Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Editorial
How does CKD affect HbA1c?
CKD如何影响HbA1c?
- Page: 270
- First Published: 10 November 2017
News
Editors' Recommendations
Performance of non-traditional hyperglycemia biomarkers by chronic kidney disease status in older adults with diabetes: Results from the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study: 在老年糖尿病患者慢性肾脏疾病状态下非传统高血糖生物标志物的检测效能:来自评估动脉粥样硬化风险社区研究的结果
- Pages: 276-285
- First Published: 20 October 2017
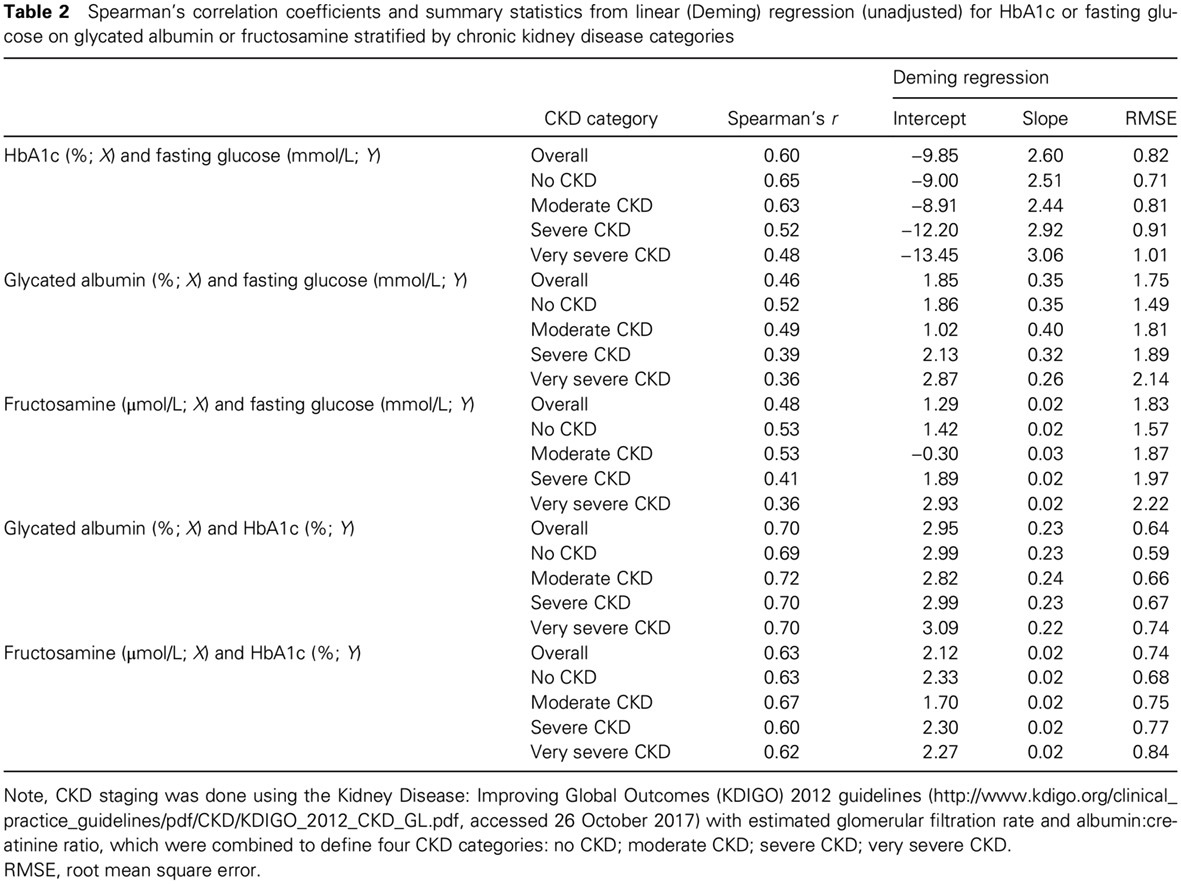
Highlights
- Correlations of glycated albumin, fructosamine, and HbA1c with fasting glucose were all lower at more severe stages of chronic kidney disease stages in older adults with diagnosed diabetes.
- Our data suggest that the limitations of HbA1c may not be overcome by glycated albumin or fructosamine in the setting of chronic kidney disease.
Original Articles
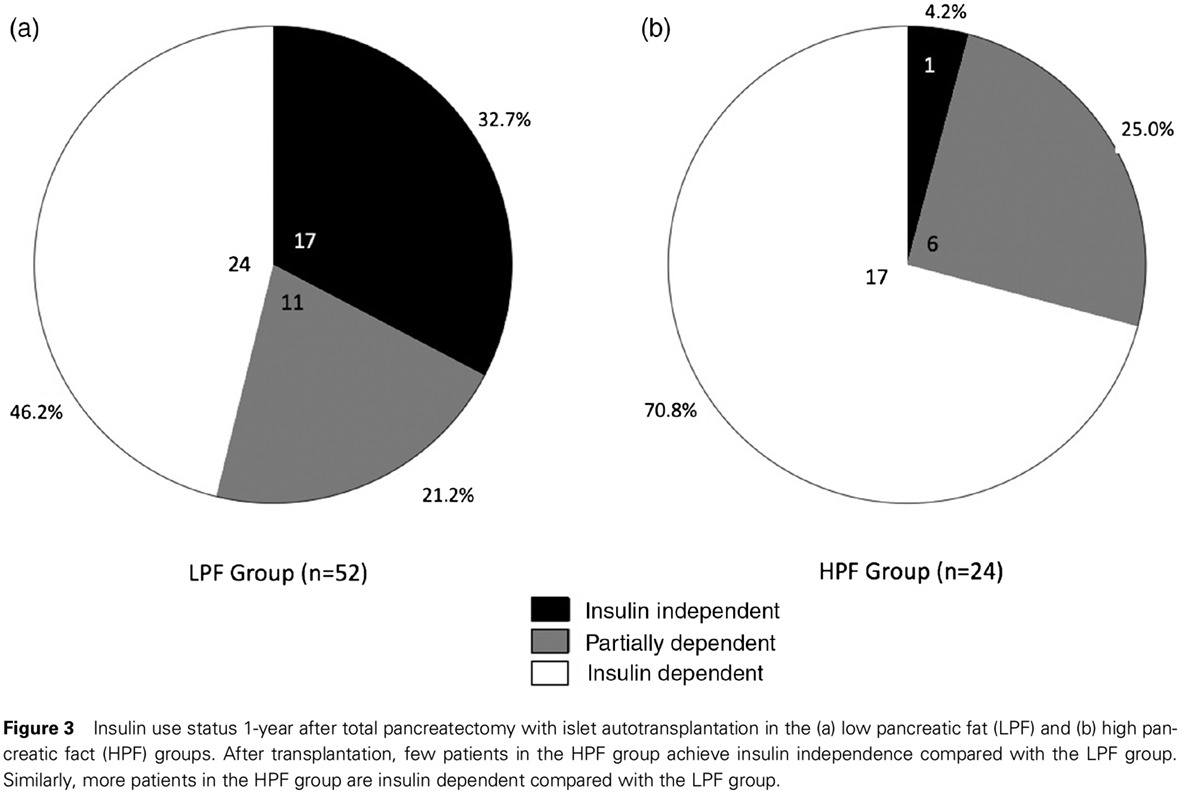
Effect of intrapancreatic fat on diabetes outcomes after total pancreatectomy with islet autotransplantation: 全胰切除术与自体胰岛移植后胰腺内脂肪对糖尿病结局的影响
- Pages: 286-295
- First Published: 10 August 2017
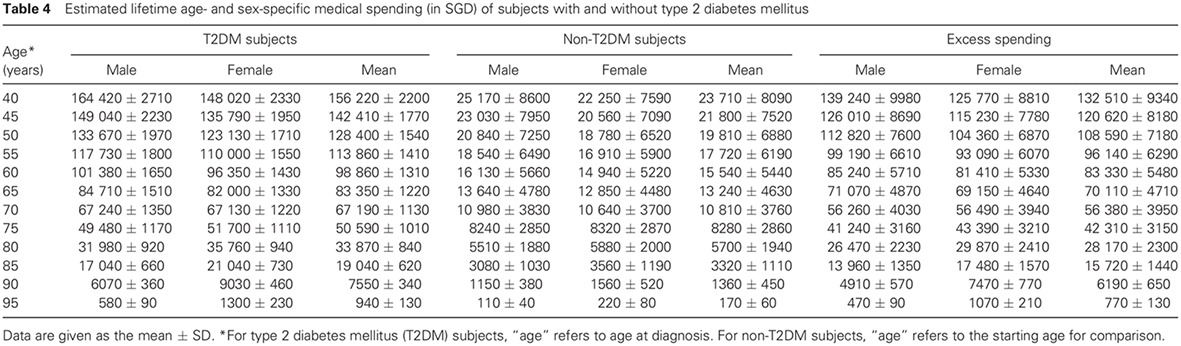
Lifetime cost for type 2 diabetes mellitus in Singapore: 新加坡2型糖尿病患者的寿命成本
- Pages: 296-301
- First Published: 23 August 2017
Association of daytime napping with prediabetes and diabetes in a Chinese population: Results from the baseline survey of the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study: 中国人群午睡与前驱糖尿病和糖尿病的关系研究:来自中国健康与养老追踪调查的基线调查结果
- Pages: 302-309
- First Published: 29 August 2017
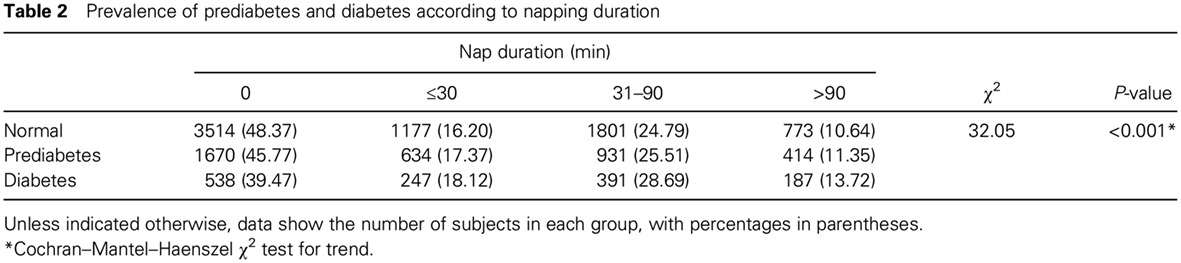
Highlights
- The association between napping and prediabetes was not clear and was investigated in the present large cross-sectional study.
- Napping groups had higher prevalence of prediabetes and diabetes than non-nappers.
- Long daytime napping duration was positively associated with prediabetes and diabetes.
Complementary and alternative medicine in US adults with diabetes: Reasons for use and perceived benefits: 美国成年糖尿病患者的补充与替代医学:使用原因与感知获益
- Pages: 310-319
- First Published: 12 September 2017
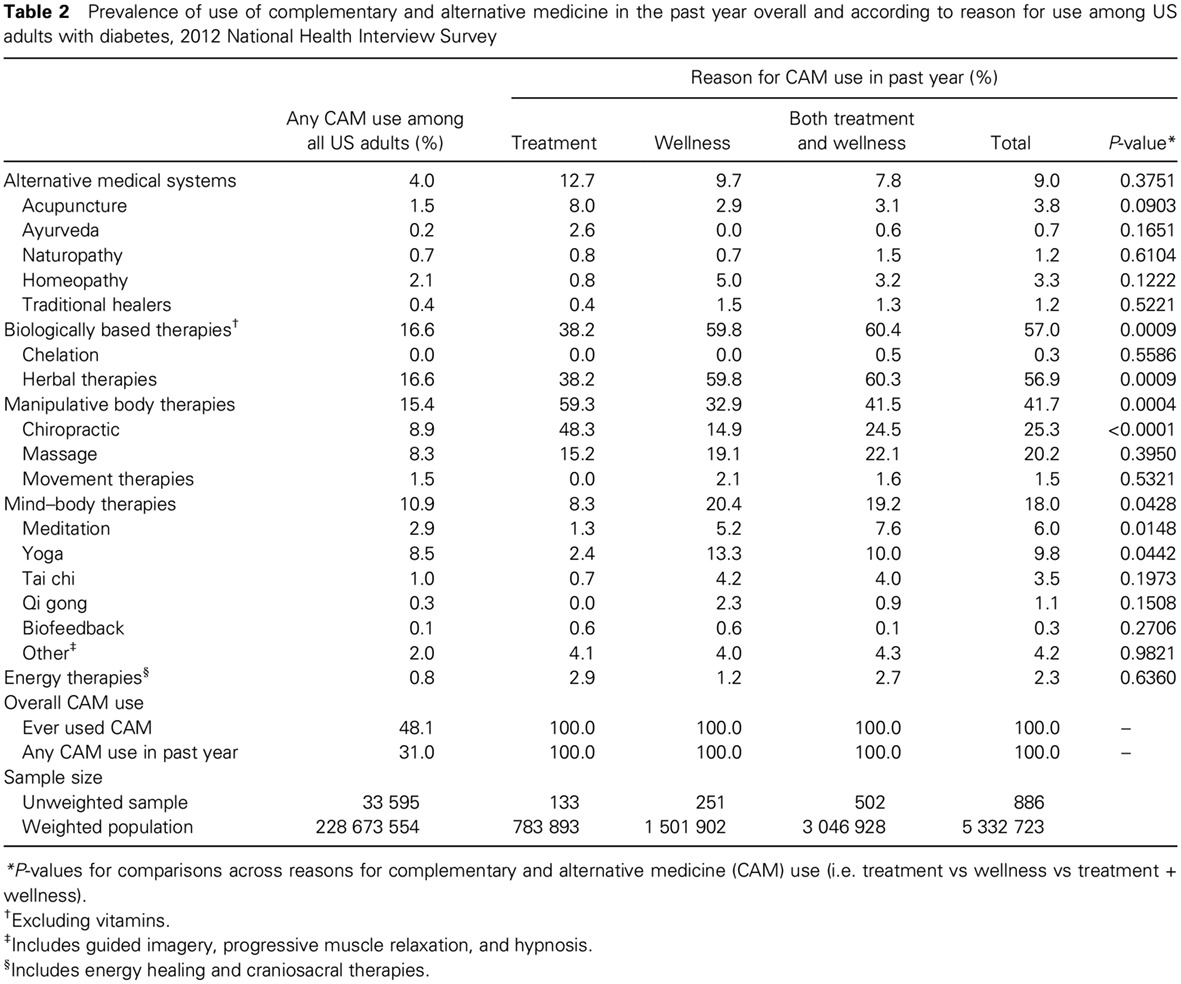
Highlights
- Of US adults with diabetes, 26.2% reported using complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) in the past year.
- Among those using CAM, 56.7% used CAM for both treatment and wellness, and 28.3% used CAM for wellness only. Only 15.0% used CAM for treatment only.
- Those who used CAM for both treatment and wellness had a higher likelihood of reporting “a better sense of control over their health” and “improved overall health and feeling better” when compared with those who used CAM for treatment only.
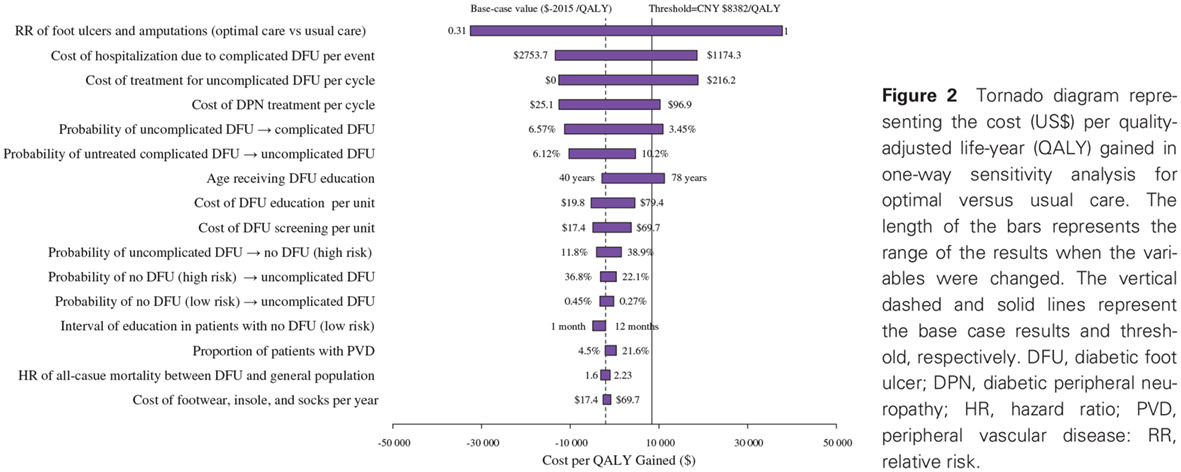
Cost-effectiveness of prevention and management of diabetic foot ulcer and amputation in a health resource-limited setting: 卫生资源有限条件下预防和治疗糖尿病足溃疡和截肢的成本效益分析
- Pages: 320-327
- First Published: 04 October 2017
Resistance training reduces metabolic syndrome and inflammatory markers in older women: A randomized controlled trial: 老年女性抗阻训练可减少代谢综合征以及炎症标志物:一项随机对照试验
- Pages: 328-337
- First Published: 14 October 2017
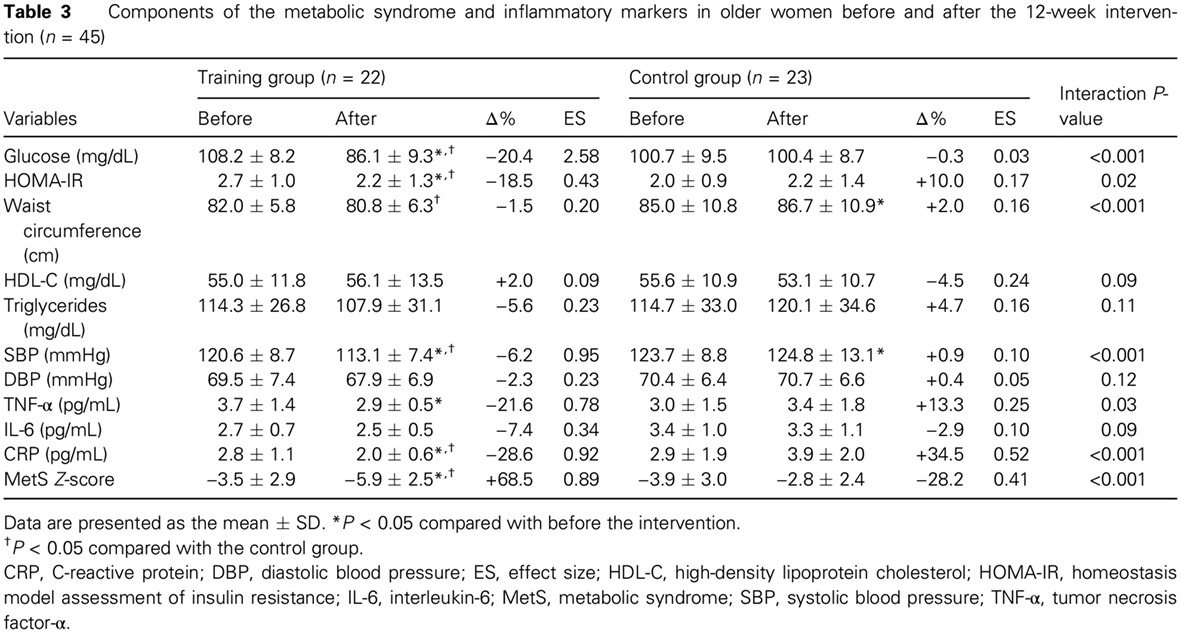
Highlights
- Resistance training decreases the risk of metabolic syndrome in older women, regardless of dietary intervention.
- Resistance training promotes improvements in inflammatory markers in older women, regardless of dietary intervention.
- The reduction in risk of metabolic syndrome after resistance training seems to be related to reduced inflammation and improved body composition and muscular strength.
Case Report
Latent autoimmune diabetes and limbic encephalitis with antibodies against glutamic acid decarboxylase: 隐匿性自身免疫性糖尿病与抗谷氨酸脱羧酶抗体阳性的边缘性脑炎
- Pages: 338-340
- First Published: 20 November 2017
Highlights
- Limbic encephalitis with antibodies against glutamic acid decarboxylase can occur in patients with latent autoimmune diabetes of the adult.
- Autoimmune encephalitis should be considered when patients with autoimmune diabetes present with seizures and memory impairment.
Letters to the Editor
Sleep habits and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Risk assessment by adjusting confounders: 睡眠习惯与非酒精性脂肪性肝病:通过调整混杂因素后再进行风险评估
- Page: 341
- First Published: 26 October 2017
Response to Kawada: Sleep habits and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Risk assessment by adjusting confounders: 对Kawada的回复:隐匿性自身免疫性糖尿病与抗谷氨酸脱羧酶抗体阳性的边缘性脑炎
- Pages: 342-343
- First Published: 22 November 2017
Challenges of the economic and social effects of diabetes in low- and middle-income countries: 在低收入与中等收入国家中糖尿病对经济以及社会影响的挑战
- Pages: 344-345
- First Published: 05 December 2017