Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Measurement of carbohydrates and organic acids in varieties of cheese using high-performance liquid chromatography
- Pages: 2081-2085
- First Published: 07 April 2023
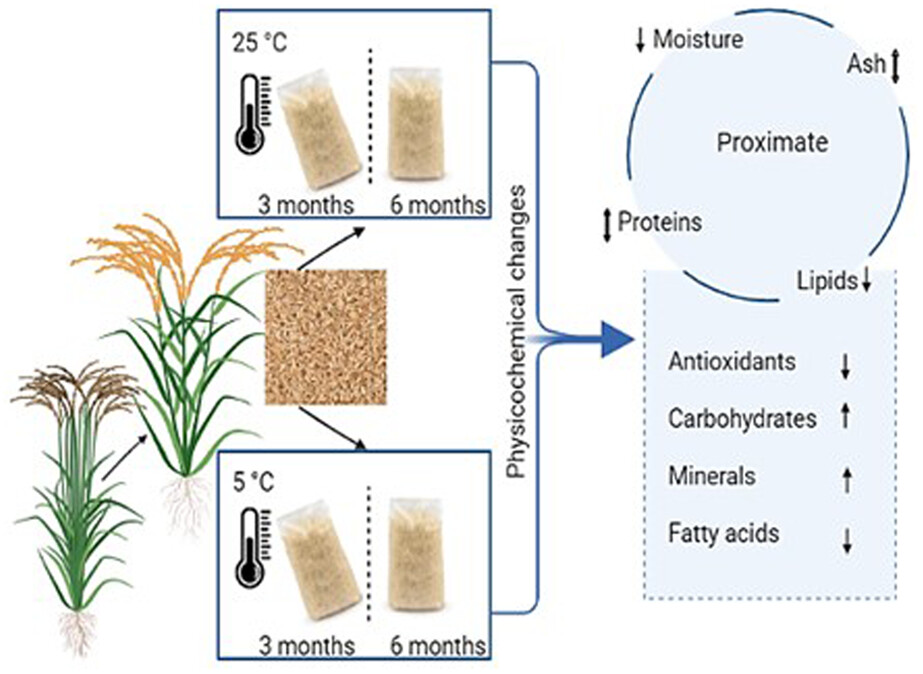
Effect of storage on the nutritional and antioxidant properties of brown Basmati rice
- Pages: 2086-2098
- First Published: 18 July 2022
Effects of Allium roseum L. extracts on the proliferation and the differentiation of the acute myeloid leukemia cell line U937
- Pages: 2099-2105
- First Published: 27 July 2022
1H nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolomics study of serum and pectoralis major for different commercial chicken breeds
- Pages: 2106-2117
- First Published: 07 April 2023
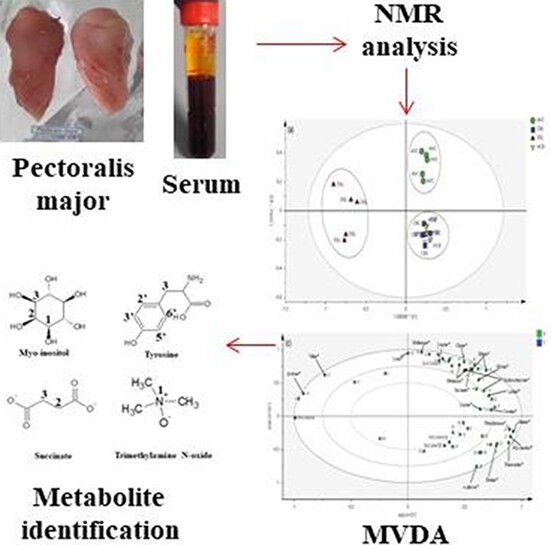
This study aimed to characterize the metabolic composition in four types of commercially available chicken breeds (village chicken, colored broiler [Hubbard], broiler [Cobb], and spent layers [Dekalb]) by 1H NMR coupled and discriminate them using multivariate analysis. The orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA) results showed an obvious separation of local village chicken from the other breeds based on the metabolites present in their serum and meat (pectoralis major). The OPLS-DA assessment identified 19 and 15 potential metabolites for discriminating different chicken breeds in serum and pectoralis major muscle, respectively.
Investigation on compression and mildew of mixed and separated maize
- Pages: 2118-2129
- First Published: 27 July 2022
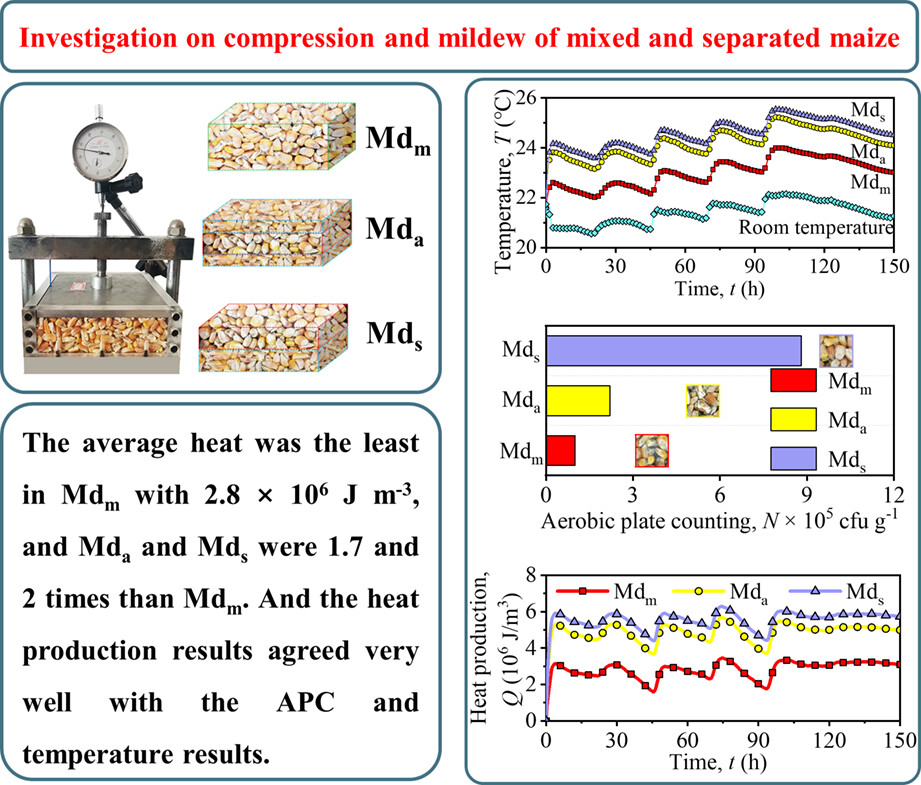
This study explores the influence of three segregation configurations on the creep behaviors and mildew of maize. A newly empirical analytical-numerical method was established to evaluate the heat generated by fungi, considering segregation configuration and compression. The aerobic plate count (APC) and the temperature of in segregated maize bulk are higher than uniform grain. And the heat production was related to the segregation configurations and agreed very well with the APC and temperature results.
Panax ginseng abuse exhibits a pro-inflammatory effect by activating the NF-κB pathway
- Pages: 2130-2140
- First Published: 03 September 2022
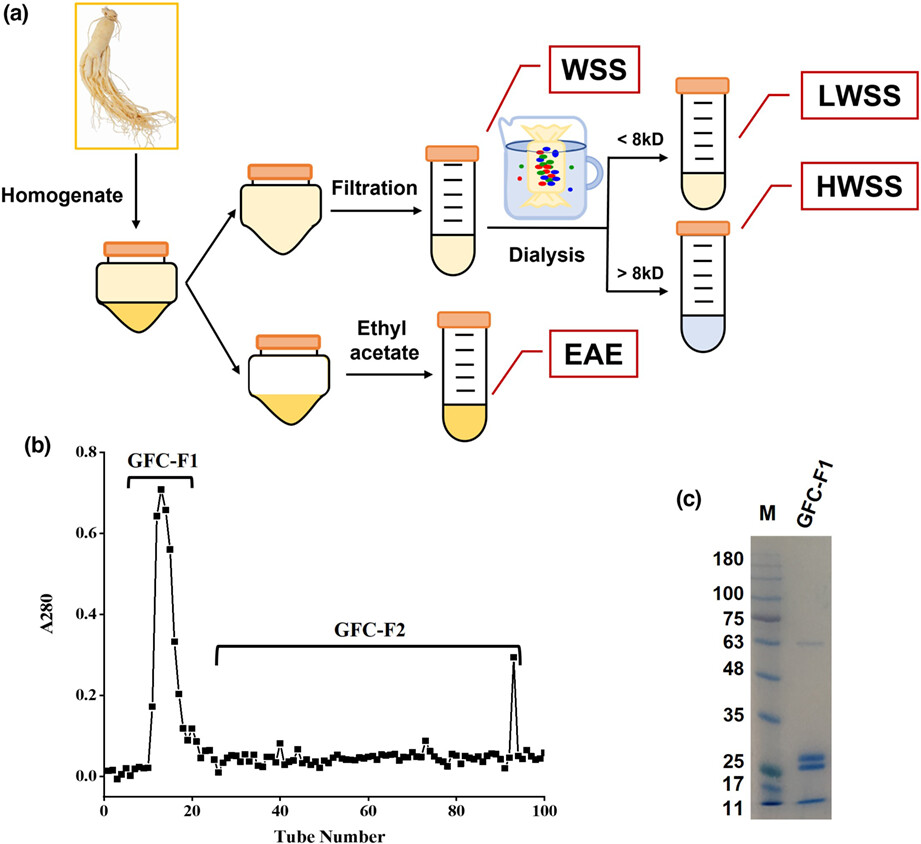
Excessive consumption of panax ginseng may cause over-activation of the immune system forming "ginseng abuse syndrome". The present results suggested that GFC-F1 purified from ginseng is the crucial component that caused "ginseng abuse syndrome". Moreover, GFC-F1 activates the NF-κB pathway to trigger the immune system leading to inflammatory responses through inducing the phosphorylation of p65 and IκBα.
Novel infrared puffing: Effect on physicochemical attributes of puffed rice (Oryza sativa L.)
- Pages: 2141-2151
- First Published: 09 August 2022
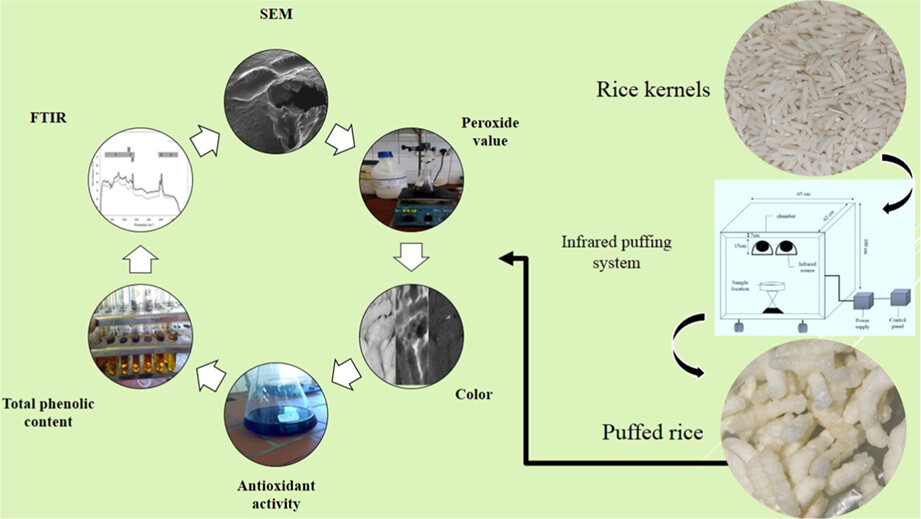
The effect of novel infrared (IR) puffing, various IR power (350, 450 and 550 watts (W)) at various distances (10, 20 and 30 cm) on physicochemical characteristics of puffed rice (puffing properties, color, total phenolic content (TPC), antioxidant activity, peroxide value and morphology) was investigated.
Neuroprotective effects of a novel peptide from Lignosus rhinocerotis against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells by inhibiting NF-κB activation
- Pages: 2152-2165
- First Published: 12 September 2022
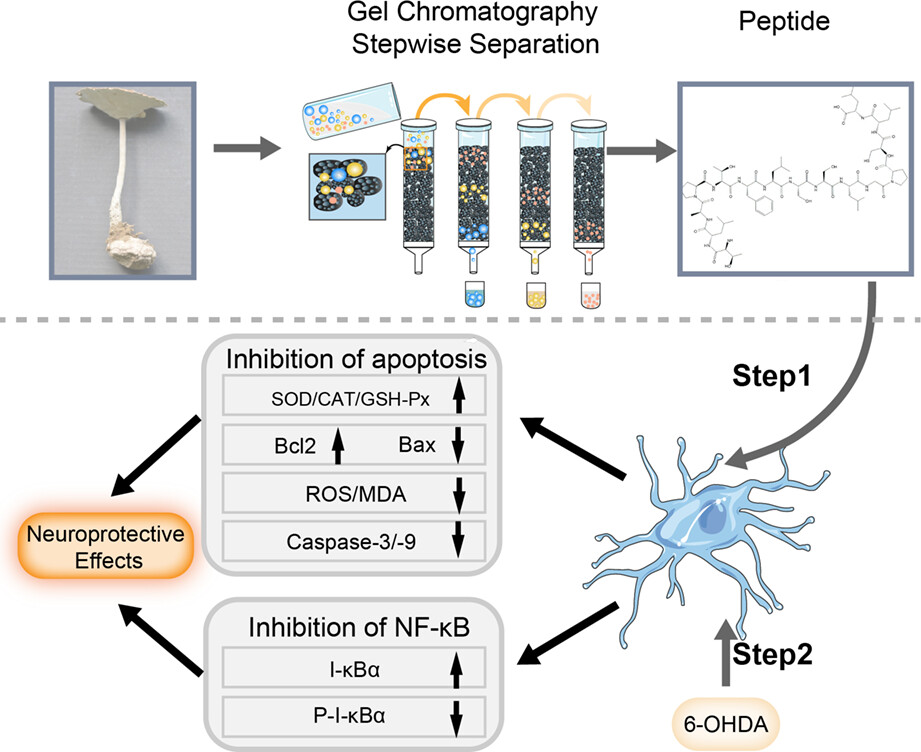
In this study, a novel peptide (LRP) was extracted from the fruiting bodies of L. rhinocerotis using gel filtration chromatography. We determined the amino acid sequence of LRP, which was conducive to its artificial synthesis. Moreover, with NF-κB as the target, the neuroprotective function of LRP was explored. LRP may have the potential to act as a neuroprotective agent.
Prediction of winter wheat leaf chlorophyll content based on VIS/NIR spectroscopy using ANN and PLSR
- Pages: 2166-2175
- First Published: 06 October 2022
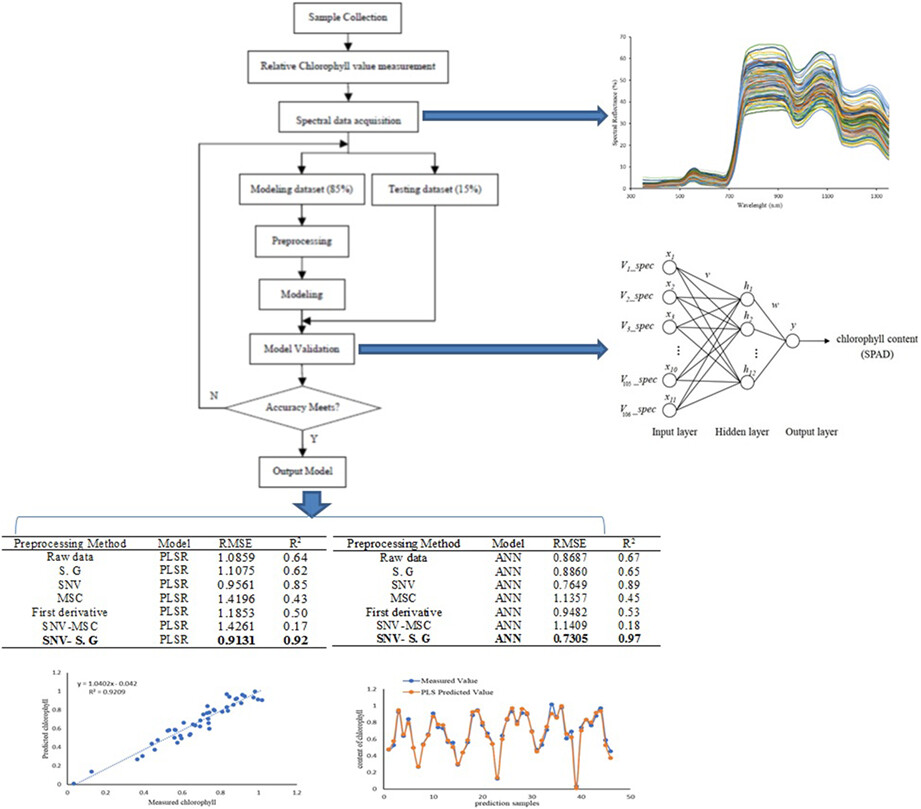
In this research, the amount of winter wheat leaf chlorophyll was nonlinearly predicted by visible–near-infrared spectroscopy by methods of artificial neural networks (ANN) along with partial least squares regression (PLSR). The consequences of estimation of LCC for ANN model (𝑅2 = .97) were better than the PLSR model (𝑅2 = .92).
Mixed fermentation and electrospray drying for the development of a novel stabilized wheat germ powder containing highly viable probiotic cultures
- Pages: 2176-2185
- First Published: 11 January 2023
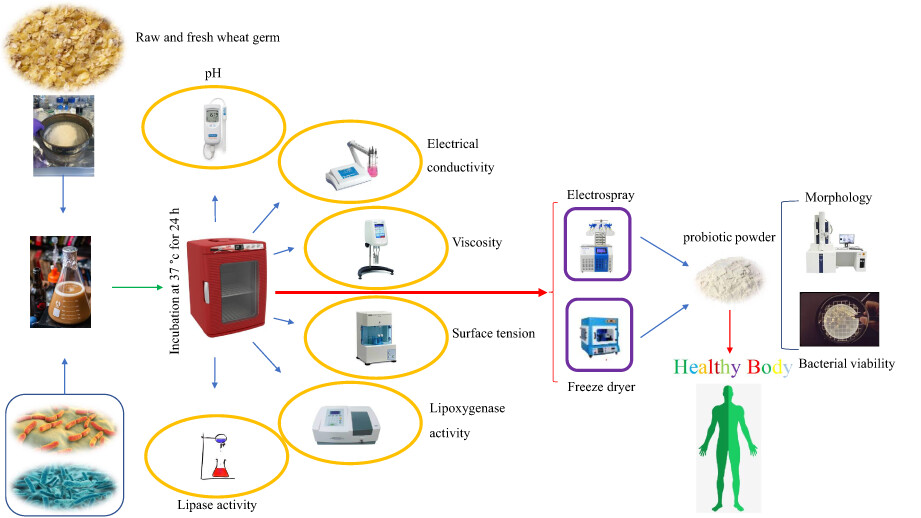
Wheat germ is a potential source of prebiotics though exhibiting an unstable nature; Mixed fermentation reduces the lipase and lipoxygenase activity of wheat germ; Fermented wheat germ solution has good electrosprayability; More than 96% of probiotics maintained their viability in electrospraying process; Electrospraying does less harm to the bacteria in comparison with freeze-drying;
REVIEW ARTICLE
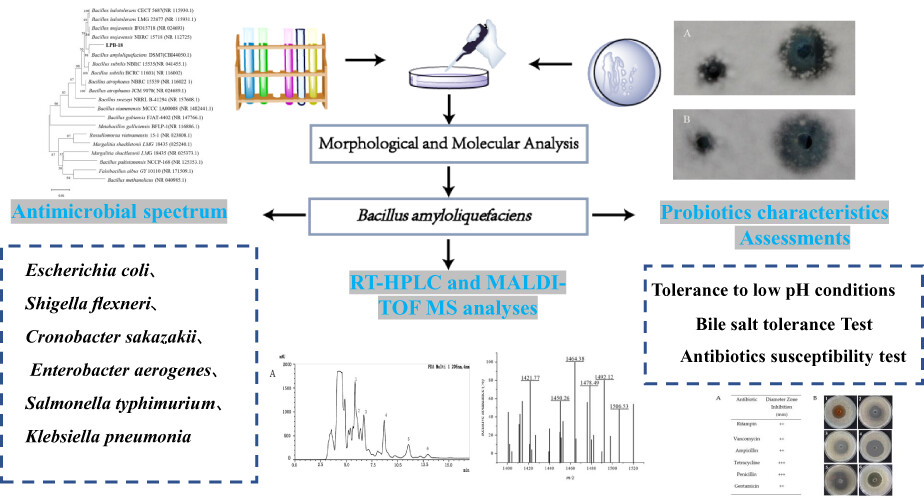
Isolation of a potential probiotic strain Bacillus amyloliquefaciens LPB-18 and identification of antimicrobial compounds responsible for inhibition of food-borne pathogens
- Pages: 2186-2196
- First Published: 12 December 2022
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
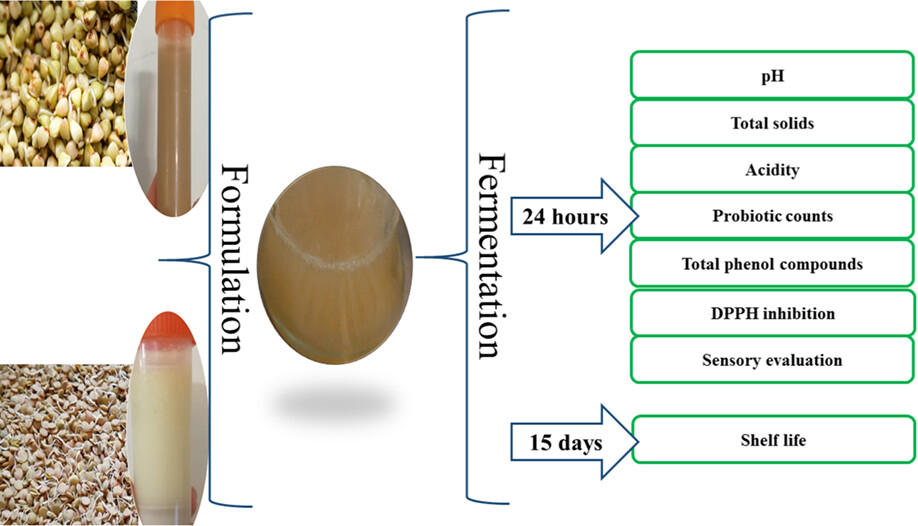
Production and characterization of nondairy gluten-free fermented beverage based on buckwheat and lentil
- Pages: 2197-2210
- First Published: 20 October 2022
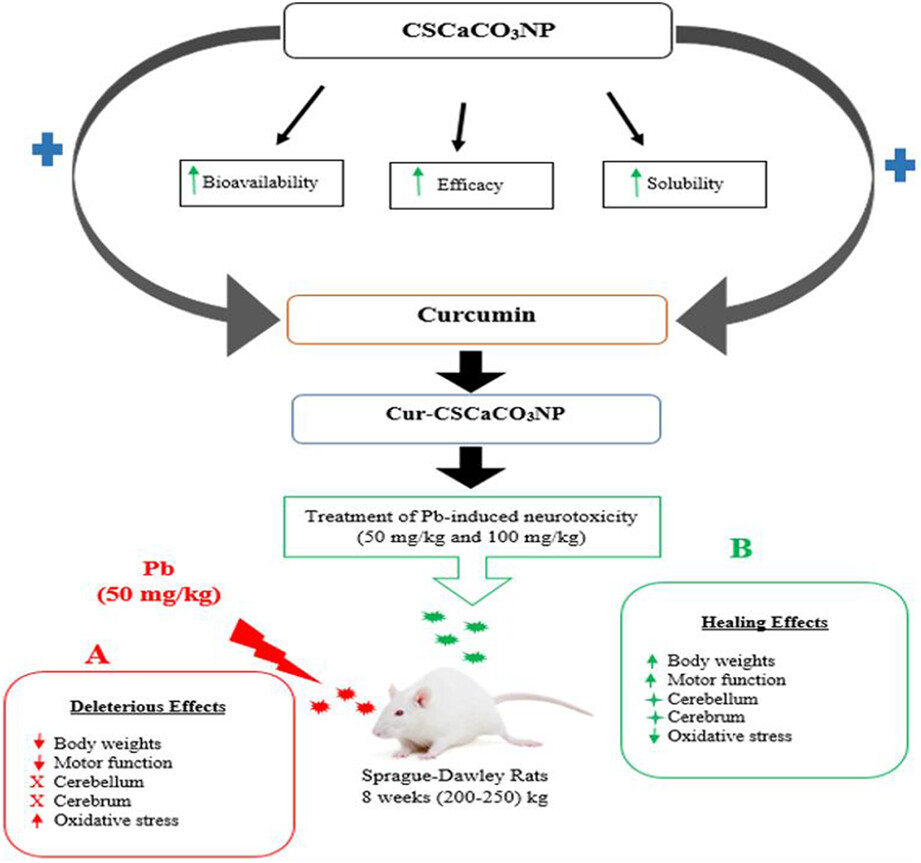
Curcumin-loaded cockle shell-derived calcium carbonate nanoparticles ameliorates lead-induced neurotoxicity in rats via attenuation of oxidative stress
- Pages: 2211-2231
- First Published: 30 October 2022
Miao sour soup influences serum lipid via regulation of high-fat diet-induced intestinal flora in obese rats
- Pages: 2232-2242
- First Published: 07 December 2022
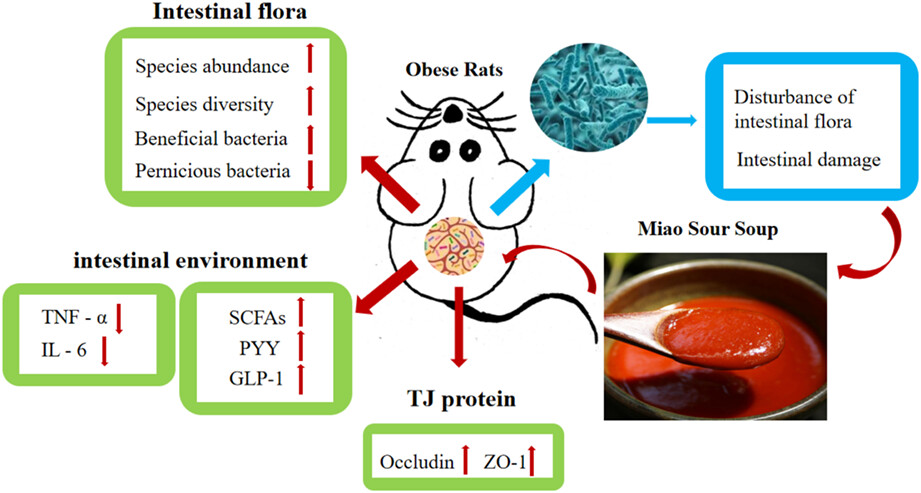
Obesity is a health condition of increasing importance. Obesity has been associated with an imbalance in the intestinal flora. Miao sour soup (SS) contains abundant short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which can be used as energy substrates to selectively stimulate the growth and reproduction of intestinal flora. This study aims to determine whether SS intervention could restore the imbalanced intestinal flora of rats with high-fat diet-induced obesity. We found improvements in the abundance and diversity of the intestinal flora, and a significant reduction in weight and serum lipid levels following intervention with SS. We believe that our study makes a significant contribution to the literature because our findings demonstrate the therapeutic potential of dietary intake of SS in achieving weight loss and reducing serum lipid levels, thus ameliorating the effects of obesity induced by high-fat diet.
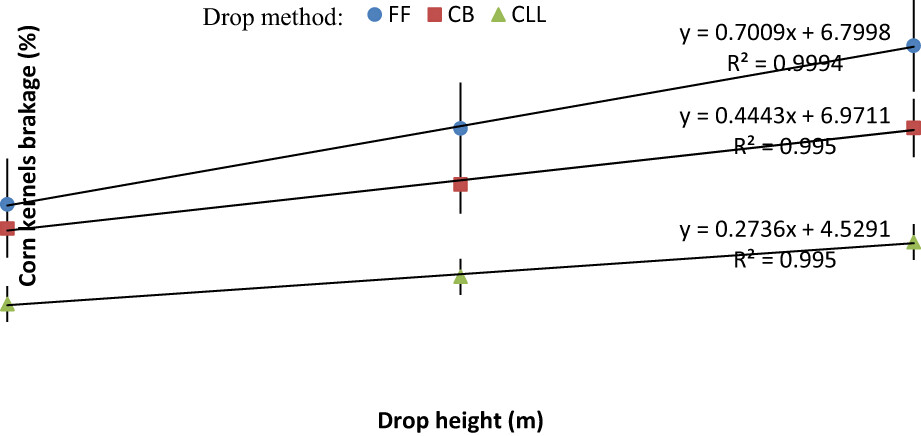
Effects of cushion box and closed let-down ladder usage on impact damage to corn kernel during handling
- Pages: 2243-2253
- First Published: 14 November 2022
EDITORIAL
The screening and prediction of functional/bioactive compounds in foods: Editorial; how to efficiently discover functional/bioactive compounds in foods?
- Pages: 2254-2255
- First Published: 15 November 2022
REVIEW ARTICLE
Nutritional and bioactive characteristics of buckwheat, and its potential for developing gluten-free products: An updated overview
- Pages: 2256-2276
- First Published: 22 December 2022
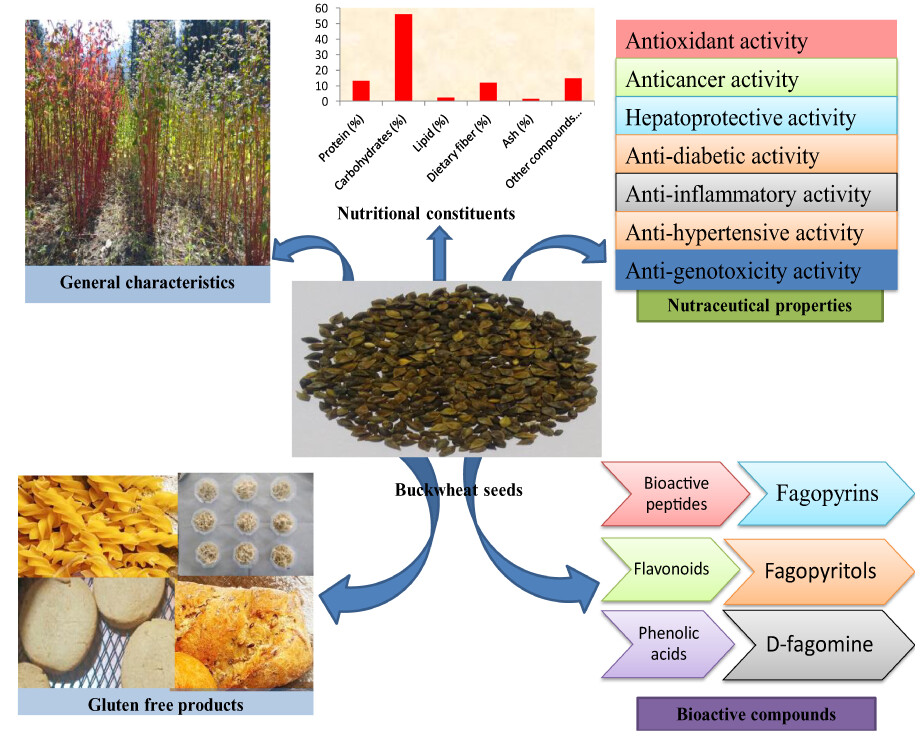
Buckwheat is one of the functional pseudocereals with nutraceutical components to target health-related diseases, malnutrition, and celiac. In recent years, buckwheat-related food products with good sensory and techno-functional qualities attractive the food market with health benefits and suitable food for people with gluten intolerance. Incorporating buckwheat in product formulation would help mitigate various health-related problems and gluten-free products with nutrient-dense ingredients.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Effects of sulforaphane on breast cancer based on metabolome and microbiome
- Pages: 2277-2287
- First Published: 31 March 2023
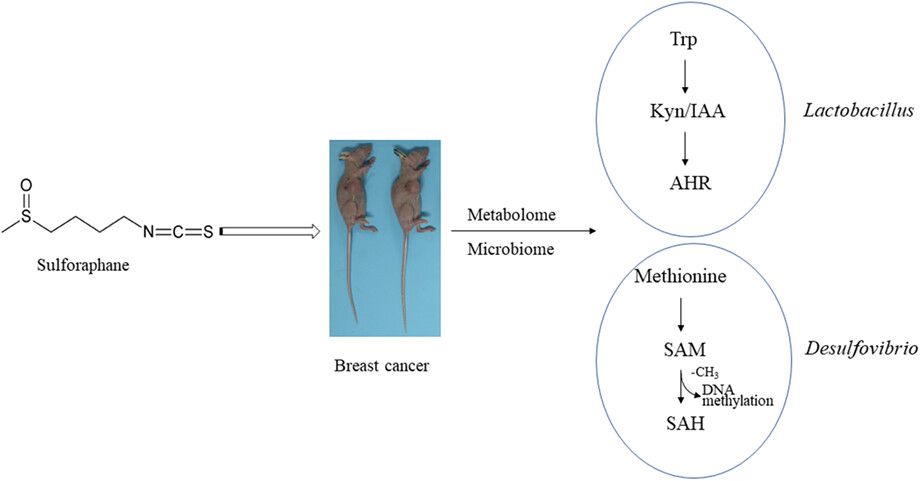
This paper provided promising insights into the role of SFN on breast cancer based on metabolome and microbiome. SFN influenced one-carbon metabolism, especially the ratio of SAM to Methionine, by which SFN can regulate DNA methylation and gene expression. SFN altered the diversity of gut microbiota to indirectly affect the methylation activity and antitumor activities by AHR signaling pathway.
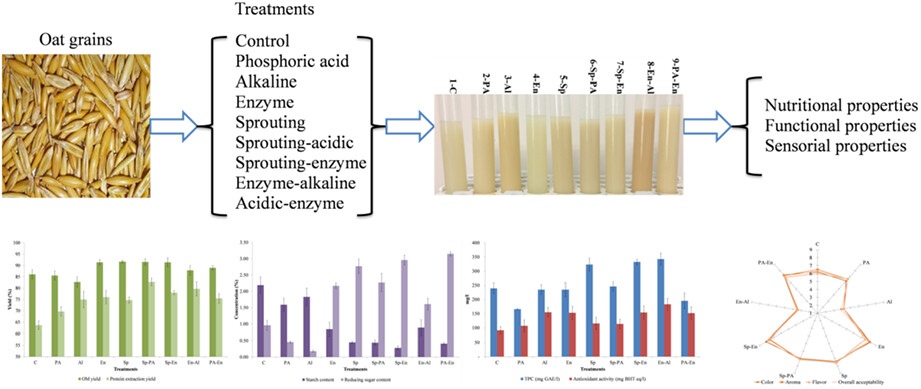
Nutritional, functional, and sensorial properties of oat milk produced by single and combined acid, alkaline, α-amylase, and sprouting treatments
- Pages: 2288-2297
- First Published: 08 December 2022
Characterization of brewer's spent grain extracts by tandem mass spectrometry and HPLC-DAD: Ferulic acid dehydrodimers, phenolamides, and oxylipins
- Pages: 2298-2320
- First Published: 21 December 2022
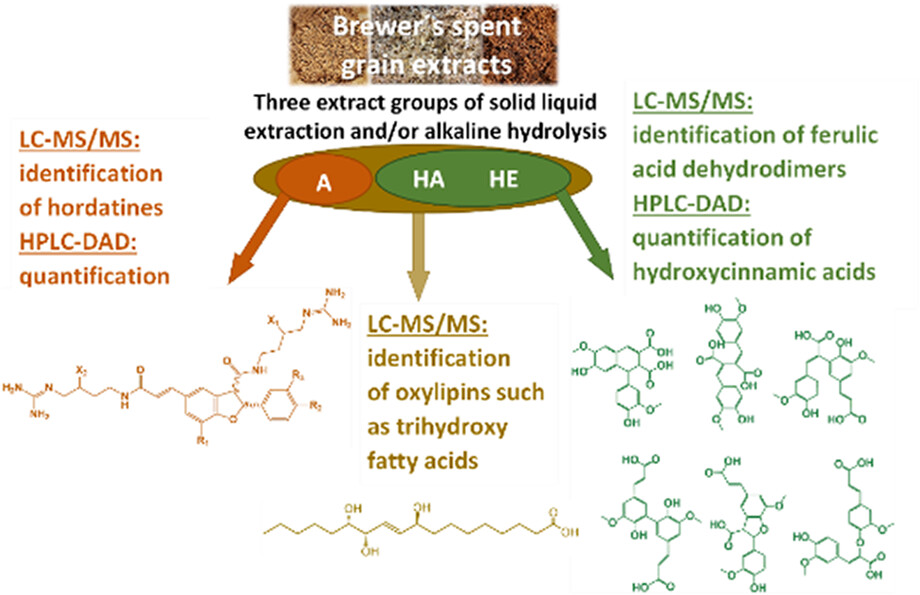
Different brewer´s spent grain extracts prepared by solid-liquid extraction were analysed for their main compounds via LC-MS/MS and HPLC-DAD. High amounts of hordatines and some other phenolamides as well as oxylipins were detected in these extracts. Extracts prepared by alkaline hydrolysis mainly contained hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives such as ferulic and p-coumaric acid as well as ferulic acid dehydrodimers and also oxylipins.
LC/MS analysis of mushrooms provided new insights into dietary management of diabetes mellitus in rats
- Pages: 2321-2335
- First Published: 27 January 2023
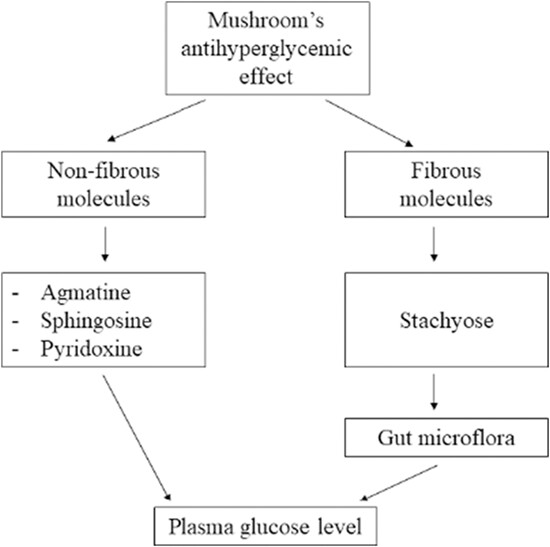
The effect of mushroom's bioactive compounds on plasma glucose level. Agmatine increases insulin secretion and glucose uptake in muscle. Sphingosine activates omega-3 fatty acid receptor (GPR120) mediating potent insulin-sensitizing effects. Pyridoxine decreases insulin resistance. Stachyose regulates the intestinal microflora balance.
Effect of the germination period on functional properties of finger millet flour and sensorial quality of porridge
- Pages: 2336-2343
- First Published: 07 February 2023
Germination enhanced the water absorption capacity, solubility, and oil absorption capacity of flour samples but reduced the bulk density and swelling power of flour samples. Twenty-four-hour germinated finger millet flour is best in all aspects compared to ungerminated, 48- and 72-h germinated flours to prepare porridge. The 24-h germinated finger millet-based porridge is recommended for infants, pregnant mothers, and breastfeeding mothers.
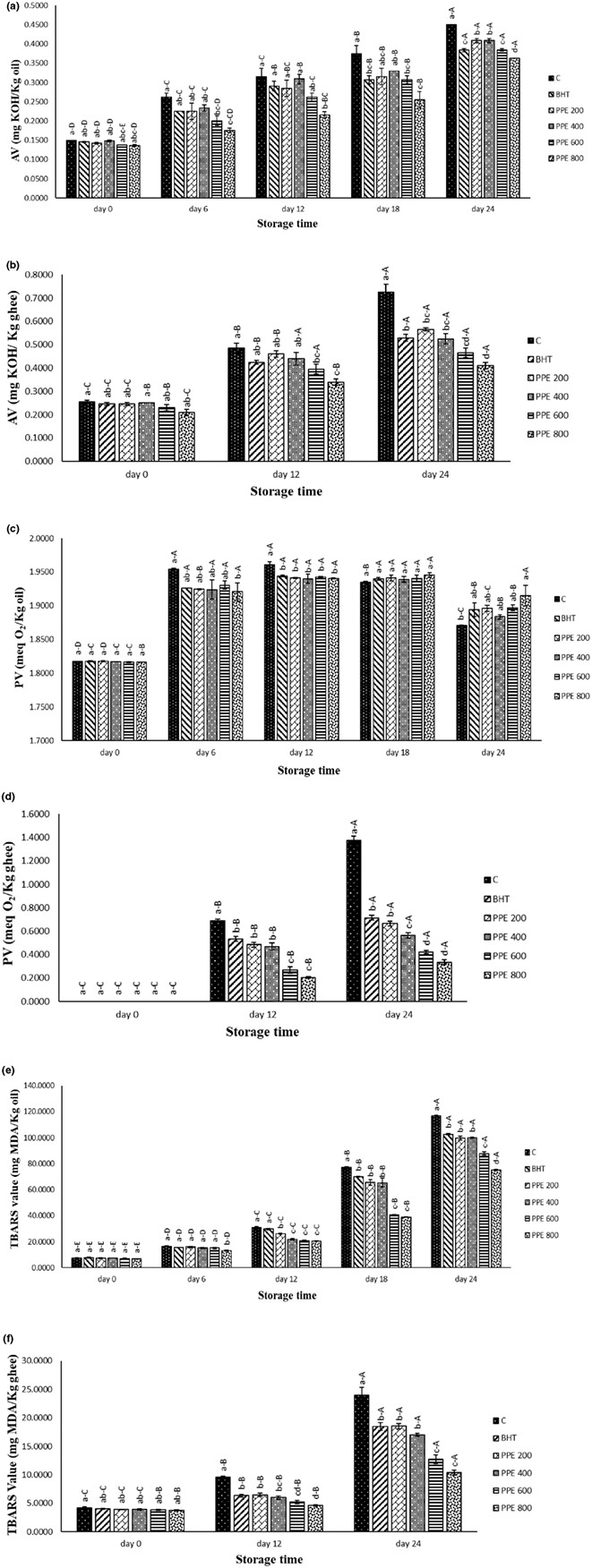
Influence of extraction techniques on the efficiency of pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) peel extracts in oxidative stability of edible oils
- Pages: 2344-2355
- First Published: 04 February 2023
Effects of Poria cocos extract and protein powder mixture on glucolipid metabolism and rhythm changes in obese mice
- Pages: 2356-2371
- First Published: 09 March 2023
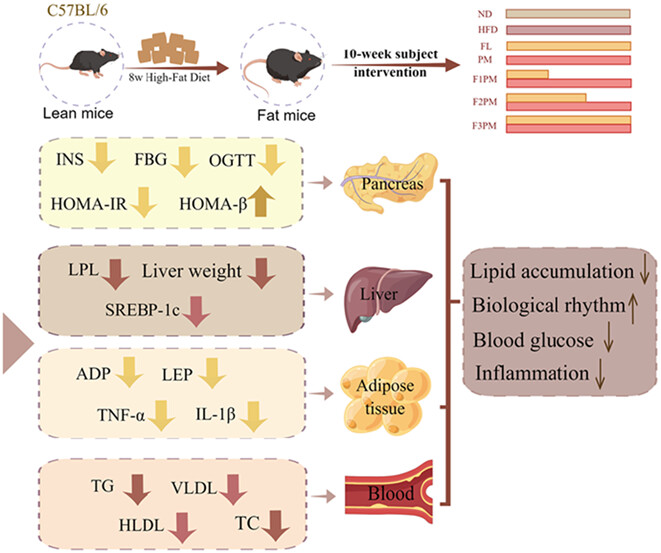
The intervention of poria cocos extract and protein powder can effectively improve the disorder of glucose and lipid metabolism and contribute to the recovery of biological rhythm. Compared with the use of P. cocos extract and protein powder alone, the combined supplementation of F3PM has more health benefits.
Qualitative analysis of the perceptions of rural communities about the use of awareness-raising videos in nutrition and health programs in Benin
- Pages: 2372-2381
- First Published: 01 February 2023
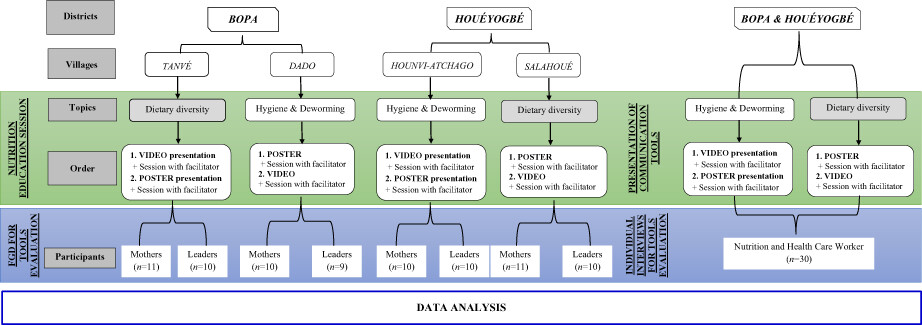
Awareness-raising videos in local languages were perceived as highly attractive, understandable, and adapted to rural communities for nutrition and health messages dissemination. Videos are not suitable for all nutrition and health messages and their use in rural areas condition faces some constraints such as the absence of electricity and lack of adequate equipment.
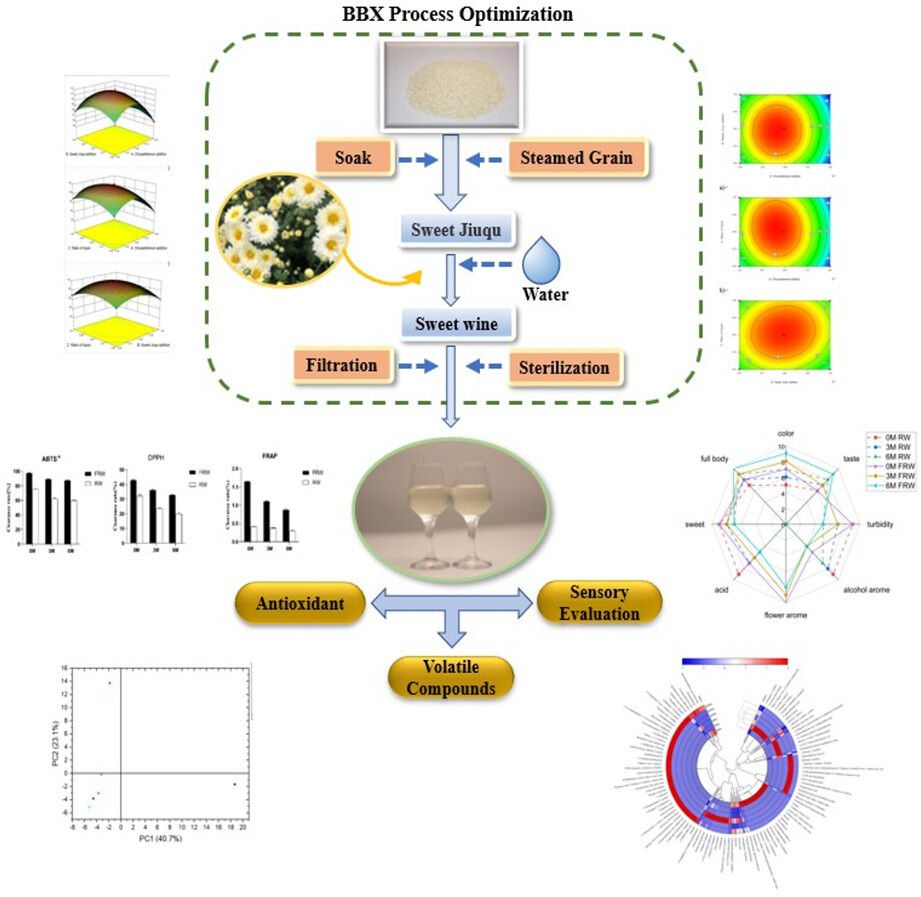
The volatile flavor and the antioxidant properties of a novel chrysanthemum rice wine during natural aging
- Pages: 2382-2392
- First Published: 28 February 2023
REVIEW ARTICLE
Effect of olive oil phenols on oxidative stress biomarkers: A systematic review and dose–response meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials
- Pages: 2393-2402
- First Published: 13 March 2023
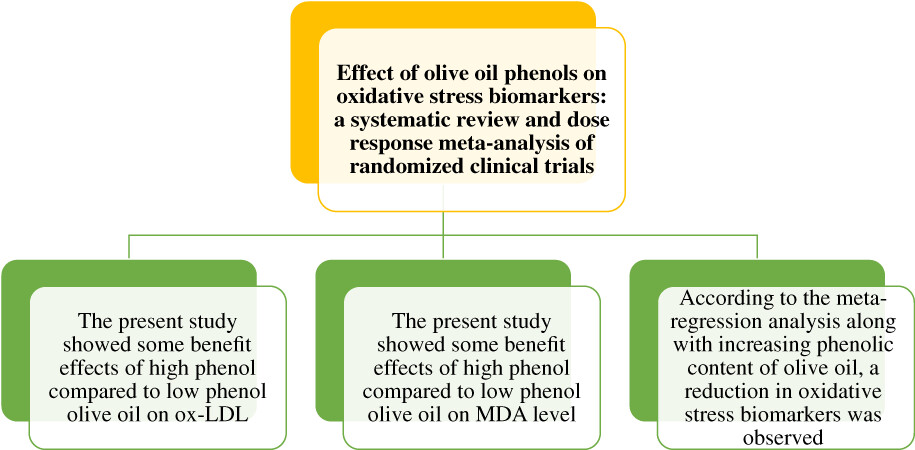
The aim of this study was to summarize the results of clinical trials which assessed the effects of high- versus low-phenol olive oil on oxidative stress biomarkers level. We searched Scopus, PubMed, Web of Science, Google Scholar, ProQuest, and Embase up to July 2021. Dose–response analysis indicated a significant linear relationship between the phenolic content of olive oil and Ox-LDL. The present study showed some beneficial effects of high-phenol compared with the low-phenol olive oil on Ox-LDL and MDA levels.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
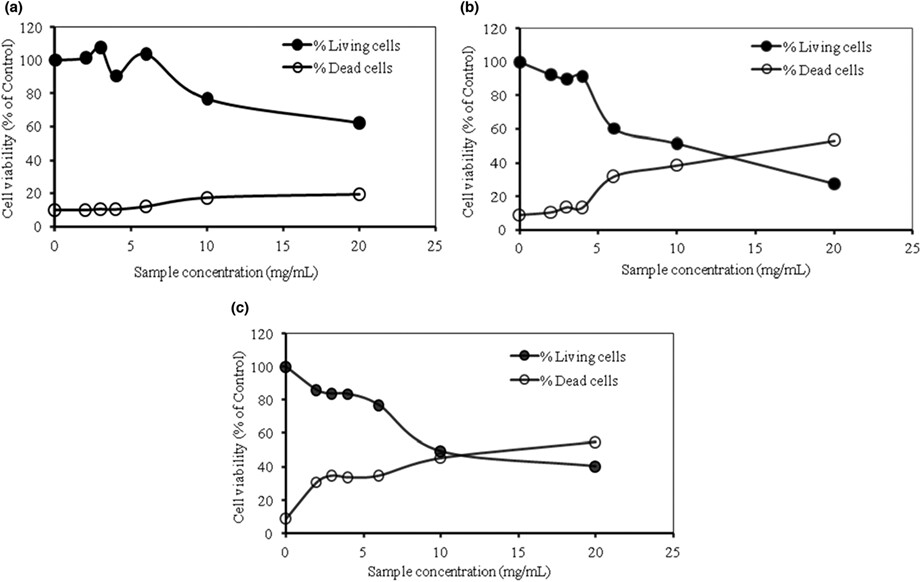
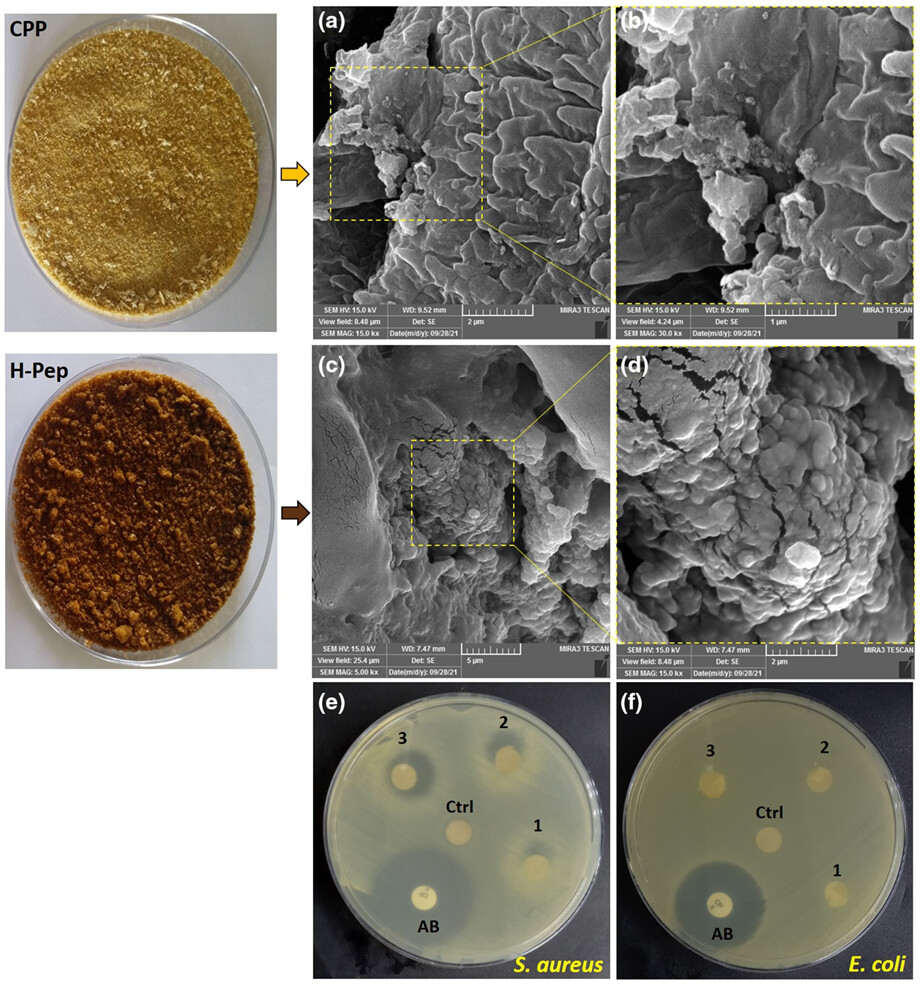
Physicochemical, antioxidant, antimicrobial, and in vitro cytotoxic activities of corn pollen protein hydrolysates obtained by different peptidases
- Pages: 2403-2417
- First Published: 14 February 2023
Curcumin/cyclodextrin polymer inclusion complex attenuates ethanol-induced liver injury by inhibition of DNA damage in mice
- Pages: 2418-2426
- First Published: 02 February 2023
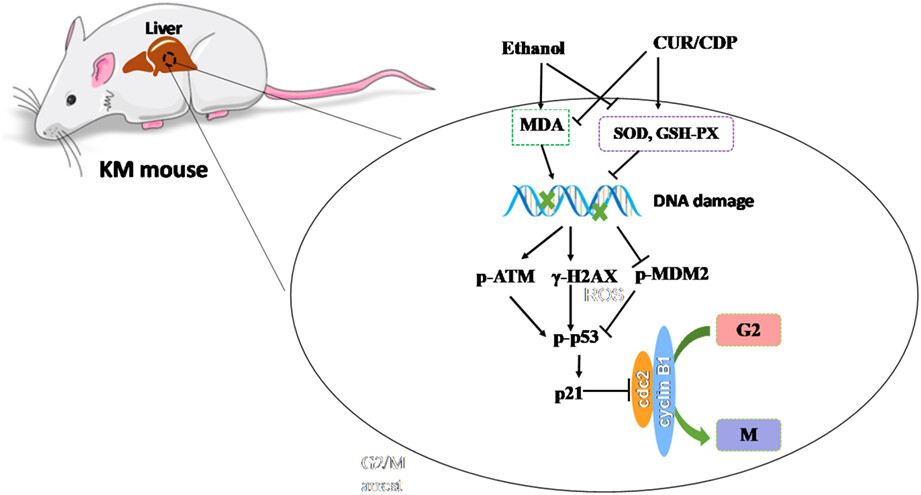
CUR/CDP exhibited excellent protective effect on ethanol-induced liver injury in mice in a dose-dependent manner, which was attributed to its antioxidant activity that alleviated oxidative stress by improvement activities of antioxidant enzymes and inhibition of lipid peroxidation, thereby avoiding DNA damage-induced G2/M arrest. CUR/CDP had the potential to be used as a novel drug or supplement for the prevention of alcoholic liver injury.