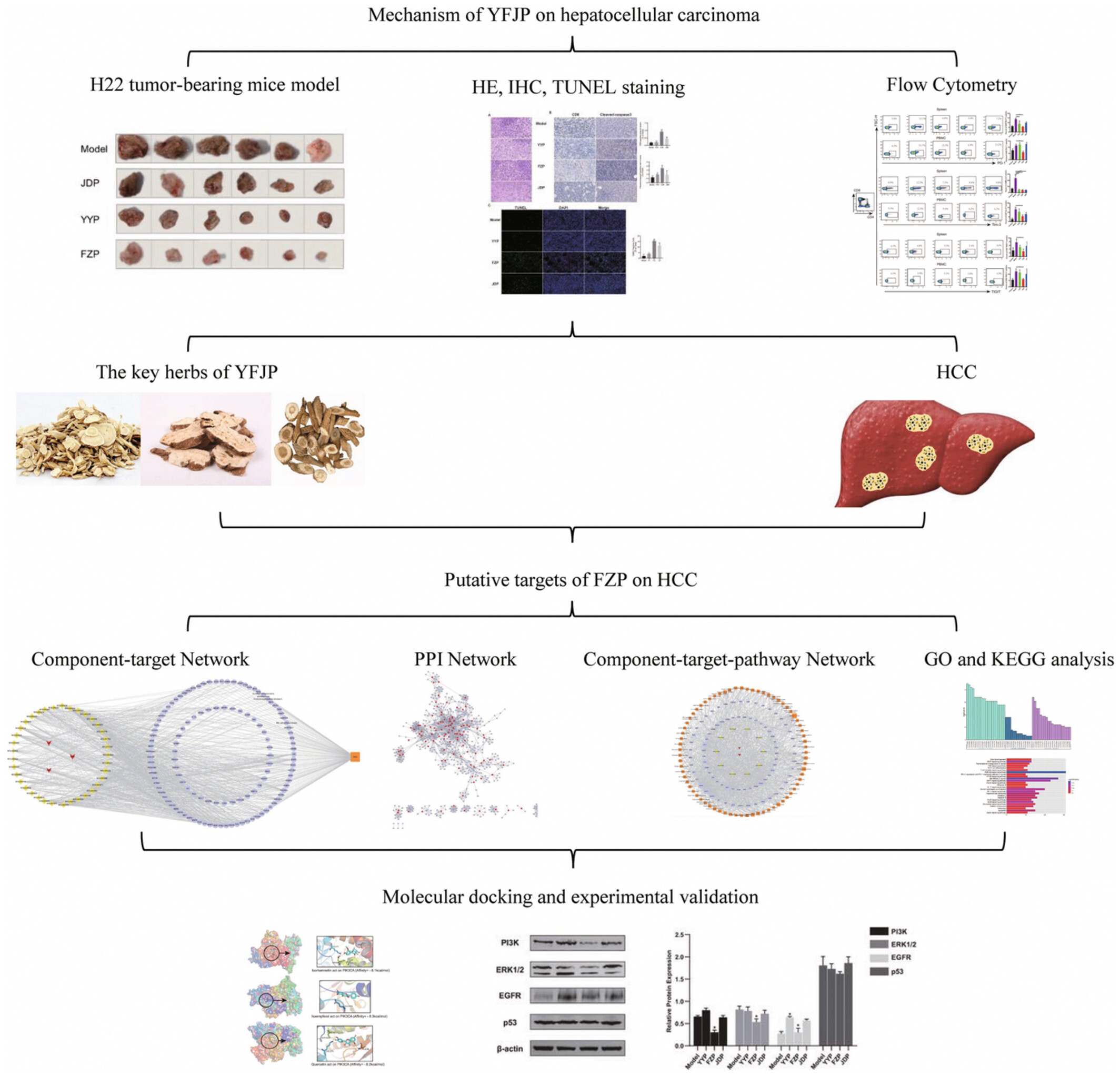
Mechanisms and network pharmacological analysis of Yangyin Fuzheng Jiedu prescription in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Pages: 3237-3259
- First Published: 31 August 2022
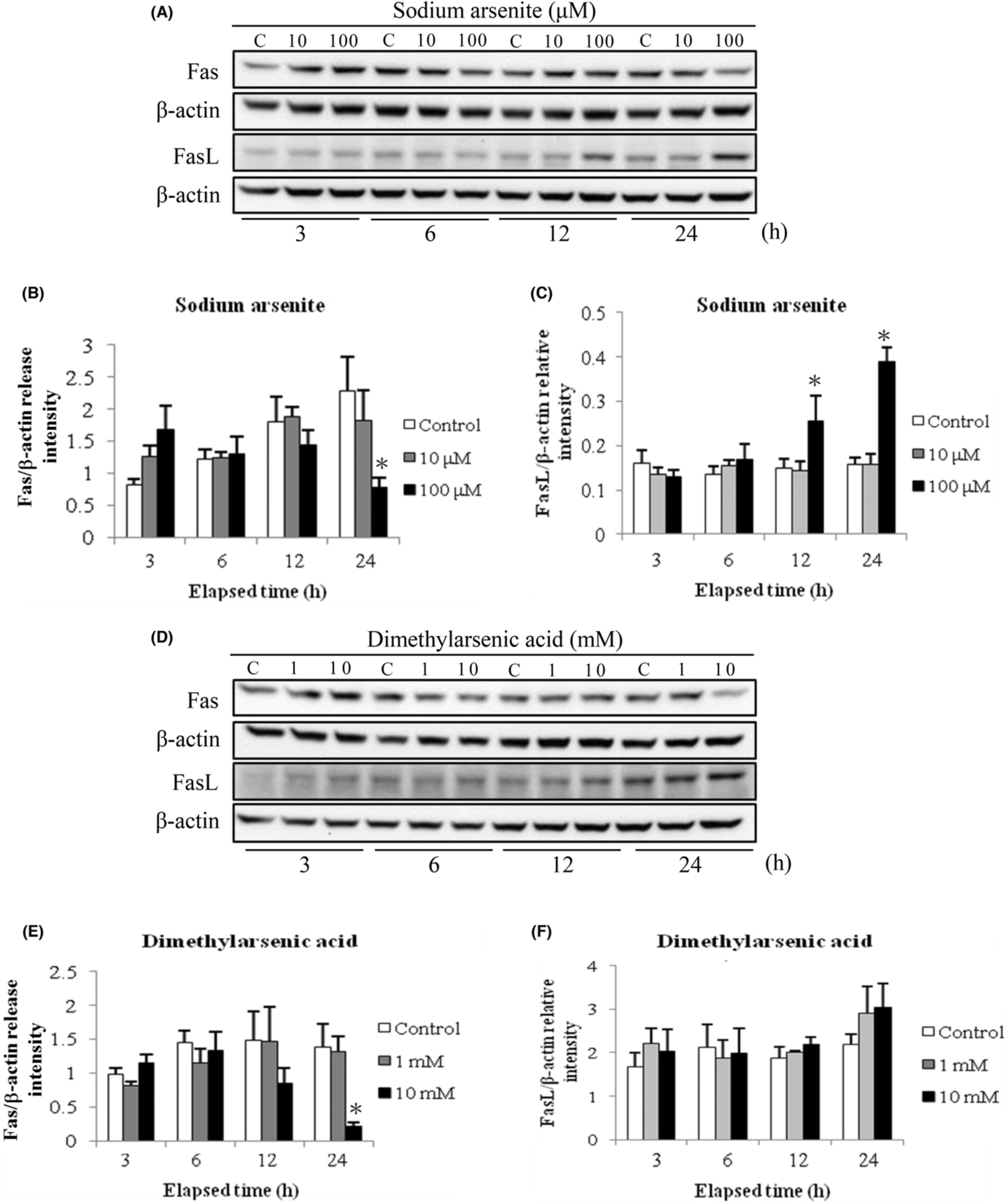
Arsenic compounds activate MAPK and inhibit Akt pathways to induce apoptosis in MA-10 mouse Leydig tumor cells
- Pages: 3260-3275
- First Published: 24 August 2022
The structural maintenance of chromosomes 5 is a possible biomarker for individualized treatment of colorectal cancer
- Pages: 3276-3287
- First Published: 27 July 2022
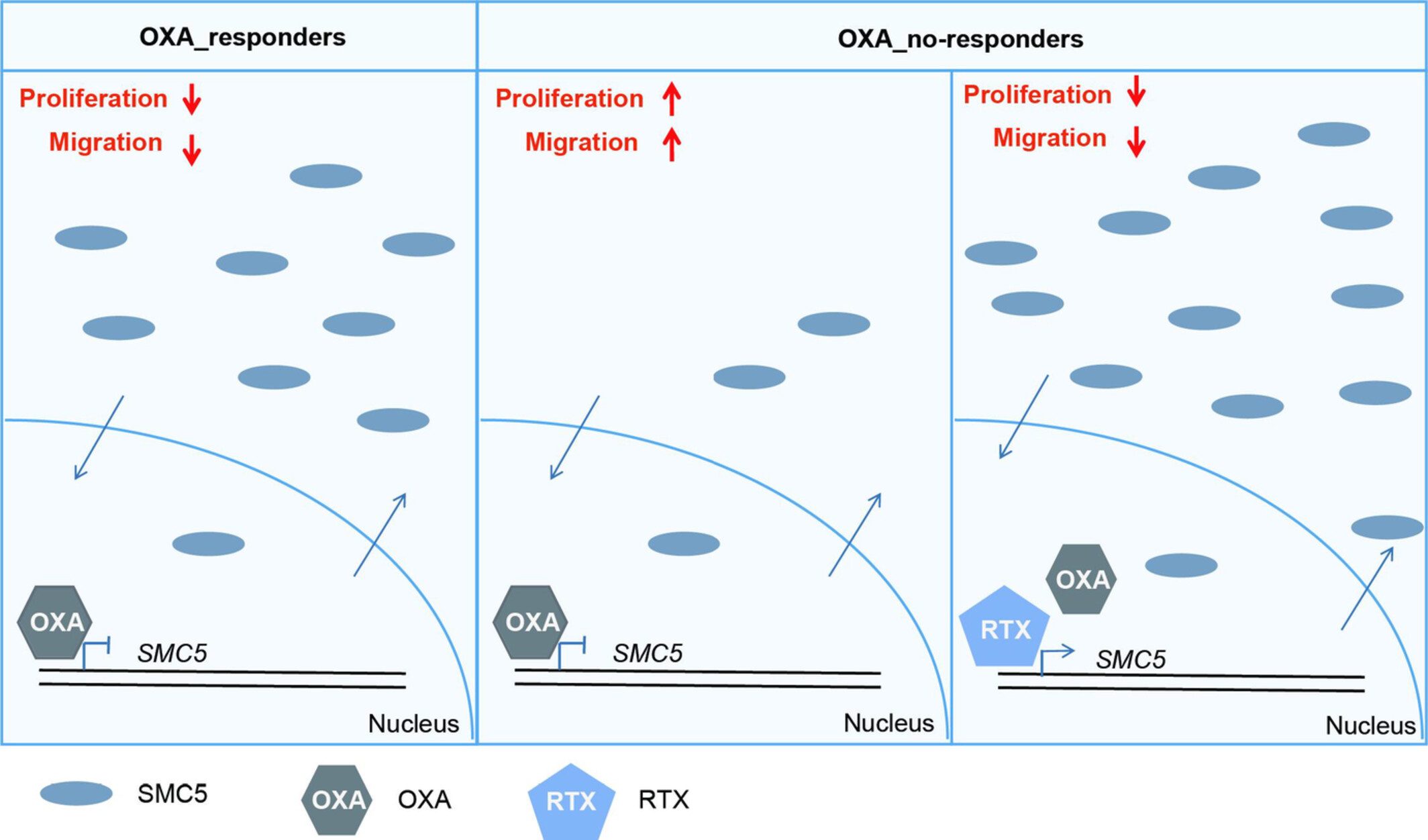
In CRC patients of OXA_responders, SMC5 is expressed normally, the proliferation and migration of the cancer cells were decreased (Left). In CRC patients of OXA_no-responders, SMC5 is downregulated in the cancer cells, OXA treatment further decreased it resulting in extremely low SMC5 content, the proliferation and migration of the cancer cells were increased (Middle). In CRC patients of OXA_no-responders, SMC5 is downregulated in the cancer cells, the combination treatment of OXA and RTX could not decreased SMC5, the proliferation and migration of the cancer cells were decreased (Right).
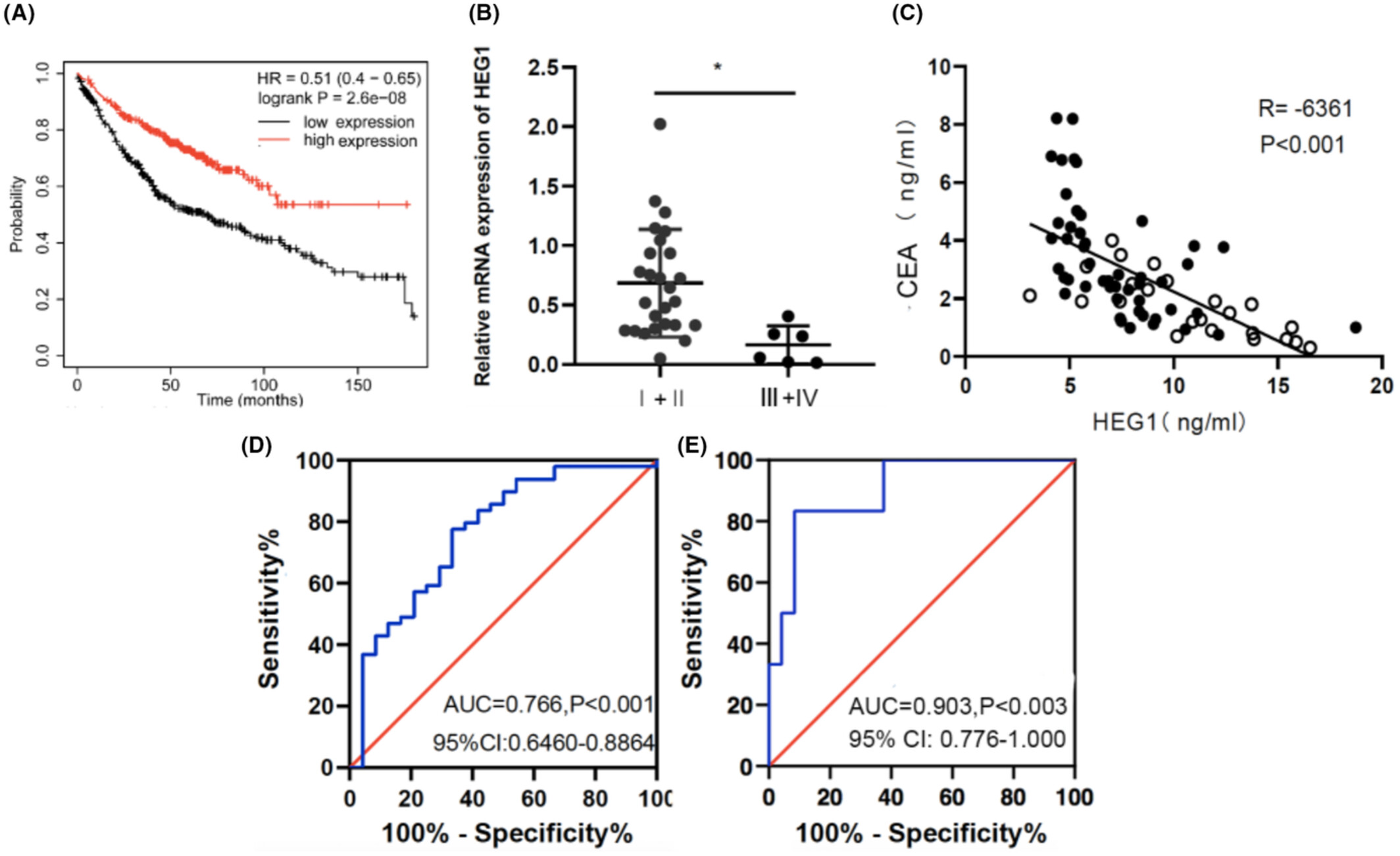
HEG1 as a novel potential biomarker for the prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma
- Pages: 3288-3298
- First Published: 10 August 2022
MARCKSL1 interacted with F-actin to promote esophageal squamous cell carcinoma mobility by modulating the formation of invadopodia
- Pages: 3299-3312
- First Published: 27 July 2022

High MARCKSL1 expression is positively correlated with poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) patients with lymph node metastasis. MARCKSL1 promotes ESCC cells migration and invasion by interacting with F-actin and cortactin to regulate invadopodia formation and ECM degeneration. MARCKSL1 may be a new biomarker and therapeutic target for esophageal cancer.
Modulation of intracellular kinase signaling to improve TIL stemness and function for adoptive cell therapy
- Pages: 3313-3327
- First Published: 26 August 2022
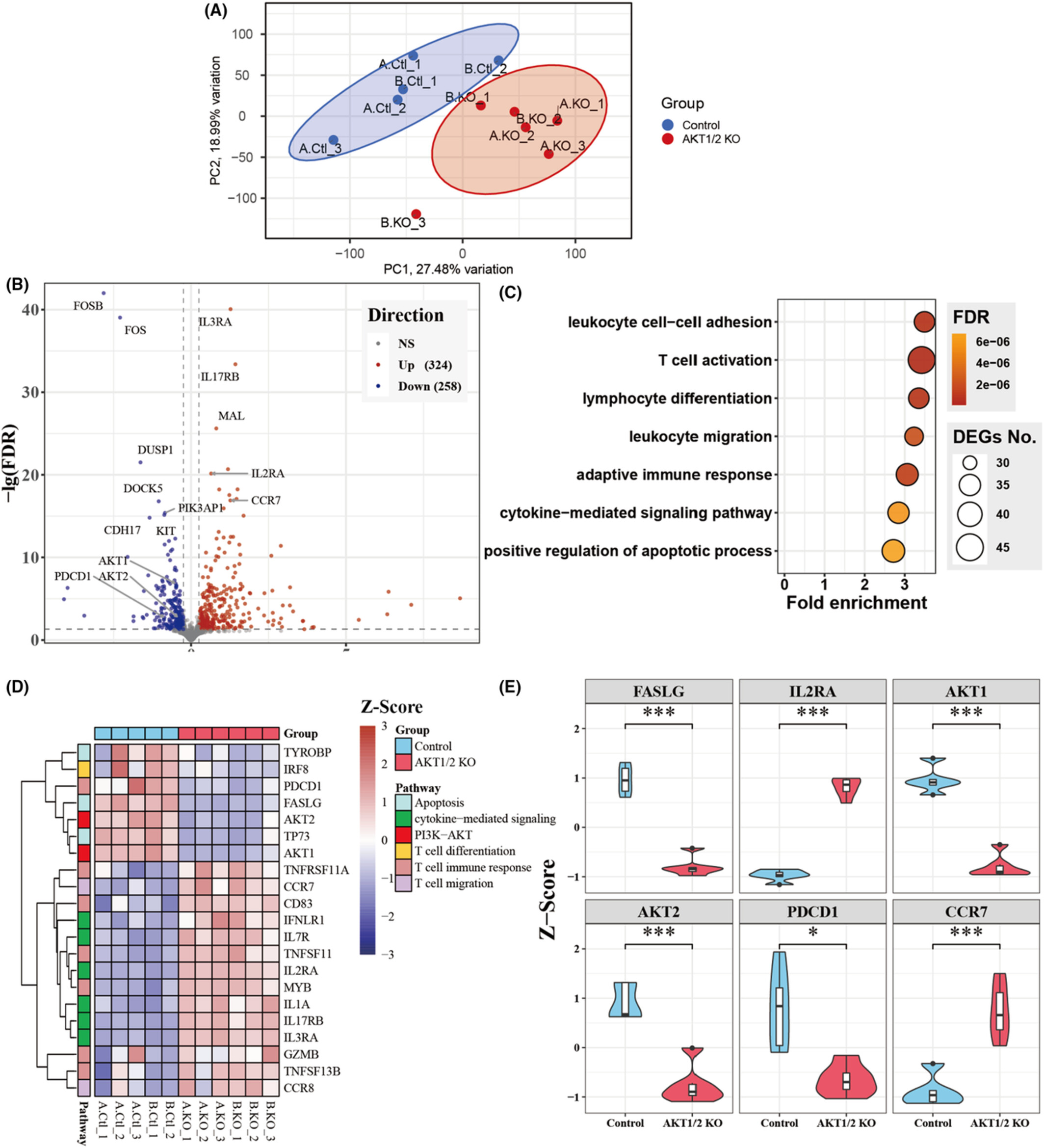
The PI3K-AKT pathway in TIL was modulated by AKT or PI3K inhibitors or CRISPR knockout of AKT1 and/or AKT2. The inhibition of either PI3K or AKT led to an increase in the population of effector CD8+ T cells with upregulation of activation marker, elevated CD39CD69 memory T cells, and significantly enhanced cytotoxicity when cocultured with tumor cell lines and patient-derived tumor samples. The results indicating that modulation of PI3K-AKT signaling represents a promising strategy to enhance TIL stemness and cytotoxicity and improve the clinical outcome of current TIL-based therapy to treat solid tumors.
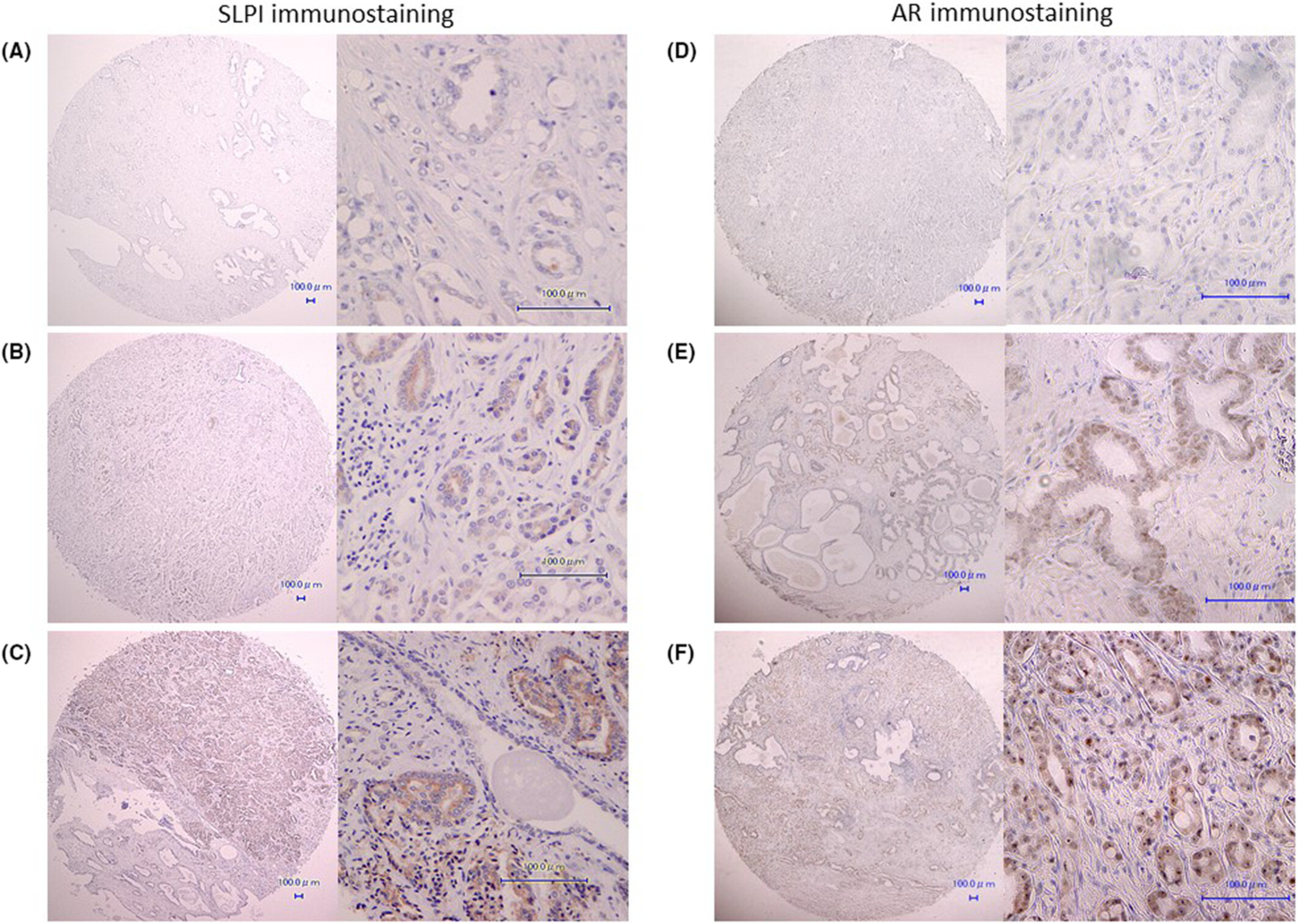
Up-regulation of secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor in human samples might have a potential role of predicting prostate cancer recurrence and progression after surgery and hormonal therapy
- Pages: 3328-3342
- First Published: 13 August 2022
REVIEWS
Cancer Prevention
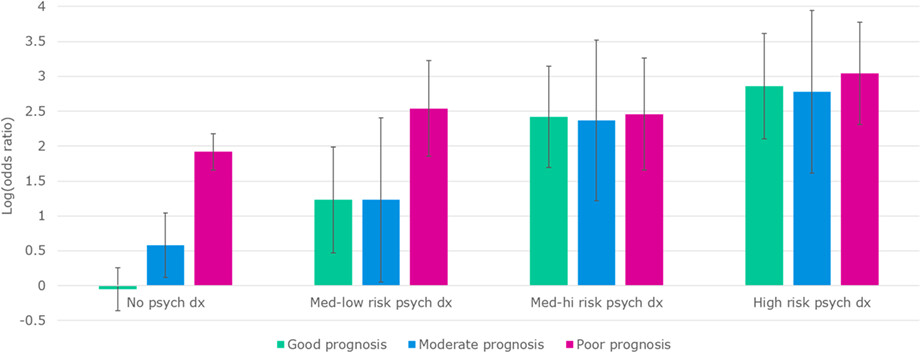
The link between psychological distress and survival in solid tumor patients: A systematic review
- Pages: 3343-3364
- First Published: 05 January 2023
Key findings from this review demonstrated a weak to moderate relationship between cancer patients’ experience of distress and overall survival, with the majority of included studies finding at least one predictive analysis to be significant when controlling for confounders. This review has significant implications for understanding the existing literature, implications for future study design and methodology, and implications for exploration of shared biologic mechanisms and identification of relevant phenotypes.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Cancer Prevention
Hematological toxicities in PARP inhibitors: A real-world study using FDA adverse event reporting system (FAERS) database
- Pages: 3365-3375
- First Published: 24 July 2022
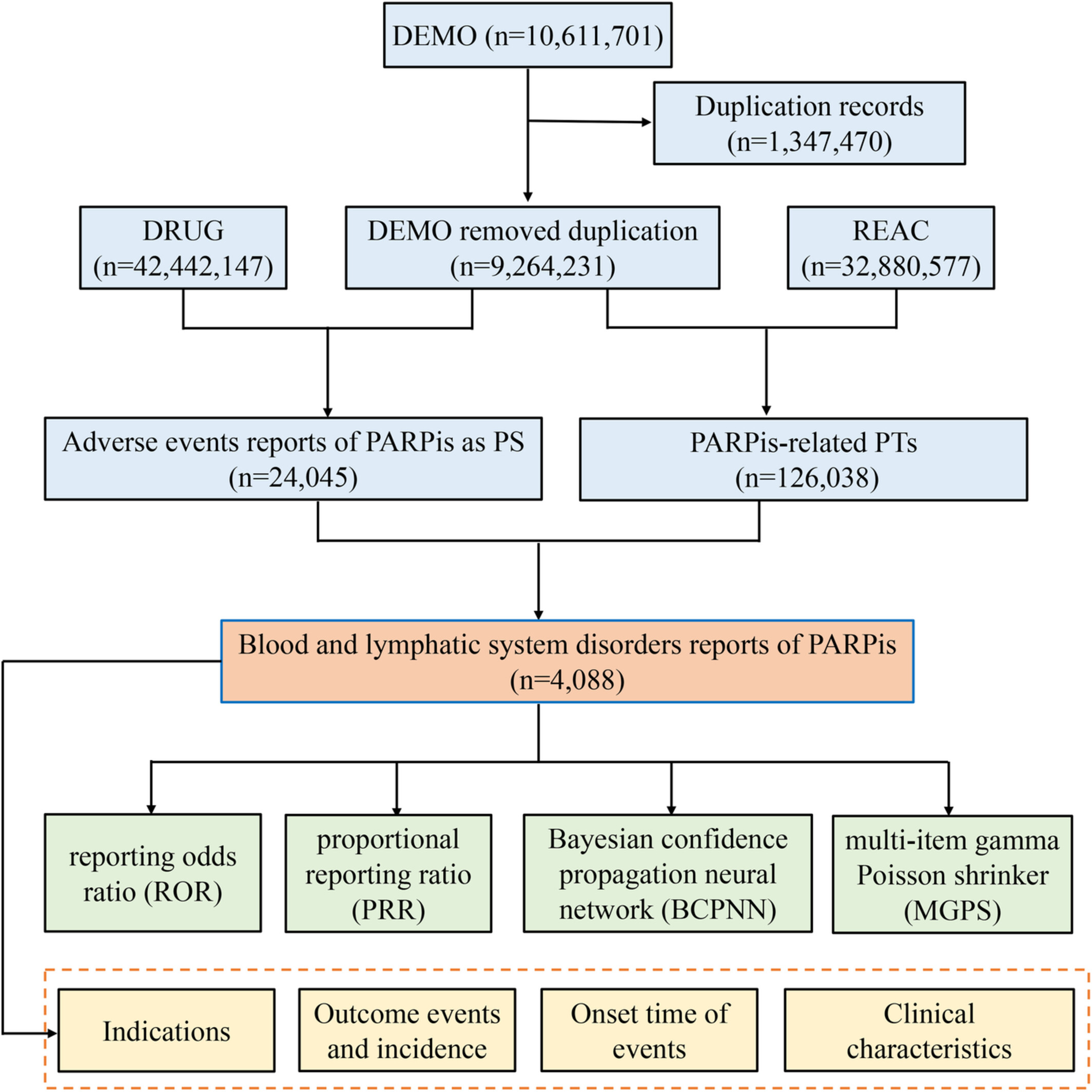
Our study extensively characterize the hematological toxicities of PARPis based on the FAERS real-world data by disproportionality analyses. 4088 hematotoxicity reports (17.00%) were analyzed and all PARPis were detected with positive safety signals of hematological toxicities in four detection methods. Unexpected significant adverse events such as lymphadenopathy, lymphoedema, and metastases to lymph nodes might also occur. The median time-to-onset was 28 (IQR 10-101) days and the fatality proportion of hematological toxicities with PARPis was 8.76%, with a statistical difference in different PARPis.
Patient preferences regarding treatment options for Waldenström's macroglobulinemia: A discrete choice experiment
- Pages: 3376-3386
- First Published: 26 July 2022
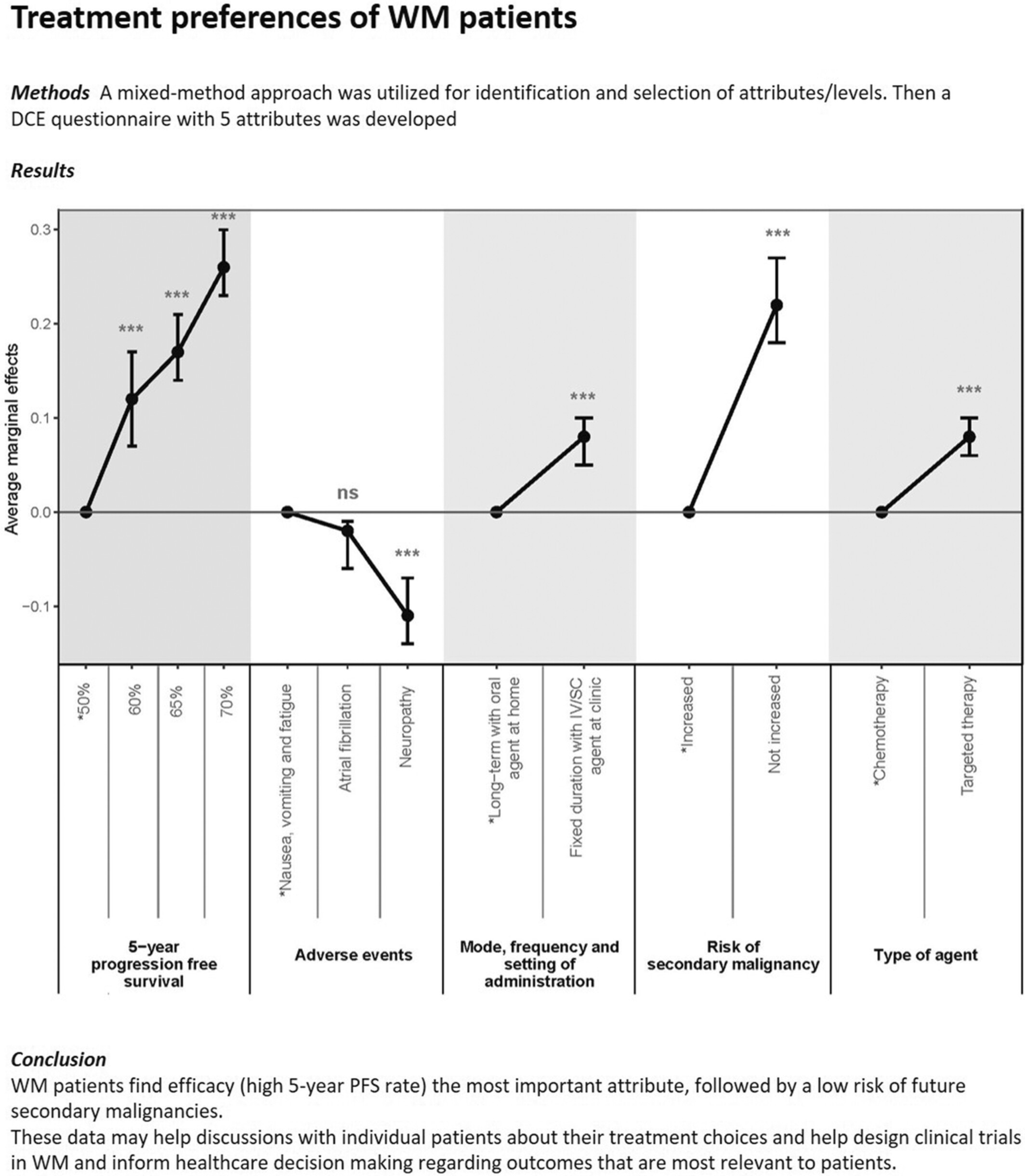
When asked about treatment preferences, WM patients prioritize avoiding the risk of secondary malignancies, avoiding peripheral neuropathy as a side effect, prefer targeted therapy over chemotherapy, but prefer fixed-duration iv/sc over long-term oral treatment. A treatment regimen that matches all these priorities is currently not available for WM.
Disparities in mortality among acute myeloid leukemia-related hospitalizations
- Pages: 3387-3394
- First Published: 04 August 2022
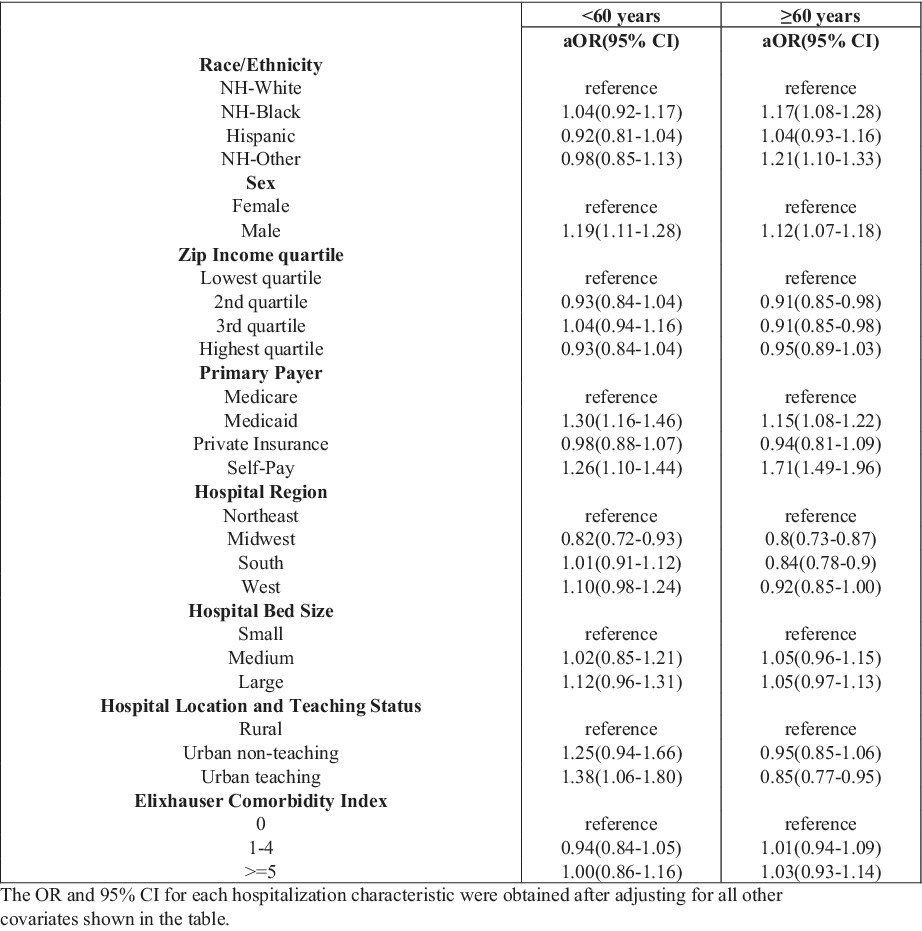
We evaluated sociodemographic disparities in the mortality of hospitalized patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) through a retrospective cohort study of hospitalizations for adults with a diagnosis of AML from 2009 to 2018 in the United States using the Nationwide Inpatient Sample (NIS). Race, gender, and teaching hospital status were found to be associated with disparate outcomes, in addition to established differences in mortality based on age. Our results highlight the increased need to recognize the role of race/ethnicity and socioeconomic factors and their contribution to outcomes in AML.
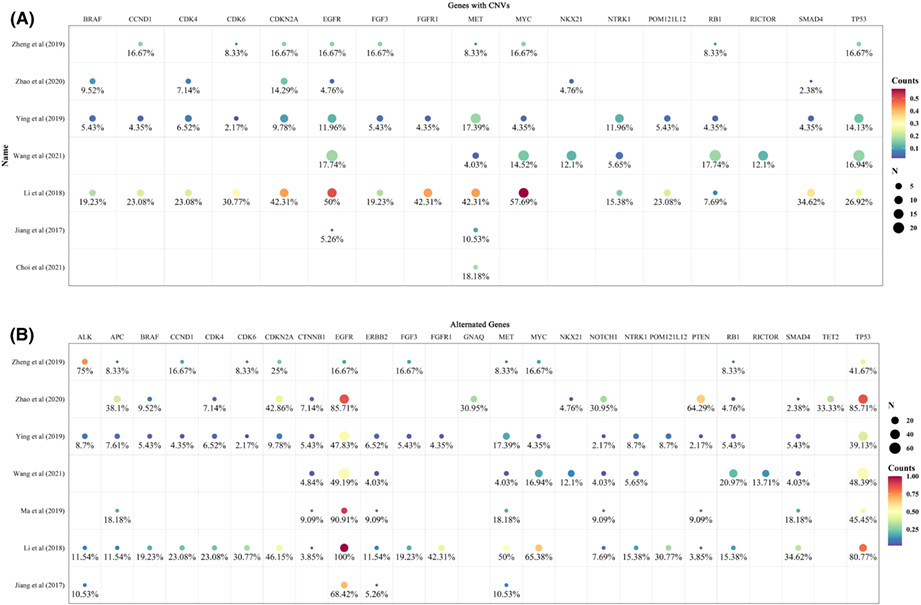
Breast cancer in East Africa: Prevalence and spectrum of germline SNV/indel and CNVs in BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes among breast cancer patients in Tanzania
- Pages: 3395-3409
- First Published: 31 July 2022
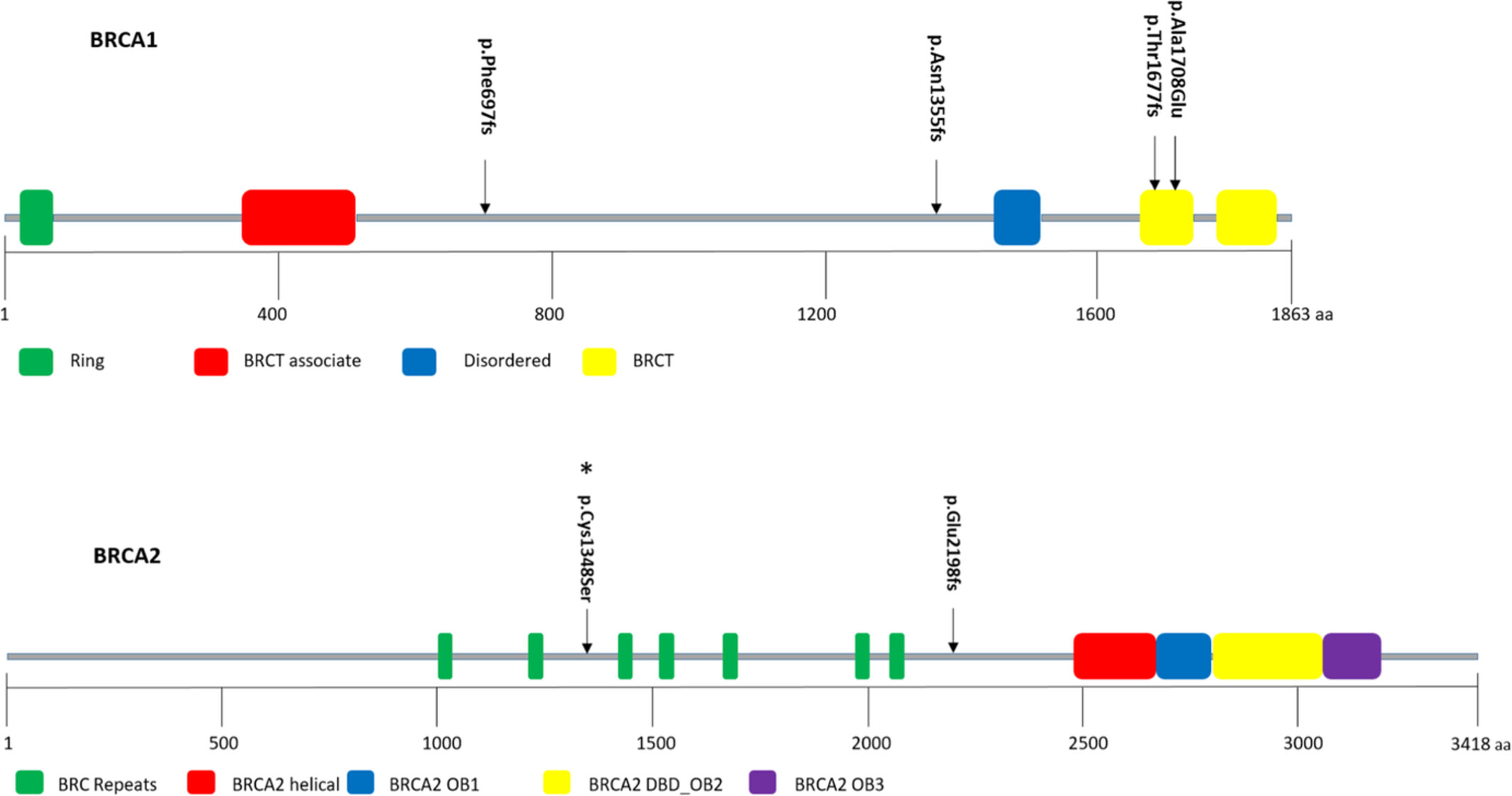
This study investigated the prevalence and spectrum of germline single nucleotide variant/insertion and deletion (SNV/indel), and copy number variations (CNVs) in BRCA1/2 among Tanzanian breast cancer patients, and evaluated the associations of identified variants with patient’s socio-demographic and histopathological characteristics. Next-generation sequencing results showed that SNV/indel were detected in 6% of patients, and CNVs was not detected in any patient. Our findings indicate that BRCA1/2 pathogenic variants may well contribute to breast cancer incidence in Tanzania. Thus, the identification of frequent variants in BRCA1/2 genes will enable implementation of rapid, inexpensive population-specific BRCA1/2 genetic testing particularly for triple-negative breast cancer patients known for their high prevalence in Tanzania.
Assisted reproductive technology and association with childhood cancer subtypes
- Pages: 3410-3418
- First Published: 05 August 2022
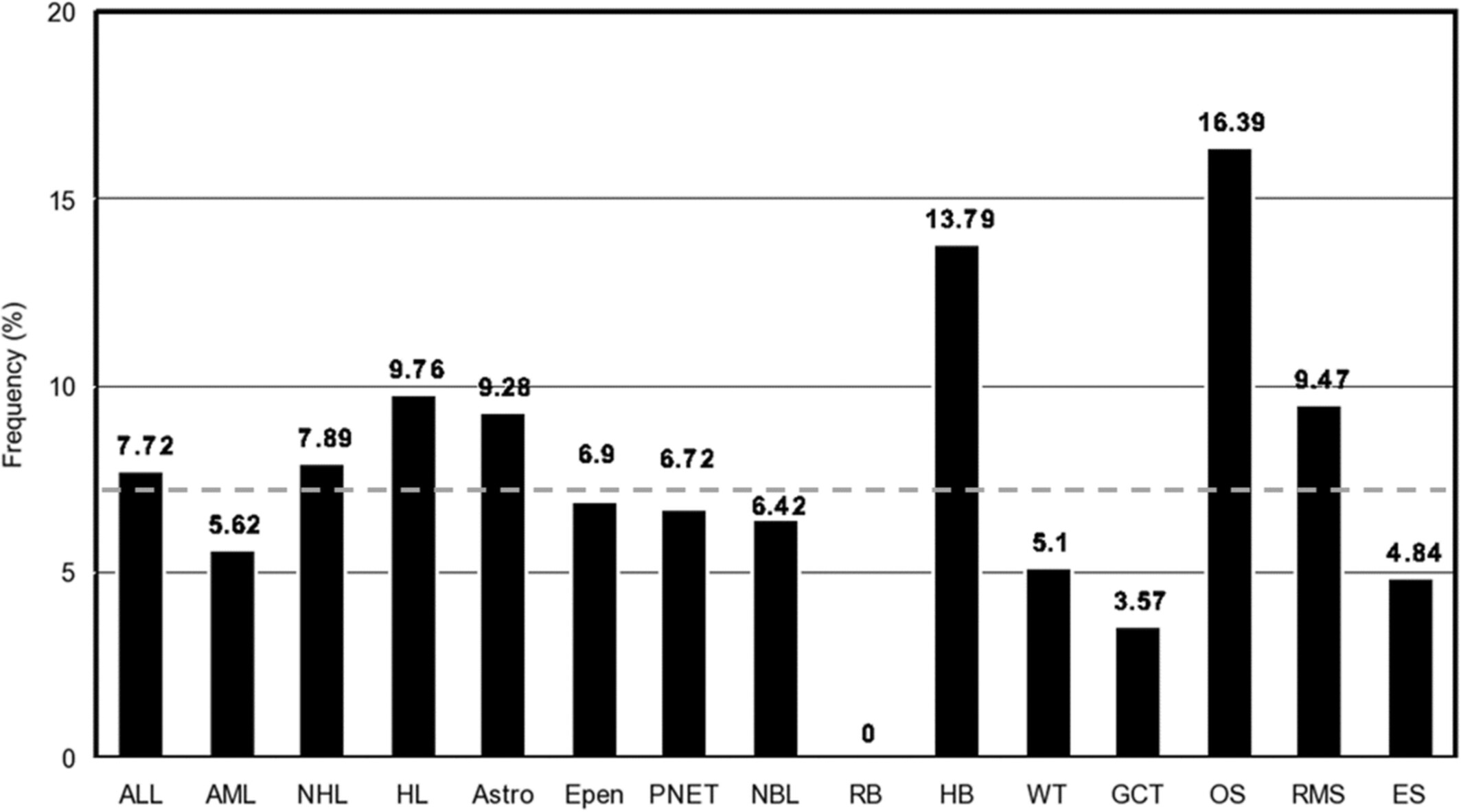
Epidemiologic data suggest an increase in U.S. childhood cancer incidence overall, though rates vary across cancer subtypes and few modifiable risk factors for childhood cancer have been identified. A cross-sectional survey of 1701 parents of children with cancer revealed associations between use of assisted reproductive technology and risk of childhood hepatoblastoma and osteosarcoma. the latter of which has not been previously observed in studies limited to cancers before adolescence. Evaluating long-term health outcomes in children conceived by ART, throughout adolescence and potentially into adulthood, appears warranted.
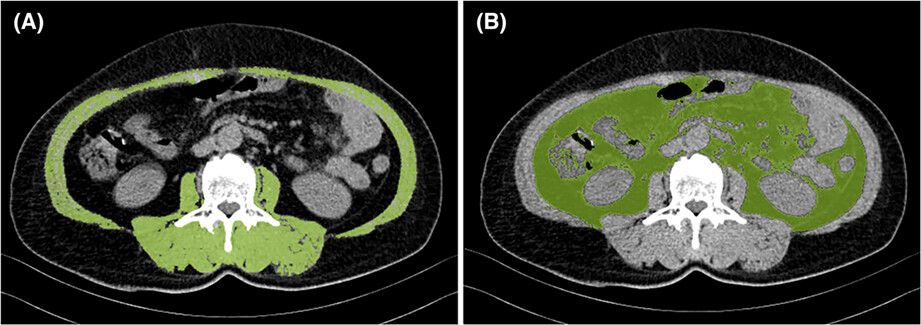
Prediction of presurgical metabolic syndrome for gastric cancer-specific mortality is more evident in smokers: The FIESTA study
- Pages: 3419-3432
- First Published: 26 August 2022
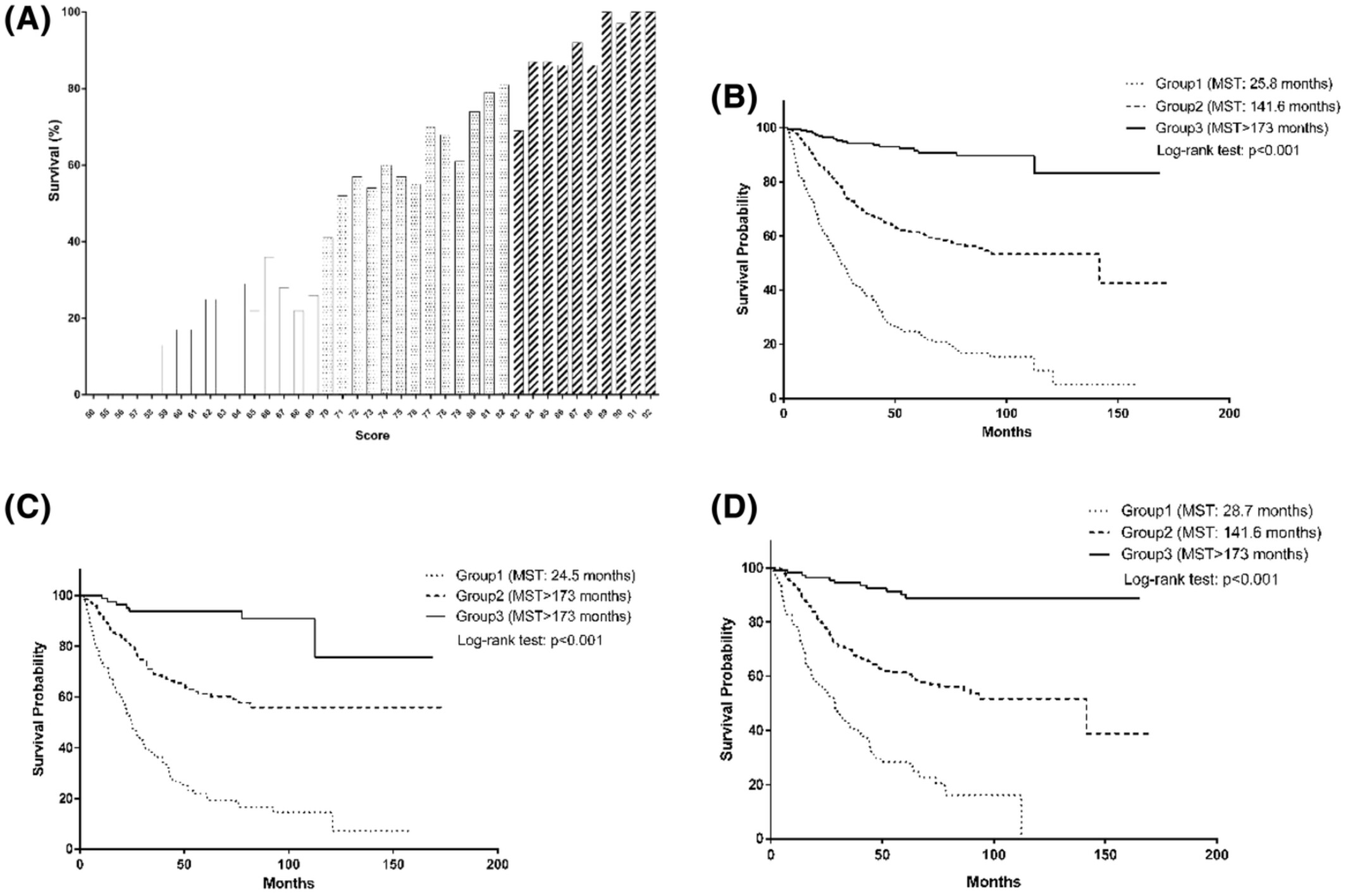
Distribution of the total risk score with postsurgical survival rate after follow-up (A), and Kaplan-Meier curves by score groups in patients overall (B) and by cigarette smoking status (panel C in smokers and panel D in never-smokers). MST, median survival time. Group 1 refers to patients with a total score ranging from 50 to 69; group 2 refers to patients with a total score ranging from 70 to 82; group 3 refers to patients with a total score ranging from 83 to 92.
Clinical spectrum of rectal cancer identifies hallmarks of early-onset patients and next-generation treatment strategies
- Pages: 3433-3441
- First Published: 05 August 2022
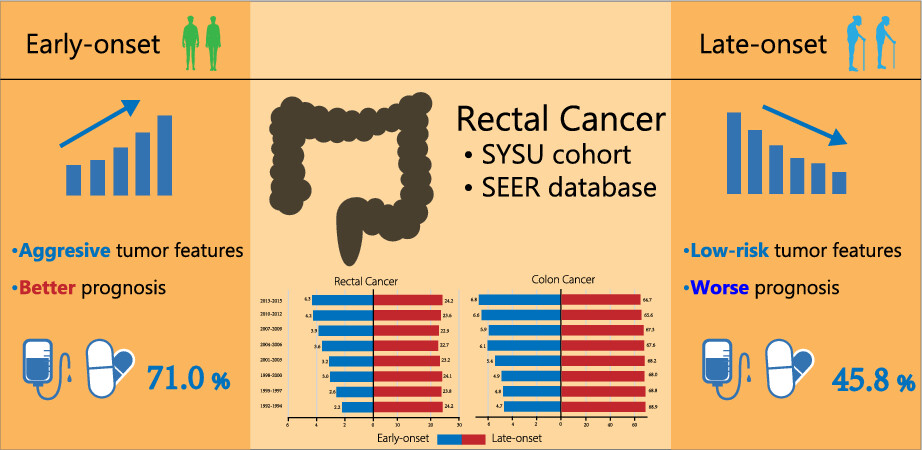
This study including two cohorts with a total of 552 and 80,341 stages I–III rectal cancer patients demonstrated that there existed a wide set of disparities in disease history, clinicopathological features, treatment modalities, and outcomes between early-onset and late-onset rectal cancer patients.
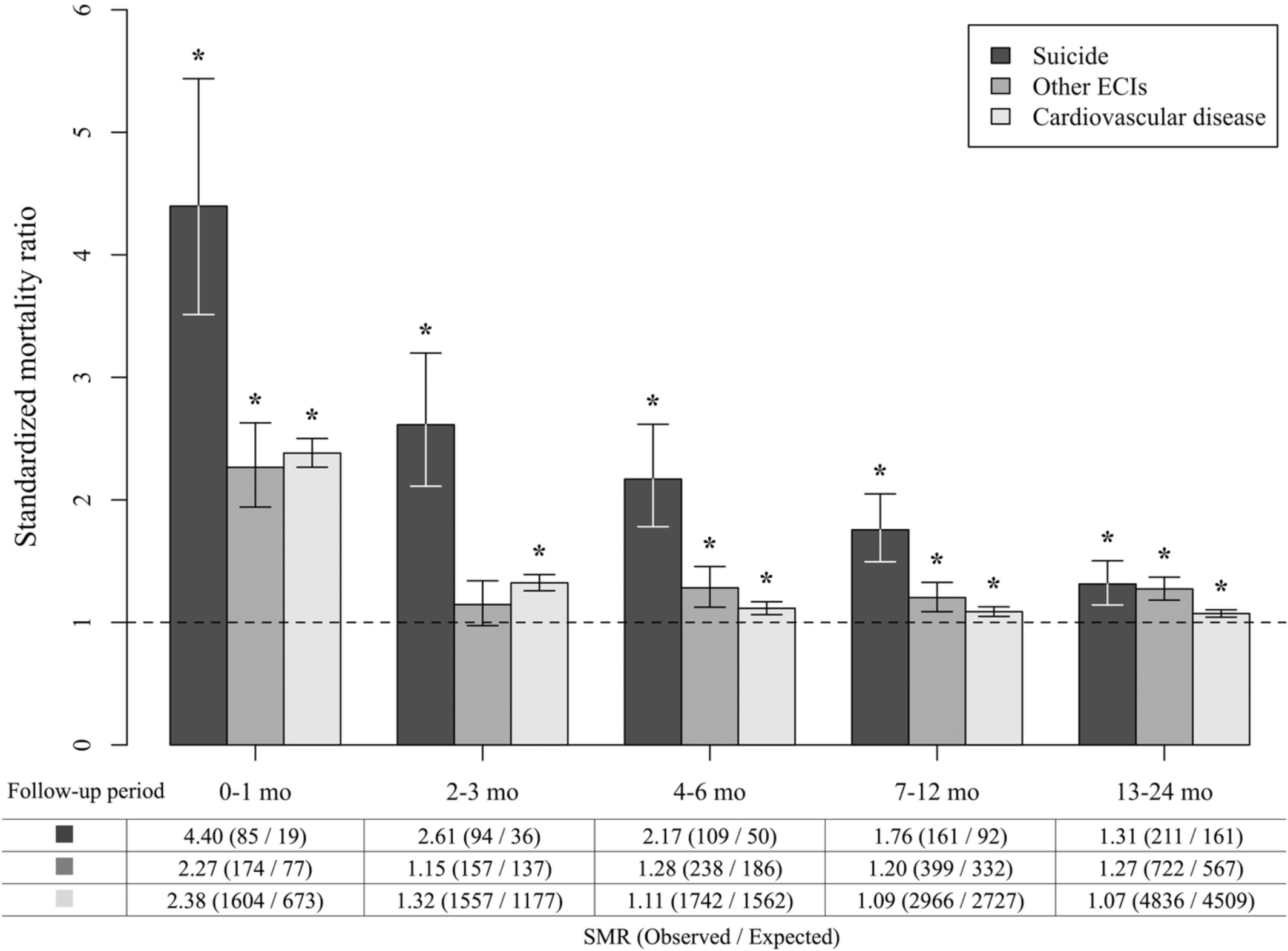
Suicide, other externally caused injuries, and cardiovascular disease within 2 years after cancer diagnosis: A nationwide population-based study in Japan (J-SUPPORT 1902)
- Pages: 3442-3451
- First Published: 08 August 2022
Effect of social disparities on 10 year survival in pediatric patients with Wilms' tumor
- Pages: 3452-3459
- First Published: 09 August 2022
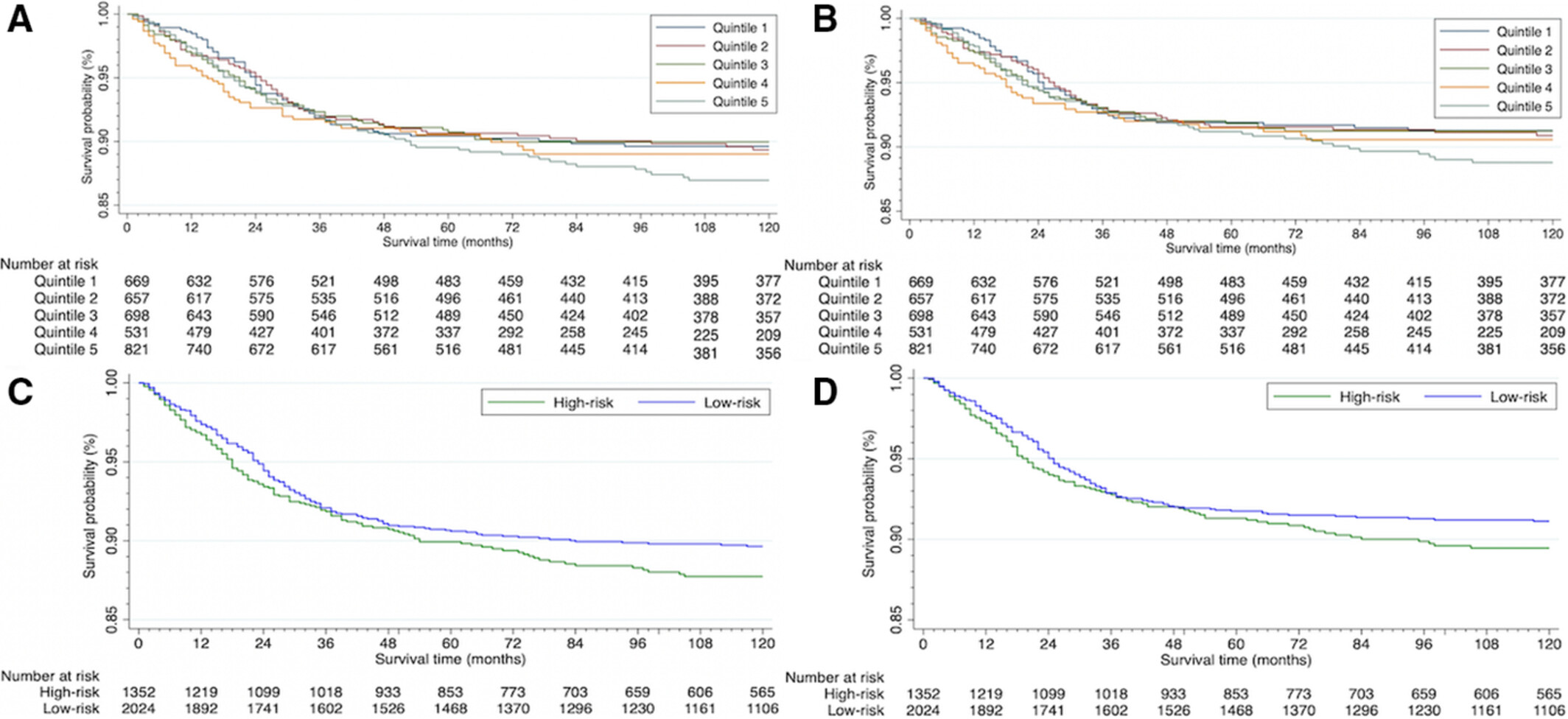
Wilm's tumor patients on a national level have significantly worse 10-year overall survival rates and noticeably different 10-year cancer-specific survival rates. Disparities in healthcare outcomes among this pediatric oncologic population can be better addressed using social determination of health metrics.
Trends in utilization of first-line palliative treatments for anal squamous cell carcinoma
- Pages: 3460-3467
- First Published: 09 September 2022
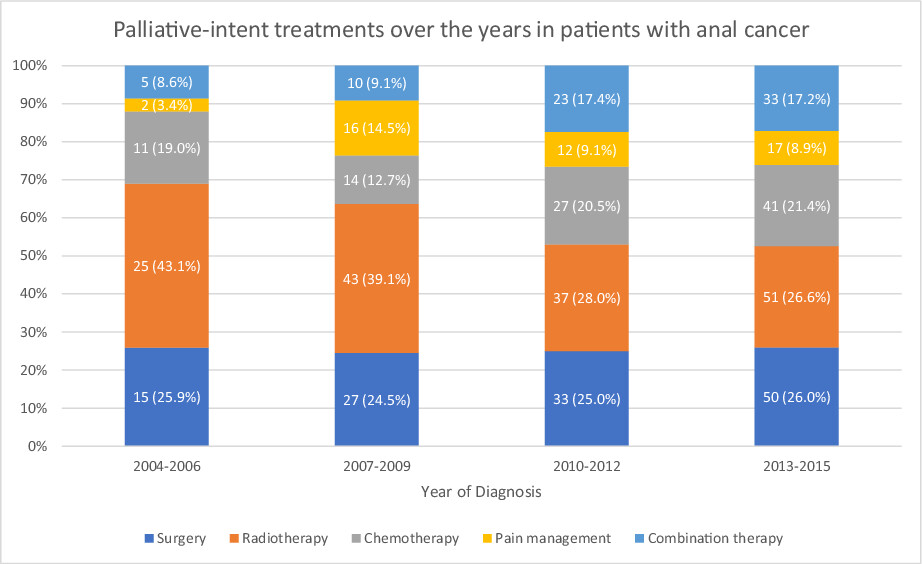
Anal squamous cell carcinoma (ASCC) presents with pain, bleeding, and obstructive symptoms, and the proportion of these patients receiving first-line palliative treatments is unknown. Therefore, patients living in the United States were evaluated using the National Cancer Database. Palliative therapy in ASCC was less utilized and associated with a higher stage of disease and near the end of life.
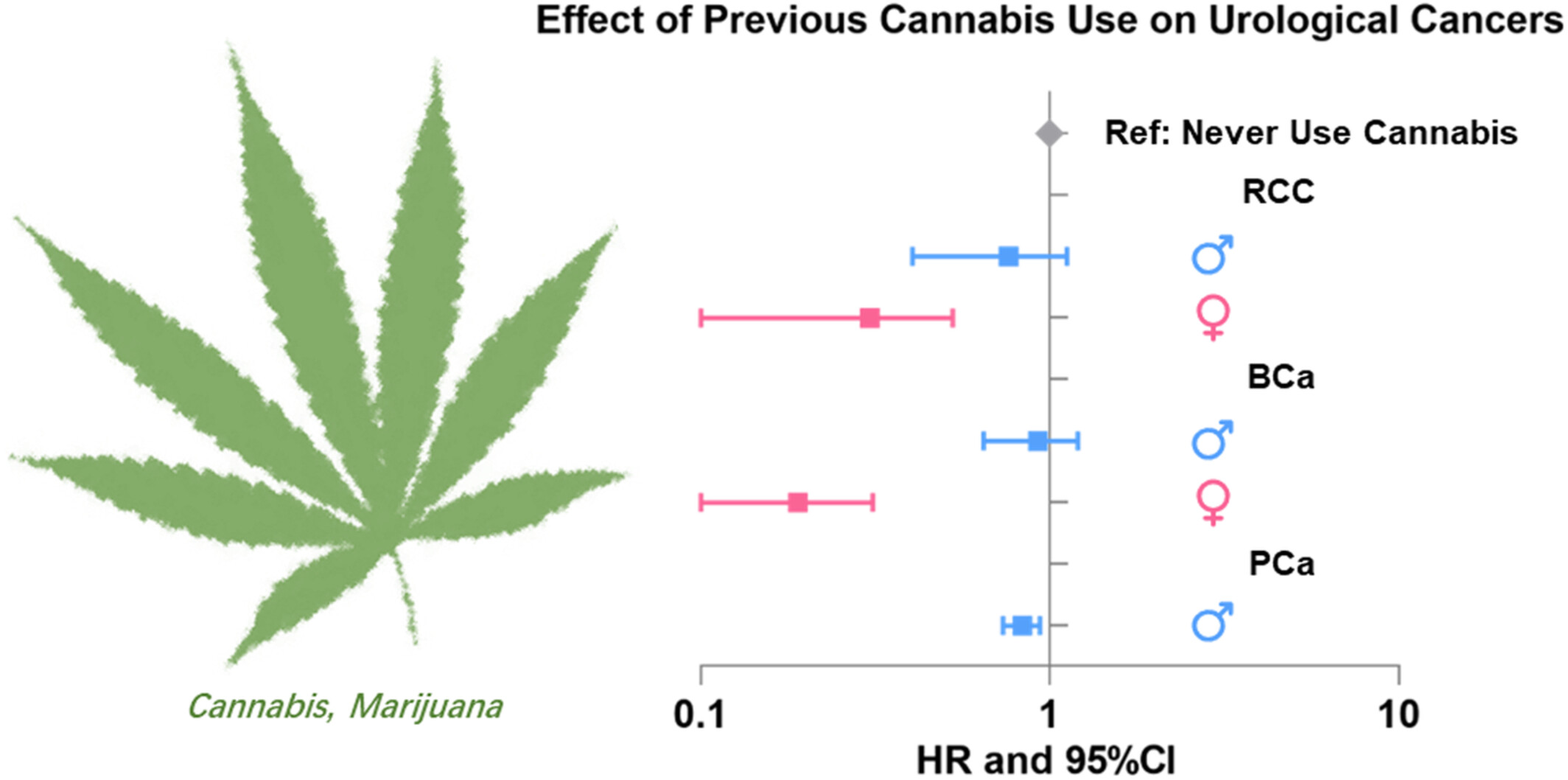
Association between cannabis use with urological cancers: A population-based cohort study and a mendelian randomization study in the UK biobank
- Pages: 3468-3476
- First Published: 17 August 2022
Home-based physical activity after treatment for esophageal cancer—A randomized controlled trial
- Pages: 3477-3487
- First Published: 18 August 2022
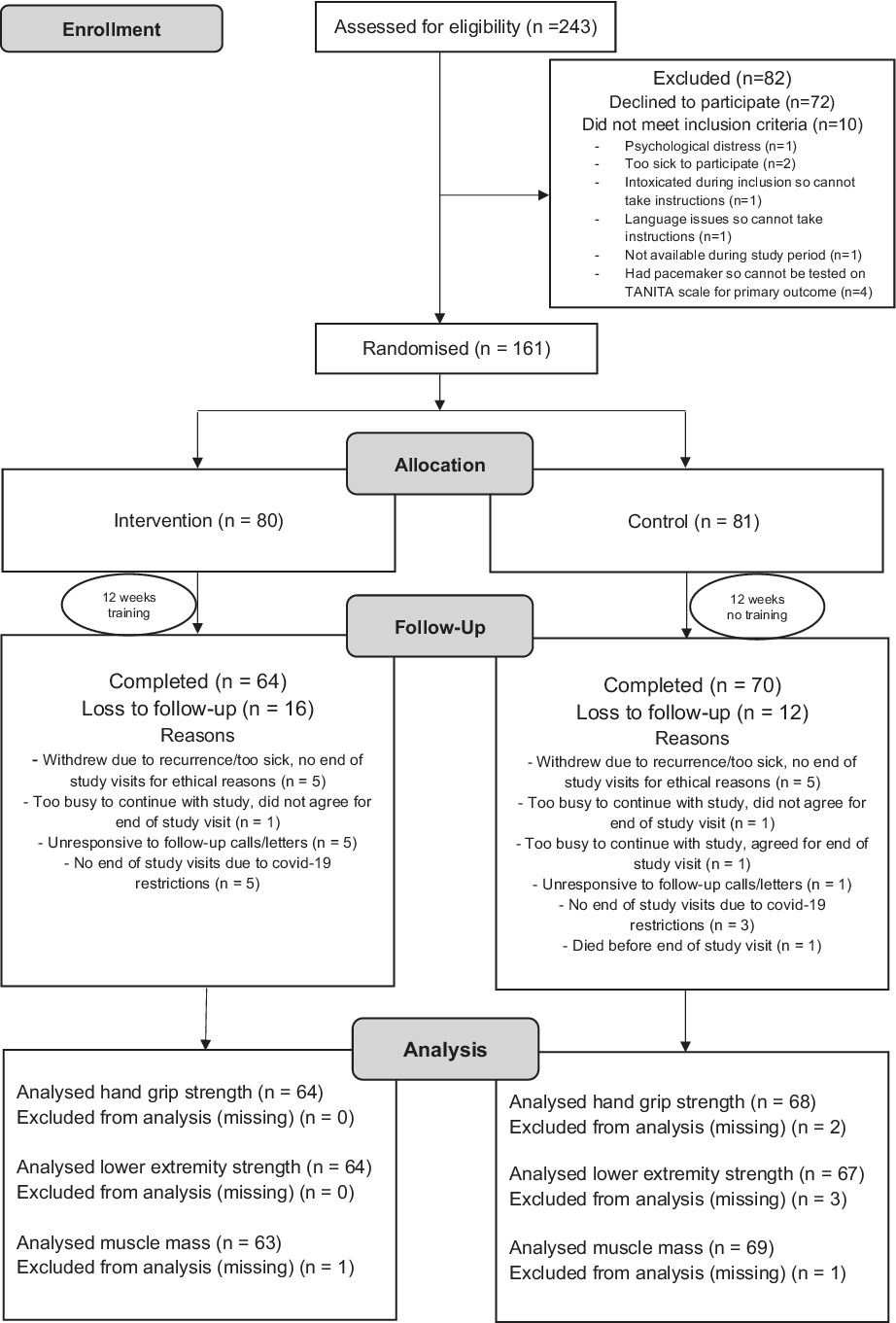
Patients operated for esophageal cancer 12 months earlier benefited from a home-based physical activity exercise program. The 12-week, home-based exercise program with resistance training showed an improvement in lower extremity muscle strength. Home-based physical activity in long-term esophageal cancer survivors may improve rehabilitation.
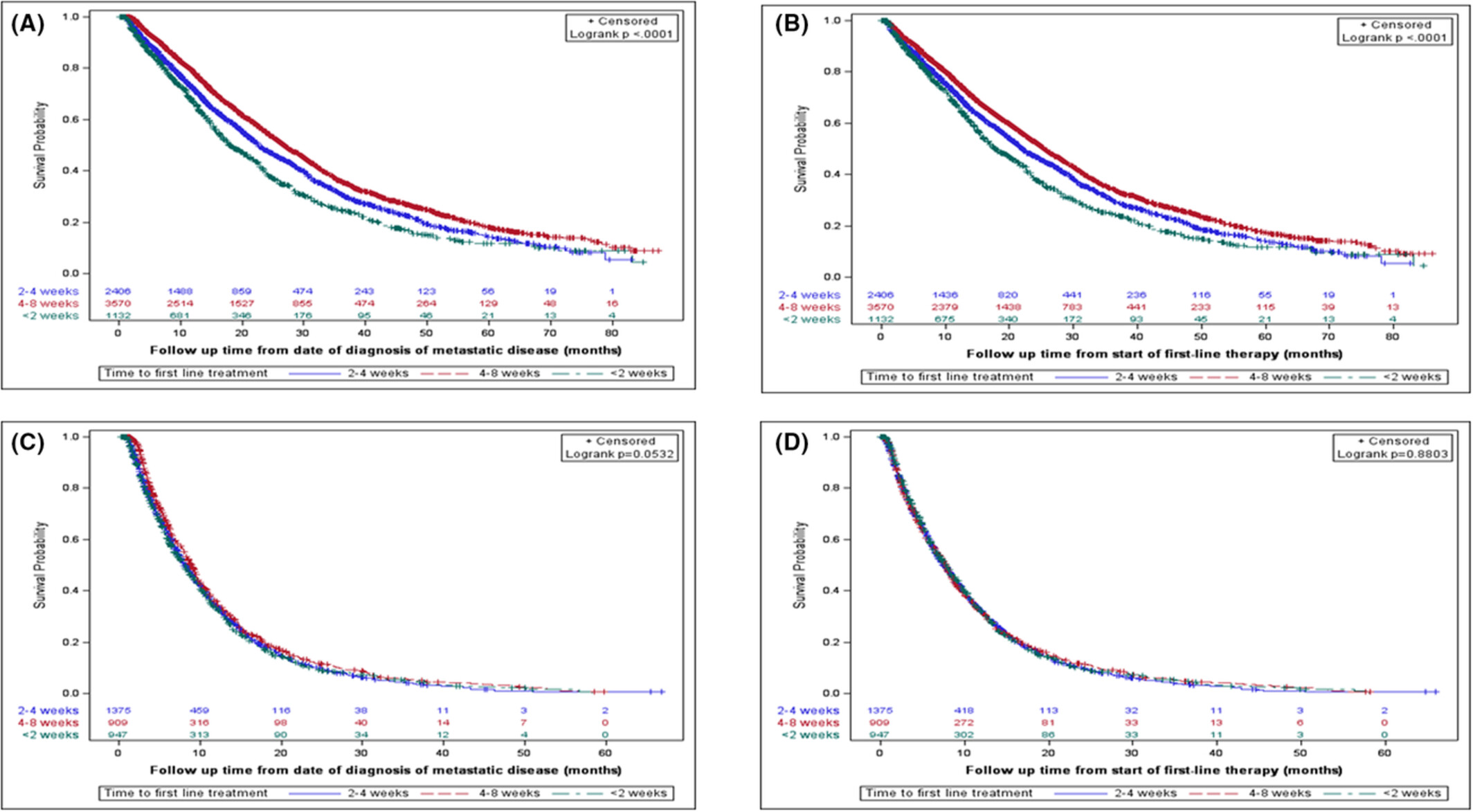
Time to treatment initiation and its impact on real-world survival in metastatic colorectal cancer and pancreatic cancer
- Pages: 3488-3498
- First Published: 17 August 2022
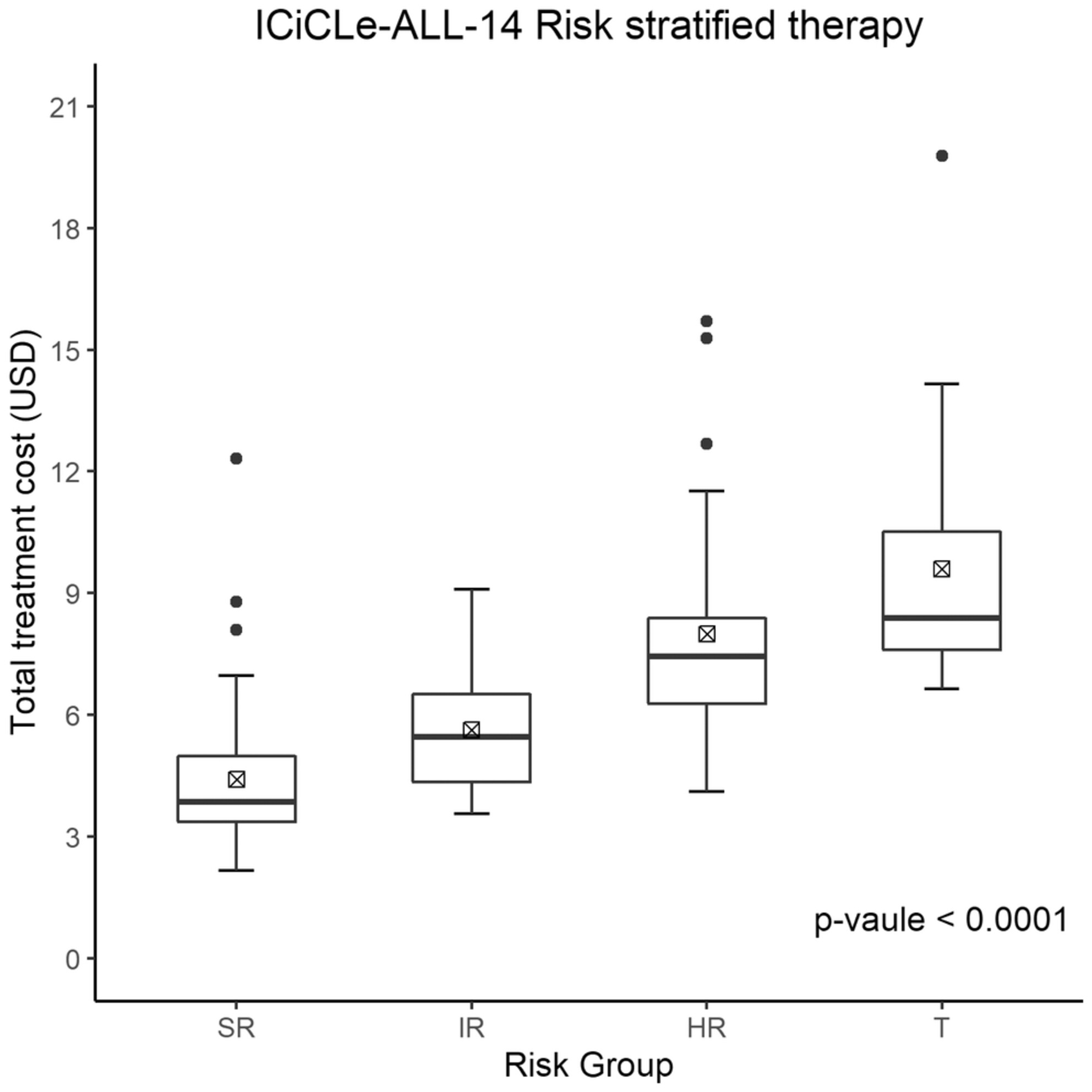
Comparative treatment costs of risk-stratified therapy for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia in India
- Pages: 3499-3508
- First Published: 15 August 2022
Temporal trends in Black-White disparities in cancer surgery and cancer-specific survival in the United States between 2007 and 2015
- Pages: 3509-3519
- First Published: 15 August 2022
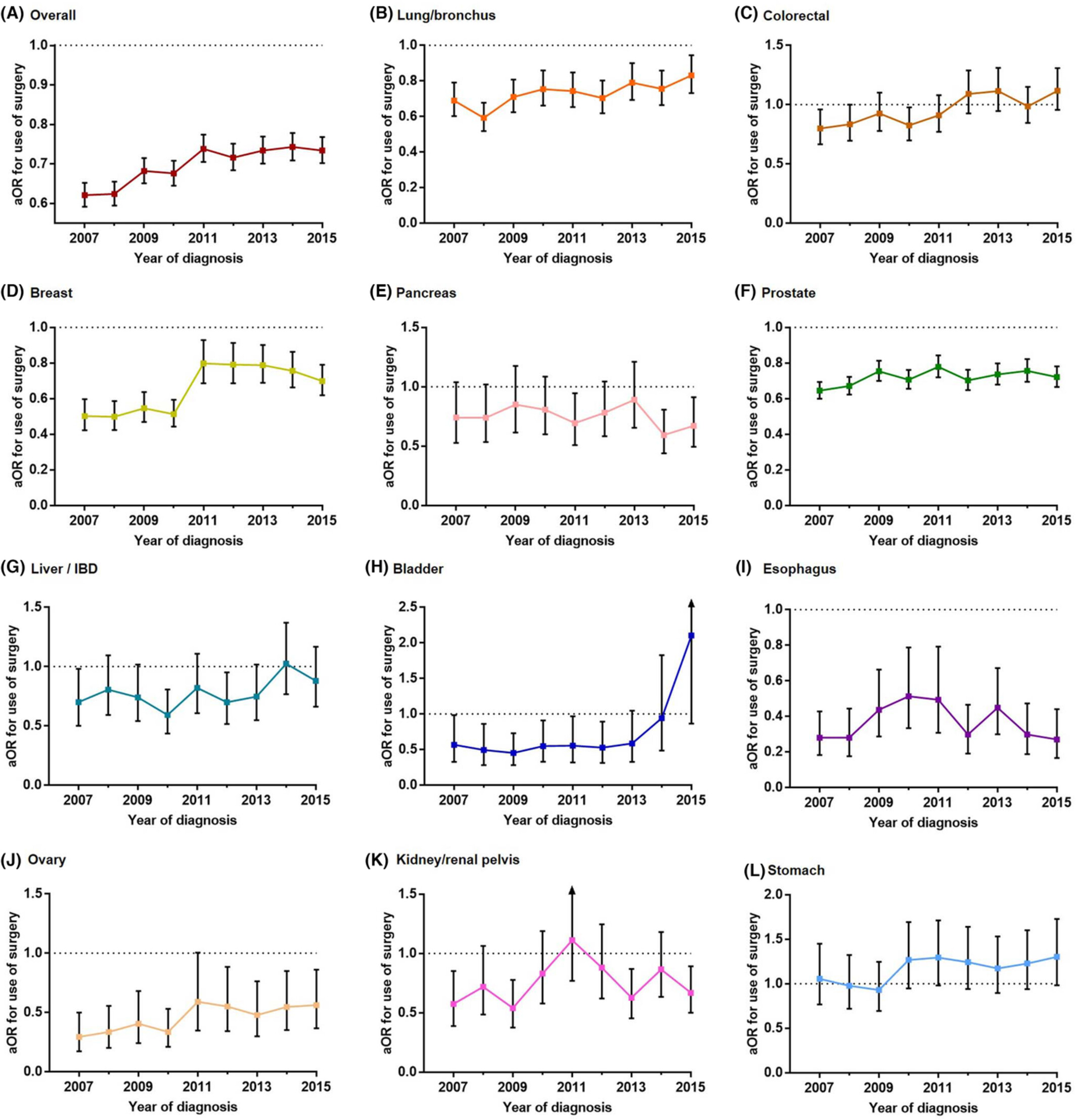
In this study, using a large SEER based data, we examined whether and how racial/ethnic disparities in cancer surgery and outcome have altered after 2009 for overall and 11 deadliest cancers in the US. We found overall significant progress has been made in narrowing the black-white gaps in cancer surgical opportunity and survival over time. " cd_value_code="text
Suicide risk following a new cancer diagnosis among Veterans in Veterans Health Administration care
- Pages: 3520-3531
- First Published: 27 August 2022
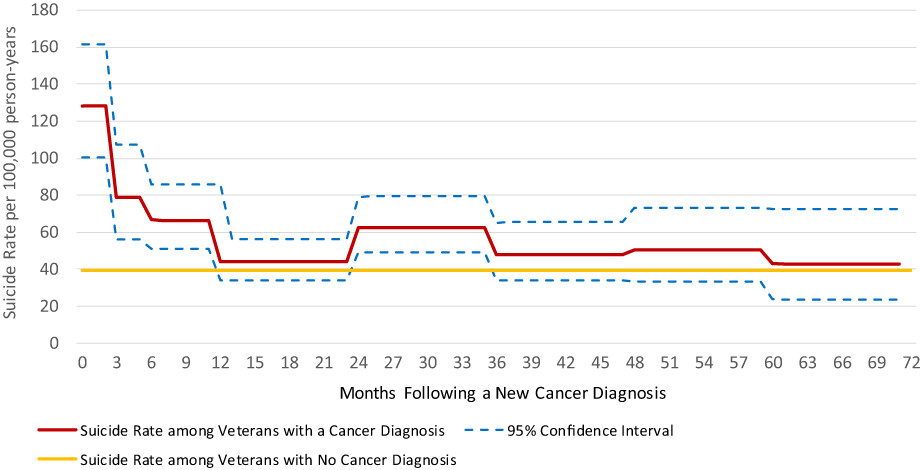
Veterans with a new cancer diagnosis are at an elevated risk for suicide, with the highest risk in the first 3 months following diagnosis. Additional screening and suicide prevention efforts may be warranted for VHA Veterans newly diagnosed with cancer, especially among high-risk subtypes including esophageal, head and neck, and lung cancer and cancers diagnosed at stages 3 and 4.
Willingness to pay for packaging cancer screening of Chinese rural residents
- Pages: 3532-3542
- First Published: 24 August 2022
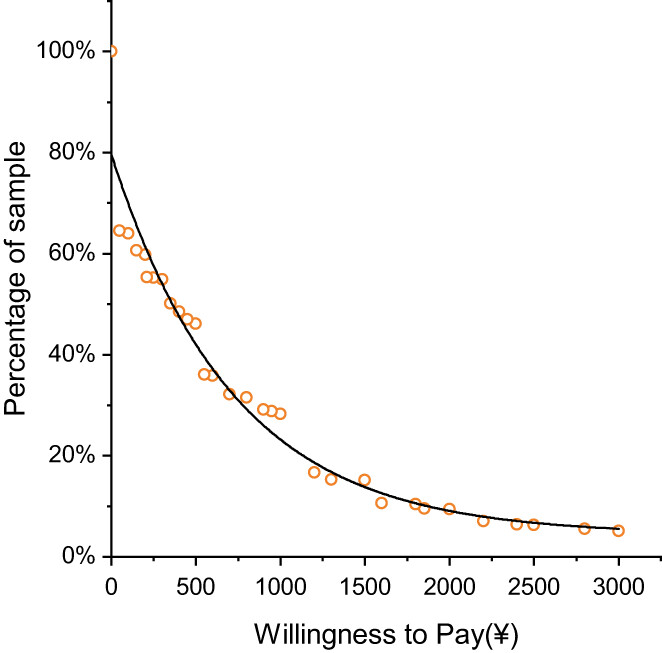
This study is the first to examine the acceptance and willingness to pay (WTP) of rural residents toward packaging cancer screening (PCS). We found that most rural residents were willing to accept free PCS, more than half of them were willing to pay part of the ¥3000 total cost, but their WTP values were low. The appropriate proportion of rural residents to pay for screening costs should be controlled at about 20%, and governments, insurance and other sources are encouraged to actively participate to cover the remaining costs.
Adherence to Guideline-Recommended cancer screening among Utah cancer survivors
- Pages: 3543-3554
- First Published: 27 August 2022
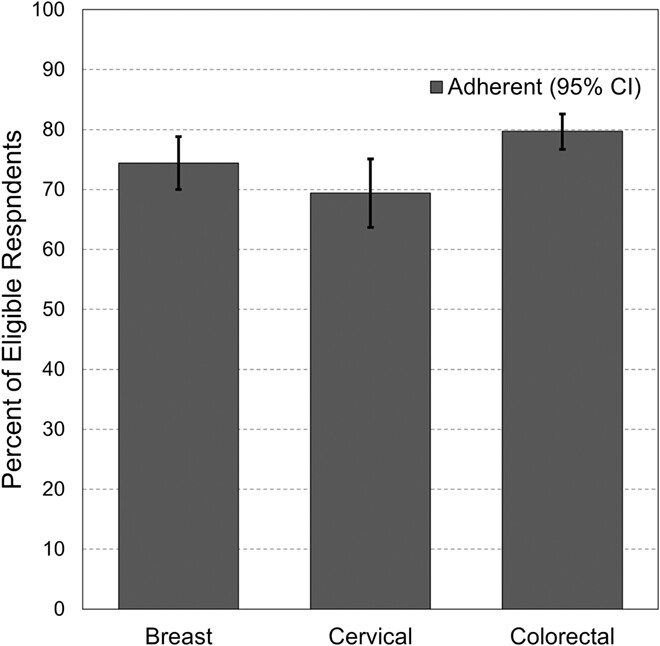
In this paper, we examine adherence to breast, cervical, and colorectal cancer screening guidelines using a population-based sample survey of cancer survivors in Utah. Our findings indicate additional work is needed to ensure all Utah cancer survivors obtain recommended cancer screenings and reduce demographic disparities in screening.
Getting patients back for routine colorectal cancer screening: Randomized controlled trial of a shared decision-making intervention
- Pages: 3555-3566
- First Published: 02 September 2022

Many patients who had their colonoscopies cancelled or postponed due to the COVID-19 pandemic were hesitant to reschedule. This randomized trial found that a brief shared decision making intervention significantly increased colorectal cancer screening uptake and improved the quality of screening decisions over usual care.
Bias reported by family caregivers in support received when assisting patients with cancer-related decision-making
- Pages: 3567-3576
- First Published: 29 August 2022
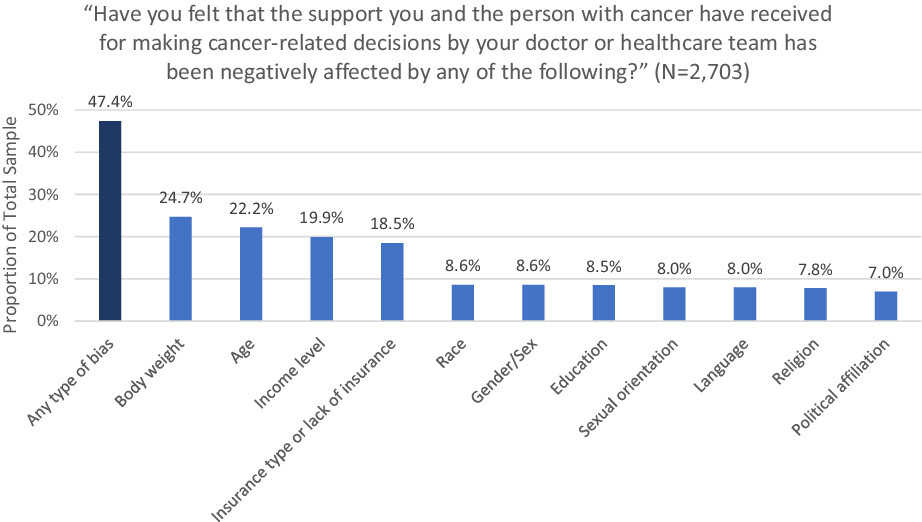
Using data from a nationally representative online panel survey of family caregivers of patients with cancer, we found that nearly half of caregivers involved in their care recipients’ cancer-related decisions reported bias in the healthcare team decision support they and the patient received. Furthermore, experiencing this bias was associated with high caregiver psychological distress.
Risk factors for heightened COVID-19-Related anxiety among breast cancer patients
- Pages: 3577-3588
- First Published: 04 September 2022
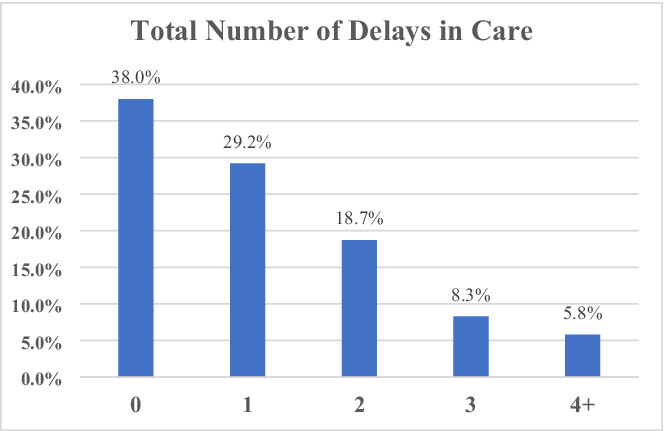
COVID-related anxiety is prevalent in breast cancer patients, particularly in those with a current diagnosis, co-morbidities, care delays and disruptions. It’s important for health care providers to measure and manage pandemic-related anxiety to improve access to care and mental health services, and to assist in COVID risk mitigation.
Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in relation to risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- Pages: 3589-3600
- First Published: 02 September 2022
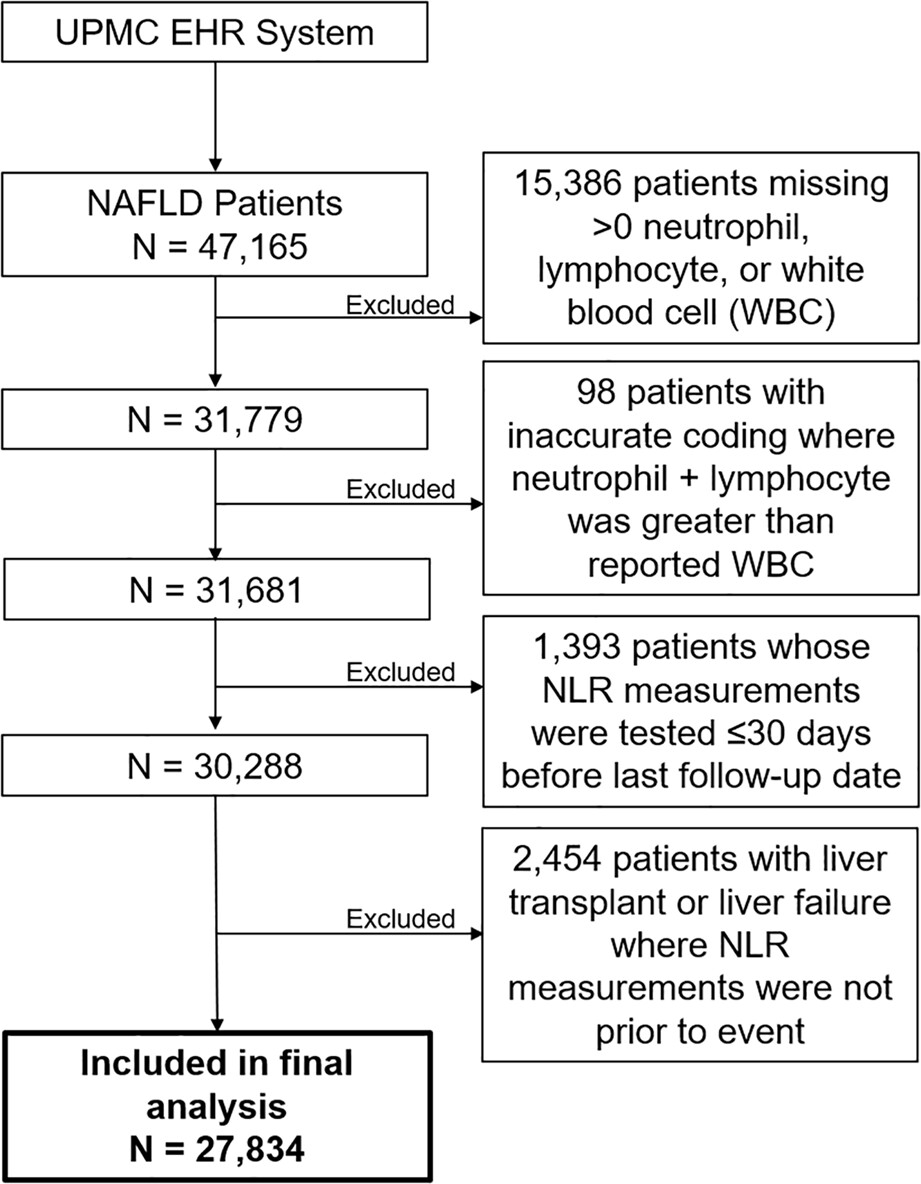
Utilizing the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center (UPMC) electronic health records, we found that higher neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and lower absolute lymphocyte count were associated with higher risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in a cohort of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients. Future studies of the impact of immune response and surveillance through neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio or lymphocyte count on hepatocellular carcinoma incidence are warranted.
Cancer and psychiatric diagnoses in the year preceding suicide
- Pages: 3601-3609
- First Published: 17 September 2022
Impairment of kidney function and kidney cancer: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Pages: 3610-3622
- First Published: 07 September 2022
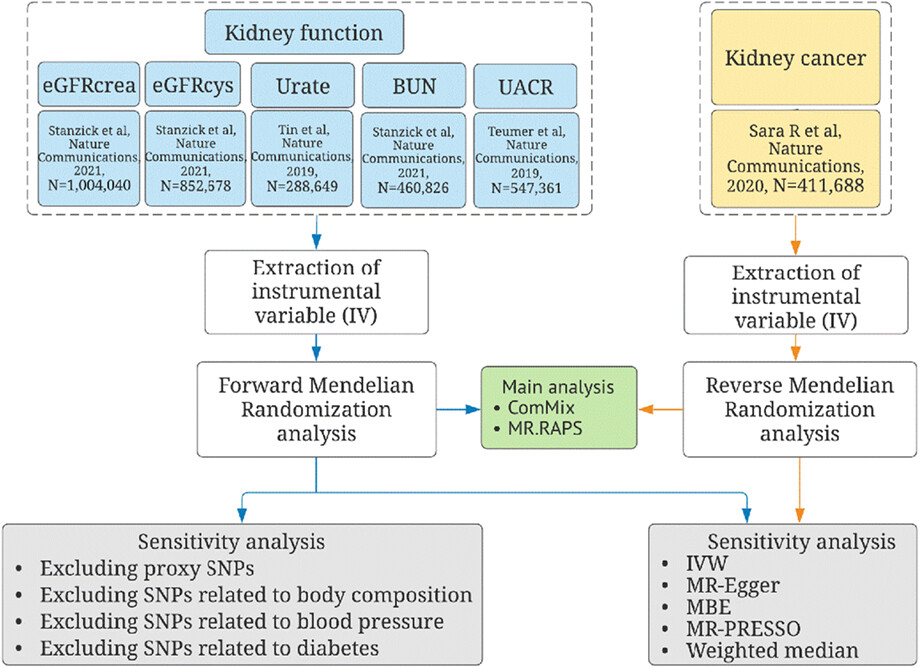
It remains unclear whether kidney cancer and impaired kidney function are causally linked. Using various Mendelian randomization methods, we found eGFRcrea and UACR might be important predictors of the risk of kidney cancer, while eGFRcys might be a key biomarker to identify whether kidney function was harmed, regardless of the partial nephrectomy performed.
Patient-reported symptom burden and impact on daily activities in chronic graft-versus-host disease
- Pages: 3623-3633
- First Published: 16 November 2022
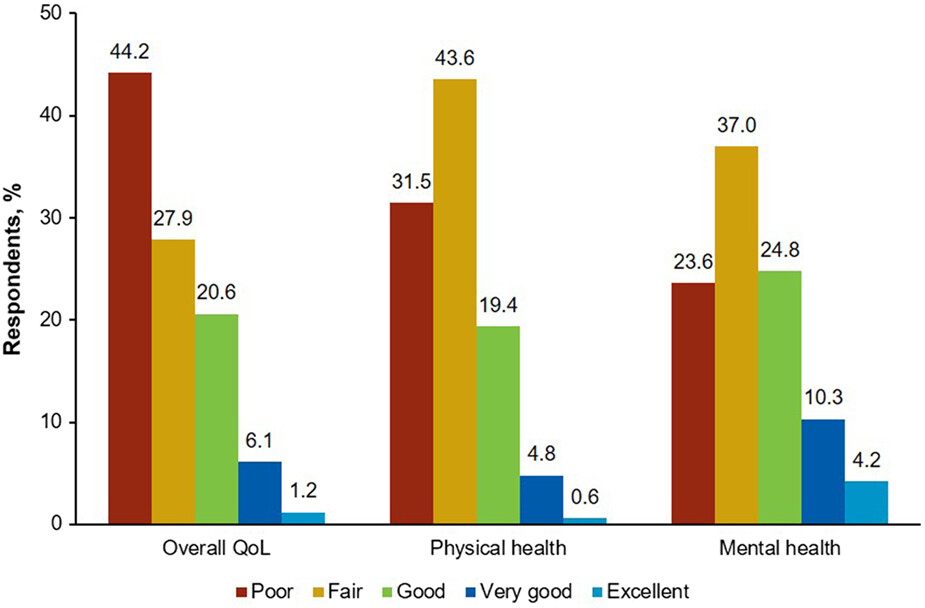
Patients with chronic GVHD experience burdensome symptoms that impair their ability to perform daily activities and reduce their quality of life. There remains an unmet need for effective therapies that alleviate symptoms of chronic GVHD and improve patients’ physical and social function.Respondent-reported condition when chronic GVHD symptoms were at their worst.
Pediatric Early Warning Systems (PEWS) improve provider-family communication from the provider perspective in pediatric cancer patients experiencing clinical deterioration
- Pages: 3634-3643
- First Published: 21 September 2022
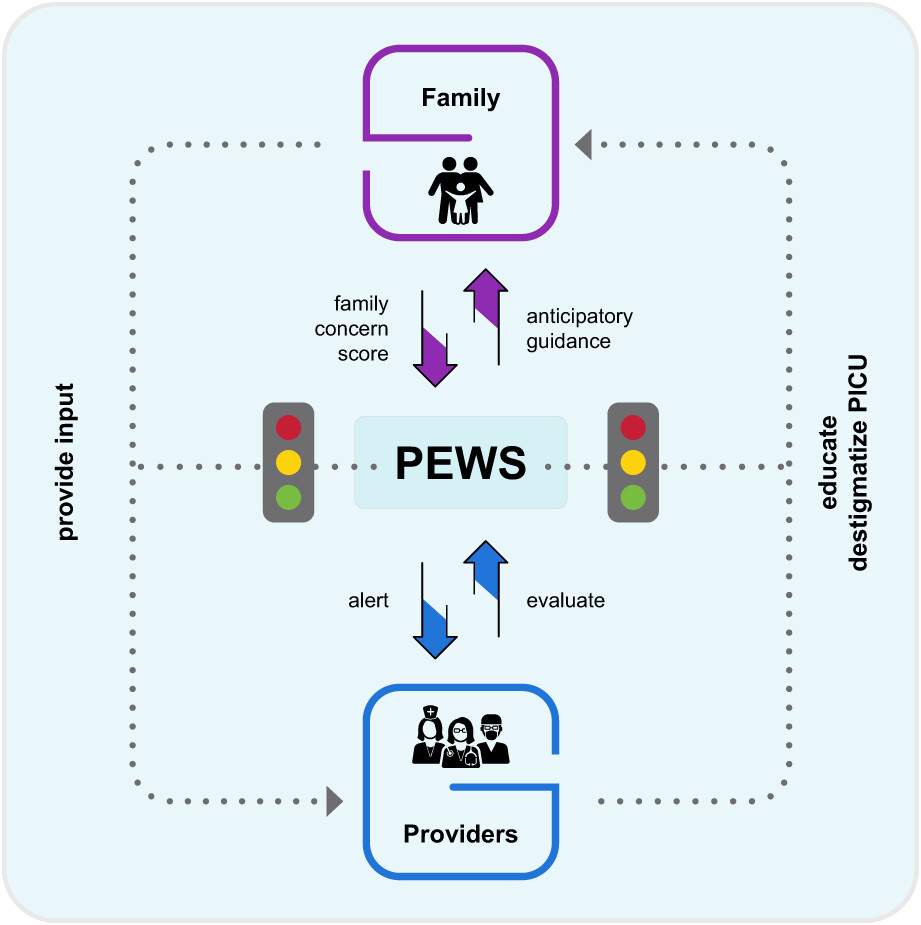
In this qualitative analysis of provider interviews, we identify PEWS as facilitators of communication between providers and patient families in resource-limited and high-resource pediatric oncology hospitals. Our findings demonstrate that providers perceive the family concern component of PEWS allows greater inclusion of patient families as a part of the healthcare team.
Pediatric rhabdomyosarcoma incidence and survival in the United States: An assessment of 5656 cases, 2001–2017
- Pages: 3644-3656
- First Published: 07 September 2022
Regional adaptation of the education in palliative and end-of-life Care Pediatrics (EPEC-Pediatrics) curriculum in Eurasia
- Pages: 3657-3669
- First Published: 08 September 2022
A lack of formal education in pediatric palliative care for clinicians caring for children in resource-constrained settings remains a significant challenge. We successfully adapted the Education in Palliative and End-of-Life Care (EPEC) - Pediatrics course for clinicians in Eurasia and demonstrate the course significantly improved provider knowledge and comfort in palliative care principles.
Clinical care in hepatocellular carcinoma: A mixed methods assessment of experiences and challenges of oncology professionals
- Pages: 3670-3683
- First Published: 15 September 2022
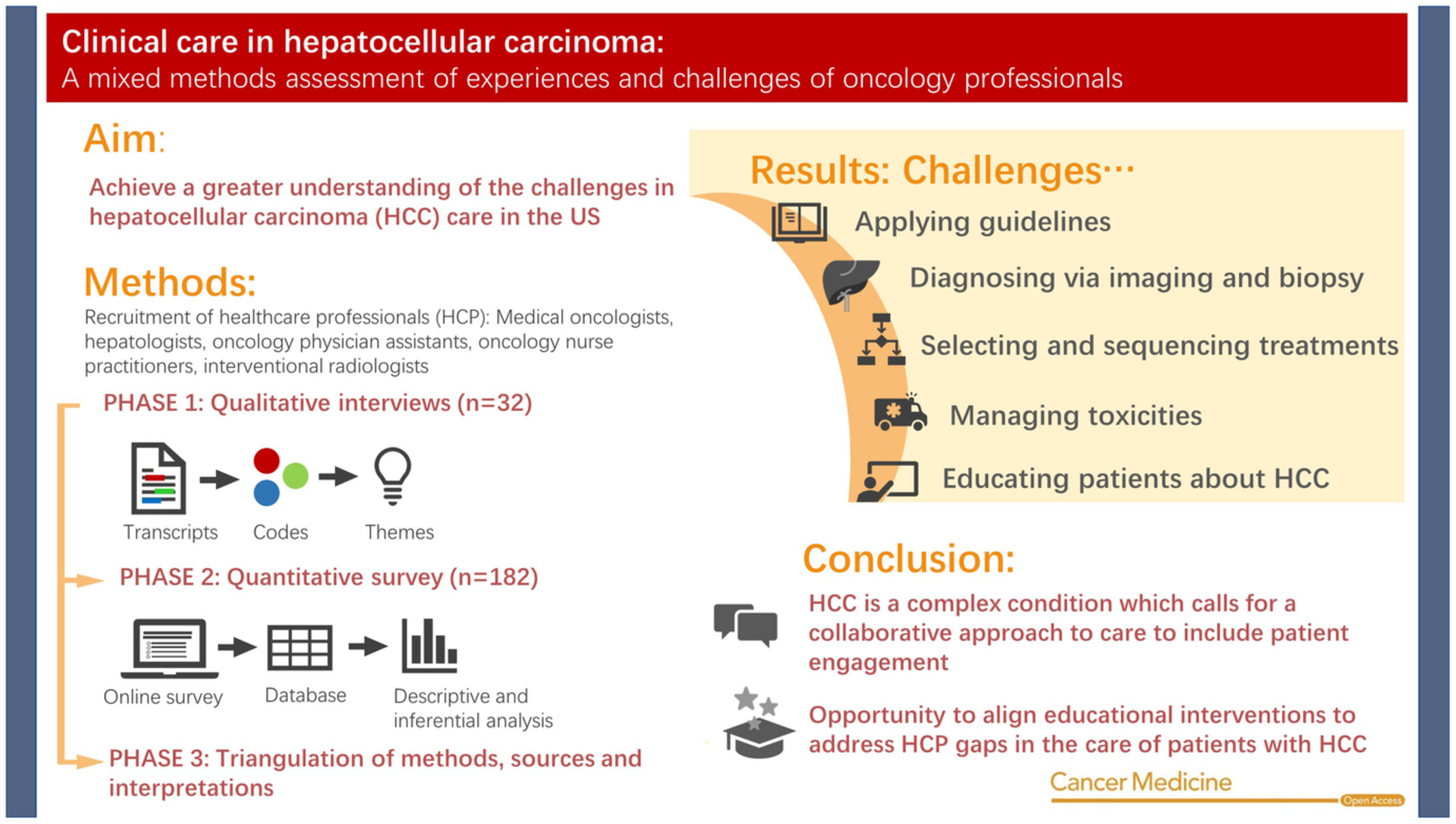
This mixed-methods study assessed the challenges faced by healthcare professionals (HCP) involved in the care ofpatients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Interviews and surveys with HCPs from across the United States indicatedchallenges applying screening and treatment guidelines, diagnosing HCC via imaging and biopsy, selecting andsequencing treatments, managing toxicities and educating patients about HCC. The findings from this needs assessmentwill help identify gaps that exist in knowledge, competence, and skill, so that subsequent educational interventions canbe designed to promote effective collaborative care and encourage patient engagement.
Antimicrobial drug use and the risk of glioma: A case–control study
- Pages: 3684-3695
- First Published: 06 September 2022
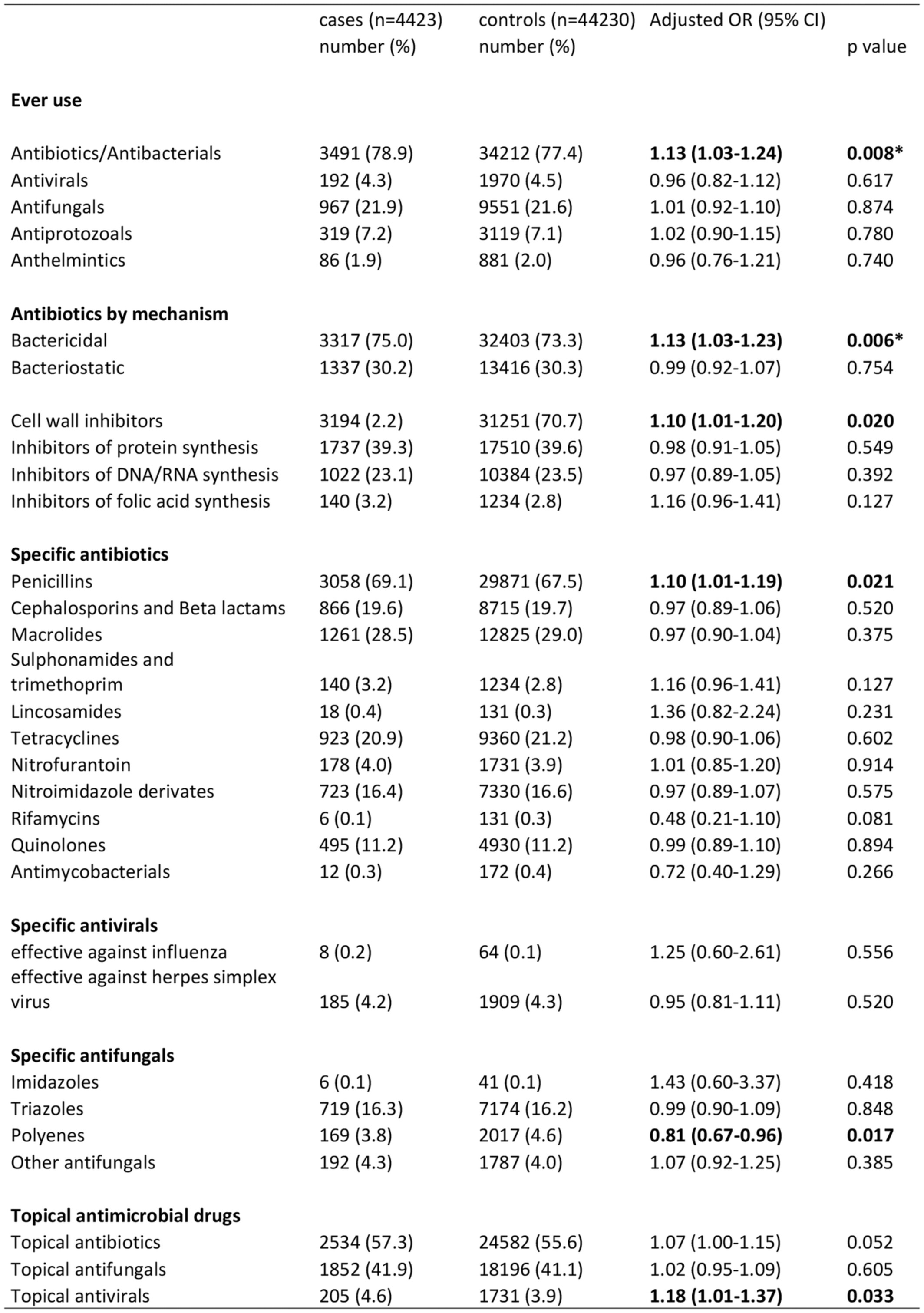
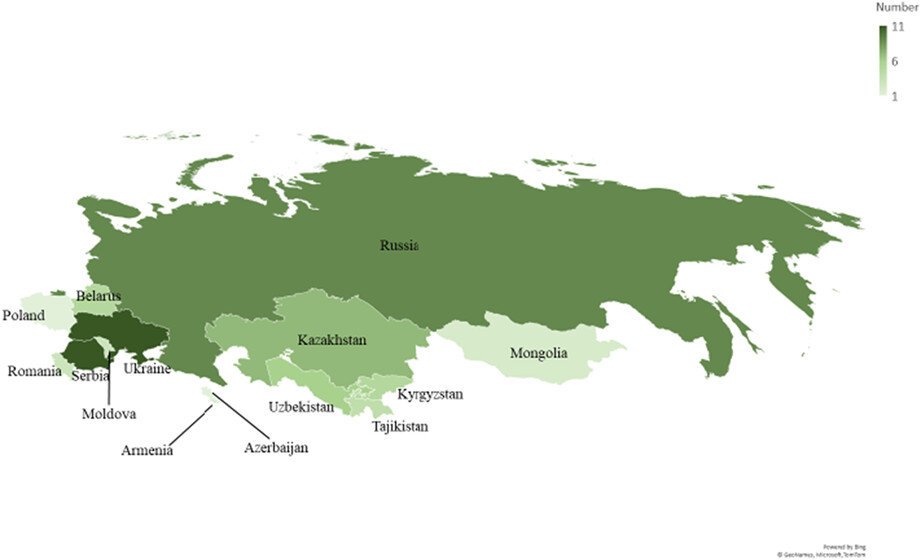
In this large case–control study, we found no substantially increased risk of glioma among users of most antimicrobial drugs. The risk did not increase with increasing numbers of prescriptions received or with increasing time from first use to cancer diagnosis. The use of polyenes yielded a weak inverse association with the risk of glioma, which needs to be confirmed independently.
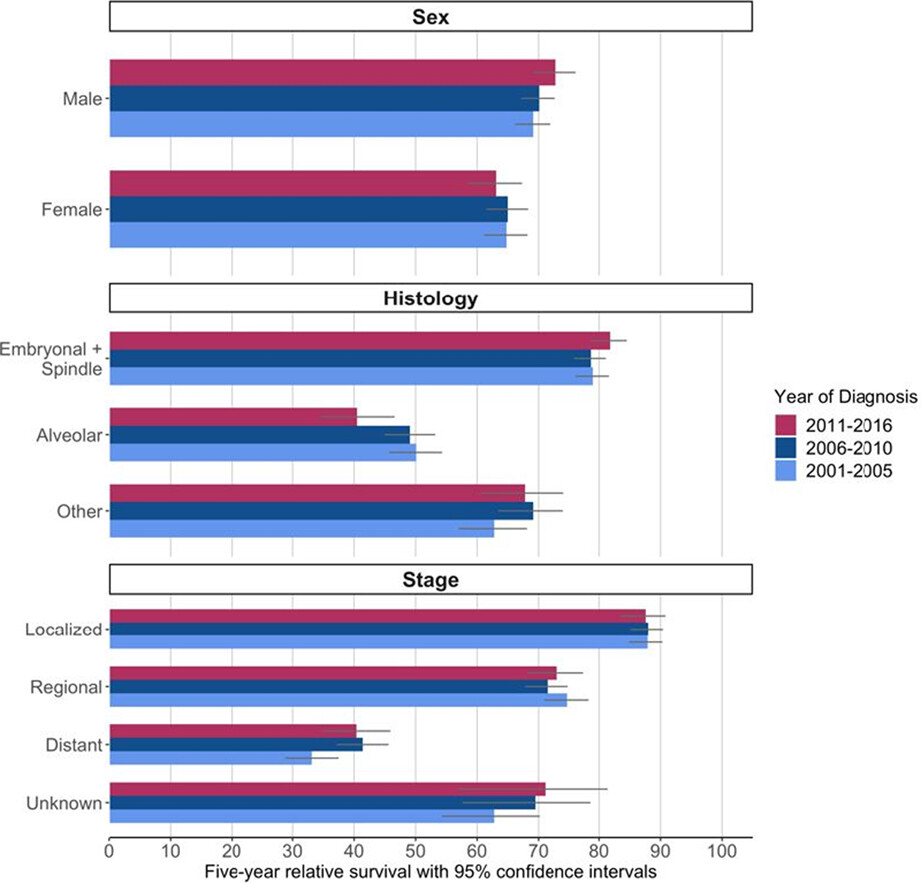
Using period analysis to timely assess and predict 5-year relative survival for colorectal cancer patients in Taizhou, eastern China
- Pages: 3696-3704
- First Published: 05 September 2022
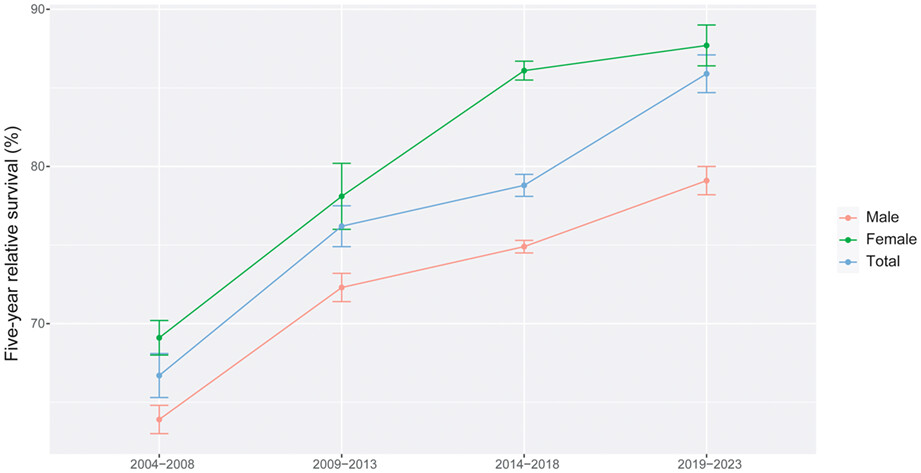
Period analysis is closest to the real 5-year survival. No studies predicted the 5-year relative survival trend of colorectal cancer in China using period analysis. An upward trend of 5-year relative survival for colorectal cancer patients in gender, age at diagnosis, and region in Taizhou City, eastern China.
Gaps in the screening process for women diagnosed with cervical cancer in four diverse US health care settings
- Pages: 3705-3717
- First Published: 15 September 2022
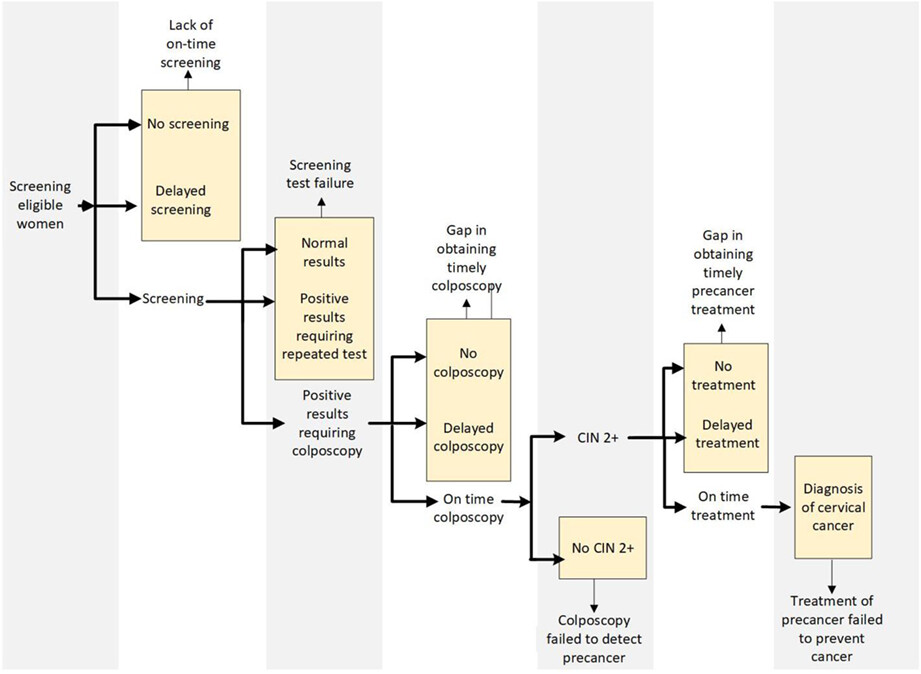
We examined potential care gaps in the cervical cancer screening process among 499 women diagnosed with cervical cancer in the era with increased human papillomavirus testing (2010-2014). Of these women, 46% lacked a screening test in the time window examined, 31% experienced a screening test failure, and 22% experienced a diagnostic/treatment care gap. Our findings demonstrate a continuing need to develop interventions targeting unscreened and under-screened women and improve detection and diagnosis in women undergoing screening and diagnostic follow-up.
Evaluation of an artificial intelligence support system for breast cancer screening in Chinese people based on mammogram
- Pages: 3718-3726
- First Published: 09 September 2022
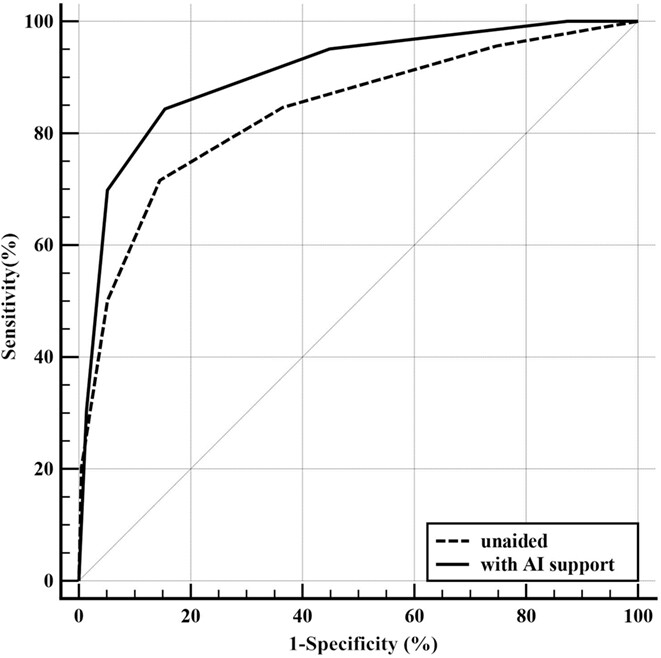
The average AUC was significantly increased from 0.84 to 0.91, average sensitivity significantly increased from 84.77% to 95.07%, and average specificity decreased but no statistical difference was observed when reading with AI support. The average reading time significantly decreased from 215 s per mammogram to 106 s per mammogram when using AI support system.
BRIEF COMMUNICATION
Cancer Prevention
Impact of COVID-19 on the incidence of localized and metastatic prostate cancer among White and Black Veterans
- Pages: 3727-3730
- First Published: 19 August 2022
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Bioinformatics
N6-methyladenosine RNA demethylase FTO regulates extracellular matrix-related genes and promotes pancreatic cancer cell migration and invasion
- Pages: 3731-3743
- First Published: 25 July 2022
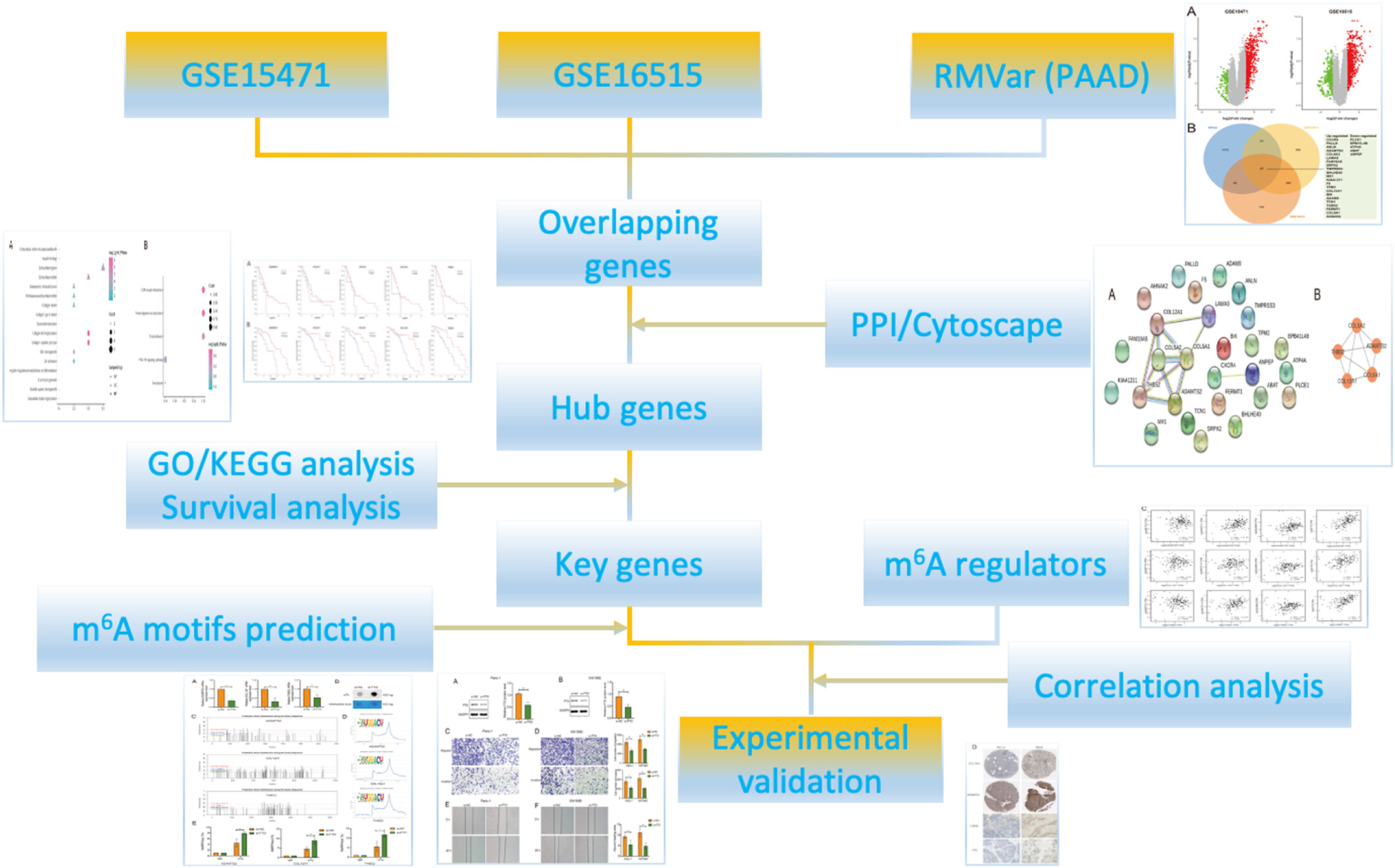
We identified, for the first time, the important role of m6A modification in the regulation of ECM related molecules in pancreatic cancer (PC). Our data revealed that ADAMTS2, COL12A1, and THBS2 may be involved in PC metastasis and progression and that this role is regulated by the m6A demethylation transferase FTO. These molecules hold promise as novel biomarkers for clinical prognosis in PC and may be served as potential therapeutic targets of PC, and this study provides a new perspective for the development of therapeutic strategies for PC.
Using machine learning for mortality prediction and risk stratification in atezolizumab-treated cancer patients: Integrative analysis of eight clinical trials
- Pages: 3744-3757
- First Published: 24 July 2022
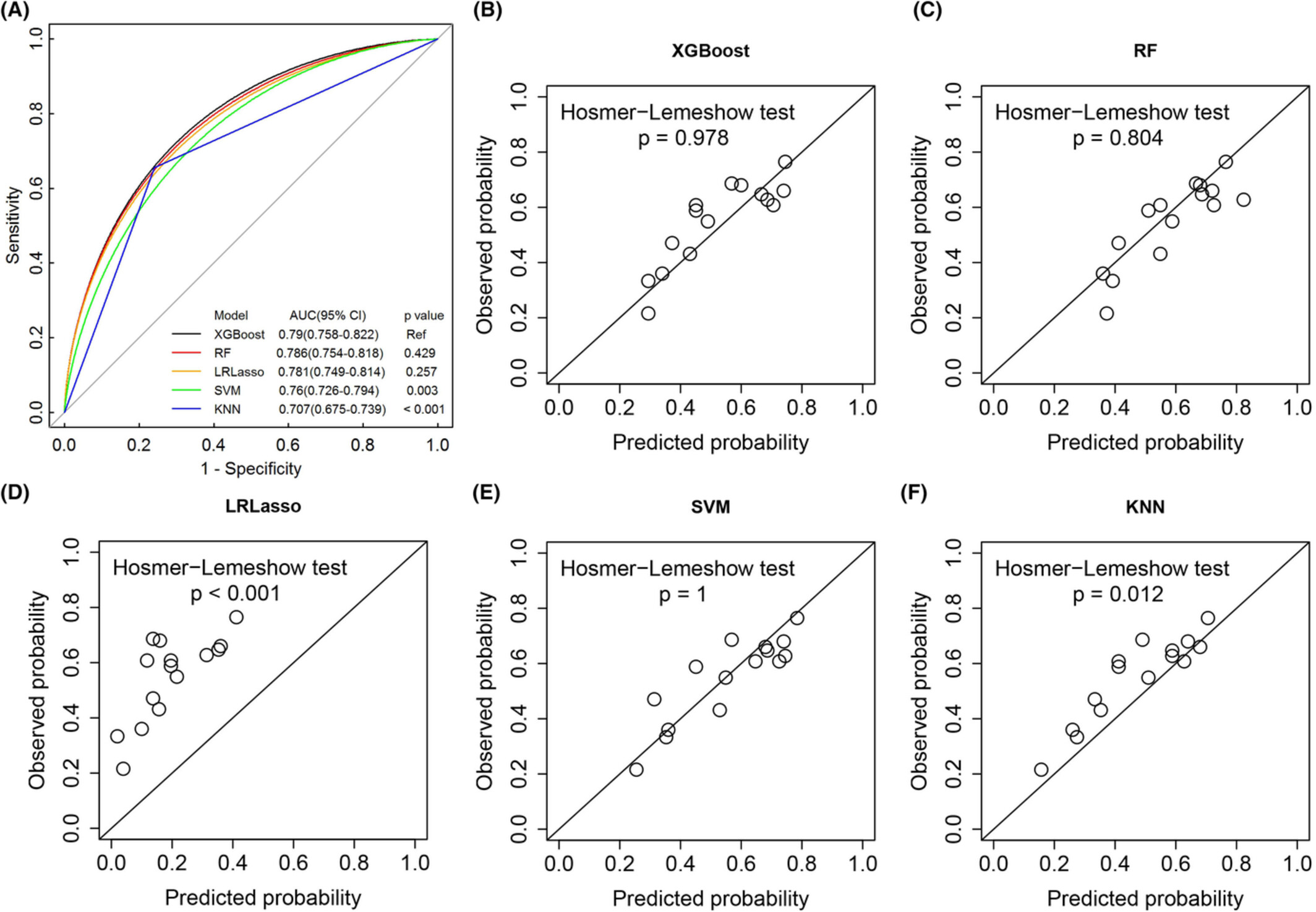
Random forest model with 12 variables could be a useful tool to identify individuals who are most likely to have adverse outcomes (death, disease progression, discontinued study, or discontinued treatment) and clinical benefit from atezolizumab monotherapy. Laboratory tests, and tumor characteristics evaluation performed at baseline before starting immunotherapy may provide an important reference for weighing benefits and risks of therapy.
Exploration of the breast ductal carcinoma in situ signature and its prognostic implications
- Pages: 3758-3772
- First Published: 26 July 2022
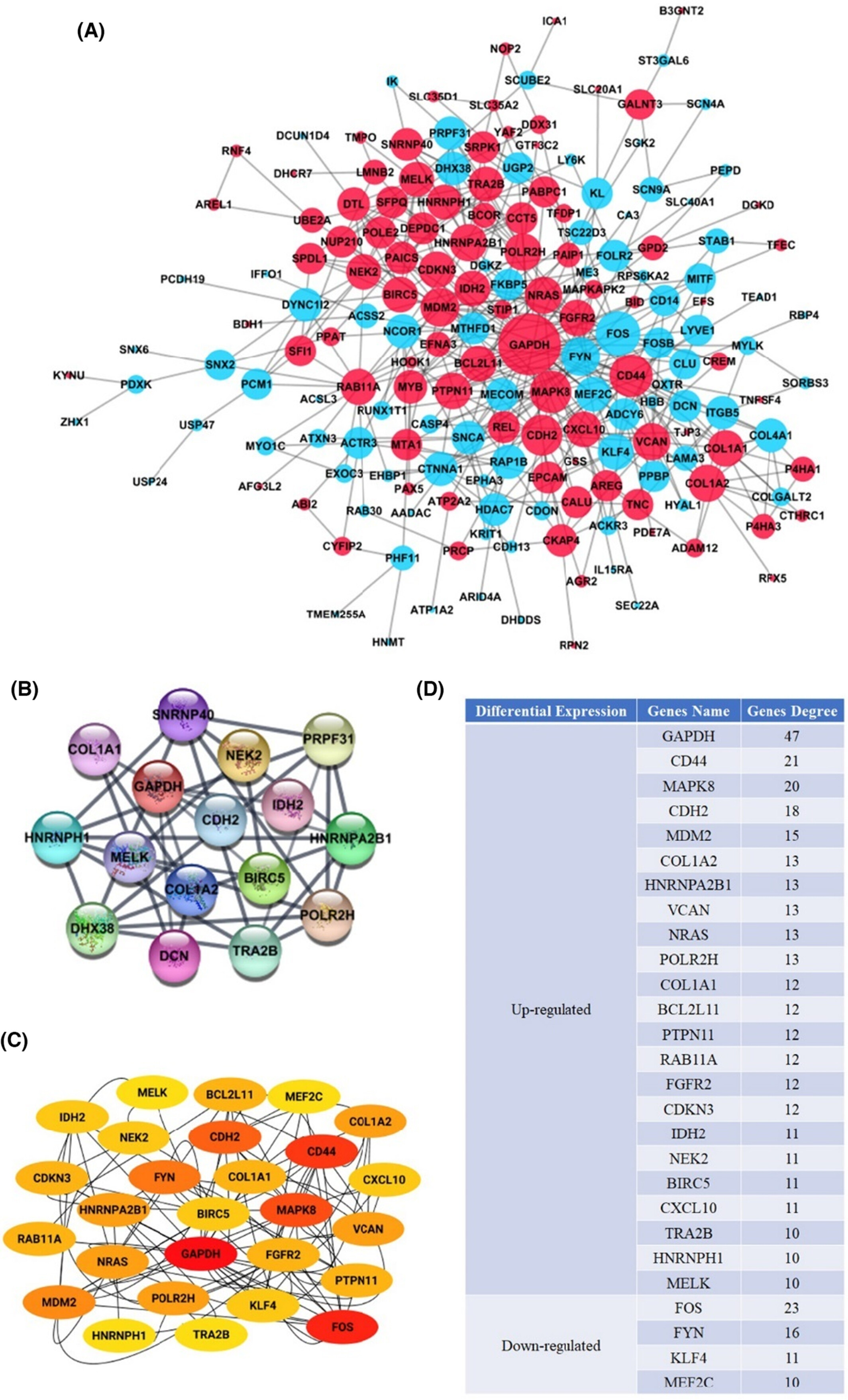
Following the implementation of breast screening programs, the occurrence of Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) as an early type of neoplasia has increased.The current investigation verified the six core genes (containing GAPDH, CDH2, BIRC5, NEK2, IDH2, and MELK) signatures for prospective DCIS biomarkers, which may aid clinical decision-making for individual care.
A hypoxia-related lncRNA model for prediction of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma prognosis
- Pages: 3773-3785
- First Published: 03 August 2022
ITGA5 and ITGB1 contribute to Sorafenib resistance by promoting vasculogenic mimicry formation in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Pages: 3786-3796
- First Published: 10 August 2022
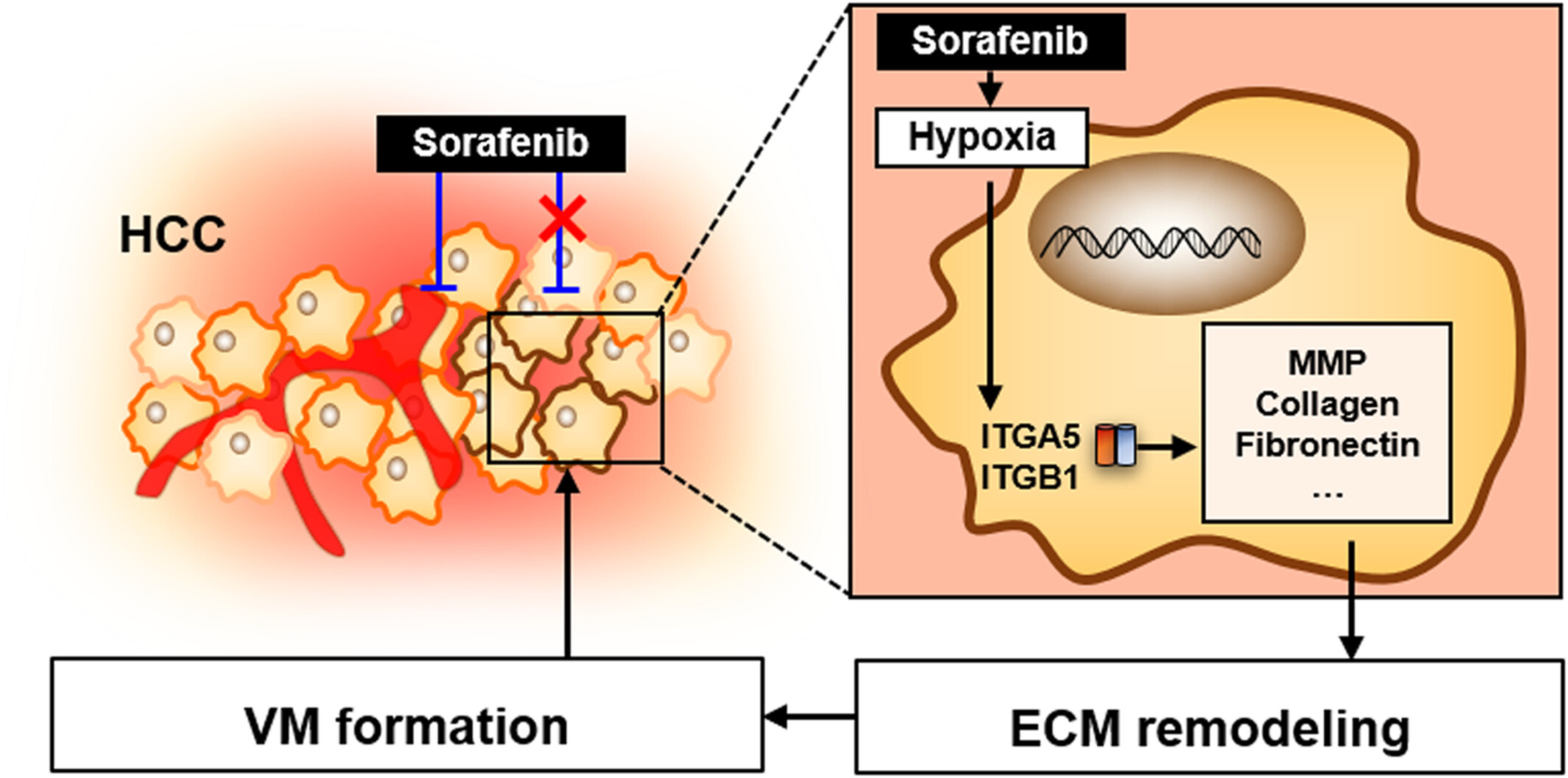
Hypoxia associated vascular mimicry account for non-response to Sorafenib treatment in hepatocellular carcinom (HCC) patients. integrins A5 and B1 may serve as effective predictors of HCC patients' outcome after Sorafenib treatment, which also provides a new target for HCC patients resistant to Sorafenib.
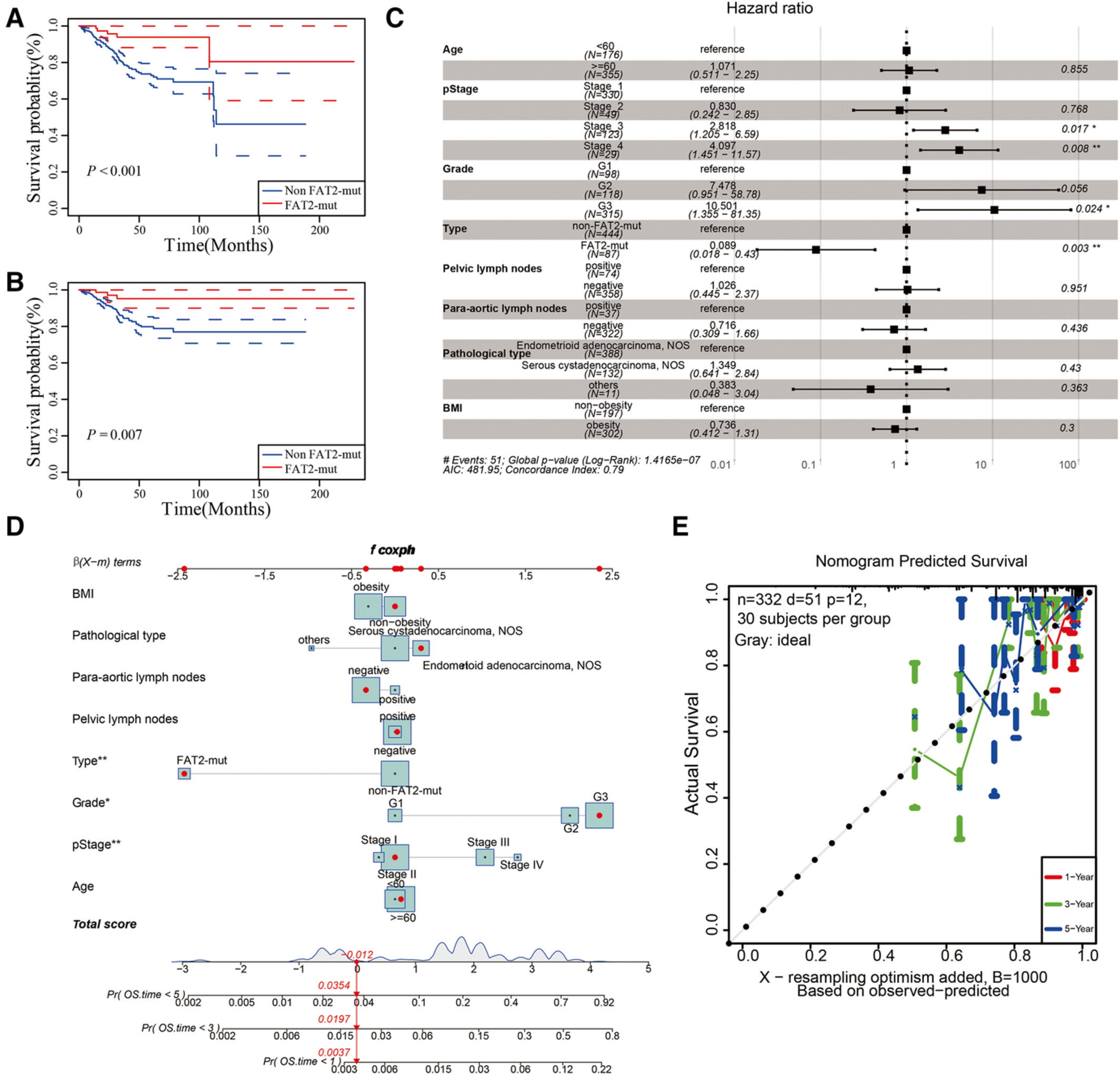
FAT2 mutation is associated with better prognosis and responsiveness to immunotherapy in uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma
- Pages: 3797-3811
- First Published: 07 August 2022
Identification of three small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) as potential prognostic markers in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- Pages: 3812-3829
- First Published: 16 August 2022
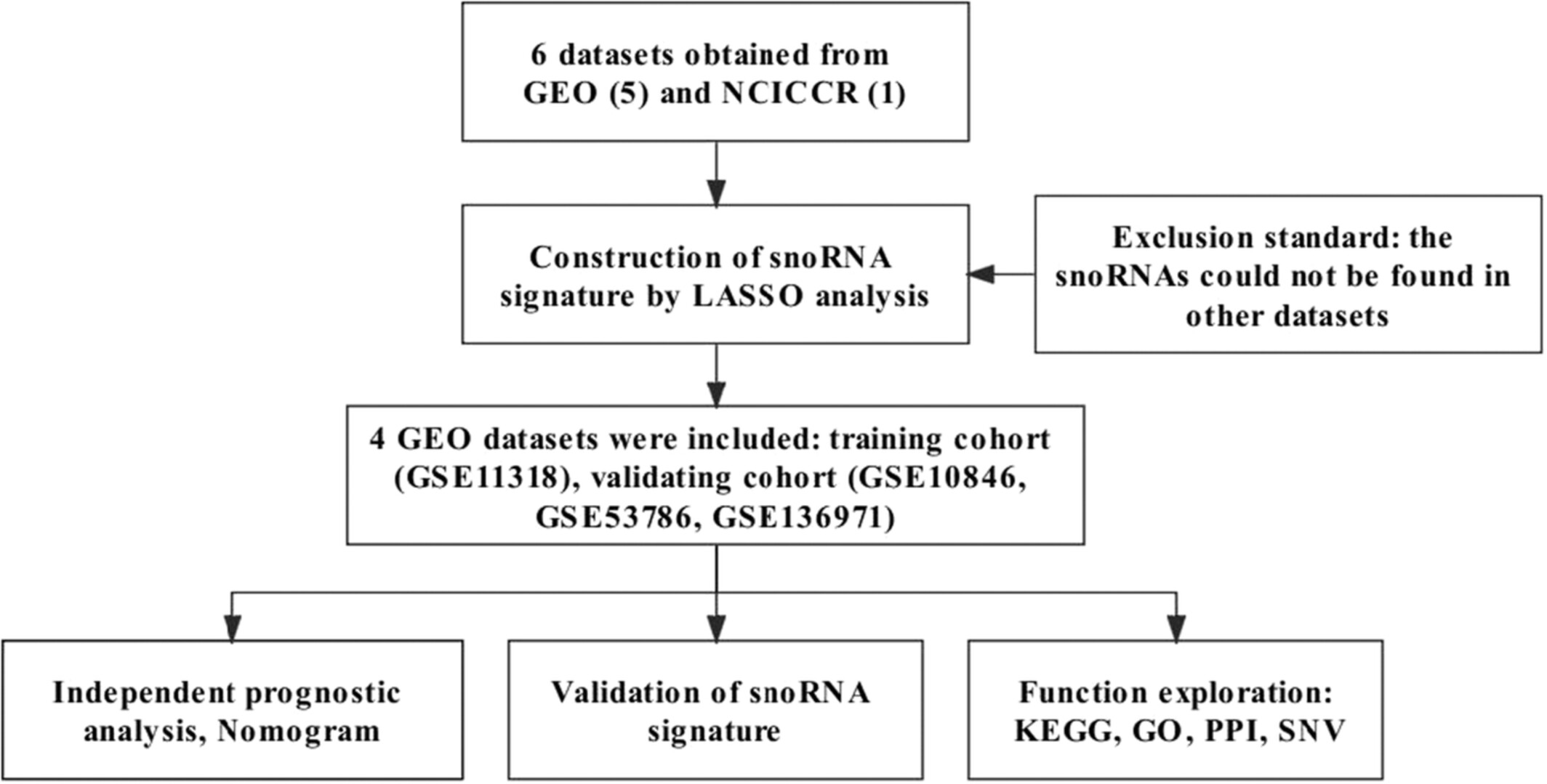
A comprehensive analysis was performed to select significant survival-related snoRNAs in DLBCL. Collectively, a prognostic signature based on three snoRNAs (SNORD1A, SNORA60, and SNORA66) was established for DLBCL patients. Also, we found snoRNA co-expressed genes that were mostly involved in ribosome-correlated pathways and processes, and the interaction of ribosomal proteins (RPL23, RPL10A) and p53.
Identification of thioredoxin domain containing family members' expression pattern and prognostic value in diffuse gliomas via in silico analysis
- Pages: 3830-3844
- First Published: 15 September 2022
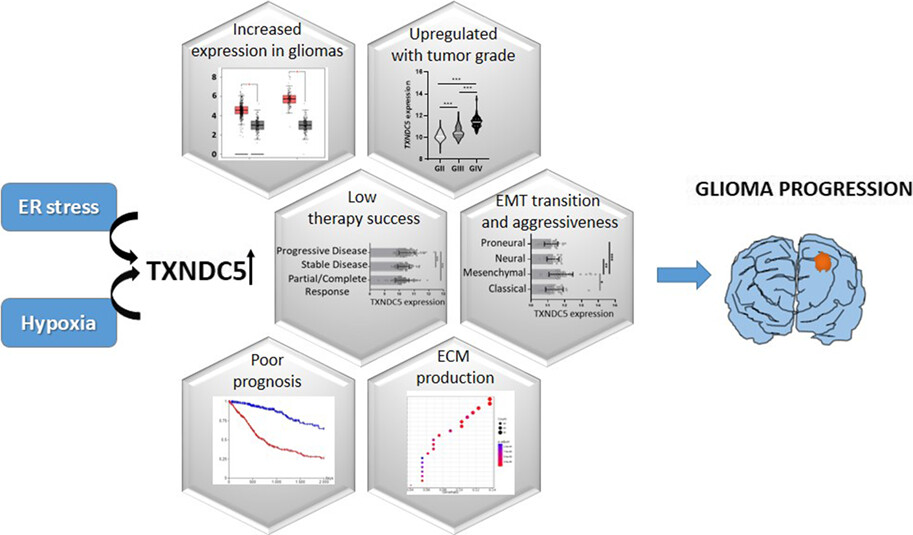
Thioredoxin domain-containing (TXNDC) family genes are potent antioxidants that also regulate protein folding. Among these genes, TXNDC5 is known to play a pro-survival function under stress conditions which prompted us to investigate it further in cancer context. Our analysis revealed that TXNDC5 levels are elevated in glioma samples and its increment is correlated with an aggressive phenotype, low therapy success and poor prognosis. In addition, ER stress and hypoxia were found to be positive regulators of TXNDC5 expression which in turn promoting ECM-related gene expression. Overall, TXNDC5 was determined to be a potential prognostic marker and target for therapy in glioma patients.