Assessment of the dynamics of human glymphatic system by near-infrared spectroscopy
Corresponding Author
Teemu Myllylä
Optoelectronics and Measurement Techniques Unit, University of Oulu, Oulu, Finland
Oulu Functional Neuroimaging Group, Research Unit of Medical Imaging, Physics and Technology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Oulu, Oulu, Finland
Correspondence
Teemu Myllylä, Optoelectronics and Measurement Techniques Unit, University of Oulu, Oulu, Finland.Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorMarkus Harju
Inverse Problems Group, Department of Mathematical Sciences, University of Oulu, Oulu, Finland
Search for more papers by this authorVesa Korhonen
Oulu Functional Neuroimaging Group, Research Unit of Medical Imaging, Physics and Technology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Oulu, Oulu, Finland
Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Medical Research Center (MRC), Oulu University Hospital, Oulu, Finland
Search for more papers by this authorAlexander Bykov
Optoelectronics and Measurement Techniques Unit, University of Oulu, Oulu, Finland
Department of Photonics and Optical Information Technology, ITMO University, St Petersburg, Russia
Search for more papers by this authorVesa Kiviniemi
Oulu Functional Neuroimaging Group, Research Unit of Medical Imaging, Physics and Technology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Oulu, Oulu, Finland
Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Medical Research Center (MRC), Oulu University Hospital, Oulu, Finland
Search for more papers by this authorIgor Meglinski
Optoelectronics and Measurement Techniques Unit, University of Oulu, Oulu, Finland
Department of Photonics and Optical Information Technology, ITMO University, St Petersburg, Russia
Institute of Biology, Irkutsk State University, Irkutsk, Russia
Institute of Engineering Physics for Biomedicine, National Research Nuclear University MEPhI (Moscow Engineering Physics Institute), Moscow, Russia
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Teemu Myllylä
Optoelectronics and Measurement Techniques Unit, University of Oulu, Oulu, Finland
Oulu Functional Neuroimaging Group, Research Unit of Medical Imaging, Physics and Technology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Oulu, Oulu, Finland
Correspondence
Teemu Myllylä, Optoelectronics and Measurement Techniques Unit, University of Oulu, Oulu, Finland.Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorMarkus Harju
Inverse Problems Group, Department of Mathematical Sciences, University of Oulu, Oulu, Finland
Search for more papers by this authorVesa Korhonen
Oulu Functional Neuroimaging Group, Research Unit of Medical Imaging, Physics and Technology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Oulu, Oulu, Finland
Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Medical Research Center (MRC), Oulu University Hospital, Oulu, Finland
Search for more papers by this authorAlexander Bykov
Optoelectronics and Measurement Techniques Unit, University of Oulu, Oulu, Finland
Department of Photonics and Optical Information Technology, ITMO University, St Petersburg, Russia
Search for more papers by this authorVesa Kiviniemi
Oulu Functional Neuroimaging Group, Research Unit of Medical Imaging, Physics and Technology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Oulu, Oulu, Finland
Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Medical Research Center (MRC), Oulu University Hospital, Oulu, Finland
Search for more papers by this authorIgor Meglinski
Optoelectronics and Measurement Techniques Unit, University of Oulu, Oulu, Finland
Department of Photonics and Optical Information Technology, ITMO University, St Petersburg, Russia
Institute of Biology, Irkutsk State University, Irkutsk, Russia
Institute of Engineering Physics for Biomedicine, National Research Nuclear University MEPhI (Moscow Engineering Physics Institute), Moscow, Russia
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
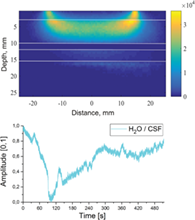
Fluctuations in brain water content has attracted increasing interest, particularly as regards studies of the glymphatic system, which is connected with the complex organization of dural lymphatic vessels, responsible for cleaning tissue. Disturbances of glymphatic circulation are associated with several brain disorders, including dementia. This article introduces an approach to noninvasive measurement of water dynamics in the human brain utilizing near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS). We demonstrate the possibility to sense dynamic variations of water content between the skull and grey matter, for instance, in the subarachnoid space. Measured fluctuations in water content, especially in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), are assumed to be correlated with the dynamics of glymphatic circulation. The sampling volume for the NIRS optode was estimated by Monte Carlo modelling for the wavelengths of 660, 740, 830 and 980 nm. In addition, using combinations of these wavelengths, this article presents the calculation models for quantifying water and haemodynamics. The presented NIRS technique allows long-term functional brain monitoring, including sleeping time. Furthermore, it is used in combination with different magnetic neuroimaging techniques, particularly magnetic resonance encephalography. Using the combined setup, we report the preliminary results on the interaction between CSF and blood oxygen level-dependent fluctuations.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| jbio201700123-sup-0001-author-biographies.docxapplication/docx, 346.1 KB | Author Biographies |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
REFERENCES
- 1H. H. Mitchell, T. S. Hamilton, F. R. Steggerda, H. W. Bean, J. Biol. Chem. 1945, 158, 625.
- 2H. Woodard, D. White, Br. J. Radiol. 1986, 59, 1209.
- 3D. A. Schoeller, Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1989, 50, 1176; discussion, 1231.
- 4R. Spector, S. Robert Snodgrass, C. E. Johanson, Exp. Neurol. 2015, 273, 57.
- 5J. Hall, E. Guyton, Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences 2005.
- 6D. Raper, A. Louveau, J. Kipnis, Trends Neurosci. 2016, 39, 581.
- 7A. Louveau, I. Smirnov, T. J. Keyes, J. D. Eccles, S. J. Rouhani, J. D. Peske, N. C. Derecki, D. Castle, J. W. Mandell, K. S. Lee, Nature 2015, 523, 337.
- 8S. B. Hladky, M. A. Barrand, Fluids Barriers CNS 2014, 11, 26.
- 9R. A. Fishman, N. Engl, J. Med. 1975, 293, 706.
- 10A. S. Thrane, V. R. Thrane, M. Nedergaard, Trends Neurosci. 2014, 37, 620.
- 11J. J. Iliff, M. Wang, Y. Liao, B. A. Plogg, W. Peng, G. A. Gundersen, H. Benveniste, G. E. Vates, R. Deane, S. A. Goldman, E. A. Nagelhus, M. Nedergaard, Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 147ra111.
- 12J. J. Iliff, M. Wang, D. M. Zeppenfeld, A. Venkataraman, B. A. Plog, Y. Liao, R. Deane, M. Nedergaard, J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 18190.
- 13M. Nedergaard, Science 2013, 340, 1529.
- 14N. A. Jessen, A. S. F. Munk, I. Lundgaard, M. Nedergaard, Neurochem. Res. 2015, 40, 2583.
- 15A. Aspelund, S. Antila, S. T. Proulx, T. V. Karlsen, S. Karaman, M. Detmar, H. Wiig, K. Alitalo, J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 991.
- 16V. Kiviniemi, X. Wang, V. Korhonen, T. Keinänen, T. Tuovinen, J. Autio, P. LeVan, S. Keilholz, Y. Zang, J. Hennig, J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2016, 36, 1033.
- 17S. Ooms, S. Overeem, K. Besse, M. O. Rikkert, M. Verbeek, J. A. Claassen, JAMA Neurol. 2014, 71, 971.
- 18P. E. Spies, M. M. Verbeek, T. Van Groen, J. A. Claassen, Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed) 2012, 17, 2024.
- 19J. M. Tarasoff-Conway, R. O. Carare, R. S. Osorio, L. Glodzik, T. Butler, E. Fieremans, L. Axel, H. Rusinek, C. Nicholson, B. V. Zlokovic, B. Frangione, K. Blennow, J. Menard, H. Zetterberg, T. Wisniewski, M. J. de Leon, Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 12, 248.
- 20L. Xie, H. Kang, Q. Xu, M. J. Chen, Y. Liao, M. Thiyagarajan, J. O'Donnell, D. J. Christensen, C. Nicholson, J. J. Iliff, T. Takano, R. Deane, M. Nedergaard, Science 2013, 342, 373.
- 21A. D. Cohen, W. E. Klunk, Neurobiol. Dis. 2014, 72, 117.
- 22P. K. Eide, G. Ringstad, Acta Radiol. Short Rep. 2015, 4, 2058460115609635.
10.1177/2058460115609635 Google Scholar
- 23T. Myllyla, N. Zacharias, V. Korhonen, A. Zienkiewicz, H. Hinrichs, V. Kiviniemi, M. Walter, Sci Rep 2017, 7, 172-017-00293-7.
- 24A. Zienkiewicz, N. Huotari, L. Raitamaa, V. Raatikainen, H. Ferdinando, E. Vihriälä, V. Korhonen, T. Myllylä, V. Kiviniemi, Int. Soc. Opt. Photon, SPIE BiOS, p. 1006311.
- 25T. Myllylä, V. Toronov, J. Claassen, V. Kiviniemi, V. Tuchin, V. Tuchin, Handbook of Optical Biomedical Diagnostics, SPIE Press, 2016.
- 26C. Cooper, M. Cope, V. Quaresima, M. Ferrari, E. Nemoto, R. Springett, S. Matcher, P. Amess, J. Penrice, L. Tyszczuk, Optical Imaging of Brain Function and Metabolism 2, Springer, 1997, p. 63.
10.1007/978-1-4899-0056-2_7 Google Scholar
- 27H. Obrig, M. Neufang, R. Wenzel, M. Kohl, J. Steinbrink, K. Einhäupl, A. Villringer, NeuroImage 2000, 12, 623.
- 28B. A. Vern, B. J. Leheta, V. C. Juel, J. LaGuardia, P. Graupe, W. H. Schuette, Brain Res. 1997, 775, 233.
- 29D. A. Boas, C. E. Elwell, M. Ferrari, G. Taga, NeuroImage 2014, 85, 1.
- 30D. A. Boas, C. Pitris, N. Ramanujam, Handbook of Biomedical Optics, CRC Press, 2016.
10.1201/b10951 Google Scholar
- 31V. Toronov, T. Myllylä, V. Kiviniemi, V. Tuchin, Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Topics 2013, 222, 2607.
- 32J. Robertson, A. Ghosh, T. Correia, D. Highton, M. Smith, C. Elwell, T. Leung, Oxygen Transport to Tissue XXXVI, Springer, 2014, p. 233.
10.1007/978-1-4939-0620-8_31 Google Scholar
- 33A. Demel, M. Wolf, C. F. Poets, A. R. Franz, BMC Pediatr. 2014, 14, 206.
- 34V. V. Tuchin, V. Tuchin, Tissue Optics: Light Scattering Methods and Instruments for Medical Diagnosis, SPIE Press, Bellingham, WA 2015.
10.1117/3.1003040 Google Scholar
- 35M. Cope, Ph.D. Thesis, University of London 1991, 342.
- 36T. Myllylä, V. Korhonen, Ł. Suraźyński, A. Zienkiewicz, H. Sorvoja, R. Myllylä, Measurement 2014, 58, 387.
- 37T. Myllylä, A. A. Elseoud, H. SS Sorvoja, R. A. Myllylä, J. M. Harja, J. Biophotonics 2011, 4, 98.
- 38T. Myllylä, V. Korhonen, V. Kiviniemi, V. Tuchin, Int. Soc. Opt. Photon., SPIE BiOS, p. 93051S.
- 39V. O. Korhonen, T. S. Myllyla, M. Y. Kirillin, A. P. Popov, A. V. Bykov, A. V. Gorshkov, E. A. Sergeeva, M. Kinnunen, V. Kiviniemi, IEEE J. Select. Topics Quantum Electron. 2014, 20, 289.
- 40A. Doronin, I. Meglinski, Biomed. Opt. Expr. 2011, 2, 2461.
- 41A. N. Bashkatov, E. A. Genina, V. I. Kochubey, V. V. Tuchin, Saratov Fall Meeting 2005: Optical Technologies in Biophysics and Medicine VII, p. 616310.
- 42J. Kalkman, A. Bykov, G. Streekstra, T. Van Leeuwen, Phys. Med. Biol. 2012, 57, 1907.
- 43A. Doronin, I. Meglinski, J. Biomed. Opt. 2012, 17, 0905041.
- 44A. V. Bykov, M. Y. Kirillin, A. V. Priezzhev, R. Myllylä, Quantum Electron. 2006, 36, 1125.
- 45S. Tseng, A. Grant, A. J. Durkin, J. Biomed. Opt. 2008, 13, 014016.
- 46E. Okada, D. T. Delpy, Appl. Opt. 2003, 42, 2906.
- 47A. Yaroslavsky, P. Schulze, I. Yaroslavsky, R. Schober, F. Ulrich, H. Schwarzmaier, Phys. Med. Biol. 2002, 47, 2059.
- 48L. Gagnon, K. Perdue, D. N. Greve, D. Goldenholz, G. Kaskhedikar, D. A. Boas, NeuroImage 2011, 56, 1362.
- 49G. Golub, C. Van Loan, Matrix Computations, 3rd Edition, The Johns Hopkins University Press, 1996.
- 50J. Assländer, B. Zahneisen, T. Hugger, M. Reisert, H. Lee, P. LeVan, J. Hennig, NeuroImage 2013, 73, 59.
- 51V. O. Korhonen, T. K. Hiltunen, T. S. Myllylä, S. Wang, J. Kantola, J. Nikkinen, Y. Zang, P. Levan, V. Kiviniemi, Brain Connect. 2014, 4, 677.
- 52M. Jenkinson, C. F. Beckmann, T. E. Behrens, M. W. Woolrich, S. M. Smith, NeuroImage 2012, 62, 782.