Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
Sixty years of ethical evolution: The 2024 revision of the Declaration of Helsinki (DoH)
- Pages: 371-373
- First Published: 17 December 2024
REVIEW
Caregiving in Asia: Priority areas for research, policy, and practice to support family caregivers
- Pages: 374-382
- First Published: 18 December 2024
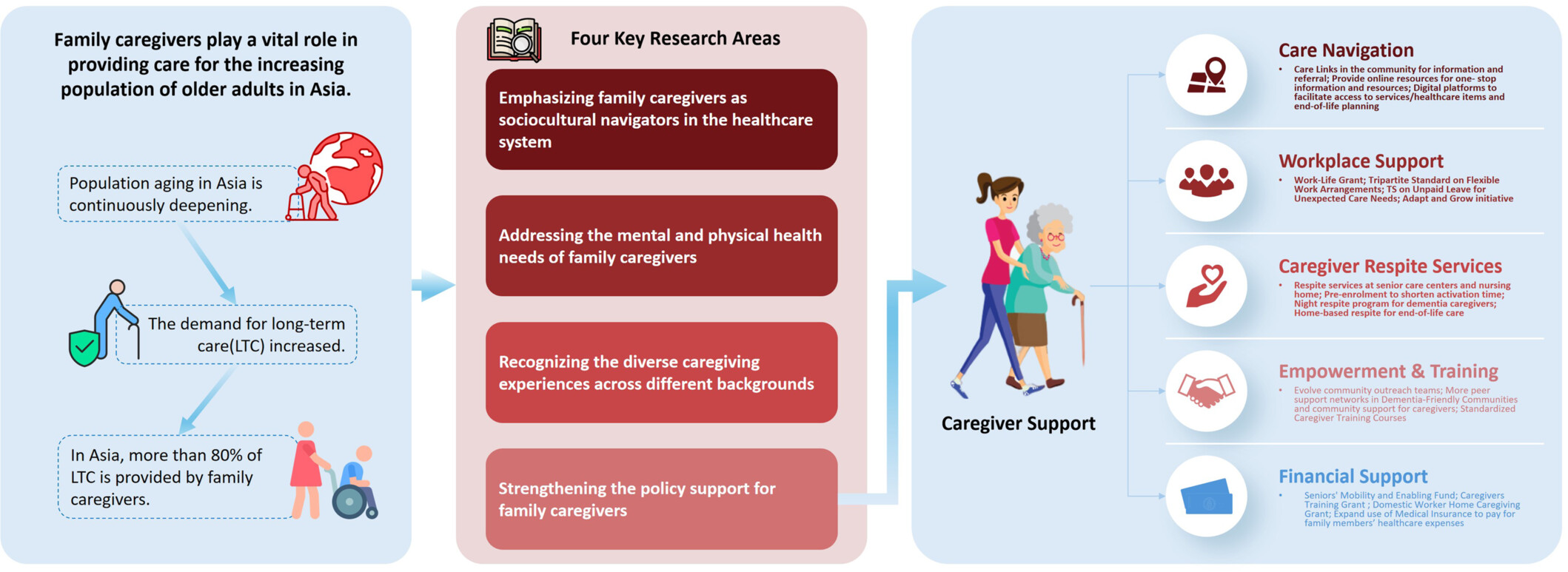
In this review, we identify four key priority areas to advance research, practice, and policy related to family caregivers in Asia: (1) Emphasizing family caregivers as sociocultural navigators in the healthcare system; (2) addressing the mental and physical health needs of family caregivers; (3) recognizing the diverse caregiving experiences across different cultural backgrounds, socioeconomic status, and countries of residence; and (4) strengthening policy support for family caregivers. We propose cross-country knowledge exchange and capacity development for better serving both the aging population and their caregivers.
Innovative public strategies in response to COVID-19: A review of practices from China
- Pages: 383-408
- First Published: 18 December 2024
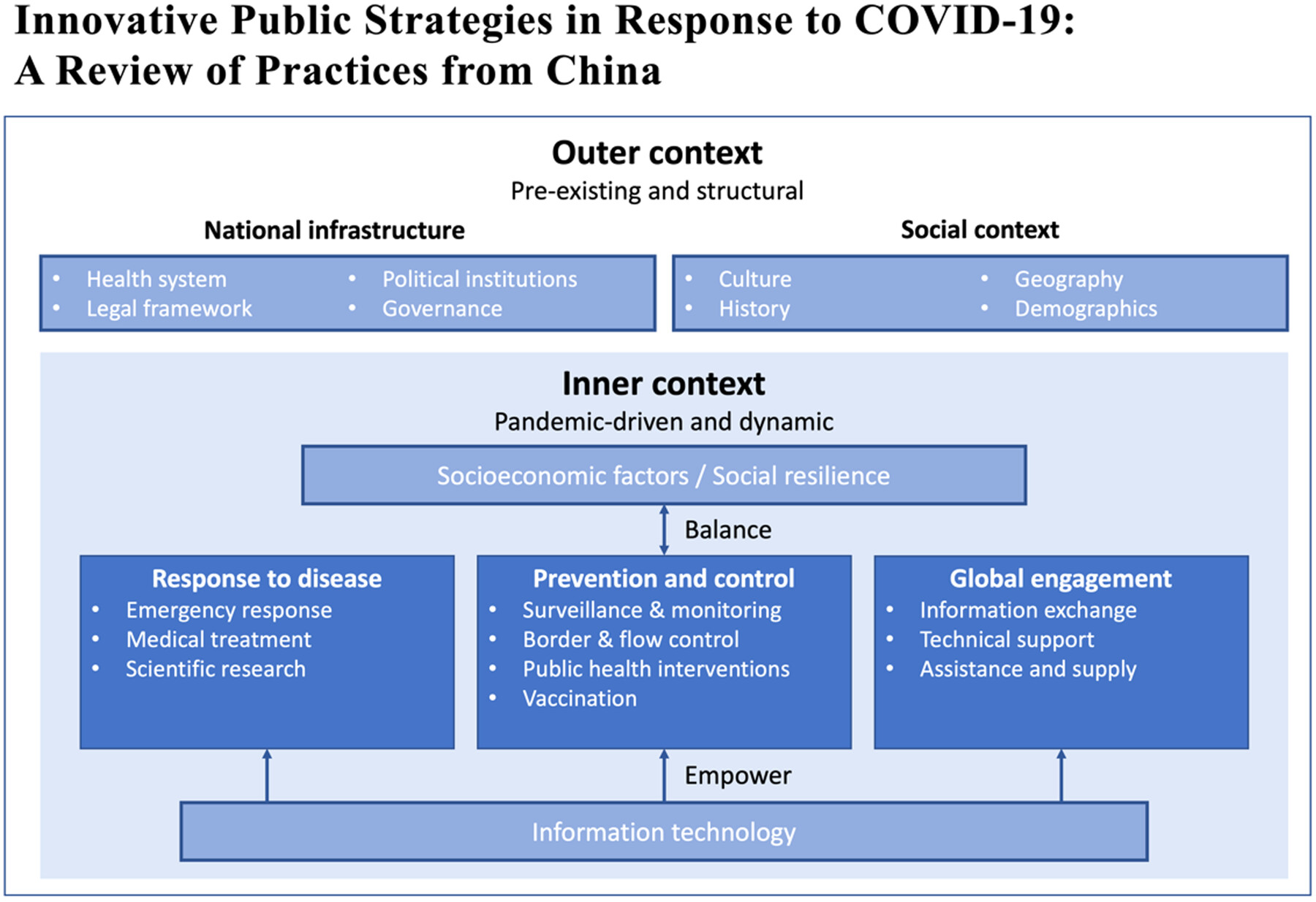
China's COVID-19 response: infrastructure, medical care, prevention, resilience, and global health engagement. Highlighted China's top-down command system, intersectoral coordination, and social governance effectiveness. Focused on coordinated emergency response, evidence-based treatment, strategic vaccine rollout, and IT support in healthcare.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
A novel ensemble ARIMA-LSTM approach for evaluating COVID-19 cases and future outbreak preparedness
- Pages: 409-425
- First Published: 15 December 2024
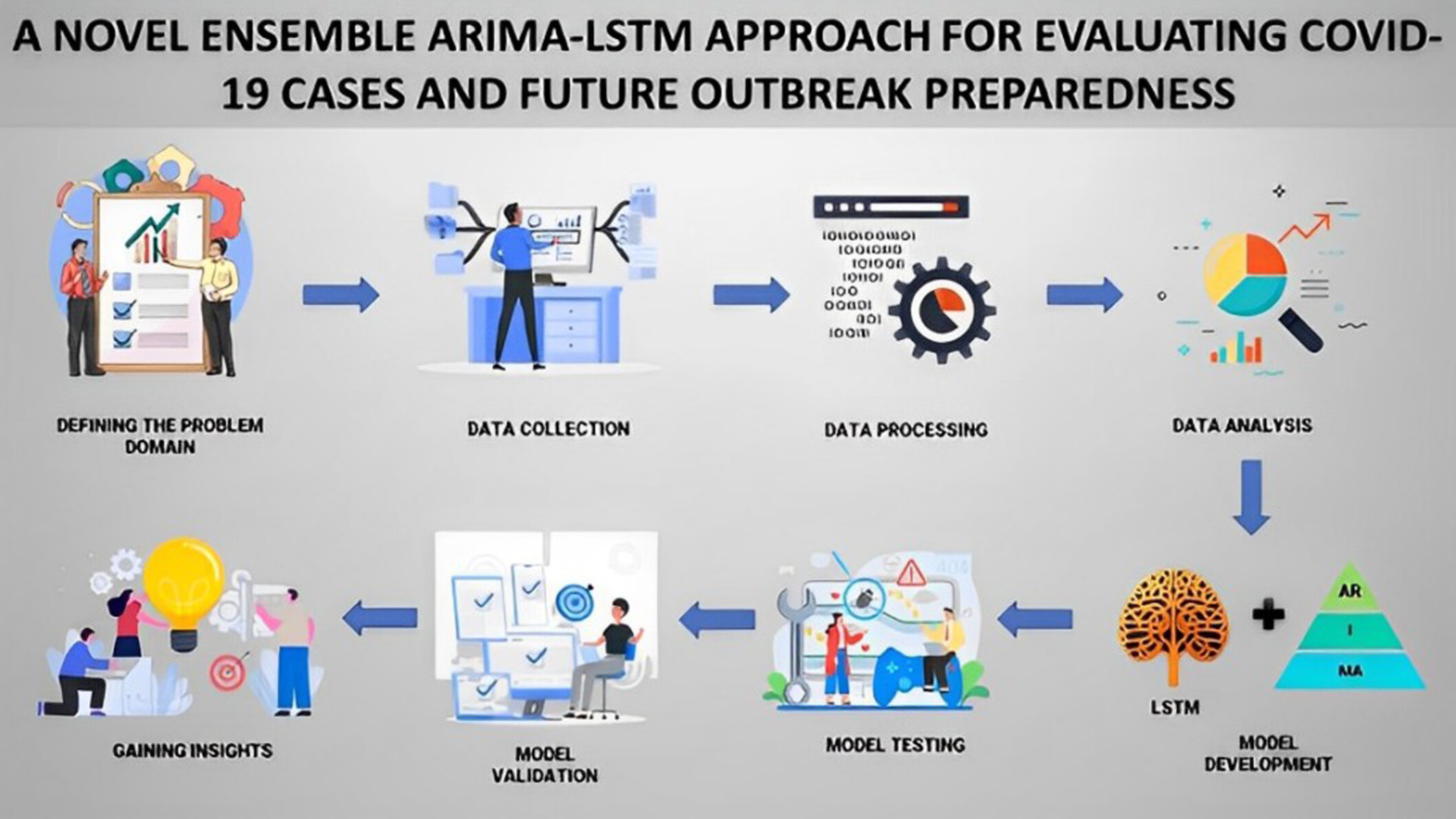
A novel ensemble model that combines auto-regressive integrated moving average (ARIMA) and long short-term memory (LSTM) models is proposed to improve the forecasting accuracy of COVID-19 cases. The proposed ensemble model achieves superior performance compared to individual ARIMA, LSTM, and other baseline forecasting models. This approach has the potential to enhance preparedness for future outbreaks by providing more accurate forecasts of COVID-19 cases.
Explainable machine learning model for pre-frailty risk assessment in community-dwelling older adults
- Pages: 426-437
- First Published: 10 December 2024
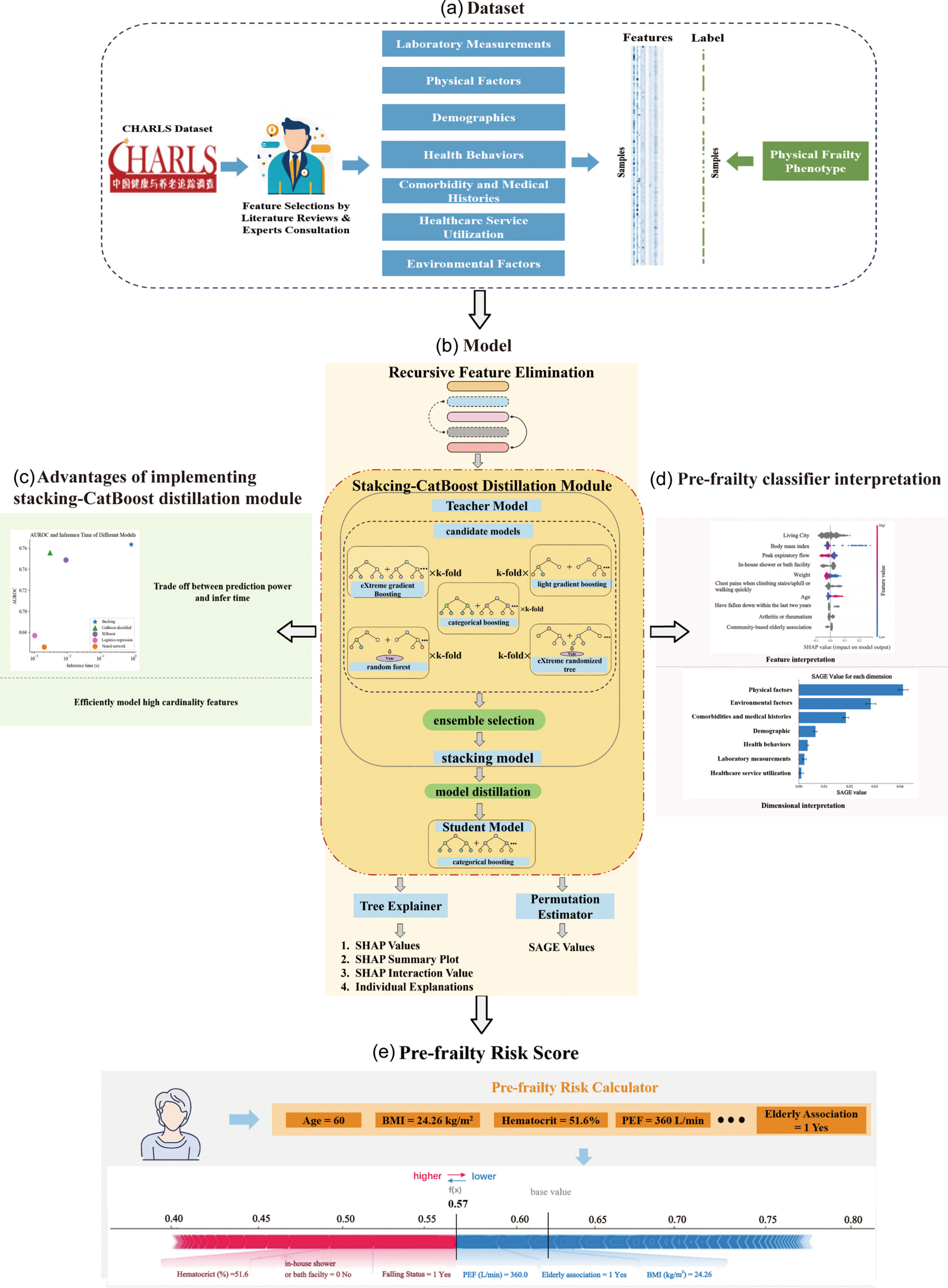
The PACIFIC framework utilizes the CHARLS (2011) data set, which consists of 80 features organized into seven dimensions, and integrates an efficient recursive feature elimination method with a stacking-CatBoost distillation module and explainable AI techniques to analyze pre-frailty risk. By employing Tree Explainer for SHAP values and SAGE values for feature contribution, PACIFIC provides individualized explanations that highlight the impact of each risk factor on the overall risk score, thereby enhancing clinical credibility.
SkinSage XAI: An explainable deep learning solution for skin lesion diagnosis
- Pages: 438-455
- First Published: 28 November 2024
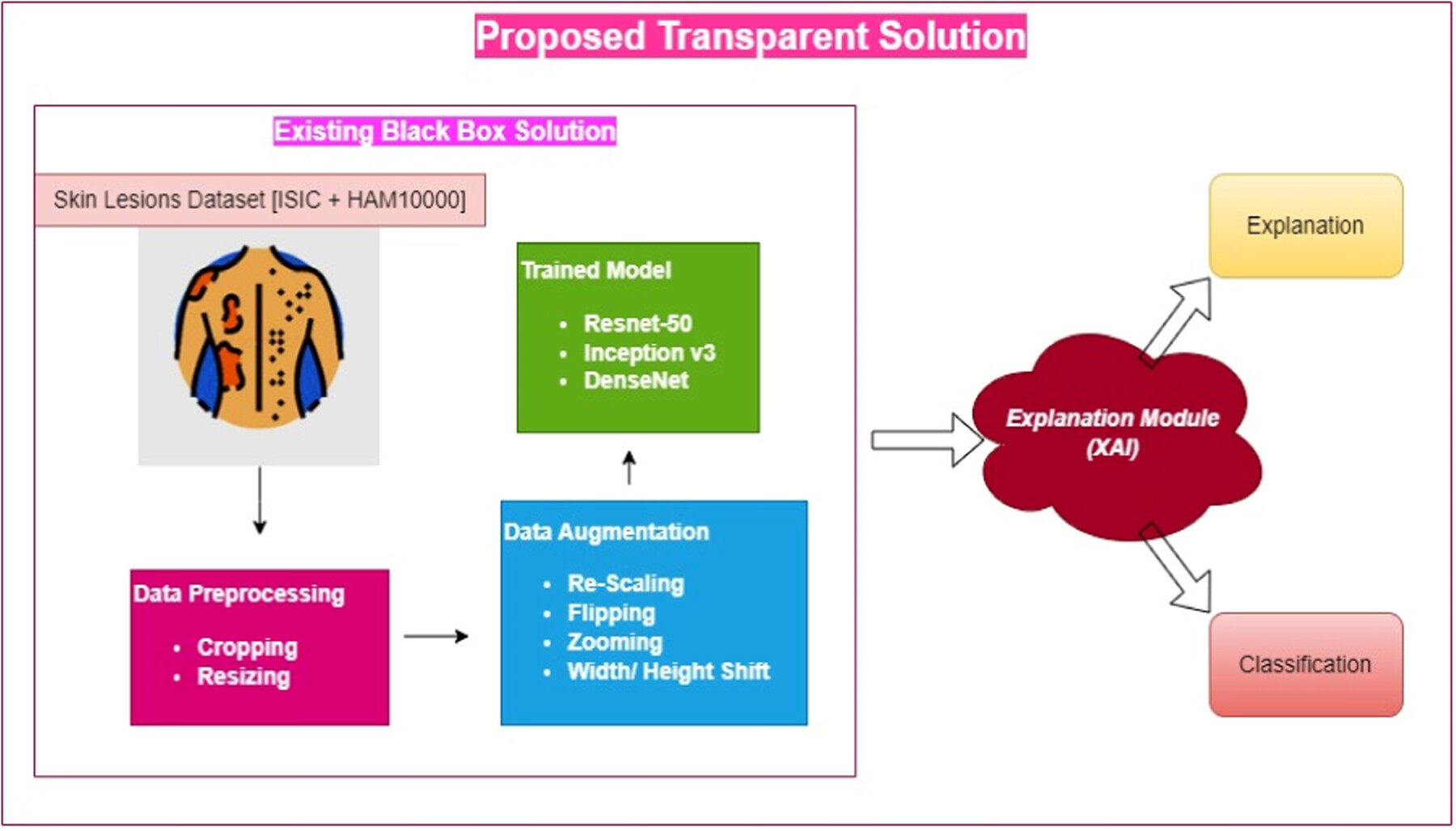
The research was meant to disentangle the difficulties of skin lesion diagnosis using a multimodal approach. Our suggested technique offers unparalleled levels of transparency and interpretability in skin lesion categorization and marks a substantial improvement in the area via methodical methodology and meticulous refining. The research focuses on proposing.
- i.
A straightforward and reliable technique for the categorization of a variety of skin lesions.
- ii.
Explore different deep learning (DL) models in the diagnosis of skin lesions and evaluate their performance and effectiveness.
- iii.
Enhanced DL model's interpretability and transparency in dermatology with the help of explainable artificial intelligence techniques.
- iv.
Helping DL models to be easily incorporated into clinical practice further supporting in skin cancer prevention, management, and improved patient outcome.
Leveraging anatomical constraints with uncertainty for pneumothorax segmentation
- Pages: 456-474
- First Published: 15 December 2024
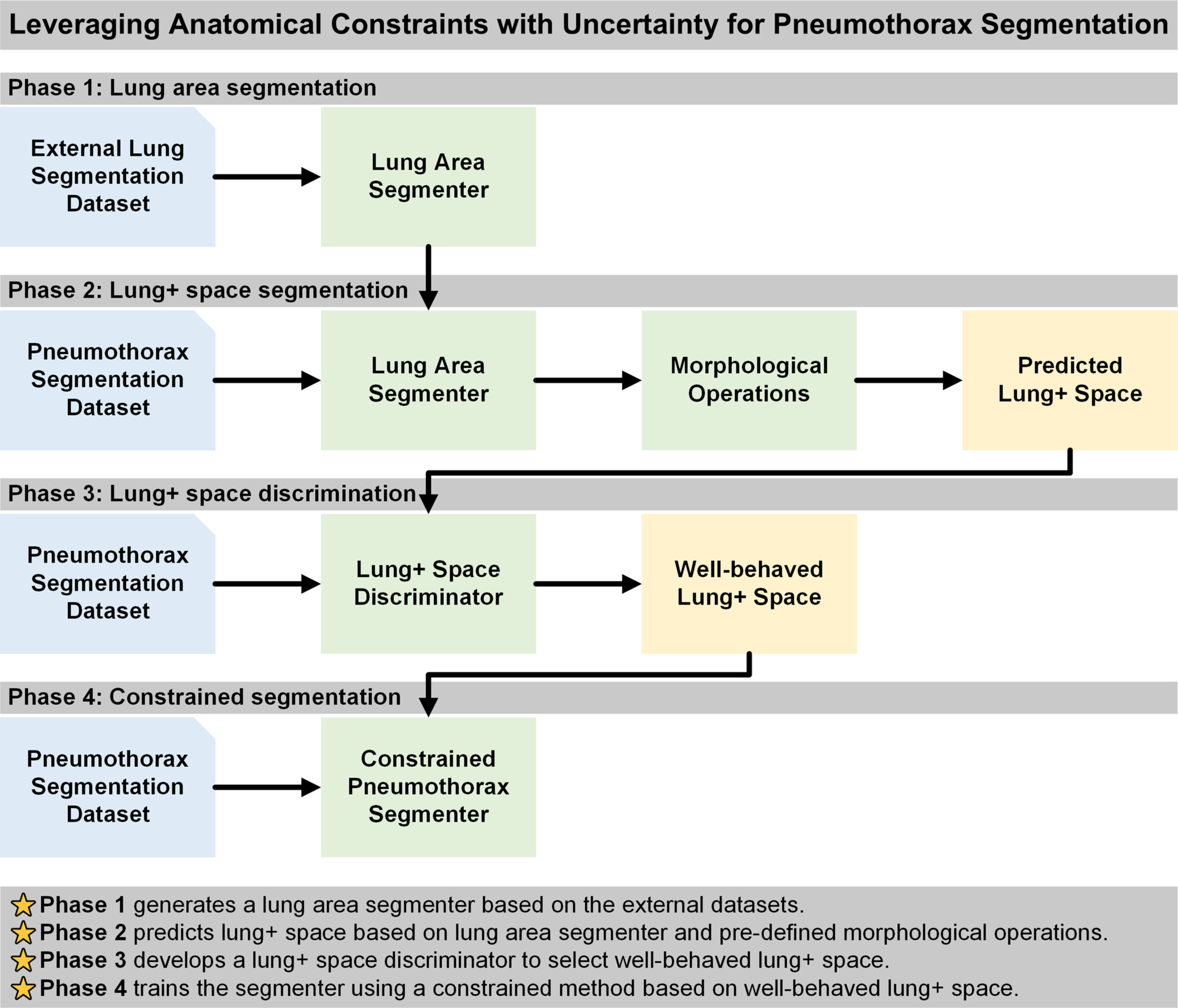
We proposed a novel approach that incorporates the lung + space as a constraint during deep learning model training for pneumothorax segmentation on 2D chest radiographs. We utilized external datasets and an auxiliary task of lung segmentation to generate a specific constraint of lung + space for each chest radiograph, circumventing the need for additional annotations. We incorporated a discriminator to eliminate unreliable constraints caused by the domain shift between the auxiliary and target datasets. Our results demonstrated consistent improvements across six baseline models built on three segmentation architectures and two convolutional neural networks backbones.
STUDY PROTOCOLS
Study protocol: A national cross-sectional study on psychology and behavior investigation of Chinese residents in 2023
- Pages: 475-492
- First Published: 20 December 2024
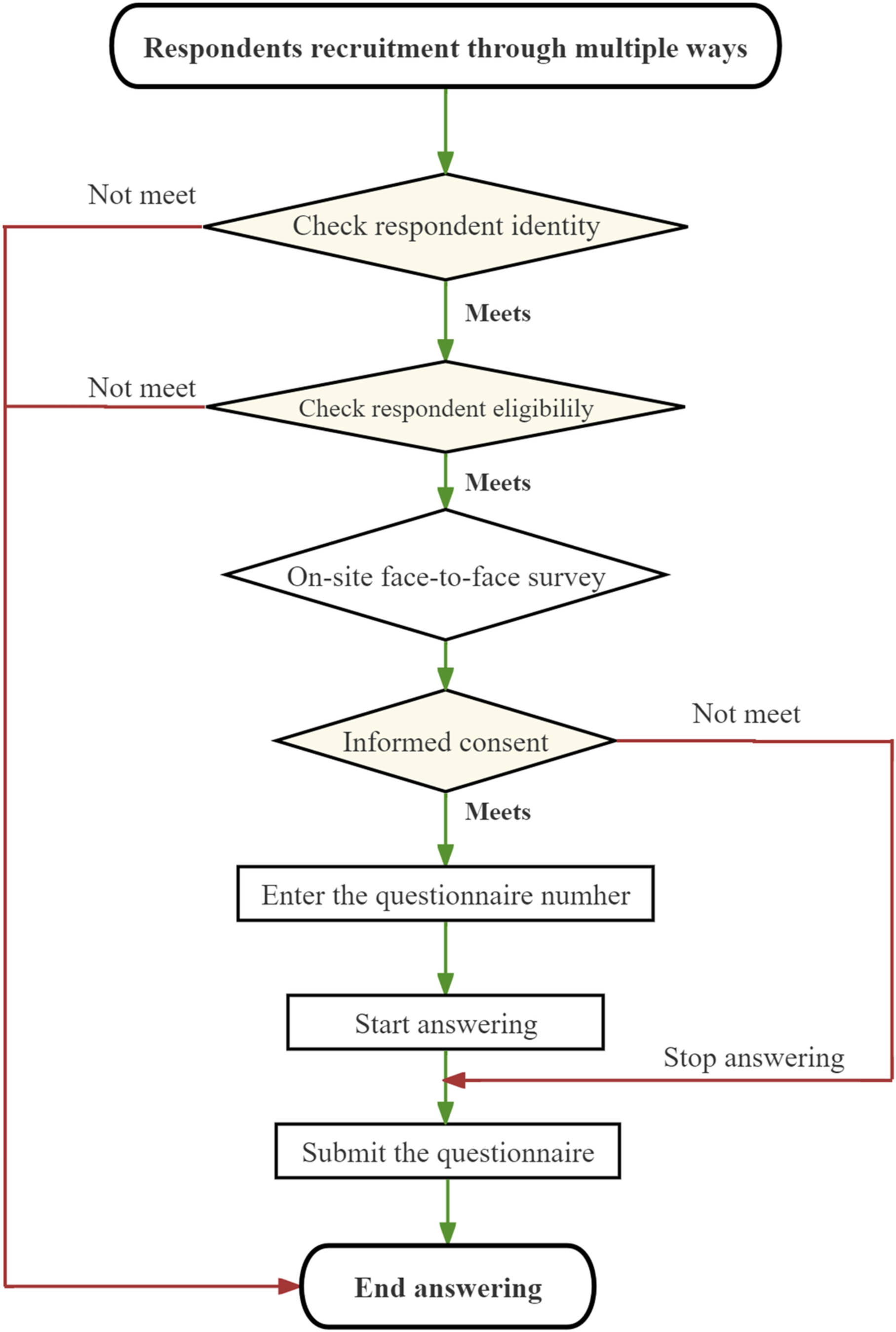
Surveyed from June 20 to August 31, 2023, across 150 cities and various urban–rural settings in China, our study employed stratified sampling to gather comprehensive data on Chinese residents' psychology and behavior. Trained surveyors conducted face-to-face interviews, covering health, family, social environment, psychological conditions, and behavioral patterns. Quality control ensured robust data for informing health policies and services.











