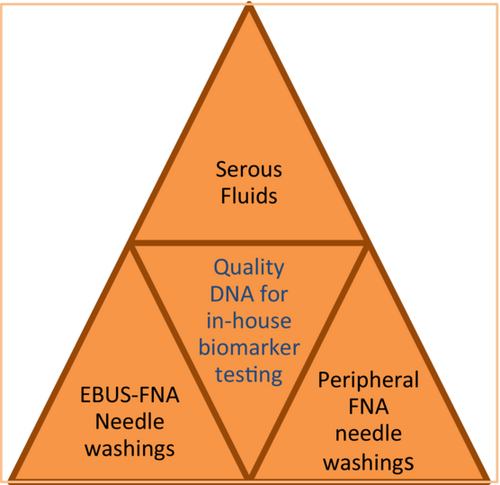
Use of cytology fluid samples for predictive biomarker testing in lung cancer patients
Abstract
Objective
To provide a method of directly using cytology fluid samples for predictive biomarker testing in lung cancer patients and to determine the efficacy of a variety of fluid sample types.
Method
A review of our in-house data from a range of cytology samples including endobronchial ultrasound (EBUS) fine-needle aspirate (FNA) needle washings (NW) and serous effusions tested on the Biocartis Idylla platform. All fluid samples were originally tested using Sanger sequencing.
Results
Using our method for fluid samples all of our cytology samples tested for epithelial growth factor receptor (EGFR) yielded valid results on this platform and all variant cases identified. The data showed serous fluids provided the best quality DNA, and variant genotype reports were obtained within 150 minutes.
Conclusion
Cytology fluid samples can be used for predictive biomarker testing for lung cancer patients to provide in-house results with all fluids providing good-quality DNA.
Graphical Abstract
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
Idylla cartridges supplied by Biocartis for original validation study; no grant or funding to declare.
Open Research
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.