Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW
Clinical Cancer Research
Recent advances in surgical strategies and liver transplantation for hepatoblastoma
- Pages: 3909-3918
- First Published: 16 November 2022
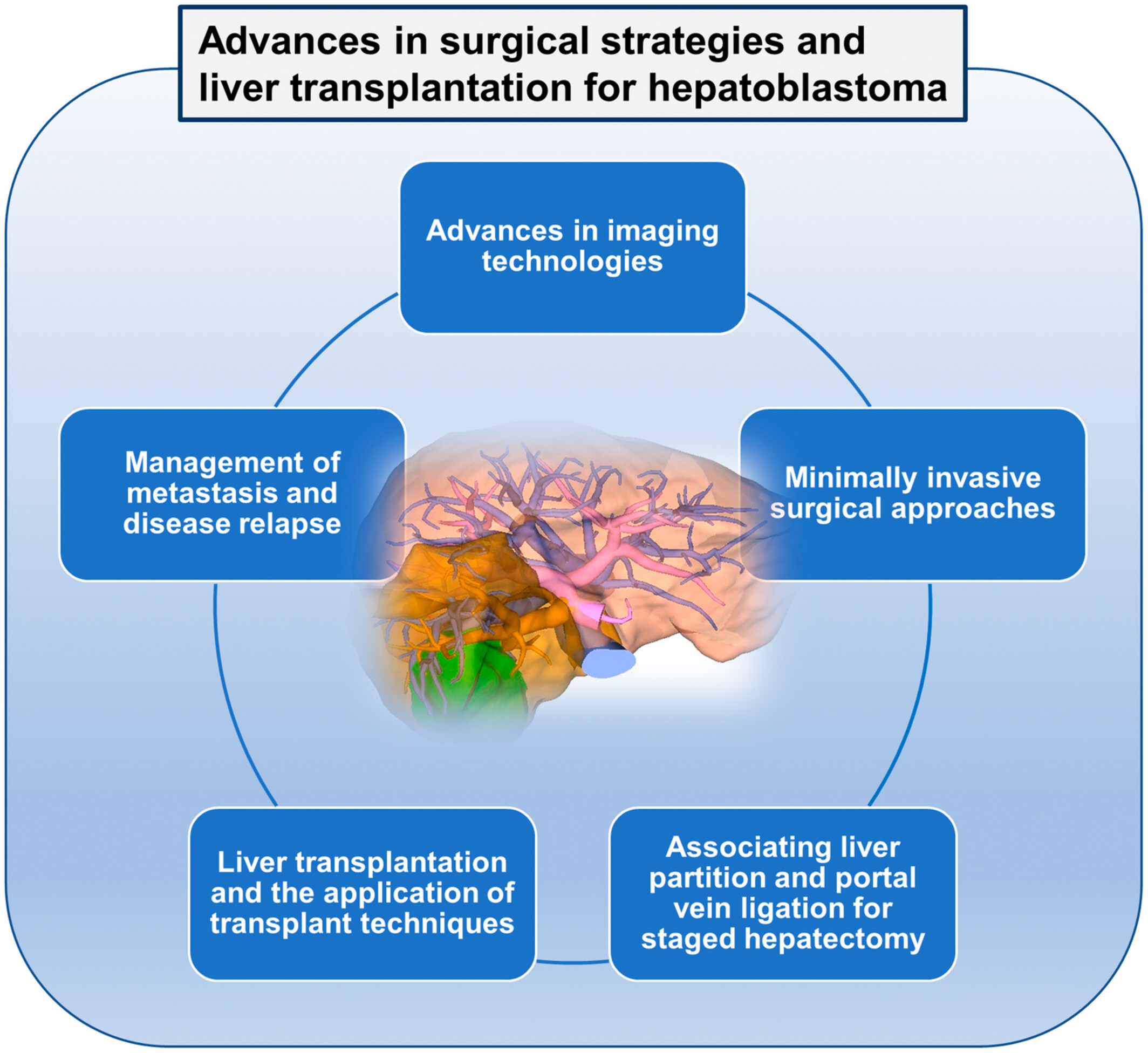
Hepatoblastoma is the most common malignant liver tumor in children. In this review, we describe the latest technologies and techniques for the surgical management of hepatoblastoma, including new imaging technologies, minimally invasive approaches, and the application of associating liver partition portal vein ligation for staged hepatectomy. We also discuss the current role of liver transplantation, liver transplant-related surgical techniques, and management of metastatic hepatoblastoma.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Clinical Cancer Research
Circulating cytokines allow for identification of malignant intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas
- Pages: 3919-3930
- First Published: 24 July 2022
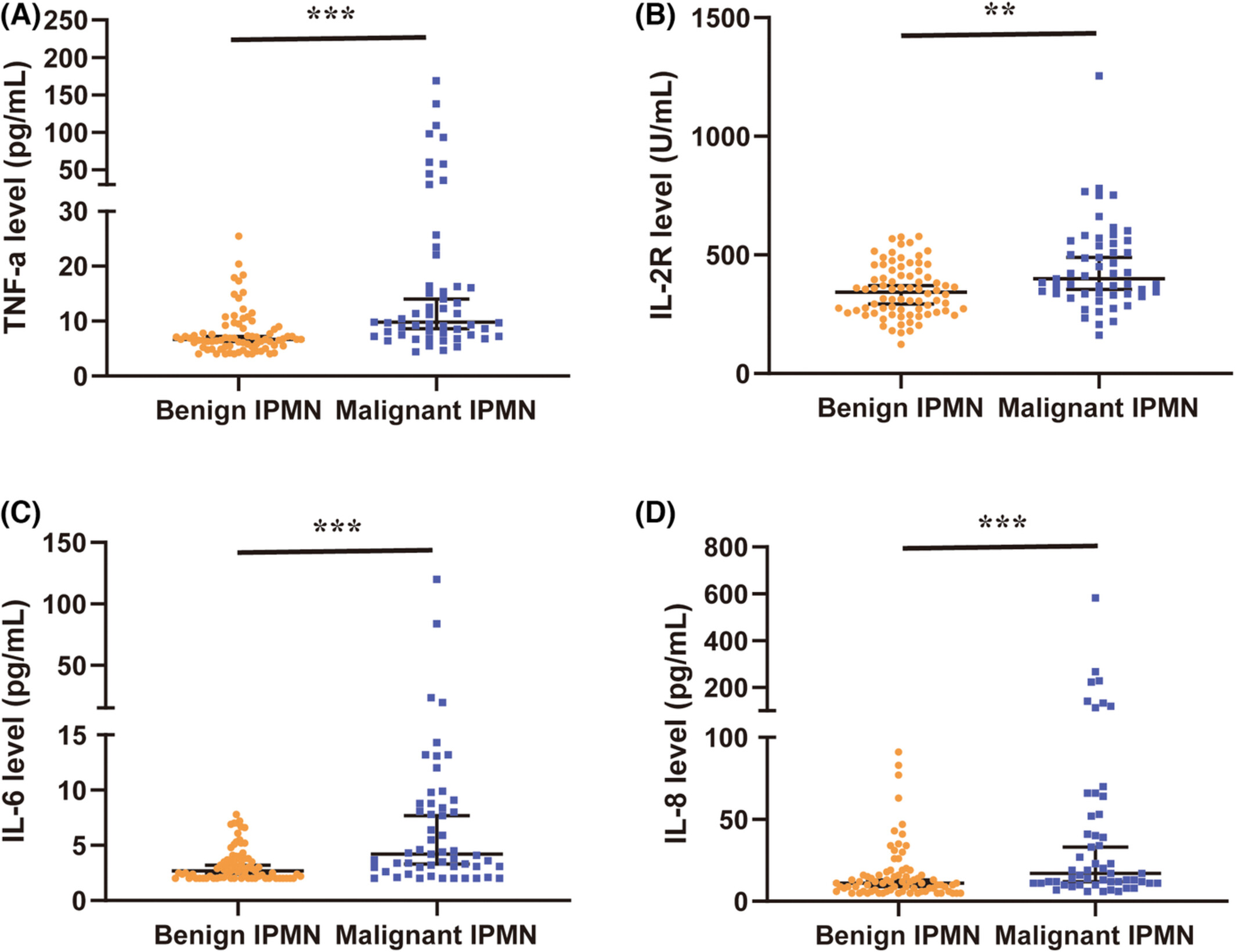
The serum TNF-, IL-2R, IL-6, and IL-8 in malignant IPMNs are significantly higher than benign ones. Circulating cytokine score (CCS) was calculated and proved as an independent predictor.A novel nomogram incorporating CCS showed a remarkable diagnostic performance for distinguishing malignant IPMNs.
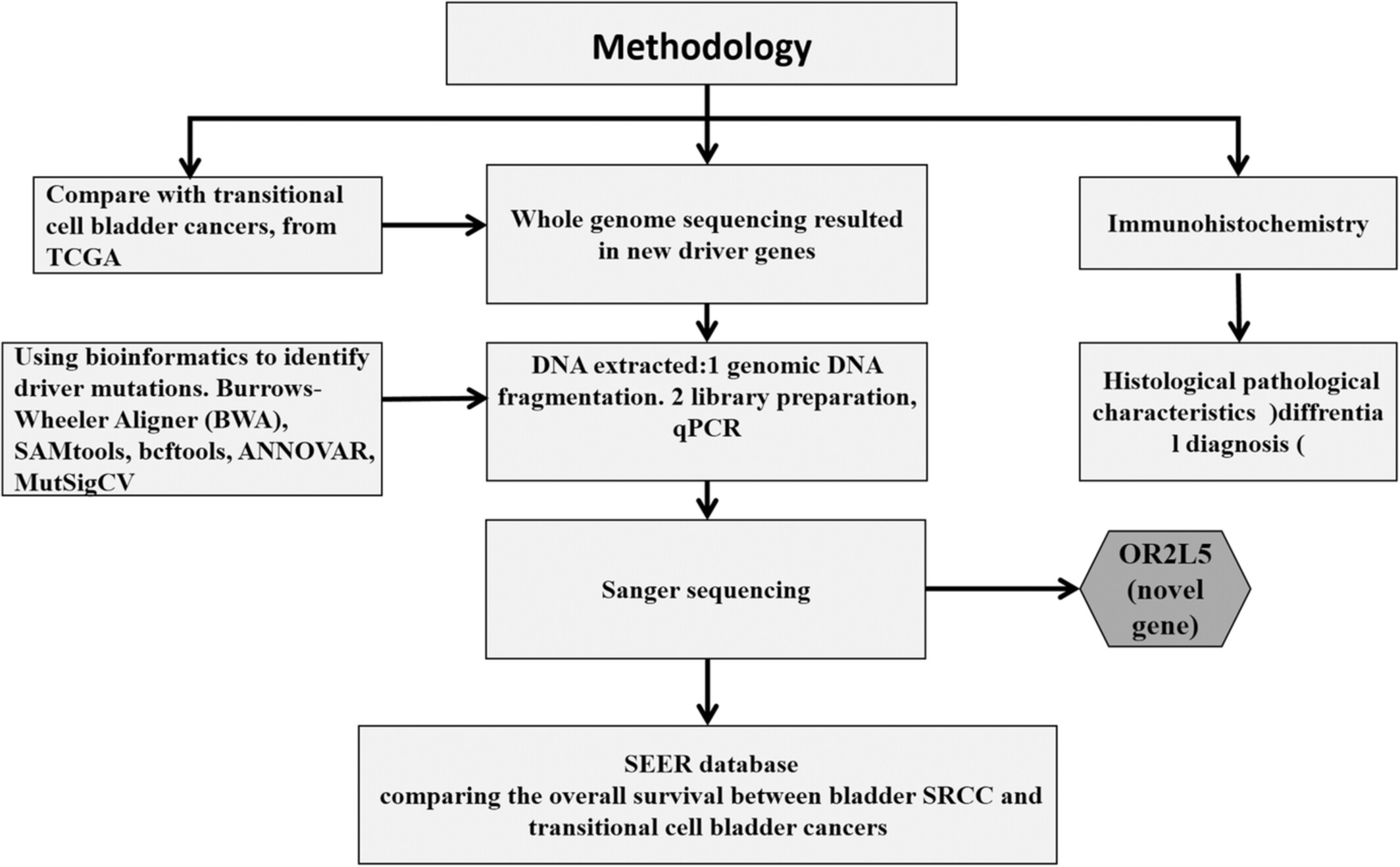
Molecular genetic and clinical characteristic analysis of primary signet ring cell carcinoma of urinary bladder identified by a novel OR2L5 mutation
- Pages: 3931-3951
- First Published: 11 August 2022
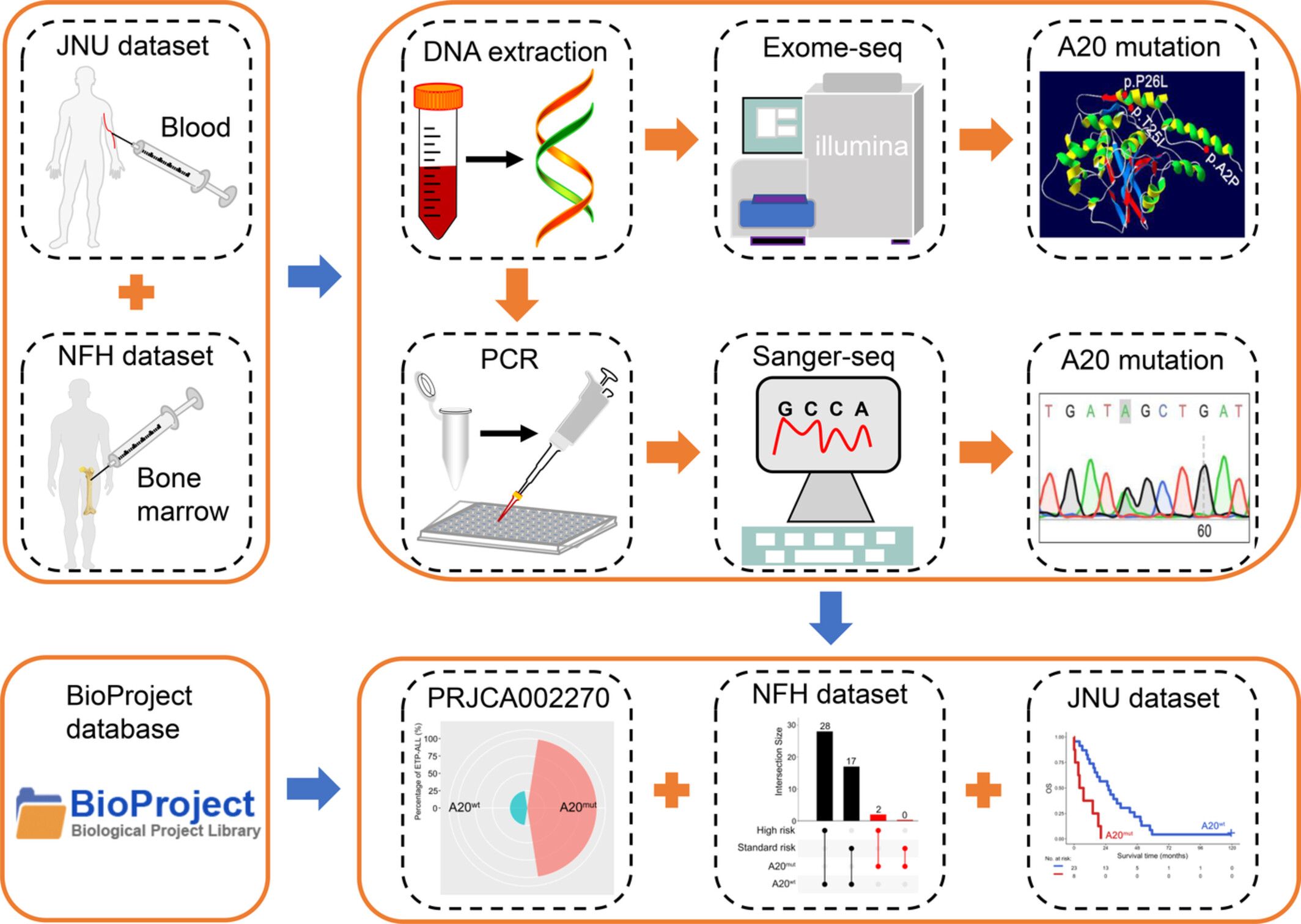
TNFAIP3 mutation is an independent poor overall survival factor for patients with T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Pages: 3952-3961
- First Published: 03 September 2022
Combining expression of RNF43 and infiltration level of CD163+ tumor associated macrophage predicts prognosis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- Pages: 3962-3971
- First Published: 12 September 2022
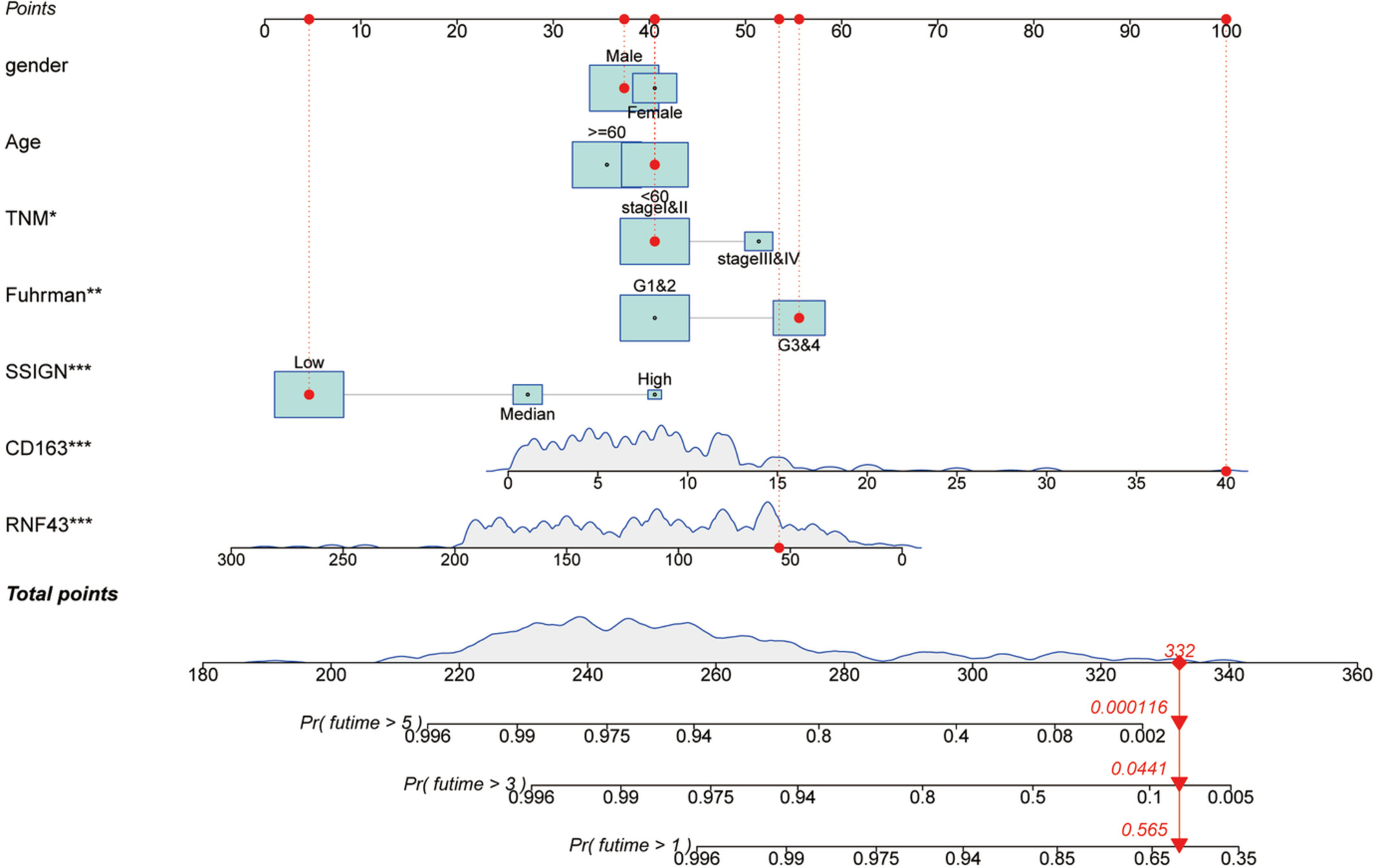
Searching for reliable indicators for evaluating prognosis diagnosed with clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) is crucial for improving clinical therapies. Our study has demonstrated that combining intratumoral RNF43 expression, CD163+ TAM infiltration, and TNM stage could significantly enhance the veracity in forecasting postoperative outcomes.
Prognostic value of circulating proteins in patients undergoing surgery for pancreatic cancer
- Pages: 3972-3986
- First Published: 17 October 2022
Clinicopathologic characteristics, outcomes, and prognostic factors of angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma in China
- Pages: 3987-3998
- First Published: 15 September 2022
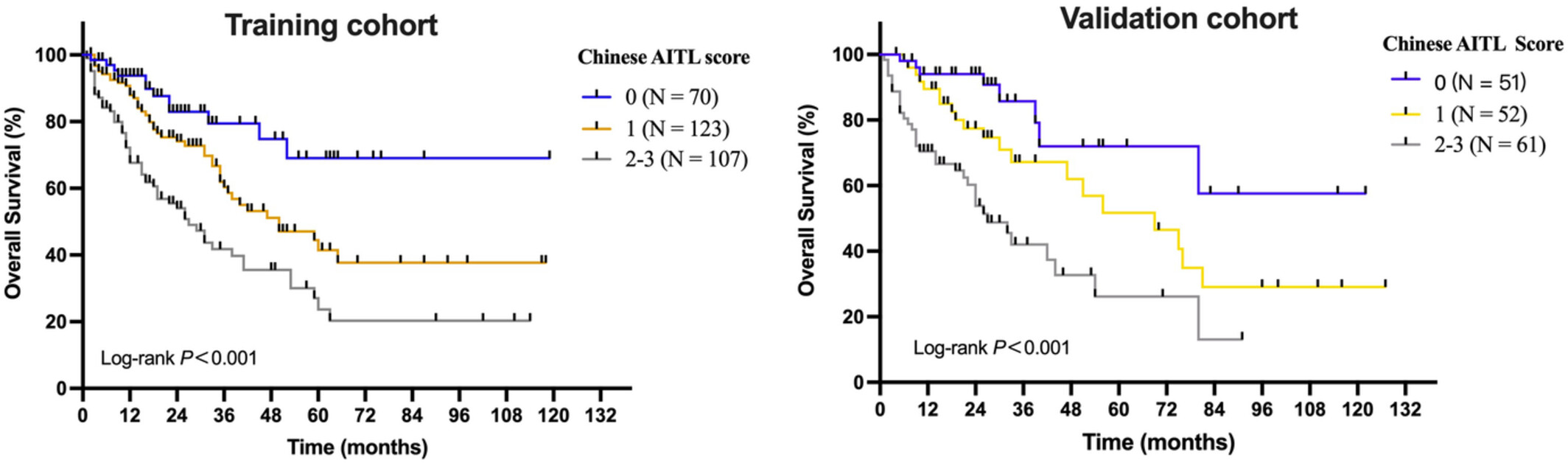
Patients with AITL in China are mainly treated with anthracycline-based regimens with low rate of autologous stem cell transplantation and unsatisfactory outcomes. A novel prognostic model combining 3 factors (age 〉 70 years, elevated LDH, and albumin level 〈 35 g/L) was proposed which stratified patients into the low, intermediate, and high-risk subgroups with differing outcomes.
Phase I study of plitidepsin in combination with bortezomib and dexamethasone in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma
- Pages: 3999-4009
- First Published: 20 September 2022
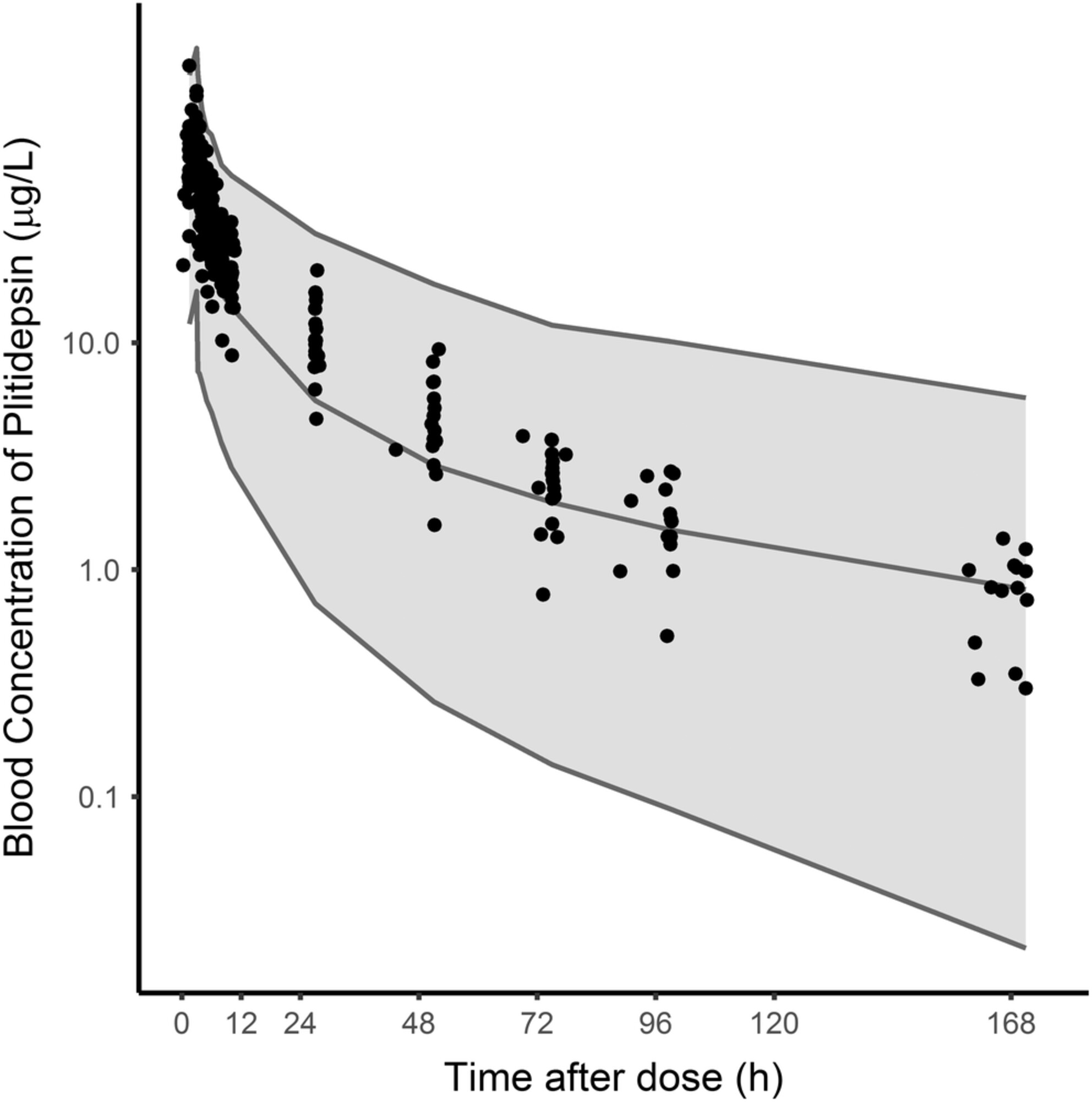
This phase I trial evaluated antitumor activity for plitidepsin plus bortezomib (BTZ) and dexamethasone (DXM) in relapsed/refractory multiple mieloma patients (r/r MM). This triple combination of plitidepsin, BTZ, and DXM showed an acceptable safety profile and had moderate activity in adult patients with r/r MM that have failed to standard common therapeutic options, including BTZ and lenalidomide.
Individualized number of induction chemotherapy cycles for locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients based on early tumor response
- Pages: 4010-4022
- First Published: 20 September 2022
The need to tailor the omission of axillary lymph node dissection to patients with good prognosis and sentinel node micro-metastases
- Pages: 4023-4032
- First Published: 20 September 2022
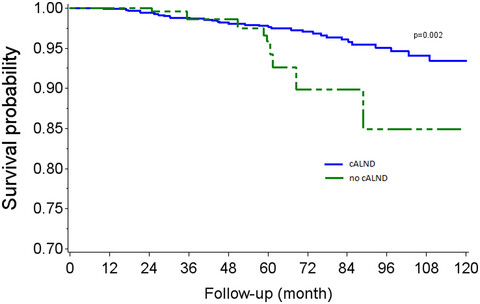
To investigate the impact of completion axillary lymph node dissection (ALND) omission in patients with sentinel node micro-metastases, we retrospectively analyzed a large cohort of 1421 patients with SN micro-metastases who underwent breast conservative surgery (BCS) in 15 French academic centers. We used inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) to obtain adjusted Kaplan-Meier estimators representing the experience in the analysis cohort. Weighted log-rank test comparing adjusted Kaplan-Meier survival curve showed significant difference for overall survival according to completion axillary lymph node dissection (cALND) or no cALND.
Differences in the performance of adjuvant chemotherapy between hemodialysis and nonhemodialysis patients
- Pages: 4033-4041
- First Published: 21 September 2022
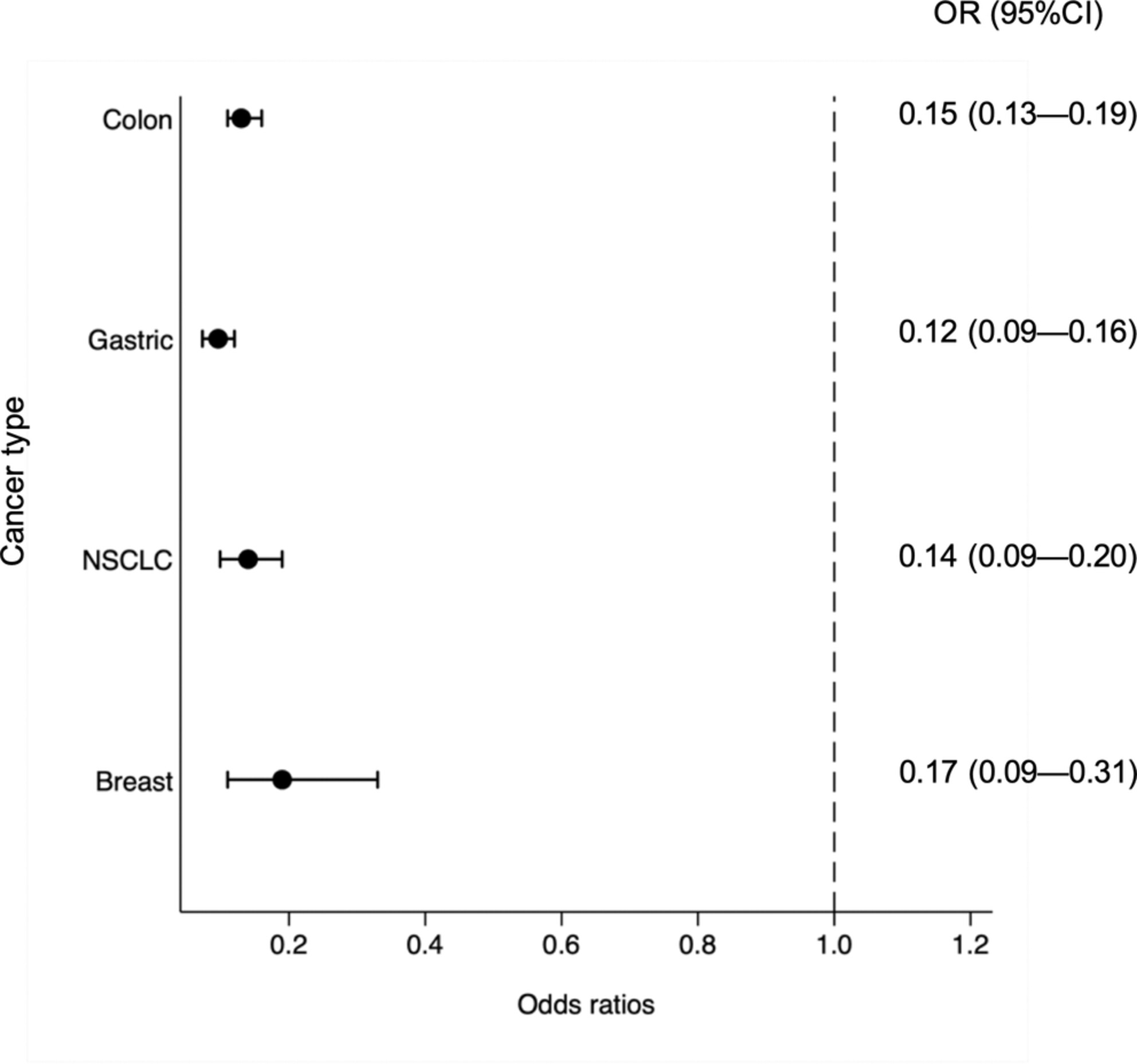
LAY SUMMARY
Among patients newly diagnosed with colon cancer, gastric cancer, breast cancer, and non-small cell lung cancer at the stages where adjuvant chemotherapy is generally required, adjuvant chemotherapy was less likely performed in hemodialysis (HD) patients than for non-HD patients. HD patients tended not to receive the standard regimens compared to non-HD patients partly due to the characteristics of each drug handling. Since the appropriate regimens for HD patients remain unclear, even in the adjuvant setting, future studies should evaluate the efficacy and safety of adjuvant chemotherapy and suggest appropriate adjuvant chemotherapy regimens for patients with HD.
PRECIS
Hemodialysis (HD) patients were less likely to receive adjuvant chemotherapy than non-HD patients.
A larger proportion of non-HD patients underwent standard chemotherapy regimens compared with HD patients.
Hemodialysis (HD) patients were less likely to receive adjuvant chemotherapy than non-HD patients. This trend was consistent among the respective cancer types that we assessed: the odds of HD patients receiving adjuvant chemotherapy was approximately 0.1-0.18 times less than non-HD patients (colon cancer: OR = 0.15, 95% CI: 0.13-0.19, P < 60; 0.001; gastric cancer: OR = 0.12, 95% CI: 0.09-0.16, P < 60; 0.001; NSCLC: OR = 0.14, 95% CI: 0.09-0.20, P < 60; 0.001; and breast cancer: OR = 0.17, 95% CI: 0.09-0.31, P < 60; 0.001)
Utilization of cytologic cell blocks for targeted sequencing of solid tumors
- Pages: 4042-4063
- First Published: 20 September 2022
Radium-223 dichloride treatment in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer in Finland: A real-world evidence multicenter study
- Pages: 4064-4076
- First Published: 26 September 2022
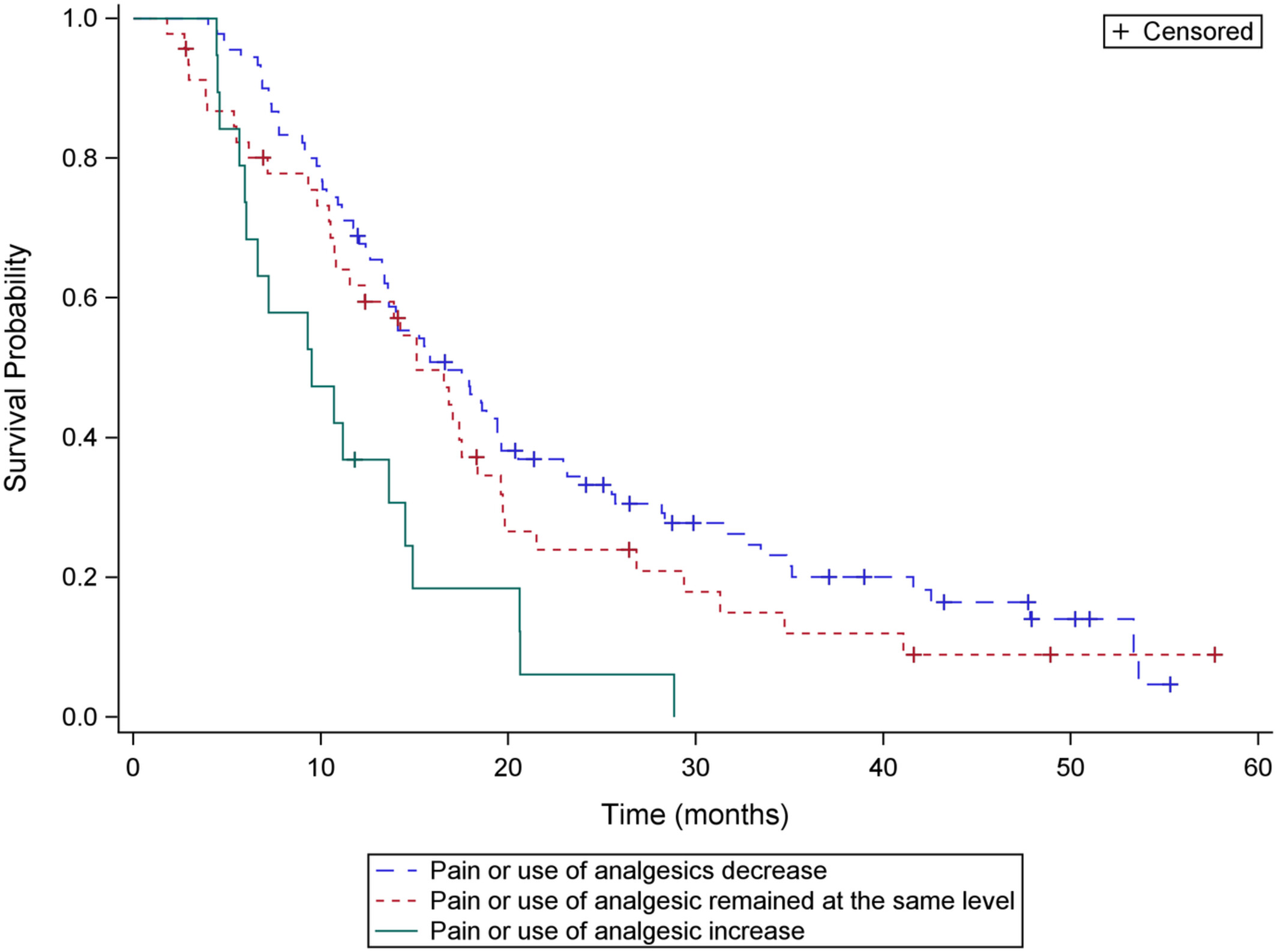
We report results of a retrospective real-world multicenter study including all patients with metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) treated with radium-223 in all five university hospitals in Finland since the introduction of the treatment. In our cohort, PSA decrease, ALP normalization and pain relief correlated with improved survival. Our results support using radium-223 for mCRPC patients with symptomatic bone metastases even in the era of new generation androgen signaling targeting agents.
Efficacy of adjuvant chemotherapy on overall survival in patients with lymph node-positive esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: Is oral chemotherapy promising?
- Pages: 4077-4086
- First Published: 22 September 2022
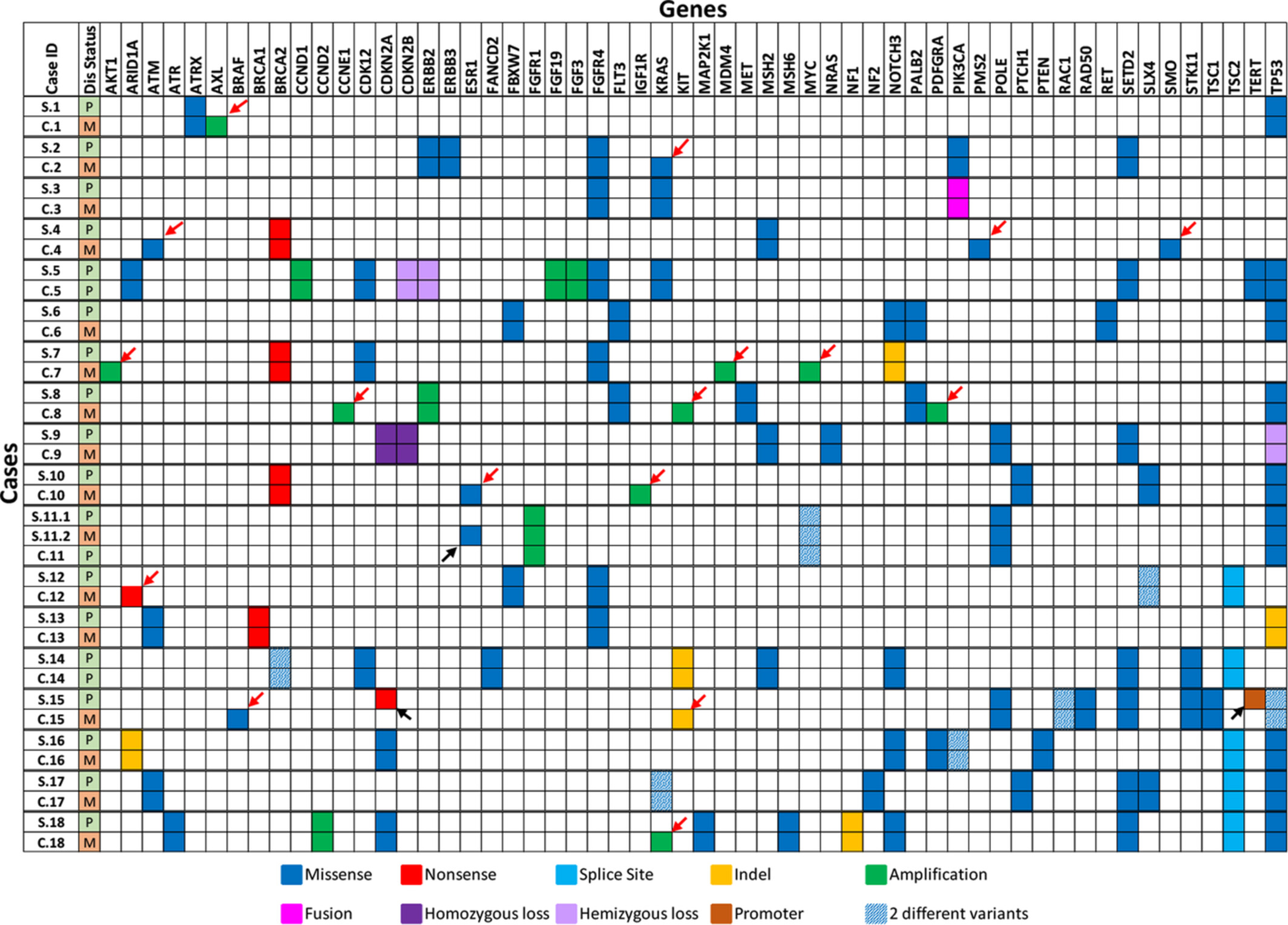
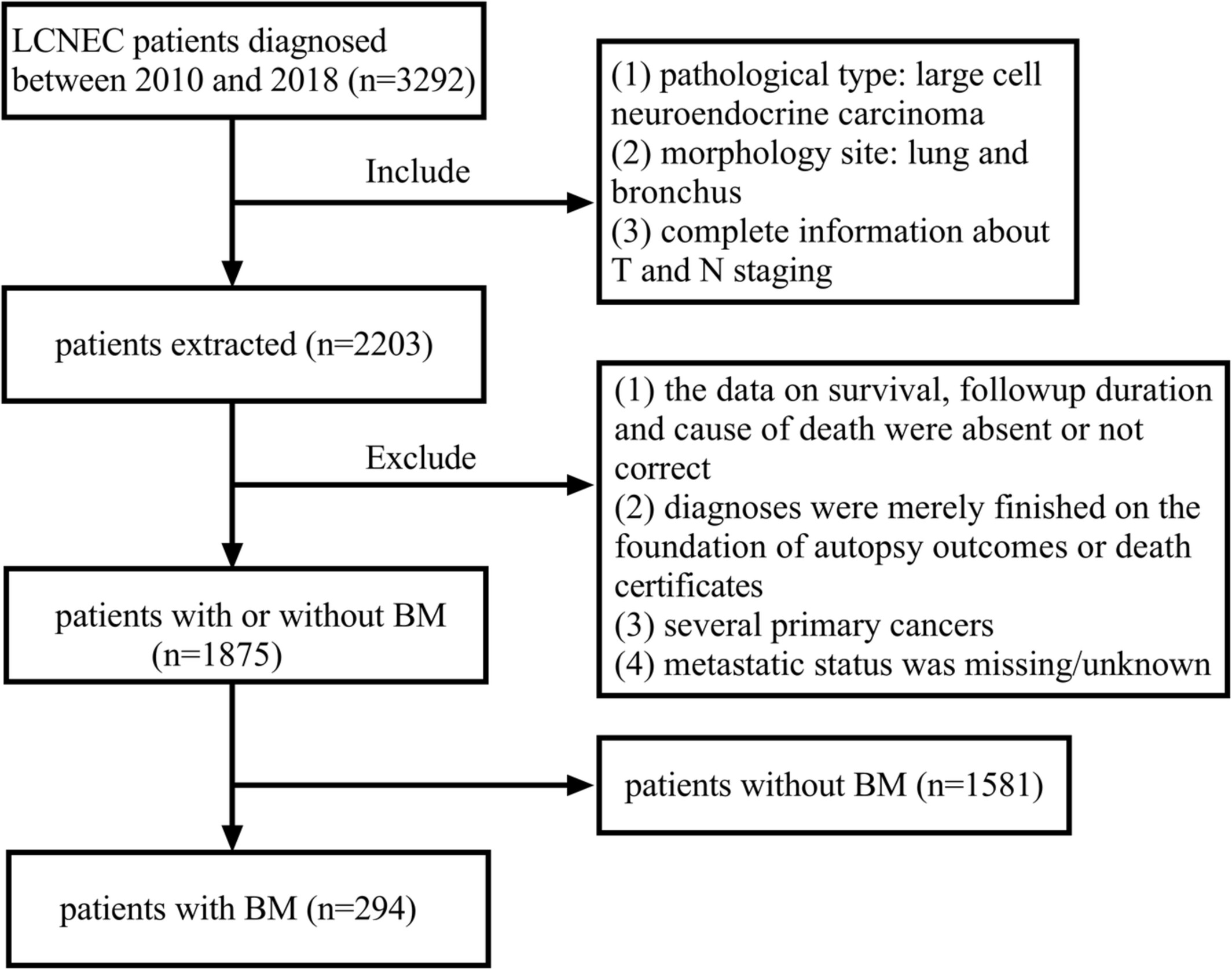
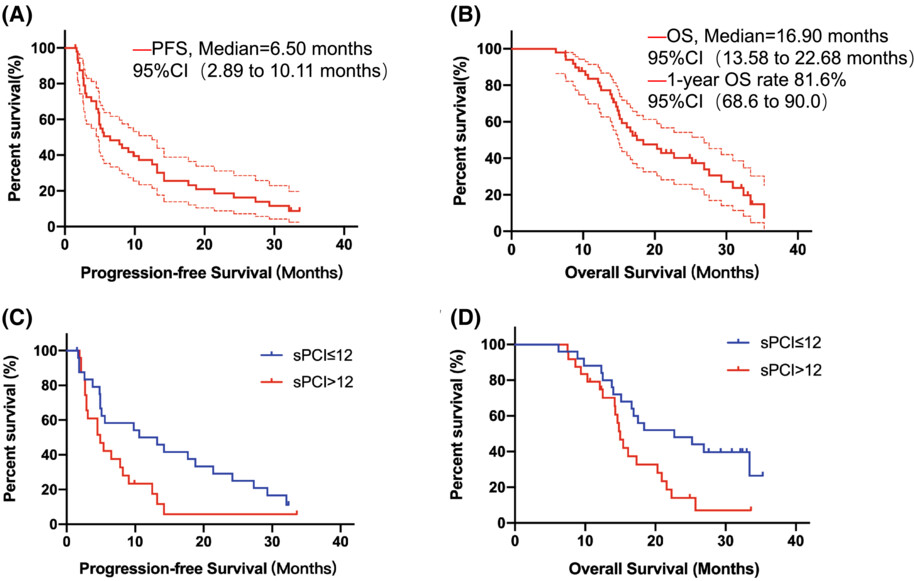
Risk factors and prognostic factors for pulmonary large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma with brain metastasis
- Pages: 4087-4099
- First Published: 20 September 2022
Clinical impact of early response to first-line VEGFR-TKI in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma on survival: A multi-institutional retrospective study
- Pages: 4100-4109
- First Published: 06 October 2022
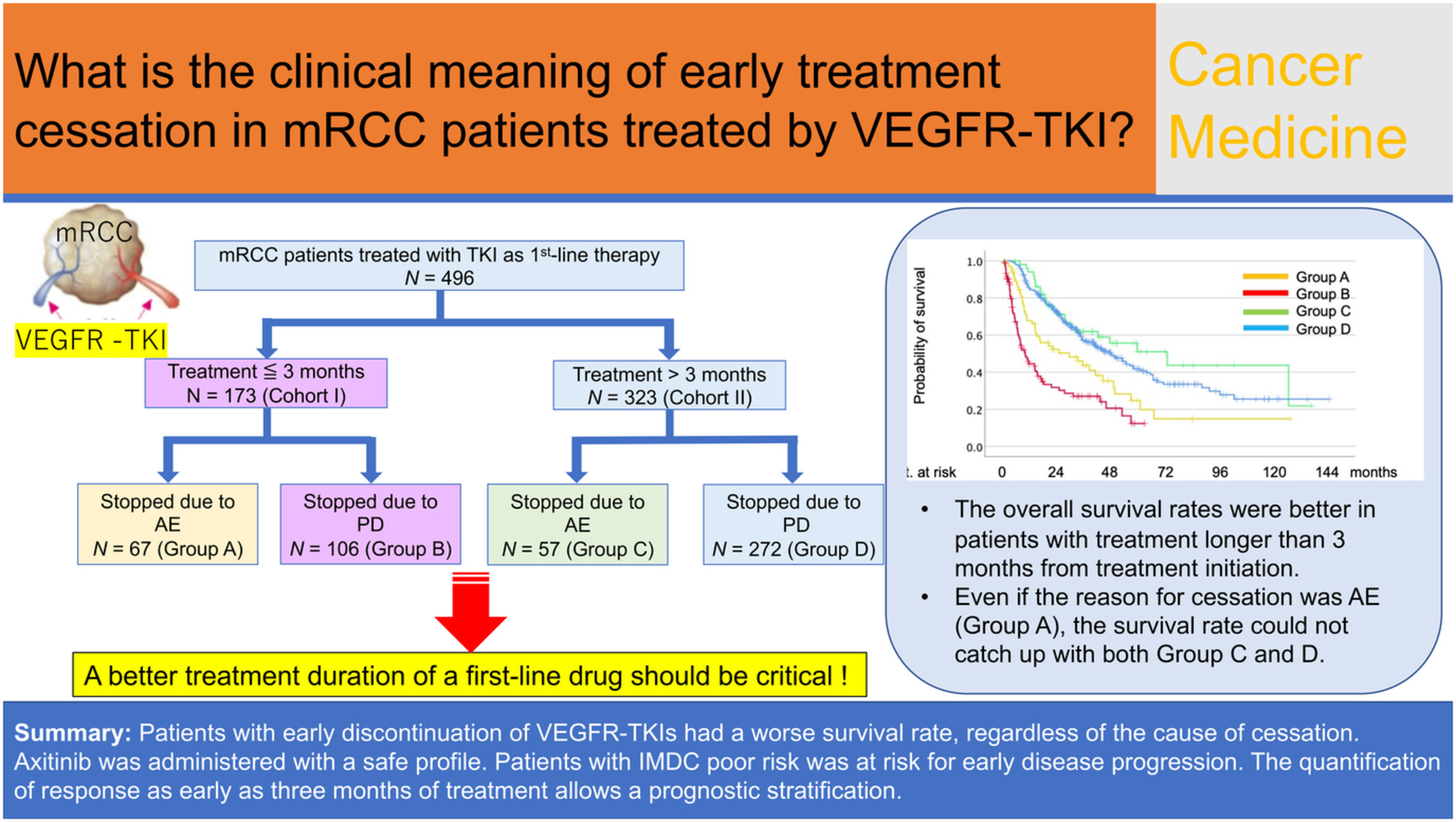
Patients with early discontinuation of VEGFR-TKIs had a worse survival rate, regardless of the cause of cessation. Axitinib was administered with a safe profile. Patients with IMDC poor risk was at risk for early disease progression. The quantification of response as early as three months of treatment allows a prognostic stratification.
Identifying HER2 from serum-derived exosomes in advanced gastric cancer as a promising biomarker for assessing tissue HER2 status and predicting the efficacy of trastuzumab-based therapy
- Pages: 4110-4124
- First Published: 08 October 2022
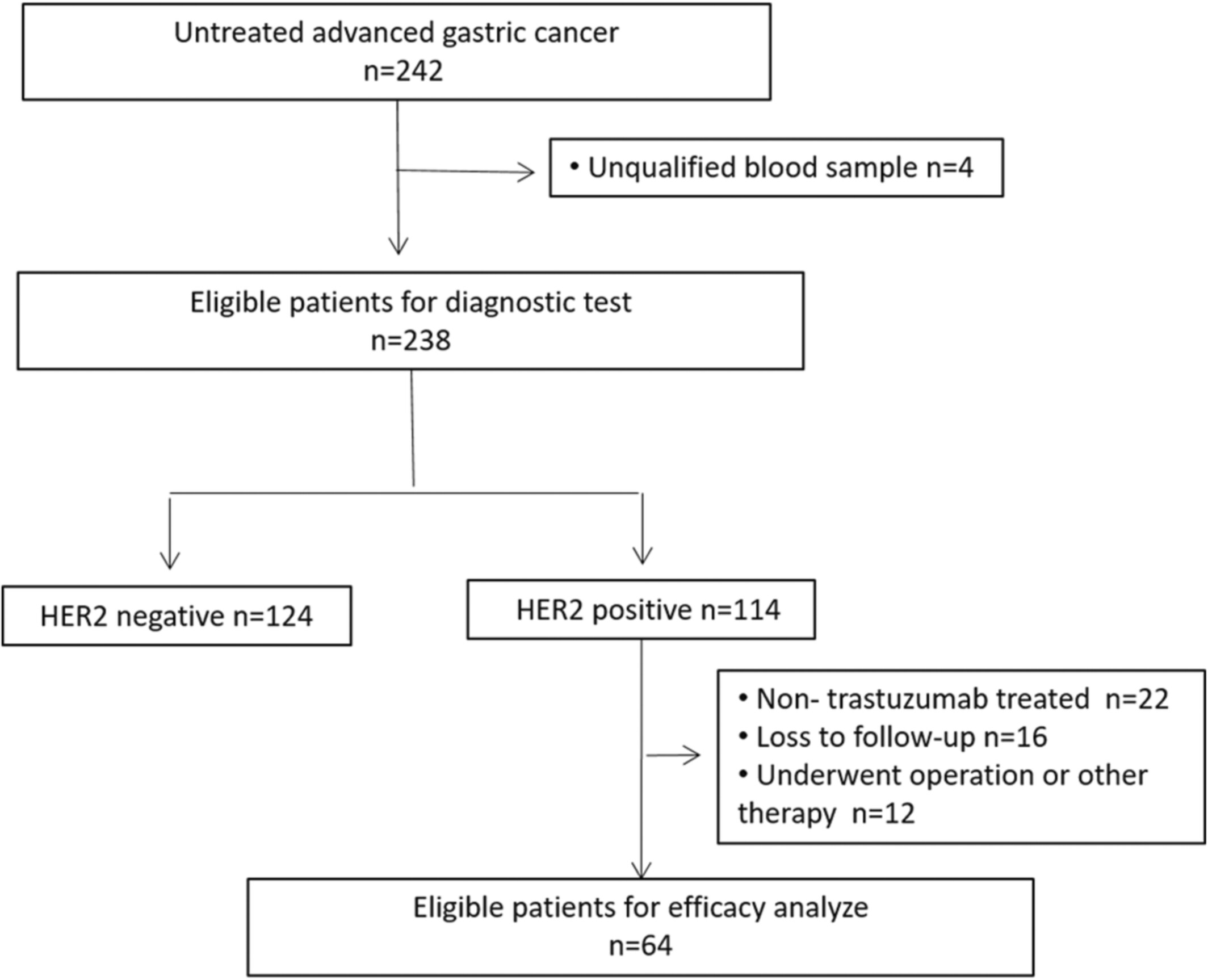
In this prospective multi-centers study, HER2 in serum-derived exosome (Exo HER2) from patients with advanced or metastatic gastric adenocarcinoma (AGC) were analyzed for its diagnostic value and predictive value for trastuzumab therapy. The results showed Exo HER2 is a promissing biomarker for assessing tissue HER2 status in AGC and predicting clinical benefits of trastuzumab based therapy.
Evaluation of different scoring systems for spinal metastases based on a Chinese cohort
- Pages: 4125-4136
- First Published: 21 September 2022
Pemigatinib in previously treated Chinese patients with locally advanced or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma carrying FGFR2 fusions or rearrangements: A phase II study
- Pages: 4137-4146
- First Published: 20 September 2022
Predictors of survival outcomes among patients with gastric cancer in a leading tertiary, teaching and referral hospital in Kenya
- Pages: 4147-4160
- First Published: 29 September 2022
Study of SOX combined with intraperitoneal high-dose paclitaxel in gastric cancer with synchronous peritoneal metastasis: A phase II single-arm clinical trial
- Pages: 4161-4169
- First Published: 26 September 2022
The impact of sarcopenia on survival and treatment tolerance in patients with head and neck cancer treated with chemoradiotherapy
- Pages: 4170-4183
- First Published: 20 October 2022
Sarcopenia in patients with head-and-neck squamous cell carcinoma treated by definitive chemoradiotherapy is an independent negative prognostic factor for disease-free survival. Sarcopenic patients did not have more grade 3+ toxicities or more treatment interruptions.
The efficacy and cardiac toxicity of different-dose pegylated liposomal doxorubicin in elderly patients with diffuse large B lymphoma
- Pages: 4184-4194
- First Published: 06 October 2022
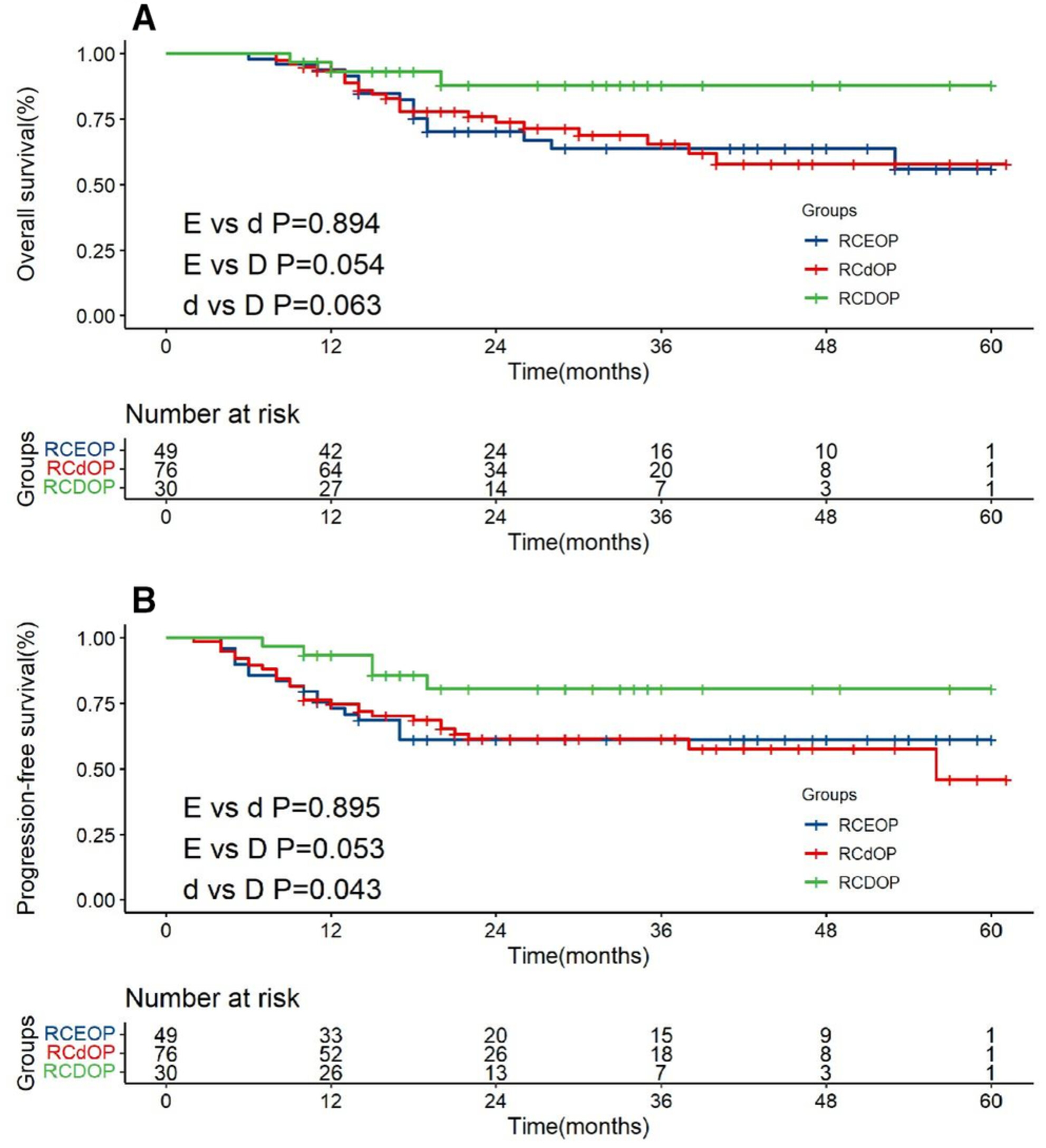
Generally, the complete remission rate of the RCDOP group was significantly higher than that of the RCdOP group. For elderly diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients with cardiovascular disease, the effect benefit brought by pegylated liposomal doxorubicin dose was more obvious, and the progression-free survival of the RCDOP group was significantly longer than that of the RCdOP group (p = 0.043).
Real-world outcomes among patients with advanced or metastatic biliary tract cancers initiating second-line treatment
- Pages: 4195-4205
- First Published: 20 October 2022
Preoperative systemic inflammation response index is an independent prognostic marker for BCG immunotherapy in patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer
- Pages: 4206-4217
- First Published: 10 October 2022
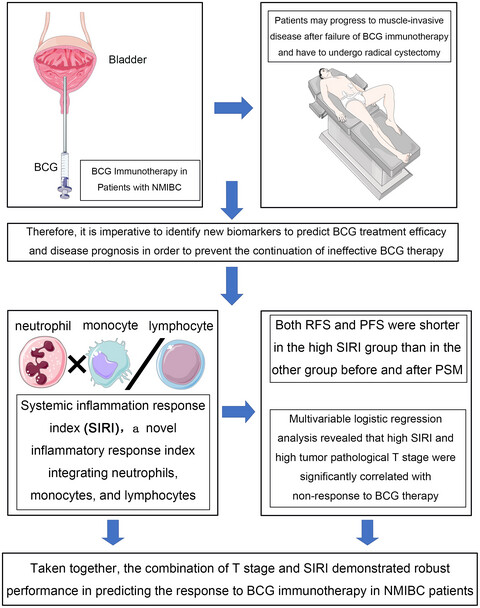
The Systemic Inflammatory Response Index (SIRI) is a novel prognostic biomarker based on peripheral blood counts of neutrophils, monocytes, and lymphocytes. However, the predictive value of the SIRI in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) patients treated with intravesical Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) immunotherapy remains elusive. Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate the potential of SIRI as a prognostic factor in these patients. A total of 540 patients with NMIBC who underwent BCG immunotherapy following transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT) were enrolled in this study. Using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves and the Youden index, patients were divided into high and low SIRI groups based on the cutoff values. Univariable and multivariable logistic regression analyses were performed to identify independent predictors of BCG non-response. Thereafter, propensity score matching (PSM) was used to eliminate bias due to confounding factors between the low and high SIRI groups. Finally, the Kaplan-Meier method was used to compare recurrence-free survival (RFS) and progression-free survival (PFS) between the two groups. Multivariable logistic regression analysis revealed that high SIRI (p = 0.001), high MLR (p = 0.015), and high tumor pathological T stage (p = 0.015) were significantly correlated with non-response to BCG therapy. In addition, both RFS and PFS were shorter in the high SIRI group than in the other group before and after PSM (both p < 0.05). Pretreatment peripheral blood SIRI can be employed to predict the response to BCG immunotherapy and the prognosis of NMIBC patients. The combination of T stage and SIRI demonstrated robust performance in predicting the response to BCG immunotherapy in NMIBC patients.
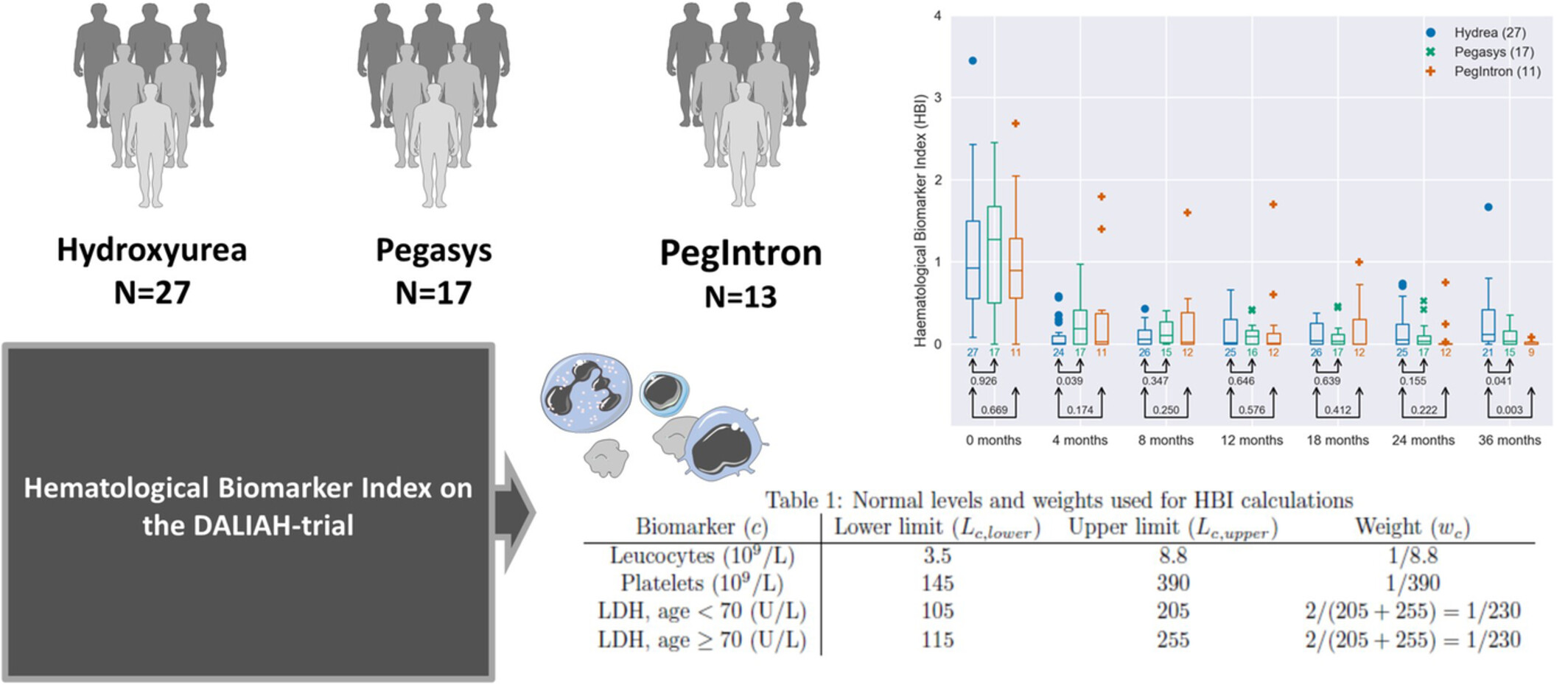
A novel integrated biomarker index for the assessment of hematological responses in MPNs during treatment with hydroxyurea and interferon-alpha2
- Pages: 4218-4226
- First Published: 17 October 2022
Increased lncRNA AFAP1-AS1 expression predicts poor prognosis in gastric cancer: Evidence from published studies and followed up verification
- Pages: 4227-4235
- First Published: 26 September 2022
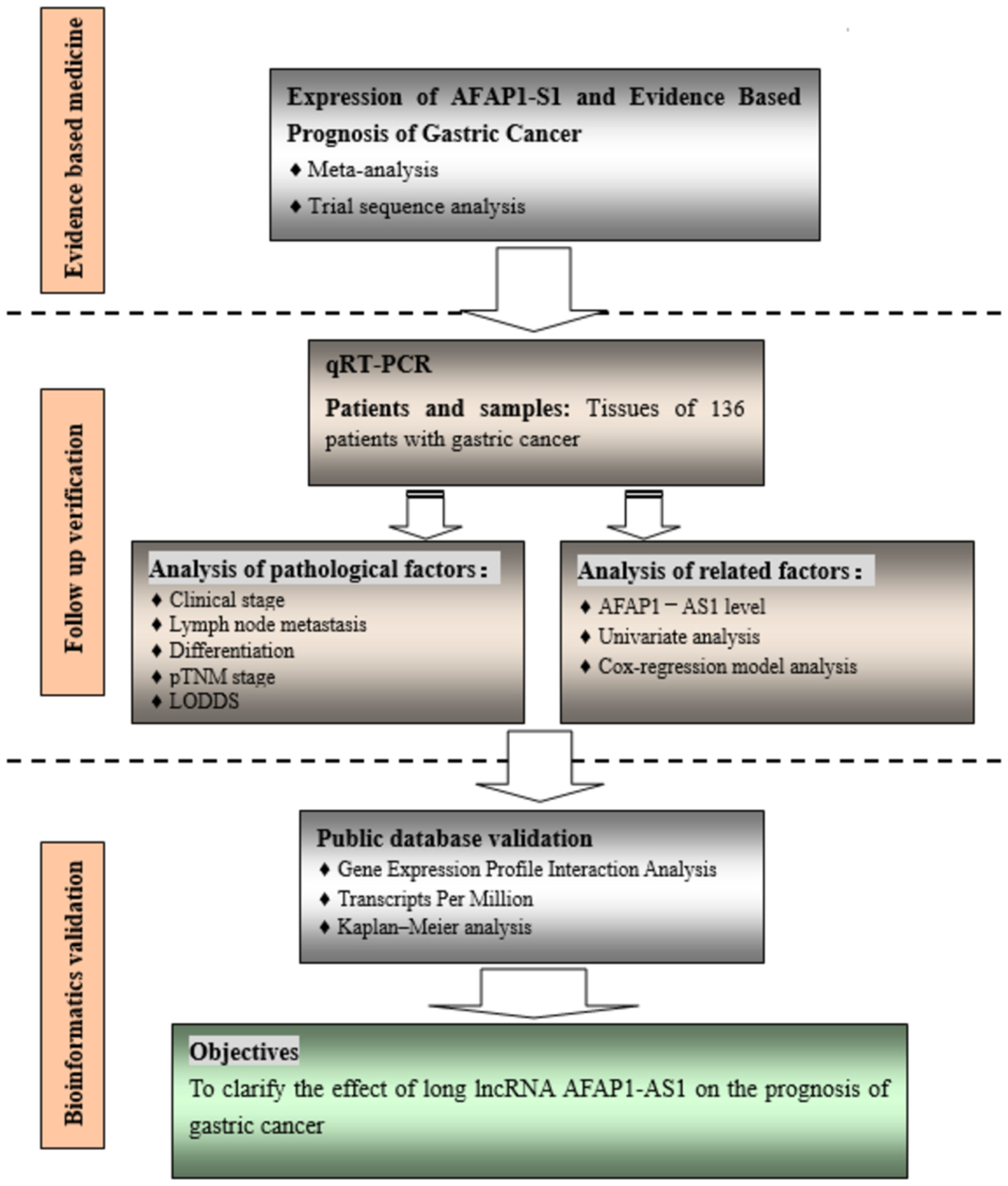
Based on meta-analysis and TSA, the association between the expression of AFAP1-AS1 and the prognosis of gastric cancer was estimated. GC tissue and non-cancer tissues were determined by qRT-PCR and verified GEPIA. Kaplan–Meier and Cox proportional hazards modelswere conducted to analyze the correlation between AFAP1-AS1 expression and gastric cancer prognosis. The pooled analysisrevealed that the AFAP1-AS1 expression was significantly associated with gastric cancer OS.Compared with non-cancer tissues, AFAP1-AS1 expression level of gastric cancer tissues were significantlyupregulated, which was confirmed by the results of GEPIA. The high expressionof AFAP1-AS1 was correlated withpoor prognosis in patients with gastric cancer. Clinical grade, pTNM LODDS andAFAP1-AS1 expression were independent prognosticfactors for gastric cancer revealed by multivariate Cox-regression analysis. This study demonstrated that the AFAP1-AS1 may be a novel biomarker for the diagnosis and prognosis of gastriccancer.
Systemic immune changes accompany combination treatment with immunotoxin LMB-100 and nab-paclitaxel
- Pages: 4236-4249
- First Published: 08 October 2022
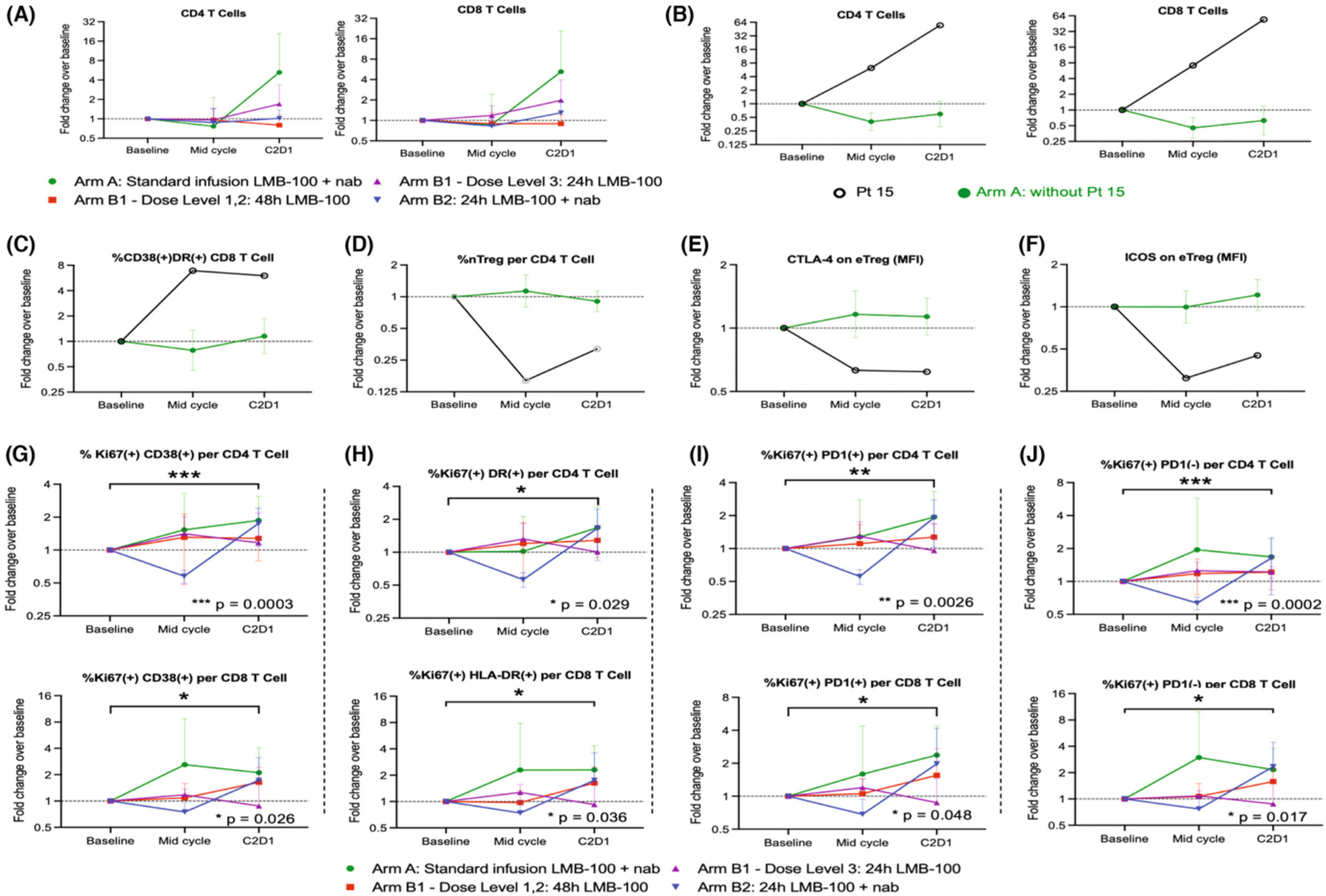
LMB-100 is an immunotoxin directed against mesothelin, a surface protein expressed by over 85% of pancreatic adenocarcinomas as well as an estimated 30% of all solid tumors. Immunotoxin therapies, while potentially promising, are limited by their side effect profiles, most notably capillary leak syndrome (CLS). This study provides the most detailed assessment to date of the systemic immune and inflammatory changes occurring in patients following LMB-100 treatment and identifies those specific to patients who develop CLS. These findings illuminate the systemic effects of immunotoxin treatment in patients and could ultimately lay the groundwork for new combinations capable of harnessing the immune activating effects of immunotoxin therapy while avoiding dangerous toxicities such as CLS.
Deep molecular response in patients with chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia treated with the plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 inhibitor TM5614 combined with a tyrosine kinase inhibitor
- Pages: 4250-4258
- First Published: 23 September 2022
The hepatocellular carcinoma modified Gustave Roussy Immune score (HCC-GRIm score) as a novel prognostic score for patients treated with atezolizumab and bevacizumab: A multicenter retrospective analysis
- Pages: 4259-4269
- First Published: 26 September 2022
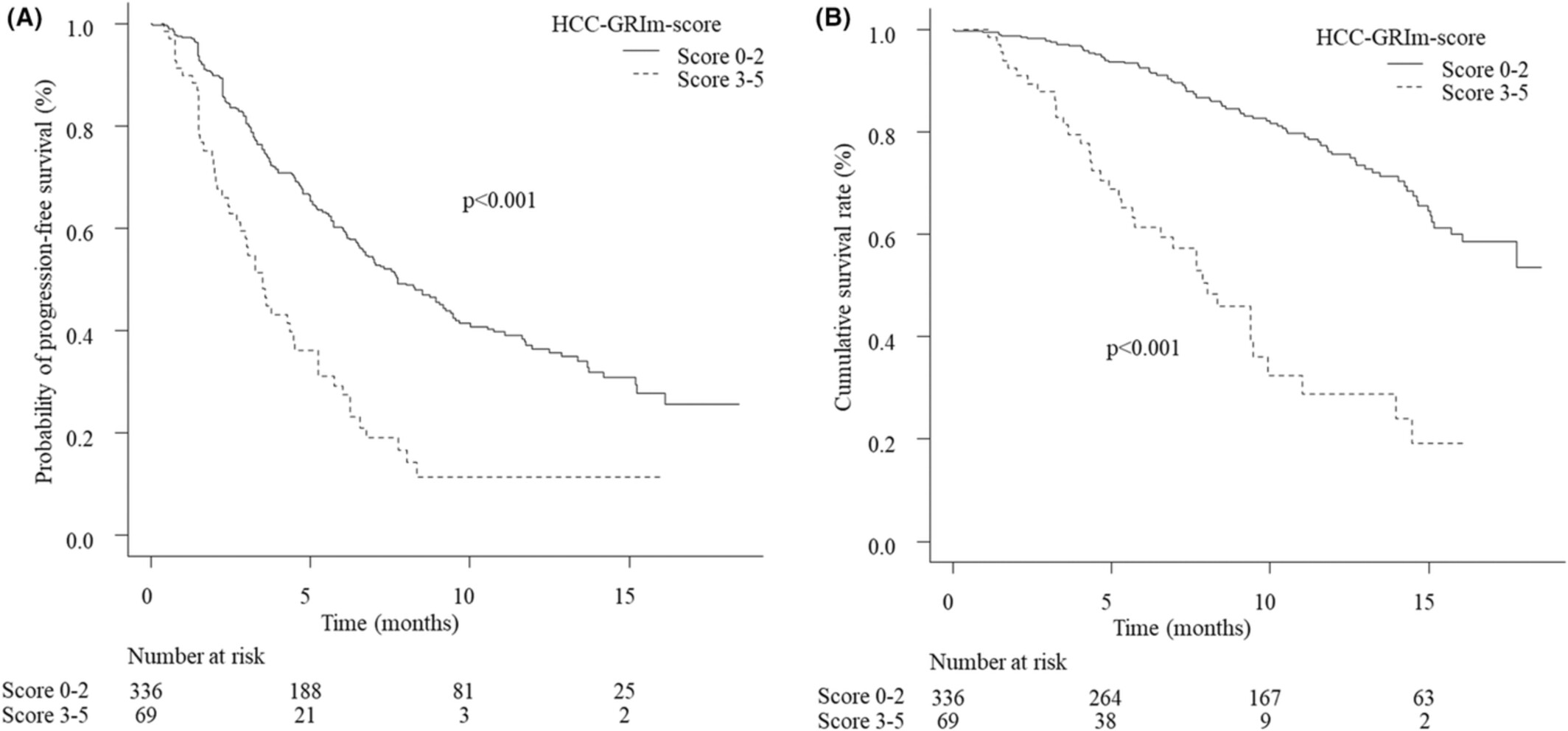
The hepatocellular carcinoma modified Gustave Roussy Immune score (HCC-GRIm-Score), which was based on the combination of the albumin level, lactate dehydrogenase, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, aspartate aminotransferase-to-alanine aminotransferase ratio, and total bilirubin level, serves as a novel prognostic score for HCC patients treated with atezolizumab and bevacizumab.
A phase I trial of metformin in combination with vincristine, irinotecan, and temozolomide in children with relapsed or refractory solid and central nervous system tumors: A report from the national pediatric cancer foundation
- Pages: 4270-4281
- First Published: 23 September 2022
Retrospective evaluation of the role of gemcitabine-docetaxel in well-differentiated and dedifferentiated liposarcoma
- Pages: 4282-4293
- First Published: 24 September 2022
Association between a single nucleotide polymorphism in the R3HCC1 gene and irinotecan toxicity
- Pages: 4294-4305
- First Published: 29 October 2022
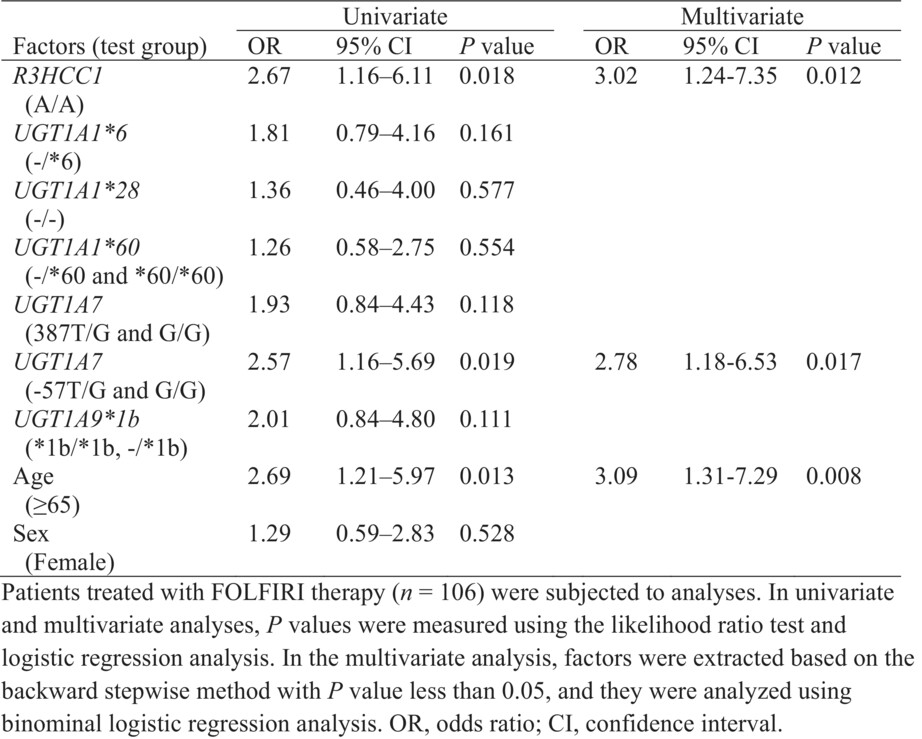
We utilized whole-exome sequencing and PCR validation with colorectal and pancreatic cancer patient data in order to identify novel biomarkers that may be predictive of adverse effects associated with irinotecan-containing chemotherapy, such as FOLFIRI, FOLFOXIRI, and modified FOLFIRINOX therapies. Among the variations identified, we found that a single nucleotide polymorphism in R3HCC1 showed a significant linear relationship with toxicity and may explain the adverse effects in patients who did not harbor known susceptibility-conferring polymorphisms in UGT1A. Our findings offer a new target to test for when deciding on chemotherapy regimen choice and dosages and improves our approach of precision medicine in colorectal and pancreatic cancer patients.
Metabolic pathways enriched according to ERG status are associated with biochemical recurrence in Hispanic/Latino patients with prostate cancer
- Pages: 4306-4320
- First Published: 03 November 2022
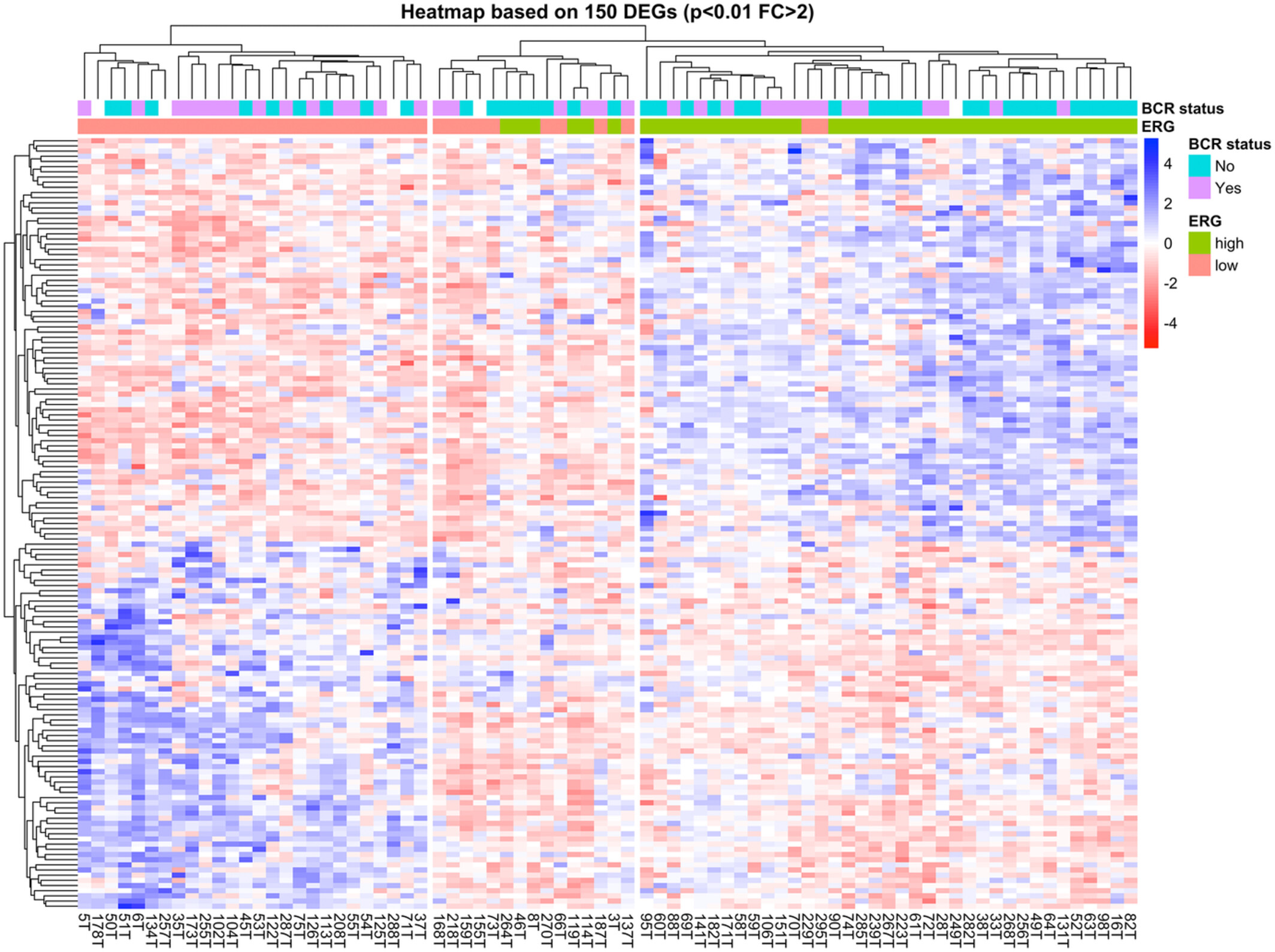
Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between ERGhigh and ERGlow tumors revealed clustering of most of the non-BCR cases into de ERGhigh group and most of the BCR cases in ERGlow group. Subsequent analyses confirmed an association between ERG status with BCR, showing a worst BCR-free survival for ERGlow patients compared to the ERGhigh group. Enrichment pathway analysis of the 150 DEGs identified an important participation of metabolic-related pathways in the BCR progression.
The factors influencing the accuracy of pre-operative endoscopic ultrasonography assessment in endoscopic treatments for gastrointestinal tumors
- Pages: 4321-4331
- First Published: 29 September 2022
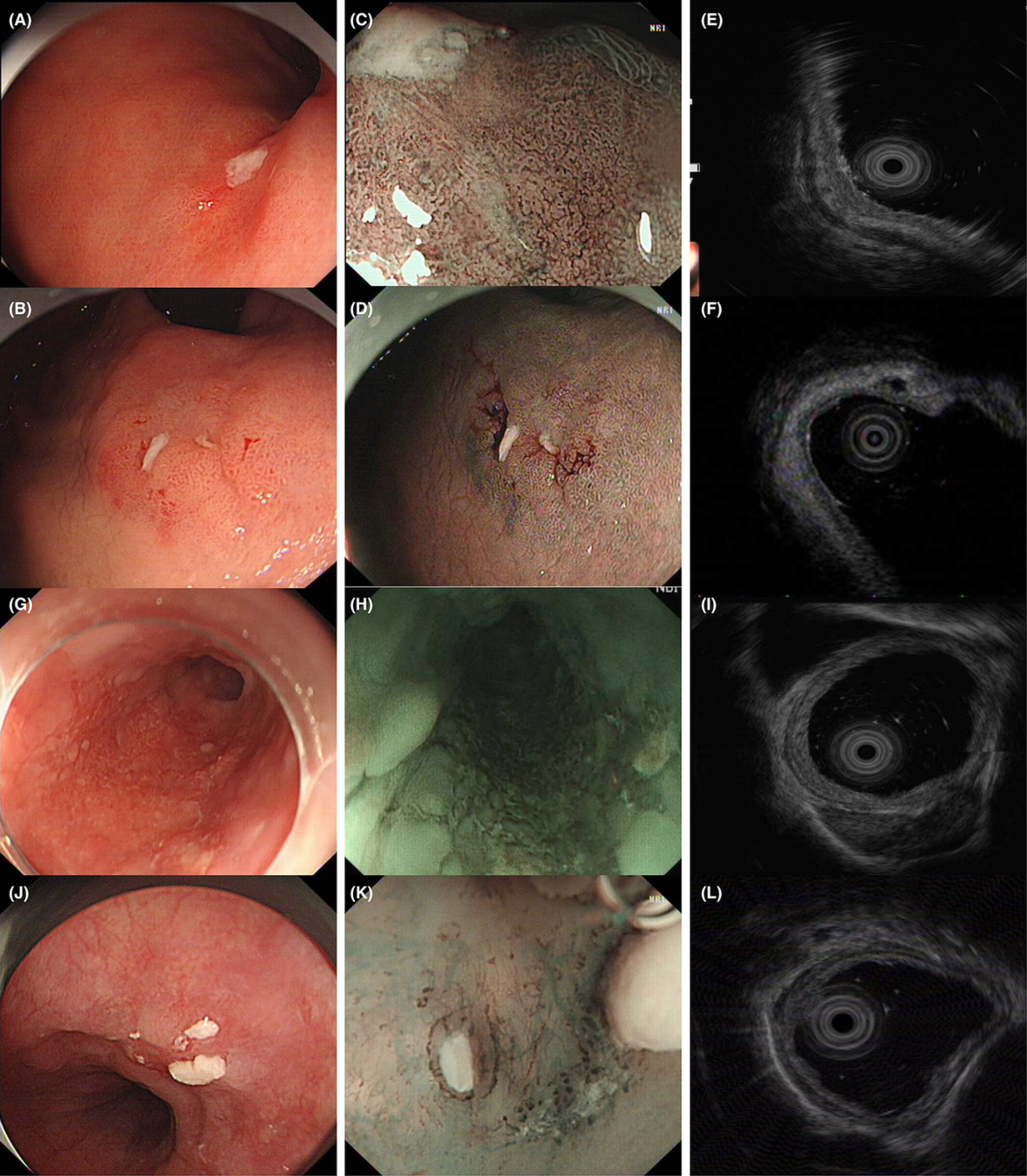
Preoperative staging of superficial gastrointestinal tumors is crucial for choosing the most appropriate treatment. Our findings suggested that endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) was a reliable and easy-to-use diagnostic tool in decision-making regarding appropriate endoscopic treatment for gastrointestinal tumors. However, the diagnostic accuracy of EUS appeared questionable in the presence of ulceration.
Health-related quality-of-life analyses from a multicenter, randomized, double-blind phase 2 study of patients with differentiated thyroid cancer treated with lenvatinib 18 or 24 mg/day
- Pages: 4332-4342
- First Published: 04 December 2022
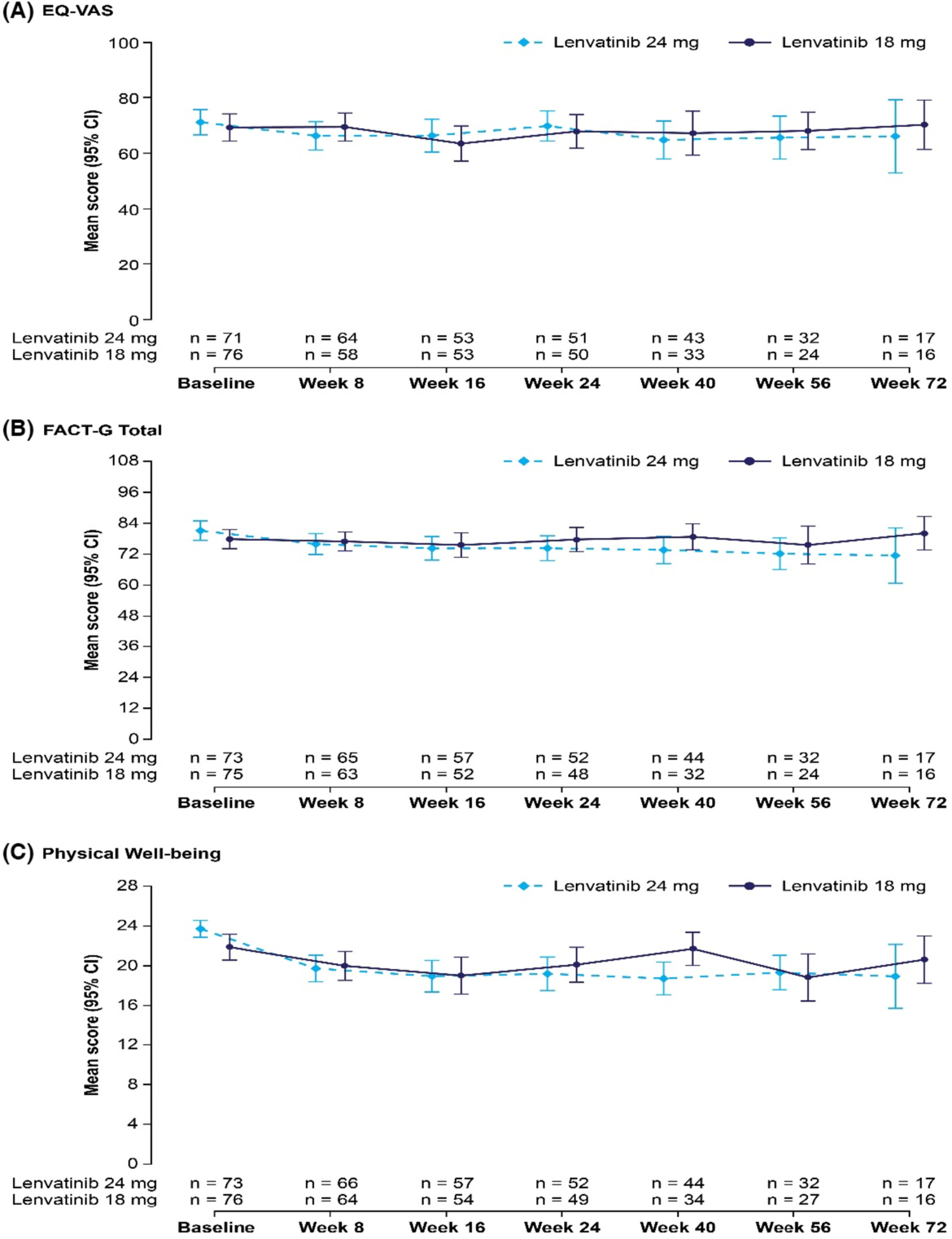
Evaluation of the impact of lenvatinib treatment on health-related quality-of-life was a secondary objective of the phase 2 double-blinded Study 211. This study compared a starting dose of lenvatinib 18 mg/day with the approved starting dose of 24 mg/day in patients with radioiodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer. Health-related quality-of-life of patients in the 18 mg/day arm was not statistically different from that of patients in the 24 mg/day arm. These data, combined with results from the primary analysis (where the lenvatinib starting dose of 18 mg/day did not demonstrate noninferiority to the approved starting dose of lenvatinib 24 mg/day), support the use of the approved lenvatinib starting dose of 24 mg/day in patients with radioiodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer.
Oral application of magnesium-L-threonate enhances analgesia and reduces the dosage of opioids needed in advanced cancer patients—A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
- Pages: 4343-4351
- First Published: 26 January 2023
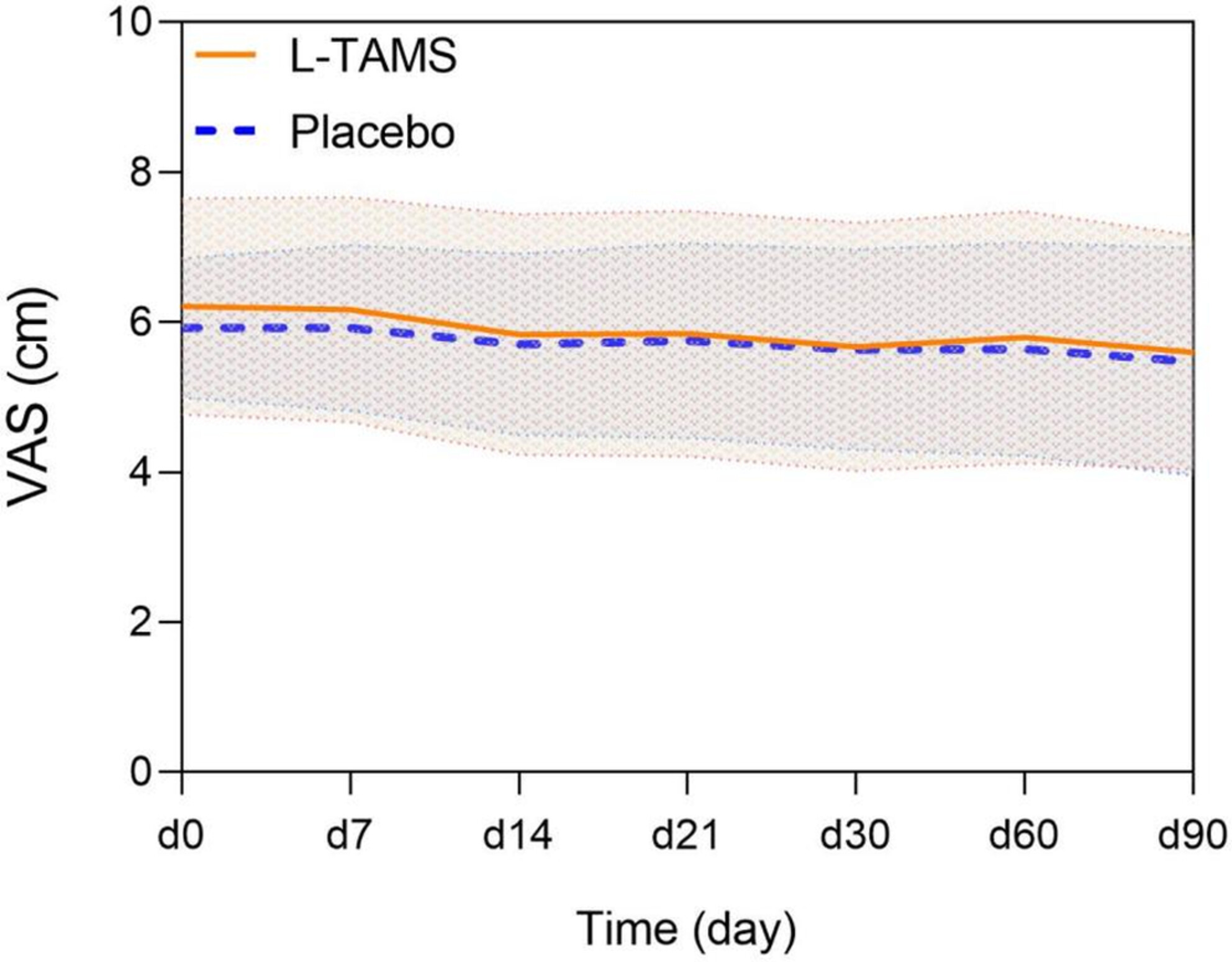
A randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled prospective clinical trial. Oral magnesium-L-threonate enhances the analgesia and reduces the dosage of opioids needed in advanced cancer patients. Magnesium-L-threonate inhibits or eases morphine tolerance. Magnesium-L-threonate relieves opioid-induced constipation
BRIEF COMMUNICATION
Clinical Cancer Research
Neoadjuvant androgen deprivation therapy combined with abiraterone acetate in patients with locally advanced or metastatic prostate cancer: When to perform radical prostatectomy?
- Pages: 4352-4356
- First Published: 15 September 2022
Real-world data on lenalidomide dosing and outcomes in patients newly diagnosed with multiple myeloma: Results from the Canadian Myeloma Research Group Database
- Pages: 4357-4362
- First Published: 26 September 2022
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Clinical Cancer Research
A comparative study of diagnostic accuracy in 3026 pleural biopsies and matched pleural effusion cytology with clinical correlation: A methodological issue
- Pages: 4363-4364
- First Published: 19 December 2022
REPLY
Clinical Cancer Research
Reply to: A comparative study of diagnostic accuracy in 3026 pleural biopsies and matched pleural effusion cytology with clinical correlation: A methodological issue
- Pages: 4365-4366
- First Published: 07 December 2022
REVIEWS
Cancer Biology
Implications of estrogen and its receptors in colorectal carcinoma
- Pages: 4367-4379
- First Published: 07 October 2022
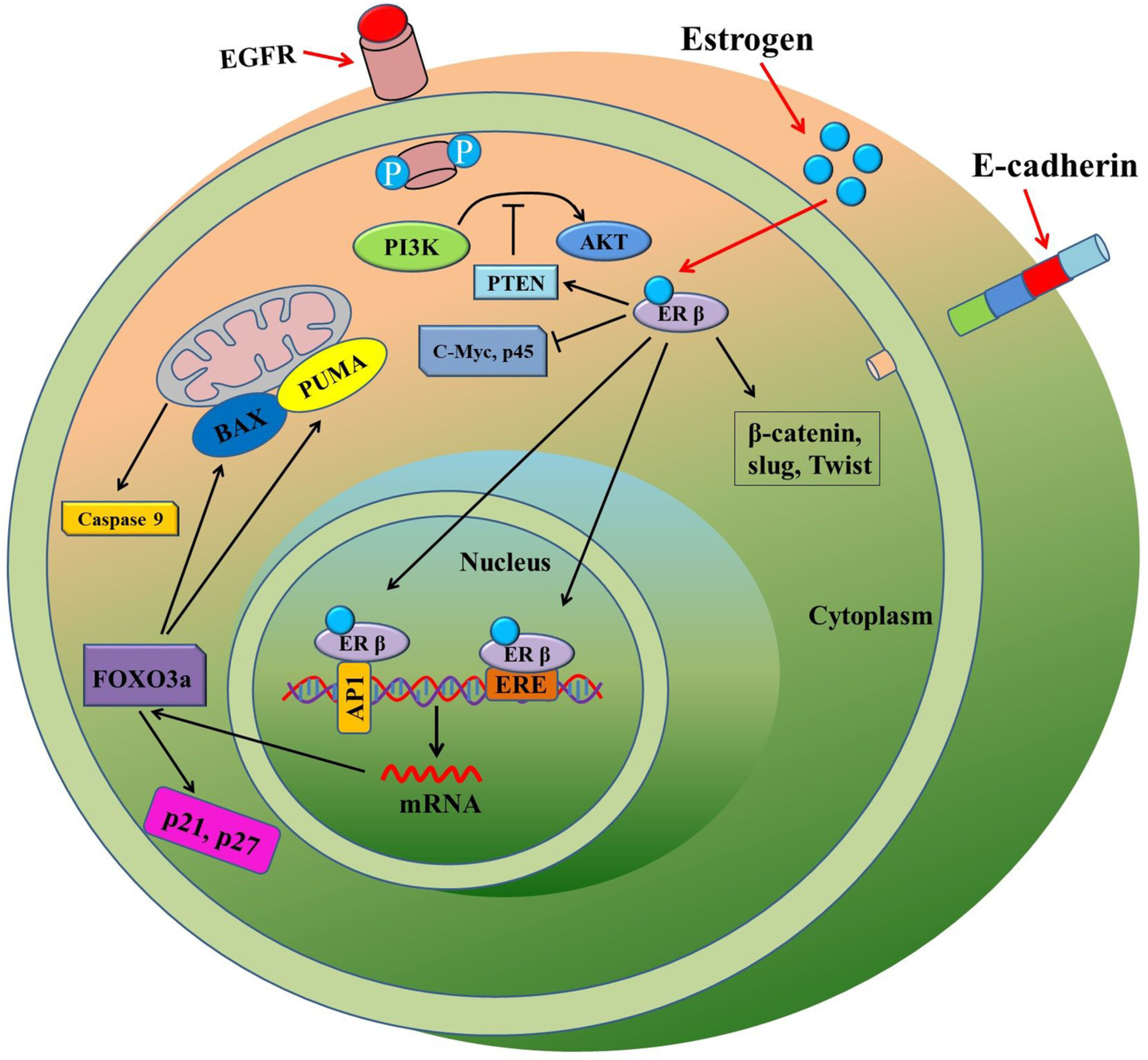
ERß, the predominant estrogen receptor expressed in both normal and non-malignant colonic epithelium, has a protective role in colon carcinogenesis. ERß may exert the anti-tumor effect through selective activation of pro-apoptotic signaling, increasing DNA repair, inhibiting expression of oncogenes, regulating cell cycle progression, and also by changing the micro-RNA pool and DNA-methylation.
DNA damage response signaling: A common link between cancer and cardiovascular diseases
- Pages: 4380-4404
- First Published: 26 September 2022
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Cancer Biology
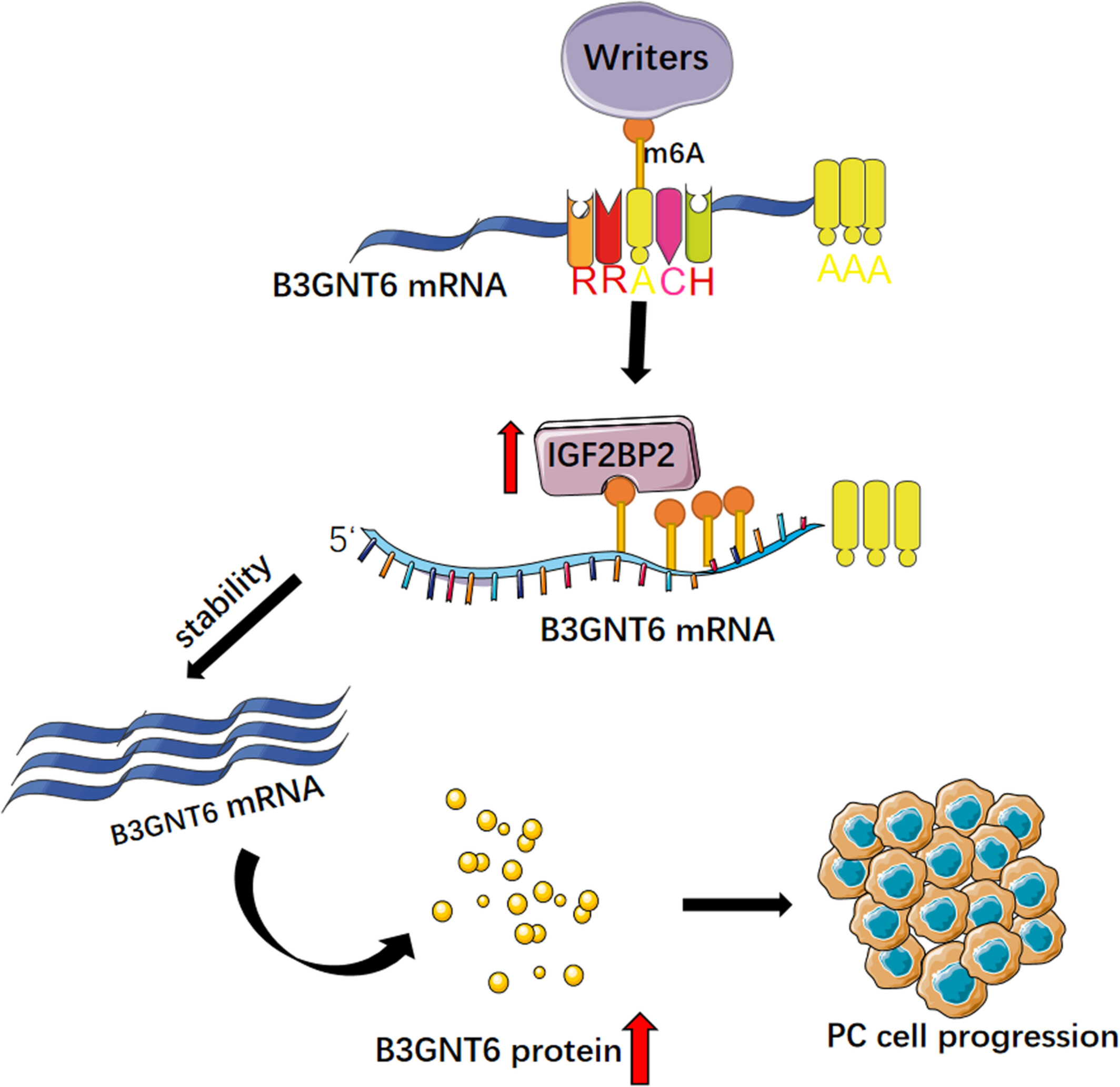
IGF2BP2 promotes pancreatic carcinoma progression by enhancing the stability of B3GNT6 mRNA via m6A methylation
- Pages: 4405-4420
- First Published: 31 July 2022
The long noncoding RNA HOXA11-AS promotes lung adenocarcinoma proliferation and glycolysis via the microRNA-148b-3p/PKM2 axis
- Pages: 4421-4433
- First Published: 04 August 2022
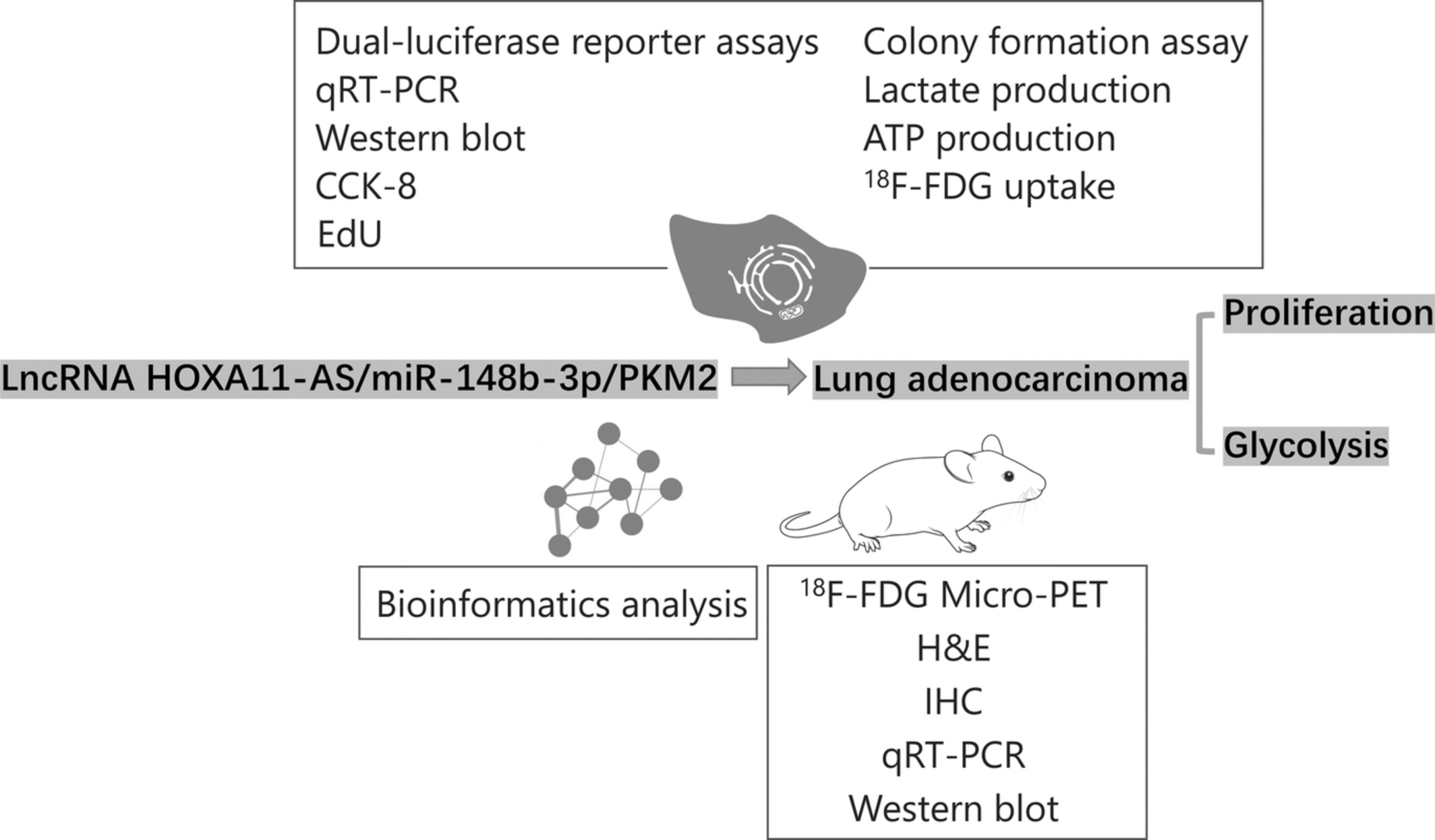
This paper elaborately explored the role of lncRNA HOXA11-AS and miR-148b-3p in glycolysis and proliferation of lung adenocarcinoma, and demonstrated that the lncRNA HOXA11-AS is involved in the regulation of PKM2, a key protein of glycolysis, through sponging miR-148b-3p, which in turn affects the proliferation and glycolysis of lung adenocarcinoma.
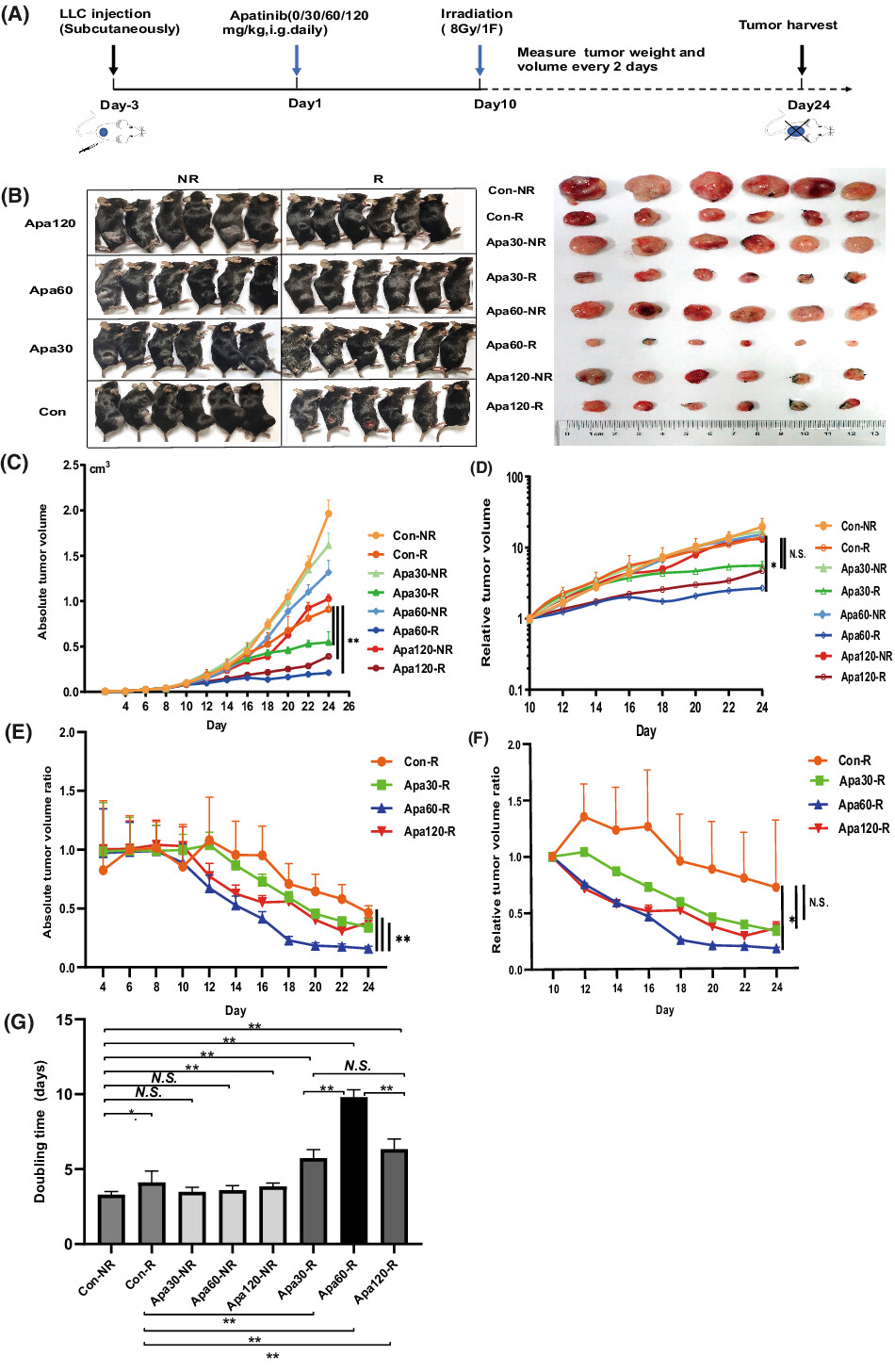
Low- dose Apatinib promotes vascular normalization and hypoxia reduction and sensitizes radiotherapy in lung cancer
- Pages: 4434-4445
- First Published: 06 September 2022
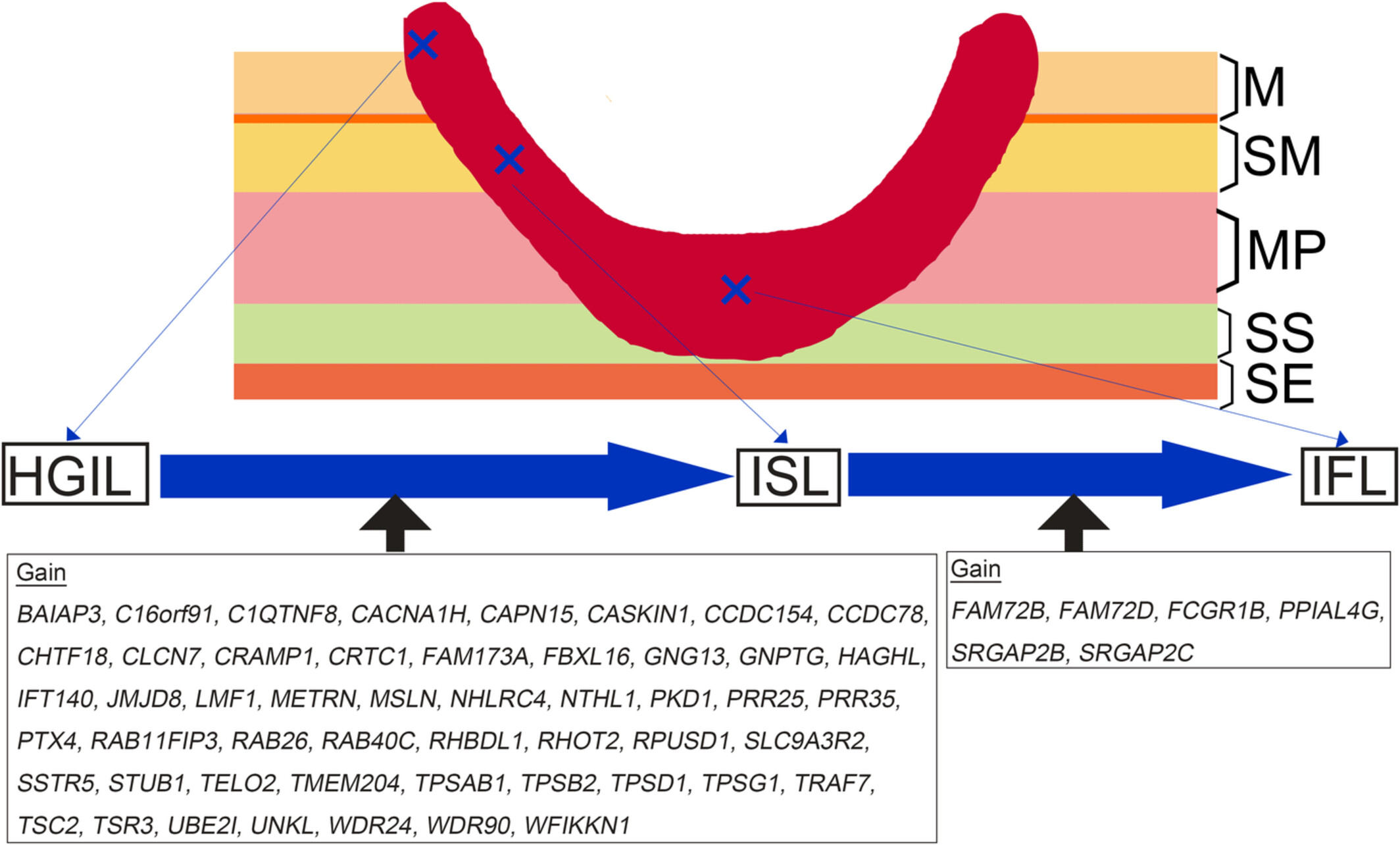
Genome-wide analysis of colorectal cancer based on gene-based somatic copy number alterations during neoplastic progression within the same tumor
- Pages: 4446-4454
- First Published: 03 August 2022
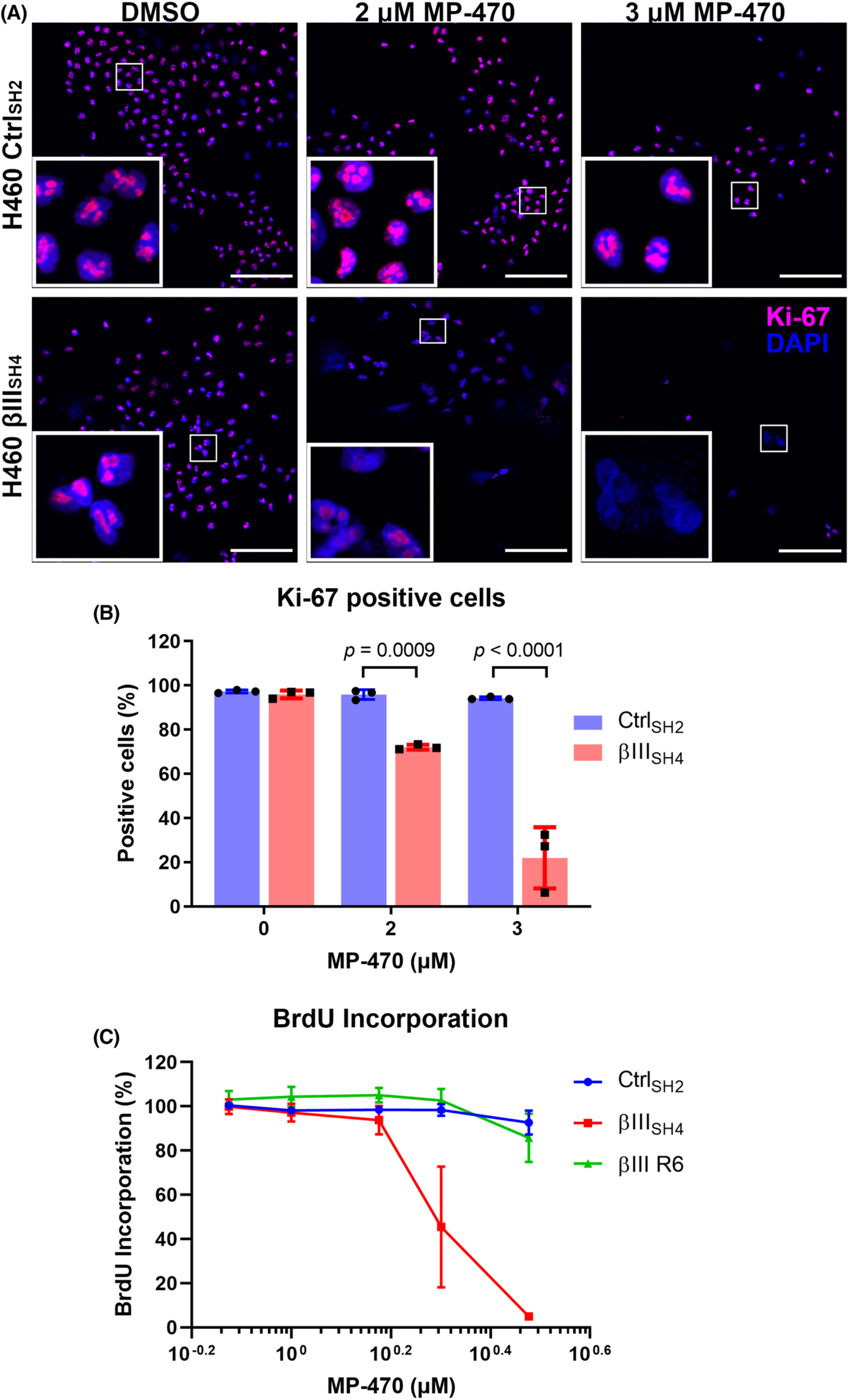
βIII-tubulin suppression enhances the activity of Amuvatinib to inhibit cell proliferation in c-Met positive non-small cell lung cancer cells
- Pages: 4455-4471
- First Published: 10 August 2022
BMAL1 promotes colorectal cancer cell migration and invasion through ERK- and JNK-dependent c-Myc expression
- Pages: 4472-4485
- First Published: 10 August 2022
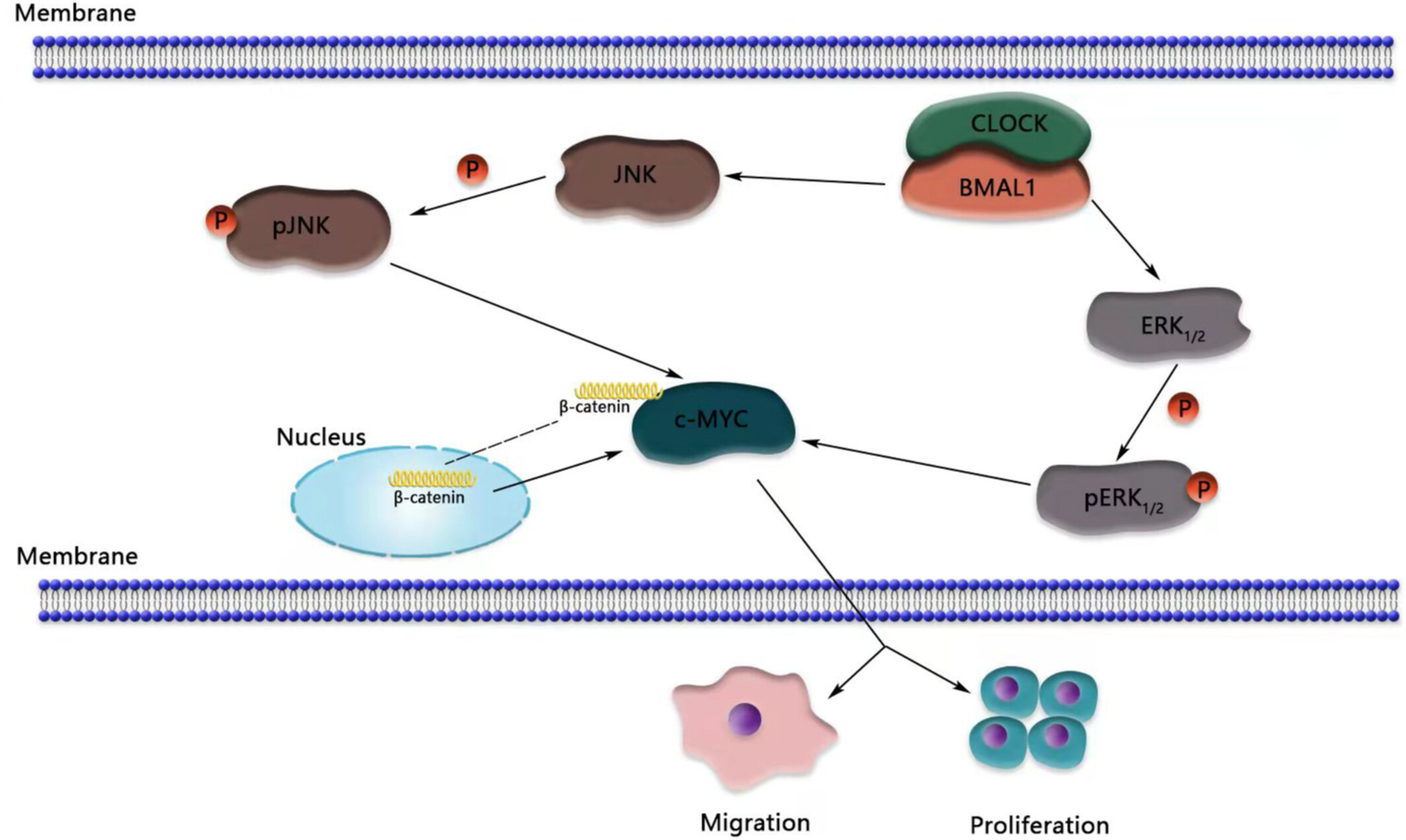
Our study demonstrate that BMAL1 plays a critical role in cell migration and invasion of CRC cells via MAPK-c-Myc pathway. Our results may deepen our understanding in the relationship of BMAL1 and tumorigenic phenotypes and be developed into a promised therapeutic target for the BMAL1-overexpression CRC.
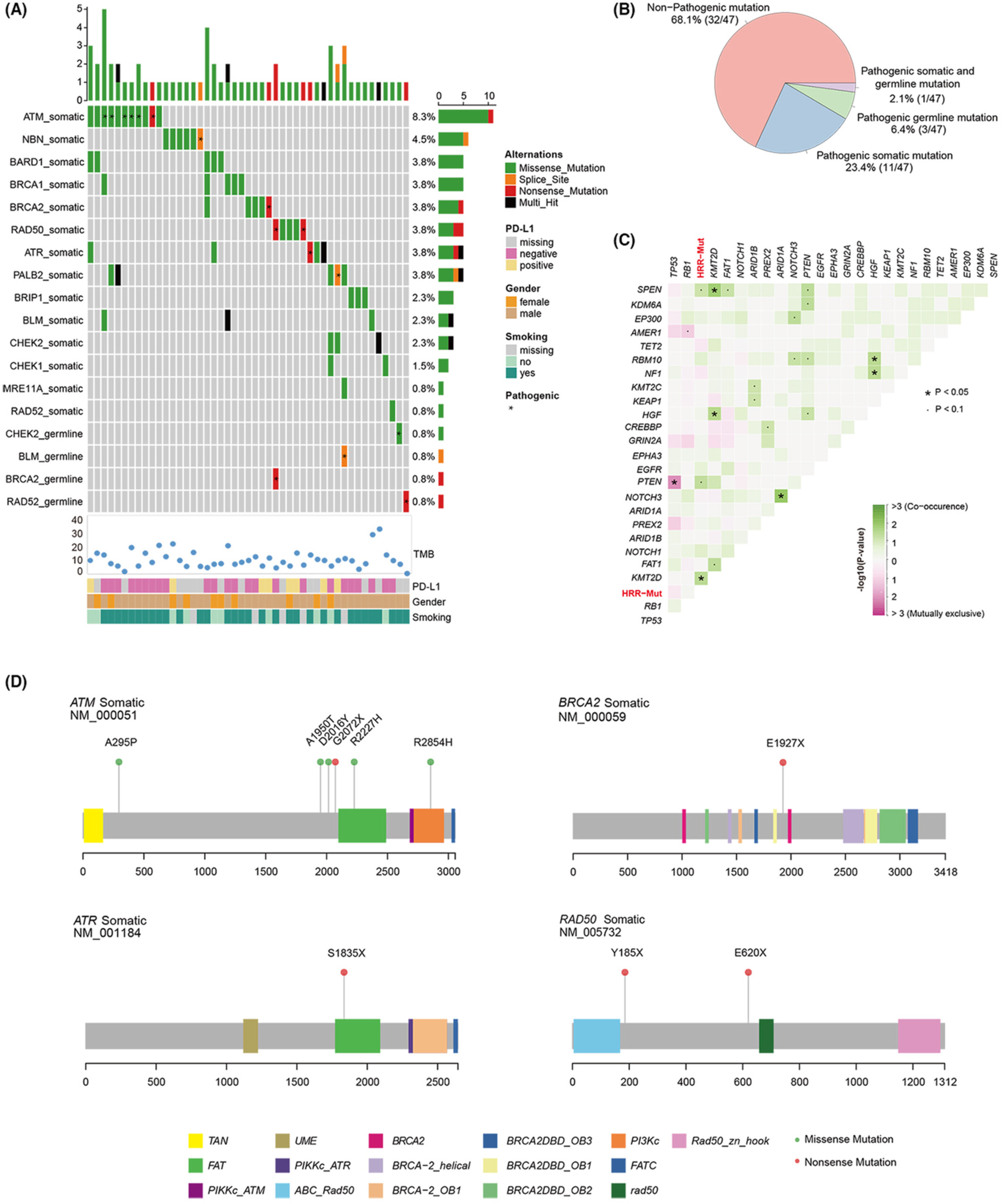
Mutational landscape of homologous recombination-related genes in small-cell lung cancer
- Pages: 4486-4495
- First Published: 26 August 2022
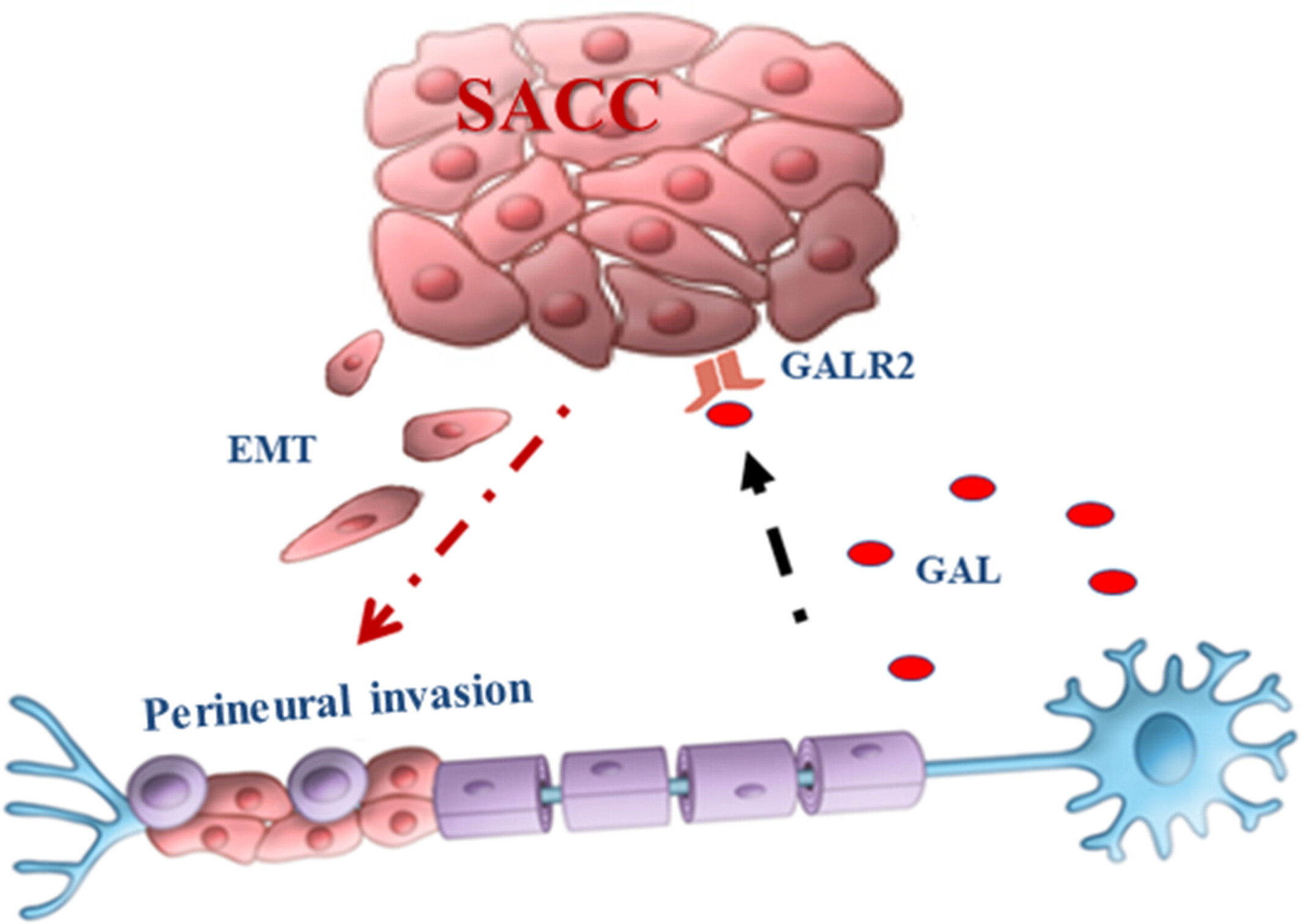
The GAL/GALR2 axis promotes the perineural invasion of salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma via epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
- Pages: 4496-4509
- First Published: 29 August 2022
Palladin promotes cancer stem cell-like properties in lung cancer by activating Wnt/Β-Catenin signaling
- Pages: 4510-4520
- First Published: 01 September 2022
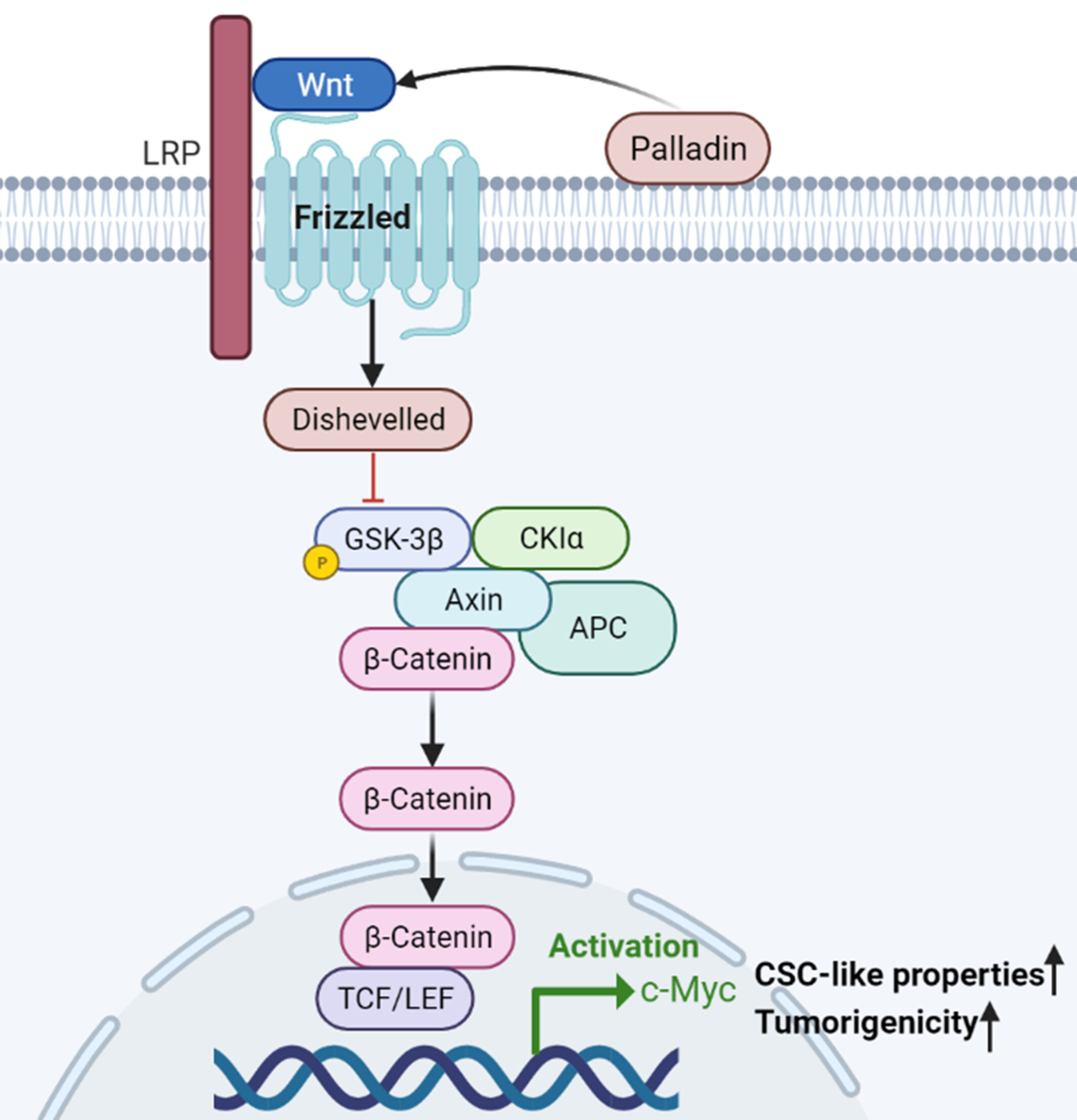
Palladin was identified to be specifically expressed in the cytomembrane of patients with NSCLC, suggesting its potential as a cell surface marker for LCSCs identification. More importantly, we demonstrated that Palladin might serve as a tumor oncogene and promote the biological properties of LCSCs, possibly by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling in NSCLC for the first time. The elucidation of this new molecular mechanism for Palladin and Wnt/β-catenin signaling activation is conducive to understand the pathogenesis of NSCLC, providing a novel possibility of the development of novel therapeutic target for CSCs targeted therapy.
CEACAM6 serves as a biomarker for leptomeningeal metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma
- Pages: 4521-4529
- First Published: 09 September 2022
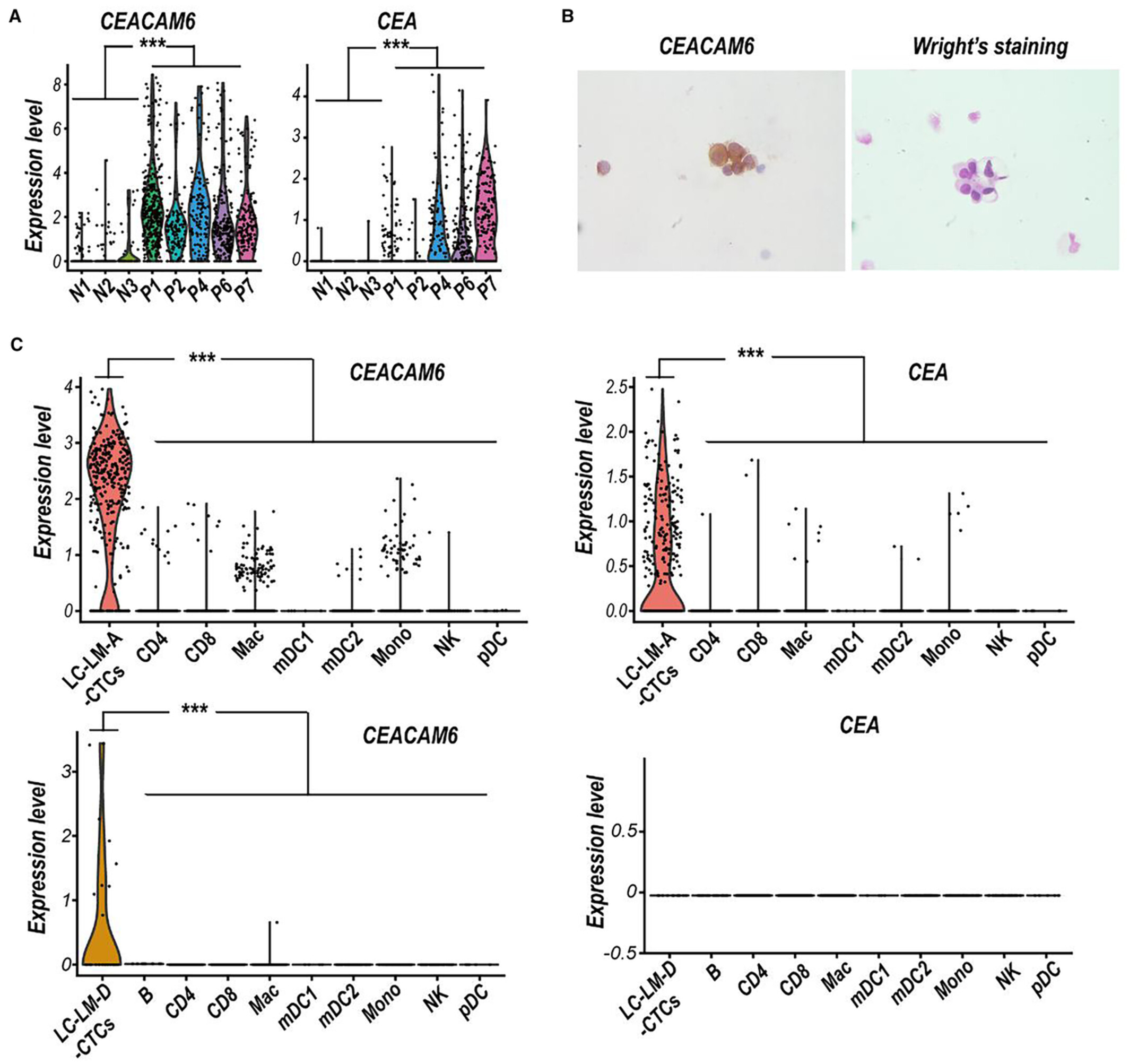
CEACAM6 in the CSF was higher in LUAD-LM than benign diseases. LUAD-LM patients had a higher level of serum CAECAM6 than healthy controls and non-LM LUAD patients. Serum CEACAM6 had a higher AUC than CEA in differentiating LM from non-LM in LUAD. CEACAM6 may serve as a potential biomarker in diagnosing LUAD-LM.
Vaspin accelerates the proliferation, invasion and metastasis of Triple-Negative breast cancer through MiR-33a-5p/ABHD2
- Pages: 4530-4542
- First Published: 20 September 2022
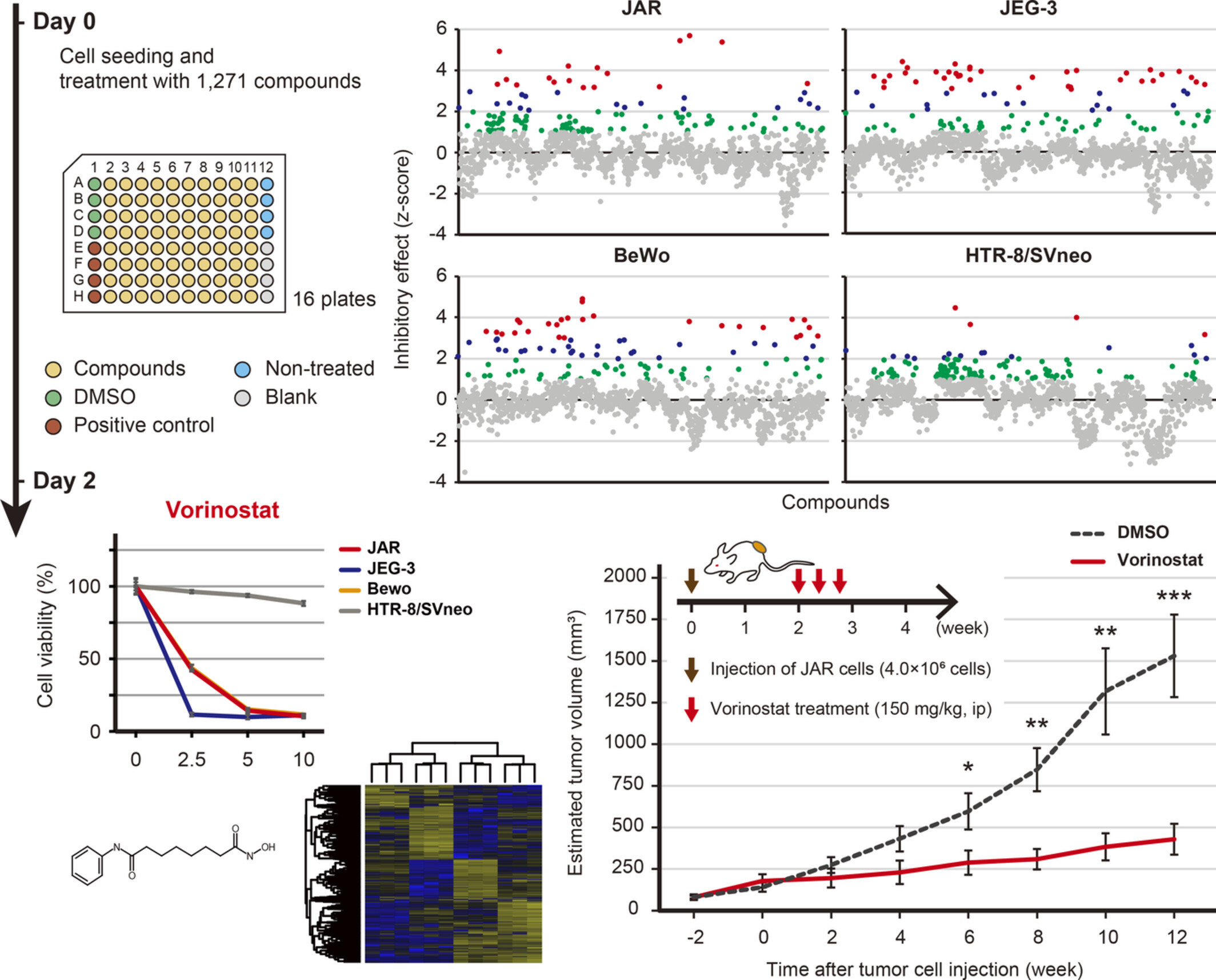
Drug library screening identifies histone deacetylase inhibition as a novel therapeutic strategy for choriocarcinoma
- Pages: 4543-4556
- First Published: 15 September 2022
Dirty necrosis in renal cell carcinoma is associated with NETosis and systemic inflammation
- Pages: 4557-4567
- First Published: 20 September 2022
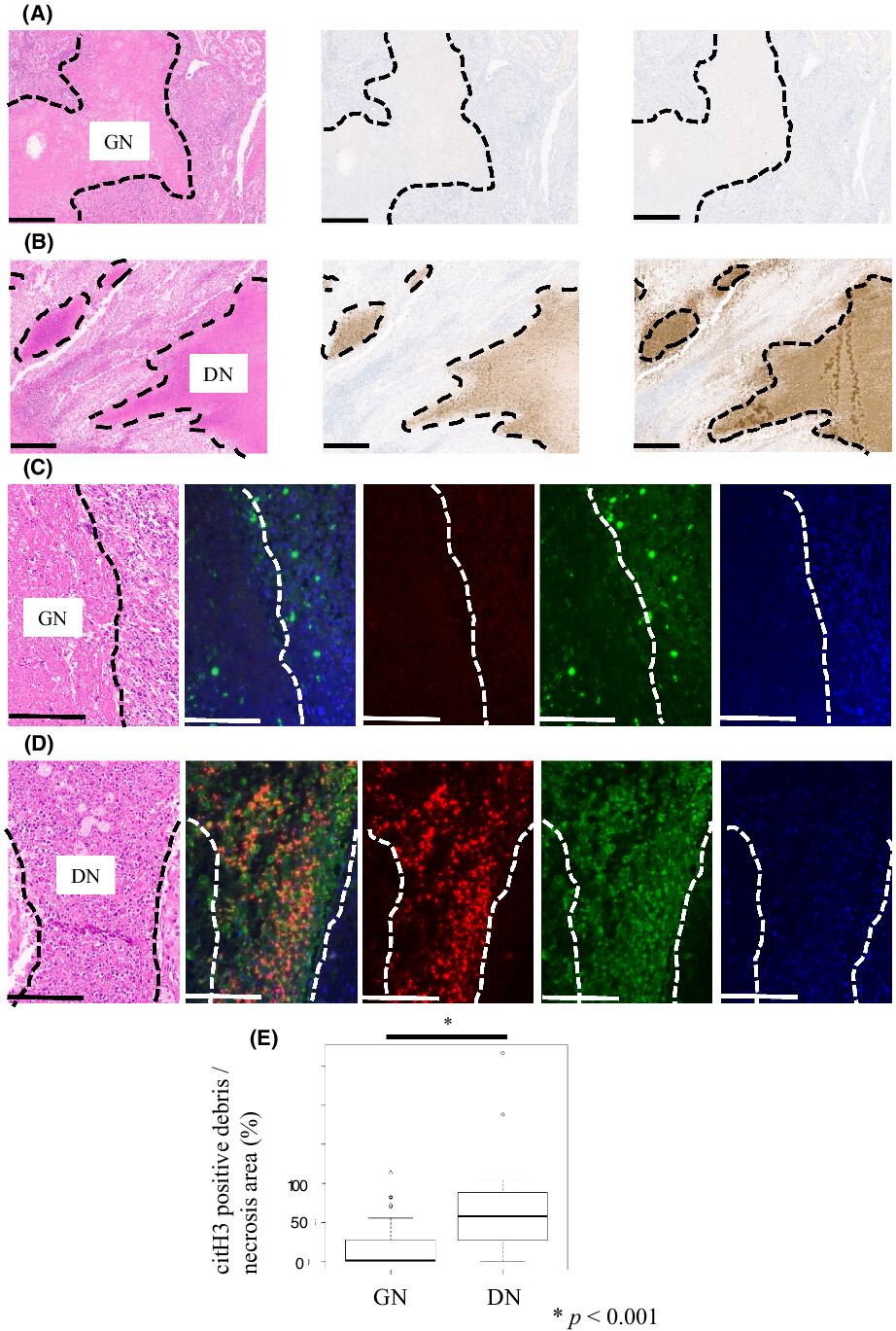
Dirty necrosis (DN) in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is morphologically characterized by abundant neutrophil infiltration and has significant potential as an unfavorable prognostic indicator. In addition, DN in RCC is characterized by neutrophil extracellular traps production and systemic inflammation.
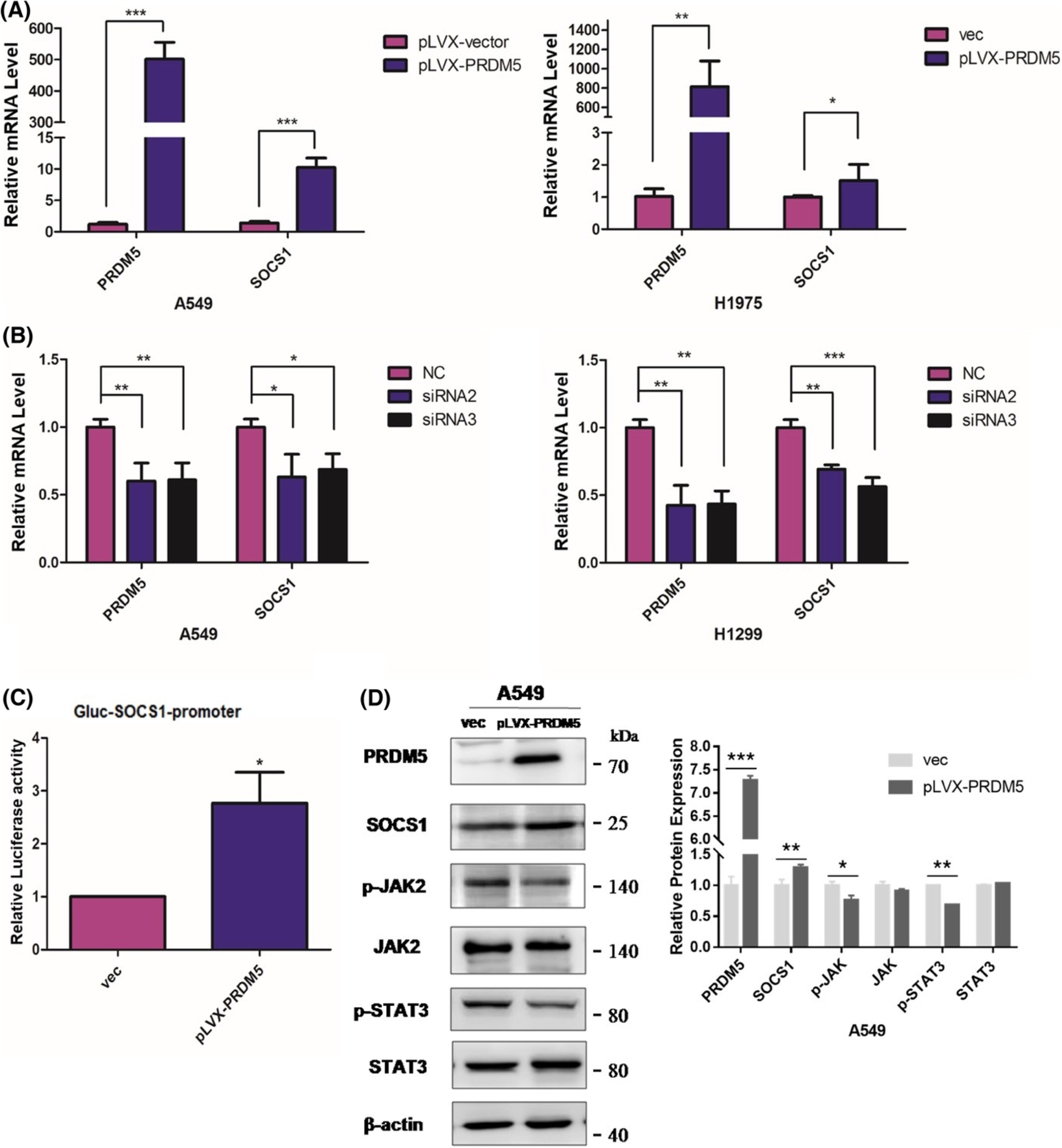
Deregulation of PRDM5 promotes cell proliferation by regulating JAK/STAT signaling pathway through SOCS1 in human lung adenocarcinoma
- Pages: 4568-4578
- First Published: 20 September 2022
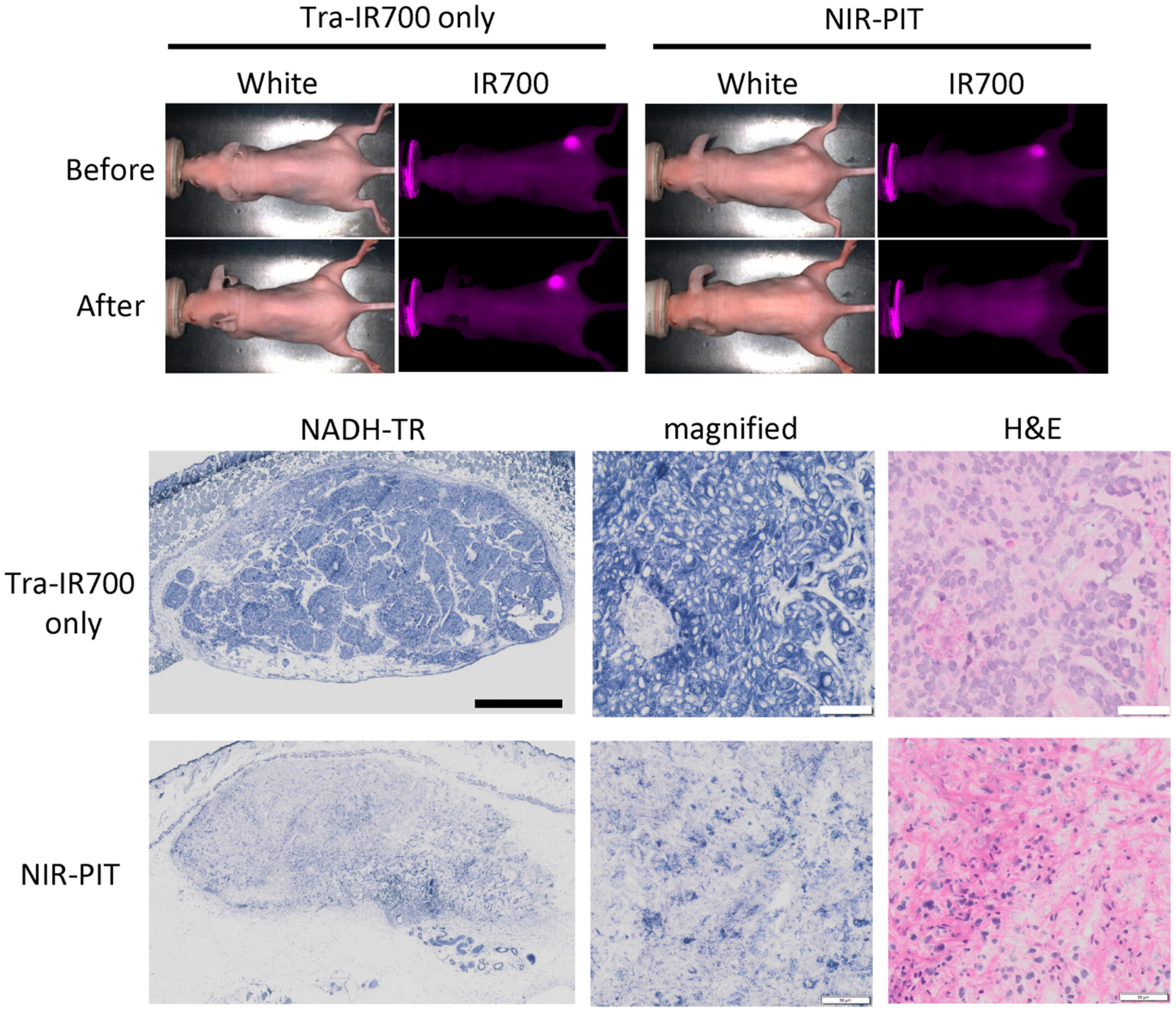
Trastuzumab-based near-infrared photoimmunotherapy in xenograft mouse of breast cancer
- Pages: 4579-4589
- First Published: 18 October 2022
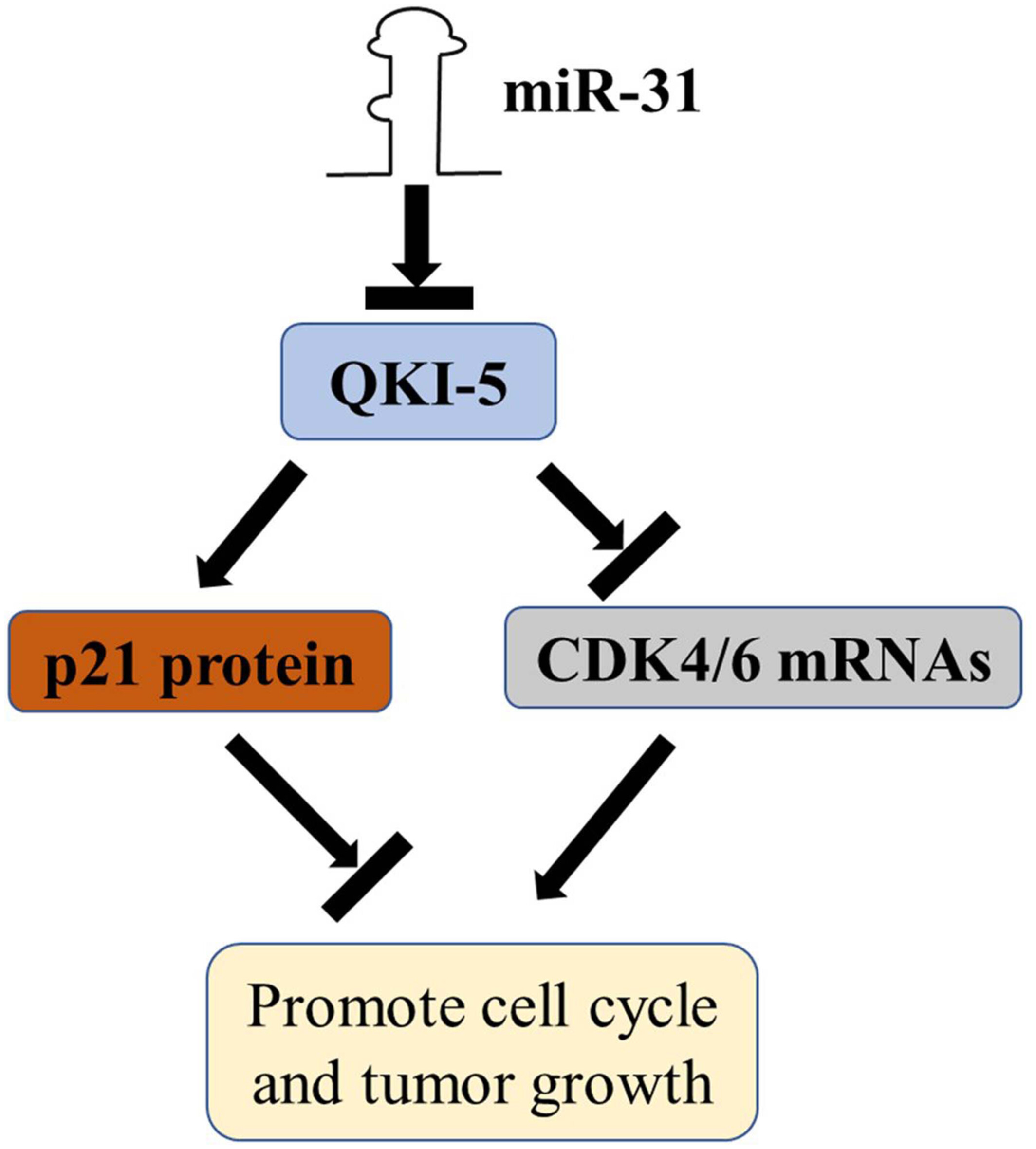
miR-31/QKI-5 axis facilitates cell cycle progression of non-small-cell lung cancer cells by interacting and regulating p21 and CDK4/6 expressions
- Pages: 4590-4604
- First Published: 29 September 2022
Cisplatin-induced HSF1-HSP90 axis enhances the expression of functional PD-L1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma
- Pages: 4605-4615
- First Published: 06 October 2022
In this report, we demonstrated that CDDP increased the cell surface expression of PD-L1 on HSC2 OSCC cells and was mediated by HSF1 and HSP90.
REVIEW
Cancer Prevention
Breastfeeding reduces the risk of breast cancer: A call for action in high-income countries with low rates of breastfeeding
- Pages: 4616-4625
- First Published: 26 September 2022
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Cancer Prevention
Survival disadvantage of male children with retinoblastoma in the United States: Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results (2000–2017) Evidence
- Pages: 4626-4637
- First Published: 31 January 2023
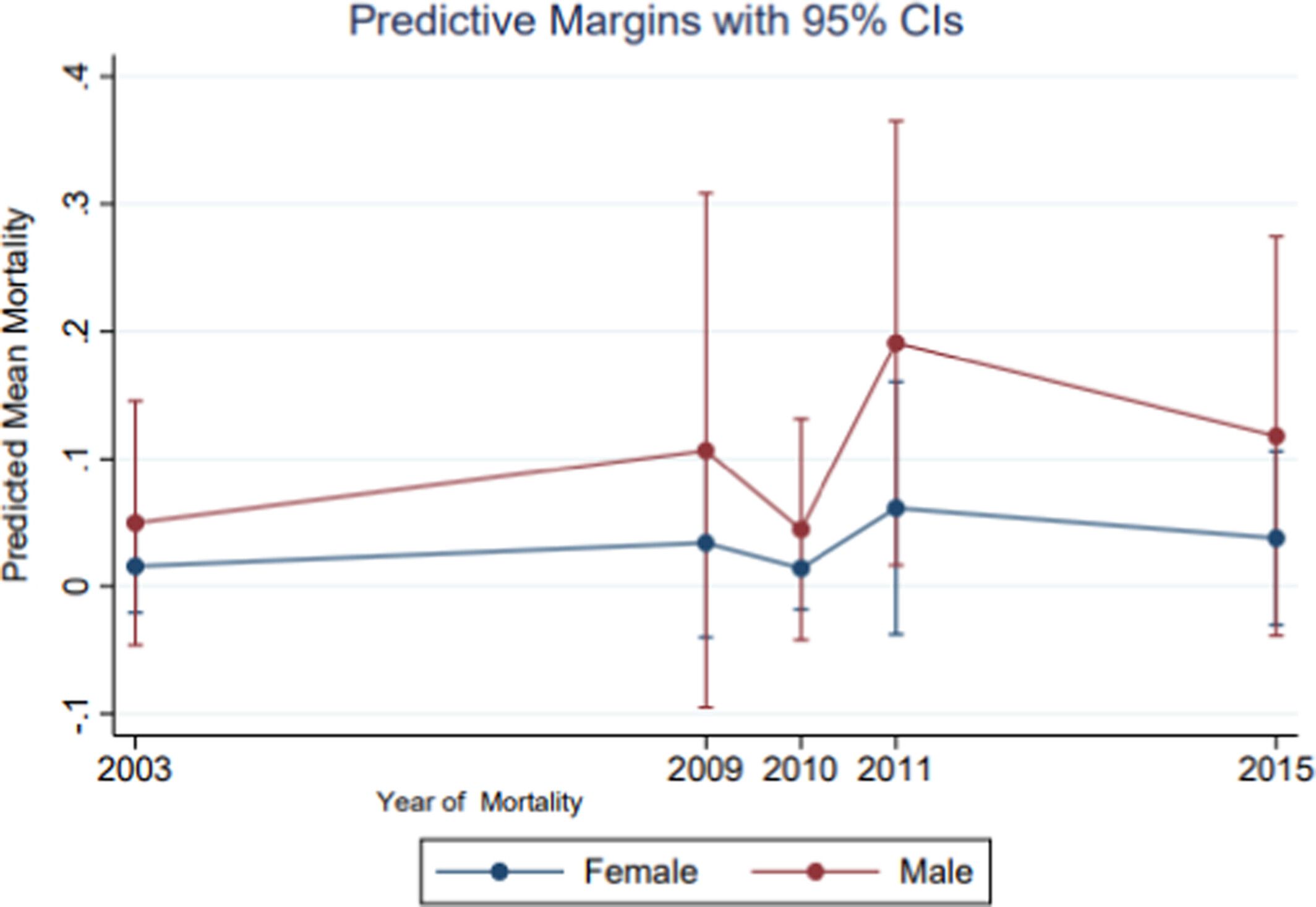
Retinoblastoma is a rare malignancy involving the retina, although more common among children, with genetic inheritance explaining the incidence as well as acquired forms. The incidence varies among race and sex as well as mortality and survival. The current study aimed to assess retinoblastoma cumulative incidence, mortality, and survival by sex. In a representative sample of pediatric retinoblastoma, there was a sex differential in survival with excess risk of dying identified among males relative to females, which may be explained in X-linkage in males.
Financial burden among cancer patients: A national-level perspective
- Pages: 4638-4646
- First Published: 19 July 2022
Given that this study cohort is primarily senior citizens, it is especially troubling that an active working status seems to be an important requirement for managing cancer treatment without severe financial hardship. In the absence of more robust financial support for these patients, financial planning has become a vital part of the treatment process for cancer patients. Until the introduction of legislation that makes cancer treatment financially viable, health systems have a responsibility to direct resources toward the education and assistance of these patients.
Impact of U.S. Preventive Services Task Force lung cancer screening update on drivers of disparities in screening eligibility
- Pages: 4647-4654
- First Published: 24 July 2022
Physical activity, polygenic risk score, and colorectal cancer risk
- Pages: 4655-4666
- First Published: 26 July 2022
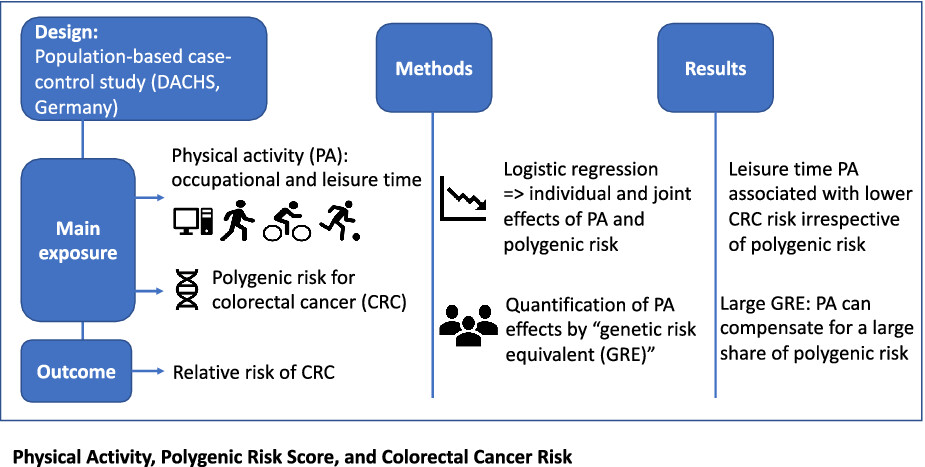
This study, based on a large ongoing case-control study (the DACHS study) on CRC in Germany, adds to the limited evidence of the individual and joint association of PA and polygenic risk score (PRS) with CRC risk and compares these associations using a novel metric of GRE for effective risk communication. We found that leisure time PA, in particular sports, was associated with reduced CRC risk regardless of PRS levels. The high GREs suggest that adequate sports activity can compensate for a large share of predetermined polygenic risk for CRC.
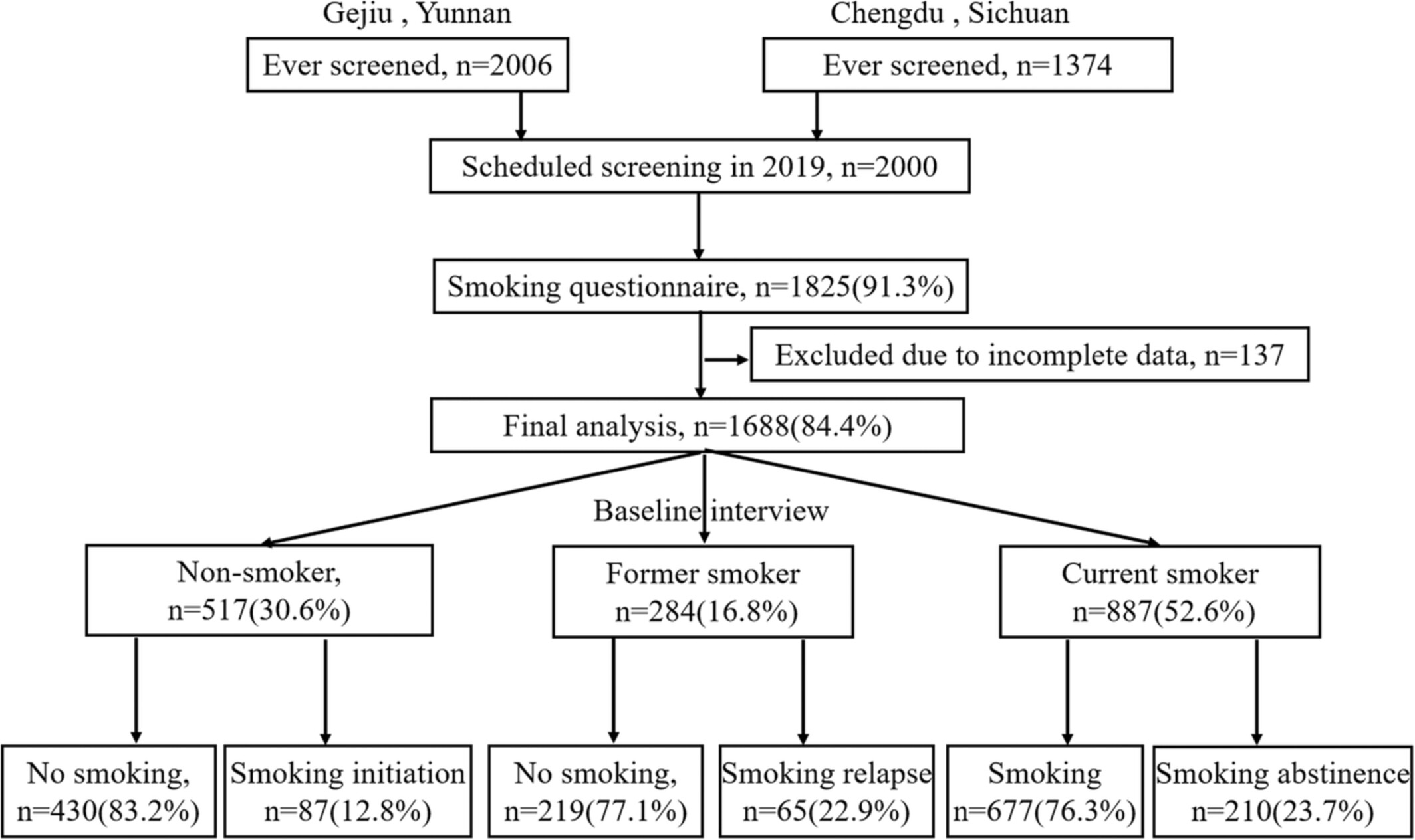
The impact of low-dose CT on smoking behavior among non-smokers, former-smokers, and smokers: A population-based screening cohort in rural China
- Pages: 4667-4678
- First Published: 27 July 2022
Ex vivo NMR metabolomics approach using cerebrospinal fluid for the diagnosis of primary CNS lymphoma: Correlation with MR imaging characteristics
- Pages: 4679-4689
- First Published: 08 August 2022
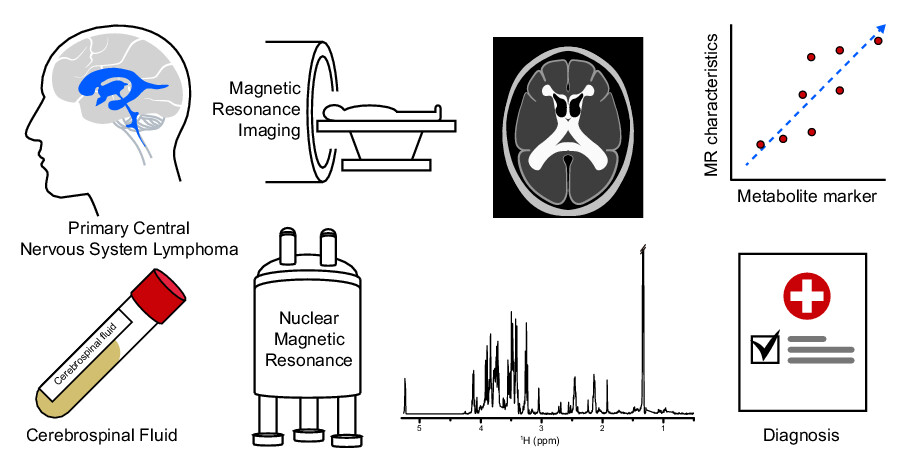
For the treatment and prognosis of primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL), an early and precise diagnosis is critical, but brain biopsy and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) cytology are invasive and has poor diagnostic accuracy, respectively. In our study, NMR-based analysis of CSF in PCNSL patients revealed a different metabolic profile. This is significantly correlated with magnetic resonance imaging characteristics. This approach could reduce costs, avoid invasive diagnostic procedures, and allow treatment to begin immediately for PCNSL patients.
Association between dietary intake of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and risk of colorectal cancer in the Japanese population: The Japan Collaborative Cohort Study
- Pages: 4690-4700
- First Published: 10 August 2022
Behavioral beliefs about genetic counseling among high-risk Latina breast cancer survivors in Florida and Puerto Rico
- Pages: 4701-4706
- First Published: 08 August 2022
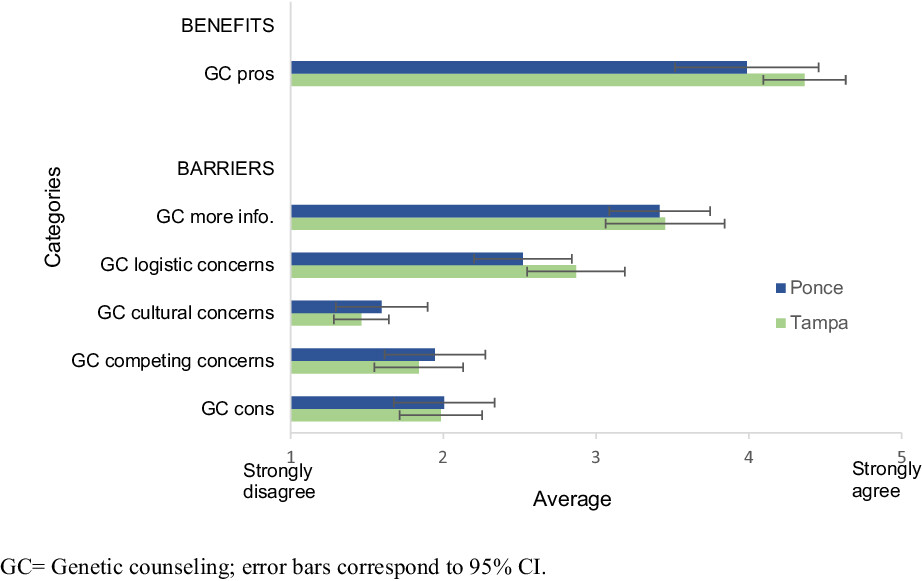
Spanish-preferring Latina breast cancer survivors had high positive beliefs about genetic counseling and their reported benefits and barriers for genetic counseling were similar for survivors residing in Florida and Puerto Rico. The study findings highlight the factors that should be considered when designing culturally sensitive interventions for Latina breast cancer survivors and suggest that similar intervention contents to promote uptake of genetic counseling could be implemented in Florida and Puerto Rico.
Effects of the different periods and magnitude of COVID-19 infection spread on cancer operations: Interrupted time series analysis of medical claims data
- Pages: 4707-4714
- First Published: 20 September 2022
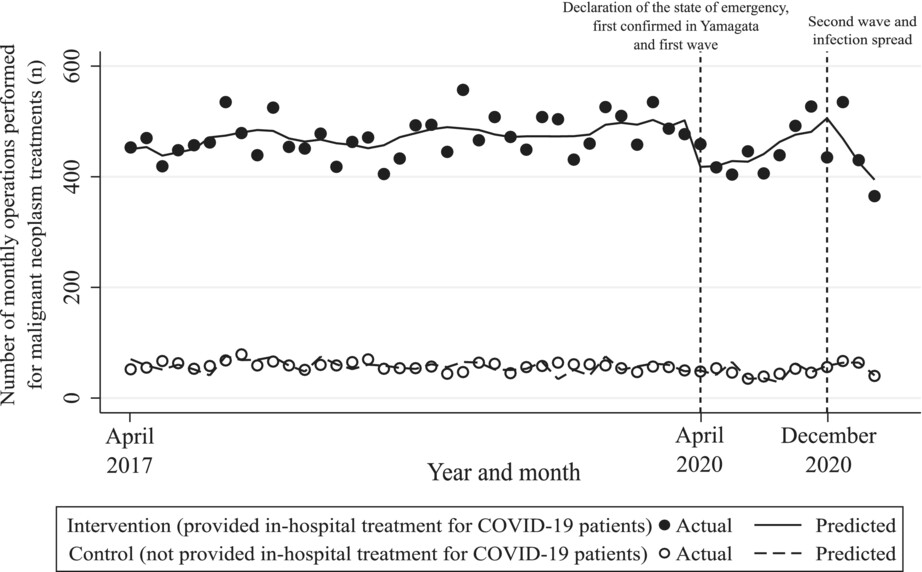
This retrospective observational study used medical claims data in Japan to examine the effects of different COVID-19 periods and magnitudes of its spread on in-hospital cancer operations. We confirmed that cancer operations were significantly reduced in hospitals where in-hospital treatments for patients with COVID-19 were provided during the COVID-19 pandemic. Our findings suggest that a statement of emergency by the government as well as the spread of COVID-19 both have an influence on the number of cancer operations performed in Yamagata prefecture during the COVID-19 era.
Growth in eligibility criteria content and failure to accrue among National Cancer Institute (NCI)-affiliated clinical trials
- Pages: 4715-4724
- First Published: 18 November 2022
Protein and amino acid intakes in relation to prostate cancer risk and mortality—A prospective study in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition
- Pages: 4725-4738
- First Published: 23 September 2022
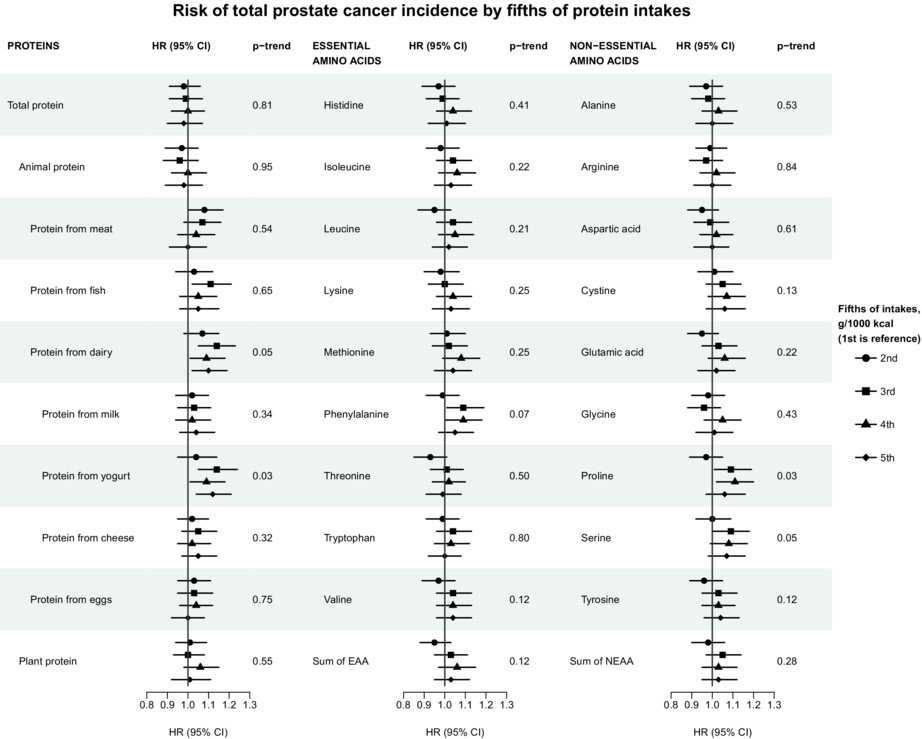
In this large, prospective cohort study, we found no strong associations of protein and amino acid intakes with prostate cancer incidence or mortality. Nonetheless, the results suggested weak positive associations for dairy and yogurt protein with prostate cancer risk, and possibly for egg protein with prostate cancer death. These results deserve further investigation in large-scale, pooled analyses aimed at clarifying these associations.
Patient-reported outcomes in childhood head and neck rhabdomyosarcoma survivors and their relation to physician-graded adverse events—A multicenter study using the FACE-Q Craniofacial module
- Pages: 4739-4750
- First Published: 07 October 2022
Physician graded adverse effects are not sufficient to provide tailored care for head and neck cancer survivors. Patient reported outcome scores for appearance, health related quality of life and facial function was reported negatively by many survivors. This study highlights the importance of incorporating patient reported outcome measures in follow-up clinic.
Financial toxicity of patients with lung cancer in China: Results from a National Survey Study
- Pages: 4751-4760
- First Published: 21 September 2022
Genetic ancestry, differential gene expression, and survival in pediatric B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Pages: 4761-4772
- First Published: 20 September 2022

Using genotype, gene expression, and survival data, we analyzed the relationship between race/ethnicity and survival in pediatric B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL), when accounting for genes associated with genetic ancestry. Our results suggest that genetic ancestry and its associated genes play meaningful roles in the occurrence and magnitude of racial/ethnic disparities in B-ALL.
Patient-reported disruptions to cancer care during the COVID-19 pandemic: A national cross-sectional study
- Pages: 4773-4785
- First Published: 07 October 2022
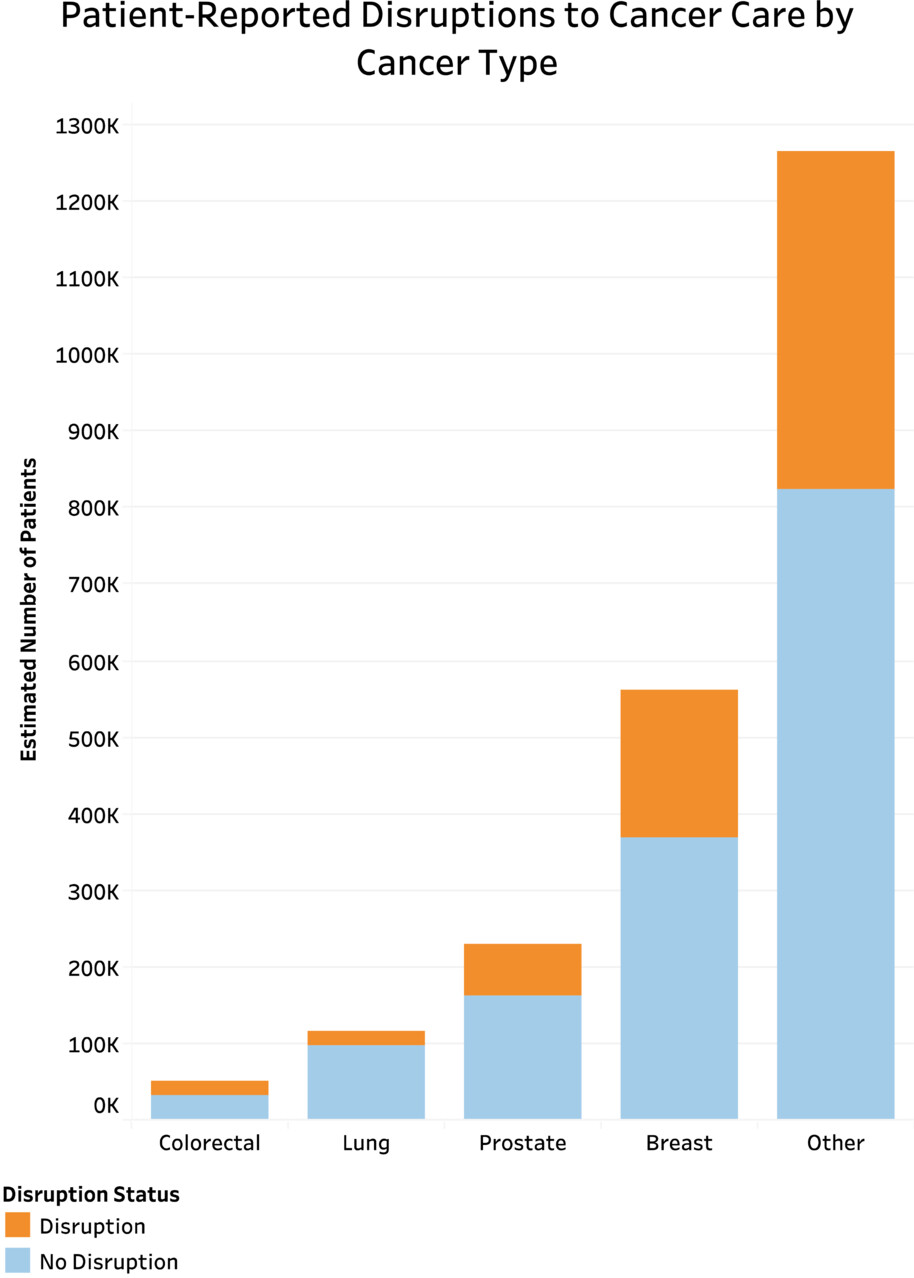
In an analysis of National Health Interview Survey (NHIS) data from 2020, we found nearly 1/3 of patients reportedly requiring cancer treatment or other cancer care experienced disruptions due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Patients experiencing disruptions were significantly more likely to be younger or female, as well as reported higher rates of anxiety. The long term impact of these care disruptions on outcomes merits further study.
Decision regret related to urinary diversion choices after cystectomy among Chinese bladder cancer patients
- Pages: 4786-4793
- First Published: 21 October 2022
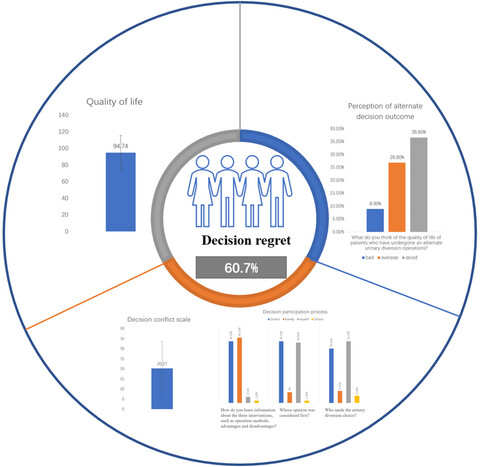
It is important to acknowledge that Chinese mainland culture and medical practice are distinct which presents a number of issues that need to be considered in more detail. Understanding how these distinctions influence regret and outcomes may enable us to develop patient education programs and to promote participation.
Association between depression and anxiety status of breast cancer patients before adjuvant chemotherapy and chemotherapy-induced adverse events
- Pages: 4794-4800
- First Published: 26 September 2022
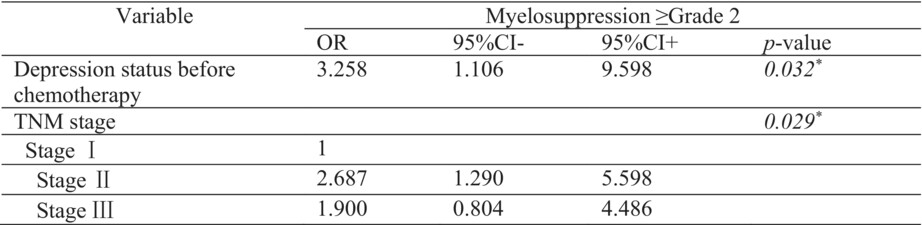
We explored the relationship between depression/anxiety status and adverse events induced by adjuvant chemotherapy. Patients with depression were more likely to develop myelosuppression. Monitoring the psychological status of breast cancer patients before chemotherapy may help to optimize the management of adverse events.
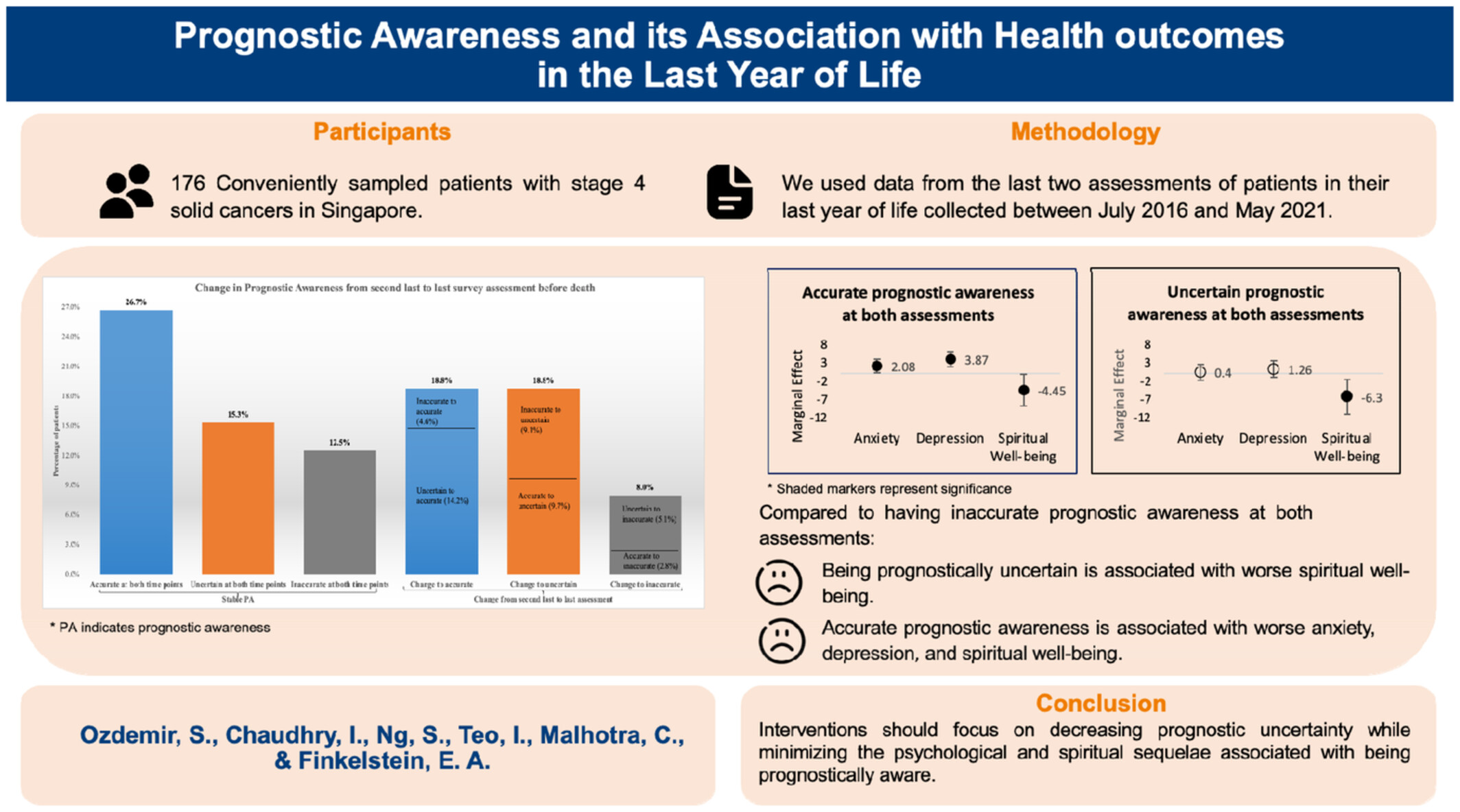
Prognostic awareness and its association with health outcomes in the last year of life
- Pages: 4801-4808
- First Published: 06 October 2022
Describing settings of care in the last 100 days of life for cancer decedents: a population-based descriptive study
- Pages: 4809-4820
- First Published: 24 October 2022
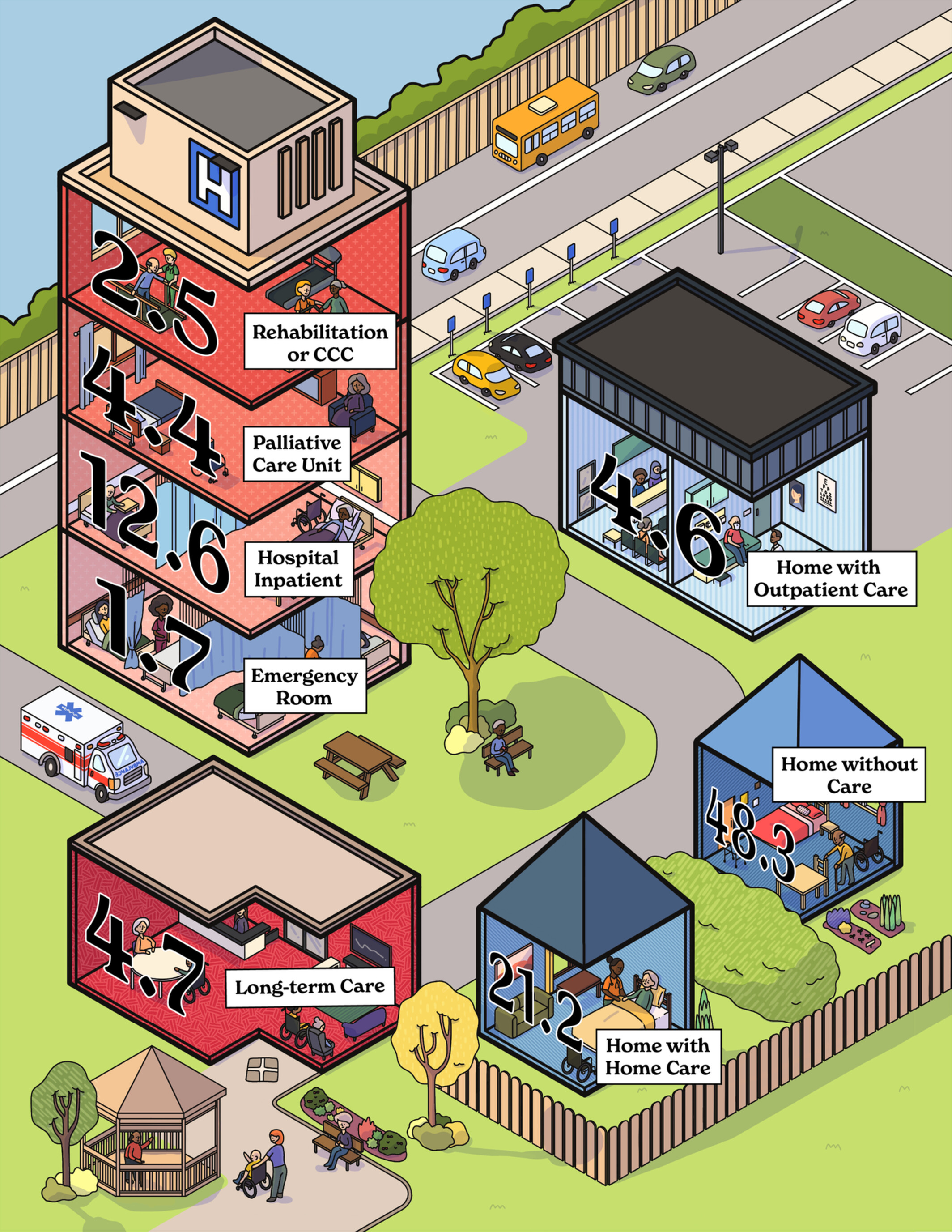
A population-based descriptive study using linked health administrative data in Ontario, Canada, described where patients dying of cancer spent their last 100 days of life. From 2013 to 2017, patients dying with cancer spent most of their time in either institutions (25.9 days) or at home without any care (48.3 days).
Cognitive impairment in adolescent and young adult cancer patients: Pre-treatment findings of a longitudinal study
- Pages: 4821-4831
- First Published: 11 October 2022
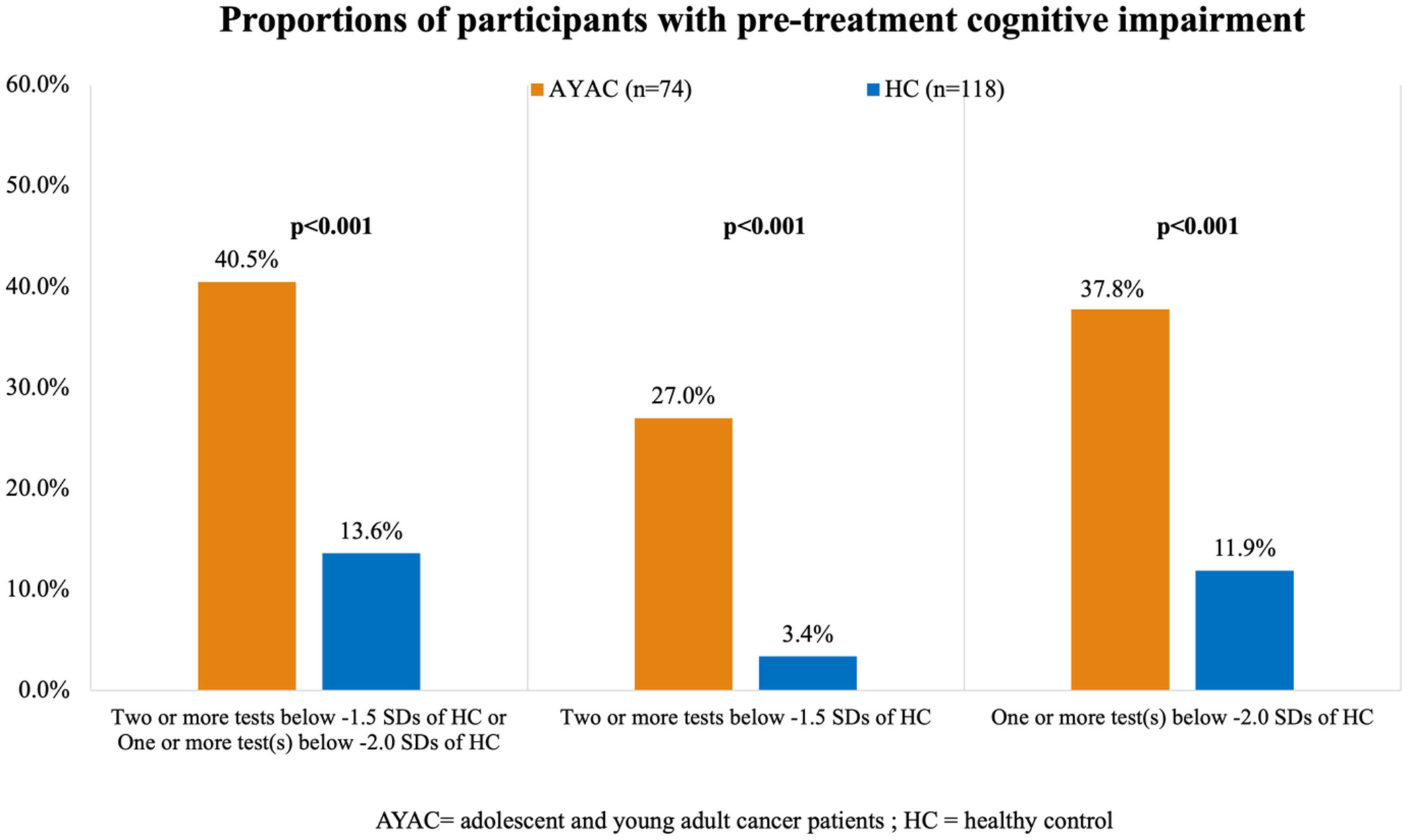
This study reported about pre-treatment cancer-related cognitive impairment between newly diagnosed AYAC and age-matched healthy control. There were higher proportions of subjects with impairment and elevated inflammatory marker levels among AYAC compared to controls. At the same time, lower levels of self-perceived impairment and lower baseline BDNF levels were reported in this patient group.
Worsened outcomes of newly diagnosed cancer in patients with recent emergency care visits: A retrospective cohort study of 3699 adults in a safety net health system
- Pages: 4832-4841
- First Published: 16 November 2022
Prostate cancer-related anxiety among long-term survivors after radical prostatectomy: A longitudinal study
- Pages: 4842-4851
- First Published: 18 October 2022
Findings of the current study highlight PC-related anxiety as a burden of survivors many years after diagnosis and treatment. The respective disease-specific anxiety was the strongest predictor of this anxiety 5 years later, which emphasizes the need of screening and monitoring in a timely manner for PC-related anxiety. Treating urologists should screen, identify, and monitor patients at risk for targeted referrals to psychosocial services.
The long-term survival of esophageal cancer in elderly patients: A multi-center, retrospective study from China
- Pages: 4852-4863
- First Published: 10 October 2022
Bioinformatics
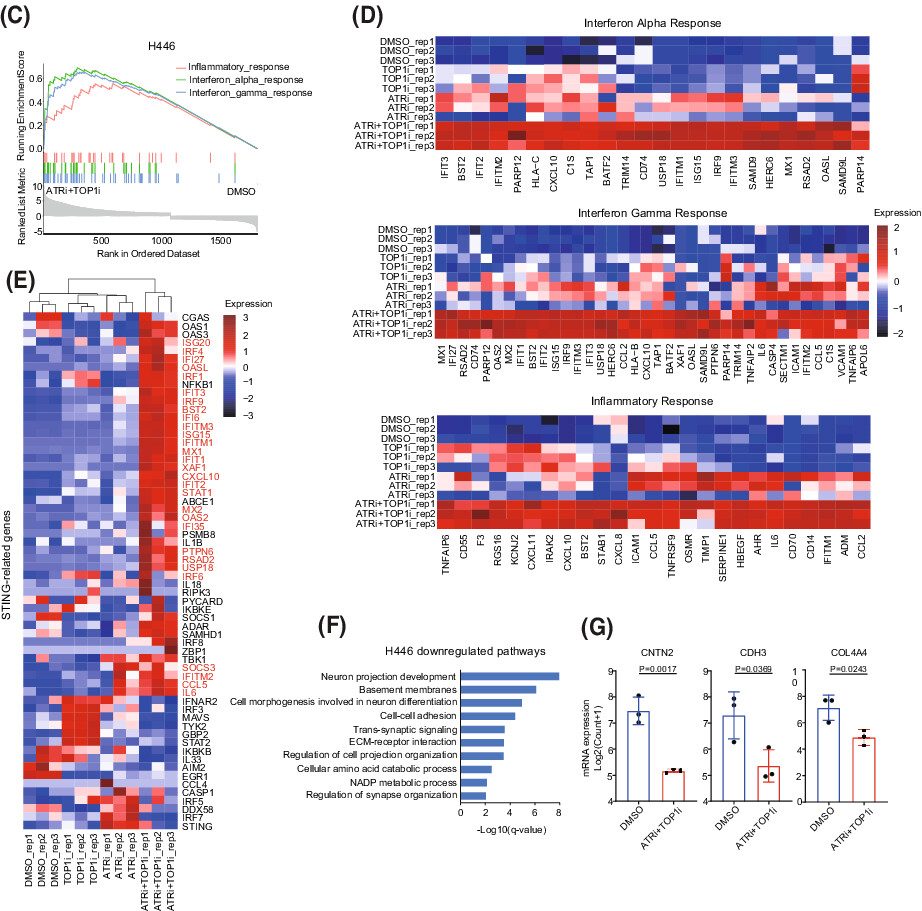
Immunogenicity of small-cell lung cancer associates with STING pathway activation and is enhanced by ATR and TOP1 inhibition
- Pages: 4864-4881
- First Published: 11 August 2022
COL3A1: Potential prognostic predictor for head and neck cancer based on immune-microenvironment alternative splicing
- Pages: 4882-4894
- First Published: 29 August 2022
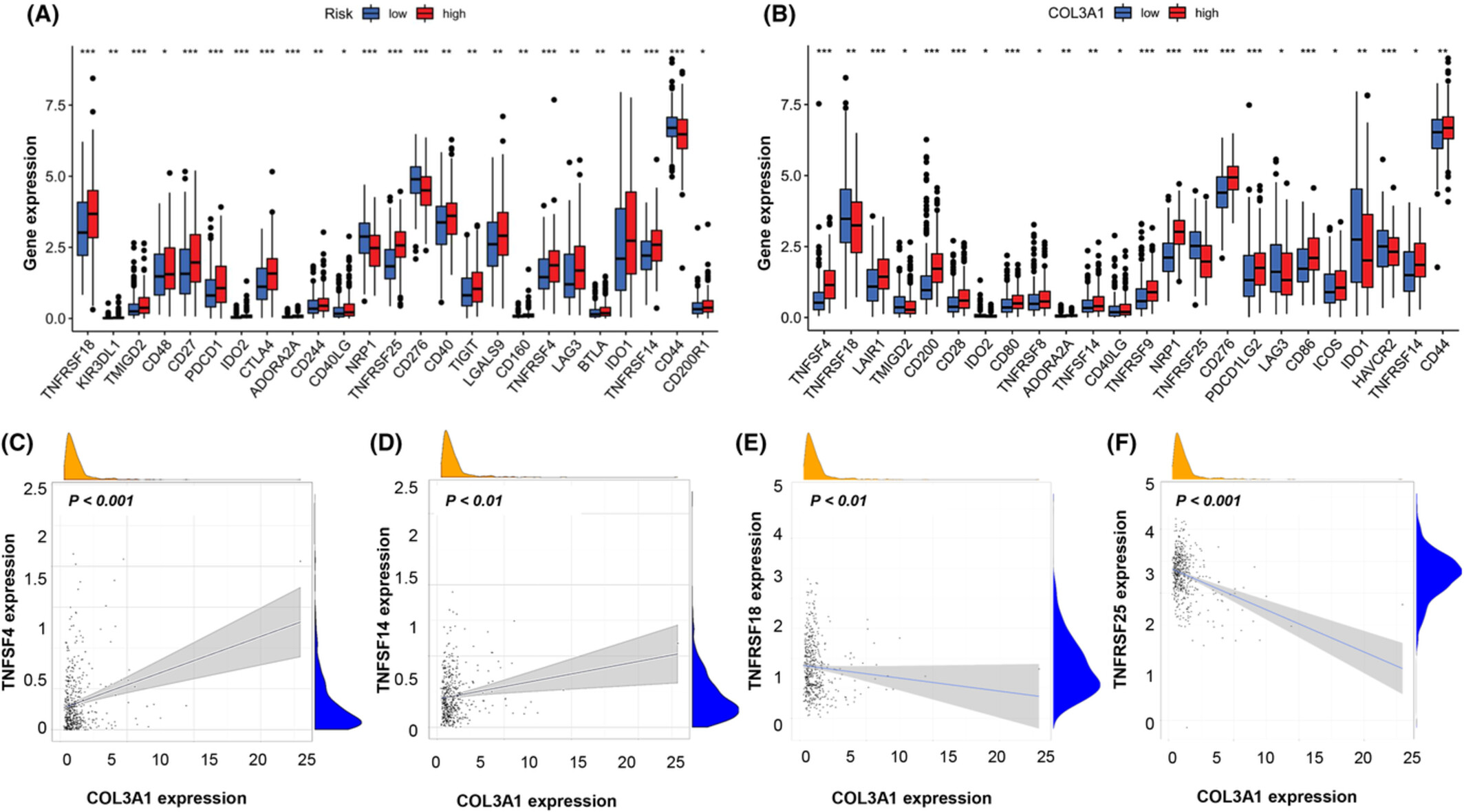
Expression levels of COL3A1 were correlated with HNSCC differentiation but were found to be independent factors affecting HNSCC patients CloseCurlyQuote; overall survival rates. #10;COL3A1 exhibited good performance in evaluating immune cell infiltrations, immune activities, and immune checkpoint gene expressions in HNSCC.
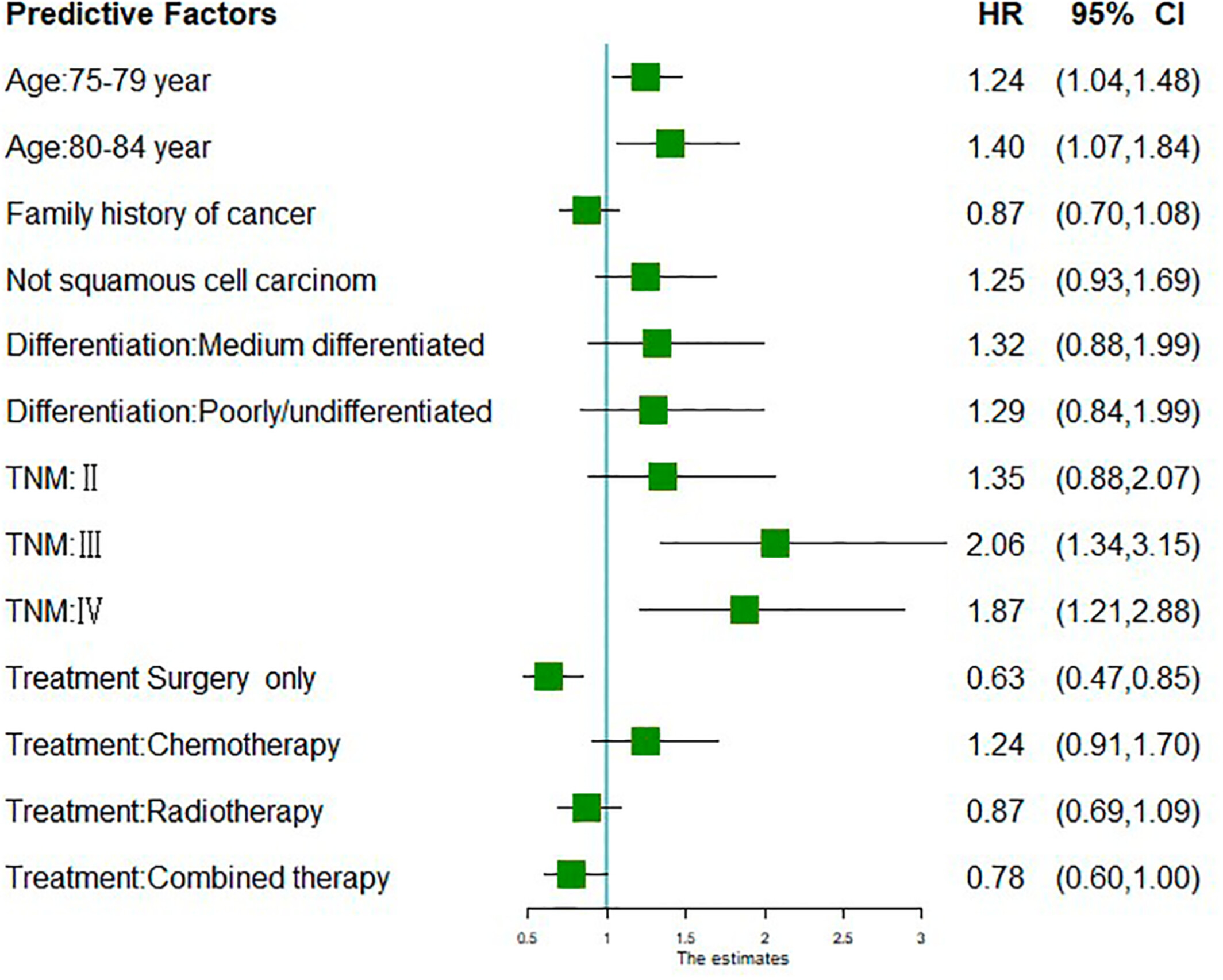
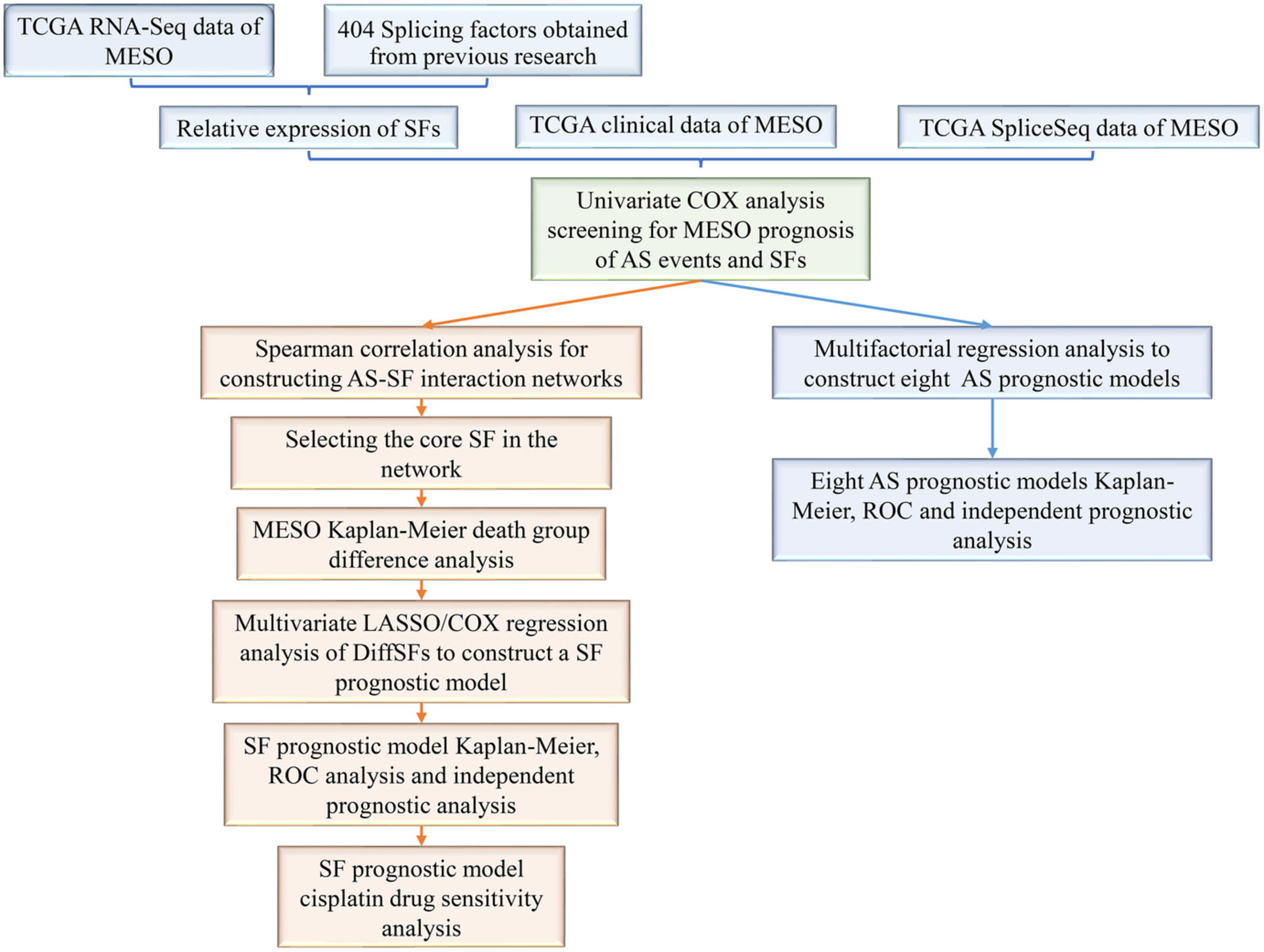
Prognostic risk assessment model for alternative splicing events and splicing factors in malignant pleural mesothelioma
- Pages: 4895-4906
- First Published: 28 August 2022
Clinical implication and immunological landscape analyses of ANLN in pan-cancer: A new target for cancer research
- Pages: 4907-4920
- First Published: 28 August 2022
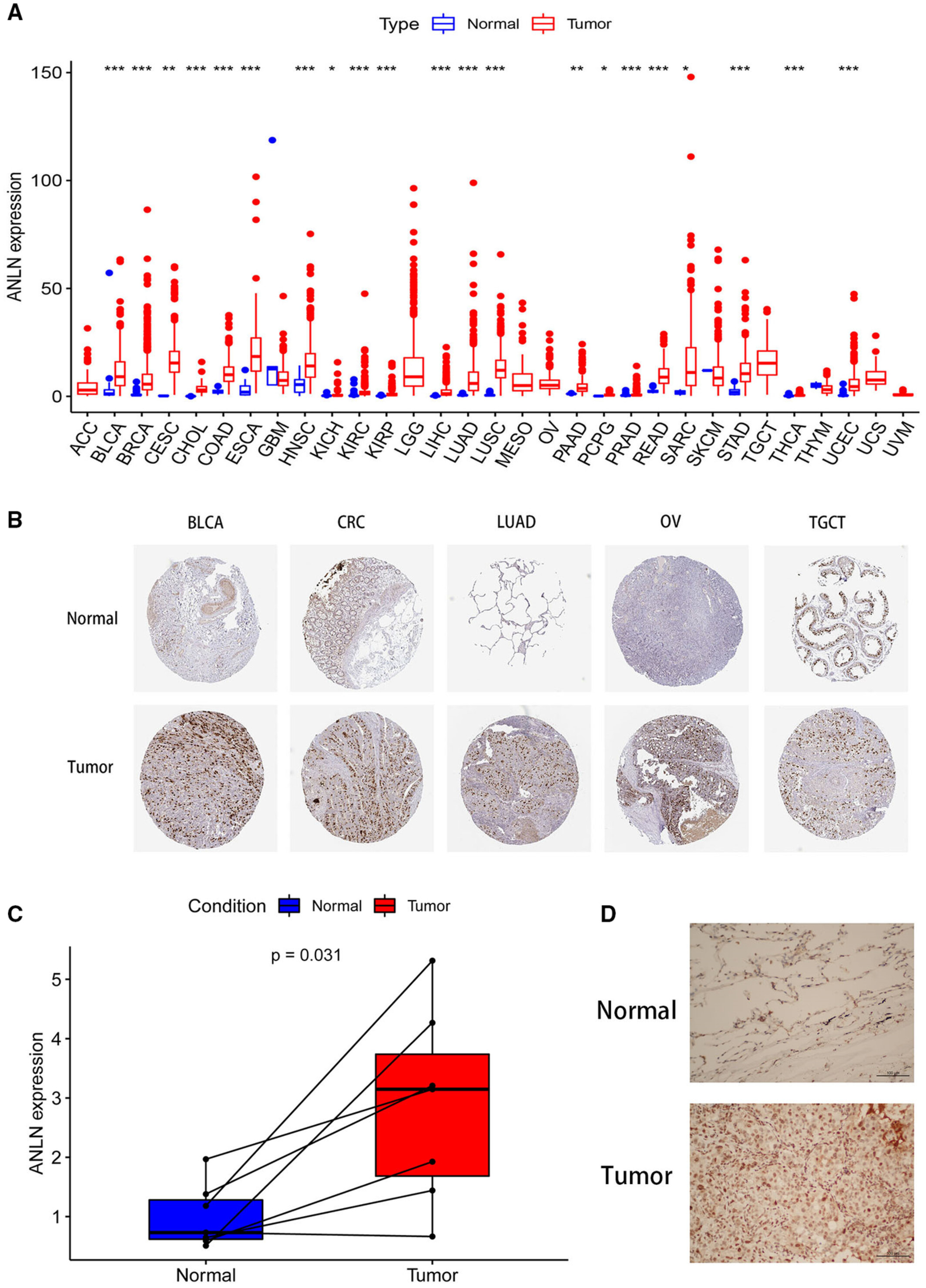
Upregulation of ANLN was associated with worse clinical outcomes in most solid tumors. ANLN was positively related with TMB, MSI, immune cells infiltration and immune checkpoint genes in various cancers. Higher ANLN level predicted better immune responses and longer OS in BLCA patients receiving immunotherapy.
Identification of a pyroptosis-based model for predicting clinical outcomes from immunotherapy in patients with metastatic melanoma
- Pages: 4921-4937
- First Published: 23 September 2022
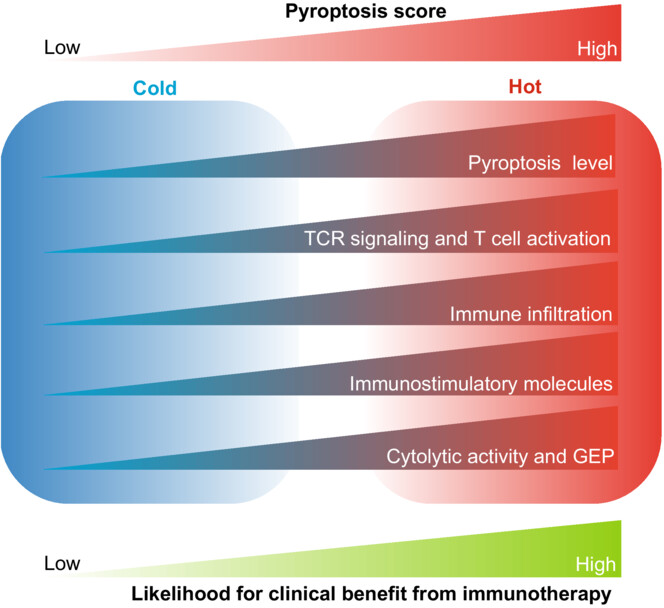
This study identified the pyroptosis-related model associated with multiple immune-inflamed characteristics as a reliable tool for predicting clinical benefit and survival outcomes from immunotherapy in melanoma. Preliminary data from four published cohorts consistently suggested better treatment outcomes from immunotherapy in melanoma with high pyroptosis scores, which was characterized as the immune-inflamed phenotype in TME.
Highly expressed carbohydrate sulfotransferase 11 correlates with unfavorable prognosis and immune evasion of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Pages: 4938-4950
- First Published: 05 September 2022
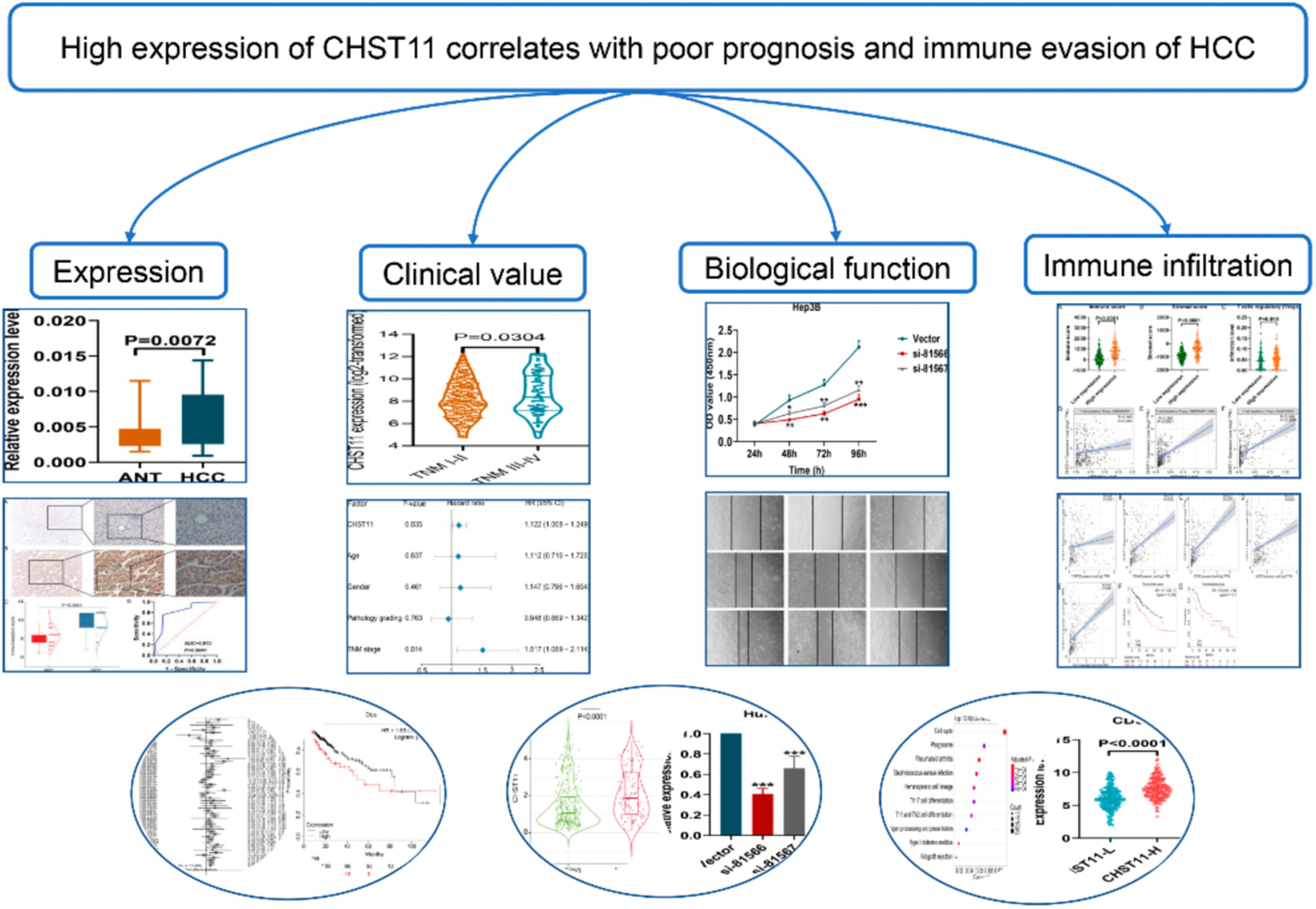
This is the first study to elucidate the relationship between CHST11 expression and prognosis as well as immune infiltration in HCC. These findings are potentially valuable in advancing our current understanding of CHST11 as a biomarker for HCC prognosis predicting and a molecular target for HCC immunotherapy.
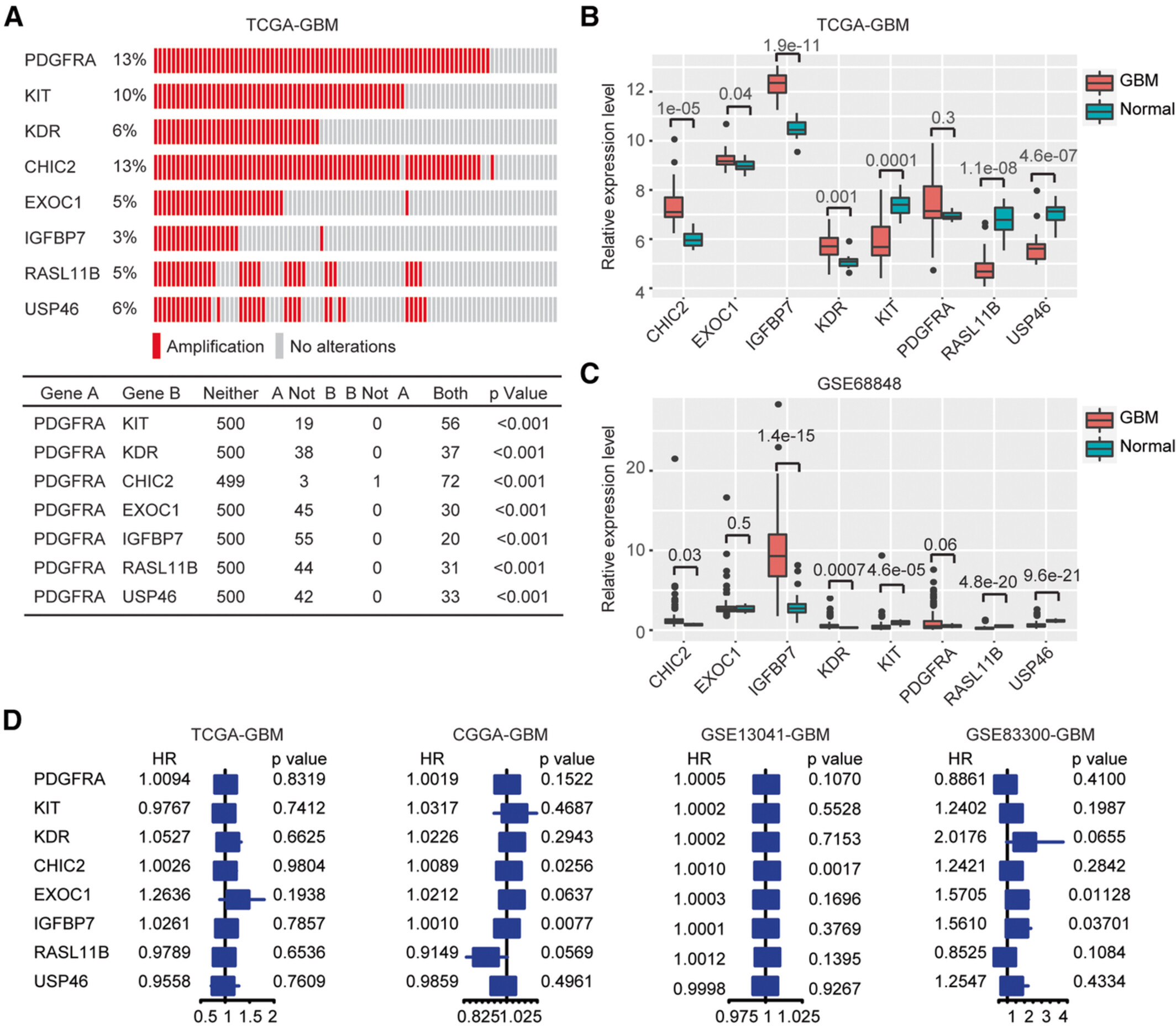
Co-amplified with PDGFRA, IGFBP7 is a prognostic biomarker correlated with the immune infiltrations of glioma
- Pages: 4951-4967
- First Published: 31 August 2022
Risk stratification and prognosis prediction based on inflammation-related gene signature in lung squamous carcinoma
- Pages: 4968-4980
- First Published: 03 September 2022
Dynamic alteration and prognostic significance of tumor-associated CD68+ and CD68+PD-L1− macrophages in muscle-invasive bladder cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy
- Pages: 4981-4992
- First Published: 31 August 2022
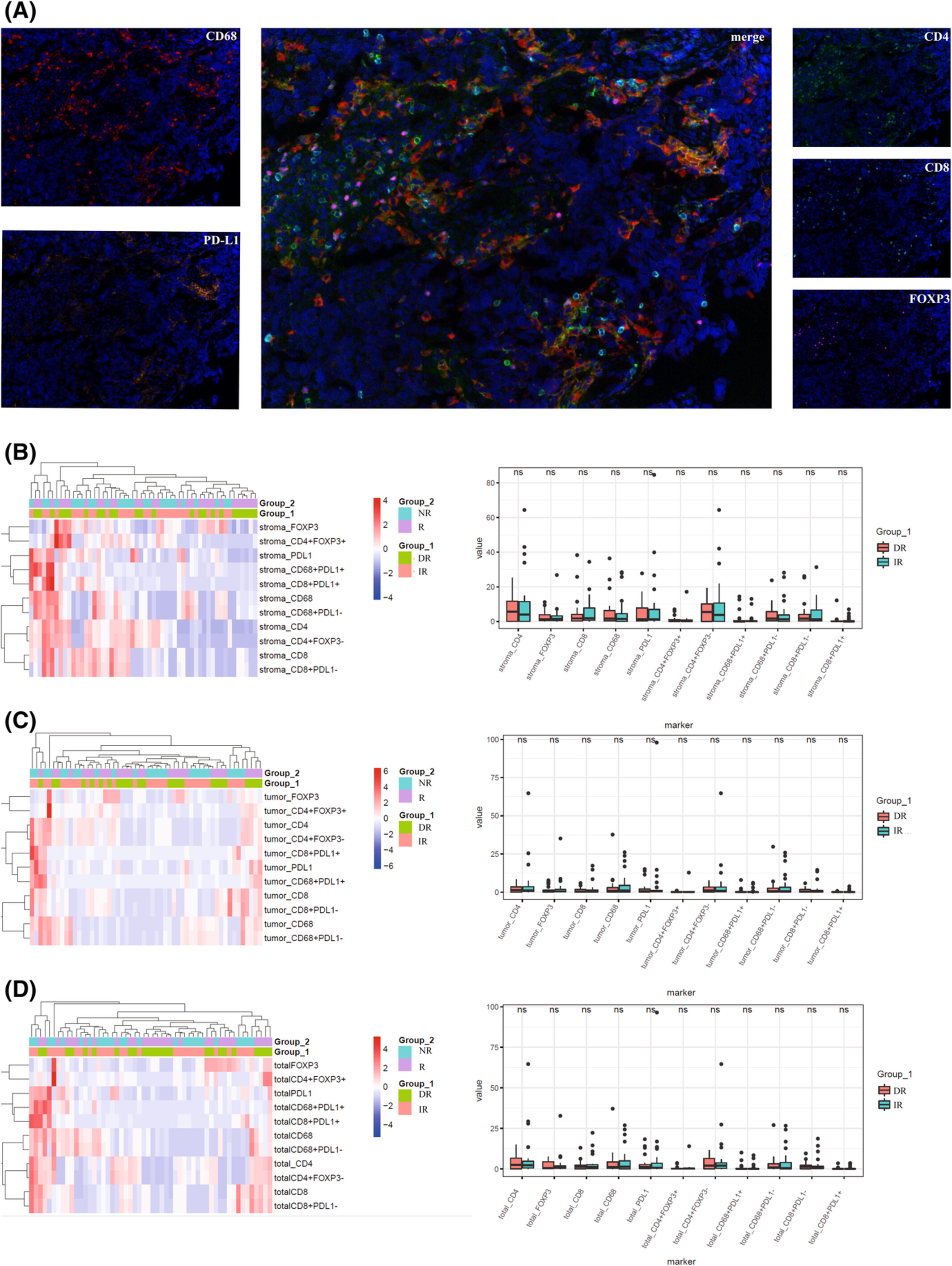
In this study, we performed multiplex immunofluorescence to test CD68+TAMs, FOXP3+ Treg cell, CD4+ T cell, CD8+ T cell, and PD-L1 expression in MIBC before and after NAC. The results revealed that CD68+ and CD68+PD-L1− TAM infiltration levels decreased significantly after NAC and pre-treatment TAM infiltration levels were independent prognostic factors for MIBC patients. However, there was no sufficient evidence demonstrating that pre-treatment TILs or TAMs could predict response to NAC in MIBC patients.
Investigation on the regulatory T cells signature and relevant Foxp3/STAT3 axis in esophageal cancer
- Pages: 4993-5008
- First Published: 13 October 2022
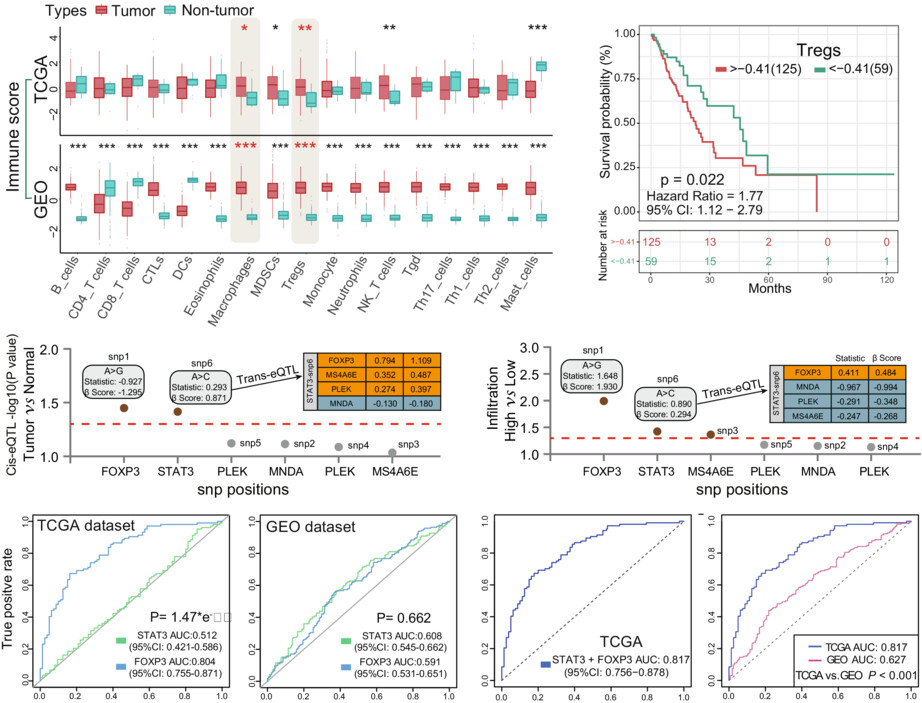
Regulatory T cells (Tregs) are well-known immunosuppression factor in most human malignancies. We gave a comprehensive analysis of Tregs disorder and observed that high Tregs accumulation potentially acted as a prognostic indicator for esophageal cancer (EC) and was associated with tumor deterioration.
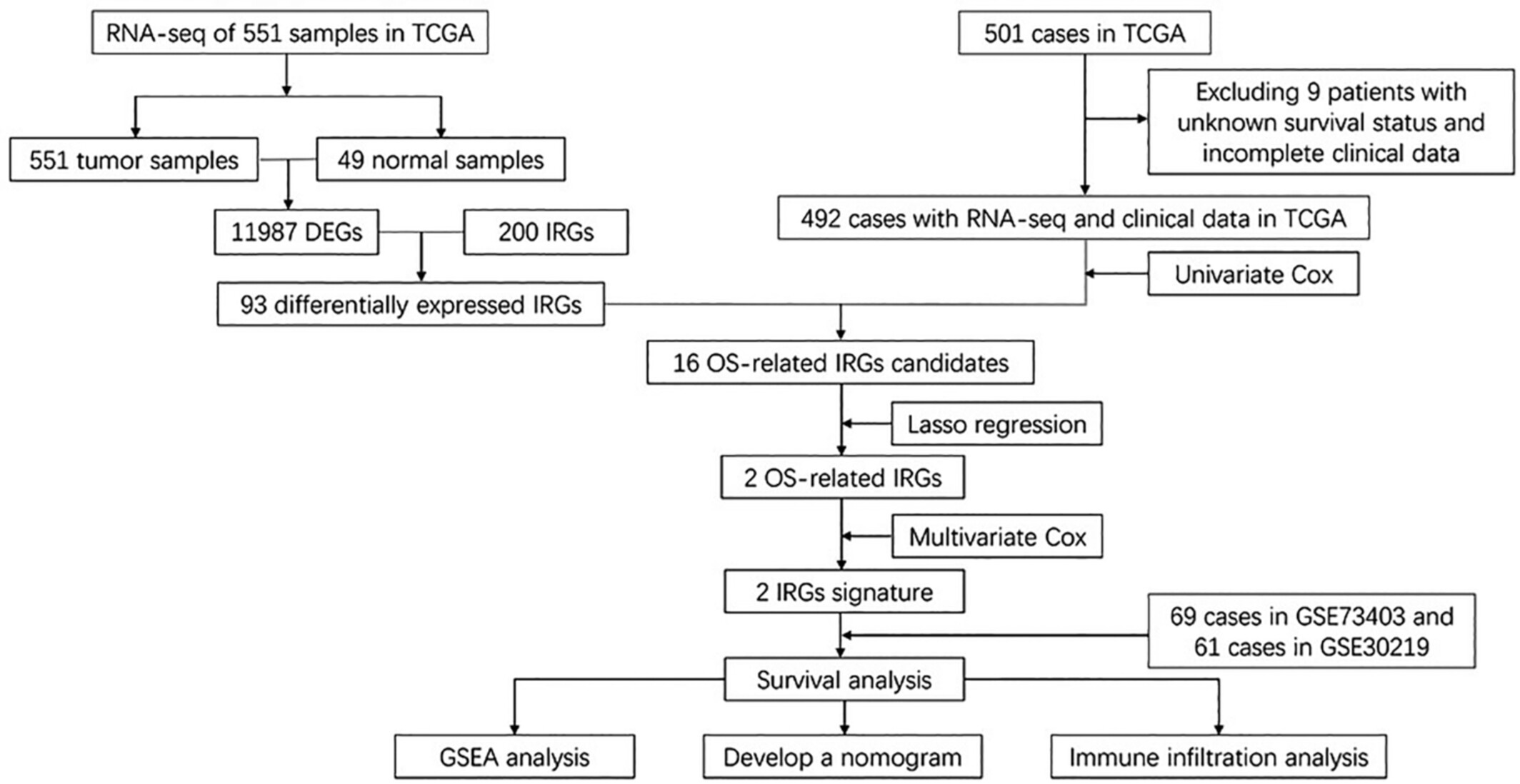
Construction of a cuproptosis-related lncRNA signature for predicting prognosis and immune landscape in osteosarcoma patients
- Pages: 5009-5024
- First Published: 21 September 2022
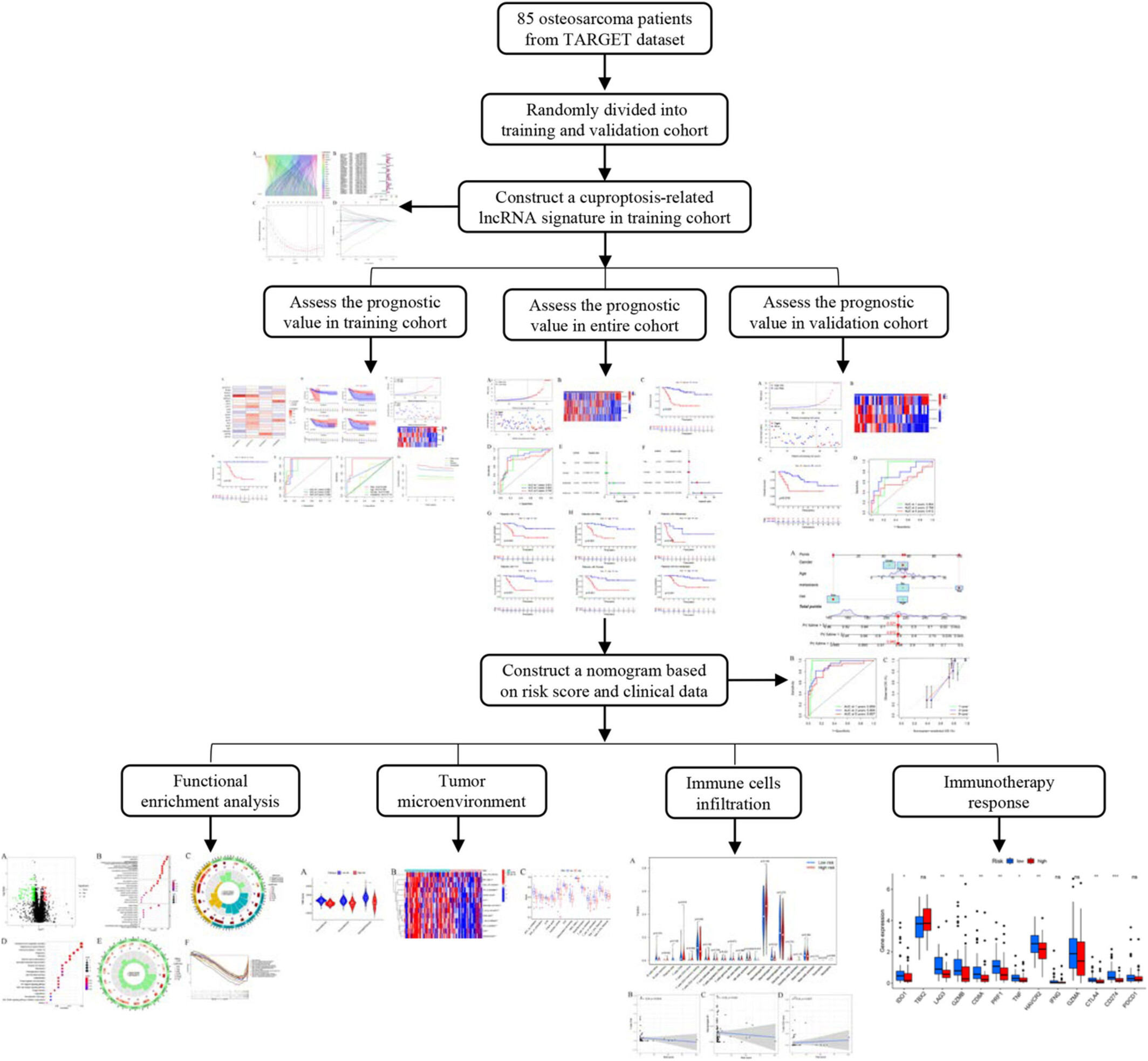
Application of interpretable machine learning algorithms to predict distant metastasis in osteosarcoma
- Pages: 5025-5034
- First Published: 09 September 2022
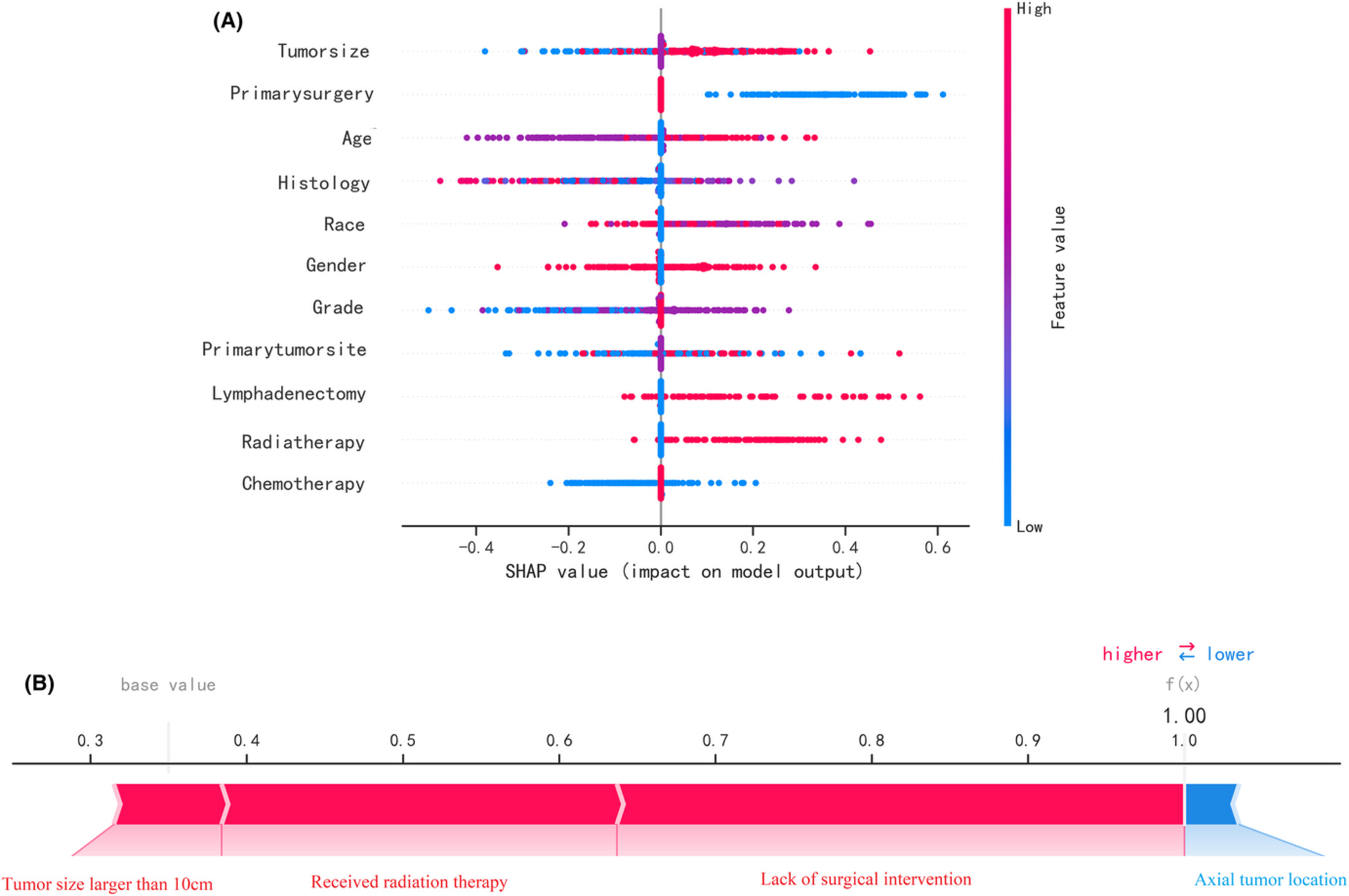
We developed a machine learning-based model to predict the explore potential risk factors for metastatic disease in osteosarcoma patients according to the tumor features and the treatment duration in this study. As a result, the Random Forest model outperformed all other models in training and validation sets. To improve the interpretability of our machine learning model, we reported the SHAP values and a list of highly influential features.
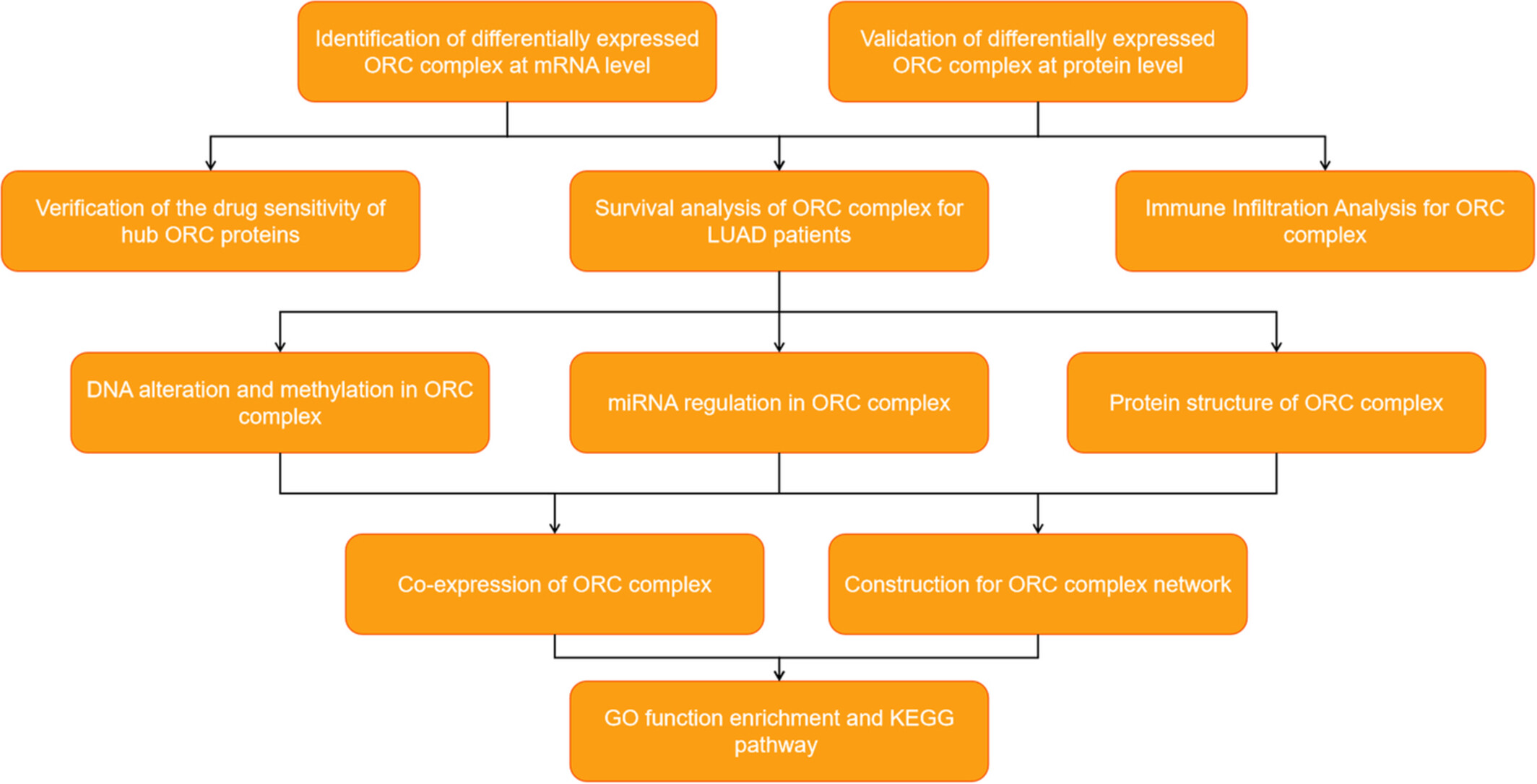
Systemic analysis of the DNA replication regulator origin recognition complex in lung adenocarcinomas identifies prognostic and expression significance
- Pages: 5035-5054
- First Published: 07 October 2022
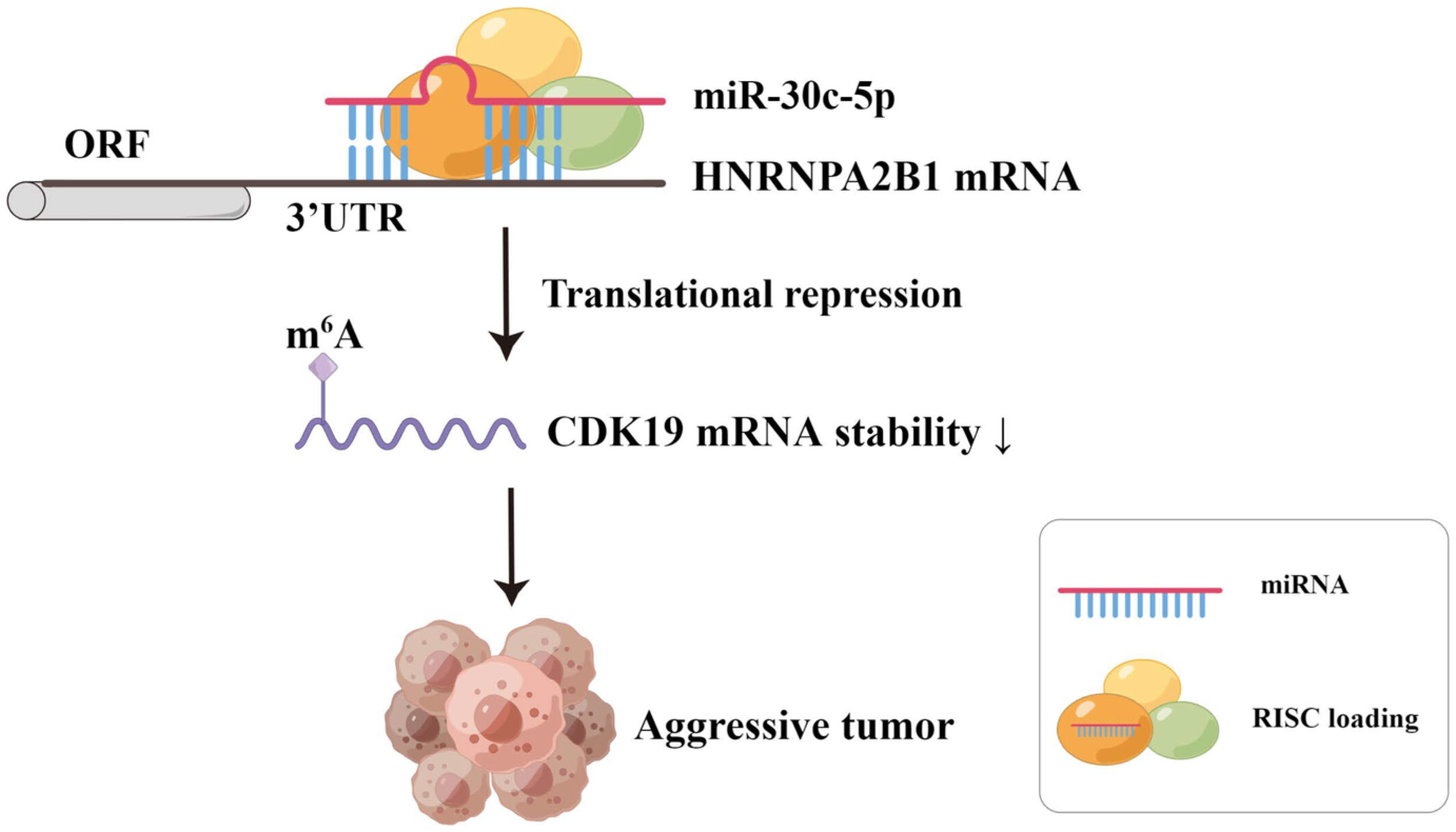
Identification of miR-30c-5p as a tumor suppressor by targeting the m6A reader HNRNPA2B1 in ovarian cancer
- Pages: 5055-5070
- First Published: 18 October 2022
A pyroptosis-related signature predicts prognosis and indicates immune microenvironment infiltration in glioma
- Pages: 5071-5087
- First Published: 26 September 2022
Optimized decision support for selection of transoral robotic surgery or (chemo)radiation therapy based on posttreatment swallowing toxicity
- Pages: 5088-5098
- First Published: 13 October 2022
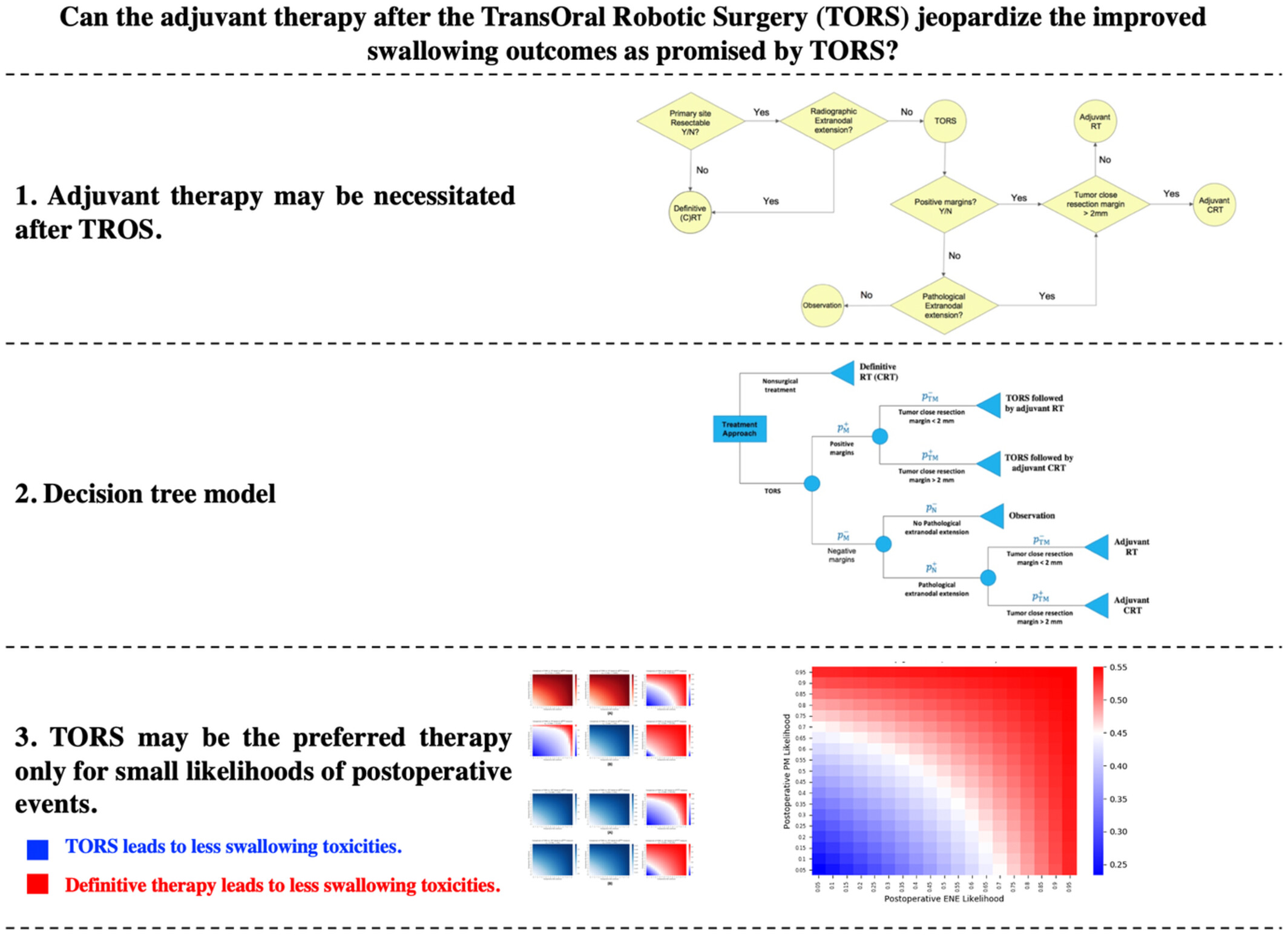
The primary aim of transoral robotic surgery (TORS) in overall toxicity level reduction in eligible oropharyngeal squamous cell cancer (OPSCC) patients may be jeopardized in the presence of postoperative extranodal extension (ENE) and/or positive margin (PM) that necessitate adjuvant therapy. Our decision analysis model shows that Moderate-to-high likelihoods associated with postoperative PM or ENE that trigger adjuvant therapy leave definitive non-surgical therapies as the optimal treatment for TORS-eligible OPSCC patients leading to less overall toxicity burden.
Predicting survival in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer patients with poor ECOG-PS: A single-arm prospective study
- Pages: 5099-5109
- First Published: 26 September 2022
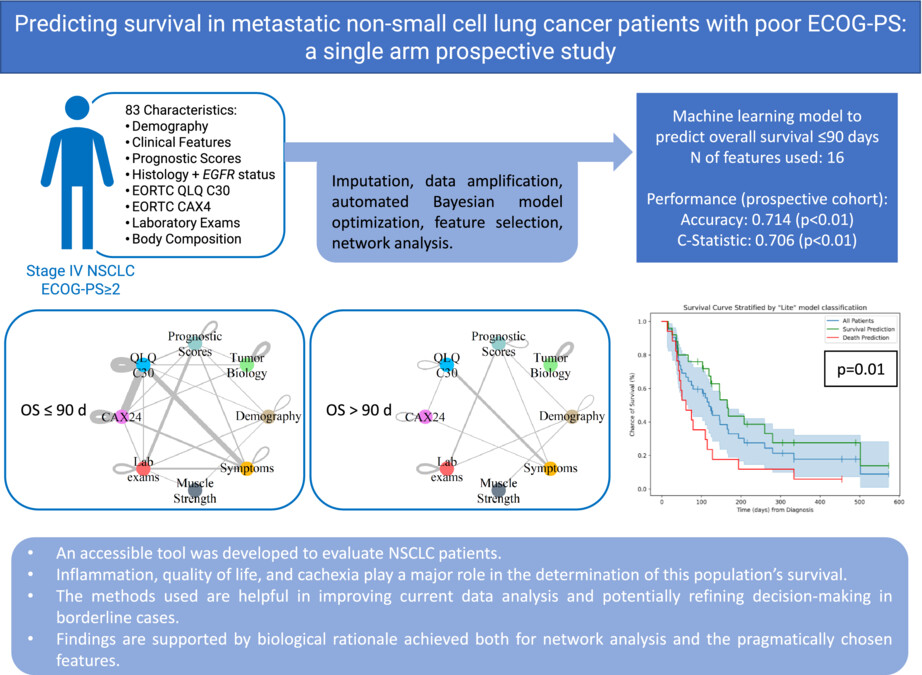
A machine learning (ML) model was developed to predict whether patients with advanced NSCLC and ECOG-PS >1 would have an overall survival (OS) >90 d. Thereafter, a lite model with 16 easily accessible features was created, and its prospective validation yielded a C-statistic of 0.706 (p < 0.01) and accuracy of 0.714 (p < 0.01). The features used in the ML model and network analysis of significant relations between features suggest that inflammation, QoL and cachexia play a major role in determining OS in these patients.
nc-RNA-mediated high expression of CDK6 correlates with poor prognosis and immune infiltration in pancreatic cancer
- Pages: 5110-5123
- First Published: 01 December 2022
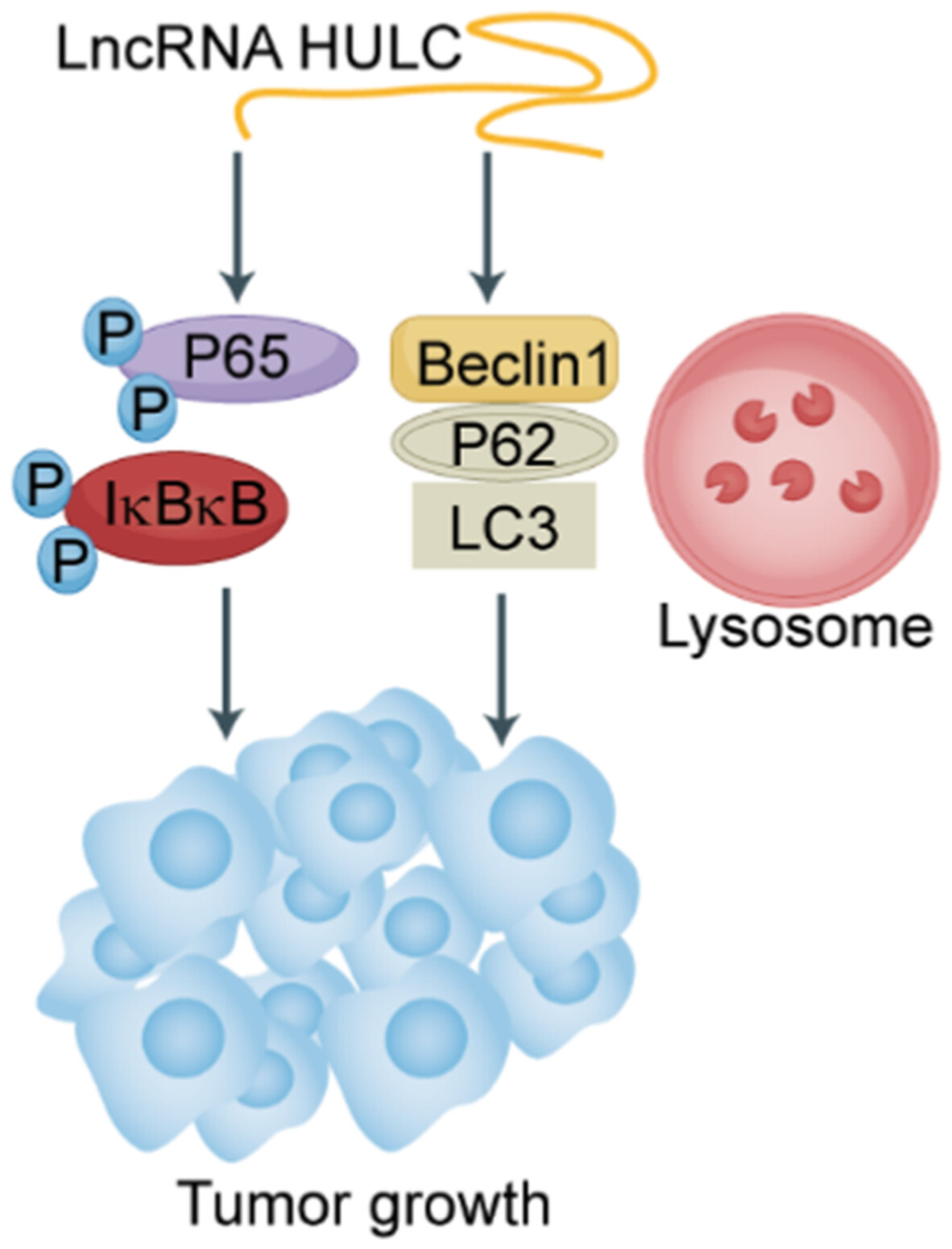
Long noncoding RNA HULC regulates the NF-κB pathway and represents a promising prognostic biomarker in liver cancer
- Pages: 5124-5136
- First Published: 10 October 2022
Glucose metabolism and lncRNAs in breast cancer: Sworn friend
- Pages: 5137-5149
- First Published: 24 November 2022
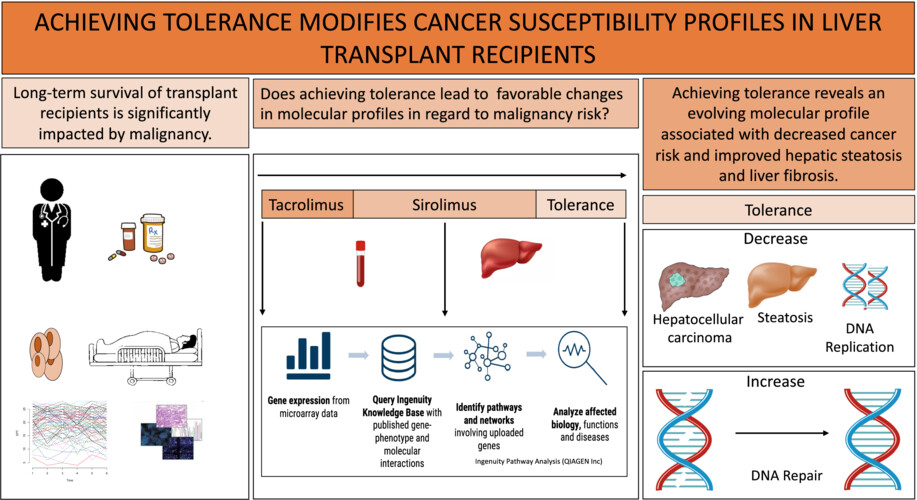
Achieving tolerance modifies cancer susceptibility profiles in liver transplant recipients
- Pages: 5150-5157
- First Published: 07 October 2022
Biomarkers for pancreatic cancer based on tissue and serum metabolomics analysis in a multicenter study
- Pages: 5158-5171
- First Published: 26 September 2022
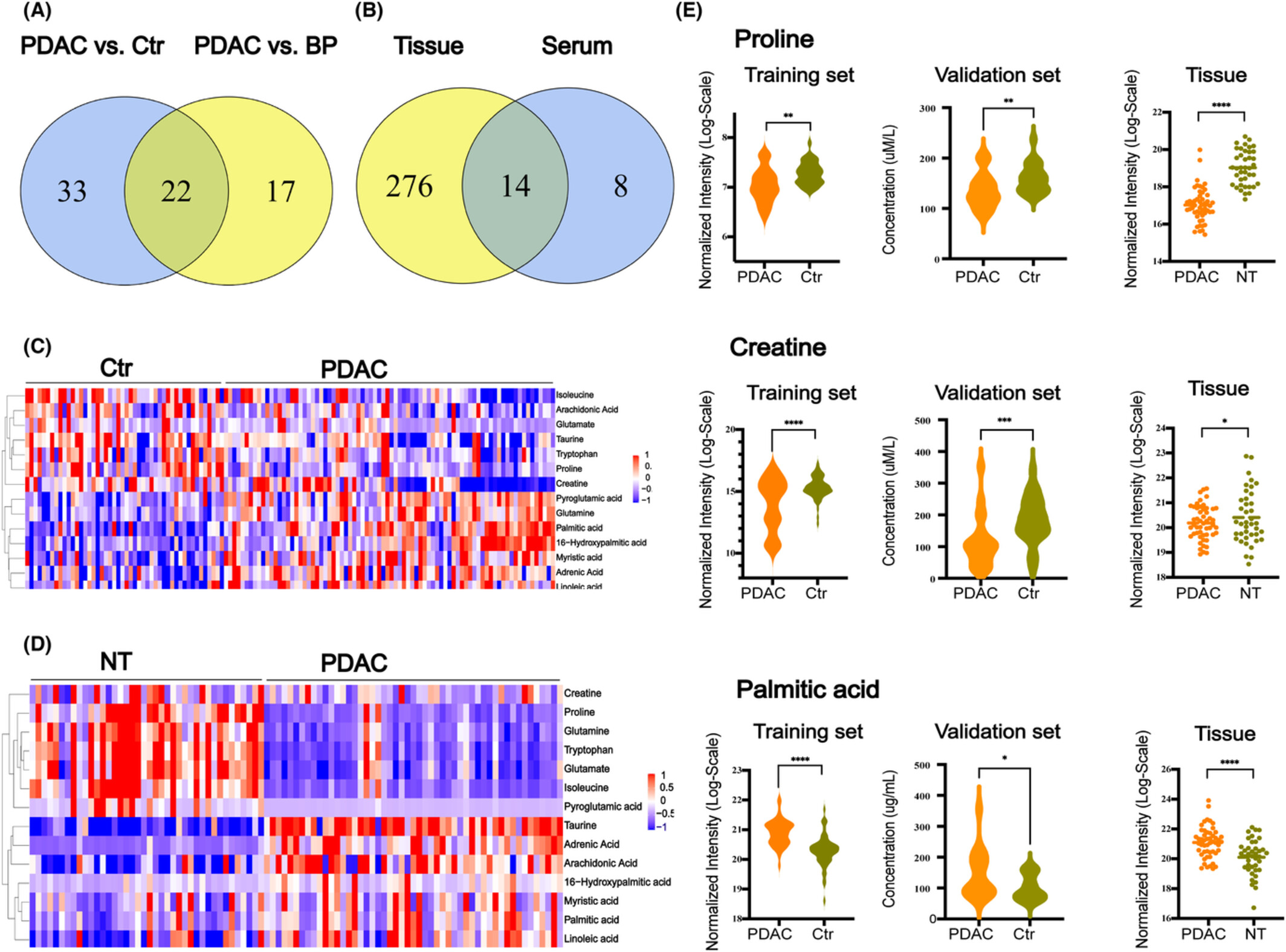
We identified the metabolic features of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) and developed a metabolite biomarker panel for early detection of PDAC based on tissue and serum metabolomics analysis. This panel exhibited promising performance in distinguishing PDAC from benign pancreatic neoplasms (BP) or healthy controls (Ctr), especially in combination with CA19-9.