Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Editorial Board
Overview
Contents
Contents: Chem. Eng. Technol. 8/2013
- Pages: 1276-1282
- First Published: 24 July 2013
Highlights
Editorial
Industrial Crystallization: Trends and Challenges
- Page: 1286
- First Published: 24 July 2013
Research Articles
Excipients-Induced Salt-to-Free Base Phase Transformation
- Pages: 1287-1291
- First Published: 25 April 2013
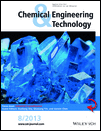
The mechanisms of the transformation from salt to free form drug during processing of a model drug are investigated with special emphasis on the interplay of salt solubility and pH of the excipients. The obtained results can provide a reliable guidance for selecting excipients for robust formulation design of solid dosage pharmaceuticals in salt forms.
Novel Glutaric Acid Cocrystal Formation via Cogrinding and Solution Crystallization
- Pages: 1292-1299
- First Published: 24 July 2013

A novel approach to discover new pharmaceutical cocrystals in the early development stage is applied to develop cocrystals of piracetam with some aliphatic diacids. A 1:1 cocrystal of piracetam and glutaric acid is screened by a mechanochemical method and the process of cocrystal formation during solution-mediated phase transformation is discussed.
Insights into the Evaporation Kinetics of Indomethacin Solutions
- Pages: 1300-1306
- First Published: 04 July 2013
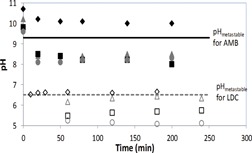
Controlling crystal polymorphism is a challenging task. The effect of crystallization conditions on the crystal polymorphs of indomethacin was studied by evaporation crystallization from a free solvent surface and in a mesoporous solid material. The approach was based on a mass transfer model of evaporation and experimental solvent flux measurements were used for model evaluation.
Scale-up of a Fluidized Bed Crystallizer on the Basis of Solid Suspension
- Pages: 1307-1312
- First Published: 09 July 2013

The scale-up of crystallization processes is an important research area and has been studied for many years. The scale-up of a fluidized bed crystallizer was studied based on the solid spatial concentration distribution in the crystallizer. A strategy for the scale-up of the crystallization process was suggested based on the different states of solid suspension.
Population Balance Modeling of the Solution-Mediated Transformation of DL-Methionine Polymorphs
- Pages: 1313-1319
- First Published: 04 July 2013
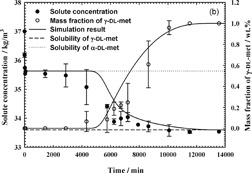
The population balance equation (PBE) model for crystallization and the solution-mediated transformation (SMT) of the metastable α-DL-methionine into the stable γ-DL-methionine in water was derived. The crystallization and dissolution kinetics of each polymorph were applied to the PBE model and compared with the results from the SMT experiment.
Kinetic Study on Polyethylenimine-Assisted Reactive Crystallization of Monodisperse Strontium Sulfate Microcrystals
- Pages: 1320-1326
- First Published: 08 July 2013

The effect of polyethylenimine (PEI) addition on nucleation and growth of SrSO4 is determined and a simple kinetic model is proposed. Time-dependent behaviors of crystal size and crystal number are statistically analyzed by a nonlinear least-square program. Kinetic aspects under the condition of obtaining monodisperse crystals are discussed.
Solution-Mediated Phase Transformation of a Hydrate to its Anhydrous Form of Donepezil Hydrochloride
- Pages: 1327-1334
- First Published: 09 July 2013
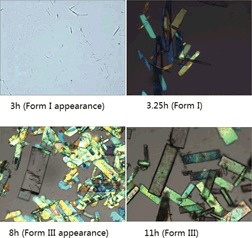
First studies on solution-mediated phase transformation of a hydrate (form I) to its anhydrous form (form III) of donepezil hydro-chloride are reported. Mechanisms involved in this process are investigated by in situ and offline measurement technologies. A tentative correlation between thermodynamic properties and phase transformation is presented.
Investigation of Nucleation Kinetics by Nephelometric Measurements
- Pages: 1335-1340
- First Published: 05 July 2013
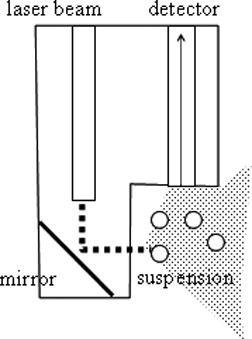
An experimental investigation of the application of a nephelometric probe to study nucleation kinetics is reported. The nephelometric signal proved to be proportional to the surface of the solids in suspension. It allowed to accurately detect the metastable zone width and the induction time and to monitor the first period of time after nucleation.
Effects of Sonocrystallization on the Crystal Size Distribution of Cloxacillin Benzathine Crystals
- Pages: 1341-1346
- First Published: 05 July 2013
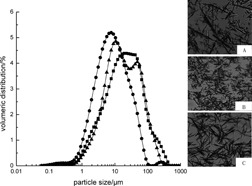
Ultrasonic technology shows great potential in the crystallization industry with respect to the effects on crystal size distribution and morphology of the products. A novel combination of conventional reactive crystallization process and insonated disturbance is introduced to prepare uniform cloxacillin benzathine crystals with fewer aggregates.
Adjustment of Process Conditions in Seeded Batch Cooling Crystallization
- Pages: 1347-1354
- First Published: 04 July 2013

The effects of seed addition temperature, seed surface area, seed loading, and seed origin on the granulometric properties, crystal size distribution, and polymorphism of the model amino acid glycine prepared by batch cooling crystallization were investigated. Polymorphism was examined by differential scanning calorimetry and X-ray diffraction analysis.
Solvent Effect on Crystal Structure of Tetracycline Hydrochloride
- Pages: 1355-1358
- First Published: 10 July 2013
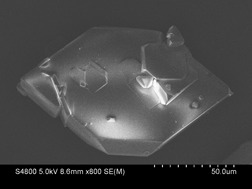
The crystal structure of tetracycline hydrochloride was predicted by single-crystal data via Bravais-Friedel-Donnay-Harker and modified attachment energy models. Based on simulations of the pure crystal, morphological modifications induced by solvents were examined by calculation of interaction energies between solvents and each cleaved crystal surface.
Communication
Wet Flue Gas Desulfurization Process: Phase Equilibrium of a Quaternary System at Various Temperatures
- Pages: 1359-1364
- First Published: 05 July 2013
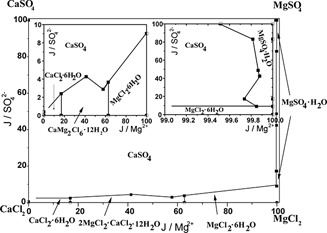
The phase equilibria of the system Mg2+, Ca2+//Cl–, SO42–-H2O at different temperatures are decisive for producing MgSO4·7H2O using the mother liquid origin in magnesium-based wet flue gas desulfurization. The solubility of this quaternary system is evaluated by means of isothermal solution saturation.
Research Articles
Modification of Disposable Red-Mud Catalysts for Slurry-Phase Hydrocracking of Vacuum Residue
- Pages: 1365-1370
- First Published: 05 July 2013
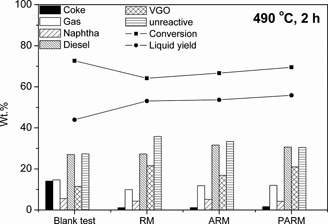
Different dissolution-precipitation methods served for modification of a disposable iron-based catalyst, red mud. The resulting materials were evaluated as catalysts for the slurry-phase catalytic hydrocracking of vacuum residue. Red mud activated by phosphoric acid treatment exhibited the best performance due to the caused particle size reduction.
Transesterification of Soybean Oil with Ethylene Glycol, Catalyzed by Modified Li-Al layered double hydroxides
- Pages: 1371-1377
- First Published: 24 July 2013
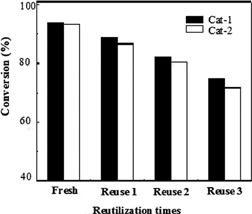
Modified Li-Al layered double hydroxides are effective solid catalysts for transesterification of soybean oil (SBO) and ethylene glycol. They can be separated, reused, and regenerated easily and they have the potential to simplify the production process by using continuous packed-bed reactors. The SBO fatty acid esters products were anchored with end hydroxyl groups by ethylene glycol, which provide reaction sites for further modification of long chains.
Partitioning Studies of Glutaminase in Polyethylene Glycol and Salt-Based Aqueous Two-Phase Systems
- Pages: 1378-1386
- First Published: 24 July 2013
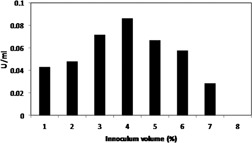
Commercially valuable glutaminase produced from Zygosaccharomyces rouxii NRRL-Y 2547 was partitioned in polyethylene glycol (PEG)-salt aqueous two-phase systems. Effects of salt type and concentration, PEGs with different molecular weight, and tie line lengths on partitioning and purification factor were evaluated and defined for optimum results.
Beckmann Rearrangement of Cyclohexanone Oxime in a Microreactor Setup with Internal Recirculation
- Pages: 1387-1394
- First Published: 14 June 2013
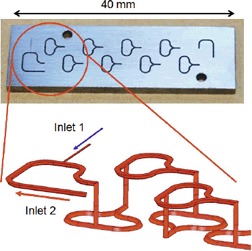
A microreactor setup with internal recirculation operated in continuous mode was used to demonstrate Beckmann rearrangement of cyclohexanone oxime dissolved in cyclooctane with oleum to ϵ-caprolactam. At 100 °C, the conversion of cyclohexanone oxime was complete; selectivity towards ϵ-caprolactam was 99 %. However, cyclooctane as solvent reduced the purity of the produced ϵ-caprolactam.
Power Consumption of Liquid and Liquid/Solid Systems in a Rotating-Drum Bioreactor
- Pages: 1395-1401
- First Published: 05 July 2013
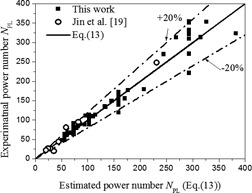
The effects of lifter arrangement and operation conditions on power consumption in a rotating-drum bioreactor (RDB) were investigated. Empirical correlations of the power number related to reactor configuration and operation parameters are proposed for liquid and liquid/solid systems to estimate the power consumption for RDB design and scale-up.
Improving Physical Absorption of Carbon Dioxide by Ionic Liquid Dispersion
- Pages: 1402-1410
- First Published: 04 July 2013

The ionic liquid 1-butylimidazole hexafluoride phosphate [bmim]PF4 is dispersed into water to create an ionic liquid-in-water emulsion which is applied to absorb CO2. The presence of dispersed ionic liquid droplets significantly enhances the CO2 mass transfer rate at a gas-liquid interface due to both the shuttle effect and hydrodynamic effect.
Chemical and Enzymatic Polymerization of Polyaniline/Ag Nanocomposites
- Pages: 1411-1416
- First Published: 09 July 2013

Enzymatic polymerization is a powerful tool to synthesize electronically and optically active polymers. Polyaniline/Ag nanocomposites were obtained using chemical and enzymatic polymerization of aniline based on 2-aminothiophenol-capped Ag nanoparticles. The enzymatic method resulted in smaller nanocomposites with higher thermal stability compared to the chemical method.
Dynamics and Control of Coupled Continuous Chromatography and Crystallization Processes for the Production of Pure Enantiomers†
- Pages: 1417-1429
- First Published: 10 July 2013
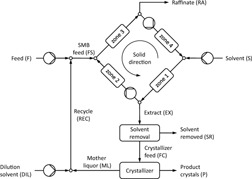
Dynamics and control of an enantioseparation by coupled continuous chromatography and subsequent crystallization with recycle of the mother liquor were studied. The combination of both processes can improve significantly the separation efficiency. Some simple control strategies are proposed to compensate unforeseen disturbances and stabilize the process.
Communication
Sequestration of Carbon Dioxide with Simultaneous Formation of Fine Calcium Carbonate Particles in Liposomes
- Pages: 1430-1434
- First Published: 14 June 2013
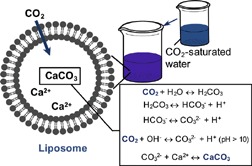
CaCO3 particles can be synthesized by mixing CaCl2-containing liposome suspension and CO2-saturated water as demonstrated by scanning transmission electron microscopy and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. The liposomal reaction system can be applied to the formation of fine CaCO3 particles through sequestration of CO2 under optimized conditions.
Overview
Overview Contents: Chemie Ingenieur Technik 8/2013
- Page: 1435
- First Published: 24 July 2013