Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Pictures
Front Cover: Vascular tree extraction for photoacoustic microscopy and imaging of cat primary visual cortex (J. Biophotonics 6-7/2017)
- Page: 749
- First Published: 29 June 2017

Photoacoustic imaging allows label-free, three-dimensional visualization of blood vessel morphology down to capillary level. By virtue of the acquired high contrast blood vessel images, a vascular tree extraction method based on the ray-casting concept could automatically track complex cortical blood vessel networks of cats with numerous crossovers and branches, while extracting important parameters of the whole vascular tree, such as the vessel diameters, the center lines and three-dimensional orientations. Further details can be found in the article by Qian Li et al. on pp. 780–791.
Inside Cover: In vivo assessment of periodontal structures and measurement of gingival sulcus with Optical Coherence Tomography: A pilot study (J. Biophotonics 6-7/2017)
- Page: 750
- First Published: 29 June 2017

Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) was applied to visualize relevant periodontal structures in healthy patients, allowing non-invasive, quantitative evaluation of sulcus depth. Further details can be found in the article by Luana Osório Fernandes et al. on pp. 862–869.
Inside Back Cover: Effects of temperature on multiparametric evaluation of hindlimb ischemia with dynamic fluorescence imaging (J. Biophotonics 6-7/2017)
- Page: 941
- First Published: 29 June 2017
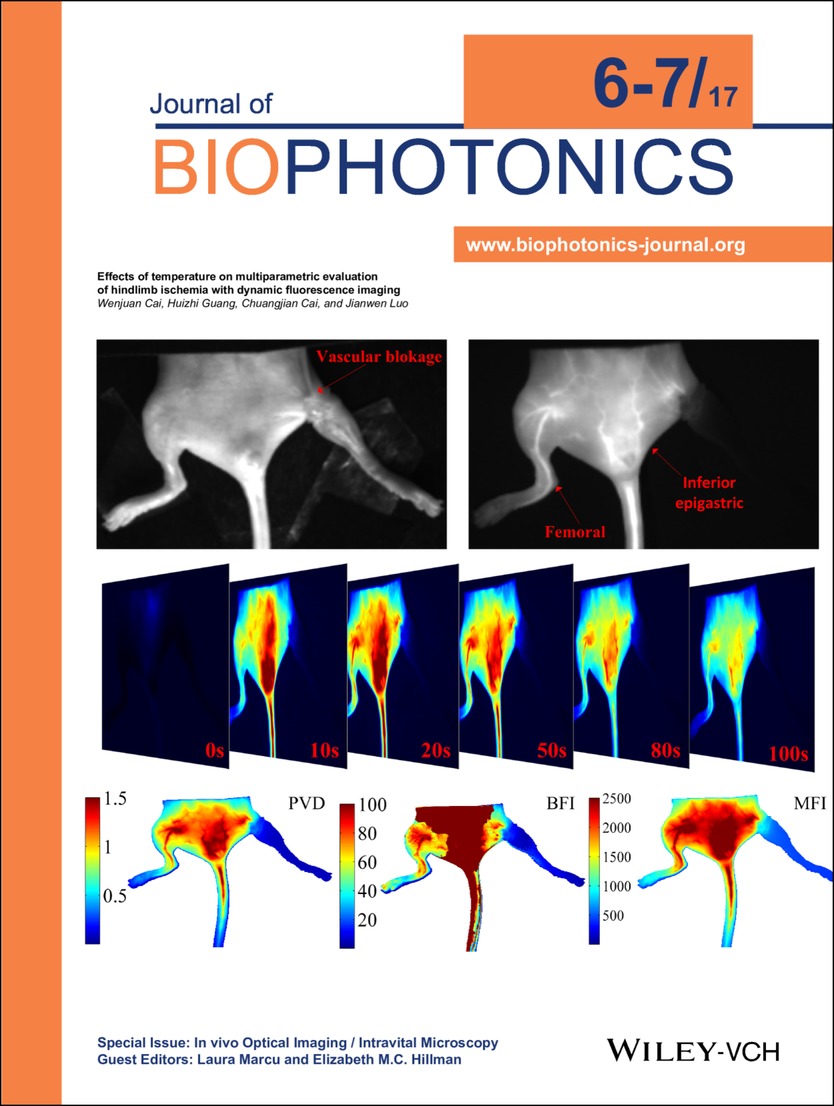
Time-series fluorescence images are obtained to provide both anatomical and functional information. Perfusion vascular density (PVD), blood flow index (BFI) and mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) are quantitatively evaluated to distinguish normal and ischemic hindlimbs at different temperatures. This quantitative and comprehensive evaluation method may contribute to the diagnosis of vascular occlusive diseases and preclinical development of new drugs. Further details can be found in the article by Wenjuan Cai et al. on pp. 811–820.
Back Cover: Second generation slit-based photoacoustic tomography system for vascular imaging in human (J. Biophotonics 6-7/2017)
- Page: 942
- First Published: 29 June 2017
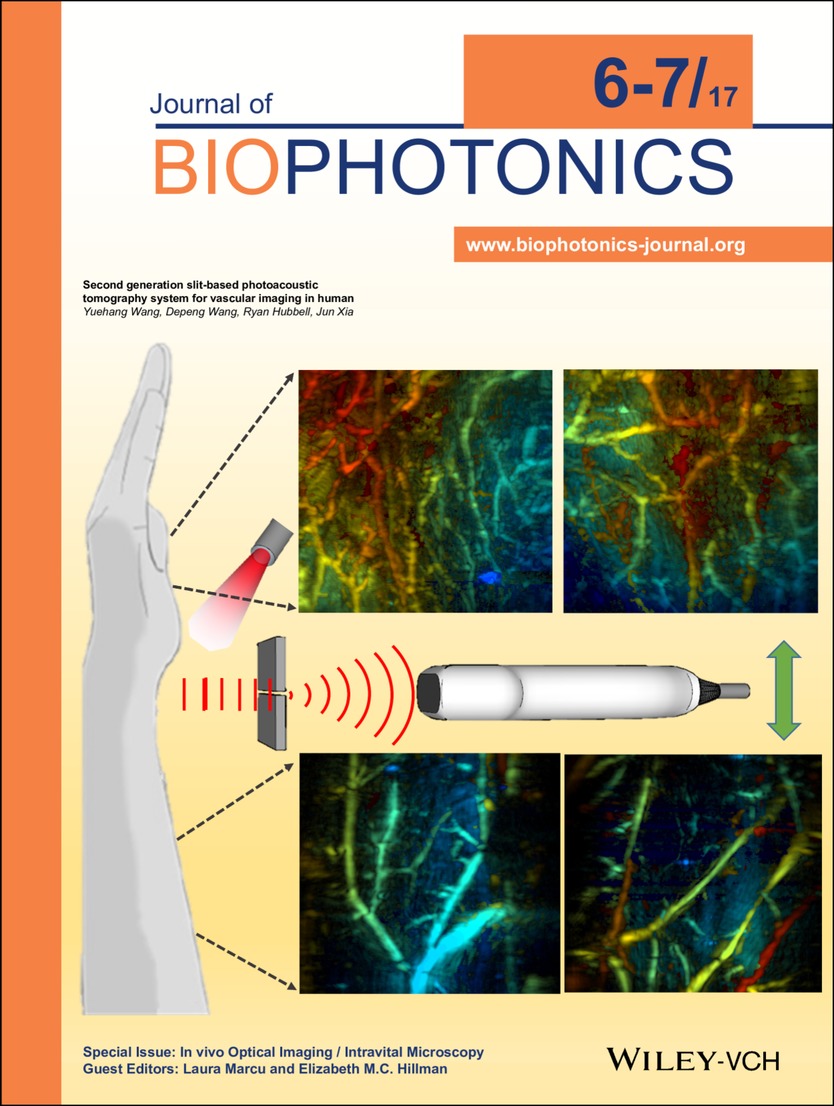
Capitalizing on the principle of acoustic diffraction, Wang et al. developed a second-generation slit-based photoacoustic tomography technique, which dramatically improved the elevation resolution of a linear transducer array and enabled high-quality three dimensional imaging of human arm and palm vasculatures in vivo. The cover picture includes depth-encoded (0 to 15 mm) vascular images from different volunteers. Further details can be found in the article by Yuehang Wang et al. on pp. 799–804.
Issue Information
Contents
Editorial
In vivo Optical Imaging / Intravital Microscopy
- Pages: 760-761
- First Published: 29 June 2017
Full Articles
Motion-free endoscopic system for brain imaging at variable focal depth using liquid crystal lenses
- Pages: 762-774
- First Published: 08 March 2016
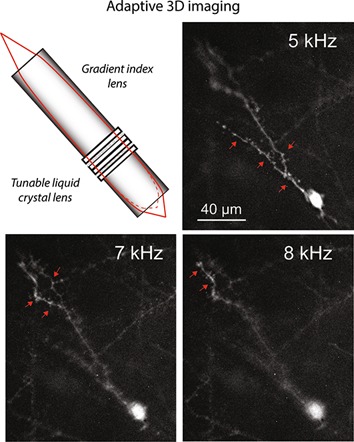
An imaging system is introduced, based on gradient index and electrically tunable liquid crystal lenses, allowing motion-free imaging of neural circuitry at variable focal depth in vivo. Electrical tuning of the liquid crystal lens at constant voltage, but variable frequency enables about 75 µm focal shift allowing interrogation of morpho-functional properties of neural networks in various deep brain regions.
Three-dimensional fiber-optic readout of single-neuron-resolved fluorescence in living brain of transgenic mice
- Pages: 775-779
- First Published: 09 May 2016

Studies on isolated nerve cells play a pivotal role in neuroscience. As a parallel trend, methods enabling a recording of distributed neuronal circuitries are in great demand. Here we show that both single-neuron recording and wider-field fiber-bundle brain imaging can be combined on a platform of a bundle of individually addressable optical fibers. Experiments on live brain demonstrate that such a probe enables a three-dimensional optogenetic recording from single neurons.
Vascular tree extraction for photoacoustic microscopy and imaging of cat primary visual cortex
- Pages: 780-791
- First Published: 22 August 2016
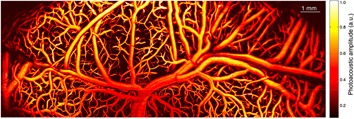
A vascular tree extraction algorithm is proposed to automatically extract independent vascular trees from background and other crossed vascular trees for photoacoustic microscopy (PAM). The algorithm is applied on the OR-PAM images of the intricate cortical vasculatures of the cat primary visual cortex. It successfully extracts a complex arteriole tree with multiple loops and penetrating arterioles. Its performance is discussed based on the results for phantom and true OR-PAM images.
Editor's Choice
High-speed photoacoustic microscopy of mouse cortical microhemodynamics
- Pages: 792-798
- First Published: 23 December 2016
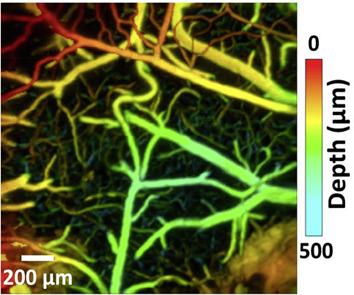
We present a high-speed optical-resolution photoacoustic microscopy (OR-PAM) with micrometer-level resolution and a millisecond-level cross-sectional imaging speed over a millimeter-level field of view. Using this high-speed OR-PAM, we quantified the blood flow redistribution in response to spontaneous microhemorrhage, as well as to laser induced occlusions of single microvessels. We also imaged cerebral autoregulation on single microvessels in an intact mouse brain.
Second generation slit-based photoacoustic tomography system for vascular imaging in human
- Pages: 799-804
- First Published: 09 December 2016
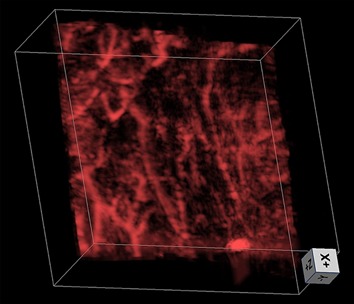
Slit-based photoacoustic tomography (PAT) is a newly developed technique that improves the elevation numerical aperture of a linear array through acoustic diffraction, achieving near isotropic spatial resolution along all three dimensions. In this report, the original slit-PAT system has been significantly improved to allow for easy slit width adjustment and in vivo human imaging. We successfully used the system to image vasculatures in the palm and forearm of human volunteers.
Letters
Dynamic laser speckle angiography achieved by eigen-decomposition filtering
- Pages: 805-810
- First Published: 29 November 2016
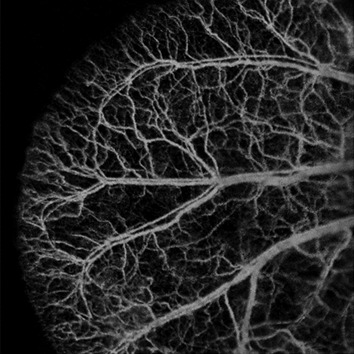
A novel method is proposed for statistical analysis of laser speckle signals based on eigen-decomposition to separate the dynamic speckle signals due to moving blood cells from the static speckle signals due to static tissue components. The method is demonstrated by providing detailed angiography of tissue in vivo vascular networks with high contrast, and high temporal and spatial resolutions.
Full Articles
Effects of temperature on multiparametric evaluation of hindlimb ischemia with dynamic fluorescence imaging
- Pages: 811-820
- First Published: 07 December 2016
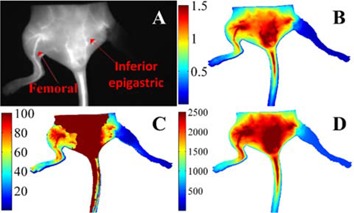
Perfusion vascular density from a mathematical model of ICG pharmacokinetics, blood flow index and mean fluorescence intensity from time-series analysis of ICG hemodynamics are evaluated to obtain quantitative functional and hemodynamic information. The results show that these parameters can distinguish normal and ischemic hindlimbs at different temperatures. This quantitative and comprehensive evaluation method may contribute to the diagnosis of vascular occlusive diseases and development of preclinical new drugs.
Intravital excitation increases detection sensitivity for pulmonary tuberculosis by whole-body imaging with β-lactamase reporter enzyme fluorescence
- Pages: 821-829
- First Published: 18 October 2016
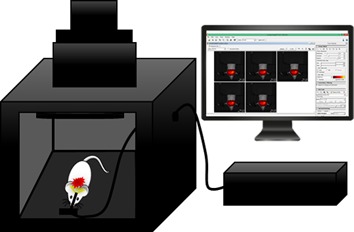
We demonstrate an integrated imaging platform that increases the sensitivity of in vivo optical detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) in mouse lungs. Mtb-specific near-infrared fluorogenic substrate is detected with whole-animal imaging and fiber-microendoscope intravital illumination. By combining these bacteria-sensing methodologies, detection threshold was improved by 100× over whole-animal imaging with epi-illumination, and by 10× over previous intravital illumination experiments with recombinant reporter strains in the visible range.
Snapshot hyperspectral retinal imaging using compact spectral resolving detector array
- Pages: 830-839
- First Published: 19 July 2016
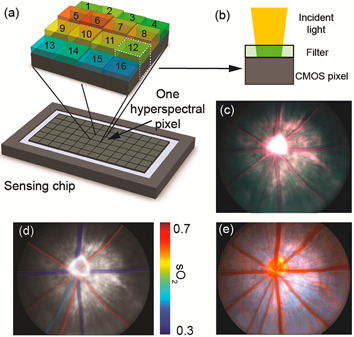
Hyperspectral retinal imaging provides spectral information and could benefit retinal diseases diagnosis and treatment. The key challenges in hyperspectral retinal imaging are how to achieve snapshot imaging to avoid motions between the images from multiple spectral bands, and how to design a compact snapshot imager suitable for clinical use. A compact, snapshot hyperspectral fundus camera for rodents using a novel spectral resolving detector array (SRDA) is reported, which captures hyperspectral retinal images at 20 fps. The advantages of hyperspectral imaging are demonstrated through spectral-analysis-based false-color vessel contrast enhancement and retinal oxygen saturation measurement.
Fluorescence hyperspectral imaging (fHSI) using a spectrally resolved detector array
- Pages: 840-853
- First Published: 09 May 2017
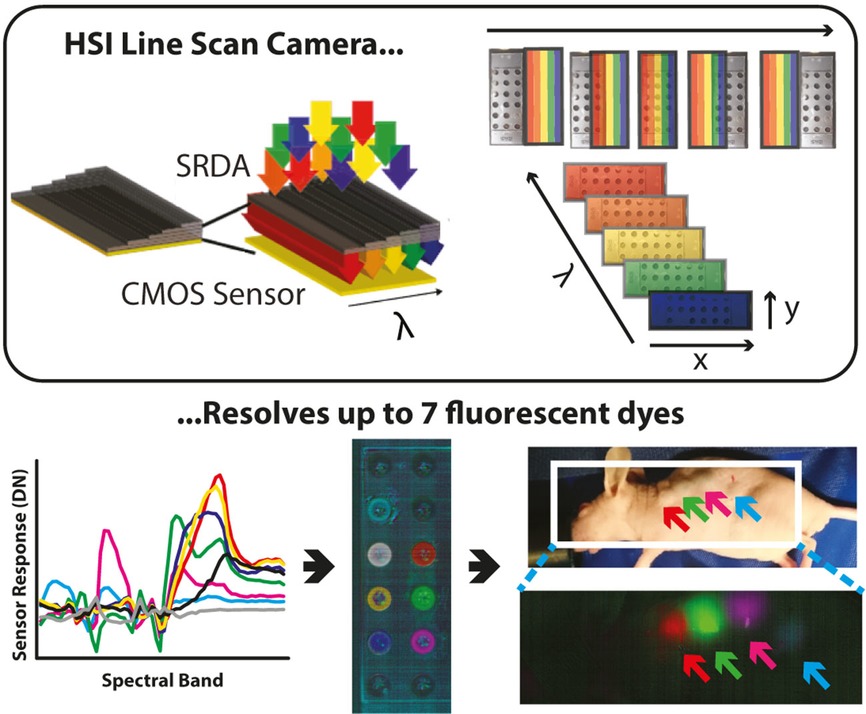
Hyperspectral imaging (HSI) can now be performed robustly and at low cost using spectrally resolved detector arrays (SRDAs). We used a line scan ‘pushbroom’ SRDA to perform HSI and delineate fluorescent emissions with a focus on biomedical applications. Following detailed calibration and statistical analysis, we could accurately resolve at least 7 fluorescent dyes in solution and 4 fluorescent dyes in vivo in a mouse model using this novel SRDA technology.
Comparative study of presurgical skin infiltration depth measurements of melanocytic lesions with OCT and high frequency ultrasound
- Pages: 854-861
- First Published: 23 December 2016
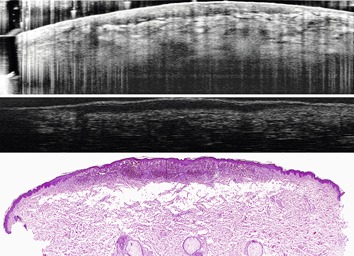
Malignant melanoma is the most dangerous skin cancer type. A very important criteria for risk evaluation is the skin infiltration depth of the melanoma. Non-invasive preoperative in vivo thickness assessment can provide additional information for histopathologists and has the potential to decrease false positive cases and avoid different steps of surgical intervention. With optical coherence tomography as well as high frequency ultrasound such thickness assessment is possible.
In vivo assessment of periodontal structures and measurement of gingival sulcus with Optical Coherence Tomography: a pilot study
- Pages: 862-869
- First Published: 09 August 2016
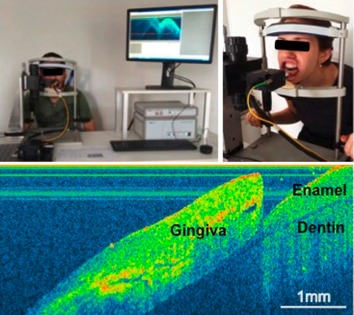
Imaging diagnostic by Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) technique was applied to visualize periodontal structures and compare to traditional probes evaluation in patients. The OCT images identified relevant anatomic dental and periodontal regions. Painless sulcus depth measured by OCT was compared to values obtained by invasive manual and automated probing. OCT is a reliable tool for in vivo periodontal tissues evaluation and for reproducible sulcus depth measurements in healthy sites.
In vivo and in situ imaging of controlled-release dissolving silk microneedles into the skin by optical coherence tomography
- Pages: 870-877
- First Published: 18 January 2016
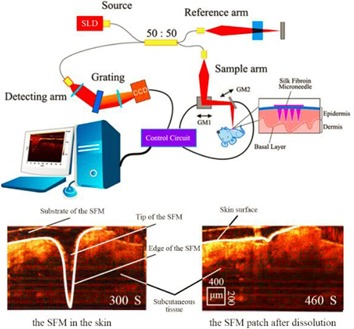
The silk fibroin microneedle patch can penetrate and dissolve in the skin for drug delivery. Hence, it is important to reflect the situation of microneedles dissolution and drug controlled release by in vivo and in situ imaging in real time. In this paper OCT was used to realize assessment of dissolving microneedles delivery efficiency in vivo and in situ imaging (AQ – please check the sense of this sentence).
Retroreflective-type Janus microspheres as a novel contrast agent for enhanced optical coherence tomography
- Pages: 878-886
- First Published: 24 May 2016
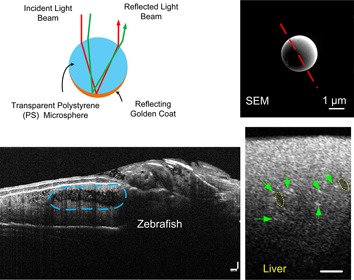
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a well-developed technology that utilizes near-infrared light to reconstruct three-dimensional images of biological tissues with micrometer resolution. In this study, Janus microspheres were developed and used as a positive contrast agent for enhanced OCT imaging. Phantom and ex vivo liver tissue experiments as well as in vivo animal tests were conducted, which validated that Janus microspheres, as a novel type of OCT tracer, were very effective in improving the OCT imaging contrast.
A useful way to develop effective in vivo skin optical clearing agents
- Pages: 887-895
- First Published: 23 December 2016
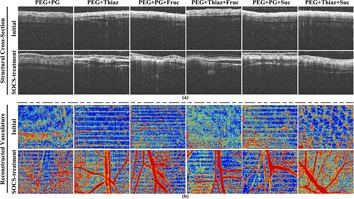
Six kinds of SOCAs were assessed based on imaging performance optimization, optical clearing efficacy, and permeability rate. Experimental results demonstrated that PEG+Thiaz+Suc exerted the optimal capacity in optimizing the aforementioned parameters, which indicated that the optimal SOCA can be developed directly by means of additionally adding or replacing the similar category substance in pre-existing SOCAs with some more effective reagents.
Editor's Choice
Multimodal fiber-probe spectroscopy allows detecting epileptogenic focal cortical dysplasia in children
- Pages: 896-904
- First Published: 09 January 2017
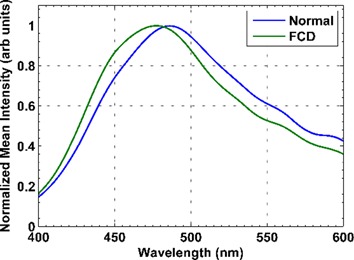
Here we investigate the application of fluorescence spectroscopy (at 378 nm and 445 nm excitation) and Raman spectroscopy (at 785 nm excitation) to discriminate normal brain tissue and focal cortical dysplasia. Multimodal spectroscopic approach yielded 100% sensitivity and 90% specificity by exploiting the information obtained from different spectroscopic techniques. Our results demonstrate the application of multimodal spectroscopic approach for the possible surgical resection of the dysplastic tissue during surgery for epilepsy.
Letters
Fluorescing fatty acids in rat fatty liver models
- Pages: 905-910
- First Published: 16 December 2016
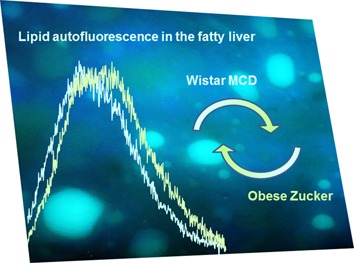
Fluorescing fatty acids contribute to the autofluorescence of liver lipids. The emission of arachidonic acid at longer wavelengths than the other fluorescing fatty acids allows to detect the differences in their balance in liver lipid extracts from different rat liver models. Apart wide-ranging applications of spectrofluorometry in biological substrate analysis, the distinct emission of arachidonic acid further validates autofluorescence based in situ, real time diagnosis in hepatology.
Full Articles
Second harmonic generation (SHG) imaging of cancer heterogeneity in ultrasound guided biopsies of prostate in men suspected with prostate cancer
- Pages: 911-918
- First Published: 22 August 2016
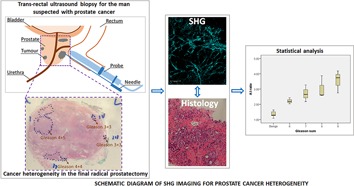
Histological analysis using Gleason grade of multiple biopsies from prostate gland in men suspected with prostate cancer is the only method to study cancer heterogeneity for risk stratification at present. We, in this study, report that collagen distribution depicted by second harmonic generation (SHG) imaging using A:I ratio (a ratio of the anisotropic and isotropic collagen fibres) varied according to degree of cancer grading with which it correlated accurately.
Investigating fibroblast cells under “safe” and “injurious” blue-light exposure by holographic microscopy
- Pages: 919-927
- First Published: 18 April 2016
A study on the temporal evolution of cell morphology and volume during blue light exposure is reported. The results reveal a behaviour that is typical of necrotic cells, with early swelling and successive leakage of the intracellular liquids when the laser is set in the “injurious” operation. The approach may open the route to a deep investigation of light-cell interactions, with information about death pathways and threshold conditions between healthy and damaged cells when subjected to light-exposure.
Live endothelial cells imaged by Scanning Near-field Optical Microscopy (SNOM): capabilities and challenges
- Pages: 928-938
- First Published: 22 August 2016
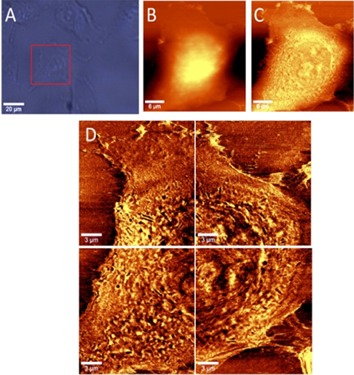
Paper presents the results of the SNOM measurements carried out in air and in the buffer environments, on fixed as well as on living cells. Moreover, the effect of TNF-α stimulation on EA.hy 926 cells and the details of cell morphology (EA.hy 926 and HLMVEC lines) based on their optical images is demonstrated. This paper address also to the challenges associated with the application of SNOM to study such heterogenic samples as cells.