Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Table of Contents
Fabrication of Solvent-Resistant Copolyimide Membranes for Pervaporation Recovery of Amide Solvents
- First Published: 15 November 2017
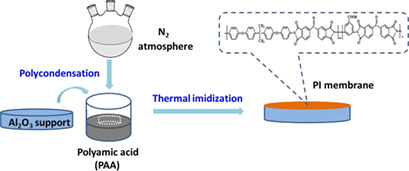
An innovative ceramic-supported copolyimide membrane was fabricated via the two-step thermal imidization method and applied to pervaporation recovery of dimethylformamide and dimethylacetamide. The prepared copolyimide membrane demonstrated high resistance to these amide solvents and superior separation performance, proving great potential for the application in recovery of amide solvents.
Affinitive Poly(vinylidene difluoride) Membranes for Enhancing Au(III) Separation with Extremely High Selectivity
- First Published: 08 November 2017

Affinitive membrane chromatography is an appropriate alternative technology for low-concentration gold recovery, e.g., from wastewater. The addition degree of thiourea to poly(vinylidene difluoride) resin was elevated by using NaOH as a catalyst in the grafting process. The separation ability of the resin and the corresponding membrane made thereof toward Au(III) were significantly improved.
Facile Preparation of Positively Charged and Solvent-Resistant Cellulose Acetate/LSCF Nanofiltration Membranes
- First Published: 27 October 2017

For a broader application of nanofiltration (NF) membranes, the development of positively charged and solvent-resistant membranes by a simple method seems highly important. The nanosized hydrophilic inorganic additive LSCF was added to the casting solution to improve the performance of cellulose acetate NF membranes which exhibit positively charged characteristics and excellent solvent resistance.
Thin-Film Nanocomposite Nanofiltration Membranes Incorporated with Graphene Oxide for Phosphorus Removal
- First Published: 27 October 2017
Conventional thin-film composite membranes suffering from limited lifespans due to high fouling propensity can be improved by modifying the thin layer with hydrophilic nanoparticles. The production of thin-film nanocomposite membranes with incorporated graphene oxide can save time and cost, working well in both water flux and phosphorus rejection with enhanced separation performance.
Supported Electrospun Ultrafine Fibrous Poly(tetrafluoroethylene)/ZnO Porous Membranes and their Photocatalytic Applications
- First Published: 24 October 2017
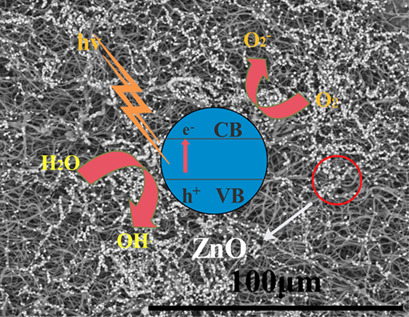
An effective method of photocatalyst immobilization on an electrospun poly(tetrafluoroethylene) fibrous membrane obtained by a simple combination of electrospinning technique and sintering processing is proposed. The membranes were utilized as supports with excellent flexibility, chemical stability, a high specific surface area, high efficiency, and stable photocatalytic properties.
Synthesis of Nanocomposite Poly(vinyl alcohol)-Tin Oxide Mixed-Matrix Membranes for Textile Effluent Treatment
- First Published: 24 October 2017
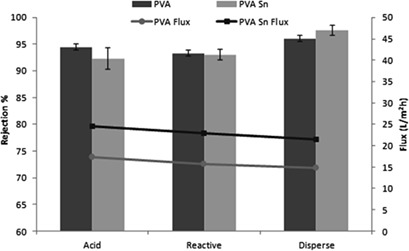
Thin-film nanocomposite membranes prepared by dip-coating were studied by spectroscopic and analytical methods and tested for their performance in dye-containing wastewater filtration. Incorporation of SnO2 nanoparticles improved the rejection for disperse dyes, but no significant change was observed for acid and reactive dyes. Structural properties of the membranes were calculated using a modified Nernst-Planck equation.
Chitosan-Functionalized Graphene Oxide for Enhanced Permeability and Antifouling of Ultrafiltration Membranes
- First Published: 20 October 2017
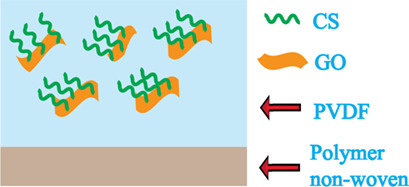
The incorporation of chitosan-functionalized graphene oxide (CS-GO) into a poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) ultrafiltration membrane improves the properties of the membrane. An optimum amount of CS-GO incorporation leads to an increase in permeability and a reduction in fouling of the membrane through changes in hydrophobicity.
Surface Modification of Polysulfone Membranes Using Poly(Acrylic Acid)-Decorated Alumina Nanoparticles
- First Published: 18 September 2017
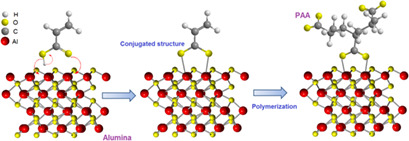
Fouling problems associated with polymeric membranes affect the efficiency of many membrane filtration processes. Poly(acrylic acid)-decorated alumina nanoparticles were embedded in a polysulfone membrane matrix via nanofiller dispersion in the casting solution. The thus improved membrane hydrophilicity and surface softness resulted in less fouling and enhanced flux recovery.
Preparation of High-Performance Membranes Derived from Poly(4-methyl-1-pentene)/Zinc Oxide Particles
- First Published: 02 June 2017
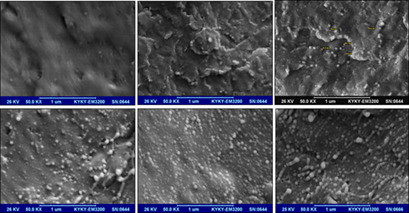
The addition of nanoparticles to polymeric precursors and the preparation of mixed-matric membranes are considered as suitable alternative to improve mechanical properties, transferability, and selectivity in commercial polymer membranes. The efficiency of gas separation by mixed-matrix membranes developed from poly(4-methyl-1-pentene) filled with zinc oxide nanoparticles is investigated.
Assessment of a Thermally Modified Cellulose Acetate Forward-Osmosis Membrane Using Response Surface Methodology
- First Published: 19 June 2018
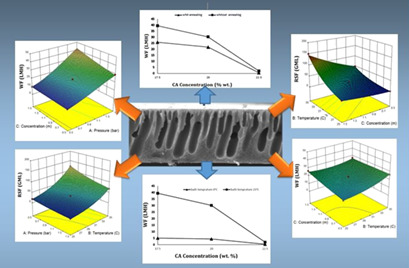
Forward osmosis (FO) has become an emerging desalination technology but the fabrication of high-performance and low-price membranes for FO is still a concern. Cellulose acetate was investigated as starting material for production of flat sheet FO membranes. The performance of such membranes was evaluated for different operational conditions. Two validated models were elaborated.









