Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover: Synthesis of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube Modifi ed BiOCl Microspheres with Enhanced Visible-Light Response Photoactivity
- First Published: 11 July 2016

Sheng Yin, Jun Di, Ming Li, Wenmin Fan, Jiexiang Xia, Hui Xu, Yilin Sun and Huaming Li
Clean – Soil, Air, Water 2016, 44 (7), 781–787
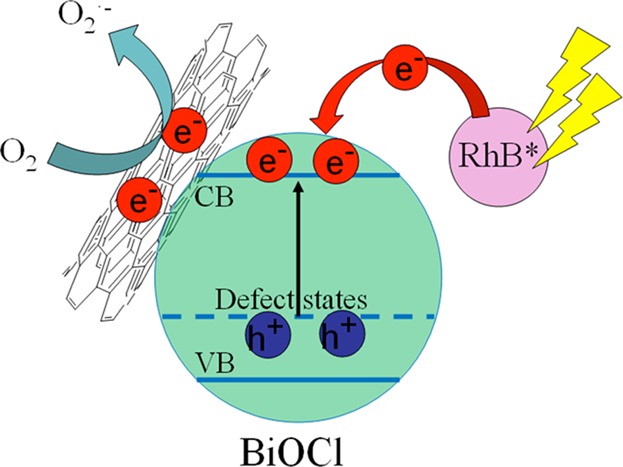
Multiwalled carbon nanotube (MWCNT)/BiOCl microspheres are synthesized via a reactive ionic liquid (IL)-assisted solvothermal process. The IL improves the dispersity of MWCNTs efficiently and promotes the combination of MWCNTs and BiOCl. The introduction of MWCNTs facilitates the separation of electron–hole pairs, and thus leads to an improved photocatalytic activity.
Masthead
Contents
Contents: Clean Soil Air Water. 7/2016
- Pages: 739-744
- First Published: 11 July 2016
Research Articles
Influence of Nonionic Surfactants on Fungal and Bacterial Degradation of Hexane
- Pages: 745-752
- First Published: 18 February 2016
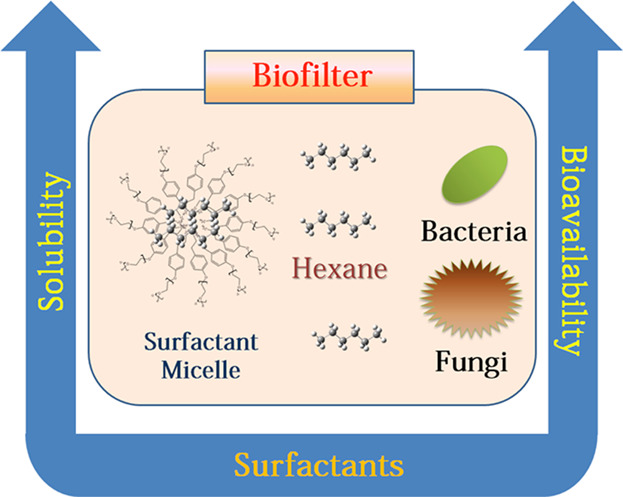
Addition of nonionic surfactants improves the removal of hydrophobic volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in biofilter systems. The results illustrate that added surfactants enhance both the solubility and bioavailability of hexane under different microconsortia conditions. This advances the understanding of process parameters useful for optimizing the biodegradation of hydrophobic VOCs in biofilter systems.
Chemical Characterization and Source Apportionment of Atmospheric Particles Across Multiple Sampling Locations in Faisalabad, Pakistan
- Pages: 753-765
- First Published: 24 February 2016
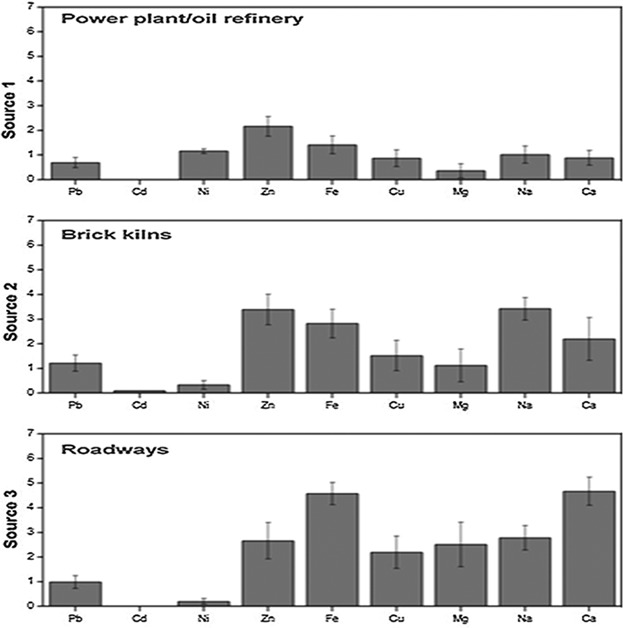
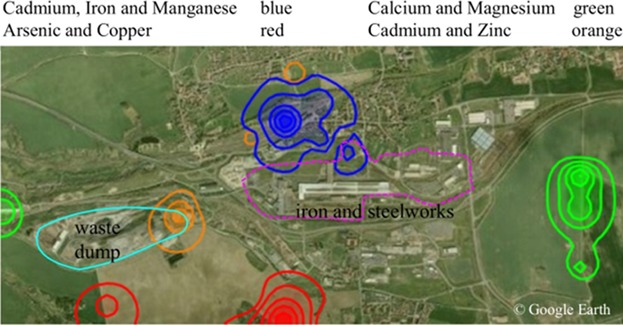
Airborne particles mass and element concentrations are determined at nine sampling locations in Faisalabad, Pakistan, during 2012–2013. The particles and elements concentrations are found the highest at the industrial and traffic locations and during the dry season. Three main pollution sources, power plant/refinery, brick kilns, and roadways, are identified in the local area using the combination of wind direction analysis and UNMIX model.
Global Warming Potential in an Intensive Vegetable Cropping System as Affected by Crop Rotation and Nitrogen Rate
- Pages: 766-774
- First Published: 14 March 2016

Optimizing the crop rotation by including legumes can reduce the N2O emissions by 23.9% and increase the net economic benefit by 32.6%; and the sum of global warming potential can be reduced by 25% or more if fertilizer rates and crop rotations are optimized simultaneously in an intensive vegetable production system.
Short Communication
Transmission Sources of Waterborne Viruses in South Sudan Refugee Camps
- Pages: 775-780
- First Published: 17 February 2016
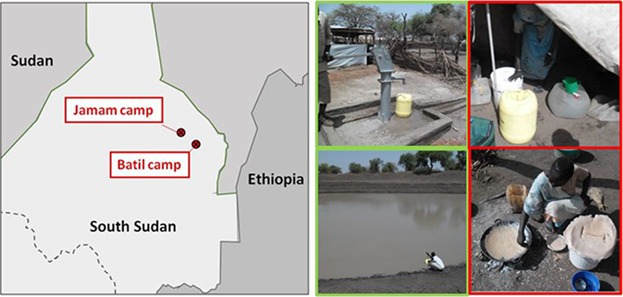
An environmental investigation at the end of an outbreak of hepatitis E virus (HEV) during the dry season in north South Sudan analyzed HEV and Human Adenovirus (HAdV) in surface and groundwater, household water and food samples. HAdV contamination was observed at the household level both in water and food samples.
Research Articles
Synthesis of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube Modified BiOCl Microspheres with Enhanced Visible-Light Response Photoactivity
- Pages: 781-787
- First Published: 06 March 2016
Separation and Preconcentration of Aluminum by Candida albicans Immobilized on Cellulose Acetate Biomass
- Pages: 788-793
- First Published: 17 February 2016
Candida albicans immobilized on cellulose acetate biomass (CAICAB) is a good biosorbent for the separation and preconcentration of aluminum ions in various water samples. The results suggest that the developed separation method by using CAICAB has good reproducibility, accuracy, a high preconcentration factor, and a low detection limit.
Antibacterial, Anti-Biofouling, and Antioxidant Prospects of Metal-Based Nanomaterials
- Pages: 794-802
- First Published: 18 February 2016
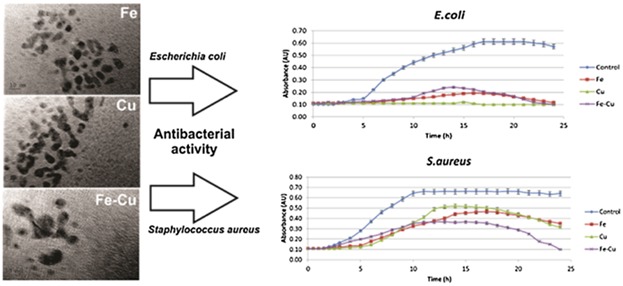
Zero-valent iron, copper, and bimetallic iron–copper nanoparticles are synthesized, characterized, and evaluated regarding their antibacterial and anti-biofouling properties against two bacterial strains: Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Total bacteria growth inhibition is achieved with low concentrations, although differences arise between the two bacterial strains. The results signify their potential as alternate antibacterial agents.
Comparison of Chemical Toxicity to Different Algal Species Based on Interspecies Correlation, Species Sensitivity, and Excess Toxicity
- Pages: 803-808
- First Published: 23 February 2016
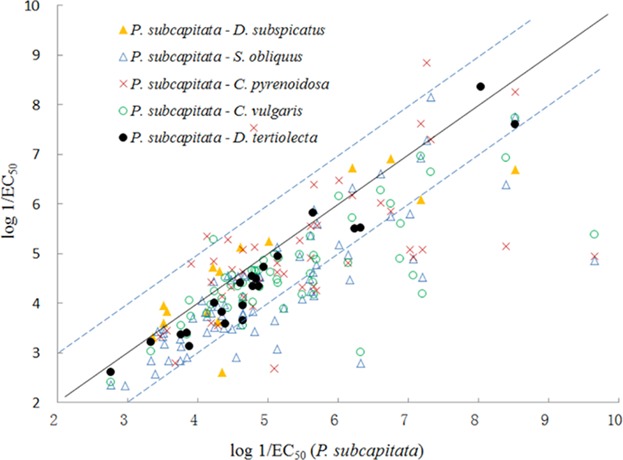
Although algal toxicity is species dependent, it is not clear if compounds have the same toxicity sensitivity among algal species. The interspecies correlations show that most of the tested compounds have the same toxicity sensitivity and share the same modes of action (MOA) in algal toxicity, but some share different MOA. This information will help understanding toxic mechanisms and developing quantitative structure–activity relationships.
Hybrid Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Photocatalytic Processes for Removal of Triphenylmethane Dyes: Artificial Neural Network Modeling
- Pages: 809-817
- First Published: 24 February 2016
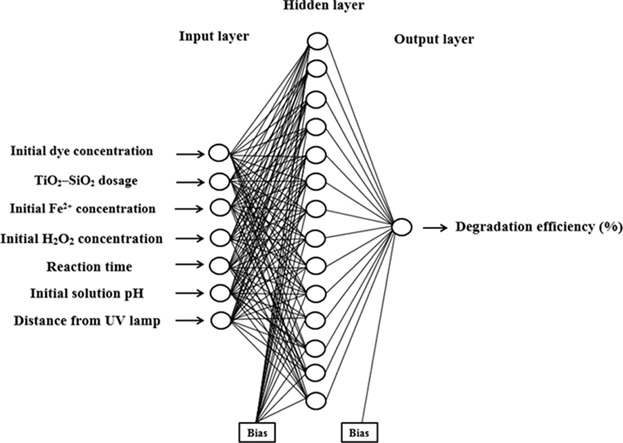
Individual and hybrid advanced oxidation processes of homogeneous (UV/Fe2+/H2O2) and heterogeneous (UV/TiO2−SiO2) photocatalysis are used for the removal of two triphenylmethane dyes. A comparison of the efficiency of various processes show that utilizing hybrid photocatalysis leads to rapid removal of pollutants. An artificial neural network model is intended to predict the removal efficiency of the hybrid photocatalysis.
Investigating the Roles of Dissolved Organic Matter on Arsenic Mobilization and Speciation in Environmental Water
- Pages: 818-828
- First Published: 28 April 2016
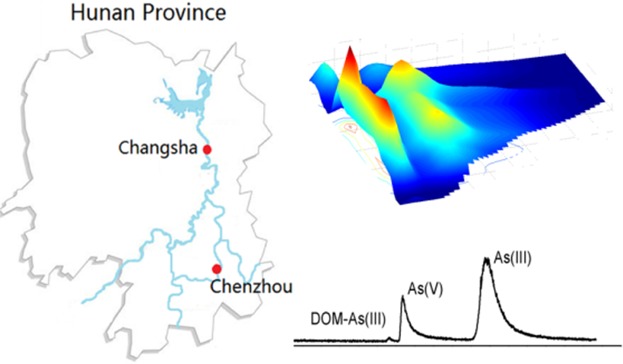
Arsenic contamination has attracted much attention in recent years. Water samples collected from the most heavily As-contaminated rivers in China are investigated using SEC-HPLC, combined with ICP-MS and 3DEEM-PARAFAC fluorescence spectroscopy. DOM-bound As, As(V), AsB, and As(III) are found in water samples, and the quenching effects of dissolved organic matter (DOM) and As(III) provide evidence for complexation between As(III) and DOM components.
Microbial Community Structures in Petroleum Contaminated Soils at an Oil Field, Hebei, China
- Pages: 829-839
- First Published: 15 February 2016

Microbial diversity, abundance, and community in petroleum contaminated subsurface soil ecosystems are highly influenced by the chemical constituents of petroleum hydrocarbons. Known petroleum degrading bacteria are abundantly observed, whereas they differ greatly under a selection pressure by the complex hydrocarbons including chlorinated hydrocarbon, benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and xylene (BTEX) and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.
An Ex Situ Salinity Restoration Assessment Using Legume, Saltbush, and Grass in Australian Soil
- Pages: 840-848
- First Published: 15 February 2016
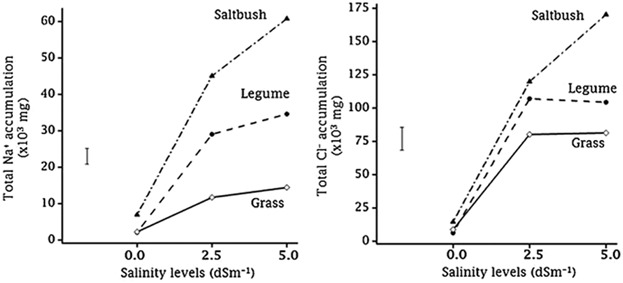
With increasing salinity in soil, total salt-ion accumulation increases in saltbush maximally, followed by legume and grass, under glasshouse conditions. Cl− moves more rapidly than Na+ indicating that Cl− accumulation is greater. The saltbush and legume perform best, accumulating more Na+ and Cl−. Both could be used in environmentally friendly remediation of saline sites in New South Wales.
Effects of Crops on Runoff and Soil Loss on Sloping Farmland Under Simulated Rainfall
- Pages: 849-857
- First Published: 17 February 2016
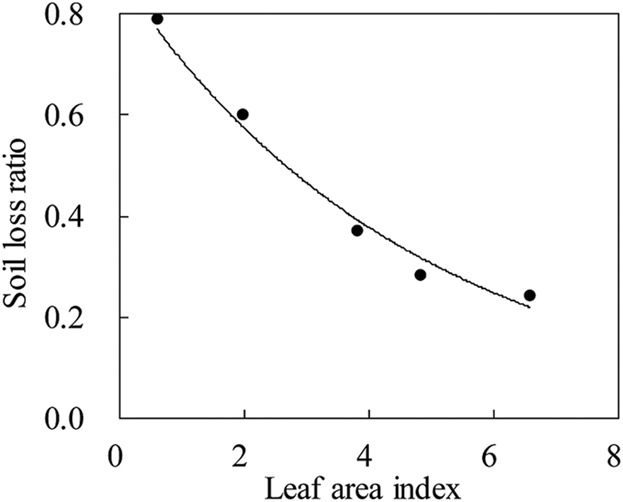
Soil erosion on sloping farmland is effected significantly by crop planting. The results indicate that crop planting could be effective in reducing the runoff rate and sediment yield during the whole crop growth stage. The inhibition effect on runoff and sediment gradually increases with the crop growth and development.
Persistence and Leaching of Two Pesticides in a Paddy Soil in Northern Vietnam
- Pages: 858-866
- First Published: 18 February 2016
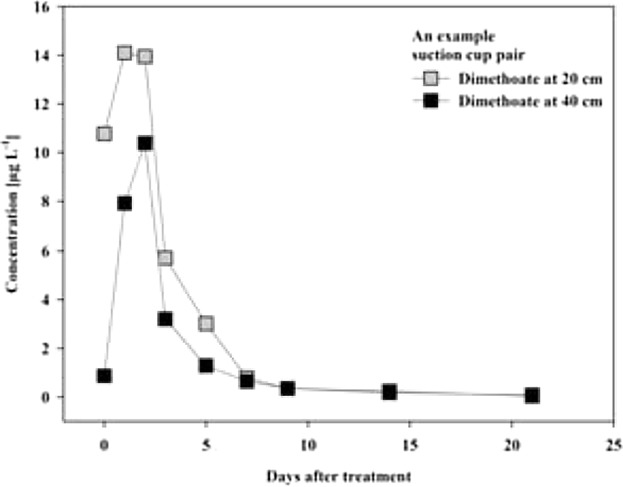
Intensive pesticide use in paddy rice fields in Vietnam can considerably affect groundwater quality. To assess this, the behavior of two different pesticides is studied in the topsoil and soil water in a paddy field. Both pesticides appeared at high levels in soil water just hours after application, confirming high groundwater vulnerability during pesticide application seasons.
Soil CO2 Emissions and Drivers in Rice–Wheat Rotation Fields Subjected to Different Long-Term Fertilization Practices
- Pages: 867-876
- First Published: 23 February 2016
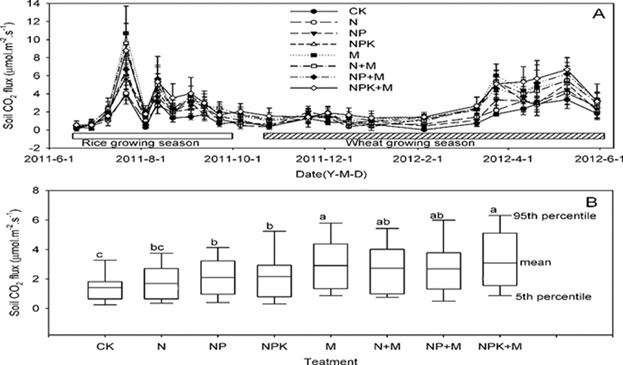
Soil CO2 emissions are key components of global carbon cycling. Soil CO2 flux is determined for different long-term fertilization practices. The findings suggest that at given temperature and soil moisture, variations in soil CO2 emissions associated with fertilization practices are strongly related to soil organic matter, and nutrient contents, microbial and enzyme activities, and physicochemical properties.
Source Apportionment and Geostatistics: An Outstanding Combination for Describing Metals Distribution in Soil
- Pages: 877-884
- First Published: 29 February 2016
Enhancement of Integrated Waste Activated Sludge Fermentation and Denitritation by Addition of Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate
- Pages: 885-890
- First Published: 14 March 2016
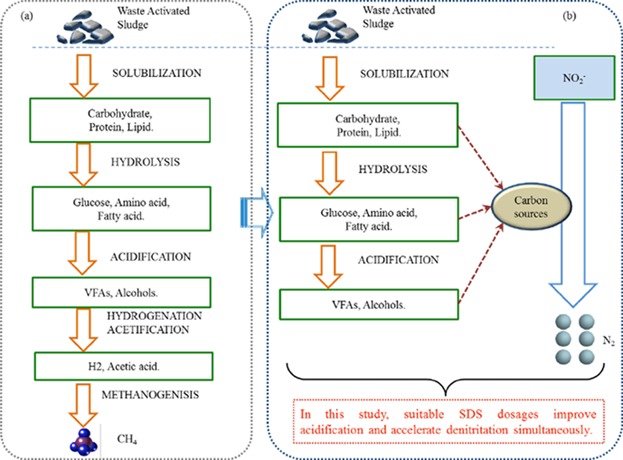
Integrated waste activated sludge fermentation and denitritation is an effective process for nitrogen removal and sludge utilization simultaneously. The effect of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) on sludge hydrolysis, acidification, and denitritation is analyzed. Experimental results suggest that an SDS dosage of 0.02 g/g is beneficial for improving volatile fatty acid content for in situ denitritation, minimizing nutrient release from sludge fermentation, and enhancing the denitritation rate.
Removal of Anthraquinone Dye by Cross-Linked Enzyme Aggregates From Fresh Horseradish Extract
- Pages: 891-900
- First Published: 01 April 2016
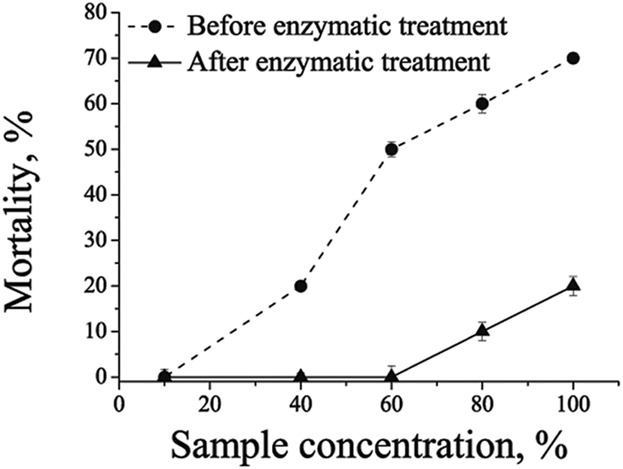
Horseradish root fresh extract is used as the source of unpurified horseradish peroxidase. The enzyme is immobilized in a form of cross-linked enzyme aggregates and used in Acid Violet 109 oxidation. The feasibility of immobilized enzyme application in dye oxidation is confirmed by significant dye oxidation percentage and reduction of the toxicity.
Review
Understanding the Development of Environmental Resistance Among Microbes: A Review
- Pages: 901-908
- First Published: 27 February 2016
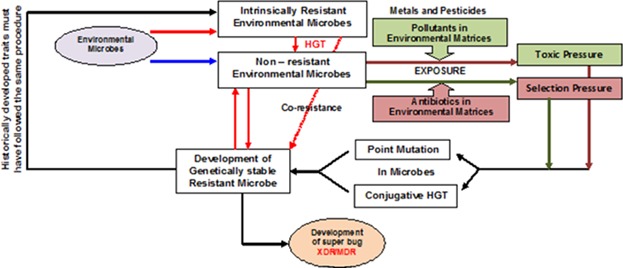
To understand environmental resistance among microbes, scientific research directly links two different fields viz., medical and environmental microbiology. Bacterial species such as Acinetobacter baumannii, Bacillus cereus, and Escherichia coli are reported to have resistance against both toxic metals and antibiotics. The development of environmental resistance among microbes having resistance to antibiotics along with the gist of associated environmental risk is reviewed.