Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER PICTURES
Front Cover: Photodynamic opening of the blood-brain barrier and pathways of brain clearing (J. Biophotonics 8/2018)
- First Published: 08 August 2018
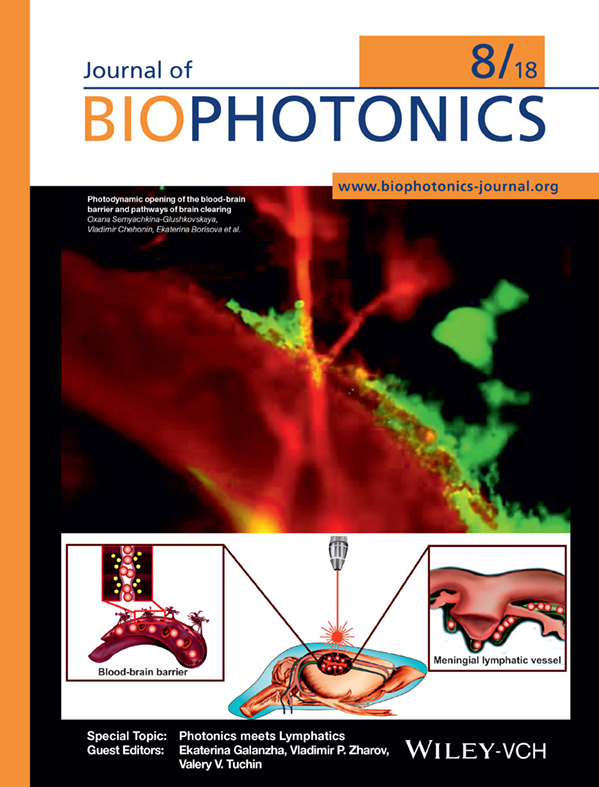
Fluorescent microscopy of the brain clearing from the FITC-dextran (red color) via the meningeal lymphatic vessels (green color, labelled by specific antibodies LYVE-1 conjugated with Alexa 488). The FITC-dextran injected intravenously immediately is observed in the Sagittal sinus (the main cerebral vein) and after photodynamic opening of blood-brain barrier it is also presented in the meningeal lymphatic vessels due to activation of brain clearing from accumulated the FITC-dextran in the brain parenchyma.
Further details can be found in the article by Oxana Semyachkina-Glushkovskaya, Vladimir Chehonin, Ekaterina Borisova, et al. (e201700287)
Inside Front Cover: Label-free bacterial colony detection and viability assessment by continuous-wave terahertz transmission imaging (J. Biophotonics 8/2018)
- First Published: 08 August 2018

A rapid, simple and one-step method for analyzing bacterial colonies was proposed using a continuous-wave terahertz (THz) imaging system in this study. The distribution of mixed bacterial colonies has been detected, and the target bacterium could also be easily recognized in mixed samples. The results clearly demonstrate the potential usage of THz imaging for bacterial colony sensing in a label-free and nondestructive manner. Further details can be found in the article by Xiang Yang, Jia Shi, Yuye Wang et al. (e201700386).
Inside Cover: Effect of tissue staining in quantitative phase imaging (J. Biophotonics 8/2018)
- First Published: 08 August 2018

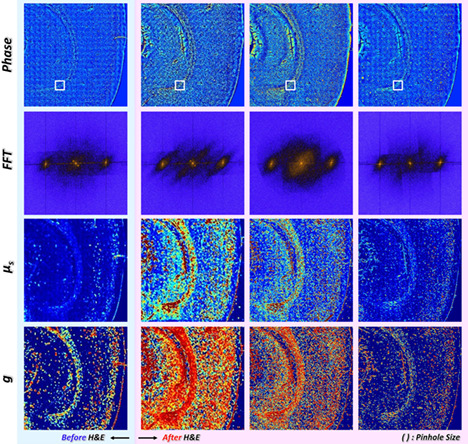
The effect of tissue staining in wide-field quantitative phase imaging is negligible when using a light source out of the absorption spectrum.
Further details can be found in the article by Sungbea Ban, Eunjung Min, Yujin Ahn, Gabriel Popescu, and Woonggyu Jung (e201700402)
Inside Back Cover: Sensitive Leptospira DNA detection using tapered optical fiber sensor (J. Biophotonics 8/2018)
- First Published: 08 August 2018
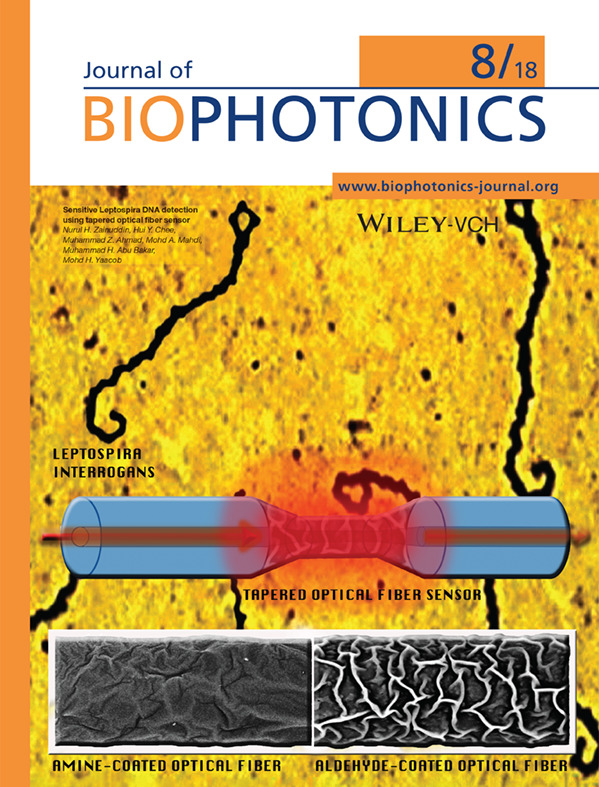
The background microscopic image shows leptospira interrogans bacteria, the source of Leptospirosis, a deadly disease but with common early flu-like symptoms and likely leads to under-diagnosed. Highly sensitive leptospira DNA sensor is developed using tapered optical fiber as shown by the schematic image. Laser transmits in the optical fiber interacts with the functionalized amine and aldehyde coatings (bottom images) to produce wavelength shifts upon DNA exposure around the tapered region.
Further details can be found in the article by Nurul H. Zainuddin, Hui Y. Chee, Muhammad Z. Ahmad et al. (e201700363).
Back Cover: Assessment of the dynamics of human glymphatic system by near-infrared spectroscopy (J. Biophotonics 8/2018)
- First Published: 08 August 2018

A functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) based approach to non-invasive monitoring of the (g)lymphatic system in the human brain. The cover figure shows depth sensitivity of fNIRS, particularly at the wavelength of 980 nm, for sensing dynamic variations of water and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) volume, e.g. in the subarachnoid space. Observed fluctuations in water content correlated with magnetic resonance encephalography (MREG) signals during visual task, further, are assumed to be connected with the glymphatic circulation.
Further details can be found in the article by Teemu Myllylä, Markus Harju, Vesa Korhonen, et al. (e201870154)
ISSUE INFORMATION
Special Topic: Photonics meets Lymphatics
EDITORIAL
Biophotonics for lymphatic theranostics in animals and humans
- First Published: 13 July 2018
FULL ARTICLES
Simultaneous measurements of lymphatic vessel contraction, flow and valve dynamics in multiple lymphangions using optical coherence tomography
- First Published: 12 July 2017
Dysfunction of the lymphatic system plays a role in many disease processes, including lymphedema, hypertension, microbial infections and cancer. Expanding our knowledge of lymphatic system function can lead to a better understanding of these disease processes and improve treatment options. Here, the first measurements to characterize lymphatic vessel function in multiple segments were made in a living animal to begin to unravel how the lymphatic system is coordinated in normal and disease settings.
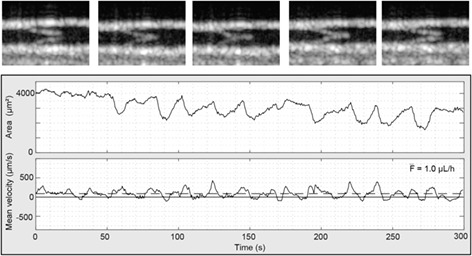
High-speed microscopy for in vivo monitoring of lymph dynamics
- First Published: 12 December 2017
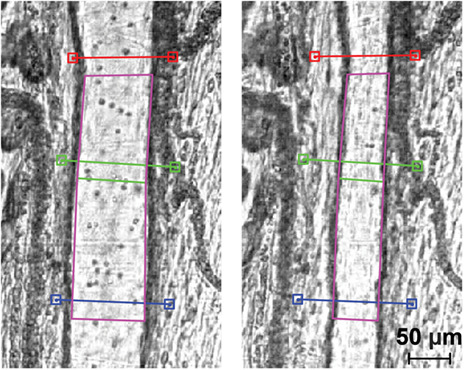
An imaging system for in vivo continuous monitoring of lymph vessels (LVs) and quantification of lymphatic function was developed. High frame rate bright-field videos of LVs were processed to automatically detect vessel diameter and flow velocity. System performance was tested on in vitro test samples and on a rat model of intestinal lymphadenectomy. Reduced LV contraction and flow rate were detected after surgical lymphadenectomy of the rat mesentery.
EDITOR'S CHOICE
Label-free volumetric imaging of conjunctival collecting lymphatics ex vivo by optical coherence tomography lymphangiography
- First Published: 19 June 2018
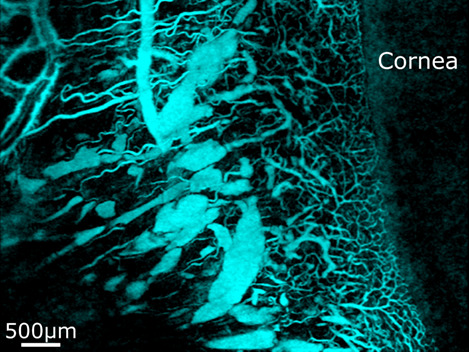
This study employs optical coherence tomography lymphangiography to image conjunctival lymphatics in porcine eyes ex vivo. The vessel segmentation, using the optical transparency of lymphatic and blood vessels, presents the ready visualization of vessel networks and indicates the varying spatial distribution of patent lymphatics. Such visualization of the conjunctival vessels provides a valuable reference on vessel morphology for subsequent in vivo label-free imaging studies of lymphatics. OCT lymphangiography imaging of conjunctival vessels from the surface to 350 μm deep.
FULL ARTICLES
Indocyanine green near-infrared lymphangiography for evaluation of effectiveness of edema fluid flow under therapeutic compression
- First Published: 20 July 2017
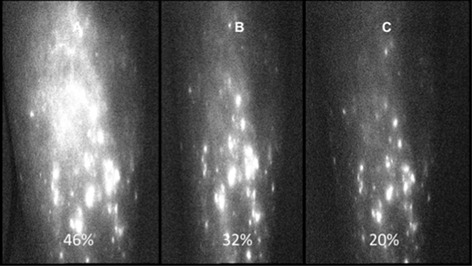
Lymphedema of limbs is caused by obstruction of main lymphatic channels with subsequent accumulation of excess tissue fluid (lymph) in tissue spaces. It is treated by manual, mechanical pneumatic and bandage compression of swollen tissues. Evaluation of results is based on measurement of girth and volume of the limb. However, these methods do not give insight into how does edema fluid move during external compression. The indocyanine green lymphography enables live observation of fluid flow and sites of its relocation where absorption takes place. Imaging and estimation of local fluorescence level provide information of the efficacy of the applied compression method. Decreasing level of fluorescence is seen on consecutive pictures.
Imaging lymphatics in human normal and lymphedema limbs—Usefulness of various modalities for evaluation of lymph and edema fluid flow pathways and dynamics
- First Published: 31 August 2017
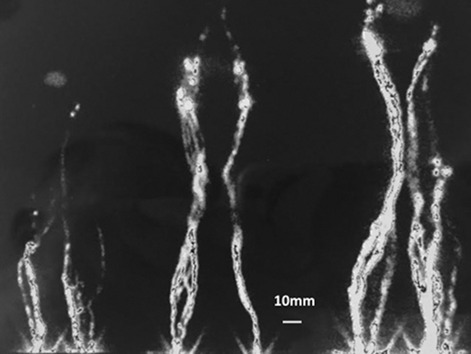
The lymphatic system in human tissues regulates the physico-chemical environment of cells by maintaining hydration, ions, nutritional and regulatory substances levels, draining away the metabolic products, senescent and damaged cell debris, and nonself antigens penetrating body as bacteria and viruses. Intercellular space is connected to a network of lymphatic vessels starting from capillaries and ending up as a 5 mm diameter wide thoracic duct merging with jugular-subclavian vein. All segments contract spontaneously rhythmically depending on how much lymph fluid fills them up. How does the lymphatic network look like in human limbs? Lymphoscintigram depicts main lower limb vessels between most distant tissues and the inguinal lymph nodes acting as a biological filters. Imaging lymphatics in human normal and lymphedema limbs—usefulness of various modalities for evaluation of lymph and edema fluid flow pathways and dynamics.
Optimal range of injection rates for a lymphatic drug delivery system
- First Published: 20 February 2018
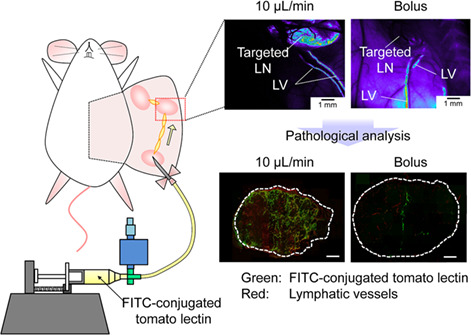
A lymphatic drug delivery system (LDDS) allows drugs to be injected into upstream lymph nodes (LNs) and to deliver drugs to downstream LNs via the lymphatic vessels. Here, we evaluated drug deliverability during the development of LDDS in MXH10/Mo-lpr/lpr mice with swollen LNs up to 10 mm in diameter. The distribution of fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled tomato lectin into the downstream LN was dependent on the injection rates into the upstream LN.
Photodynamic opening of the blood-brain barrier and pathways of brain clearing
- First Published: 30 January 2018
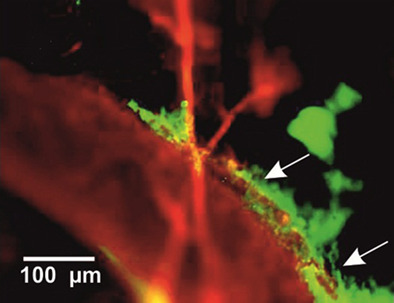
It is a crucial physiological role of blood-brain barrier to protect the central nervous system against pathogens and toxic substances. However, this protective mechanism limits 98% of the beneficial drugs delivery as well. Our results contribute to a better understanding of the cerebrovascular effects of photodynamic treatment (PDT) and shed light on mechanisms, underlying brain clearing after PDT-related opening of blood-brain barrier, including clearance from nanoparticles as drug carriers.
Assessment of the dynamics of human glymphatic system by near-infrared spectroscopy
- First Published: 12 August 2017
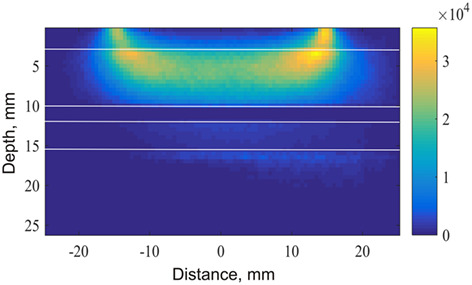
Monte Carlo-simulated scattering map for photons at a wavelength of 980 nm propagating inside the human head model. Most scattering takes place in the skull layer. However, a significant amount of photons travels further through the areas where cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flows. Our experiments demonstrate that using 980 nm in combination with 830 and 660 nm or 740 nm allows the simultaneous sensing of dynamic variations in water volume and haemodynamics in the human brain cortex. Observed fluctuations are assumed to be correlated with the dynamics of glymphatic circulation.
PERSPECTIVES & TRENDS
EDITOR'S CHOICE
Current status, pitfalls and future directions in the diagnosis and therapy of lymphatic malformation
- First Published: 29 August 2017
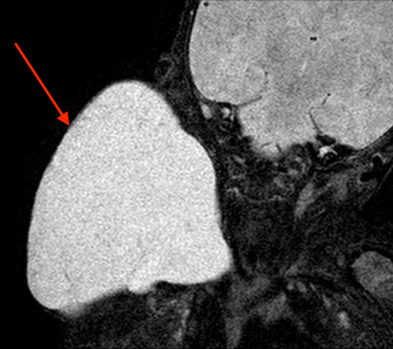
Lymphatic malformations are complex vascular lesions composed of abnormal lymph vessels that can result in significant esthetic and physical impairment due to relentless growth. Here, we review the capability and limitations of current imaging technologies (e.g., ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging) to diagnose lymphatic malformations, and discuss perspectives to overcome existing challenges using new and emerging methods of vascular imaging and characterization such as the integration of photoacoustics, nanotechnology, and optical clearing for the advanced diagnosis and therapy (theranostics) of lymphatic malformations.
Utilizing lymphatic cell markers to visualize human lymphatic abnormalities
- First Published: 04 September 2017
Regular Contributions
LETTERS
Gold/silver/gold trilayer films on nanostructured polycarbonate substrates for direct and label-free nanoplasmonic biosensing
- First Published: 01 May 2018
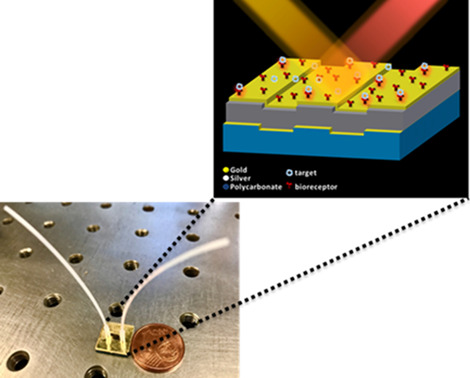
Gold/silver/gold nanostructured sensors based on commercial Blu-ray optical discs as substrates and with integrated microfluidics have been designed and optimized. Ultrasmooth and chemically stable trilayer nanoslit-based nanostructures were obtained following a simple and reproducible fabrication process. The direct and label-free detection of C-reactive protein (CRP) biomarker in undiluted urine was achieved with a LOD in the pM order.
FULL ARTICLES
Spatio-temporal map for early cancer detection: Proof of concept
- First Published: 07 February 2018
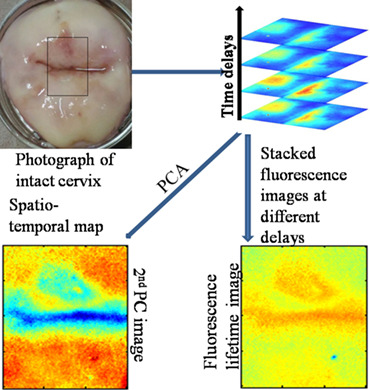
Cervical cancer is the leading cause of death in women; it has no symptoms until the cancer stage. Hence, early diagnosis becomes extremely crucial. The environment of a natural fluorophore is probed through fluorescence lifetime and is useful in monitoring the development of cancer. Detection of abnormal region is enhanced by application of principal component analysis on FLIM images.
Red blood cell membrane damage by light-induced thermal gradient under optical trap
- First Published: 02 March 2018

Rapid membrane damage of optically trapped red blood cells (RBCs) was observed presumably due to temperature gradient-induced electropermeabilization effect. When RBCs from type II diabetic patients were studied, a noticeable change in the damage rate compared to normal RBCs was seen suggesting a novel optical diagnosis method for the disease.
Wavelength-dependent scattering in human eye with cataracts
- First Published: 02 March 2018
Early cataract formation is foretold by comparing scattering radial profiles light pattern distributions reflected upon the retina at 2 different wavelengths. The computational model developed presents wavelength-dependent scattering distributions with angular crossovers in them. We obtained that the crossover angular point is inversely proportional to the size of the particle distributions associated with the nucleation precursor of eye cataracts.
In vitro photoacoustic spectroscopy of pulsatile blood flow: Probing the interrelationship between red blood cell aggregation and oxygen saturation
- First Published: 12 February 2018
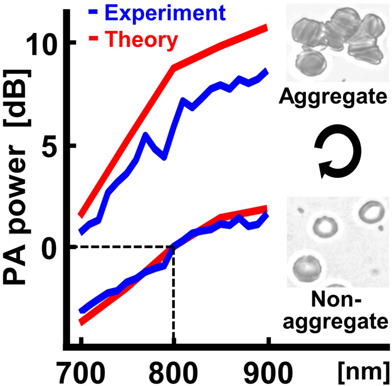
We propose that the quantitative photoacoustic spectroscopy of pulsatile blood flow can be a potential tool for probing hemodynamics and oxygen transport. Red blood cell aggregation during the pulsatile blood flow simultaneously affects the absorber size and the oxygen saturation (and, in turn, the absorption coefficient), so that the increasing slope of photoacoustic power as a function of wavelength for aggregation is steeper than that for nonaggregation.
Label-free quantification of the effects of lithium niobate polarization on cell adhesion via holographic microscopy
- First Published: 06 February 2018
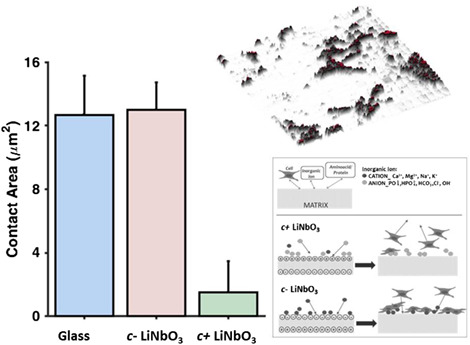
The surface of a c− cut ferroelectric crystal at room temperature is characterized by screening surface charges, able to compensate the charge due to the spontaneous polarization. Here, we use holographic TIR microscopy show that cell adhesion is significantly different between the positive and negative face of a crystal of lithium niobate.
Intravital molecular tagging velocimetry of cerebral blood flow using Evans Blue
- First Published: 30 March 2018
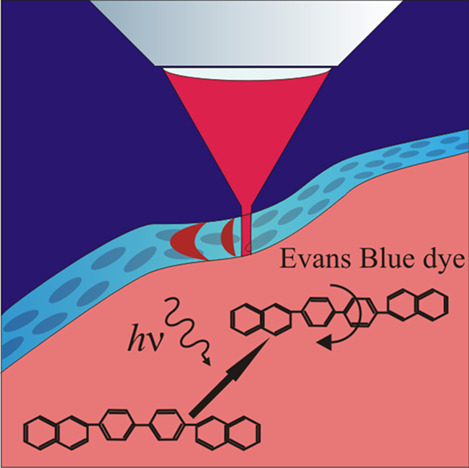
Light driven enhancement of fluorescence of Evans Blue dye complexes with blood plasma proteins was detected. It was observed both in vitro and in vivo. The possible background of the effect concerns the photochemical cis-trans isomerization of the dye molecules. We applied the effect for intravital molecular tagging velocimetry of the blood flow in a living animal circulating system that was performed for the first time..
EDITOR'S CHOICE
Assessing glycation-mediated changes in human cortical bone with Raman spectroscopy
- First Published: 25 March 2018
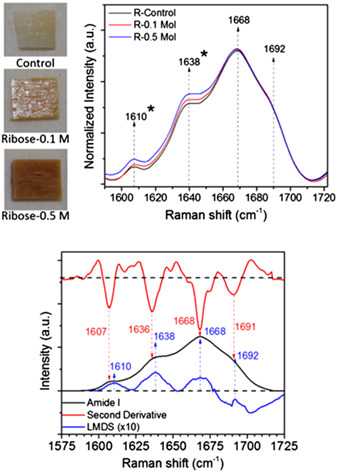
Accumulation of advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) within bone matrix is thought to adversely affect fracture resistance. Yet, there is no non-destructive method to assess effects of AGEs on collagen I structure. Herein, we demonstrate the use of Raman spectroscopy to detect glycation-mediated changes in human bone ex vivo and highlight the effects of data collection and processing on probing spectral changes. Amide I sub-peak ratios are sensitive to AGE accumulation.
FULL ARTICLES
Polarized light microscopy for 3-dimensional mapping of collagen fiber architecture in ocular tissues
- First Published: 06 April 2018
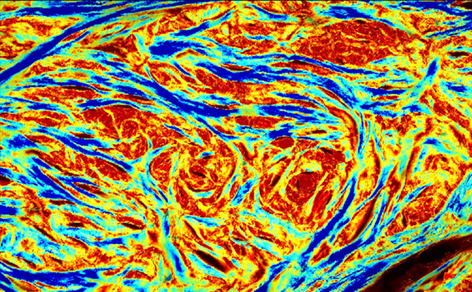
Ocular tissues have a complex collagen architecture, with fibers exhibiting 3D orientation, with both and orientations. Imaging techniques traditionally applied to the study of ocular tissues only quantify in-plane (IP) fiber orientation, providing little information on out-of-plane (OP) fiber orientation. 3dPLM, a technique based on polarized light microscopy, was developed to quantify both IP and OP fiber orientations of ocular tissues.
Sensitive Leptospira DNA detection using tapered optical fiber sensor
- First Published: 23 March 2018
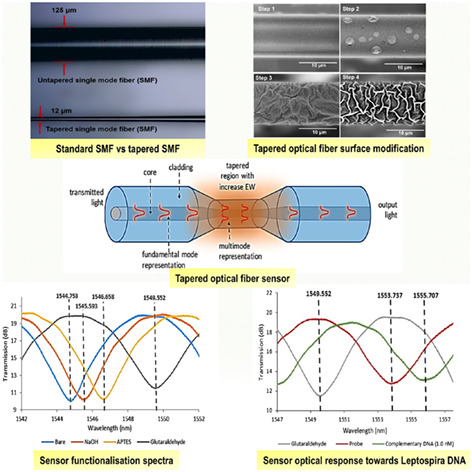
We developed a novel optical fiber sensor to detect DNA of Leptospira bacteria that causes Leptospirosis, a deadly disease typically spread by rodents. The challenge in the disease early detection is its symptoms are similar to flu. Significant sensitivity improvement in femtomolar concentrations is achieved by tapering (shrinking) and functionalizing the fiber toward the bacteria DNA. The sensor response is unique and highly potential for the disease early detection kit.
Isotropic differential phase contrast microscopy for quantitative phase bio-imaging
- First Published: 16 May 2018
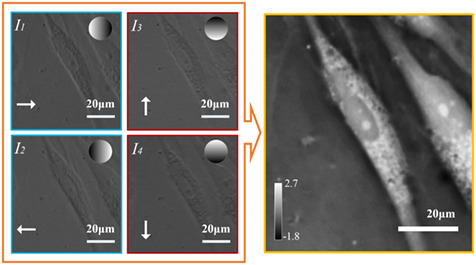
The left-hand side panel shows individual phase contrast images in isotropic differential phase contrast (iDPC) dataset with corresponding gradient amplitude mask on top-right side. White arrows denote phase gradient direction of each phase contrast image. The figure in right-hand side is quantitative phase image of alive human adipose-derived stem cells reconstructed using iDPC dataset.
An ultra-low-cost smartphone octochannel spectrometer for mobile health diagnostics
- First Published: 30 March 2018
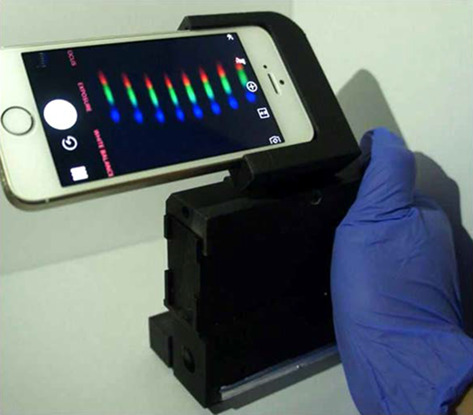

A portable and low-cost smartphone octochannel spectrometer (SOS) that enables simultaneous detection of optical spectra of 8 samples. In a clinical validation using 180 patient samples, the SOS achieved a 100% accuracy compared to a clinical instrument. The SOS costs less than $20 and is self-illuminated. It is an ideal mobile health tool to bring diagnostics requiring spectrophotometry from central laboratory to patient side.
Label-free bacterial colony detection and viability assessment by continuous-wave terahertz transmission imaging
- First Published: 06 April 2018
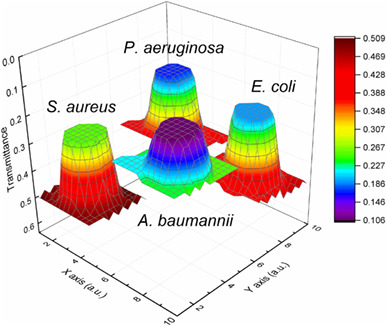
In this study, we used terahertz (THz) imaging to investigate the characteristics and distributions of different bacterial colonies and mixed bacterial samples. Single bacterial colonies of 4 bacterial species were directly distinguished as a result of their different THz absorption. In addition, same bacteria in different living states were successfully distinguished based on their different hydration levels and structural characteristics, demonstrating the potential of THz imaging for the label-free assessment of bacterial viability.
Interrogation of an autofluorescence-based method for protein fingerprinting
- First Published: 14 March 2018
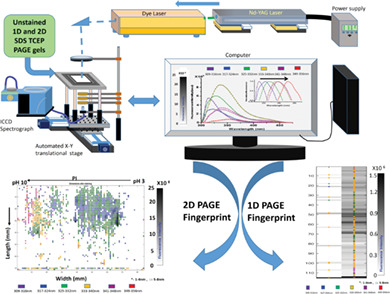
Autofluorescence-based protein fingerprinting for separation, visualization, differentiation and identification of proteins on Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine (SDS-TCEP) polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE). The technique gives quick information regarding protein's molecular weight, isoelectric point, fluorescence intensity (approximate measure of tyrosine and tryptophan concentration) and fluorescence wavelength (microenvironment of the fluorophores) on a single platform. Since there are no stains/tags used, technique is amenable to couple with High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)-mass-spectrometric measurements.
Cerebral capillary flow imaging by wavelength-division-multiplexing swept-source optical Doppler tomography
- First Published: 30 March 2018
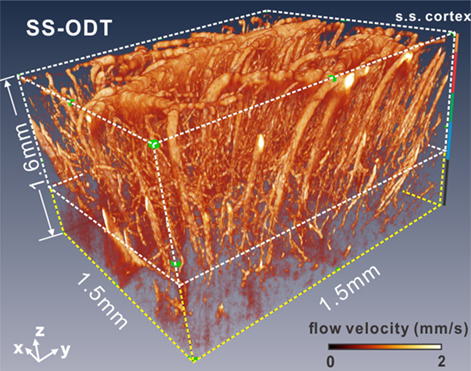
Swept-source-based optical coherence tomography (SS-OCT) is well recognized for fast imaging rate and long imaging distance; however, due to excess phase noise, there has been very limited success of SS-OCT in quantitative capillary flow imaging in deep cortical layers. A wavelength-division-multiplexing approach is reported to improve the flow sensitivity by minimizing the random phase noises. Quantitative capillary flow imaging is demonstrated in the mouse cortex at 1.6 mm cortical depth based on the proposed method.
Multiband modulation spectroscopy for the determination of sex and species of mosquitoes in flight
- First Published: 05 March 2018

Four disease-carrying mosquito species are investigated with a dual-band polarimetric instrument. We report on cross sections for both the insect body and the oscillatory wing component and interpret the results. We find several aspect invariance parameters and contrast for species and sex. We demonstrate benefits for multiple bands. The promising results pave the way for target classification in entomological lidar.
In vivo metabolic imaging and monitoring of brown and beige fat
- First Published: 09 March 2018
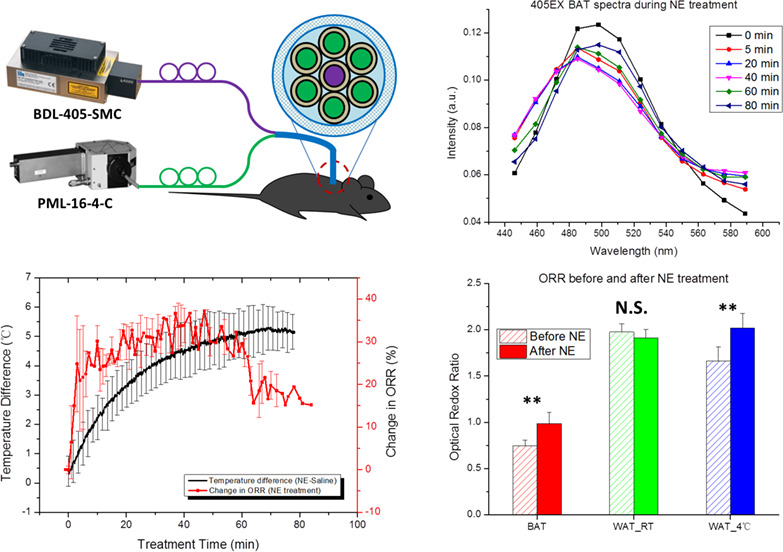
Metabolic characterization of adipose tissues provides remarkable insight into the mechanism of obesity-related diseases. This paper presents a label-free method to assess the metabolism and thermogenesis of mouse adipose tissues in vivo. The optical redox ratio is used as a real-time biomarker to determine the thermogenic response of brown, beige and white adipose tissues to different physiological stimulations. This technique may be used to identify the recruitment and activation of thermogenic adipocytes in animals and humans.
Antimicrobial photodynamic inactivation is potentiated by the addition of selenocyanate: Possible involvement of selenocyanogen?
- First Published: 28 February 2018
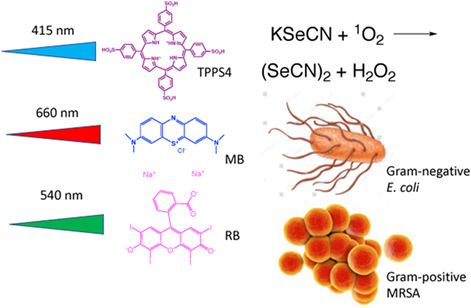
Addition of the inorganic salt potassium selenocyanate potentiates antimicrobial photodynamic inactivation by several logs of killing. This occurs with both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, and with 3 different photosensitizers, rose bengal, methylene blue and anionic porphyrin 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-sulfonatophenyl)porphyrin dihydrochloride. The mechanism is proposed to be the generation of the pseudohalogen (selenocyanogen) by singlet oxygen oxidation of selenocyanate.