Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEWS
Liquid biopsy: A promising tool for driving strategies and predicting failures in patients with classic Hodgkin lymphoma
- Pages: 182-187
- First Published: 21 June 2023
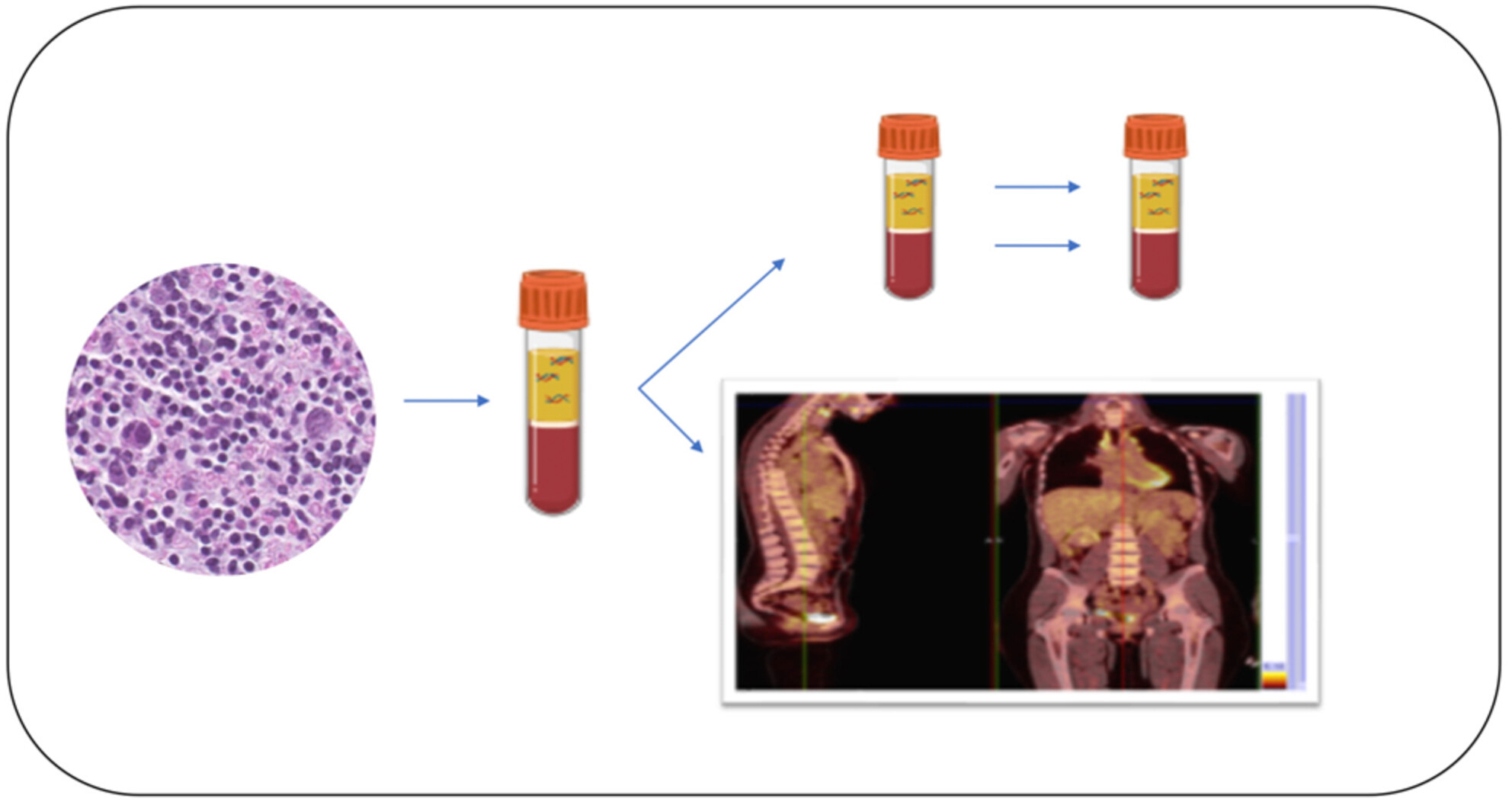
Liquid biopsy is considered an emerging tool able to integrate conventional tissue specimens for molecular analysis and FDG-PET results to evaluate residual minimal disease and early detection of chemorefractory patients. A combined approach with liquid biopsy may integrate FDG-PET results in order to evaluate residual disease for the early identification of chemorefractory cHL patients.
Second edition of the Milan System for Reporting Salivary Gland Cytopathology: Refining the role of salivary gland FNA
- Pages: 188-198
- First Published: 16 November 2023
The second edition of the Milan System for Reporting Salivary Gland Cytopathology, published in July 2023, includes refined risks of malignancy based on systematic reviews and meta-analyses, a new chapter summarising the use of salivary gland imaging, new advances in ancillary testing, updates in nomenclature and a guide to the practical application of the latest ancillary markers for the diagnosis of selected salivary gland fine-needle aspiration cases.
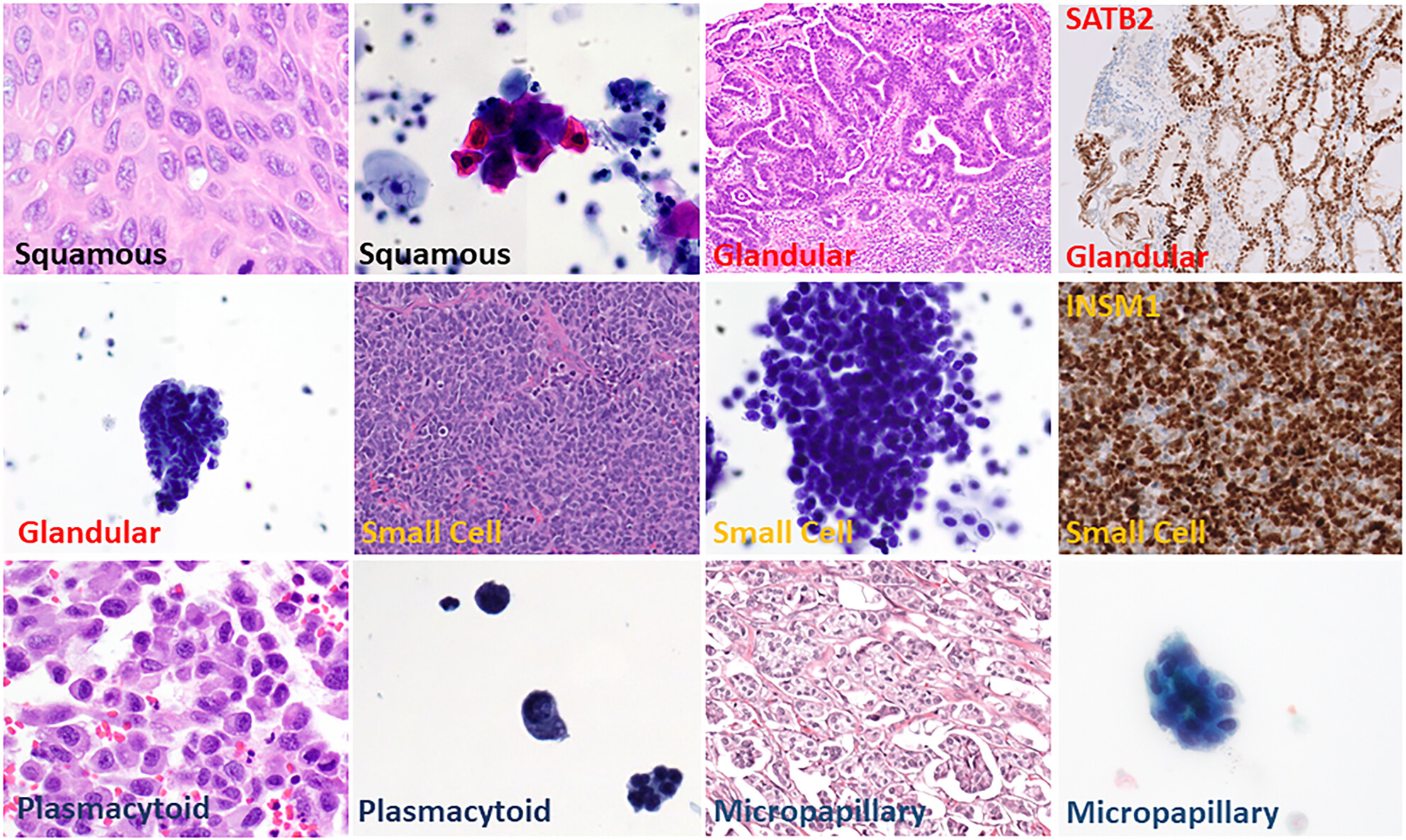
Urinary tract cytology showing variant morphology and divergent differentiation
- Pages: 199-212
- First Published: 02 November 2023
Immunotherapy and lung cytopathology: Overview and possibilities
- Pages: 213-217
- First Published: 15 November 2023
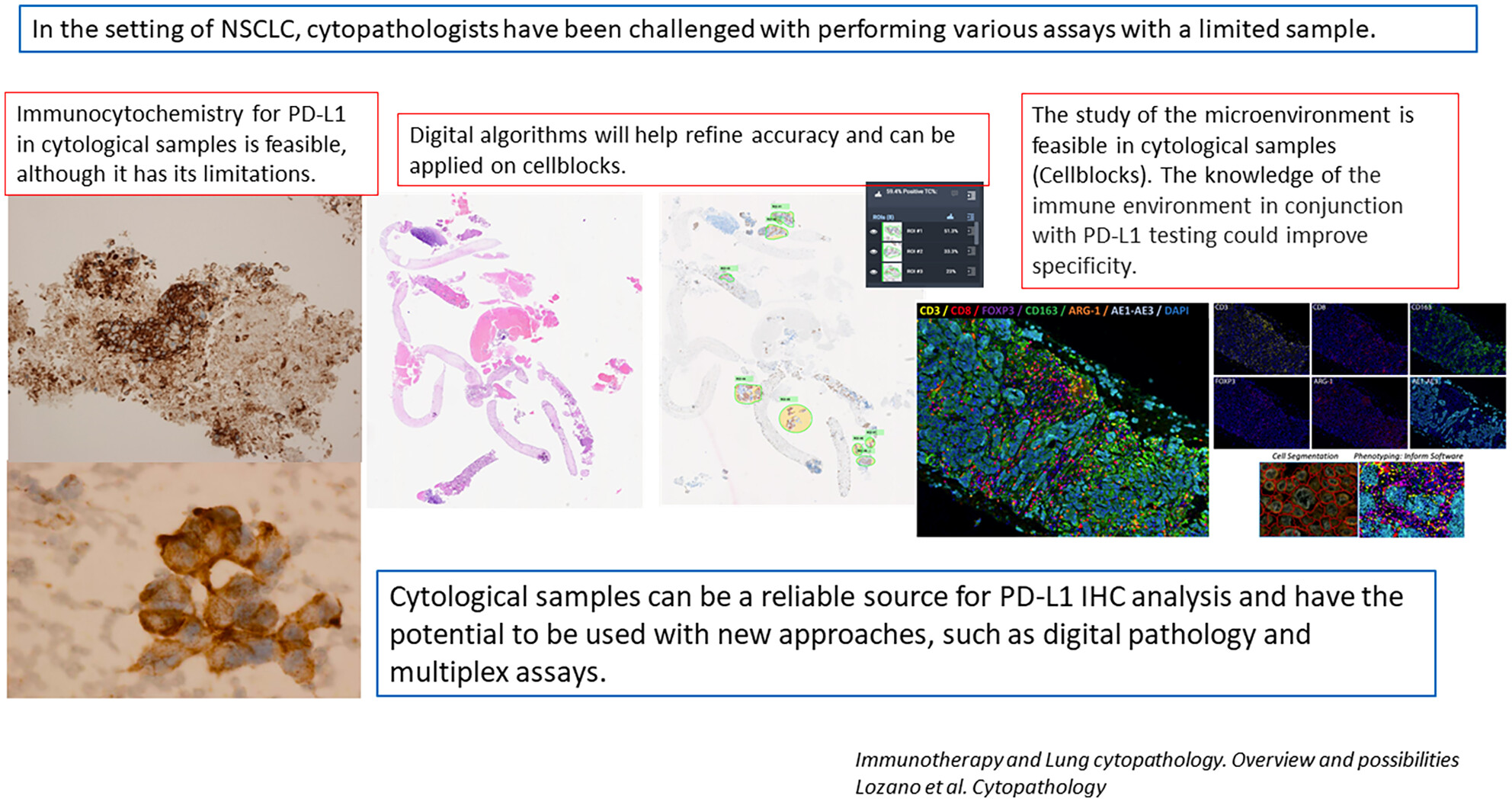
Although not formally validated on cytology specimens, cytopathologists are increasingly being asked to assess the expression of PD-L1 in NSCLC to select patients for treatment with PD1/PD-L1 inhibitors. PD-L1 staining and quantitation on cytology samples is feasible, provided that appropriate protocols and validation studies are in place. PD-L1 image analysis algorithms can improve scoring consistency. Digital pathology combined with multiplex immunofluorescence (IF)/IHC assays could be a powerful tool for PD-L1 assessment. Cytological samples can be a reliable source for PD-L1 IHC analysis and have the potential to be used with new approaches, such as digital pathology and multiplex assays.
Immunocytochemical markers, molecular testing and digital cytopathology for aspiration cytology of metastatic breast carcinoma
- Pages: 218-225
- First Published: 20 November 2023
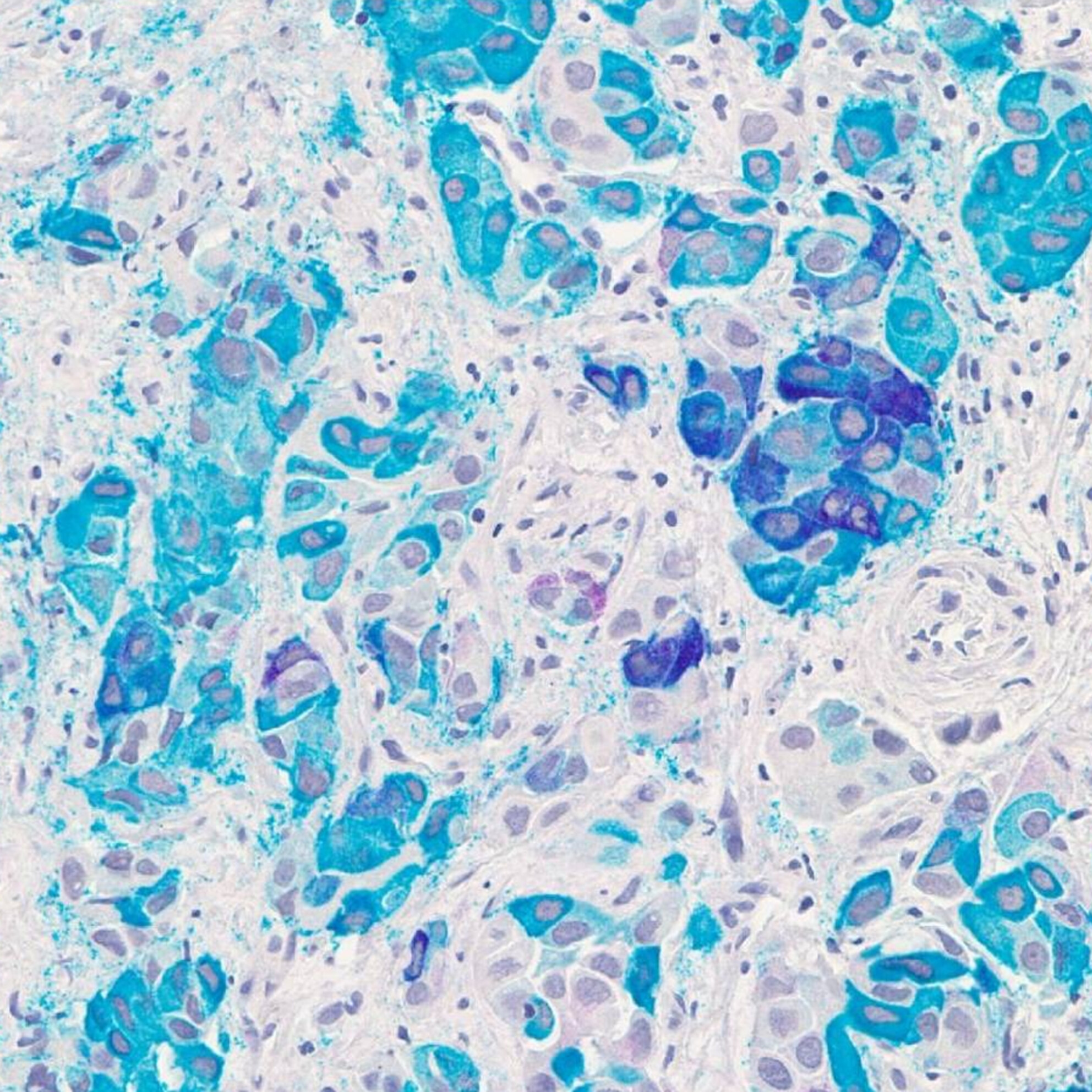
Understanding the applications of immunocytochemistry, molecular testing, and digital cytopathologic techniques for detection, confirmation, subtyping and theragnosis metastatic breast carcinoma in cytology is necessary for a comprehensive cytologic assessment.
This review summarizes the applications of immunocytochemistry—detection of carcinoma cells, confirmation of breast primary, assessment of surrogate immunostains and theragnostic biomarkers, with discussion on potential diagnostic pitfalls, followed by the application of molecular tests and digital cytopathologic techniques for assessing metastatic breast carcinoma in cytology.
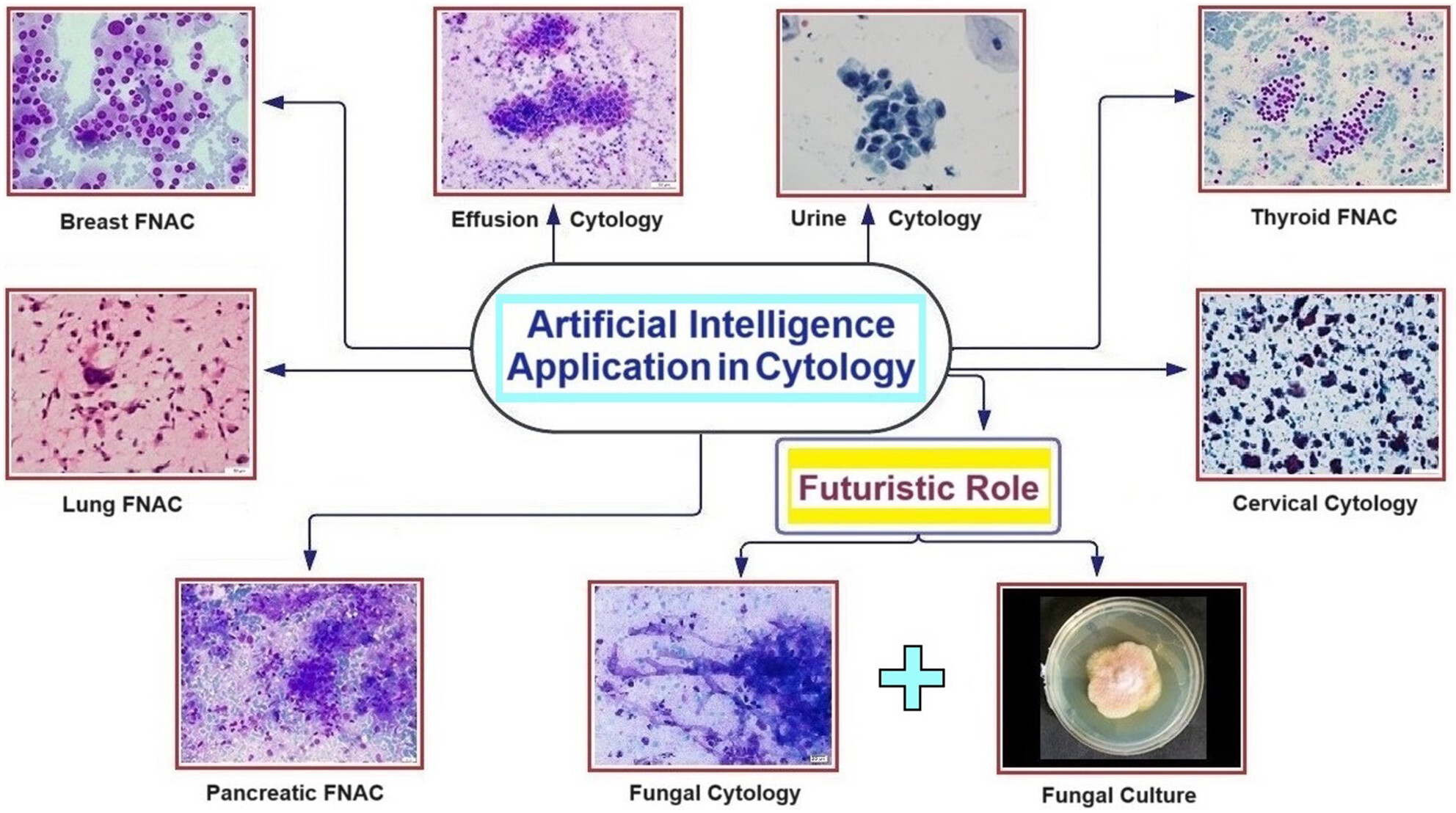
Artificial Intelligence: Exploring utility in detection and typing of fungus with futuristic application in fungal cytology
- Pages: 226-234
- First Published: 16 November 2023
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Cytologic evaluation of upper urinary tract specimens: An institutional retrospective study using The Paris System for Reporting Urine Cytology second edition with histopathologic follow-up
- Pages: 235-241
- First Published: 02 November 2023
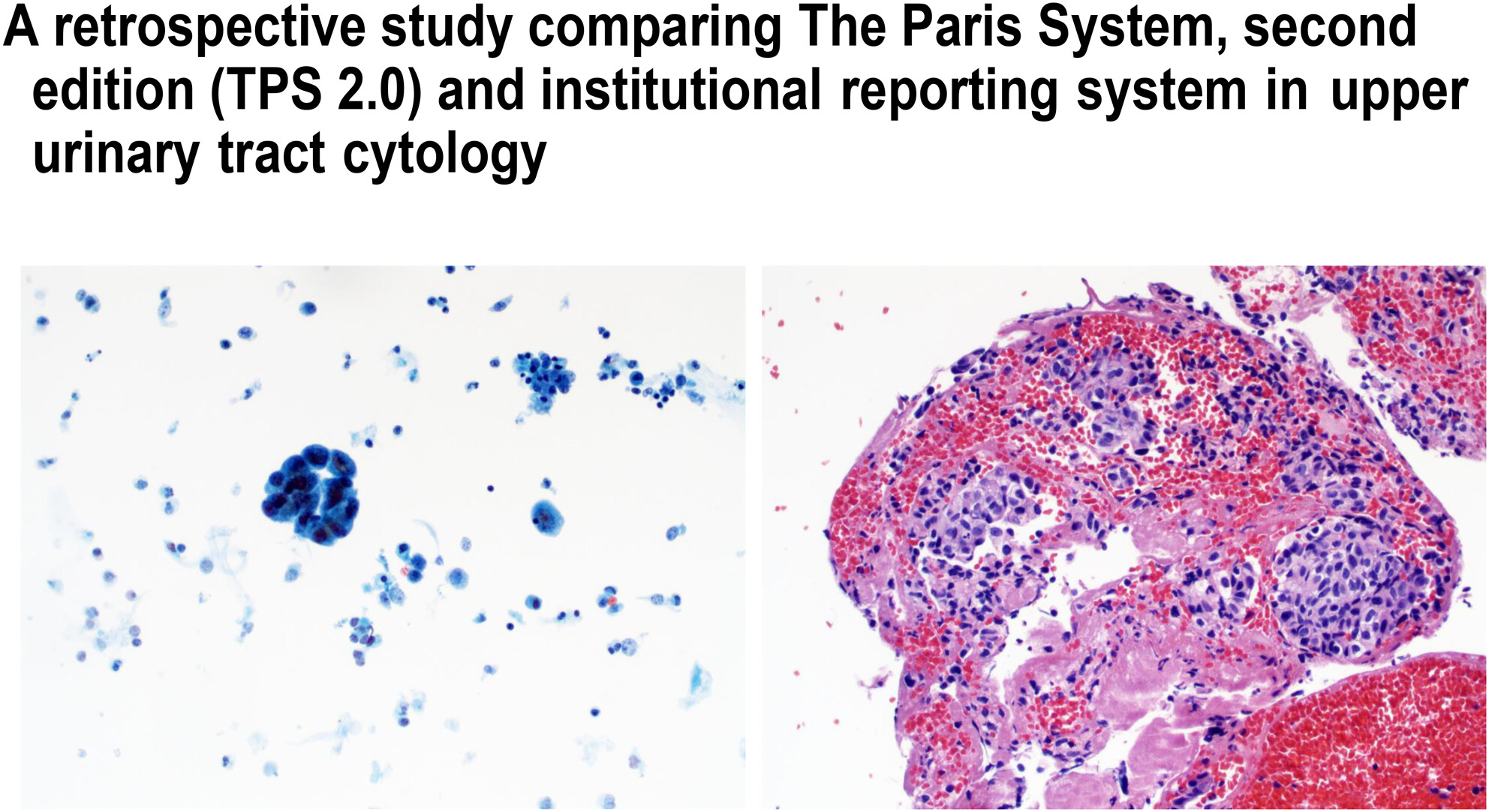
The study retrospectively evaluated cytology specimens of the upper urinary tract (UUT) based on The Paris System for Reporting Urinary Cytopathology, second edition (TPS 2.0). TPS 2.0 can reliably identify high-grade urothelial carcinoma in the UUT, while the detection of low-grade urothelial carcinoma remains a challenge.
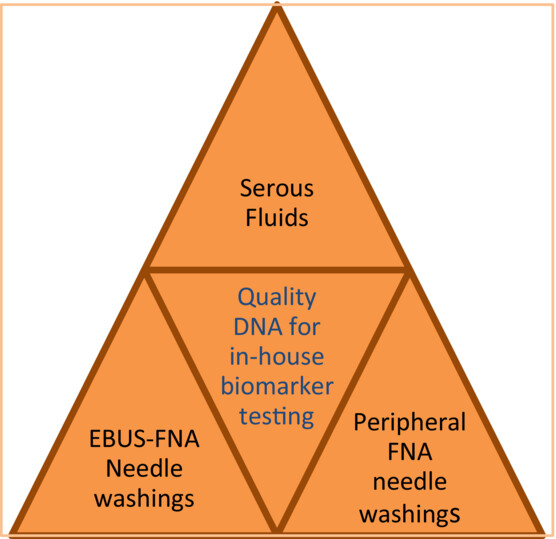
Use of cytology fluid samples for predictive biomarker testing in lung cancer patients
- Pages: 242-249
- First Published: 01 December 2023
Impact of rapid on-site evaluation in expediting the fast investigative lung cancer pathway
- Pages: 250-255
- First Published: 06 December 2023
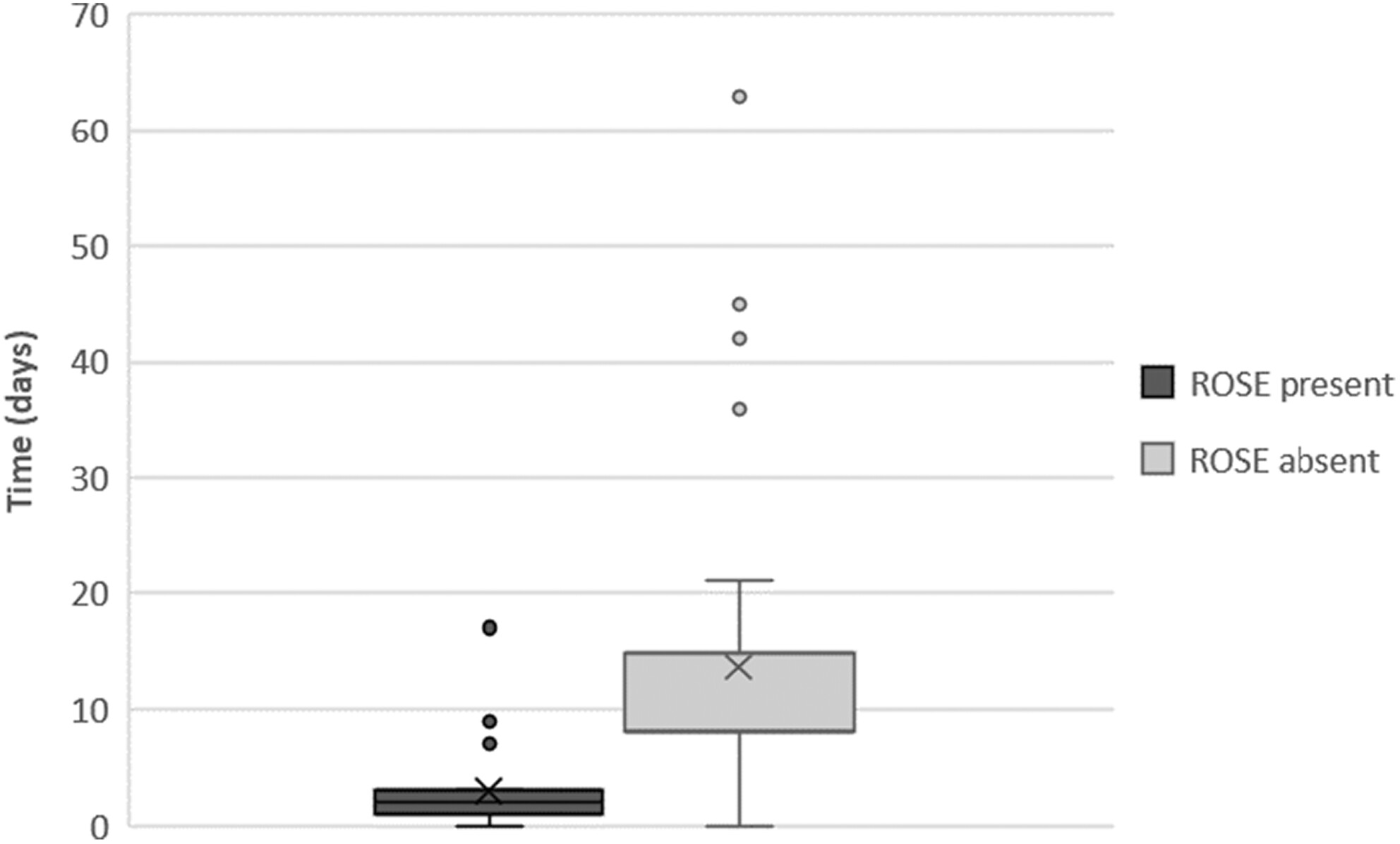
Rapid on-site evaluation (ROSE) is a method of assessing tissue samples during an Endobronchial Ultrasound Transbronchial Needle Aspiration (EBUS-TBNA) procedure. We aimed to investigate the impact of ROSE on the length of the lung cancer pathway and the number of passes per malignant and non-malignant sites.
Rapid on-site evaluation (ROSE) is a method used during Endobronchial Ultrasound Transbronchial needle aspiration (EBUS-TBNA) procedures to provide instant feedback on sample adequacy and a provisional cytomorphological diagnosis. This allows cases to be discussed at lung cancer multidisciplinary team (MDT) meetings rapidly, significantly reducing the length of the lung cancer diagnostic pathway.
Grading pancreatic adenocarcinomas on fine needle aspiration cytology. The outstanding issues
- Pages: 256-265
- First Published: 05 December 2023
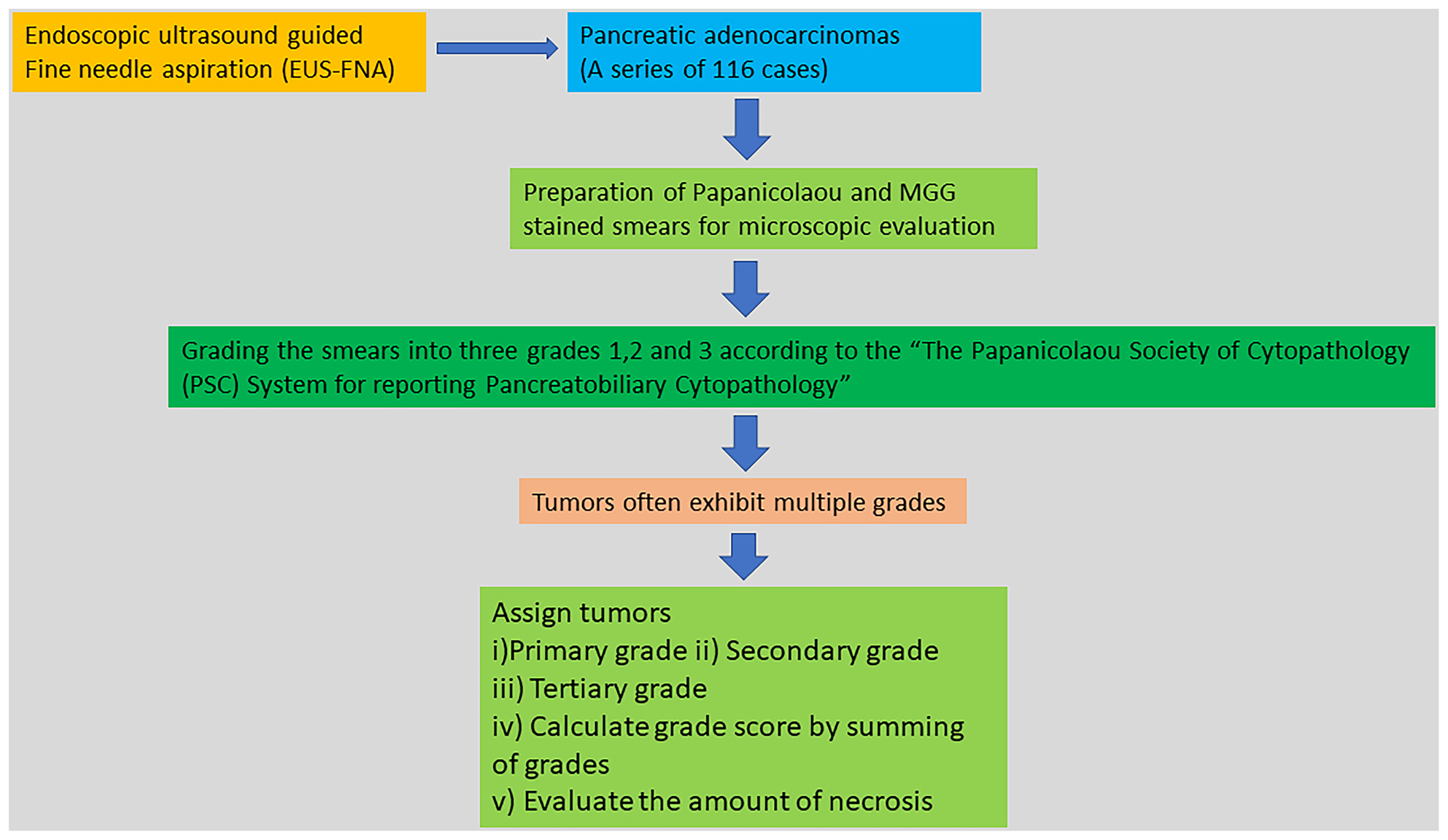
On grading endoscopic ultrasound-guided FNA smears from pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas using a three-tier grading system, it was found that tumours often exhibited multiple grades. Accordingly, tumours were assigned primary, secondary and tertiary grades. Subsequently, grade scores were calculated by summing the grades.
In this study, an alternative system of grading pancreatic adenocarcinomas using fine-needle aspiration cytology has been explored. This will hopefully help in the management of these tumours.
Development and validation of a minimally invasive protocol for assessing oxidative stress markers in exfoliated oral cells
- Pages: 266-274
- First Published: 27 November 2023
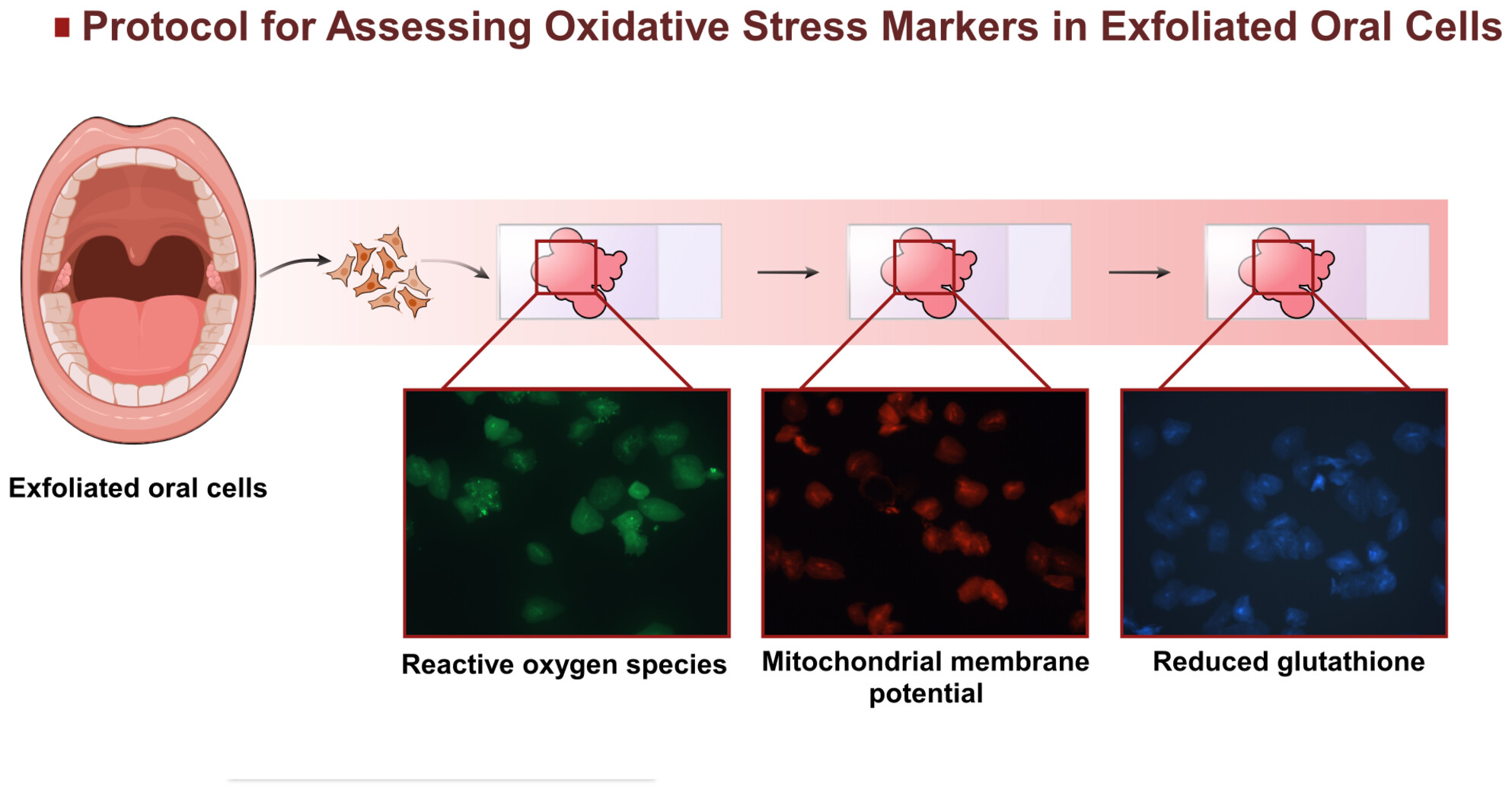
A standardized protocol using fluorescent probes (H2DCFDA, MitoTracker Red and ThiolTracker Violet) was developed to measure reactive oxygen species (ROS), mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm) and reduced glutathione (GSH) in exfoliated oral cells.
This article presents a standardized protocol for assessing oxidative stress markers in exfoliated oral cells, including reactive oxygen species (ROS), mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm) and reduced glutathione (GSH).
The urgency of Burkitt lymphoma diagnosis in fluid cytology—A tertiary care experience
- Pages: 275-282
- First Published: 14 December 2023
CASE REPORTS
Pleomorphic adenoma with extensive squamous and mucinous metaplasia and a novel MALAT1::PLAG1 fusion gene
- Pages: 283-285
- First Published: 12 December 2023
Optic nerve pilomyxoid astrocytoma: Intraoperative squash smear cytology of a rare entity
- Pages: 286-291
- First Published: 06 November 2023
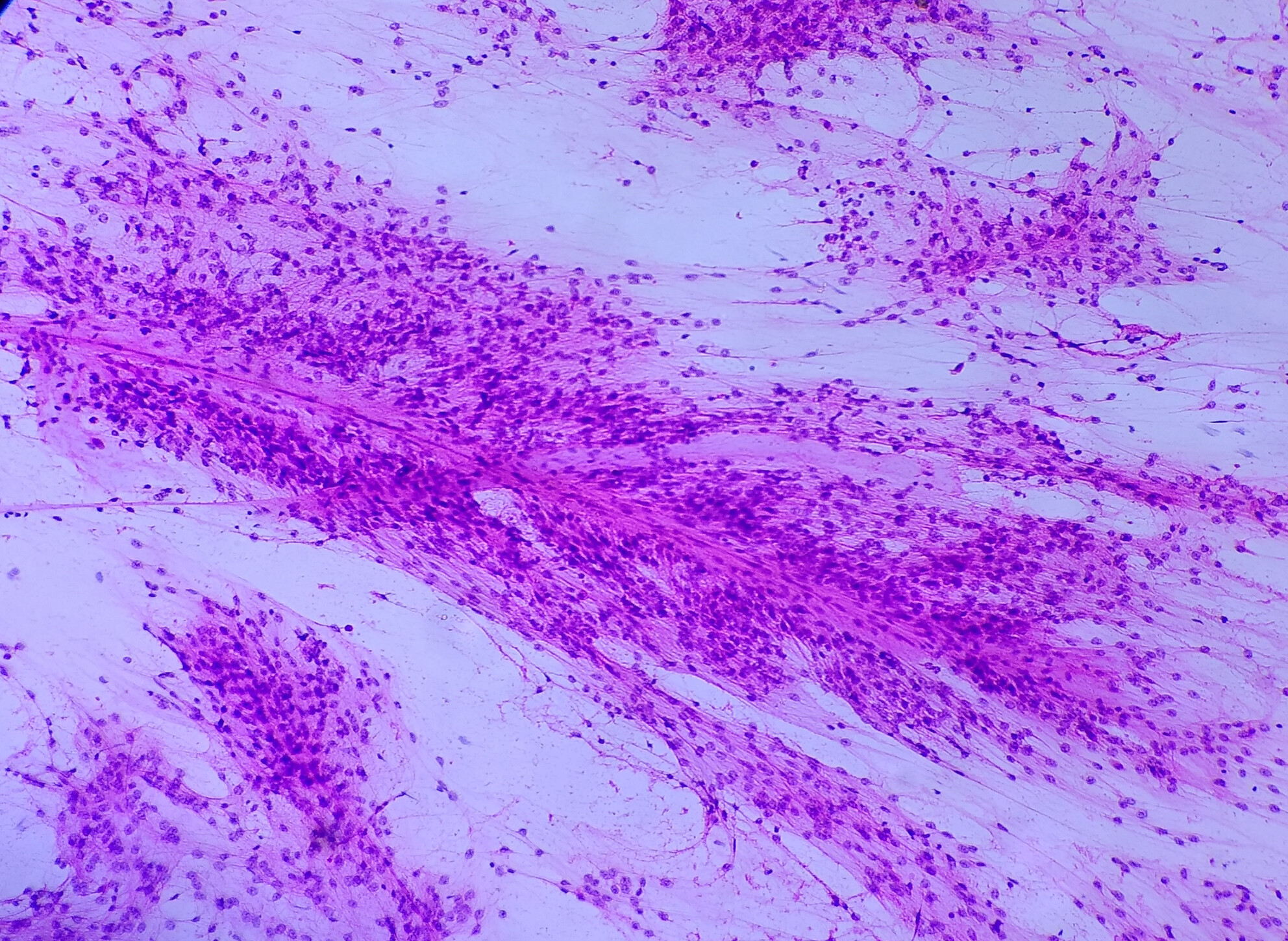
The cytomorphological features of pilomyxoid astrocytoma recapitulate their histopathological characteristics. The presence of monomorphic piloid cells, angiocentric arrangement, myxoid background, absence of Rosenthal fibres and eosinophilic granular bodies helps to arrive at an accurate cytomorphological diagnosis of PMA.
Regular resident becomes aggressive enemy: Diagnosed on cytology
- Pages: 292-295
- First Published: 02 November 2023
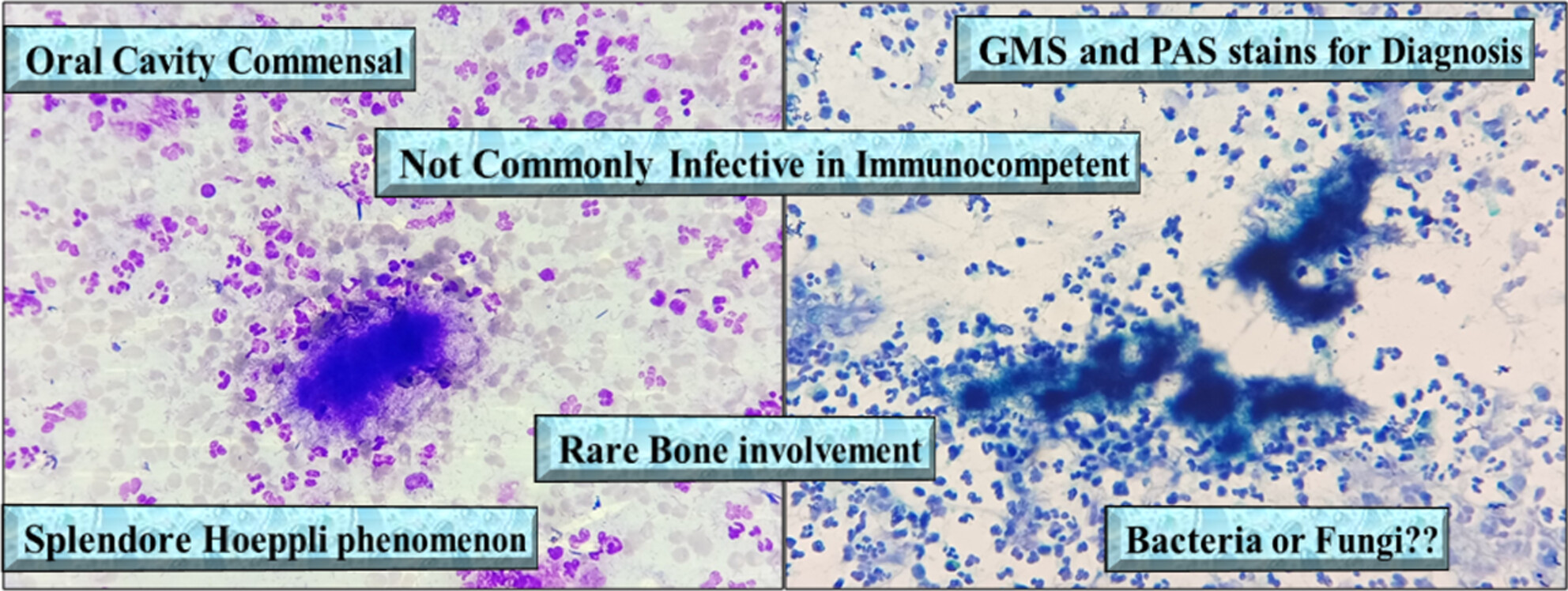
A microorganism which is an oral cavity commensal, not commonly infective in immunocompetent, rarely shows bone involvement, show splendore hoeppli phenomenon, GMS and PAS stains help for diagnosis. Is it bacteria or fungi?
Actinomycosis in immunocompetent individuals is rare. Bone involvement in cervicofacial actinomycosis is uncommon. Cytopathology examination may help in early diagnosis and efficient management.
Hobnail subtype of papillary carcinoma of the thyroid—a rare case with uncommon features
- Pages: 296-300
- First Published: 11 November 2023
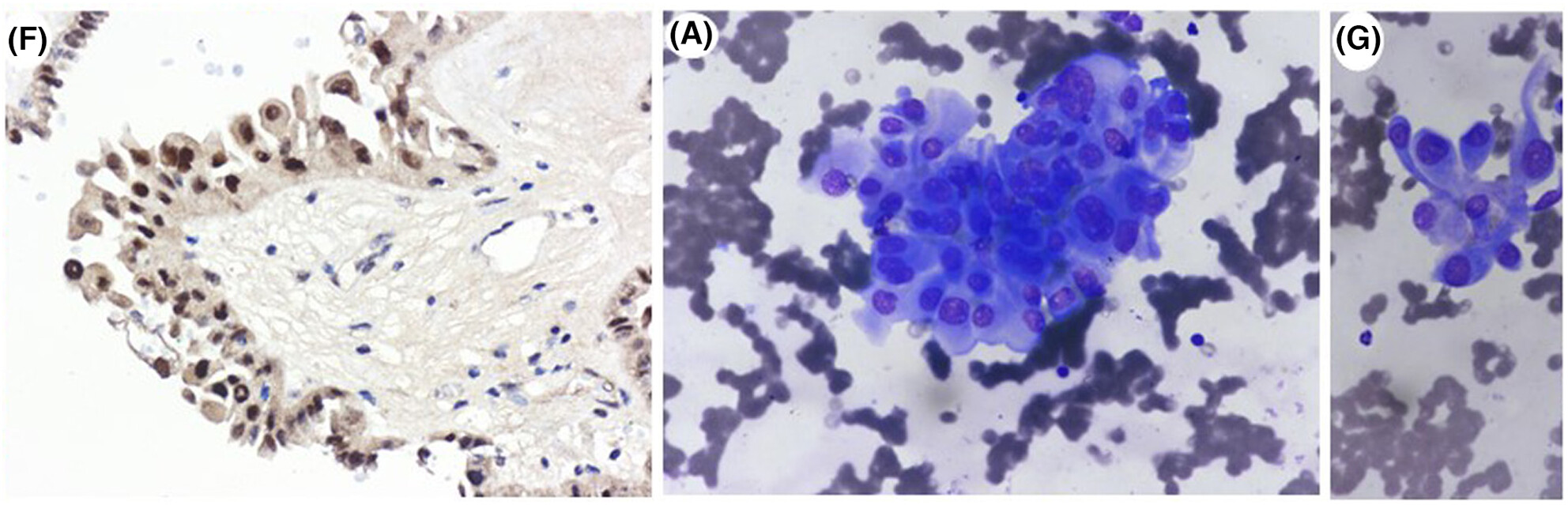
The cytological features of the hobnail variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma may be subtle. It is important to recognize this variant because it may influence the corresponding surgical treatment and follow-up due to its aggressive nature.
The hobnail subtype of papillary thyroid carcinoma is a rare entity with aggressive features. It presents extrathyroidal extension or lymph nodal metastasis in a high percentage of the cases.
Cutaneous eccrine spiradenoma: Insights into cytomorphological features via fine needle aspiration biopsy and a comprehensive literature review
- Pages: 301-306
- First Published: 12 December 2023
Eccrine spiradenoma (ES) is an uncommon and benign adnexal tumour originating from sweat glands. The cytological examination of ES poses a diagnostic challenge, as it can be mistaken for various benign and malignant basaloid skin neoplasms. The cytomorphologic features of ES are infrequently documented in existing literature. This study seeks to present a thorough exploration of the cytomorphologic traits associated with ES, accompanied by an analysis of ancillary testing that contribute to the accurate identification of this entity in cytological specimens.
Eccrine spiradenoma is infrequently encountered in fine needle aspiration (FNA) cytopathology, and the available literature on its cytomorphologic features is limited. The challenge arises from its similarity to other benign and malignant dermal basaloid neoplasms, emphasizing the critical role of clinicopathologic correlation and immunohistochemical staining in achieving a precise diagnosis.
IMAGES IN CYTOLOGY
Myelomatous meningitis diagnosed by cerebrospinal fluid cytology examination
- Pages: 307-309
- First Published: 25 October 2023
ENIGMA PORTAL
Usual breast lump with unusual features
- Pages: 310-312
- First Published: 24 October 2023

The co-existence of granulomatous mastitis and collagenous spherulosis in a breast lump is an uncommon finding. The awareness of cytomorphological features can help corroborate a cytological diagnosis.
A palpable breast lump in an elderly female warrants urgent attention and fine needle aspiration is a rapid, reliable method of evaluation. An elderly female with a firm breast lump mimicking malignancy was subjected to fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC). Smears showed ill-formed granulomas, inflammatory cells and homogeneous hyaline stromal globular elements intermingled with the benign ductal epithelial and myoepithelial cells.
Cytology of a parietal swelling in a 52-year-old man
- Pages: 313-316
- First Published: 30 October 2023
Fine-needle aspiration cytology of presacral myelolipoma: Cytomorphological features of a rare entity and review of the literature
- Pages: 317-320
- First Published: 04 December 2023
Presacral myelolipoma is an uncommon benign tumor, and its diagnosis can be challenging oncytology specimens. This case emphasizes the importance of fine needle aspiration cytology as an initial and valuable diagnostic tool for evaluating presacral masses. The identification of a combination of mature adipose tissue and hematopoietic elements in varying proportions is a crucial feature in FNA cytology. This underscores the role of FNA cytology in providing an accurate diagnosis and guiding subsequent management decisions.
CORRESPONDENCE
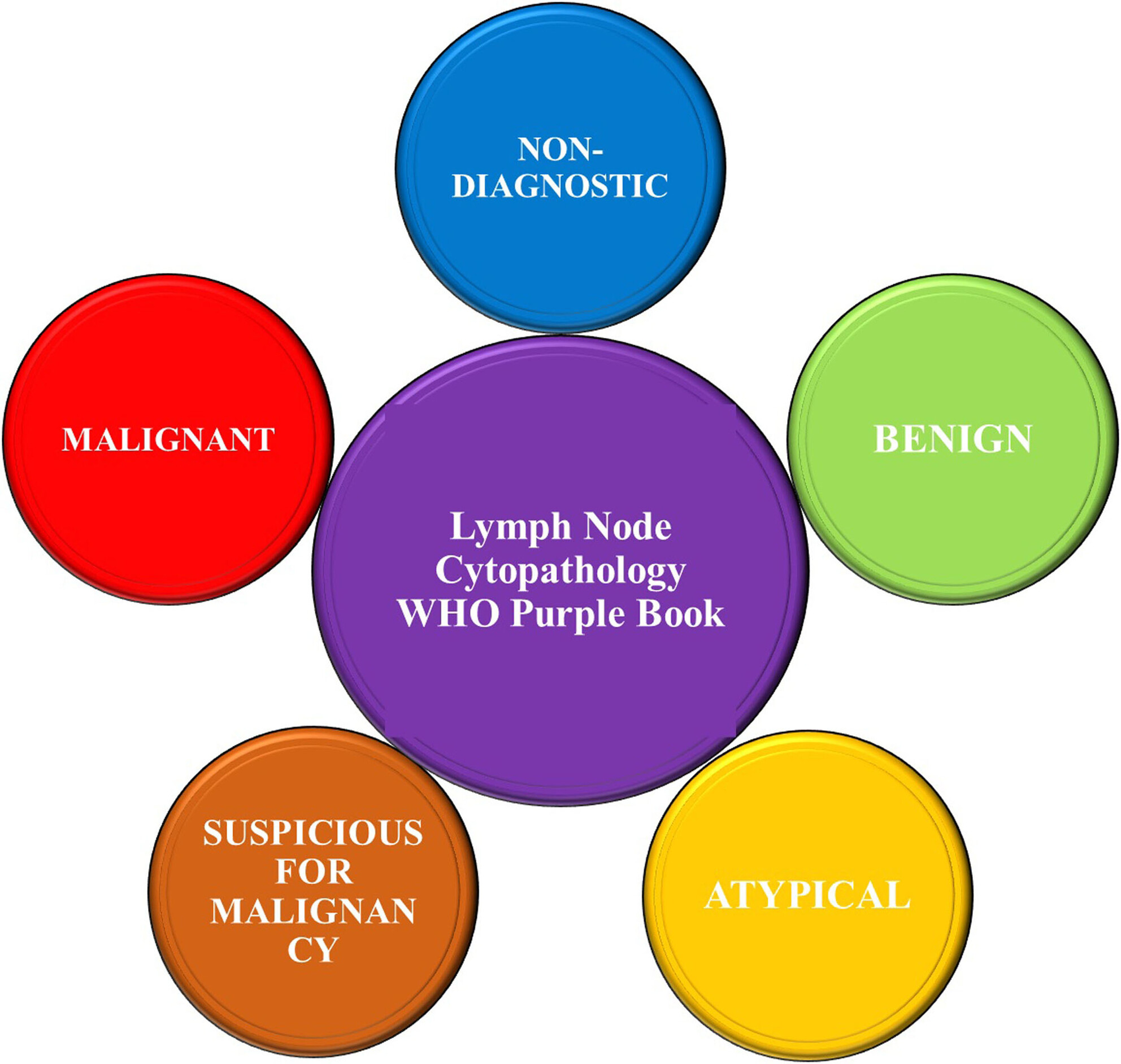
Upcoming World Health Organization system for reporting lymph node cytopathology—A preliminary outline
- Pages: 321-323
- First Published: 17 November 2023
The Kymi Odyssey Honorary Ceremony celebrated the life and career of Dr. George N. Papanicolaou; and the future, dedicated museum
- Pages: 324-325
- First Published: 18 December 2023