Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEWS
Comparison of the effect of saffron, crocin, and safranal on serum levels of oxidants and antioxidants in diabetic rats: A systematic review and meta-analysis of animal studies
- Pages: 2429-2439
- First Published: 13 March 2023
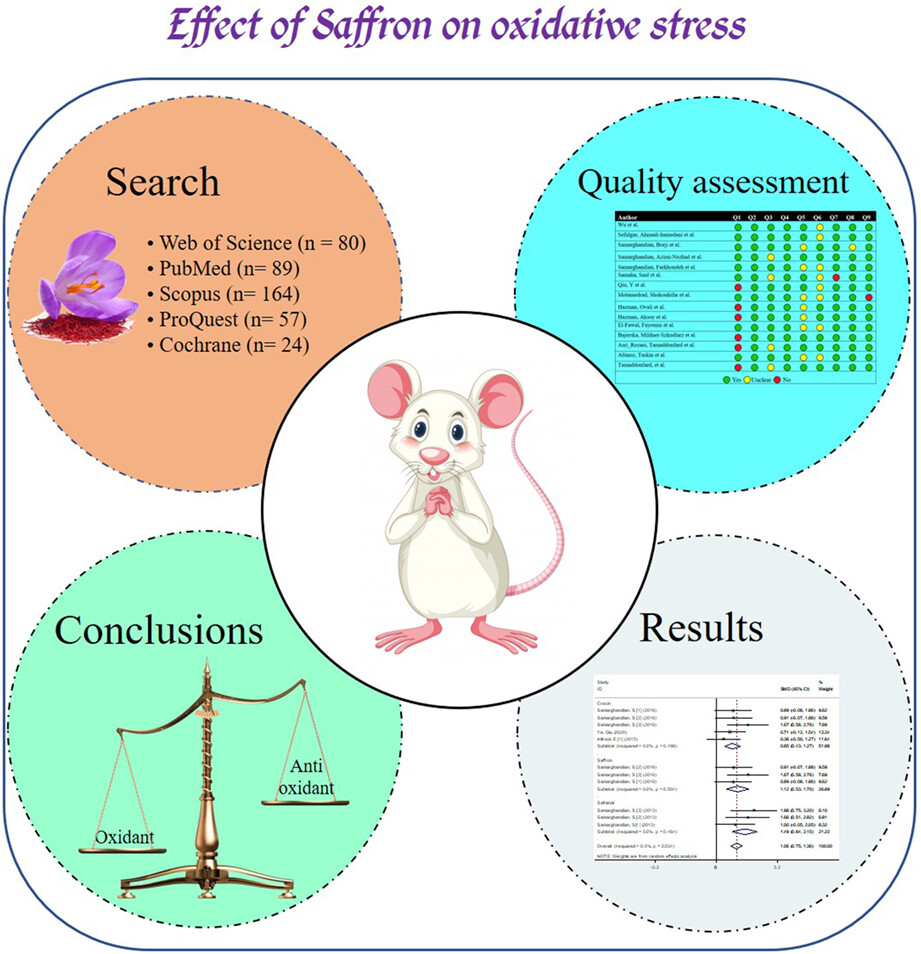
To our knowledge, this is the first systematic review and meta-analysis that has comprehensively investigated the effect of saffron and its active compounds on oxidative stress markers (oxidants and antioxidants). In this meta-analysis, 15 studies were reviewed. The results of our study showed that saffron and its active compounds (crocin and safranal) with high effectiveness led to a reduction in oxidative stress caused by long-term hyperglycemia. In addition, we showed that safranal is more effective than saffron and crocin.
Functional profile and encapsulating properties of Colocasia esculenta (Taro)
- Pages: 2440-2449
- First Published: 05 April 2023
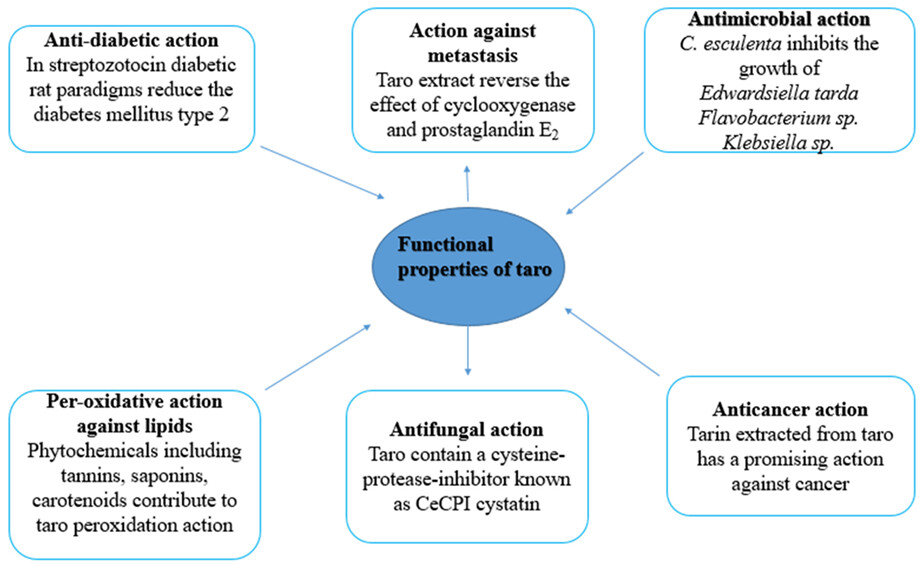
The corms of Colocasia antiquorum contain anthocyanins such aspelargonidin-3-glucoside, cyanidin-3-glucoside, and cyanidin-3-chemnoside, reported to possess anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative characteristics. This study highlights the functional properties, physicochemical composition, encapsulating properties, industrial application, probiotic, as well as prebiotic potential of taro.
Bioactivity and health effects of garlic essential oil: A review
- Pages: 2450-2470
- First Published: 07 February 2023
This paper reviews the research progress on the composition and bioactivities of garlic essential oil mixtures and the bioactivity of some typical monomeric sulfides in garlic essential oil. The active mechanisms of representative sulfides in garlic essential oil were analyzed, and the applications of garlic essential oil in functional food, food additives, and clinical treatment were discussed.
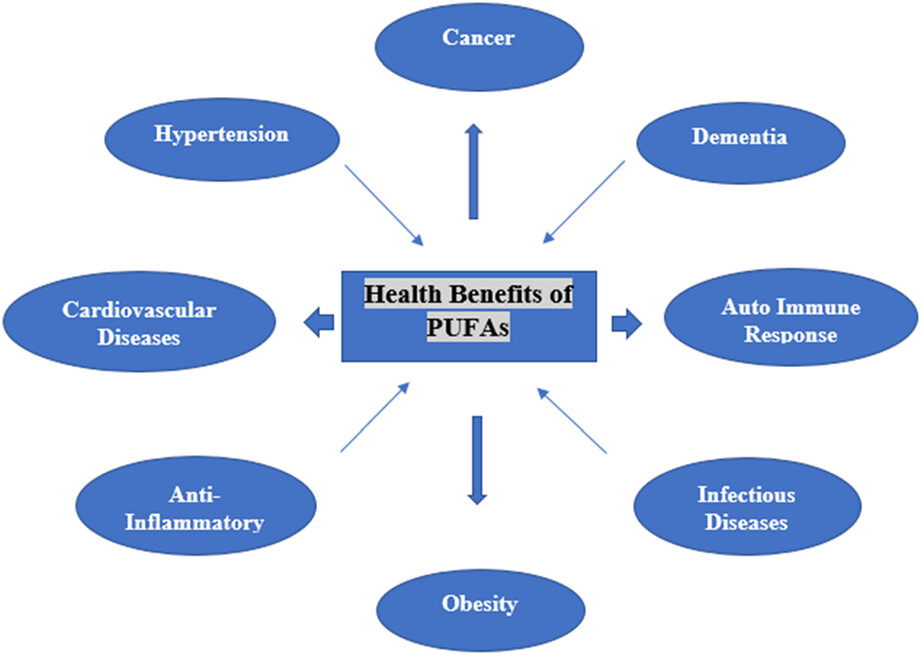
Functional roles and novel tools for improving-oxidative stability of polyunsaturated fatty acids: A comprehensive review
- Pages: 2471-2482
- First Published: 28 February 2023
Global nutritional challenges of reformulated food: A review
- Pages: 2483-2499
- First Published: 06 March 2023
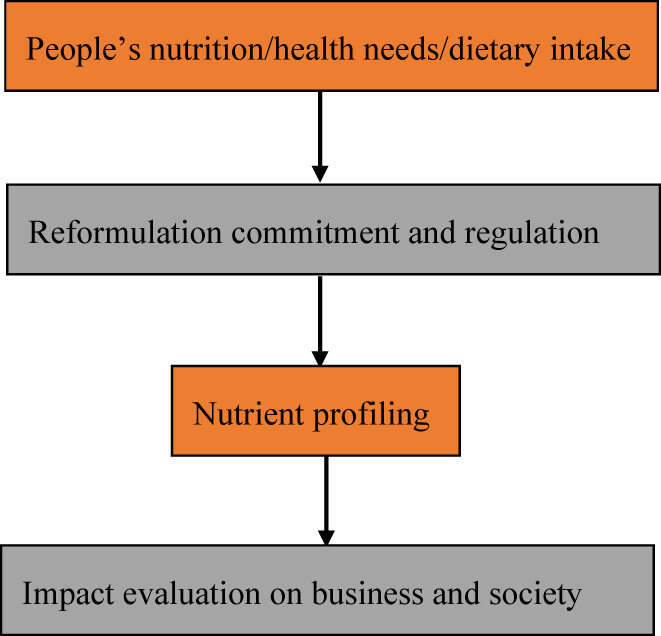
Redeveloping an existing processed food product to make it healthier is the focus of food reformulation. However, the approaches for food reformulation are diverse, and there is a consensus that the main concerns are fats, sugars, and salts. Food reformulation policy would certainly succeed if the private sector works in tandem with and/or responds to government pressure.
Phytobioactive compounds as therapeutic agents for human diseases: A review
- Pages: 2500-2529
- First Published: 17 April 2023
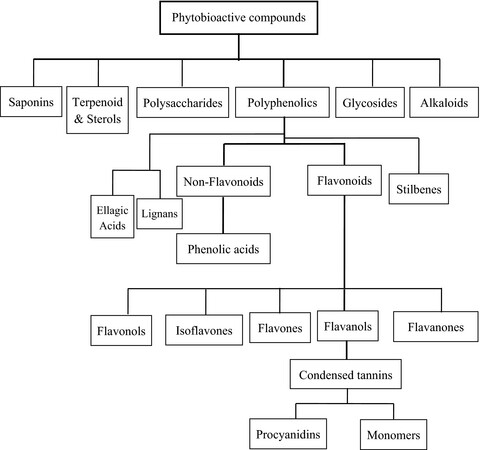
Phytobioactive compounds are plant secondary metabolites and have remarkable therapeutic potential. Polyphenols, alkaloids, terpenes, and polysaccharides isolated from medicinal plants showed remarkable antioxidant, anticancer, cytotoxic, anti-inflammatory, cardioprotective, hepatoprotective, immunomodulatory, neuroprotective, and antidiabetic activities. Phytobioactive compounds may be used as a potential alternative to synthetic compounds and as therapeutic agents for the treatment of various diseases.
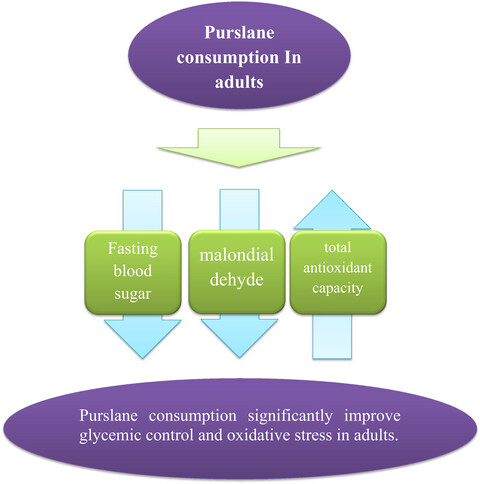
The effects of purslane consumption on glycemic control and oxidative stress: A systematic review and dose–response meta-analysis
- Pages: 2530-2546
- First Published: 15 March 2023
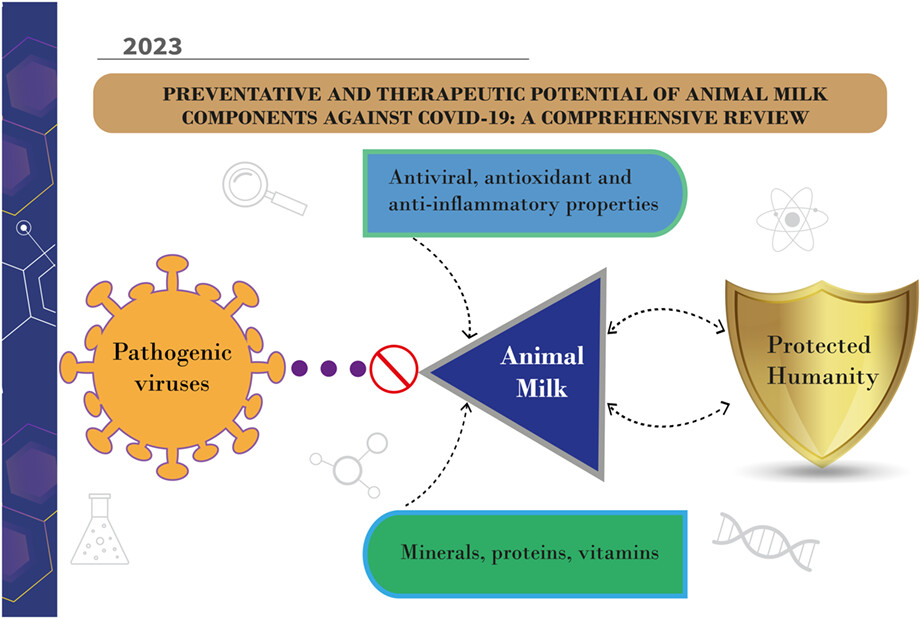
Preventative and therapeutic potential of animal milk components against COVID-19: A comprehensive review
- Pages: 2547-2579
- First Published: 23 March 2023
Effects of coenzyme Q10 supplementation on lipid profiles and liver enzymes of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- Pages: 2580-2588
- First Published: 13 March 2023
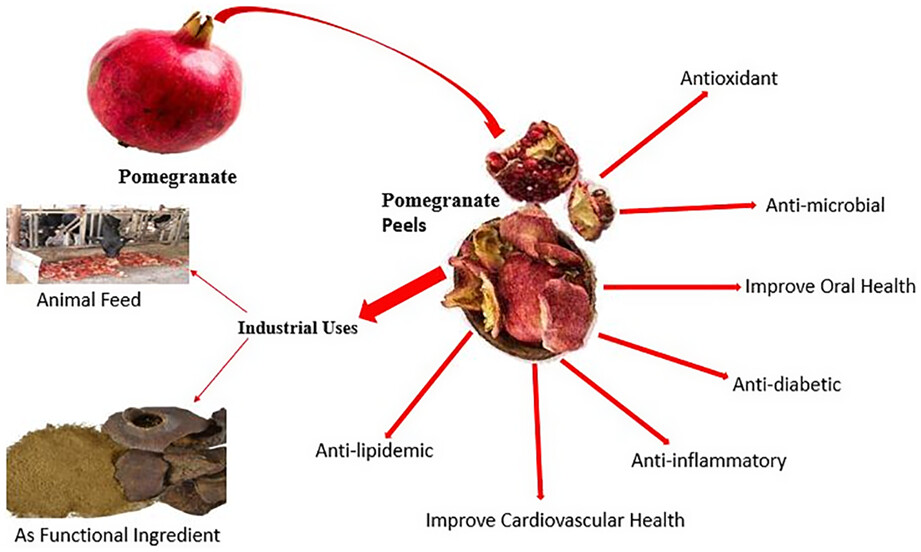
Nutritional importance and industrial uses of pomegranate peel: A critical review
- Pages: 2589-2598
- First Published: 23 March 2023
Innovative applications and therapeutic potential of oilseeds and their by-products: An eco-friendly and sustainable approach
- Pages: 2599-2609
- First Published: 22 March 2023
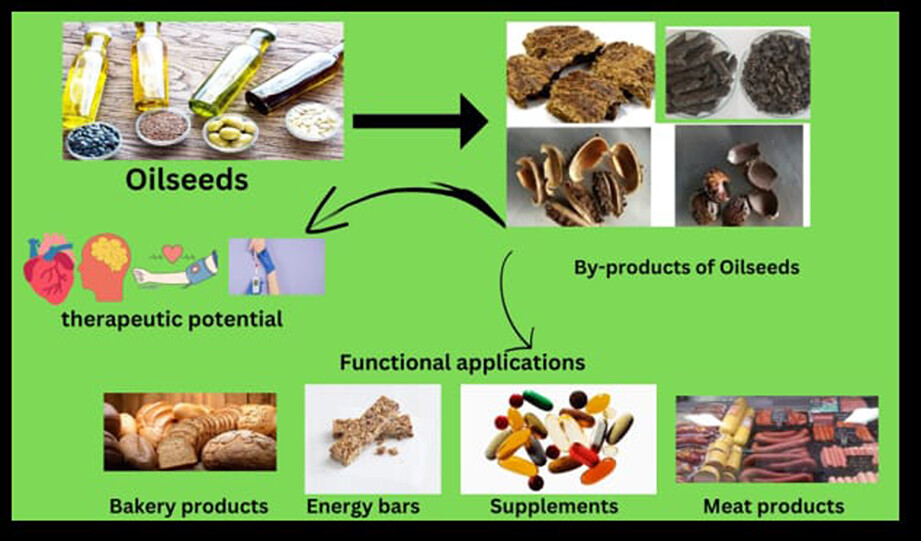
A broad range of valuable bioactive compounds has been obtained from oilseeds either in pure form or in a homogenous mixture. Oilseed cake or meal had been undervalued by-products or waste, which conventionally had been utilized for feed in many countries. In addition to a wide range of carbohydrates, proteins, fibers, vitamins, antioxidants, and bioactive compounds are also present in varying quantities. Oilseeds are widely used for human consumption and industrial application. To overcome this problem, they are in constant search to find ways to reutilize agro-industrial waste or by-products.
Environmental exposure assessment of lead and cadmium in street vended foods sold in selected locations in Kenya
- Pages: 2610-2619
- First Published: 28 March 2023
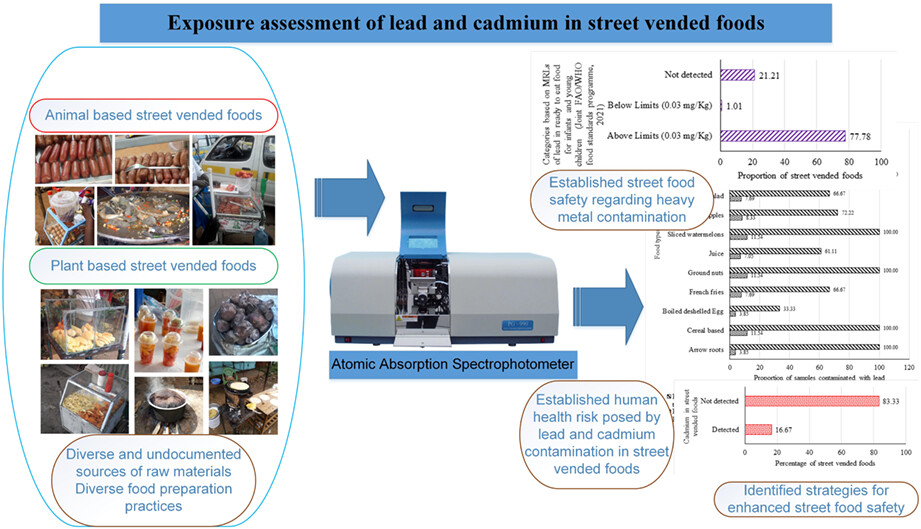
Heavy metals, such as lead and cadmium are extremely toxic to human health and capable of bioaccumulation. Continuous ingestion of these heavy metals has a damaging effect on human health. The presence of lead and cadmium in street vended foods therefore poses a public health concern considering the huge population of people who consume these foods.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Secoisolariciresinol diglucoside and anethole ameliorate lipid abnormalities, oxidative injury, hypercholesterolemia, heart, and liver conditions
- Pages: 2620-2630
- First Published: 18 February 2023
Cucumeropsis mannii seed oil protects against Bisphenol A-induced testicular mitochondrial damages
- Pages: 2631-2641
- First Published: 07 February 2023
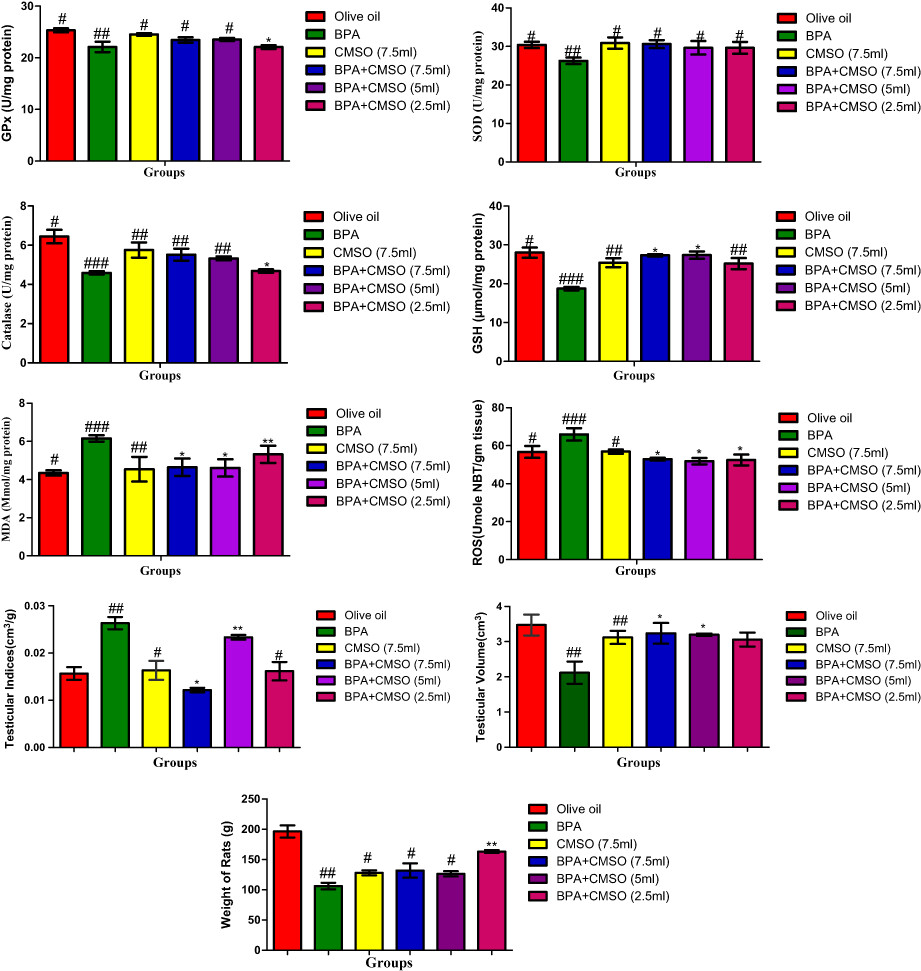
Co-administration of Cucumeropsis mannii seed oil and bisphenol A significantly reversed abnormal trends observed in the dysregulated biochemical biomarkers. This finding shows that C. mannii seed oil has considerable antioxidant potential which can be explored in therapeutic development against systemic toxicity induced by exposure to bisphenol A.
Cucumeropsis mannii seed oil ameliorates Bisphenol-A-induced adipokines dysfunctions and dyslipidemia
- Pages: 2642-2653
- First Published: 18 February 2023
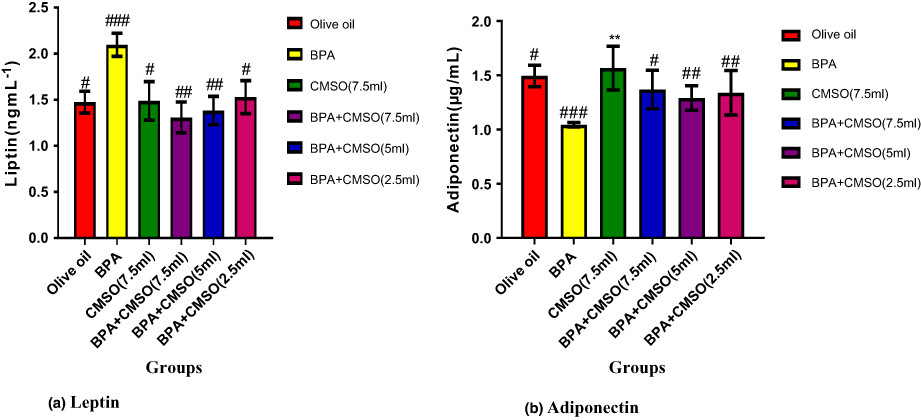
BPA plus CMSO reduced triglycerides, cholesterol, leptin, LDL-C, and atherogenic and coronary risk indices while increasing adiponectin levels and HDL-C in adipose tissue and plasma (p < .05). Treatment with CMSO reduced the toxicities caused by BPA in rats by modulating the body weight, adiponectin and leptin levels, and lipid profiles in adipose tissue and serum.
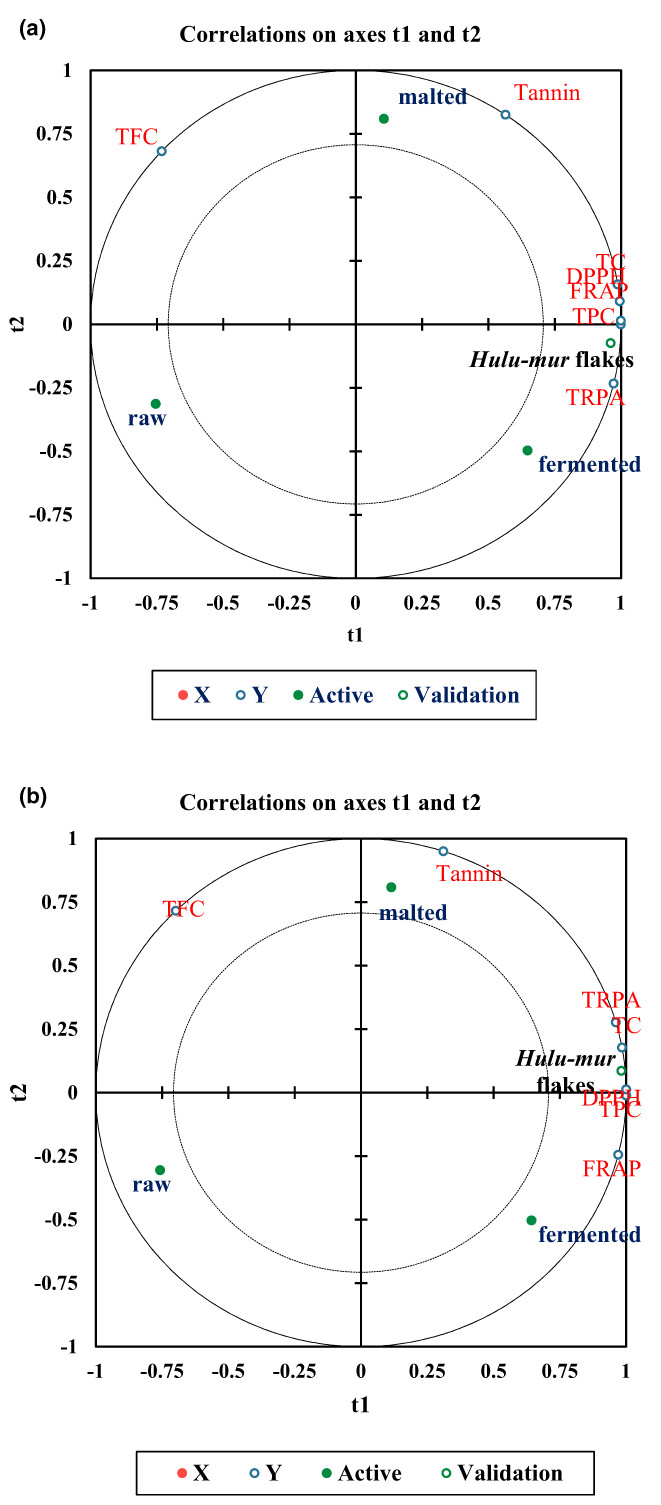
Indigenous Sudanese sorghum-based food: Secondary metabolites and antioxidant activities of traditional Sudanese nonalcoholic beverage Hulu-mur from two sorghum landraces
- Pages: 2654-2662
- First Published: 18 February 2023
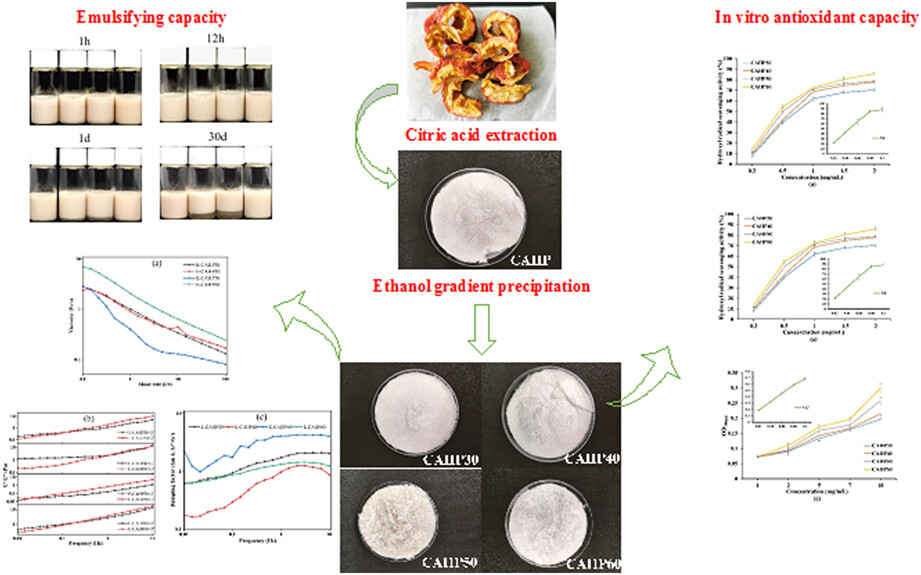
Characterization of hawthorn pectin gained via different ethanol concentrations
- Pages: 2663-2676
- First Published: 17 March 2023
High-pressure acidified steaming with varied citric acid dosing can successfully detoxify mycotoxins
- Pages: 2677-2685
- First Published: 17 March 2023
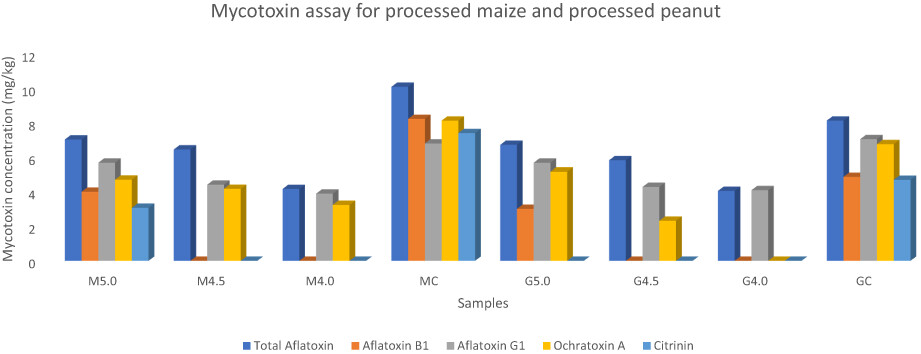
The HPAS process either completely detoxified the mycotoxins or at least reduced them to levels below the maximum limits of 4.00–6.00, 2.00, 2.00, 5.00, and 100 μg/kg for AT, AFB1, AFG1, OTA, and citrinin, respectively, set by the European Union, WHO/FAO, and USDA. The study clearly demonstrates that mycotoxins can be completely detoxified using HPAS at CCC adjusted to pH 4.0 or below. MC = mycotoxin content of the raw (unprocessed) maize samples; M5.0 = mycotoxin content of the maize samples after high-pressure acidified steaming adjusted to pH 5.0; M4.5 = mycotoxin content of the maize samples after high-pressure acidified steaming adjusted to pH 4.5; M4.0 = mycotoxin content of the maize samples after high-pressure acidified steaming adjusted to pH 4.0; GC = mycotoxin content of the raw (unprocessed) groundnut (peanut) samples; G5.0 = mycotoxin content of the groundnut (peanut) samples after high-pressure acidified steaming adjusted to pH 5.0; G4.5 = mycotoxin content of the groundnut (peanut) samples after high-pressure acidified steaming adjusted to pH 4.5; and G4.0 = mycotoxin content of the groundnut (peanut) samples after high-pressure acidified steaming adjusted to pH 4.0.
Physicochemical property changes of Dendrobium officinale leaf polysaccharide LDOP-A and it promotes GLP-1 secretion in NCI-H716 cells by simulated saliva-gastrointestinal digestion
- Pages: 2686-2696
- First Published: 31 March 2023
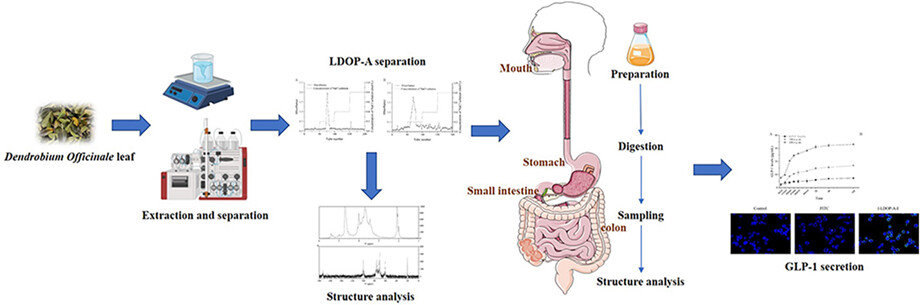
In order to inspect the anti-diabetes effect of the polysaccharide extracted from Dendrobium officinale leaf named LDOP-A, the present work first investigated the structure and simulated digestion of LDOP-A in vitro and then explored secretion of GLP-1 from endocrine L cells in vitro under the direct stimulation of digested LDOP-A.
Functional exploration of taro starch (Colocasia esculenta) supplemented yogurt
- Pages: 2697-2707
- First Published: 28 April 2023

The results of the study showed that maximum moisture and protein content was taken by using 0.5% taro starch and stored for 0 days while maximum fat percentage was attained in 1.5% taro starch treatment and storage time was 0 days. The maximum water-holding capacity was increased by adding 1.5% taro starch under 14-day storage time. Water-holding capacity started decreasing with the increasing taro concentration.
African Jointfir (Gnetum africanum) and Editan (Lasianthera africana) leaf alkaloid extracts exert antioxidant and anticholinesterase activities in fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster)
- Pages: 2708-2718
- First Published: 13 March 2023
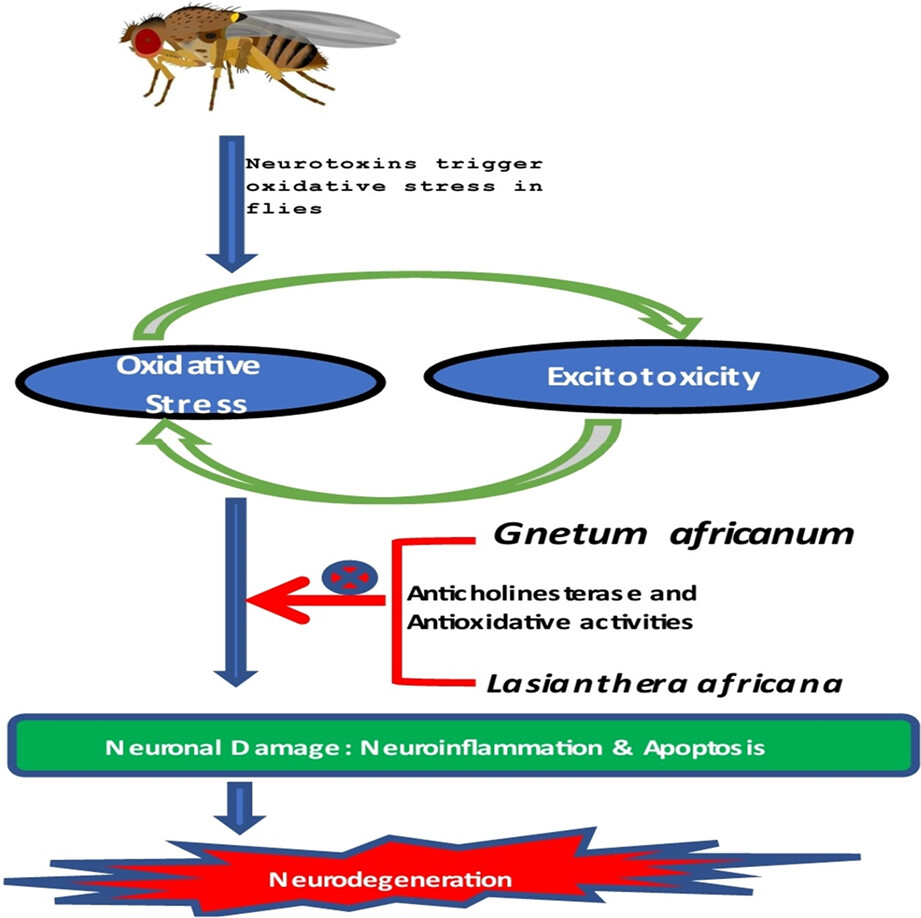
This study reveals that alkaloid extracts from Editan (Lasianthera africana) and African Jointfir (Gnetum africanum) could possess antioxidant and anticholinesterase activities in Drosophila melanogaster. Desulphosinigrin and atropine were revealed through high-performance liquid chromatography to be the predominating plant chemicals in L. africana and G. africanum, respectively. Alkaloid extracts from both plants exhibited outstanding lipid peroxidative ability.
Optimizing the effect of plant protease on different properties of analog cheese containing functional corn leachate
- Pages: 2719-2732
- First Published: 17 May 2023
Flavor profile of “Dao Ban Xiang” (a traditional dry-cured meat product in Chinese Huizhou cuisine) at different processing stages in winter and summer
- Pages: 2733-2750
- First Published: 04 May 2023
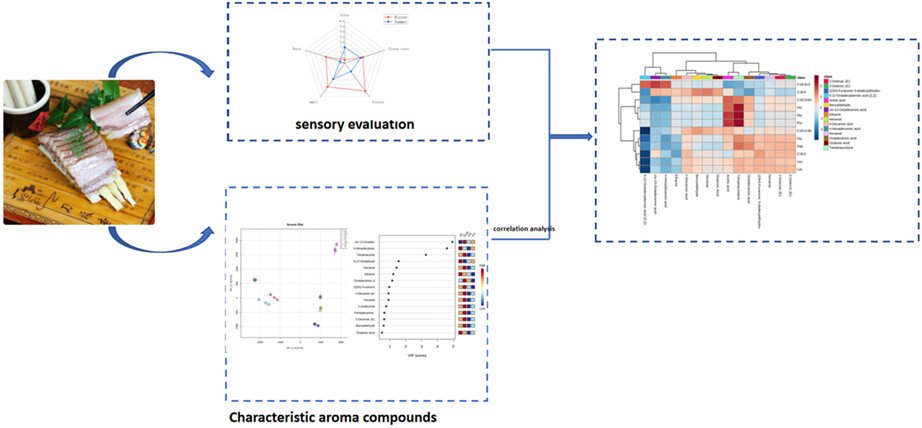
“Dao Ban Xiang” is a famous traditional Chinese dry-cured meat product. This study aimed to comparatively analyze the difference in the volatile flavor information of “Dao Ban Xiang” produced in winter and summer. This study extends our knowledge on flavors from a traditional cured meat products at different processing stages in different seasons and could be useful for the standardization of the traditional and regional meat products.
Mycotoxins in milk: Occurrence and evaluation of certain detoxification attempts
- Pages: 2751-2766
- First Published: 03 April 2023
Comparative evaluation of ethyl acetate and n-Hexane extracts of Cannabis sativa L. leaves for muscle function restoration after peripheral nerve lesion
- Pages: 2767-2775
- First Published: 06 February 2023
Effects of the dipeptides comprising leucine and lysine on lifespan and age-related stress in Caenorhabditis elegans
- Pages: 2776-2786
- First Published: 10 February 2023
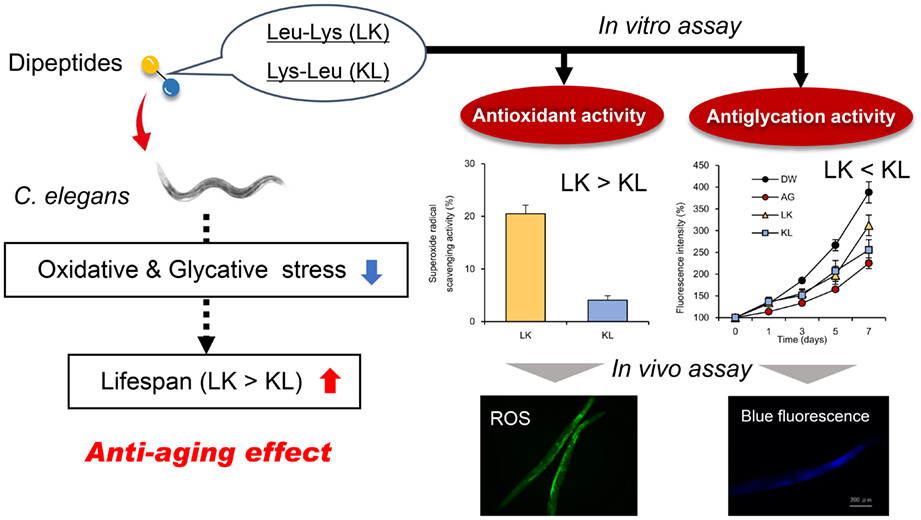
Food-derived dipeptide Leu-Lys (LK) and Lys-Leu (KL) exerts antioxidant and antiglycation activity in vitro. Treatment with LK prolonged the mean lifespan and maximum lifespan of C. elegans than that of KL. Intracellular ROS and blue autofluorescence levels (indicator of aging) were suppressed by LK.
Gryllus bimaculatus-containing diets protect against dexamethasone-induced muscle atrophy, but not high-fat diet-induced obesity
- Pages: 2787-2797
- First Published: 04 February 2023
The effect of soursop-flower-enriched fried palm olein on some biochemical and hematological parameters of rats
- Pages: 2798-2810
- First Published: 19 February 2023
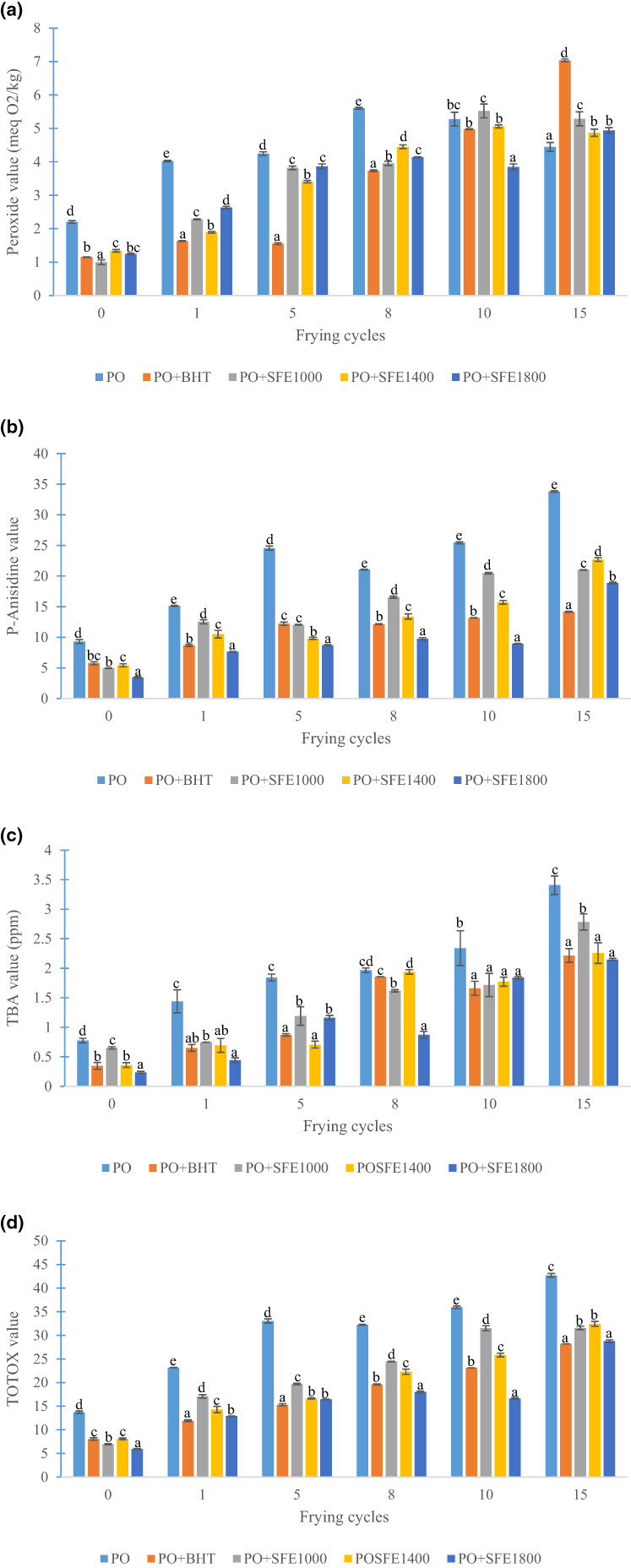
Animals fed with the different fried oils enriched with soursop flower extracts presented a decrease in serum transaminase and creatinine concentration followed by an increase in HDL cholesterol and total serum protein concentrations compared to animals fed with non-enriched fried oil. An improvement in hematological parameters was also observed through a decrease in white blood cell count and mean corpuscular hemoglobin in rats fed with soursop flower extract enriched fried oil compared to those fed the fried oil without additive.
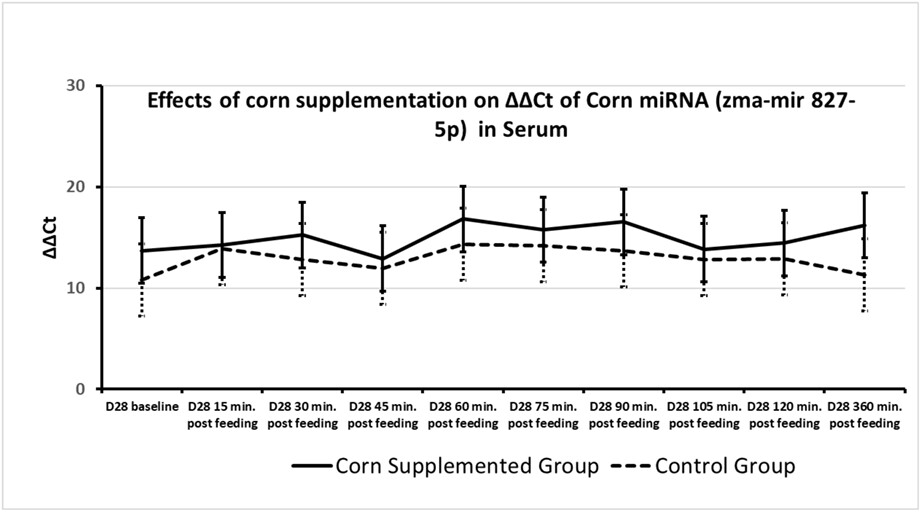
Effects of corn supplementation on serum and muscle microRNA profiles in horses
- Pages: 2811-2822
- First Published: 14 February 2023
Studying the microbial, chemical, and sensory characteristics of shrimp coated with alginate sodium nanoparticles containing Zataria multiflora and Cuminum cyminum essential oils
- Pages: 2823-2837
- First Published: 10 February 2023
Color, pH, microbiological, and sensory quality of crickets (Gryllus bimaculatus) flour preserved with ginger and garlic extracts
- Pages: 2838-2851
- First Published: 02 March 2023
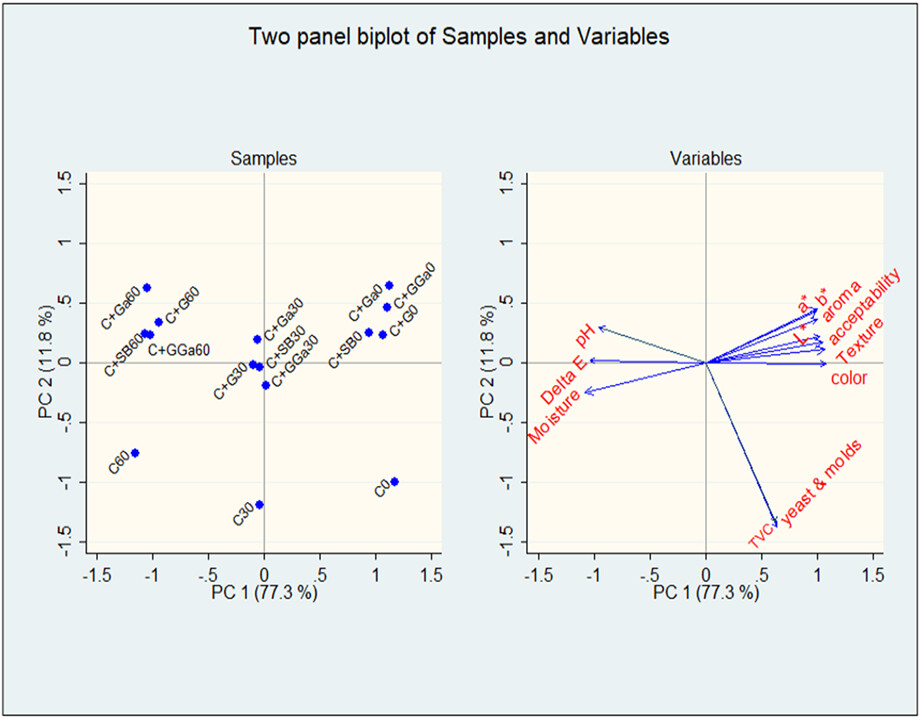
At the end of the 60-day storage period, cricket flour treated with sodium benzoate and fresh garlic extracts had the lowest microbial counts including yeast and molds. The pH, moisture content and color change remained within acceptable limits for both treated and untreated cricket flour. Consumers liked both the spice-treated and control cricket flour samples, although acceptability declined with prolonged storage.
Yield optimization, physicochemical characterizations, and antioxidant properties of food grade agar from Gracilaria tenuistipitata of Cox's Bazar coast, Bangladesh
- Pages: 2852-2863
- First Published: 15 February 2023
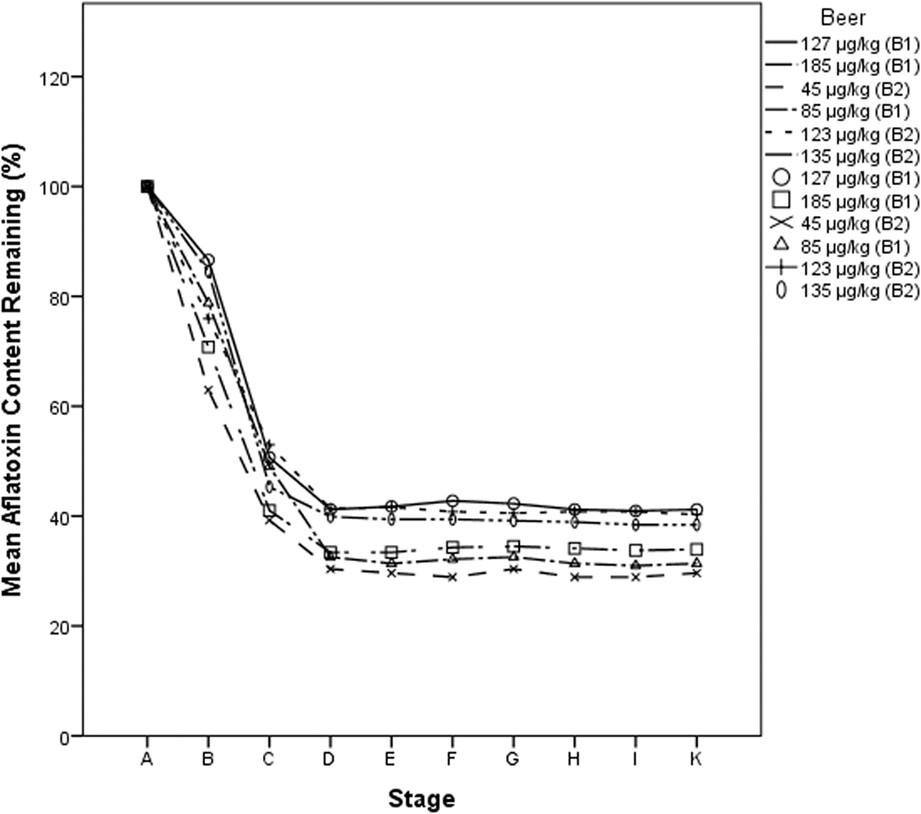
Reduction of aflatoxins during brewing of a Malawian maize-based non-alcoholic beverage, thobwa
- Pages: 2864-2871
- First Published: 13 March 2023
Nutritional and health status of Afghan refugee women living in Punjab: A cross-sectional study
- Pages: 2872-2882
- First Published: 28 March 2023
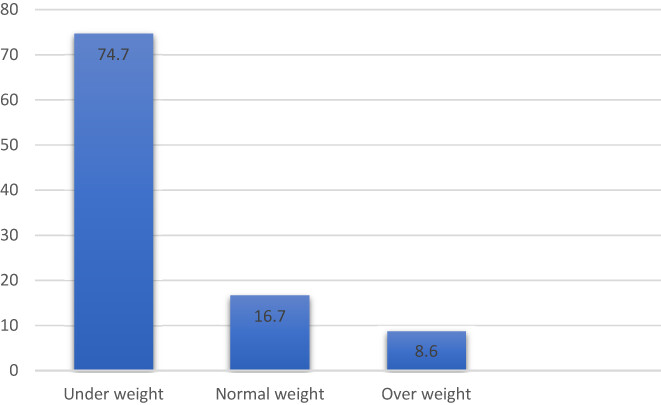
A majority of the women have extremely low Hb level, which indicates iron deficiency as well as low body mass index with regard to their age. The results indicate that there are high chances of severe malnutrition among this most vulnerable segment of the population, and this situation must be addressed immediately.
Risk assessment of lead and cadmium concentrations in hen's eggs using Monte Carlo simulations
- Pages: 2883-2894
- First Published: 08 March 2023
Analysis of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in dairy products by modified QuEChERS/GC-QqQ-MS/MS method: A risk assessment study
- Pages: 2895-2906
- First Published: 10 March 2023
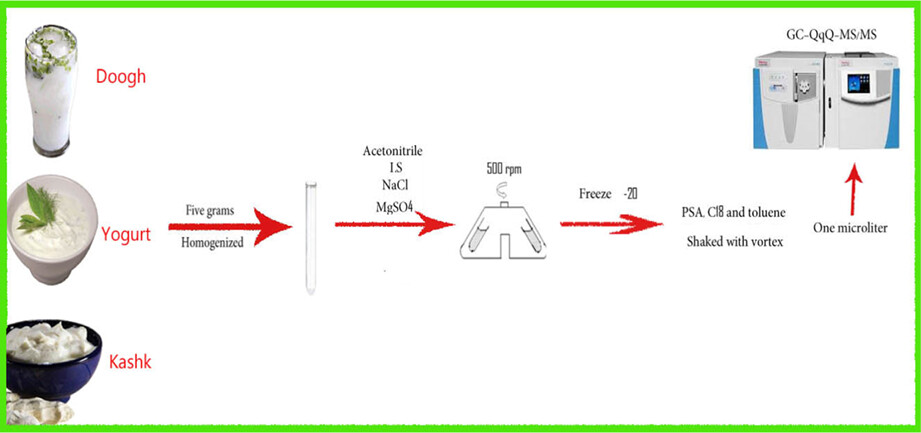
The purpose of the present research was to assess non-dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyls (NDL-PCBs) in some dairy products (yogurt, doogh, and kashk) using modified QuEChERS (Quick, Easy, Cheap, Effective, Rugged, and Safe) technique and gas chromatography–triple-quadrupole mass spectrometry (GC-QqQ-MS/MS) method and risk assessment study. The LOQs (limit of quantifications), LODs (limit of detections), and recovery for the PCB analytes were 0.180–0.360, 0.06–0.12 ng/g fat, and 97.45–102.63%, respectively. The results revealed that the mean concentrations of Ʃ6-NDL-PCBs in samples were 15.17 ± 3.44 ng/g fat which was lower than the standard level established by European Union (EU, 40 ng/g fat). Also, results showed that kashk samples had a maximum mean level of 6-NDL-PCBs (18.66 ± 2.42 ng/g fat) and doogh samples had a minimum mean level of 6-NDL-PCBs (12.21 ± 2.22 ng/g fat). The mean level of 6-NDL-PCBs in yogurt samples was 14.65 ± 2.02 ng/g fat.
Cross-sectional associations between healthy eating index and thyroid function in U.S. male Adults, NHANES 2007–2012
- Pages: 2907-2914
- First Published: 14 February 2023
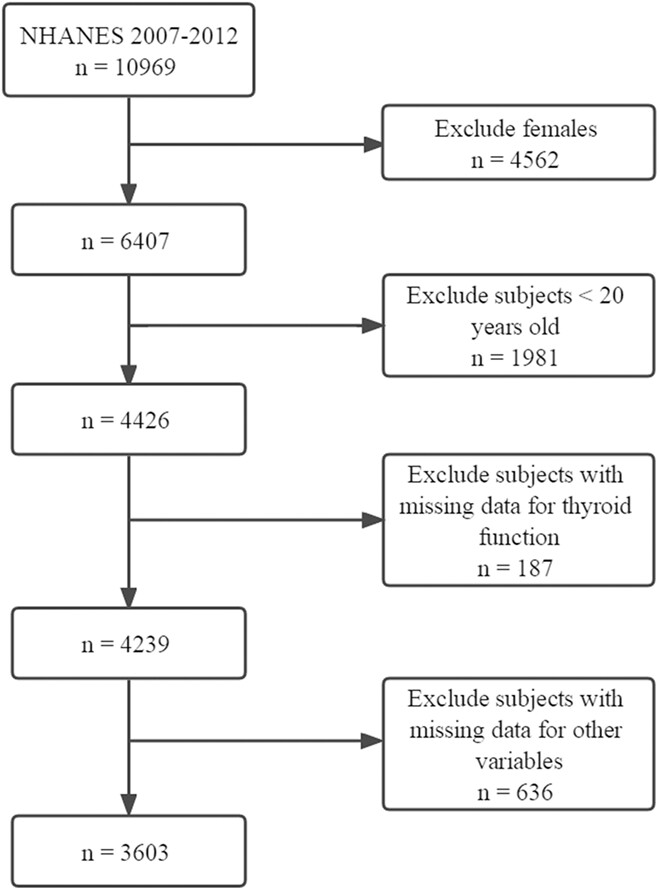
Little is known about whether diet quality is associated with thyroid function. We aimed to examine the relationship between diet quality and thyroid function. Multivariable linear regression, subgroup analyses, and interaction terms were employed to test the association between healthy eating index (HEI) and thyroid function. Higher HEI-2010 was inversely associated with lower total T3 and free T3.
Preparation of milk-based probiotic lactic acid bacteria biofilms: A new generation of probiotics
- Pages: 2915-2924
- First Published: 22 February 2023
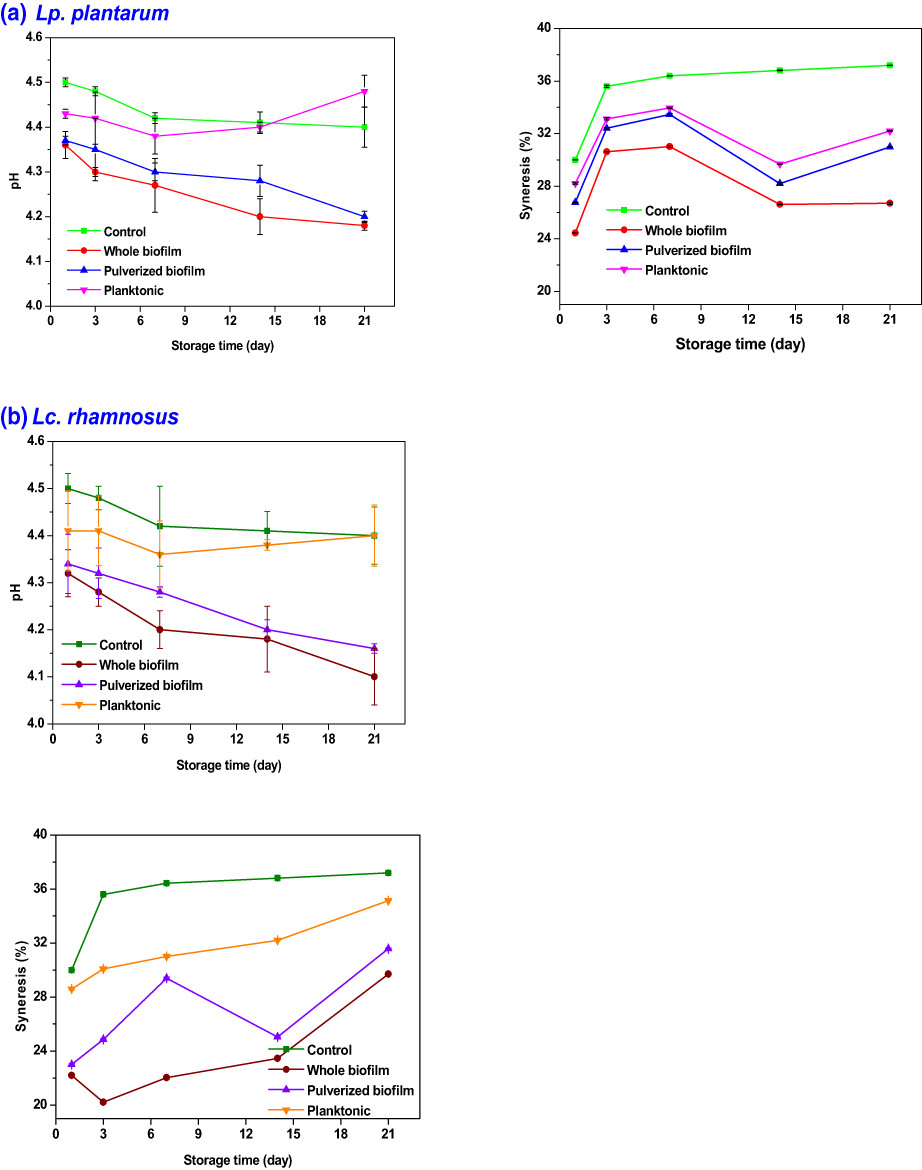
Probiotic biofilms of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum and Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus were manufactured using milk. The probiotic biofilms showed excellent gastrointestinal resistance. The probiotic biofilm was used to prepare the dairy product yogurt. The viability of the lactic acid bacteria was greatly increased in highly acidic conditions.
Preparation, characterization, identification, and antioxidant properties of fermented acaí (Euterpe oleracea)
- Pages: 2925-2941
- First Published: 28 February 2023
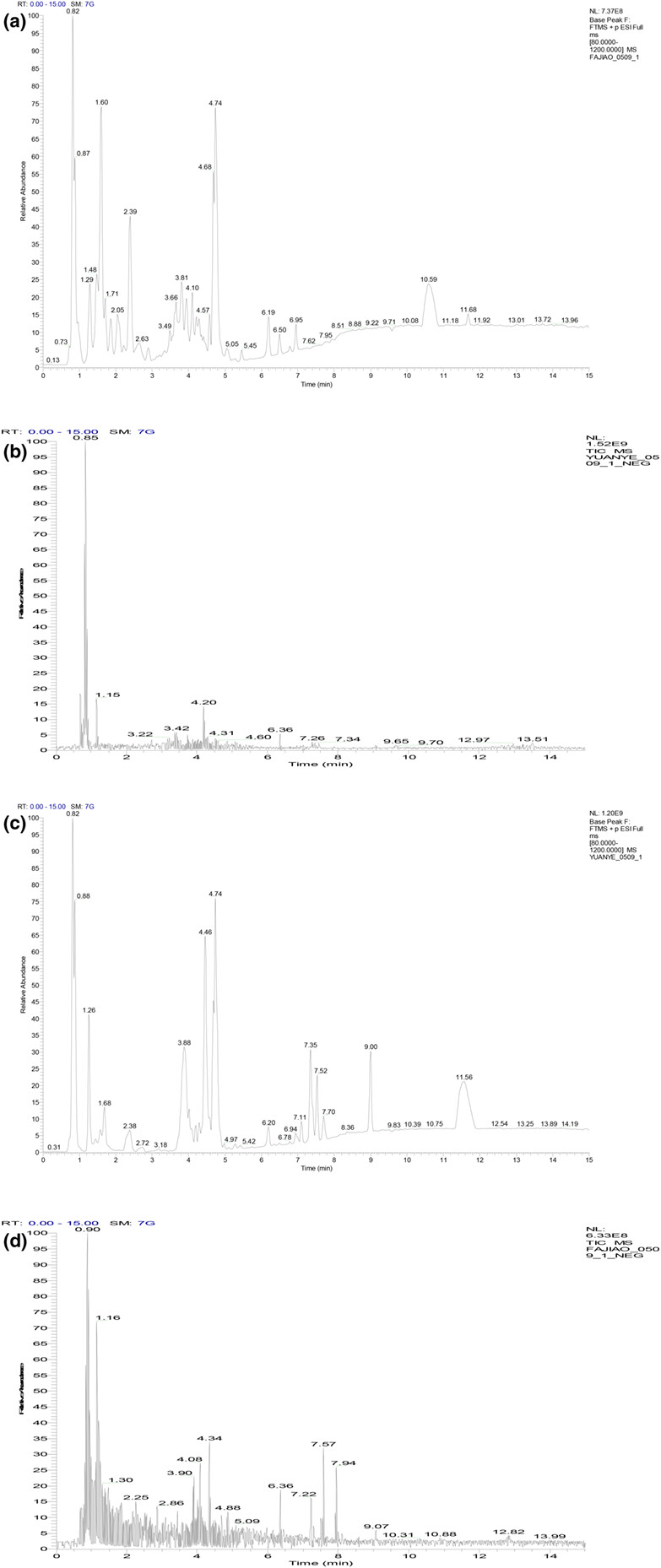
The physical, chemical, and volatile aroma components were analyzed and identified before and after acaí fermentation, showing an overall increase in these elements. Then, the oxygen radical absorbance capacity (ORAC) values, DPPH free radical scavenging capacity, hydroxyl free radical scavenging capacity, ABTS free radical scavenging capacity, and ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) values were used as indicators to confirm that the antioxidant capacity of acaí fermentation liquid improved after fermentation. This provides a theoretical basis for the comprehensive utilization of acaí.
Effect on Ziziphus jujuba Mill. fruit powders embedded on physicochemical properties, biological activities, and rheologic quality of cake
- Pages: 2942-2955
- First Published: 09 March 2023
Studying the shelf life of butter containing fucoidan, by evaluating sensory and chemical properties
- Pages: 2956-2963
- First Published: 09 March 2023
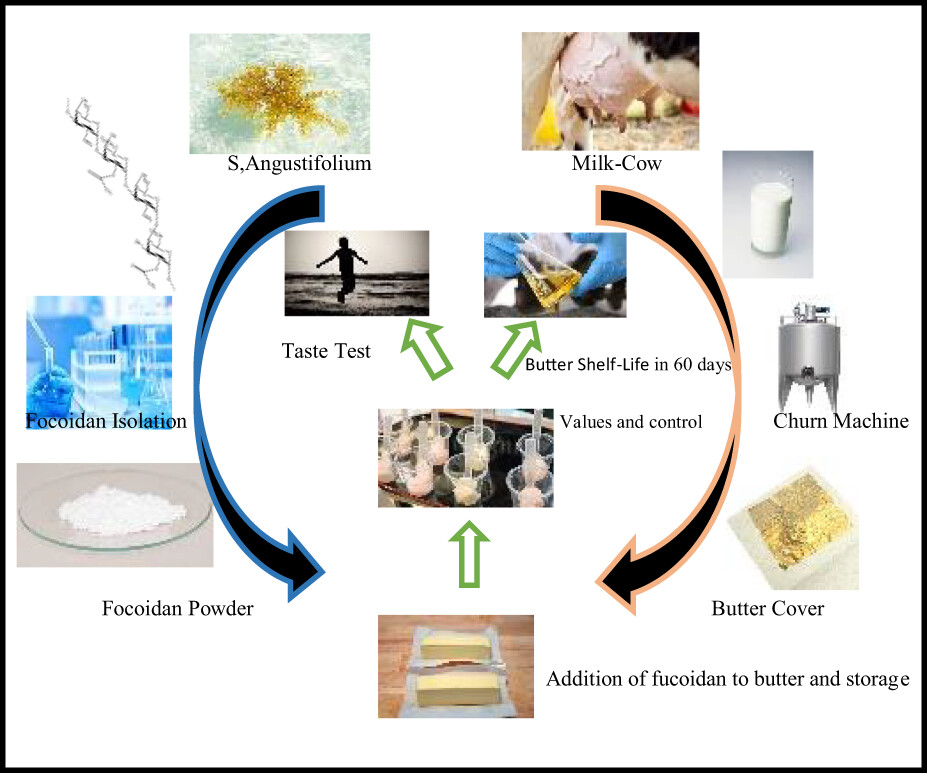
Fucoidan powder was added in amounts of 0.05%, 0.1%, 0.03%, and 0.5% to sour cream butter and sensory and chemical properties were tested on their shelf life for 60 days during storage. By increasing the amount of fucoidan in the samples, the amount of acidity and peroxide was affected, and then an acceptable product was produced due to the tastelessness of fucoidan.
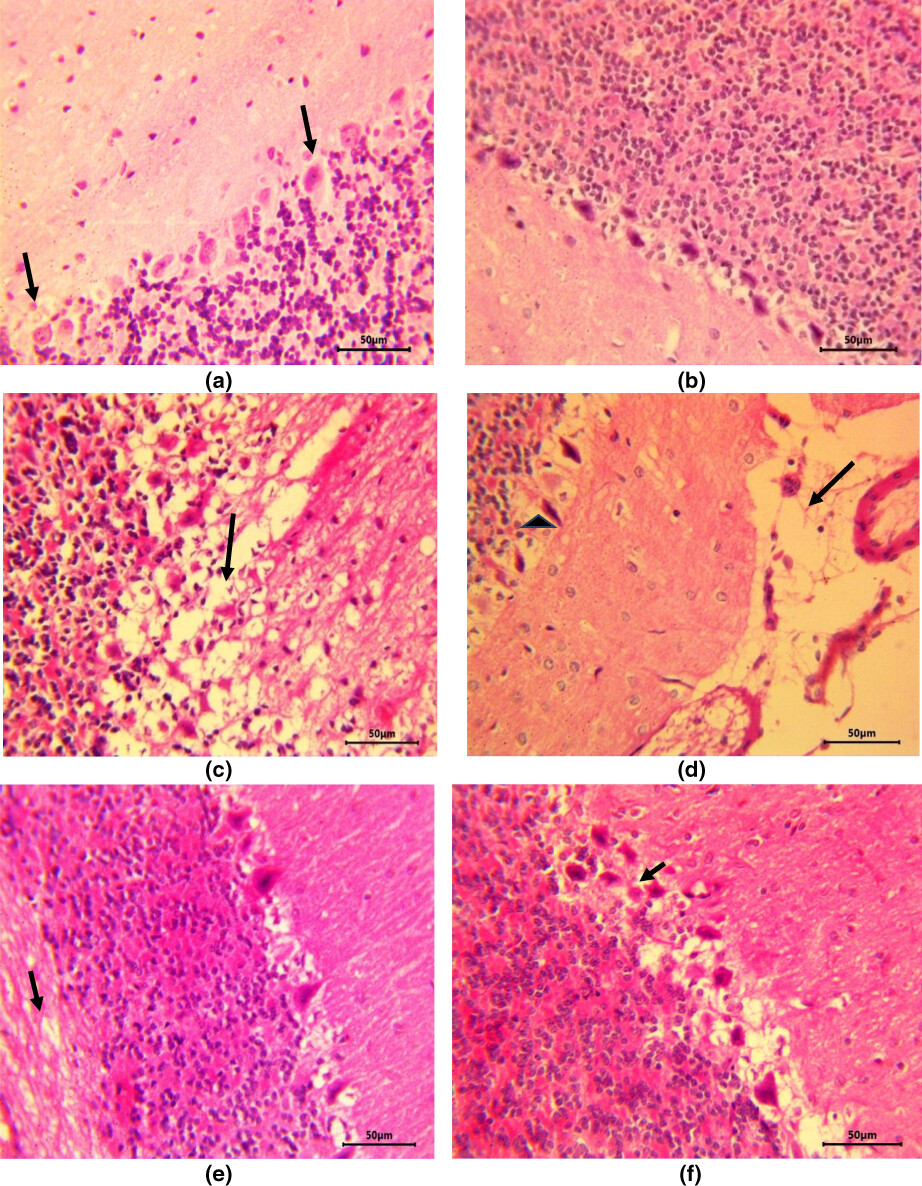
Neuroprotective effect of quercetin and Zingiber officinale on sodium arsenate-induced neurotoxicity in rats
- Pages: 2964-2973
- First Published: 28 February 2023
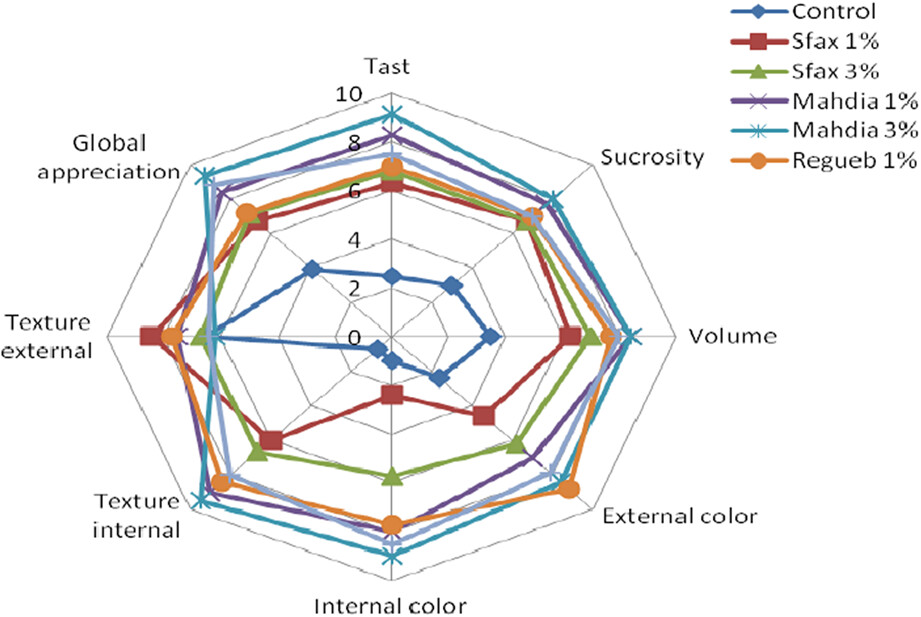
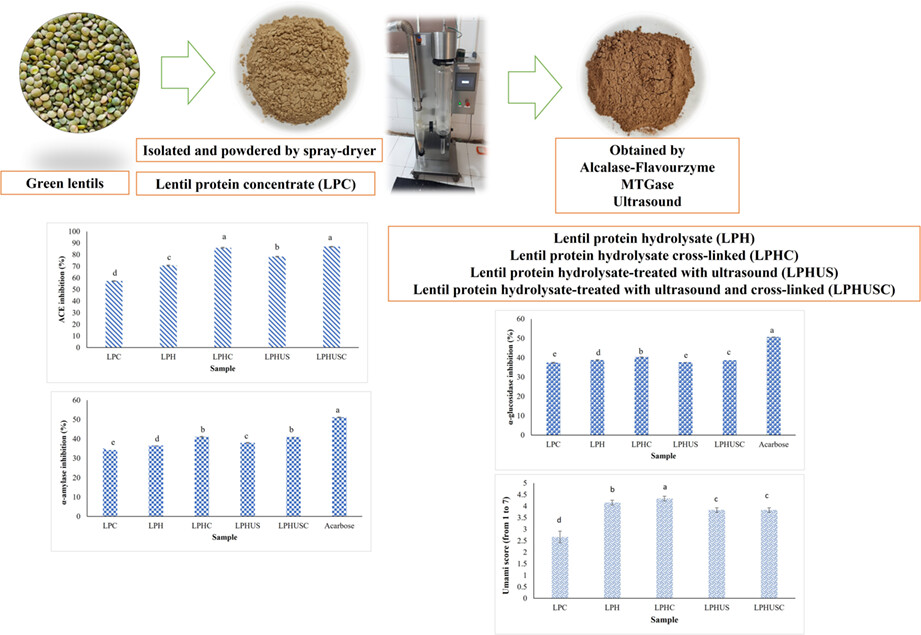
Development of lentil peptides with potent antioxidant, antihypertensive, and antidiabetic activities along with umami taste
- Pages: 2974-2989
- First Published: 27 February 2023
Combination of four bacterial strains isolated from Yamahai-shubo in traditional Japanese sake brewing
- Pages: 2990-3001
- First Published: 02 March 2023
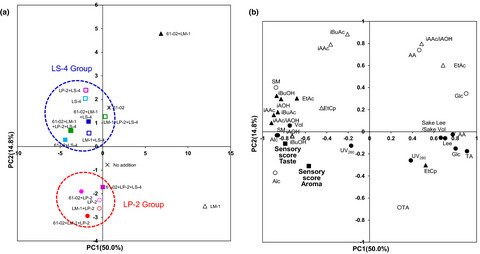
This study investigated the interactions of four bacteria strains (nitrate-reducing Pseudomonas sp. 61-02, Leuconostoc mesenteroides LM-1, Lactiplantibacillus plantarum LP-2, and Latilactobacillus sakei LS-4) isolated from Yamahai-shubo. We examined fermentation factors for Yamahai-shubo and Yamahai-shikomi sake samples to compare the suitability of their bacterial combination (16 variations). In conclusion, strain LP-2 plays a more significant role in improving Yamahai-shikomi sake quality with strains LM-1 and 61-02 rather than strain LS-4 in Yamahai-shubo preparation and Yamahai-shikomi sake brewing.
Anthocyanins improve liver fibrosis in mice by regulating the autophagic flux level of hepatic stellate cells by mmu_circ_0000623
- Pages: 3002-3018
- First Published: 11 May 2023
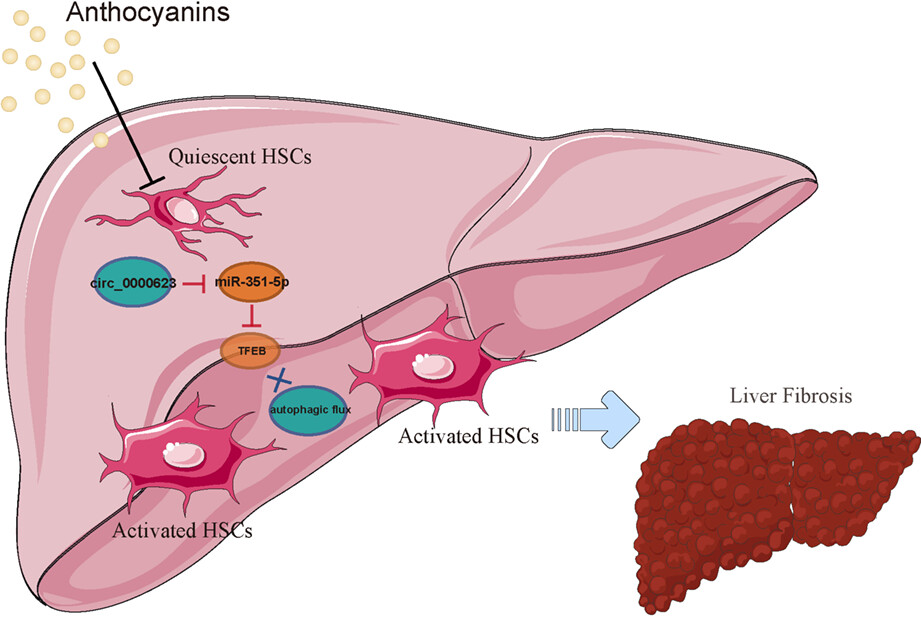
This study demonstrated for the first time that anthocyanins can participate in the process of liver fibrosis by regulating the autophagy level of hepatic stellate cells. For the first time, we confirmed the significance of mmu_circ_0000623 in the treatment of liver fibrosis with anthocyanins. Anthocyanins could treat liver fibrosis by modulating circ_0000623/miR-351-5p/TFEB-mediated changes in HSC autophagic flux.
Chimonanthus salicifolius extract alleviates DSS-induced colitis and regulates gut microbiota in mice
- Pages: 3019-3030
- First Published: 16 March 2023
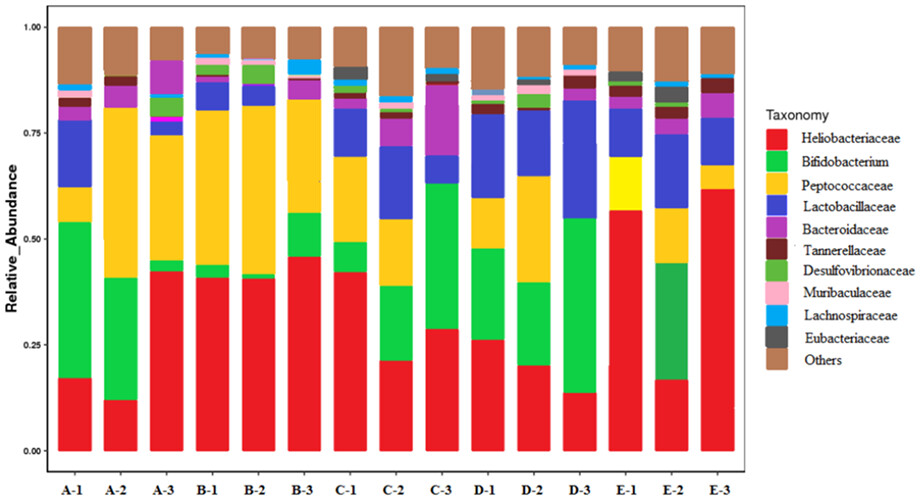
The intervention of C. salicifolius extract on colitis mice effectively regulated intestinal flora induced by DSS and restored their relative abundance. The extract group significantly increased the abundance and diversity of Lactobacillaceae compared with other treatments. Therefore, the results indicate that C. salicifolius extract presents the potential to be developed as a candidate for treating colitis.
Chemical and microbiological characterization of two traditional Mongolian high-fat dairy products produced in Xilin Gol, China
- Pages: 3031-3039
- First Published: 01 March 2023
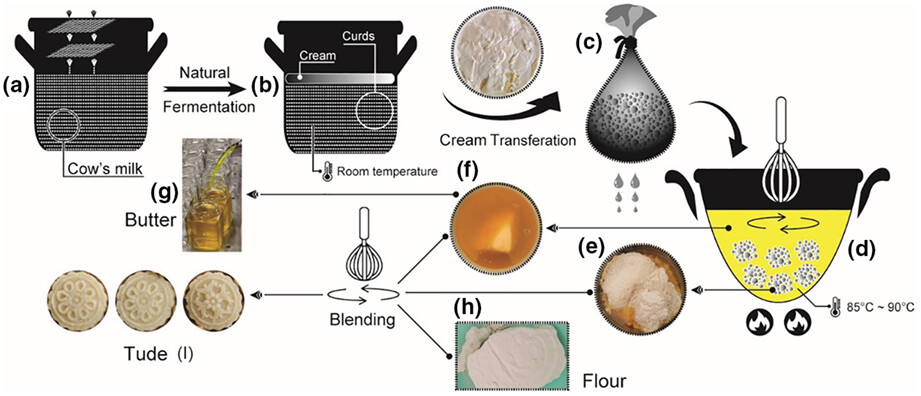
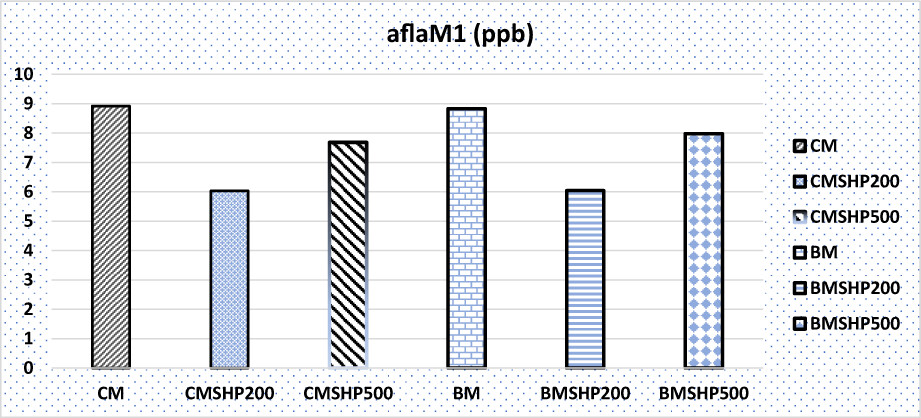
First, the findings presented are the first report of chemical and microbiological characterization of inherited food products (Mongolian butter and Tude) obtained by traditional technologies. Second, nutritional (e.g., fat, protein, moisture, and acidity), safety (e.g., benzopyrene, Listeria monocytogenes, Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella, coliform, and aflatoxin M1), and microbiological (e.g., TBC, Mold, bacterial, and fungal community) parameters were determined in this study.
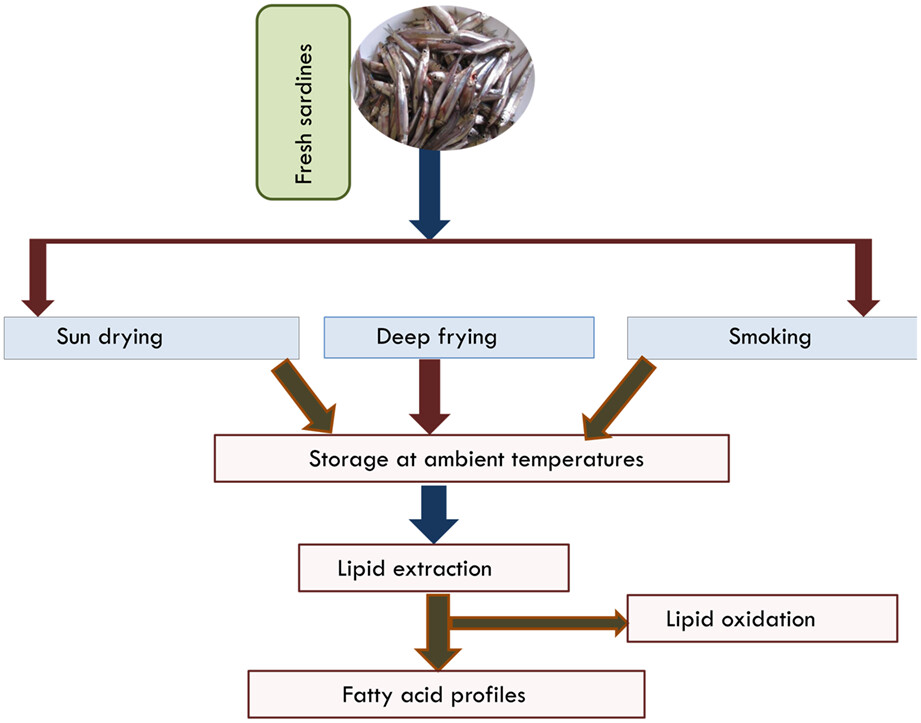
Changes in fatty acids during storage of artisanal-processed freshwater sardines (Rastrineobola argentea)
- Pages: 3040-3047
- First Published: 09 March 2023
Development of a paper strip test for colorimetric detection of urea in raw materials for animal feed
- Pages: 3048-3056
- First Published: 28 February 2023
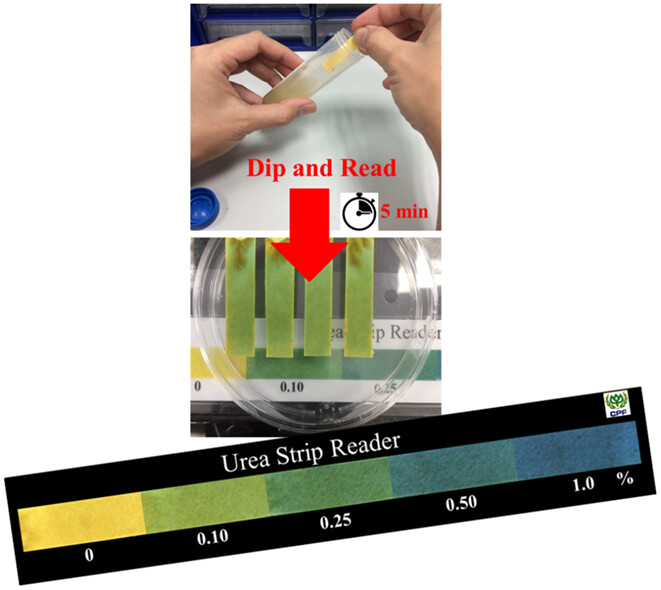
Urea determination in feed ingredients based on urease-catalyzed hydrolysis and colorimetric detection by using bromothymol blue as a pH indicator has been introduced. This design can be used both semiquantitative analysis and quantitative approach. Successful application of the urea paper strip to the determination of urea in animal protein and fish meal will be helpful for routine on-site inspection.
Development and performance evaluation of an improved electric baking oven for baked products
- Pages: 3057-3066
- First Published: 17 March 2023
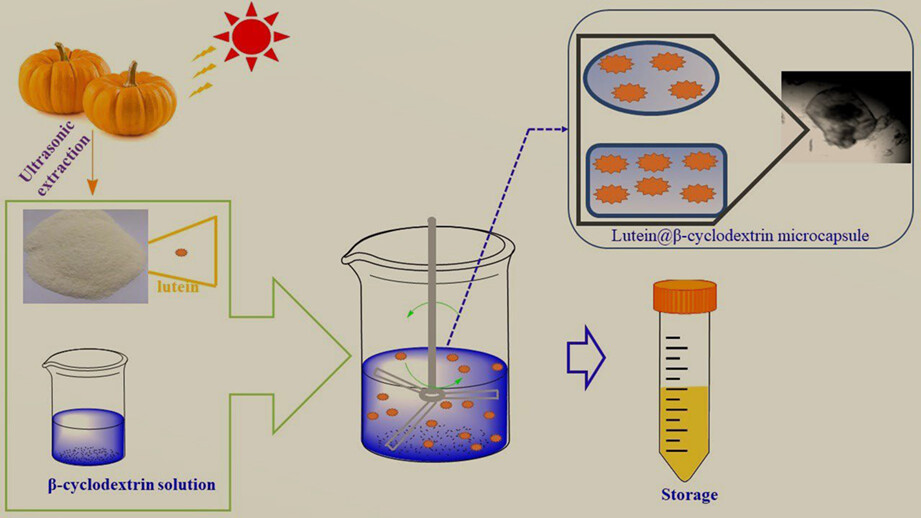
Improvement in the stability and bioavailability of pumpkin lutein using β-cyclodextrin microcapsules
- Pages: 3067-3074
- First Published: 28 February 2023
Potential inhibitory effect of fish, maize, and whey protein hydrolysates on advanced glycation end-products (AGEs)
- Pages: 3075-3082
- First Published: 28 February 2023
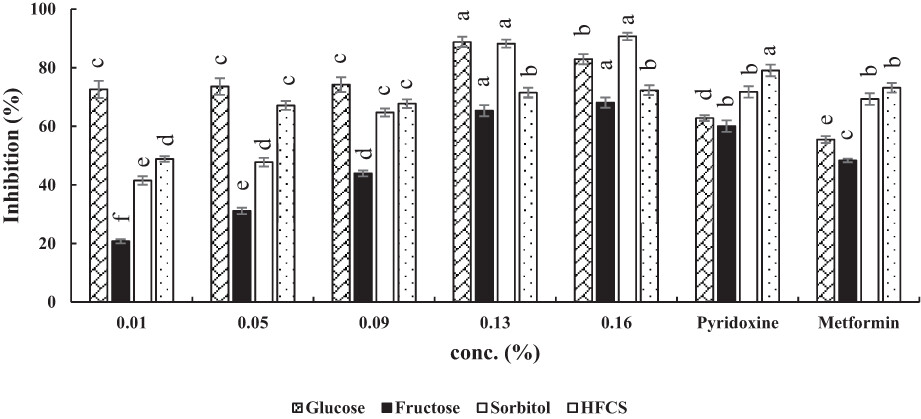
Advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) are produced in the food processing and they have some side effects on consumers. In this study, we used three natural hydrolysates of fish, maize, and whey protein as antiglycation agents. It was carried out in four model systems, Bovine serum albumin (BSA)-Glucose, BSA-Fructose, BSA-Sorbitol, and BSA-HFCS (high fructose corn syrup). Our results indicated that the investigated hydrolysates, particularly FPH, have promising antiglycation potential and can be recommended for the production of functional foods.
Trait profiling and genotype selection in oilseed rape using genotype by trait and genotype by yield*trait approaches
- Pages: 3083-3095
- First Published: 28 February 2023
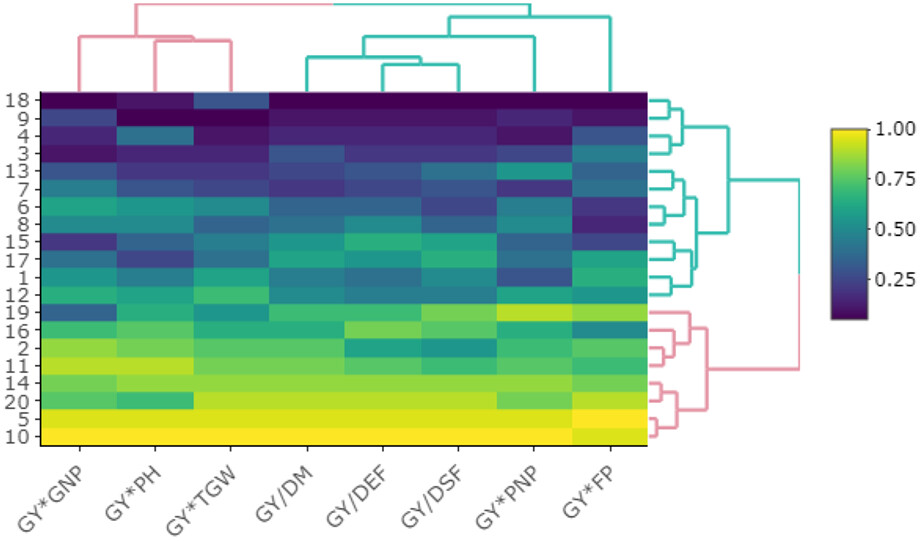
Pod number in plant and plant height were detected as the most essential selection criteria for grain yield enhancement in oilseed rape. GT ad GYT methodologies are recommended for trait profiling and genotype selection in oilseed rape breeding projects, respectively. The methodology of cluster analysis based on standardized GYT data led us to separate traits based on their direct and indirect effects in addition to genotype selection.
Effects of liposoluble components of highland barley spent grains on physiological indexes, intestinal microorganisms, and the liver transcriptome in mice fed a high-fat diet
- Pages: 3096-3110
- First Published: 21 April 2023
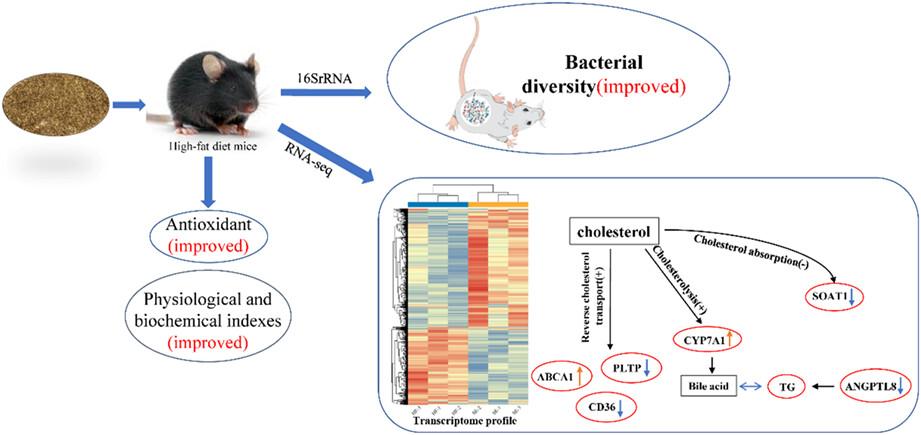
The liposoluble components of highland barley grains significantly improved physiological and biochemical indexes and liver antioxidant indexes of mice on high-fat diet. The liposoluble components of highland barley grains significantly changed the intestinal microflora diversity and community structure of high-fat diet mice. The liposoluble components of highland barley grains significantly improved cholesterol metabolism pathway in high-fat diet mice by regulating the expression of ANGPTL8, CD36, PLTP, SOAT1, CYP7A1, and ABCA1 genes.
Vitamin D status among infants and children in Shanghai, China: A hospital-based study
- Pages: 3111-3120
- First Published: 08 March 2023
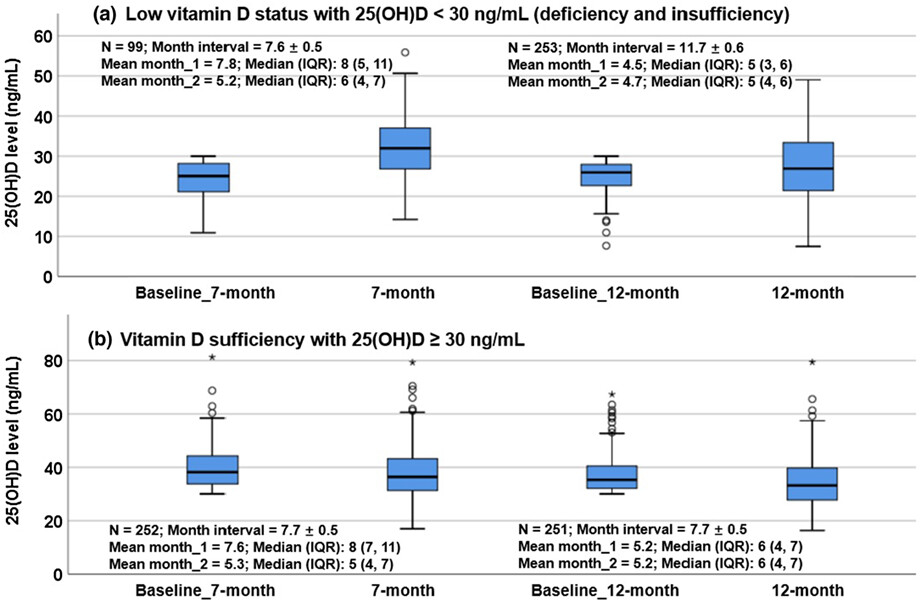
This 2-year observational study assessed serum 25(OH)D levels in 6164 children aged 0–11 years in Shanghai, China. The cross-sectional and longitudinal data documents the vitamin D status, showing that the prevalence of low vitamin D status was common among infants and children, and the situation was more severe in winter than in other seasons, in school-age children than in infants, toddlers, and preschoolers. The study suggests that repeated 25(OH)D assessments at about a 7-month interval, compared with a 12-month interval, maybe a more effective way to assist in optimizing vitamin D status for those with low vitamin D status.
Incorporation of fresh leaves of wormwood (Artemisia herba alba) and/or rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis) in the diet of rams: Effect on testicular function, sexual behavior, and blood parameters
- Pages: 3121-3130
- First Published: 28 March 2023

This study is part of the research that supports natural and ecological methods to improve reproductive performances and livestock productivity. In this paper we show that the consumption of small quantities of AMPs (Artemisia herba alba and/or Rosmarinus officinalis), which are naturally abundant in the Mediterranean rangeland can present an opportunity to improve the productivity of ecological sheep farming by improving the performance and reproductive health of rams.
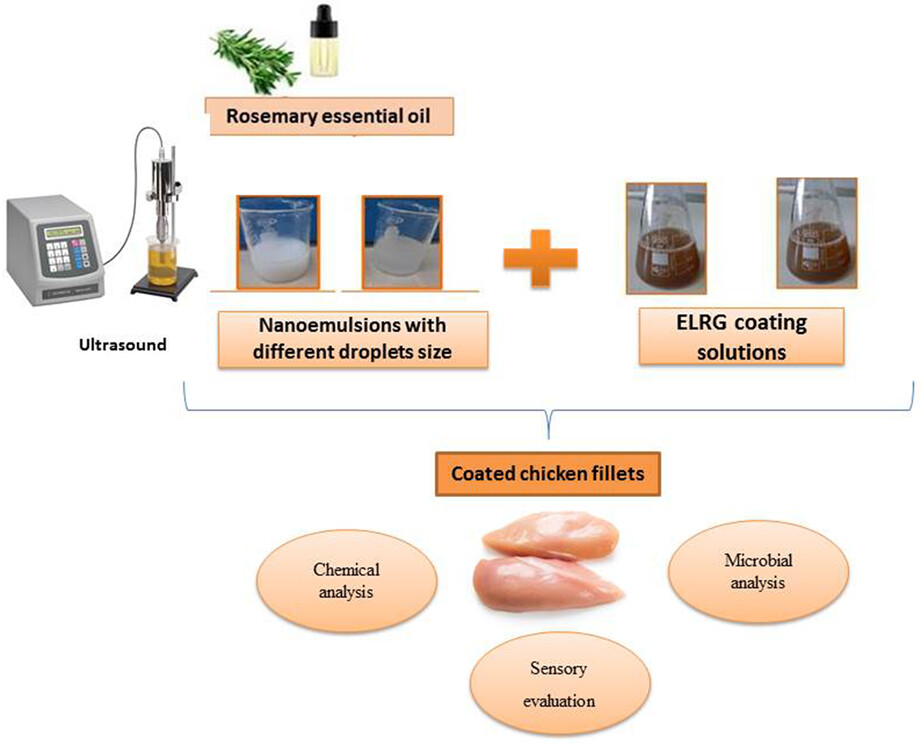
Novel antimicrobial/antioxidant Eremurus luteus root gum coating containing rosemary essential oil nanoemulsions for extension of chicken meat shelf life
- Pages: 3131-3140
- First Published: 09 March 2023
Mulberry extract upregulates cholesterol efflux and inhibits p38 MAPK-NLRP3-mediated inflammation in foam cells
- Pages: 3141-3153
- First Published: 08 March 2023
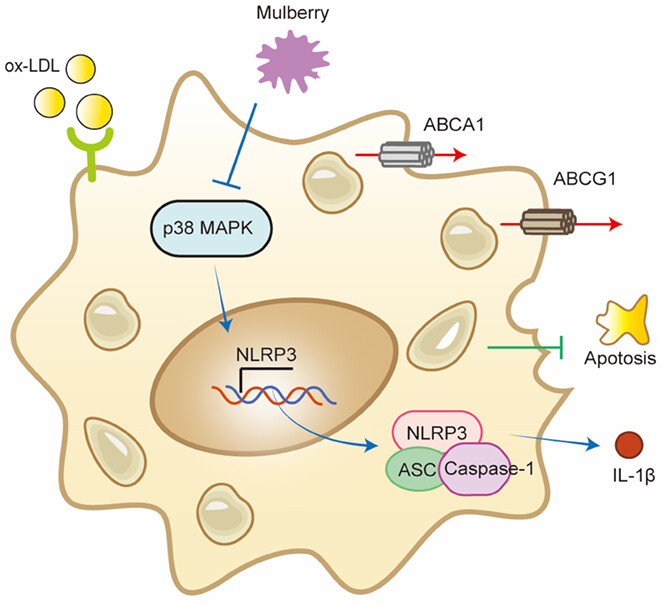
In summary, our study uncovers the elevated expression of NLRP3 in restenosis artery wall, making it a novel therapeutic target for the disease. More importantly, we found that mulberry extract plays multiple regulatory roles in the formation of restenosis. It not only inhibits the inflammation in foam cells by suppressing p38 MAPK signaling pathway-mediated inflammasome activation but also stimulates the ABCA1/ABCG1-mediated cholesterol efflux of foam cells to decrease their formation.
Analysis of the microbial community structure and flavor components succession during salt-reducing pickling process of zhacai (preserved mustard tuber)
- Pages: 3154-3170
- First Published: 17 April 2023
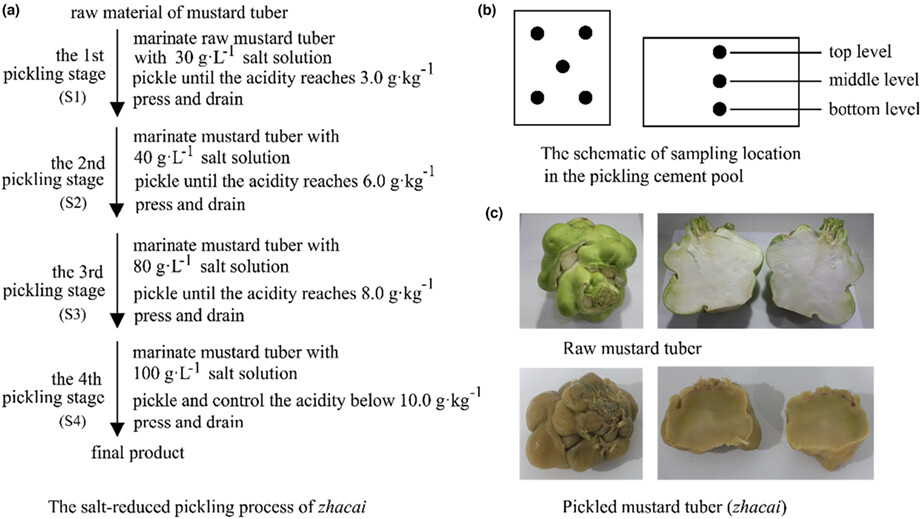
This study investigated a whole process of the salt-reducing pickling of zhacai. The microbial community structure during the four stages was analyzed by using the PacBio Sequel platform to sequence full-length 16S rRNA and ITS genes, the flavor components were measured (organic acids, VFCs, monosaccharides and amino acids), the correlations between microbial communities and flavor components were analyzed using correlation heat mapping and O2PLS modeling, the core functional flora were inferred through integrated correlation analysis, and the predicted functions of the microbial communities after using PICRUSt2 analysis were highlighted.
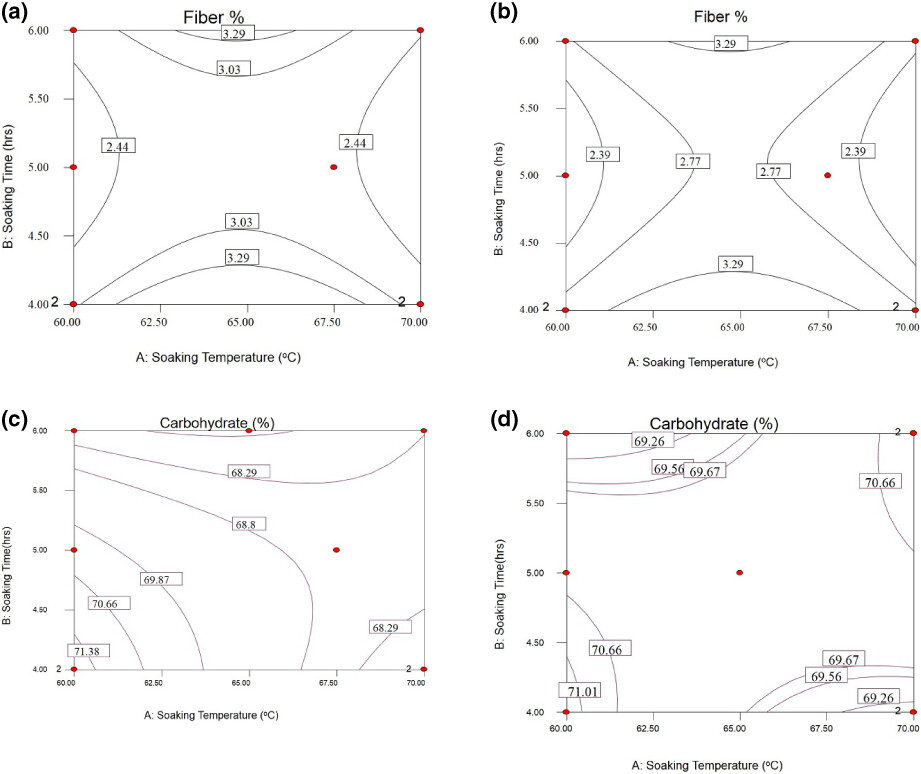
Optimization of soaking conditions (temperature and time) on physicochemical properties of selected parboiled rice varieties grown in Eastern Ethiopia
- Pages: 3171-3183
- First Published: 13 March 2023
Nutritional and microbiological effects of vermicompost tea in hydroponic cultivation of maple peas (Pisum sativum var. arvense L.)
- Pages: 3184-3202
- First Published: 06 April 2023
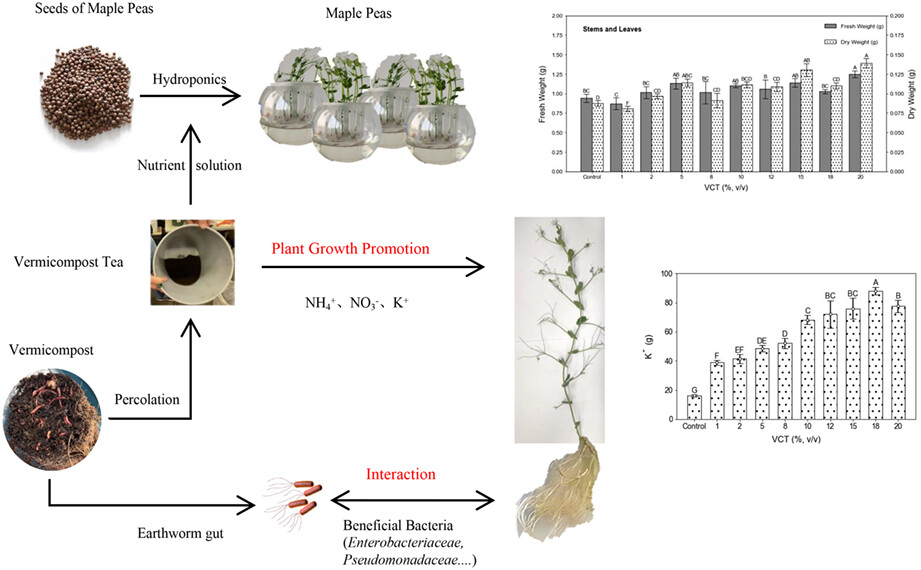
Vermicompost tea (VCT) was investigated on its suitability as a hydroponic substrate to provide both nutritional and microbiological benefits. VCT increased the biomass of maple peas (Pisum sativum var. arvense L.), increased stem length, raised the potassium ion content, and promoted the uptake of nitrogen by the roots. The microorganisms associated with earthworm guts were identified in the maple peas root system, consequently promoting the growth of maple peas.
Total meat (flesh) supply may be a significant risk factor for cardiovascular diseases worldwide
- Pages: 3203-3212
- First Published: 17 March 2023
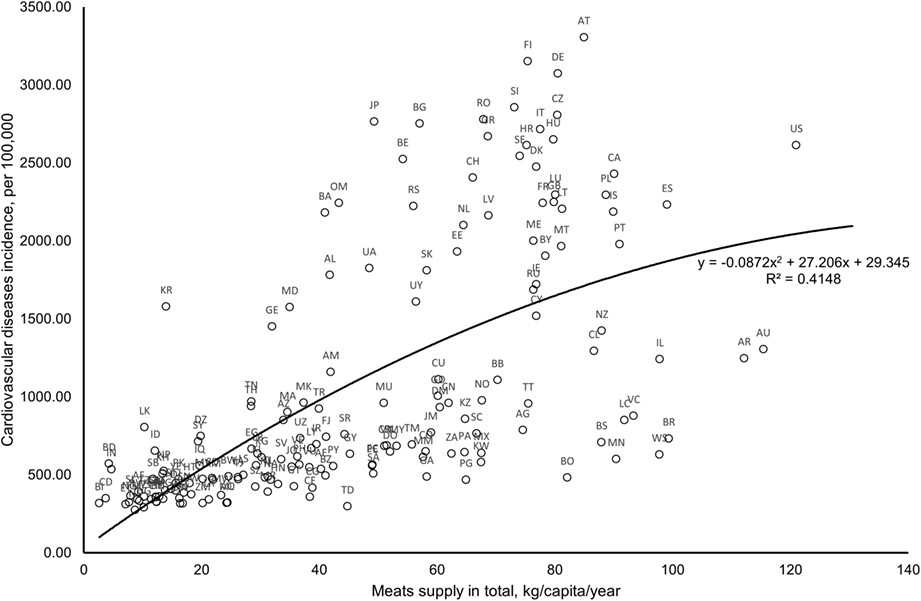
Reflecting actual diet patterns, this study explored the role of total meat in predicting cardiovascular disease (CVD) incidence worldwide. Further data analyses showed that total meat (flesh) consumption correlated to CVD incidence independently but was significantly stronger in developing countries than in developed countries.
Physical quality of gluten-free doughs and fresh pasta made of amaranth
- Pages: 3213-3223
- First Published: 14 March 2023
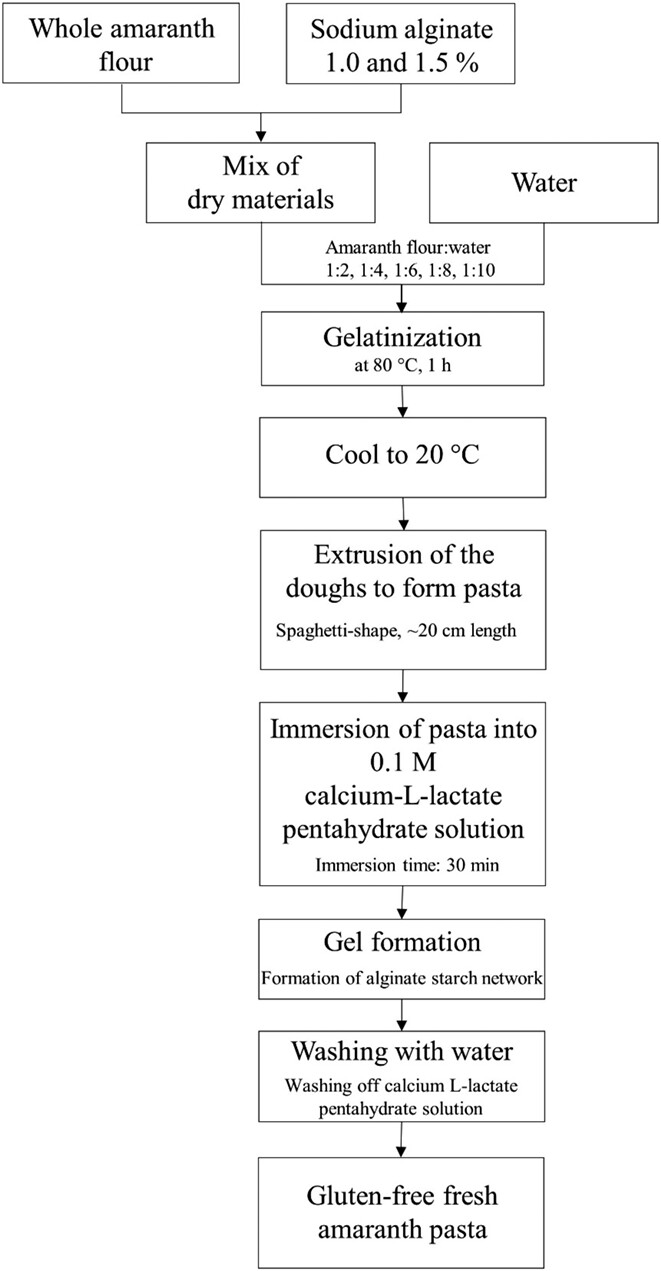
The range of gluten-free foods, such as gluten-free pasta, has grown steadily in recent years. However, fresh pasta is not widely available in this area. Therefore, in this research work, a gluten-free fresh pasta was successfully developed from the nutritionally valuable pseudocereal amaranth by successfully replacing gluten with the hydrocolloid sodium alginate.
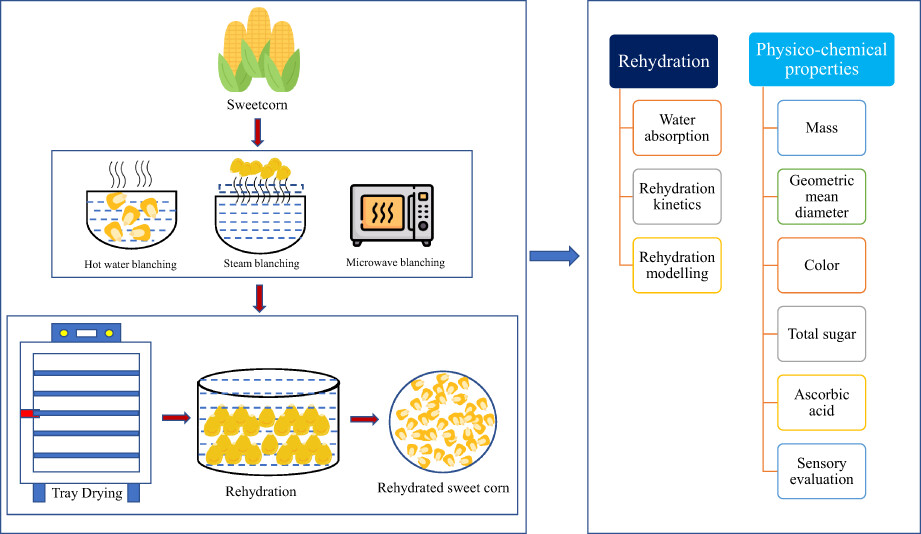
Rehydration modeling and characterization of dehydrated sweet corn
- Pages: 3224-3234
- First Published: 15 March 2023
An efficient DNAzyme for the fluorescence detection of Vibrio cholerae
- Pages: 3235-3245
- First Published: 13 March 2023
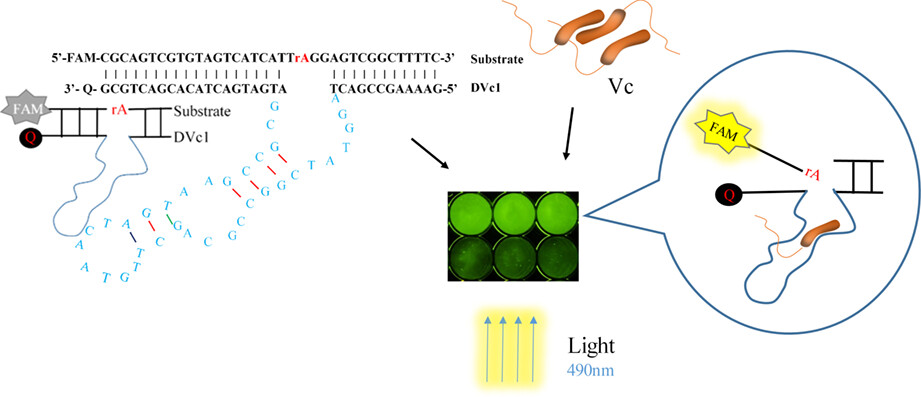
Nine rounds of in vitro selection using an unmodified DNA library were successfully performed to find specific DNAzymes of Vibrio cholerae.A DNAzyme (named DVc1) with good activity and specificity with a detection limit of 7.2×103 CFU/mL of Vc was selected. A simple biosensor based on DVc1 can effectively and fast detected V. cholerae in aquatic products.
Prevalence of food thermometers usage and temperature control in restaurants in Dammam, Saudi Arabia
- Pages: 3246-3254
- First Published: 10 March 2023
The research is of Public Health Importance as it deals with the temperature-monitoring practice followed by restaurants. Temperature monitoring is one of the principles of HACCP, which can help to reduce the risk of foodborne illness.
The association between dietary micronutrient patterns and odds of diabetic nephropathy: A case–control study
- Pages: 3255-3265
- First Published: 31 March 2023
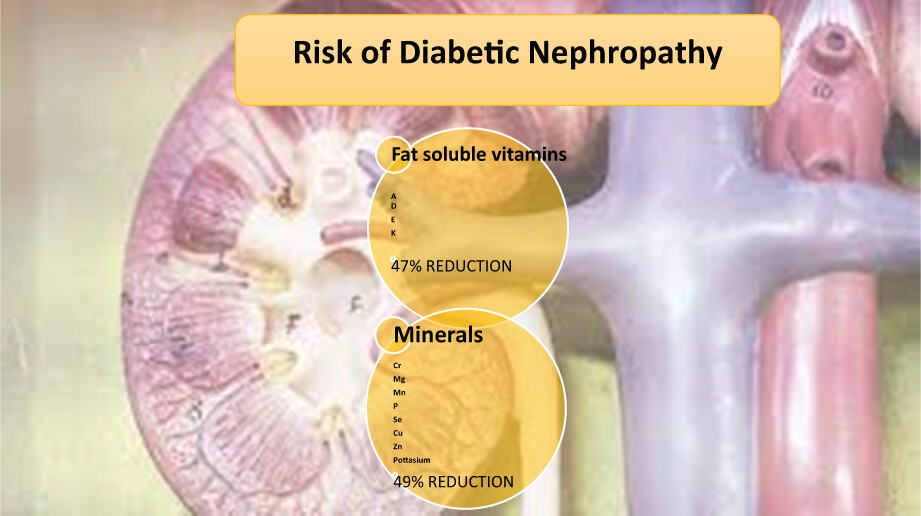
The risk of diabetic nephropathy was 47% decreased after high adherence of fat-soluble vitamin patterns. In addition, we saw a 49% decrease of risk of DN in high adherence group of mineral patterns. The findings emphasize that dietary sources of renal-protective nutrients should be encouraged among the general population.
Effects of high-protein milk powder, linseed paste, and grape molasses levels on physiochemical, rheological, and sensory attributes of linseed spread
- Pages: 3266-3278
- First Published: 13 March 2023
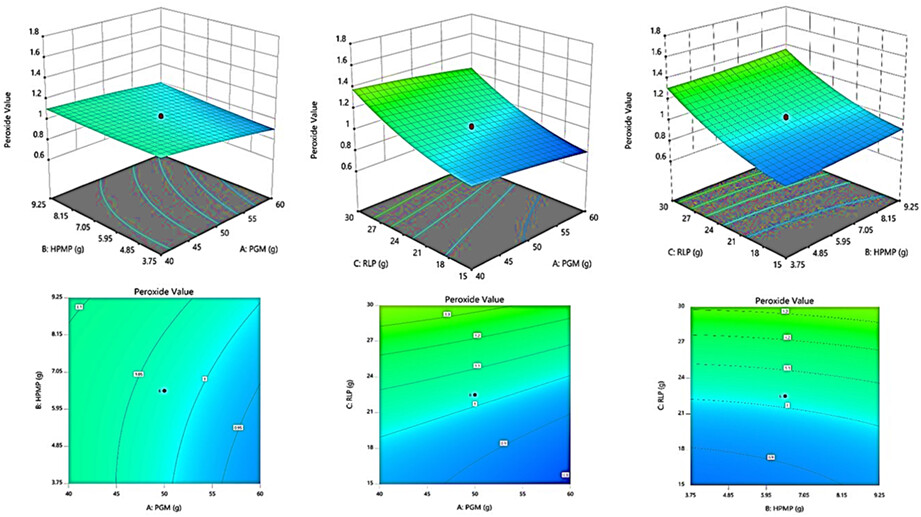
This project we studied the possibility of making nutritional spread (similar to Nutella) from the linseed, Persian grape molasses, and high protein milk powder for the first time. After applying response surface methodology and central composite design, the optimized-LS obtained with 22.5g RLP, 50g PGM, 6.5g HPMP, fine particle sizes (< 30µm), and 92% of the highest acceptable sensory scores (ASS).
Individual nutrients and serum klotho levels in adults aged 40–79 years
- Pages: 3279-3286
- First Published: 08 March 2023

Energy-adjusted intake of carbohydrates, total sugars, and alcohol from a regular diet is associated with soluble Klotho serum levels in U.S. adults aged 40–79 years. Dietary exposure to individual nutritional components should be included in deciphering Klotho turnover in populational studies, with additional research needed to investigate the relationship between cause and effect in diet composition–Klotho interplay.
Improving effect of soy whey-derived peptide on the quality characteristics of functional yogurt
- Pages: 3287-3296
- First Published: 13 March 2023
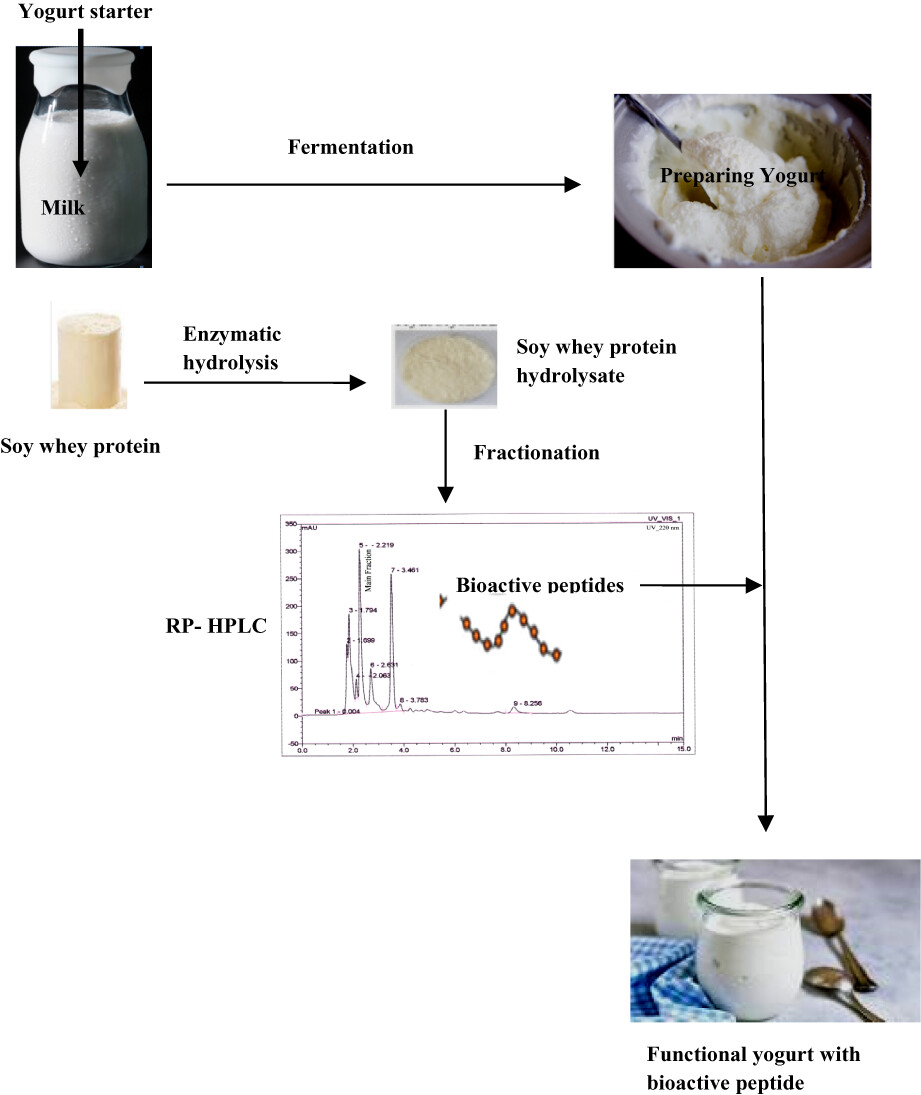
Since soy whey is a cost-effective source of peptides and little research has been done on peptides derived from this by-product, the aim of this study was to isolate and purify bioactive peptides from this by-product and use them as a natural preservative in a model food system (yogurt). The fraction with the highest antimicrobial and antioxidant activity which was added to yogurt showed a good antibacterial effect against Escheirichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Moreover, the addition of this peptide improved the physicochemical quality of yogurt. Therefore, this bioactive peptide can be used as a natural alternative to common preservatives in the food industry.
Fuzzy evaluation on the integrated benefit of regulated deficit irrigation for pear-jujube tree based on information entropy
- Pages: 3297-3308
- First Published: 13 March 2023
The analytic hierarchy model for multipurpose level evaluated that the single-stage water deficit treatments with moderate or severe in fruit maturity have the higher RDIIB, and the double-stage water deficit treatment with severe stress at bud burst to leafing stage combining moderate water deficit at fruit mature stage was also an acceptable RDI scheme in case of more water at fruit growth stage.
Sika deer velvet antler protein extract modulater bone metabolism and the structure of gut microbiota in ovariectomized mice
- Pages: 3309-3319
- First Published: 13 March 2023
In this paper, I show that velvet antler extract has a positive effect on osteoporosis model mice. I found that velvet antler extract can improve the serum biochemical indexes, bone microstructure, and intestinal flora of osteoporosis model mice. In addition, I noticed that the antler extract significantly increased the content of Akkermansia bacteria in the intestinal tract of mice, indicating that Akkermansia bacteria may be a new biomarker of osteoporosis.
Antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of two Costa Rican cultivars of ber (Ziziphus mauritiana): An underexploited crop in the American tropic
- Pages: 3320-3328
- First Published: 17 March 2023
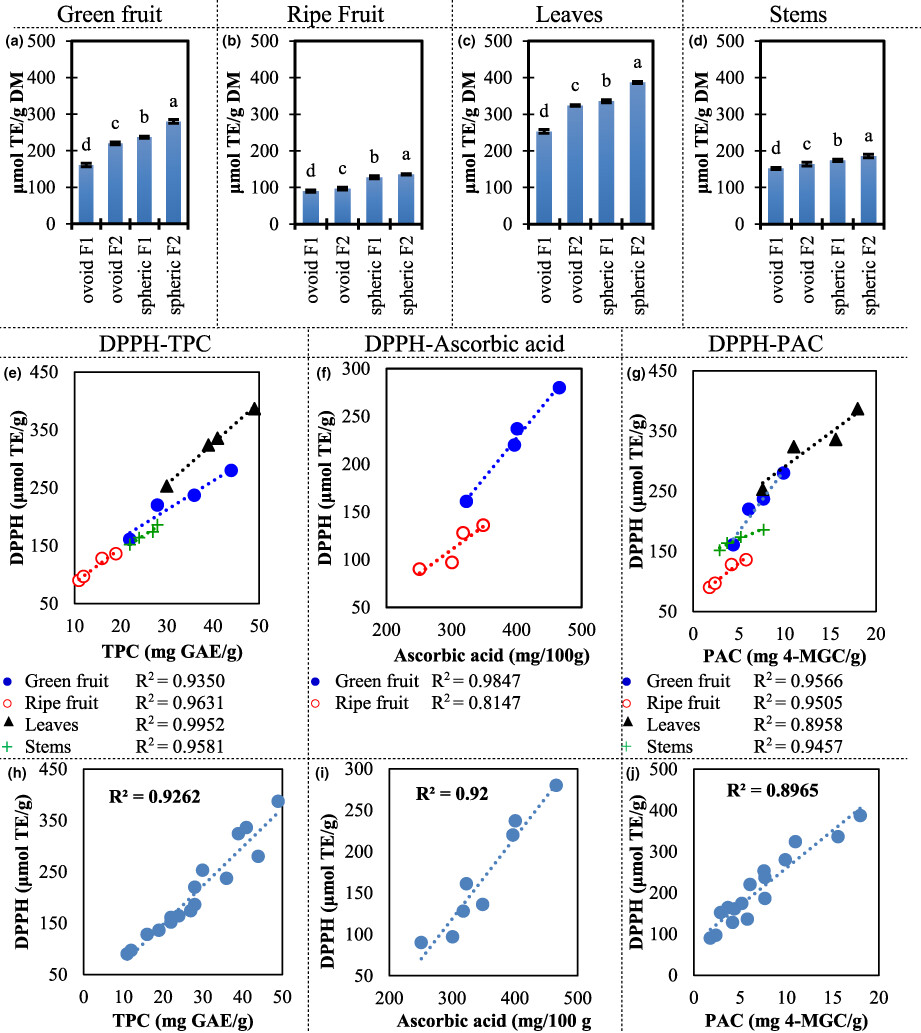
Ber has been cultivated in Asia for many years, and it has been introduced to the American tropic in recent years. We studied the characteristics and benefits of the cultivation of this fruit in Central America. We found out it produces higher antioxidant levels than many other reports, and also shows antimicrobial properties.
Characteristics of reduced-fat mayonnaise prepared by oleaster as a fat replacer and natural antioxidant
- Pages: 3329-3338
- First Published: 07 May 2023
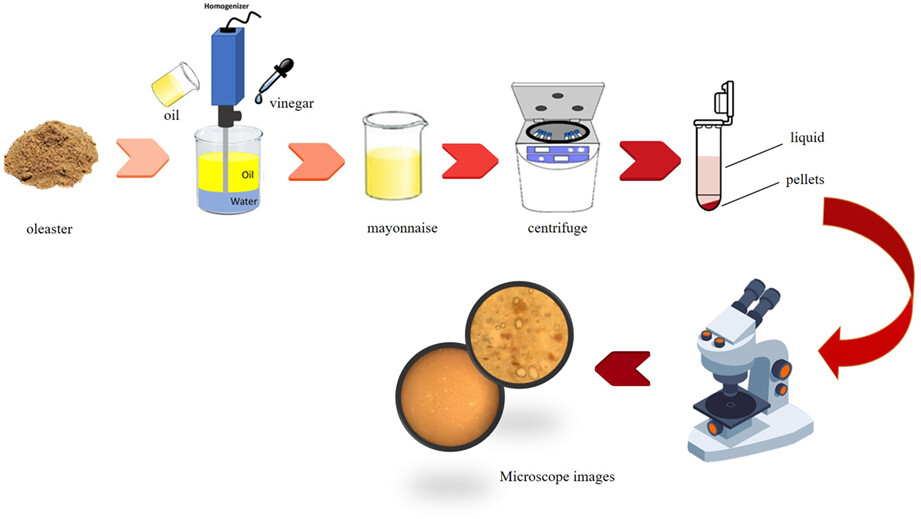
In response to high-fat related health concerns like obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer, many food scientists and technologists have aimed at developing low-calorie food products. Noteworthy, once the fat is eliminated, some unfavorable changes in many sensory attributes of reduced-fat foods, such as appearance, flavor, mouthfeel, and texture occur, which have restricted consumer acceptance and commercial success rate. So, In the current research, the impact of oleaster at different concentrations (4%, 6%, and 8% w/w), as a fat replacer, on the physical, textural and rheological characteristics and stability of reduced-fat mayonnaise (10%, 20%, 30% and 40% fat reduction) was examined.
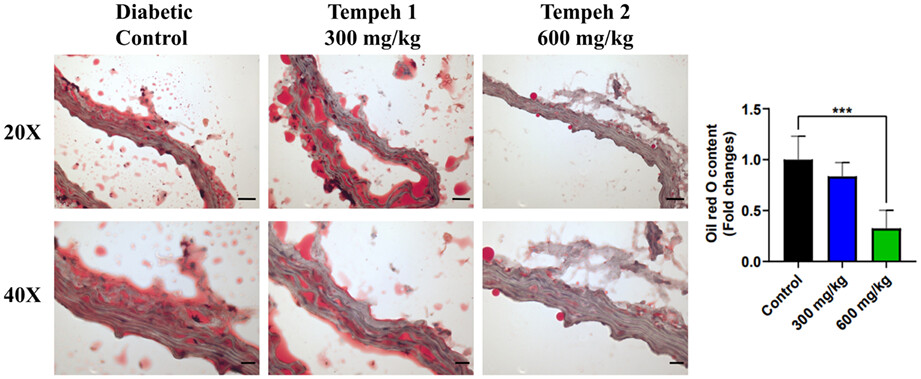
The effects of using Tempeh as a supplement for type 2 diabetes
- Pages: 3339-3347
- First Published: 17 March 2023
Adjunctive nano-curcumin therapy improves inflammatory and clinical indices in children with cystic fibrosis: A randomized clinical trial
- Pages: 3348-3357
- First Published: 28 March 2023
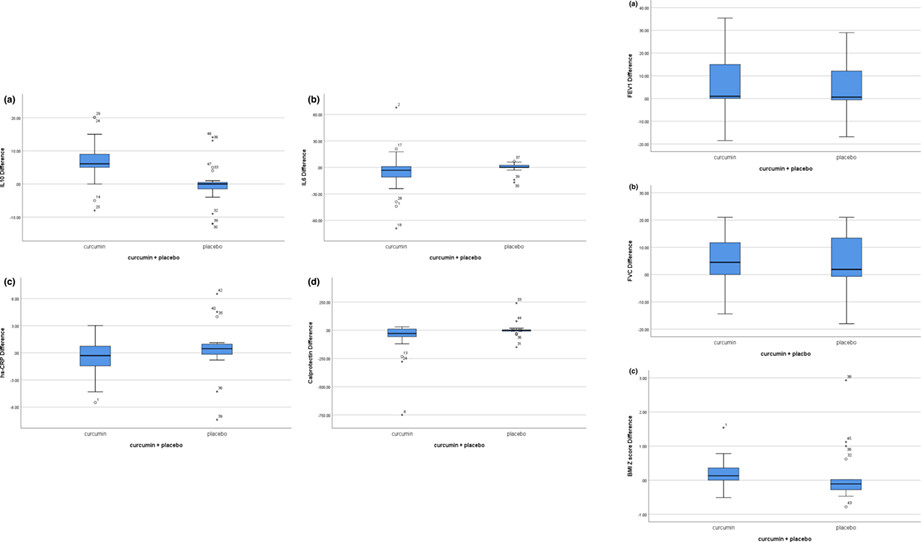
This trial aimed to ascertain the effects of nano-curcumin as an anti-inflammatory agent and a cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator modulator on clinical and inflammatory markers in children with cystic fibrosis (CF). Nano-curcumin seems to be considered as an effective nutritional supplement on hs-CRP, IL-10, fecal calprotectin level and improving quality of life on patients with CF.
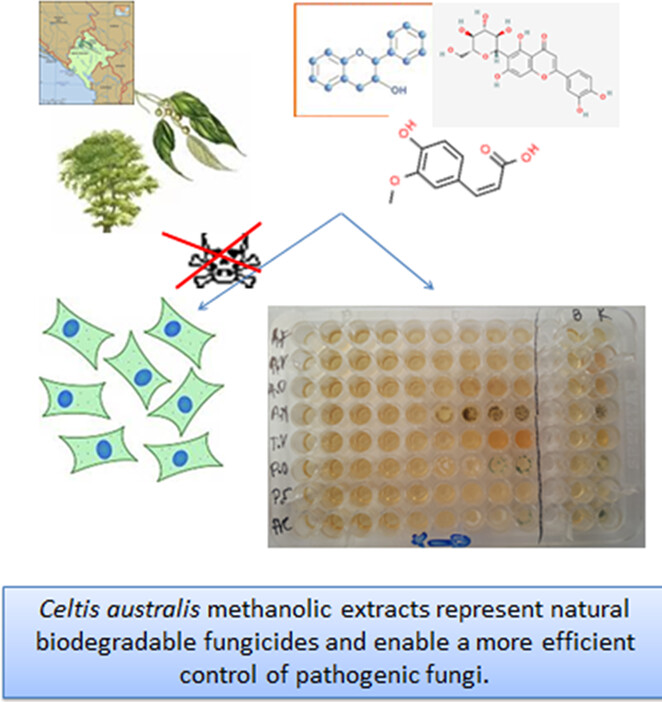
Natural extracts against agricultural pathogens: A case study of Celtis australis L.
- Pages: 3358-3364
- First Published: 20 March 2023
The effect of low dietary inflammatory index score formula on inflammatory, metabolic, and clinical outcomes in critically ill traumatic brain injury patients: A single-blind randomized controlled pilot study
- Pages: 3365-3375
- First Published: 19 April 2023
Vegetable-enriched bread: Pilot and feasibility study of measurement of changes in skin carotenoid concentrations by reflection spectroscopy as a biomarker of vegetable intake
- Pages: 3376-3384
- First Published: 22 March 2023
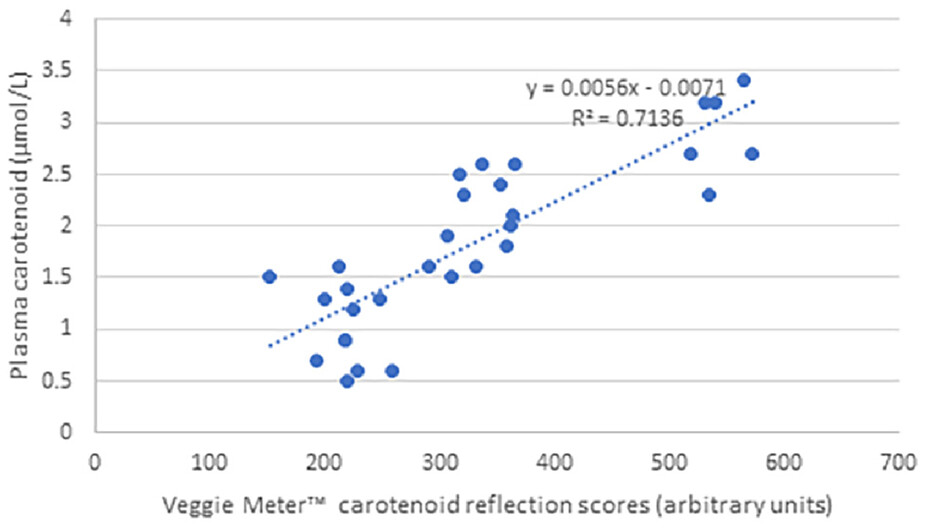
Plasma carotenoid concentrations and the carotenoid reflection scores had a large and positive association. Carotenoid status was not measurably changed with the consumption of 200 g vegetable-enriched bread each day for 2 weeks. The Veggie meter™ has the potential to provide portable measurement of circulating carotenoids and be indicative of intake of carotenoid-rich foods.
Effectiveness of combined seeds (pumpkin, sunflower, sesame, flaxseed): As adjacent therapy to treat polycystic ovary syndrome in females
- Pages: 3385-3393
- First Published: 25 March 2023
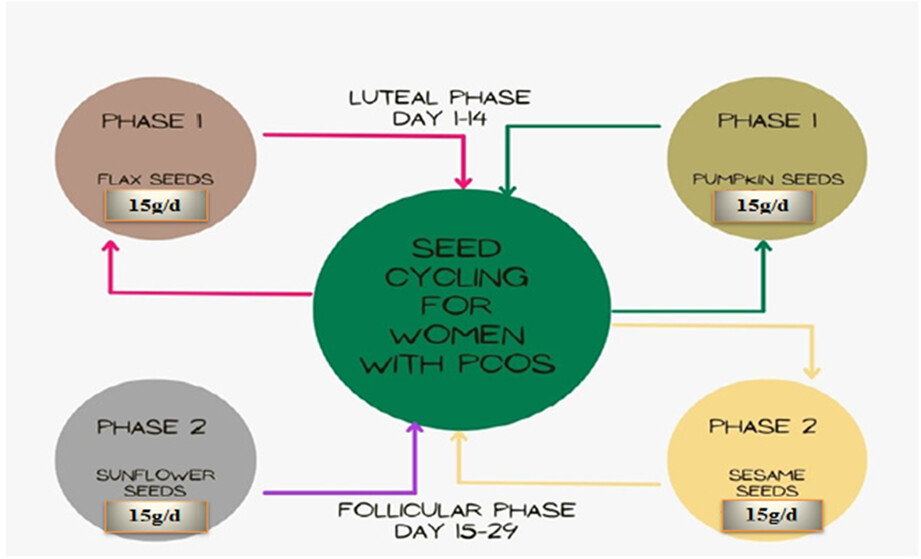
The formation and release of eggs during ovulation are impacted by high amounts of androgens. Seed cycling is powerful in the treatment of PCOS. For efficacy studies, 90 women with PCOS, between 15 and 40 years were selected from the department of gynecology, Tertiary care unit. Women with PCOS were divided into three groups (T0, T1, T2) (20 women/group). Among these three groups, first was control group (T0). The second group was experimental group (T1). In T1, 20 women with PCOS were treated with portion control diet and METFORMIN 500 mg tab/day for 90 days. Third group was also an experimental group (T2). In this group 20 women with PCOS were also treated with another treatment plan for 90 days, in which portion control diet and seed cycling were included.
Anti-Helicobacter pylori activity of Fagopyrum Tataricum (L.) Gaertn. Bran flavonoids extract and its effect on Helicobacter pylori-induced inflammatory response
- Pages: 3394-3403
- First Published: 31 March 2023
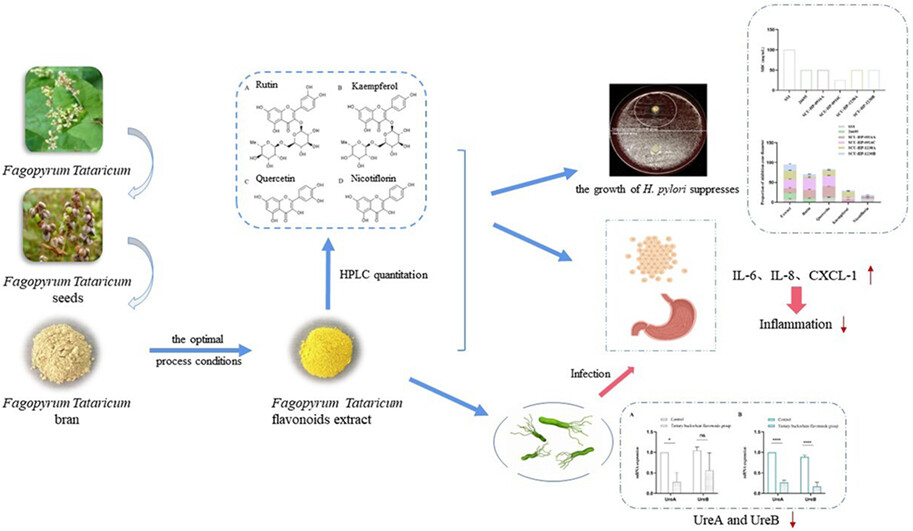
This study found that tartary buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum (L.) Gaertn.) flavonoids extract and its main monomers could not only inhibit the growth of H. pylori in vitro, but also reduce the inflammatory response induced by H. pylori in GES-1 cells. Moreover, the flavonoids extract could inhibit the expression of urease. The results provided a new idea for the development of tartary buckwheat flavonoids as health functional products.
Lyophilized royal jelly preparation in nanoscale and evaluation of its physicochemical properties and bactericidal activity
- Pages: 3404-3413
- First Published: 22 March 2023
Fresh royal jelly was subjected to the freeze-drying process with a pressure and temperature of 100 Pa and − 70°C, for 40 h. Statistical analysis of the moisture content, turbidity, total phenol content, and antioxidant activity of fresh royal jelly and royal jelly powder (RJP) indicated that during 3 months of storage, these parameters were constant for the prepared RJP; however, for the fresh royal jelly, these parameters significantly (p < .05) decreased after 2 months of storage.
Inhibition of oxidative stress and advanced glycation end-product formation in purified BSA/glucose glycation system by polyphenol extracts of selected nuts from Pakistan
- Pages: 3414-3421
- First Published: 23 March 2023
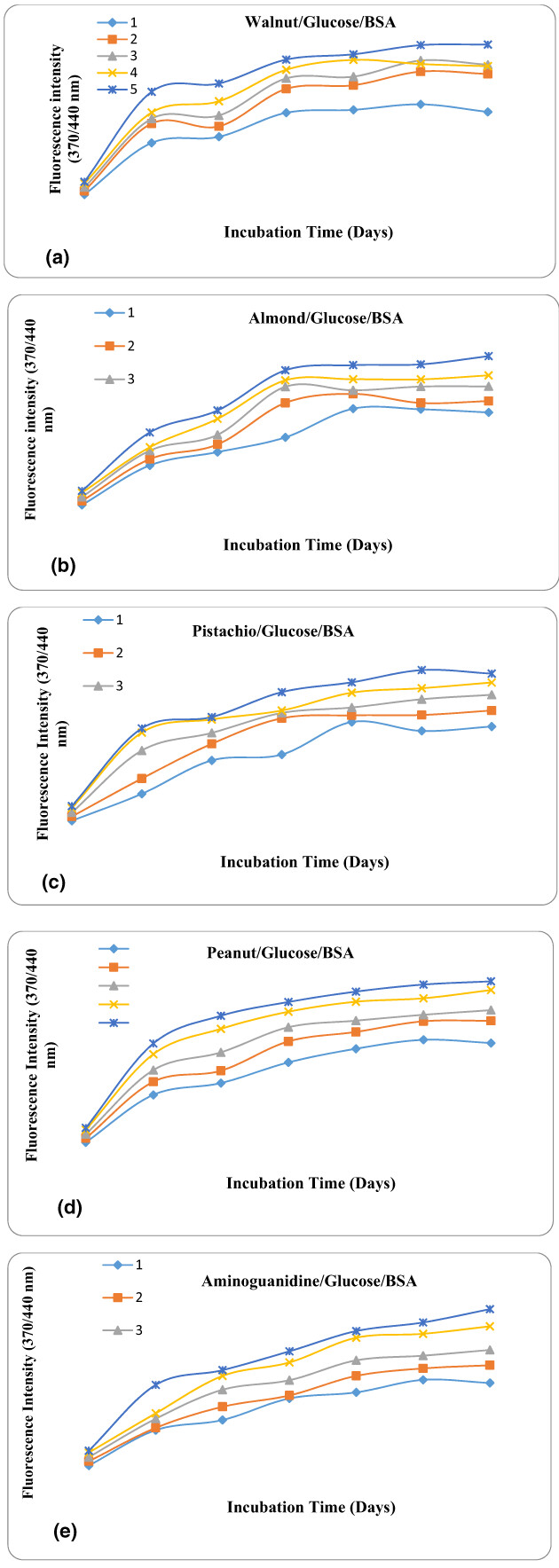
All the studied nuts have high phytonutrients content with significant antioxidant and antiglycative properties. At a dosage of 5 mg/mL, all the studied extracts successfully prevent glucose-mediated protein modification in vitro during the 18–24th days of incubation. Plant-derived foods loaded with bioactive moieties are beneficial in the inhibition of oxidative stress and AGEs formation in customizing a healthy diet for the target group.
Maternal Vitamin A deficiency during pregnancy and lactation induced damaged intestinal structure and intestinal flora homeostasis in offspring mice
- Pages: 3422-3432
- First Published: 12 April 2023
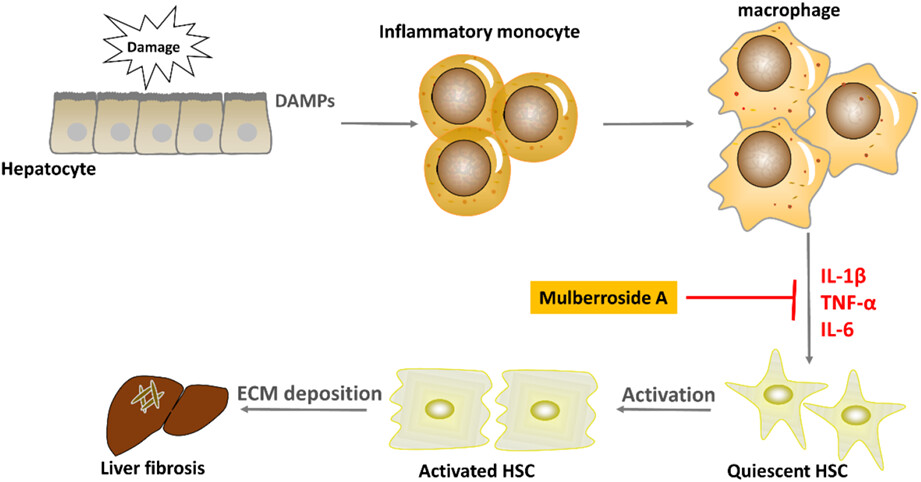
Mulberroside A ameliorates CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in mice via inhibiting pro-inflammatory response
- Pages: 3433-3441
- First Published: 31 March 2023
Functional, antioxidant, and sensory properties of mixed-fruit (pitaya, watermelon, and mint) and pitaya wines
- Pages: 3442-3449
- First Published: 04 May 2023
Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer function of Engleromyces goetzei Henn aqueous extract on human intestinal Caco-2 cells treated with t-BHP
- Pages: 3450-3463
- First Published: 06 April 2023
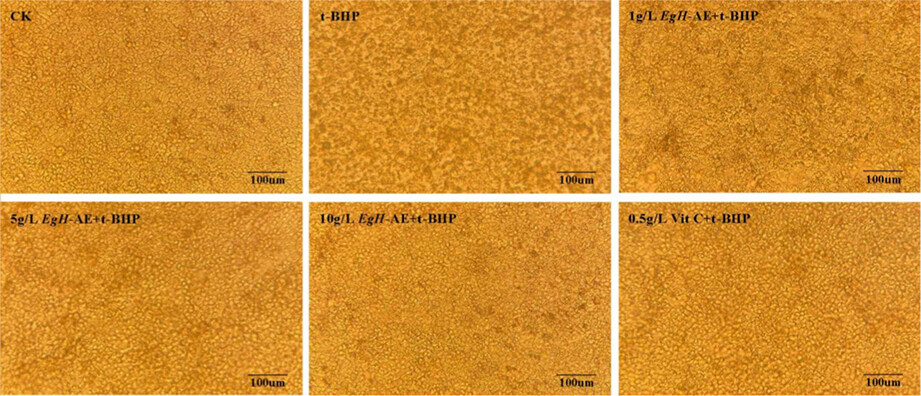
Engleromyces goetzei Henn (EgH) is a natural fungus that has been used as a traditional edible and medicine for long time in Southwest China. Our study found EgH aqueous extract (EgH-AE) has very strong activities on antioxidant and anti-inflammation. At the same time, we also found EgH-AE has good biocompatibility and cell protective function, so it is biosafe, EgH-AE may have the prospect of developing into functional beverage.
Shelf-life extension of Fragaria × ananassa Duch. using selenium nanoparticles synthesized from Cassia fistula Linn. leaves
- Pages: 3464-3484
- First Published: 21 April 2023
Isolation and antioxidant characterization of theaflavin for neuroprotective effect in mice model
- Pages: 3485-3496
- First Published: 28 March 2023
The mandate of the current investigation was to elucidate the therapeutic and antioxidant perspective of black tea. Purposely, black tea compositional analysis followed by polyphenol extraction and antioxidant characterization was done. Moreover, the theaflavin from black tea extract was also isolated through the solvent partition method. Lastly, the neuroprotective effect of isolated theaflavin was assessed through a bioefficacy trial. The outcomes delineated that black tea showed promising nutritional composition with special reference to protein and fiber. Among the extraction solvent, ethanol performed better as compared to methanol and water likewise, higher extraction was noticed at 60 min followed by 90 and 30 min.
Upcycling flavanol-rich Chardonnay and Pinot noir grape thinned clusters as potentially functional food ingredients in cocoa-based products
- Pages: 3497-3505
- First Published: 04 April 2023
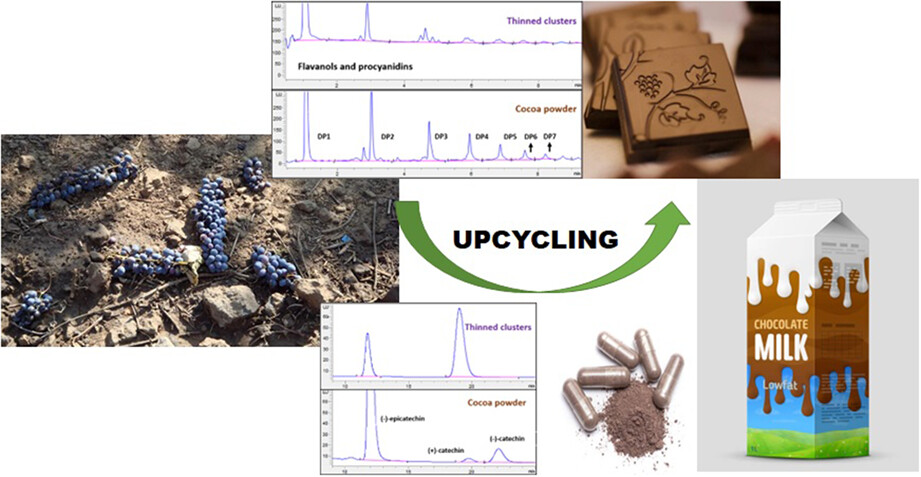
Grape thinned cluster fractions from Chardonnay and Pinot noir grapes grown in the North Coast of California showed higher concentrations of flavanol monomers and procyanidins, with 208.8–763.5 times more (+)-catechin, 3.4–19.4 times more (−)-epicatechin, and 3.8–12.3 times more procyanidins (by degree of polymerization DP 1–7) than a traditionally Dutch (alkalized) cocoa powder that has been widely used in food applications. Thus, grape thinned clusters could be considered as plant-based natural products suggesting great potential to be functional ingredients in cocoa-based products to enhance their overall dietary flavanol content.
Antioxidant activity and total phenolic compounds of Commiphora gileadensis extracts obtained by ultrasonic-assisted extraction, with monitoring antiaging and cytotoxicity activities
- Pages: 3506-3515
- First Published: 05 April 2023
Exploring the effects of palm kernel meal feeding on the meat quality and rumen microorganisms of Qinghai Tibetan sheep
- Pages: 3516-3534
- First Published: 05 April 2023
18% of PKM group exhibited superior eating quality and flavor profile while depositing more protein and fat relative to the other group. A total of 23 differential metabolites were identified in PKM-treated Tibetan sheep meat. Carbohydrate metabolism was typical metabolic pathway altered by PKM feeding. PKM feeding affected key metabolites by altering rumen microorganisms to regulate the relevant metabolic pathways
Increasing saltiness of salts (NaCl) using mid-infrared radiation to reduce the health hazards
- Pages: 3535-3549
- First Published: 19 April 2023

MIRGA is a highly economical, easy-to-use, and safe technology in which a water-based solution is contained in a pocket-sized 20-mL capacity atomizer. During spraying over the salt packets from a distance of 0.25–0.50 m, 2–6 μm mid-infrared is generated which causes chemical bond alteration in the salt molecules. This resulted in 25%–30% increased saltiness, thereby the salt use for cooking can be cut down by 25%–30% than the usual.
Role of peptide transporters in small peptide uptake of bovine mammary epithelial cells cultured in a transwell chamber
- Pages: 3550-3557
- First Published: 31 March 2023
In this study, role of oligopeptide transporter 2 (PepT2) and small peptide histidine transporter 1 (PhT1) on small peptide uptake in bovine mammary epithelial cells (BMECs) cultured in transwell chamber was studied for the first time. The results suggest that the small peptides in both upper and lower chambers of transwell can be absorbed and used for milk protein synthesis by BMECs in different ways; PepT2 plays an important role in the uptake of small peptides in both basal and apical side of BMECs, and PhT1 may be involved in the uptake of small peptides in the basal side of BMECs.
Variability in nutrient composition of the edible long-horned grasshopper (Ruspolia differens) in Uganda and its potential in alleviating food insecurity
- Pages: 3558-3574
- First Published: 11 April 2023
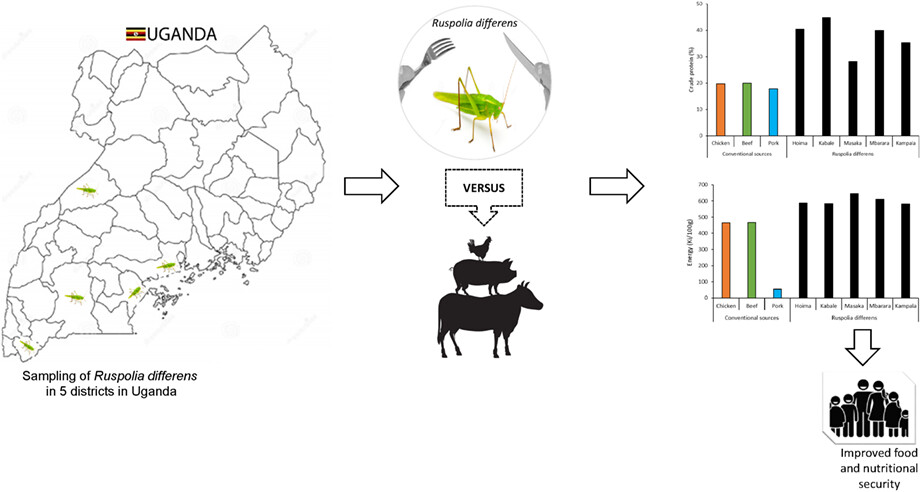
Long-horned grasshoppers are consumed in over 21 African countries. Crude protein (28%–45%), crude fat (41%–54%), and energy (582–644 Kj/100 g) of grasshoppers are comparable to that of plant and animal origins. Grasshopper meal could be considered as functional food ingredients capable of supplying adequate essential macro- and micronutrients.
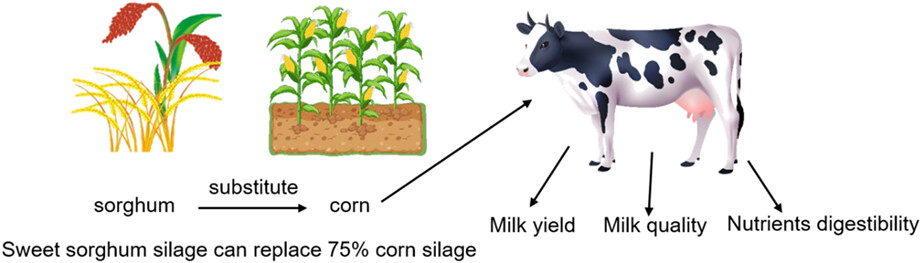
Application of different proportions of sweet sorghum silage as a substitute for corn silage in dairy cows
- Pages: 3575-3587
- First Published: 15 May 2023
The nutritional quality and contents of heavy elements due to thermal processing and storage in canned Thunnus tonggol fish change compared to fresh fish
- Pages: 3588-3600
- First Published: 28 March 2023
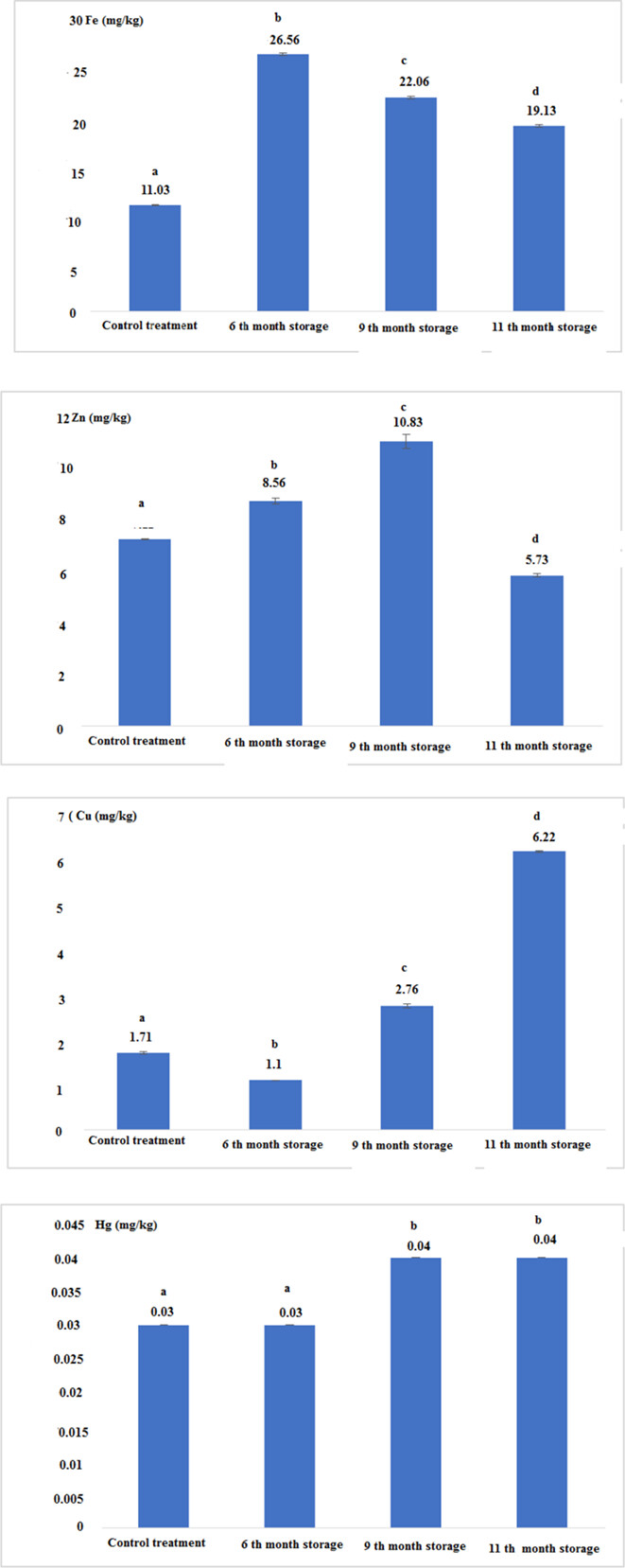
The results of the statistical analysis of the samples showed that canning and sterilization by autoclave increased the contents of elements except mercury to a significant level (p < .05). The results showed that the amount of fat significantly increased in all samples after processing (p < .05), but the amount of ash and protein significantly decreased (p < .05). The moisture content significantly increased (p < .05) except for the 9 months of storage after canning. The obtained results showed that the energy value after 6 months of storage was the highest (297.53 kcal/100 g). The results showed that the bioaccumulation of copper, iron, zinc, and mercury in the fresh and canned muscles was lower than the standard concentration recommended by the FAO and WHO. This type of fish was a high-quality food source and it was safe after 11 months of storage and was suitable for human consumption. Therefore, the consumption of canned Iranian tuna can be safe for human health despite the possible contamination with heavy metals.
Effects of ultra-high-temperature processes on metabolite changes in milk
- Pages: 3601-3615
- First Published: 06 April 2023
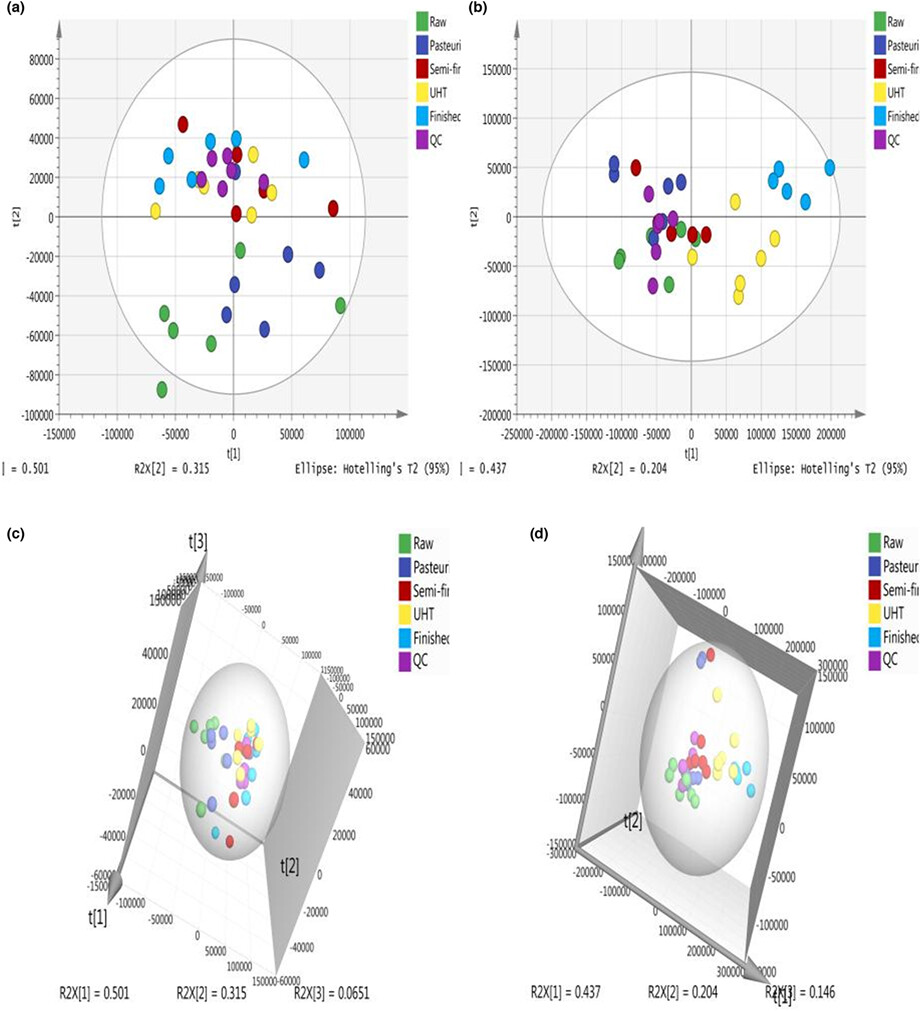
Processing can affect milk properties and alter the composition of milk metabolites, which has corresponding effects on milk flavor and quality. It is quite important to study the safe quality control of milk processing. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to identify metabolites at different steps of ultra-high-temperature-sterilized (UHT) milk processing using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS).
ERRATUM
Erratum to “Low-molecular weight oligosaccharides from gum tragacanth (Astragalus gossypinus) ameliorate nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in Wistar male rats”
- Page: 3616
- First Published: 13 April 2023
RETRACTION
Retraction statement: Hyaluronic acid-rich burger separator edible disc prepared from slaughterhouse waste
- Page: 3617
- First Published: 26 February 2023