Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Articles
Inhibition of Putative Ibrutinib Targets Promotes Atrial Fibrillation, Conduction Blocks, and Proarrhythmic Electrocardiogram Indices: A Mendelian Randomization Analysis
- First Published: 12 March 2025
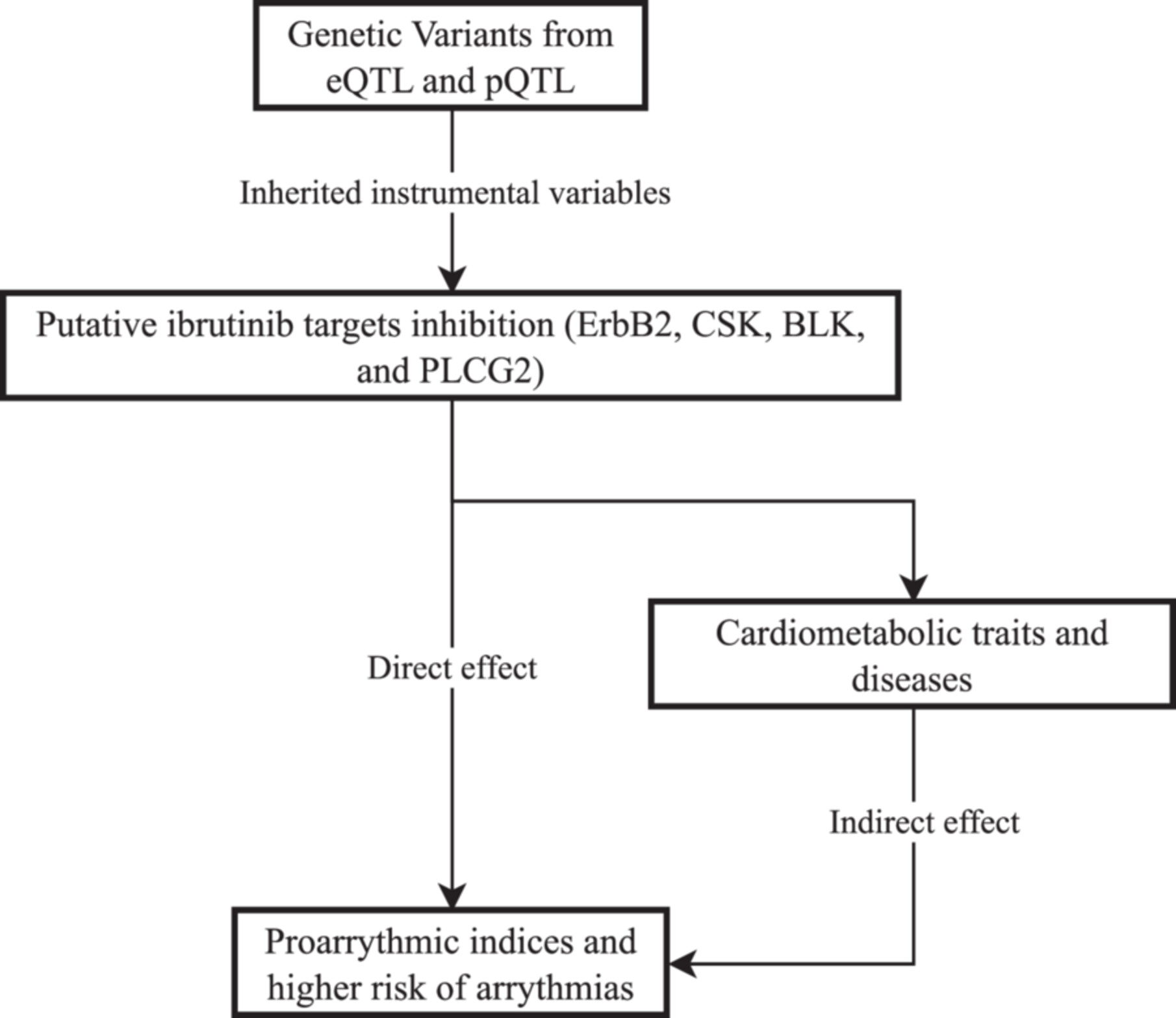
ErbB2 inhibition was associated with an increased risk of atrial fibrillation, prolonged QTc interval, and increased P wave terminal force. CSK inhibition demonstrated potential links to conduction blocks, while PLCG2 inhibition led to changes in P wave terminal force, QTc interval, and an increased risk of left bundle branch block. BLK inhibition was associated with QTc interval shortening and atrioventricular block.
Predictive Value of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Related Myocarditis Among Patients Treated for Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
- First Published: 20 February 2025
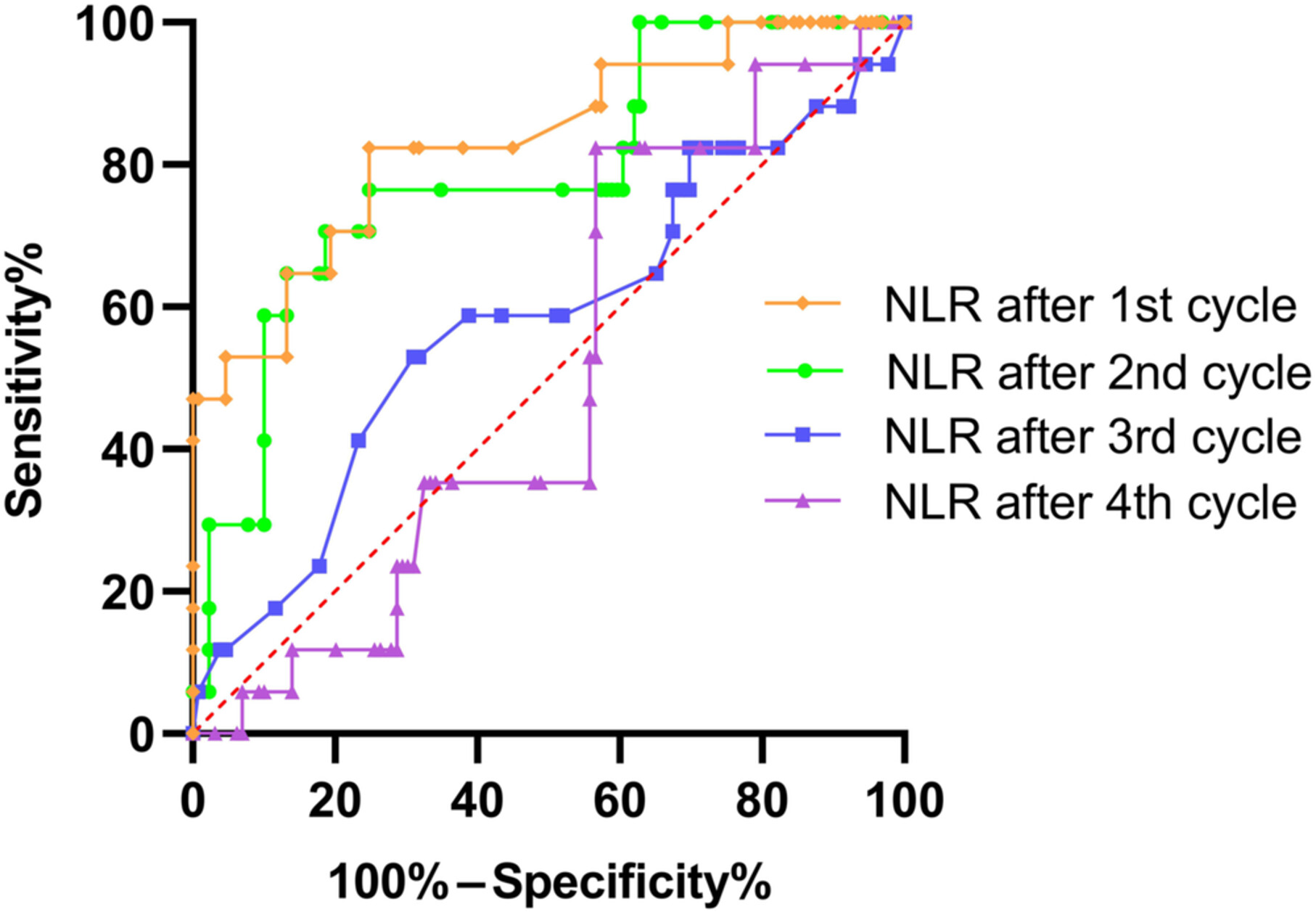
Our study found that the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio elevation in the early phase after immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) treatment in non-small-cell lung cancer is a predictive factor for ICI-related myocarditis. Regular and frequent cardiac monitoring may help to avoid the occurrence of severe and fatal cases.
Mitigating Ibrutinib-Induced Ventricular Arrhythmia and Cardiac Dysfunction With Metformin
- First Published: 13 November 2024
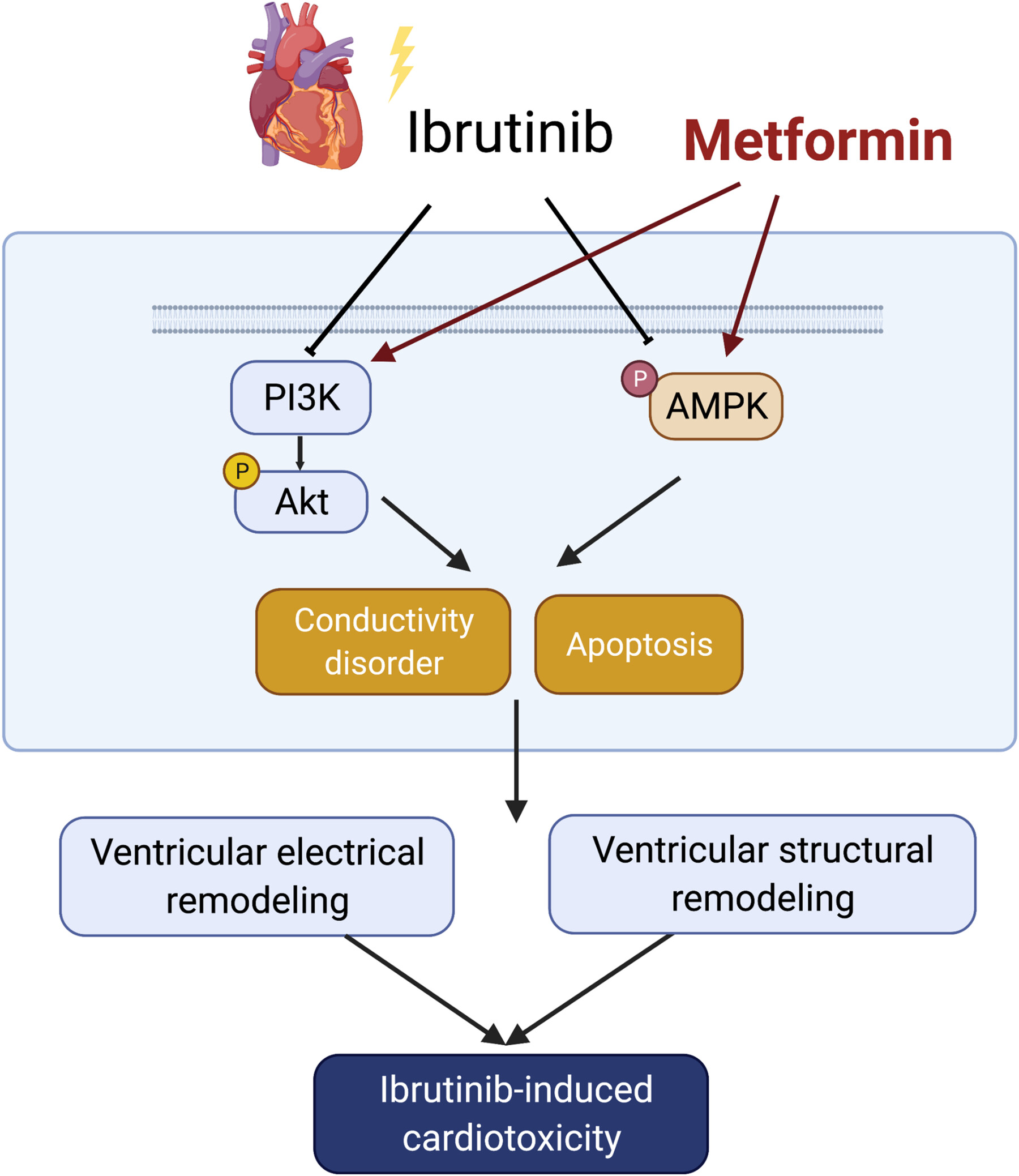
Ibrutinib, a Bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitor, has been associated with a significant increase in the risk of ventricular arrhythmias. In our present study, we aimed to investigate the cardiotoxicity of ibrutinib and explore the potential protective effects of metformin in ibrutinib-treated mice. Our findings revealed that long-term exposure to ibrutinib triggered ventricular myocardial apoptosis and fibrosis, leading to alterations in cardiac electrophysiological properties and an increased potential for ventricular arrhythmia. In this ibrutinib-induced model of cardiac toxicity, metformin demonstrated the ability to upregulate the AMPK and PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, thereby mitigating the ibrutinib-induced cardiotoxicity. As a result, we have demonstrated the protective effects of metformin in counteracting ibrutinib-induced cardiotoxicity and propose it as a potential pharmaceutical therapeutic strategy for related diseases.
Histone deacetylase 6 as a novel promising target to treat cardiovascular disease
- First Published: 07 May 2024
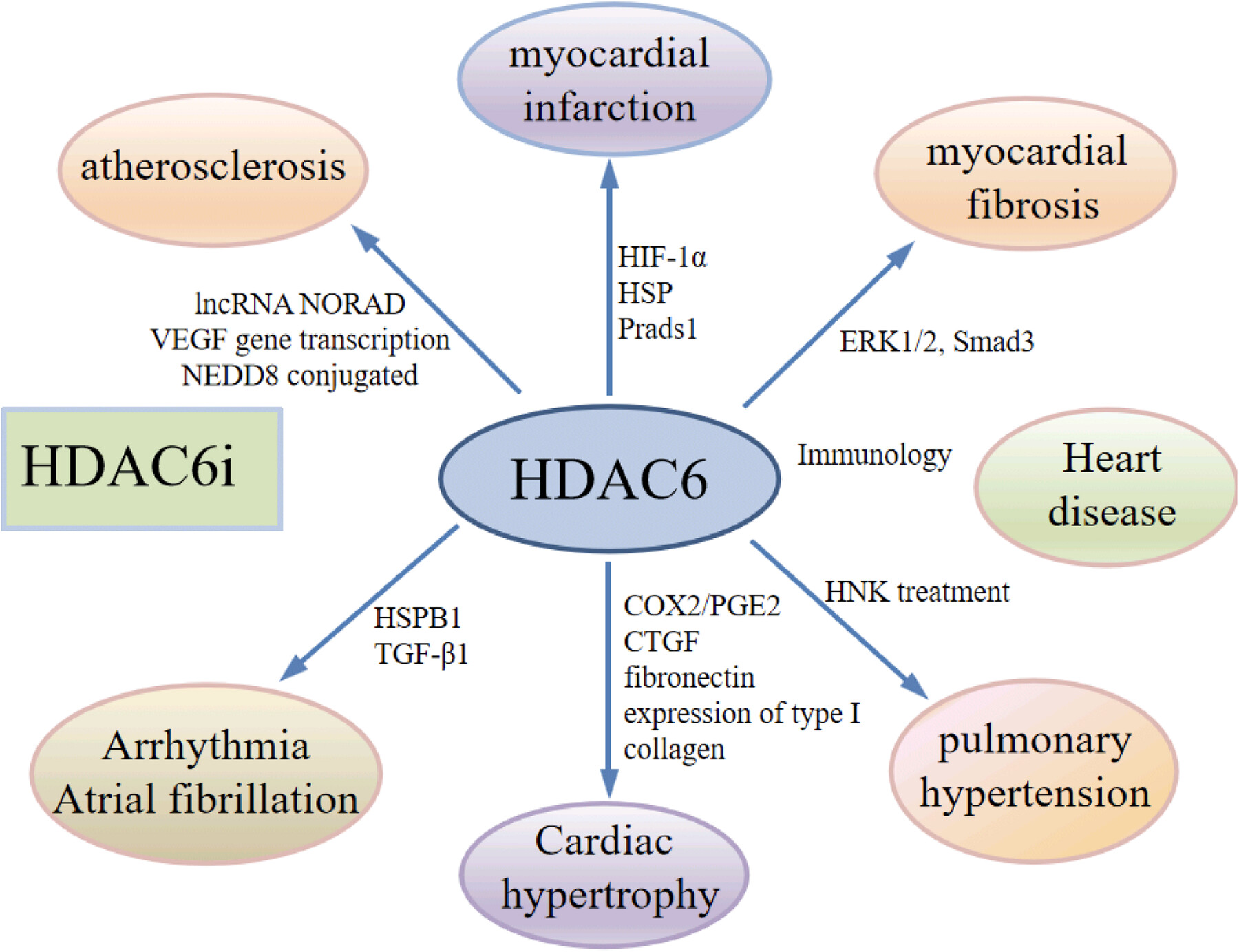
HDAC6 have been found to be a key protein in the tumor–cardiovascular association. HDAC6 inhibitors may have important moderating effects in various types of cardiovascular diseases. HDAC6 inhibitors alone or in combination with other agents have shown promising prospects in the treatment of cardiovascular disease.
Cardiovascular toxicity with CTLA-4 inhibitors in cancer patients: A meta-analysis
- First Published: 16 April 2024
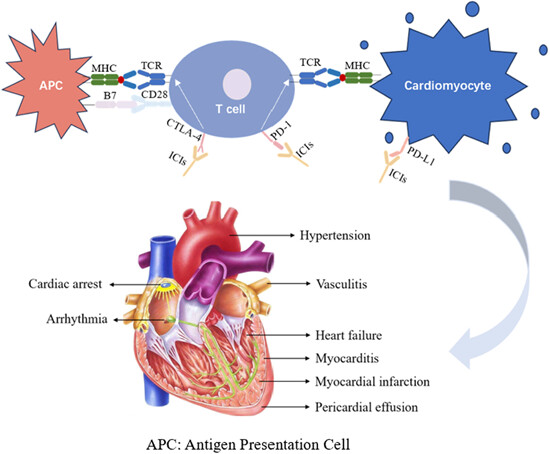
1. CTLA-4 inhibitors restore the T cell immune response against tumor cells. Tumors and cardiomyocytes, shared some muscle-specific antigens, which trigger a cross-reactivity with T cells. The inhibitors make cardiac cells susceptible to injury. 2. CTLA-4 inhibitors significantly increased the incidence of all-grade cardiovascular toxicity and severe cardiovascular toxicity in the patients. The risk of serious cardiovascular toxic events was independent of the type of adverse event.
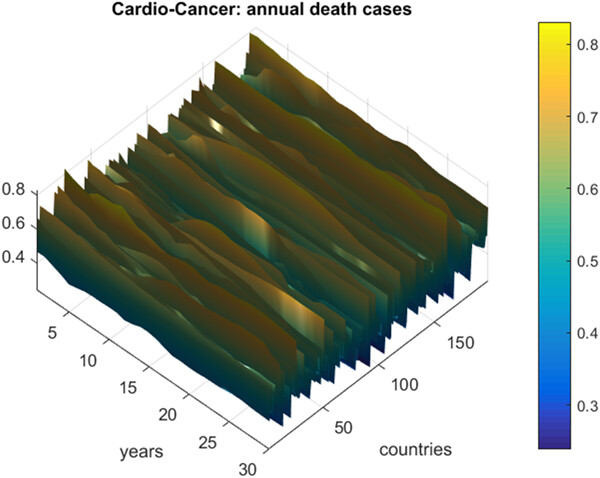
Prediction of death rates for cardiovascular diseases and cancers
- First Published: 09 February 2023




2770-9183.special-issue-on-onco-cardiology.cover.gif)