Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Editorial
Diabetes and branched-chain amino acids: What is the link?
糖尿病与支链氨基酸:有什么关联吗?
- Pages: 350-352
- First Published: 25 January 2018
News
International Diabetes Federation 2017
- Pages: 353-356
- First Published: 18 January 2018
Editors' Recommendations
High dietary intake of branched-chain amino acids is associated with an increased risk of insulin resistance in adults: 成年人饮食中高支链氨基酸摄入量与胰岛素抵抗风险增加相关
- Pages: 357-364
- First Published: 27 December 2017
Highlights
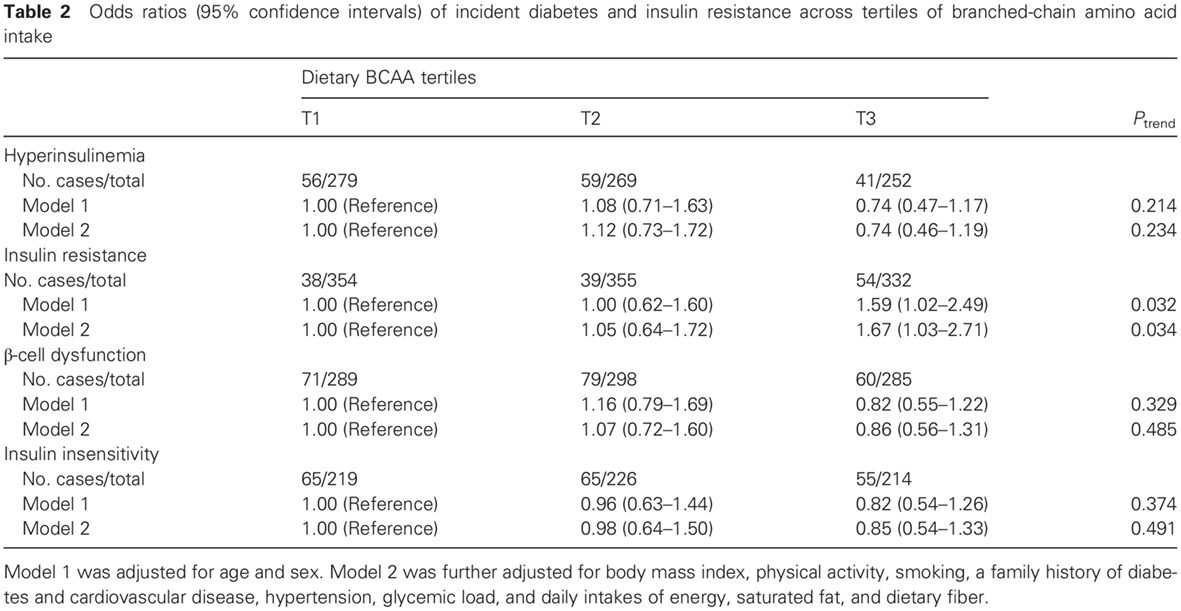
- Higher intake of dietary total branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), leucine and valine in particular, may increase the incidence of insulin resistance by more than 60% in adults and play an important role in the development of diabetes.
- No significant association of was found between the intake of total BCAAs or isoleucine, leucine, and valine individually and the risk of hyperinsulinemia, β-cell dysfunction, or insulin insensitivity in adults.
Review Article
Hemoglobin A1c and diagnosis of diabetes: 糖化血红蛋白与糖尿病诊断
- Pages: 365-372
- First Published: 02 January 2018
Highlights
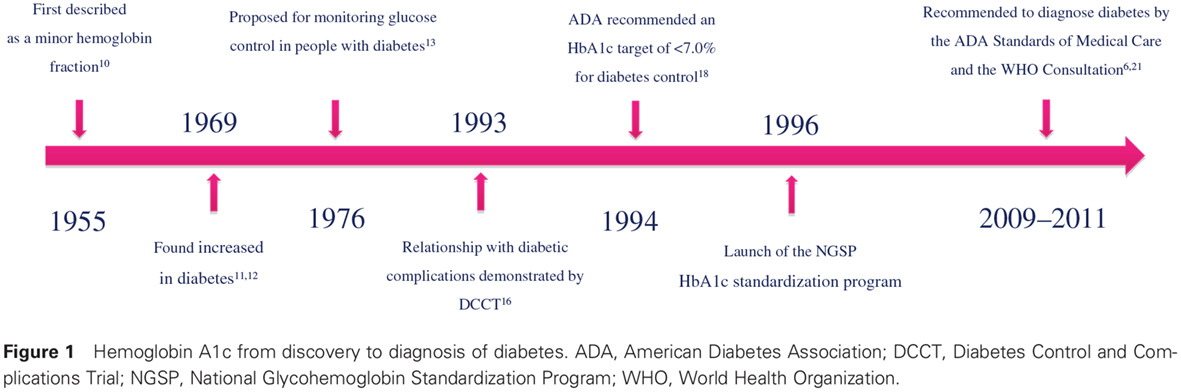
- Hemoglobin A1c should be used with caution in diagnosing diabetes among patients with disorders affecting red blood cell survival or glycosylation.
- The challenge of using HbA1c to diagnose diabetes lies in finding the “right” diagnostic cut-off value because results, to date, are vastly inconsistent.
- Differences in data collection methods in populations from different ethnic groups and with varying clinical characteristics, different assay methods for the measurement of HbA1c, and different reference criteria may all play a part in the inconsistent results.
Original Articles
Prepregnancy habitual intake of vitamin D from diet and supplements in relation to risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: A prospective cohort study: 孕前习惯从饮食以及补充剂中摄入的维生素D剂量与妊娠糖尿病风险的关系:一项前瞻性队列研究
- Pages: 373-379
- First Published: 04 October 2017
Highlights
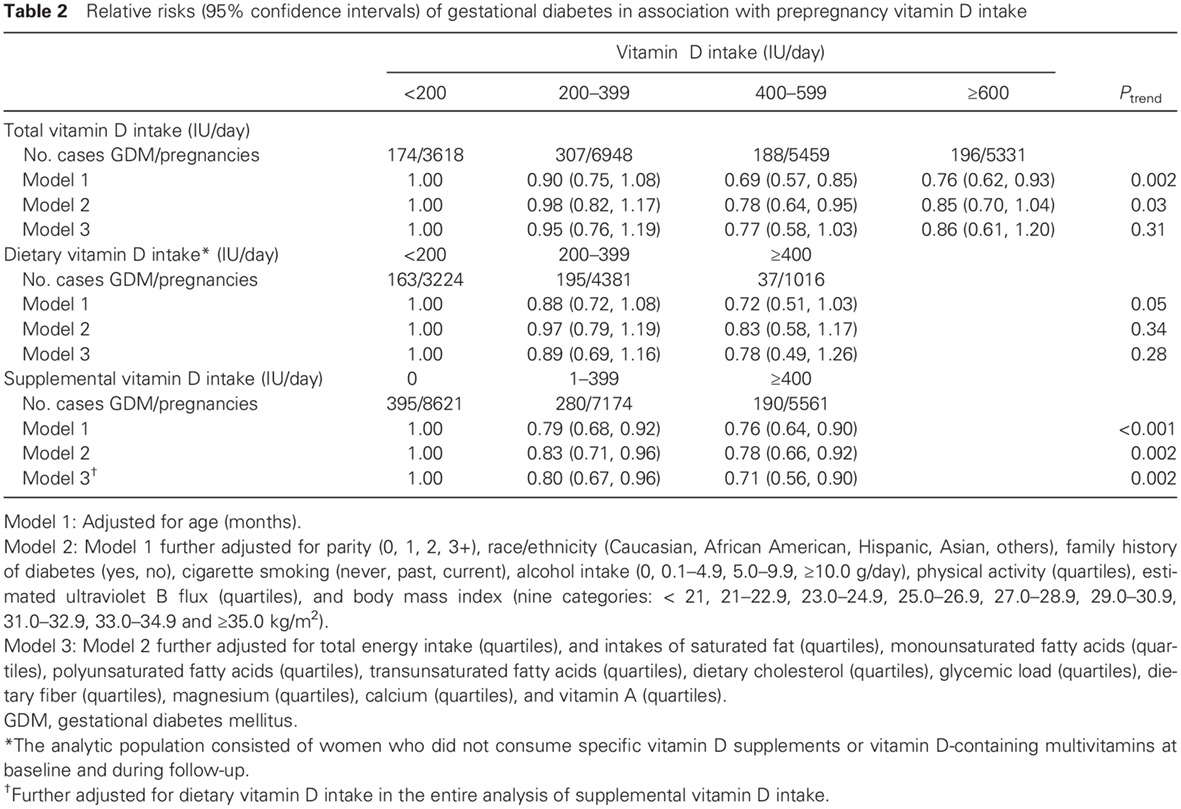
- Vitamin D insufficiency is common in pregnant women, and has been associated with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM). However, the effect of vitamin D intake, either from diet or supplements, on the development of GDM remains unknown.
- In a large prospective cohort study, we found that prepregnancy supplemental vitamin D intake was significantly and inversely associated with risk of GDM.
- These results indicate potential benefits of increasing vitamin D intake from supplements in the prevention of GDM.
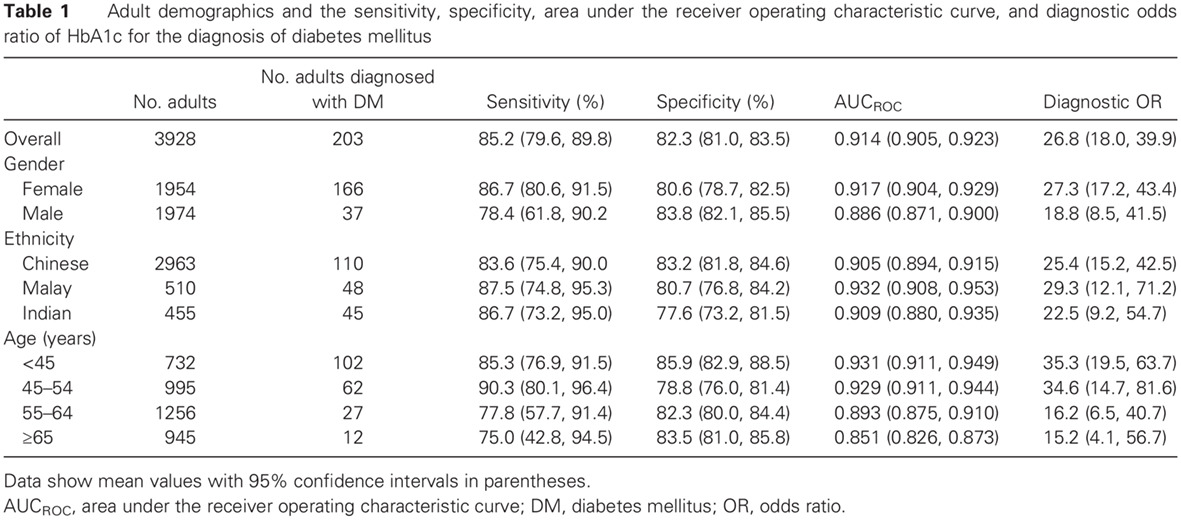
Re-examining the sensitivity of HbA1c to screen for diabetes mellitus: 重新审视HbA1c用于筛查糖尿病的敏感性
- Pages: 380-385
- First Published: 14 October 2017
Highlights
- The sensitivity of HbA1c as a screening test for diabetes in this study was significantly higher than that in other published studies in the literature.
- One reason that could explain the increased sensitivity of HbA1c in this study could be the use of repeat testing to confirm the diagnosis of diabetes.
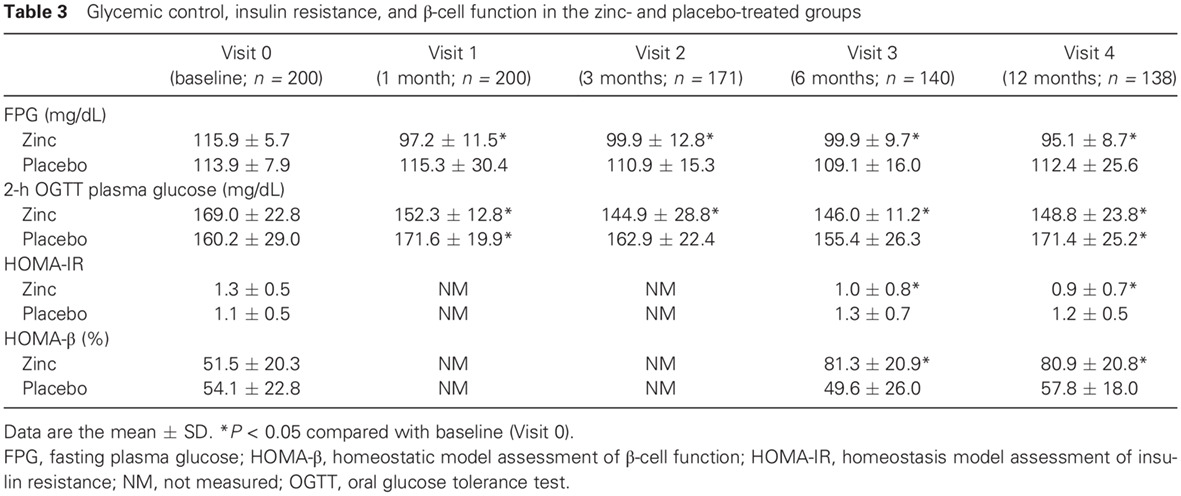
Zinc supplementation in prediabetes: A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial: 糖尿病前期补充锌治疗:一项随机双盲安慰剂对照临床试验
- Pages: 386-397
- First Published: 26 October 2017
Highlights
- Zinc deficiency is present in those with prediabetes, and can be corrected by zinc supplementation.
- Zinc supplementation in those with prediabetes reduced blood glucose and insulin resistance while improving β-cell function.
- Disease progression to diabetes was reduced with zinc supplementation.
- Zinc supplementation also had beneficial effects on total and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
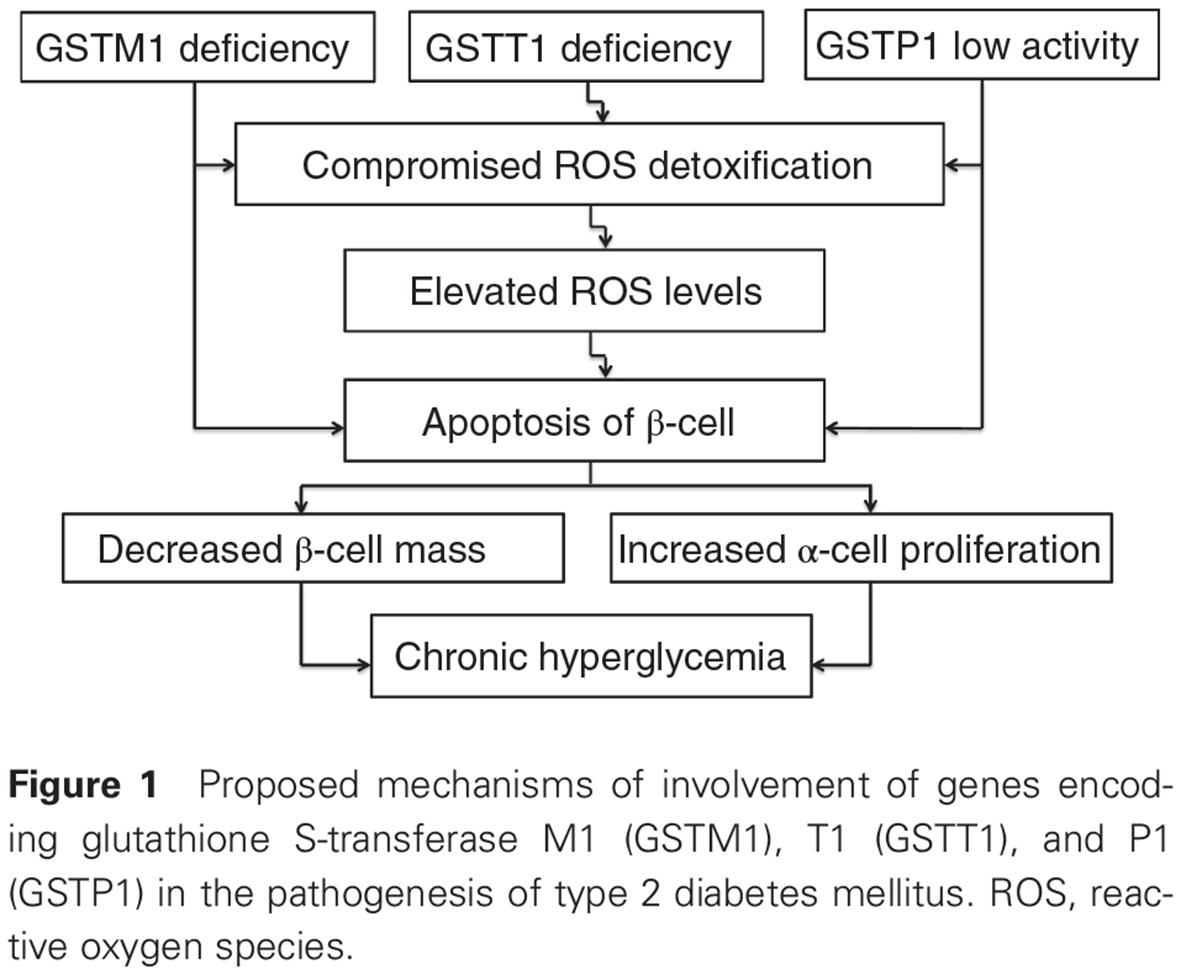
Glutathione S-transferase genes and the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus: Role of sexual dimorphism, gene–gene and gene–smoking interactions in disease susceptibility: 谷胱甘肽S-转移酶基因与2型糖尿病风险:两性异形、基因-基因以及基因-吸烟相互作用对疾病易感性的影响
- Pages: 398-407
- First Published: 07 November 2017
Highlights
- This study demonstrates that genes encoding glutathione S-transferases M1, T1, and P1 are important determinants of susceptibility to type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in Russians.
- This study is the first to show a joint contribution of these genes to the development of the disease, but the effects of these genes on disease risk are gender specific.
- A synergy between the effects of glutathione S-transferase gene polymorphisms and cigarette smoking may increase the risk of T2DM.
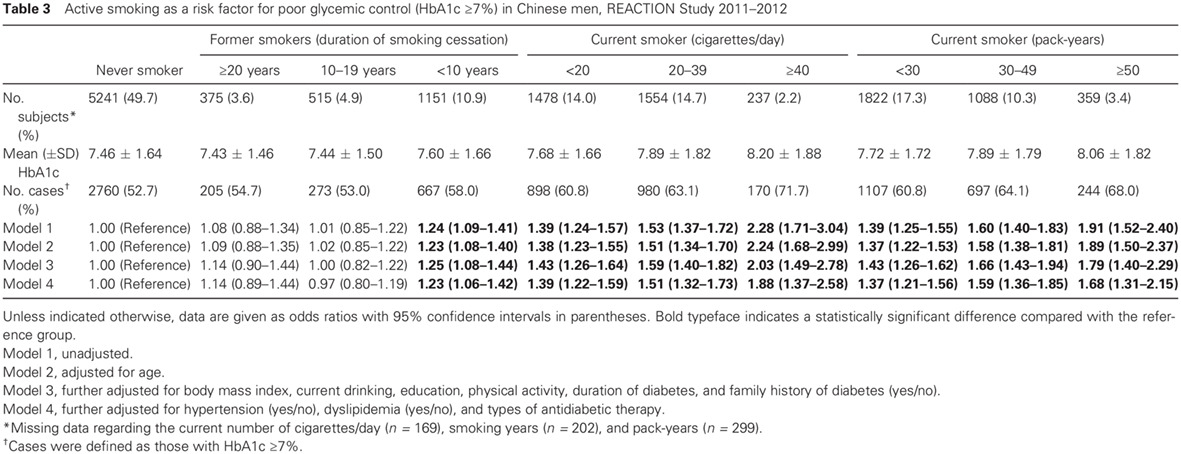
Association between smoking and glycemic control in diabetic patients: Results from the Risk Evaluation of cAncers in Chinese diabeTic Individuals: A lONgitudinal (REACTION) study: 吸烟与糖尿病患者血糖控制的相关性研究:来自中国2型糖尿病患者恶性肿瘤发生风险的纵向研究(REACTION)的发现
- Pages: 408-418
- First Published: 16 November 2017
Highlights
- Active smoking was associated with an increased risk of prevalent poor glycemic control in middle-aged or elderly diabetic adults.
- Men who quit smoking for <10 years remained at increased risk for prevalent poor glycemic control compared with never smokers, and the risk leveled off after 10 years of smoking cessation.
- Smoking cessation was associated with improvement in glycemic control compared with current smoking.
Letters to the Editor
Fulminant type 1 diabetes caused by peginterferon α-2a therapy in hepatitis C: 丙型肝炎患者使用聚乙二醇干扰素α-2a治疗后导致的暴发性1型糖尿病
- Pages: 419-420
- First Published: 19 December 2017
Type 1 diabetes mellitus associated with activated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase delta syndrome, type 2: 与2型激活磷脂酰肌醇-3激酶δ综合征相关的1型糖尿病
- Pages: 421-422
- First Published: 27 December 2017