Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Editorial
Metabolic memory: Evolving concepts: 代谢记忆:不断进化的概念
- Pages: 186-187
- First Published: 01 November 2017
News
Editors' Recommendations
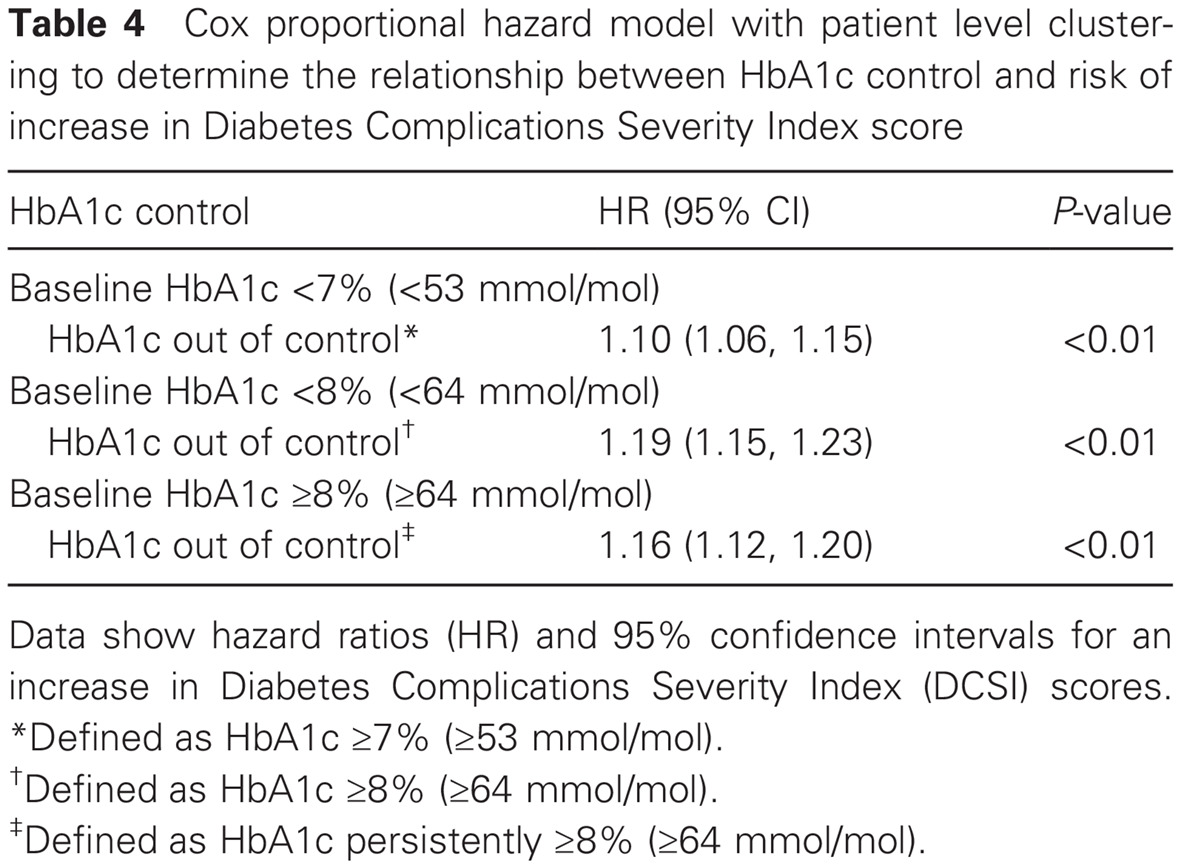
Effect of glycemic control on the Diabetes Complications Severity Index score and development of complications in people with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: 在新诊断的2型糖尿病患者中血糖控制情况对糖尿病并发症严重程度指数评分以及并发症进展的影响
- Pages: 192-199
- First Published: 04 October 2017
Highlights
- There is a lack of published real-world evidence regarding longitudinal changes in Diabetes Complications Severity Index (DCSI) scores among people with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes (T2D), including how the level of glycemic control at the time of diagnosis may affect DCSI score progression.
- This study evaluated such outcomes over an 11-year period in a very large cohort of patients with newly diagnosed T2D (n = 32 174), with data drawn from electronic health records from a large US integrated healthcare system.
- These are the first known data to demonstrate that worsening or persistently poor glycemic control, but not baseline glycemic control, is associated with increasing DCSI score over time.
Review Articles
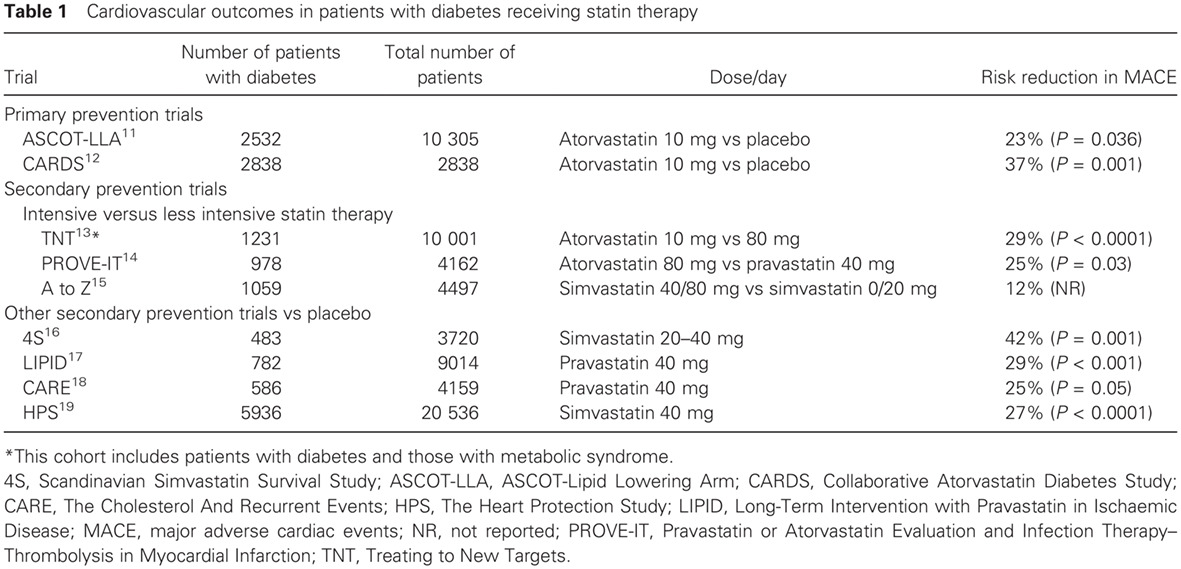
Regional evidence and international recommendations to guide lipid management in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes with special reference to renal dysfunction: 对亚洲2型糖尿病患者特别是有肾功能障碍患者的血脂管理的地区实证和国际建议
- Pages: 200-212
- First Published: 28 September 2017
Highlights
- Despite the proven effectiveness of lipid management in reducing diabetes-related complications, there are major treatment gaps, especially in Asian patients with young-onset diabetes and chronic kidney disease (CKD).
- Given the propensity of Asian patients with diabetes to develop CKD and the amplifying effect of CKD on atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease, the timely use of statins in Asian patients is particularly important.
- There is an urgent need for Asian countries to review and align their lipid-lowering treatment guidelines to reduce the burden of diabetes in Asia.
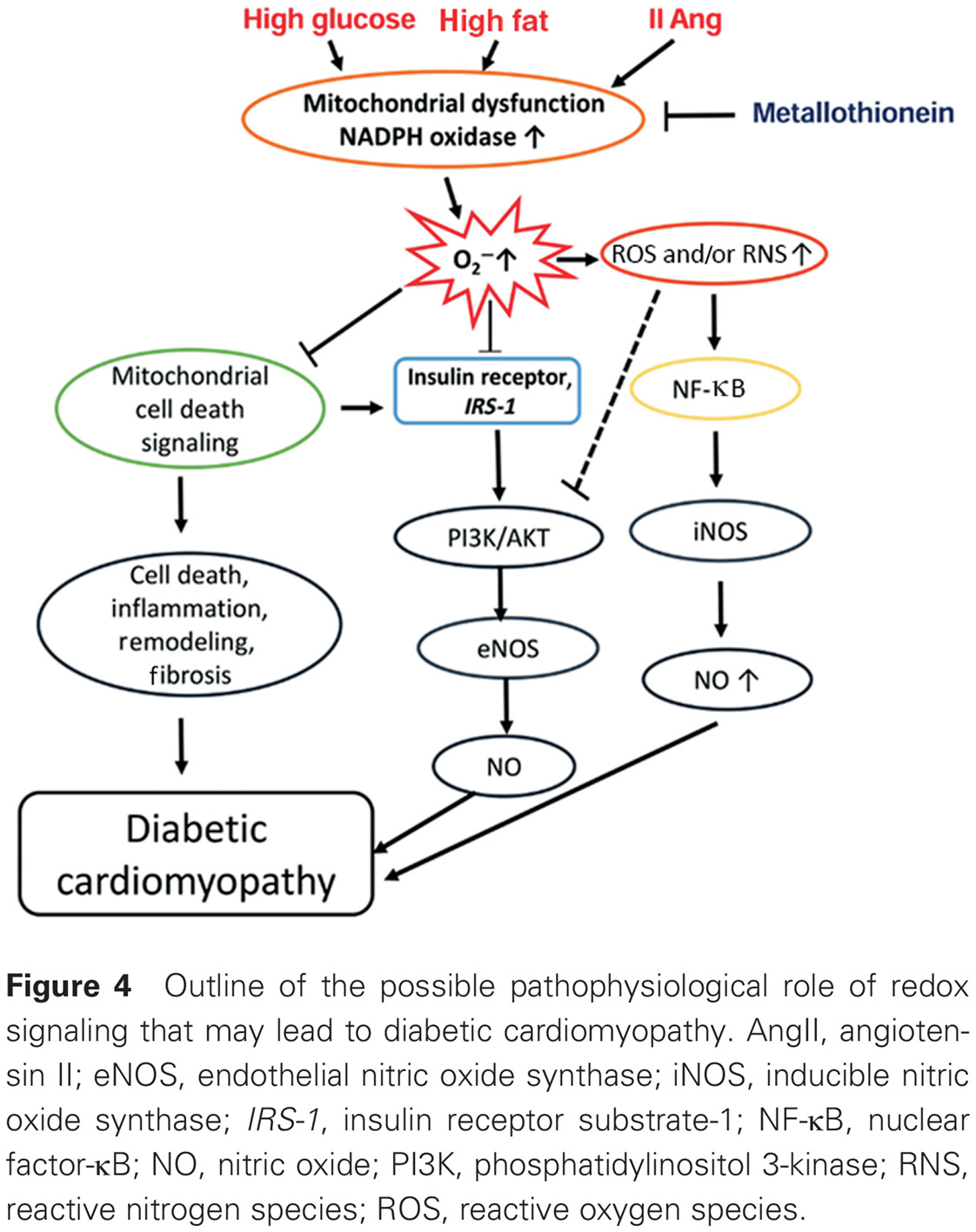
Reappraisal of metallothionein: Clinical implications for patients with diabetes mellitus: 重新评价金属硫蛋白:对糖尿病患者的临床意义
- Pages: 213-231
- First Published: 26 October 2017
Highlights
- A common key element during diabetes pathogeneses is hyperglycemia-induced overproduction of reactive oxygen species and/or species coupled with the decrease in antioxidant capacity, culminating in oxidative stress (OS).
- To reverse OS, metallothionein, a metal-binding endogenous protein with broad-spectrum antioxidant capacity, has been discussed for its potential use for the prevention, and even treatment, of diabetes and diabetic complications.
- Metallothionein, either given as an exogenous protein or induced by zinc supplementation, mediates anti-OS, anti-apoptotic, and anti-inflammatory actions to prevent or treat diabetes and its complications.
Original Articles
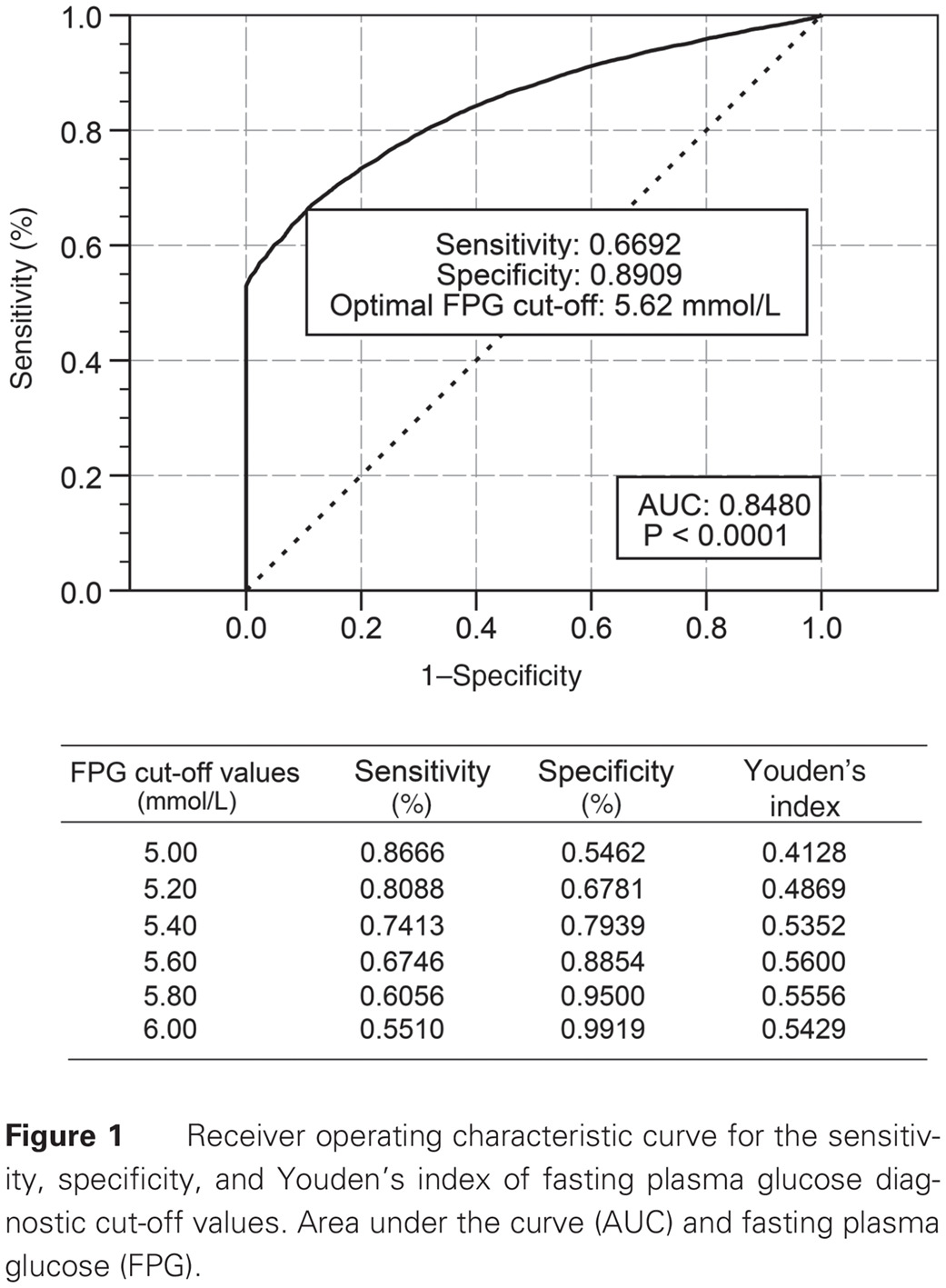
Recommendations for revision of Chinese diagnostic criteria for metabolic syndrome: A nationwide study: 关于代谢综合征的中国诊断标准的修改建议:一项来自全国调查数据的分析
- Pages: 232-239
- First Published: 22 June 2017
Highlights
- We recommend eliminating the 2-h postprandial plasma glucose (PPG) blood test for the detection of hyperglycemia as a criterion in the Chinese Diabetes Society (CDS) guidelines for the diagnosis of metabolic syndrome (MS).
- This study used representative national data to estimate the optimal fasting plasma glucose (FPG) cut-off value for a diagnosis of MS to be 5.62 mmol/L.
- The recommended FPG criterion, compared with the CDS-MS, showed better agreement with international criteria for the diagnosis of MS.
Plasma lipids affect dabigatran etexilate anticoagulation in rats with unbalanced diabetes mellitus: 在失衡的糖尿病大鼠中血脂可以影响达比加群酯的抗凝作用
- Pages: 240-248
- First Published: 03 July 2017
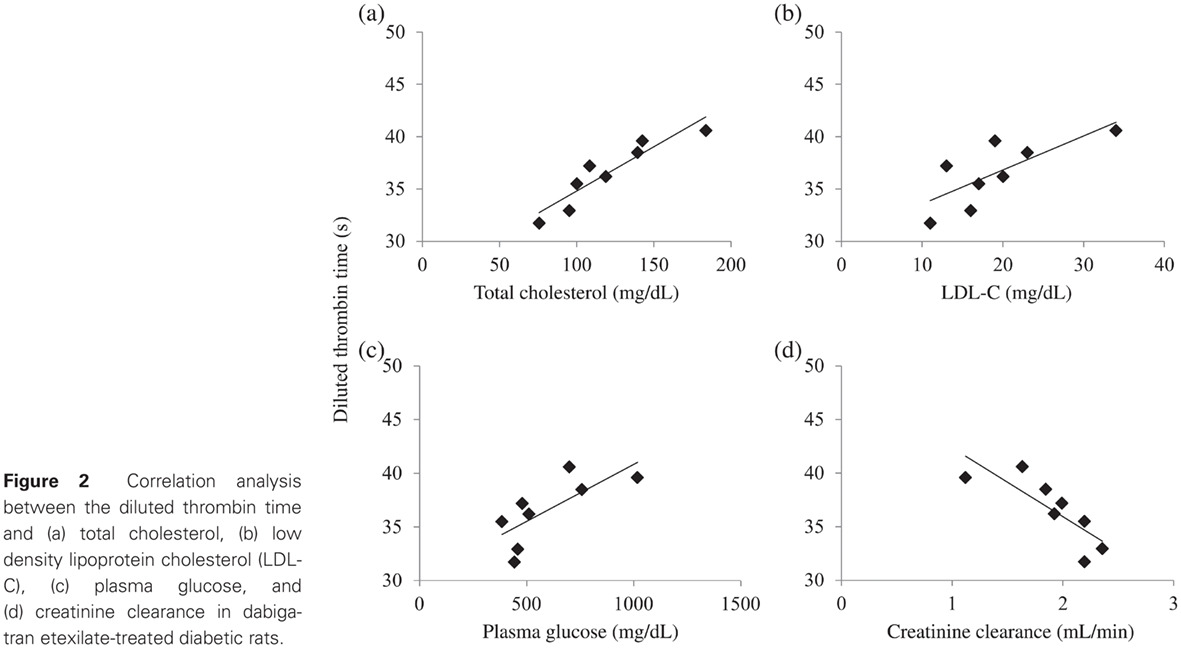
Highlights
- Diabetic rats exhibit significantly more intense dabigatran-induced anticoagulation that does not seem to be solely related to altered kidney function.
- Plasma cholesterol significantly affects dabigatran-induced anticoagulation in this setting.
- These findings could explain the similar benefits of dabigatran in reducing ischemic stroke compared with warfarin in patients with and without diabetes mellitus, despite the significantly higher intrinsic thrombotic risk in the former, as well as the lack of benefit of reducing major bleeding in diabetic patients.
Prevalence of and risk factors for diabetic ketosis in Chinese diabetic patients with random blood glucose levels >13.9 mmol/L: Results from the CHina study in prEvalence of diabetiC Ketosis (CHECK) study: 随机血糖> 13.9 mmol/L 的中国糖尿病患者糖尿病酮症患病率及危险因素分析:来自中国糖尿病酮症(CHECK)研究的结果
- Pages: 249-255
- First Published: 07 July 2017
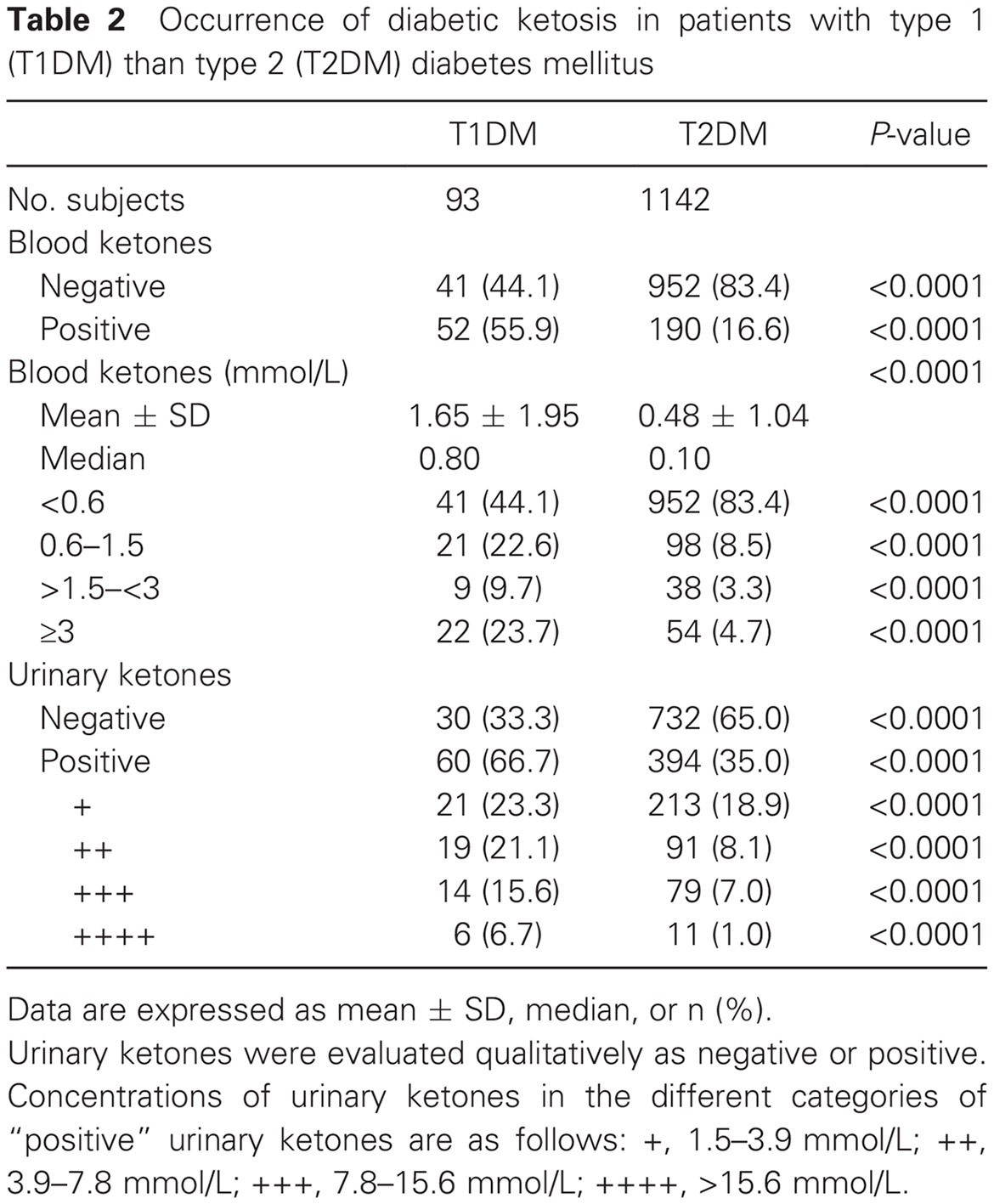
Highlights
- Diabetic ketosis (DK) was more severe in patients with type 1 (T1DM) than type 2 (T2DM) diabetes mellitus.
- Patients with episodes of diabetic ketosis were predominantly those with T2DM.
- The results indicate that T2DM patients of younger age, with a shorter duration of diabetes, and lack of antidiabetic treatment will suffer from DK more often than older patients with longer T2DM duration and receiving antidiabetic treatment.
Efficacy and safety of pregabalin for painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy in a population of Chinese patients: A randomized placebo-controlled trial: 普瑞巴林在中国痛性糖尿病周围神经病变患者治疗中的疗效及安全性:一项随机安慰剂对照试验
- Pages: 256-265
- First Published: 20 July 2017
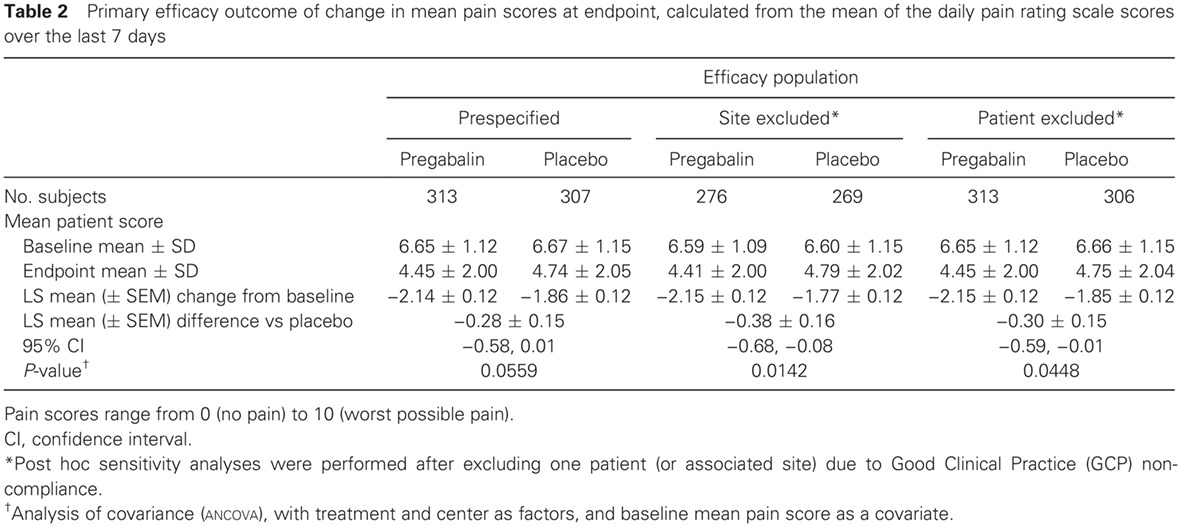
Highlights
- This is the first study of pregabalin in Chinese pDPN patients, and the findings may inform pDPN treatment in China.
- Pregabalin significantly improved pain in the subpopulation with severe pDPN. Improvements in additional measures of pain and health status were also significant.
- Pregabalin did not significantly improve pain associated with painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy (pDPN) compared with placebo in the trial. However, post hoc sensitivity analyses conducted due to good clinical practice (GCP) non-compliance in one patient showed significant improvement with pregabalin when the non-compliant patient or associated site was excluded.









