Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Picture: Chem. Eng. Technol. 11/2018
- Page: 2095
- First Published: 23 October 2018

Test bench for developing and testing of automatic and manually loaded biomass boilers in accordance with DIN EN 304 and DIN EN 303-5 using a special controllable heat dissipation system for the simulation of practical operation. Fraunhofer IBP/Bernd Müller
The special device pictured on the cover is accredited by the German Accreditation Body (DAkkS) and, in addition to the boiler (combustion system), consists mainly of a high-precision weighing machine, an exhaust gas measurement set and delivery system with regulated delivery pressure, a controllable heat dissipation system for simulating the real operation, a control, monitoring and data acquisition system as well as an exhaust gas analyzer for cold- and heated gas sampling. Using this novel technical equipment, not only research and normative testing of automatic and manually loaded biomass boilers in accordance with DIN EN 304, DIN EN 303-5, and Machinery Directive 2006/42 will be carried out, but also the combustion process with regard to energy and emissions flows will be analyzed in detail.
In comparison to the common laboratory apparatus, the combustion and exhaust gas treatment technologies can be developed target oriented by using this novel testing set-up. Moreover, fuels with high heterogeneity can be more accurately investigated for their energy content and the potential for formation of dust (organic and inorganic fine particles) and gaseous pollutant emissions (NOx, SO2, HCl, dioxins, and furans).
Thanks to the self-developed control and data acquisition system, all results can be calculated and monitored online while being visualized accordingly and saved in a big data cloud.
Editorial Board
Editorial Board: Chem. Eng. Technol. 11/2018
- Page: 2096
- First Published: 23 October 2018
Overview
Overview Contents: Chem. Eng. Technol. 11/2018
- Page: 2097
- First Published: 23 October 2018
Highlights
Editorial
Biomass Energy Use: Bioenergy – Flexible and Integrated Into the Next Age
- Page: 2100
- First Published: 23 October 2018
Research Articles
Modeling Mixing in Anaerobic Digesters with Computational Fluid Dynamics Validated by Experiments
- Pages: 2101-2110
- First Published: 22 June 2018
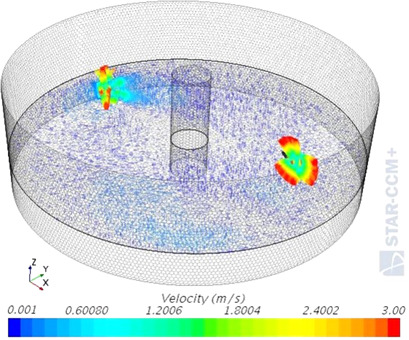
Mixing of biomass in biogas plants requires high energy input. A comprehensive computational fluid dynamics method to assess the mixing quality in biogas digesters is described and validated. Conclusions about positioning and working methodology of the mixers are indicated and can constitute the basis of rules and guidelines for the design and optimization of biomass mixing systems.
Partially Upgraded Biogas: Potential for Decentralized Utilization in Agricultural Machinery
- Pages: 2111-2119
- First Published: 22 June 2018
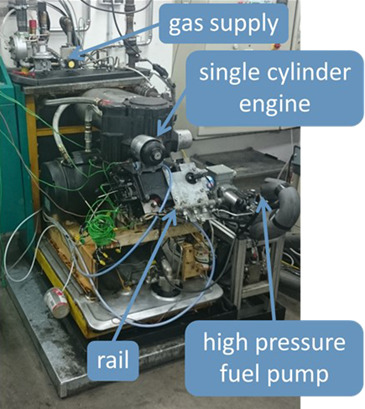
Partially upgraded biogas is a potential fuel for agricultural vehicles. Experimental investigations on a single-cylinder combustion engine and model-based analysis of a water scrubbing process show that the idea of decentralized utilization of biogas represents a promising approach for cost-efficient farm-based biogas upgrading.
Innovative Combustion System for Economic and Ecological Thermal Utilization of Solid Fuel in Heating Boilers
- Pages: 2120-2131
- First Published: 09 July 2018
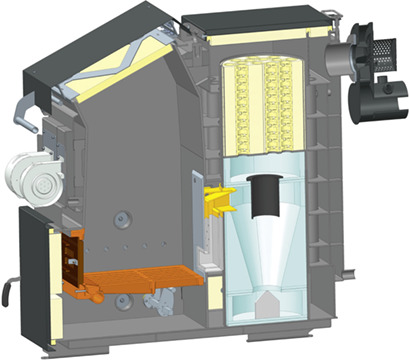
A decentralized combustion system with an integrated exhaust gas treatment unit in biomass-fueled boilers was developed. A significant reduction of gas and dust emissions in all operating phases for thermal utilization of biomass in gasification boilers is achieved, ensuring compliance with the future technical emission requirements without further costly secondary measures for exhaust gas treatment.
ThermoFlex: Heat Storage in Secondary Digesters for Flexible Power Generation of Biogas Plants
- Pages: 2132-2140
- First Published: 11 July 2018
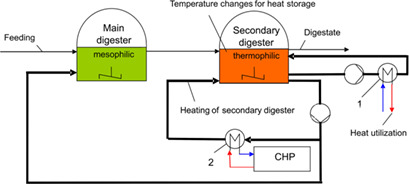
Flexibilization strategies for biogas plants are the key to their success in the energy transition to renewable sources. In the ThermoFlex process, controlled operation of a thermophilic secondary digester following a mesophilic main digester allows effective, flexible heat storage in the secondary digester for digester heating and external heat utilization without disturbing its process biology.
Exergy, Exergoeconomic and Enviroeconomic Evaluation of a Biomass Boiler-Steam Engine Micro-CHP System
- Pages: 2141-2149
- First Published: 24 July 2018
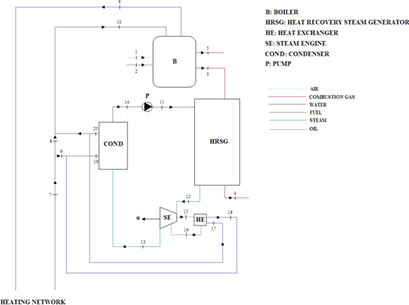
Exergy, exergoeconomic and enviroeconomic analyses made for a micro-CHP system based on a biomass boiler and a steam engine revealed that it has relatively low exergy efficiency compared to similar systems described in the literature. The considered system has improvement potential in terms of exergy efficiency, focusing on the boiler.
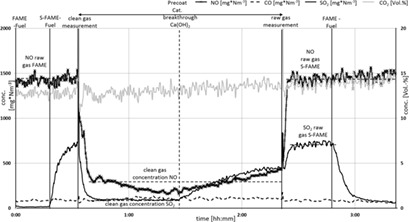
Development and Tests of a Combined Filter for NOx, Particulates, and SO2 Reduction
- Pages: 2150-2158
- First Published: 14 August 2018
Chemical and Physical Analysis of Different Ash Fractions from Small Biomass Boilers
- Pages: 2159-2167
- First Published: 20 August 2018
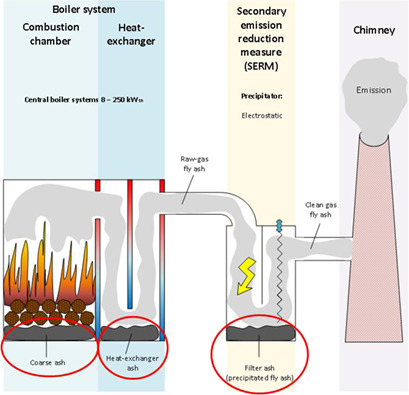
Chemical and physical analyses were carried out on different ash fractions of diverse small biomass boilers, enabling a comparison of the boilers and fuels used. Chemical composition and physical properties were shown to strongly depend on the type of the ash, the fuel, and the boiler. The investigations focused on assessing whether the ashes can be classified as fertilizer and not as waste.
Methodological Evaluation of Storage Systems for Flexible Power Generation from Solid Biomass
- Pages: 2168-2176
- First Published: 24 August 2018
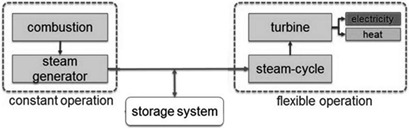
Several steam storage systems to achieve a controllable power generation from biomass combustion plants are available. These systems are evaluated according to the boundaries of the plants as well as the electricity grid and market demands. An adapted analytic hierarchy process with implementation of the Delphi survey was performed to identify the most suiting storage device.
Biomass and Lipid Productivity of Neochloris oleoabundans for CO2 Biofixation and Biodiesel Application
- Pages: 2177-2185
- First Published: 20 August 2018
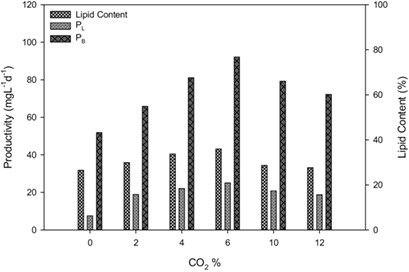
Photosynthesis-based microalgal-mediated carbon dioxide capture and usage is a promising approach to reduce the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere and provide a long-term and sustainable solution to global warming. To this end, freshwater microalgae Neochloris oleoabundans was cultured and the biomass and lipid productivity and lipid contents under different conditions were investigated.
Dehydration of Castor Oil over a NaHSO4/MCM-41 Catalyst Prepared by Supercritical Impregnation
- Pages: 2186-2195
- First Published: 24 August 2018
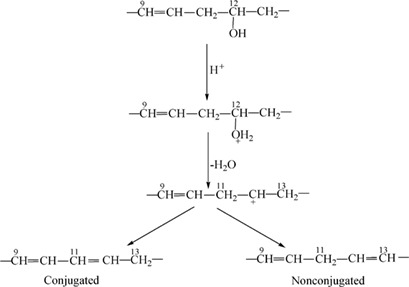
For dehydration of castor oil, the NaHSO4/MCM-41 catalyst was synthesized by supercritical impregnation, which was advantageous to improve NaHSO4 dispersion and to boost the interaction between NaHSO4 and the catalyst MCM-41. Coke formation and NaHSO4 leaching were retarded. Conversion, selectivity, and stability of the NaHSO4/MCM-41 catalyst could be significantly enhanced.
Sulfated Iron Oxide-Catalyzed Esterification of Acetic Acid with n-Butanol by Reactive Distillation
- Pages: 2196-2202
- First Published: 24 August 2018
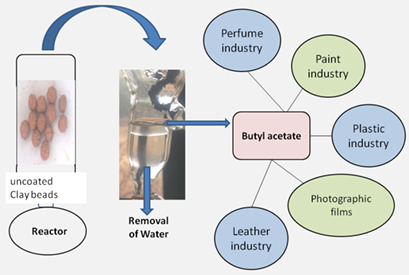
Butyl acetate is an important ester with numerous applications. The applicability of reactive distillation in the catalytic esterification of acetic acid with n-butanol was investigated with low-cost, readily available, and reusable uncoated clay beads as column packing material. High acid conversion in shorter reaction time was achieved by reactive distillation compared with the batch process.
Removal of NO from Flue Gas by a Heterogeneous Fenton-Like Process
- Pages: 2203-2211
- First Published: 24 August 2018
For removal of NO from flue gas, an innovative low-temperature method was developed based on a heterogeneous Fenton-like process using Fe-containing polyoxometalates as heterogeneous catalyst. An average removal efficiency of > 90 % was achieved under optimized conditions. The synthesized FeIIIAspPW complex was employed to activate H2O2 and investigate the effects of various factors on NO removal.
Reactive Zinc Extraction with D2EHPA in a Kühni Miniplant Column
- Pages: 2212-2222
- First Published: 24 August 2018

Selective extraction of metal ions by reactive solvent extraction is a commonly used process in hydrometallurgy. The physical mass transfer is superimposed by a complexation reaction, which solubilizes the ionic solute into the organic phase. Hydrodynamics and mass transfer in an agitated Kühni miniplant column for the reactive extraction of zinc with the liquid cation-exchanger D2EHPA are evaluated.
Air-Jet Experimental Study and Modeling of Attrition Behavior for Fluid Catalytic Cracking Catalysts
- Pages: 2223-2232
- First Published: 27 August 2018
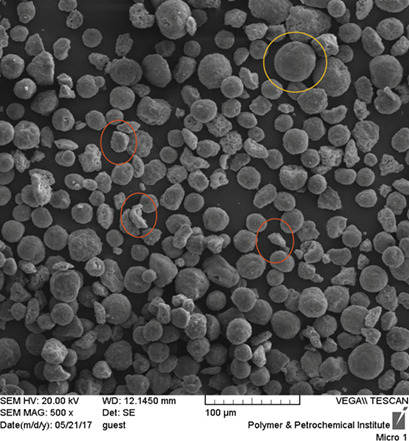

Fluid catalytic cracking (FCC) is one of the most important processes in refineries. The main part of the FCC process is the reaction and regeneration in which the catalyst is being circulated. In this work, the attrition resistance, surface properties, and catalyst loss have been investigated on a domestic refinery with residue fluid catalytic cracking catalysts in both fresh and spent forms.
Simultaneous Design and Control of a Ternary Reactive Distillation Column with Inert Material
- Pages: 2233-2240
- First Published: 10 September 2018
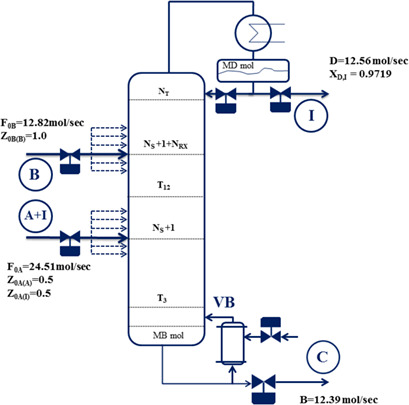
Process integration plays a key role in chemical process industries in terms of minimizing waste and energy demands. Simultaneous design and control is demonstrated for a complex ternary reactive distillation column with inert material. The optimization problem is formulated as mixed-integer dynamic optimization problem. An improved process design and control is achieved by solving this issue.
Liquid Maldistribution in Random-Packed Columns: Experimental Investigation of Influencing Factors
- Pages: 2241-2249
- First Published: 13 September 2018
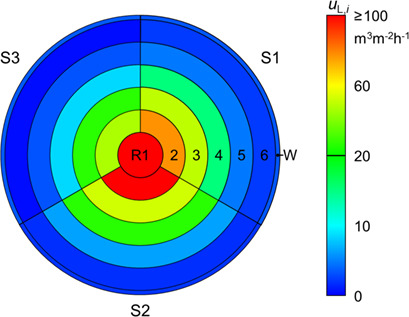
Liquid maldistribution in packed columns cannot be predicted adequately so far. Such maldistribution in random packing is experimentally investigated with varying experimental and operating parameters. Distribution spectra identify the maldistribution phenomena wall flow and liquid channeling. Evaluations by means of the maldistribution factor illustrate the degree of nonuniform distribution.
Adsorptive Removal of As(V) Ions from Water using Graphene Oxide-Manganese Ferrite and Titania Nanotube-Manganese Ferrite Hybrid Nanomaterials
- Pages: 2250-2258
- First Published: 13 September 2018
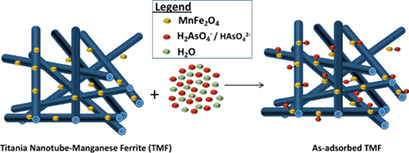
Two types of innovative hybrid nanomaterials, namely, graphene oxide-manganese ferrite and titania nanotube-manganese ferrite, with enhanced properties were synthesized and applied as adsorbent to remove As(V) from water. A high level of reusability after undergoing a simple desorption process coupled with the promising adsorption capacity make the hybrid nanomaterials highly potential.
Development of Forecast Formulas for Assessing the Dust Formation Tendency of Moist Bulk Materials Using the UNC Dustiness Tester
- Pages: 2259-2265
- First Published: 17 September 2018
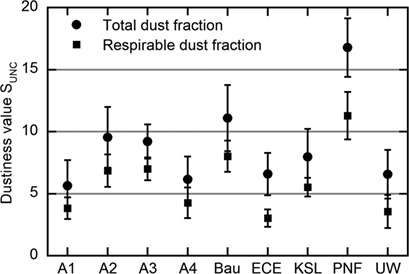
Undesired release of particles from bulk materials occurring in material-handling processes can present a hazard to humans and the environment. Dust formation tendency as an important material property depends on the specific type of stress. A semi-empirical forecast parameter was derived based on experimental analyses with a UNC dustiness tester and used to develop forecast formulas.
Tertiary Amine-Naphthenic Acid Self-Assembled Surfactants for Viscosity Reduction of Crude Oil
- Pages: 2266-2273
- First Published: 19 July 2018
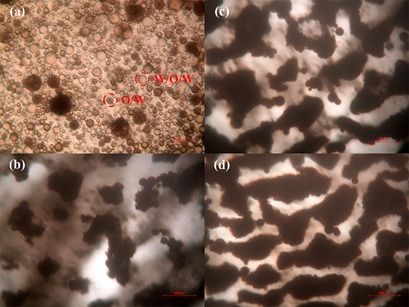
Lowering the viscosity of heavy crude oil is required for its pipeline transportation. Naphthenic acids in crude oil can self-assemble with tertiary amines to form CO2-switchable surfactants that can form low-viscosity crude oil-water (O/W) emulsions, which are readily demulsified in the presence of CO2. This provides a new concept for the pipeline transportation of heavy crude oil.
Communications
Synthesis and Properties of High Nitrogen-Oxygen Compounds Based on 5,5′-Azotetrazolate by Using Microreactors
- Pages: 2274-2281
- First Published: 27 August 2018
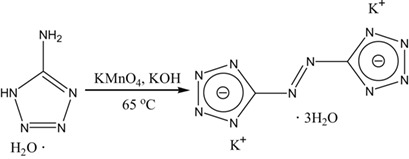
High-energy-density materials are at the frontier of energetic materials research. A continuous-flow microreactor allows the successful synthesis of oxygen-containing 5,5′-azotetrazolate salts through metathesis reactions. The present procedure is efficient and easy to handle, and oxygen-containing 5,5′-azotetrazolate salts can be obtained in minutes in high yield.
Overview
Overview Contents: Chemie Ingenieur Technik 11/2018
- Page: 2282
- First Published: 23 October 2018