Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Editorial
The kidney and cardiovascular outcome trials: 肾脏与心血管结局试验
- Pages: 88-89
- First Published: 14 October 2017
News
European Association for the Study of Diabetes 2017
- Pages: 90-93
- First Published: 20 October 2017
Editors' Recommendations
Improving postprandial hyperglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes already on basal insulin therapy: Review of current strategies: 改善既往已在使用基础胰岛素治疗的2型糖尿病患者餐后高血糖:当前治疗策略综述
- Pages: 94-111
- First Published: 05 June 2017
Highlights
- This article provides an overview for primary care physicians of the strategies available for treating patients with type 2 diabetes who do not achieve glycemic control with basal insulin alone.
- Treatment guidelines from expert bodies and current evidence regarding the use of insulin and non-insulin agents for improving postprandial hyperglycemia are reviewed, including their efficacy, safety, and cost-effectiveness.
Original Articles
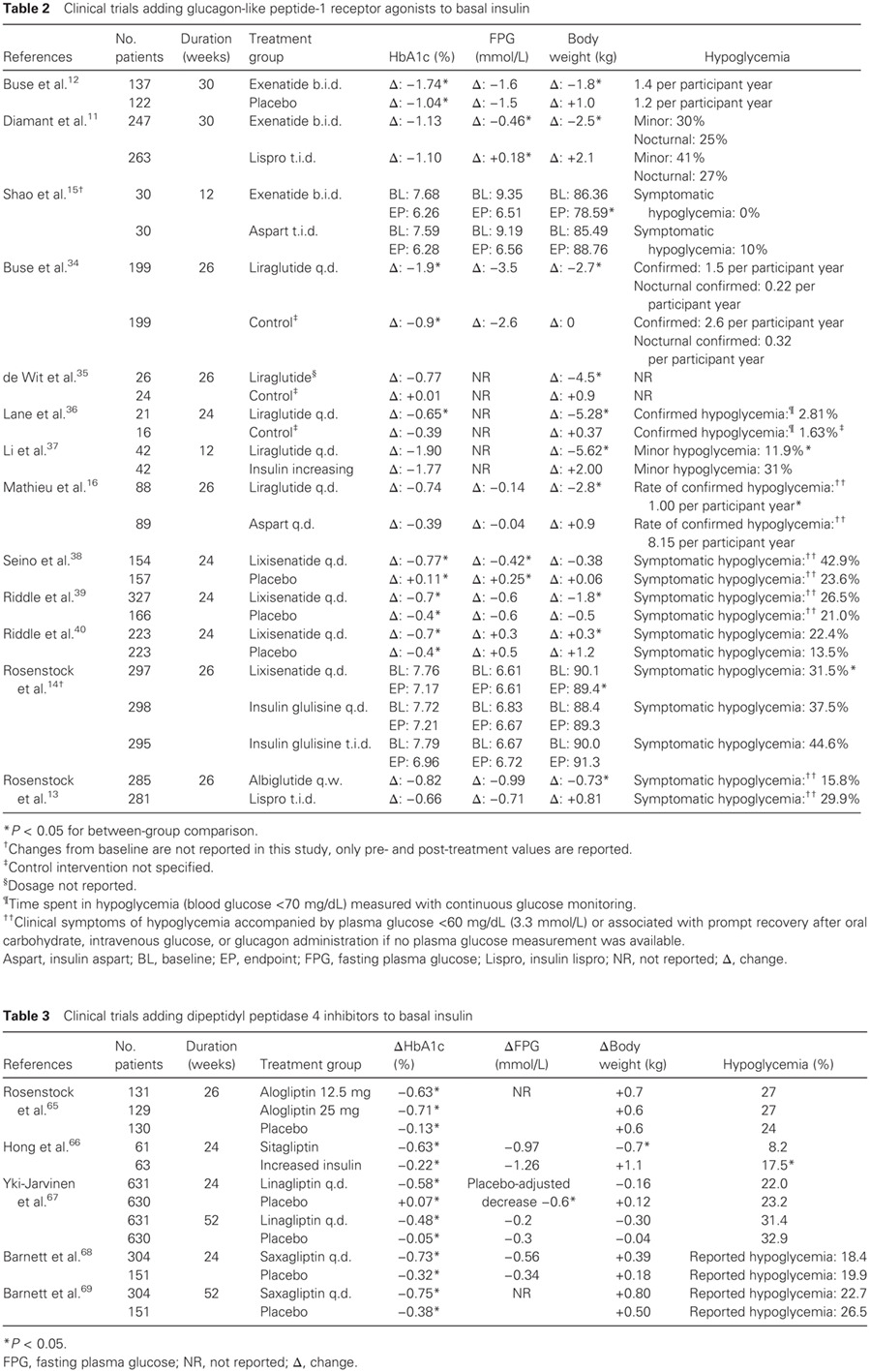
Evaluation of the Chinese herbal medicine Jinlida in type 2 diabetes patients based on stratification: Results of subgroup analysis from a 12-week trial: 中草药津力达治疗2型糖尿病的分层分析:12周临床试验的亚组分析结果
- Pages: 112-120
- First Published: 18 April 2017
Highlights
- Jinlida significantly improved glycemic control in a wide range of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients ineffectively managed by metformin monotherapy, with greater improvements in patients with poor glycemic control and who were male, elderly, of normal weight, or had a long disease course.
- Jinlida could alleviate insulin resistance with hyperinsulinemia and promote secretion with hypoinsulinemia.
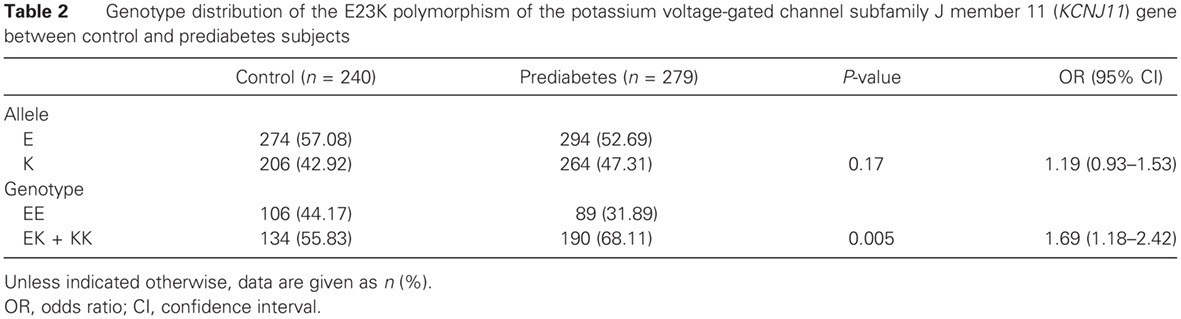
Prediabetes is associated with genetic variations in the gene encoding the Kir6.2 subunit of the pancreatic ATP-sensitive potassium channel (KCNJ11): A case-control study in a Han Chinese youth population: 糖尿病前期与编码ATP敏感性钾通道(KCNJ11)kir6.2亚单位的基因变异相关:在中国汉族青年人群中的研究
- Pages: 121-129
- First Published: 27 April 2017
Highlight
- Our results suggest that common polymorphism of E23K of the KCNJ11 carries higher susceptibility to the development of prediabetes in Chinese Han population. It is also found that E23K variant of the KCNJ11 may have a greater impact on the development of type 2 diabetes in female youth in China.
Ganglioside GM3 content in skeletal muscles is increased in type 2 but decreased in type 1 diabetes rat models: Implications of glycosphingolipid metabolism in pathophysiology of diabetes: 骨骼肌中神经节苷脂GM3的含量在2型糖尿病大鼠模型中增加但在1型糖尿病大鼠模型中减少:鞘糖脂代谢在糖尿病病理生理学中的作用
- Pages: 130-139
- First Published: 22 May 2017
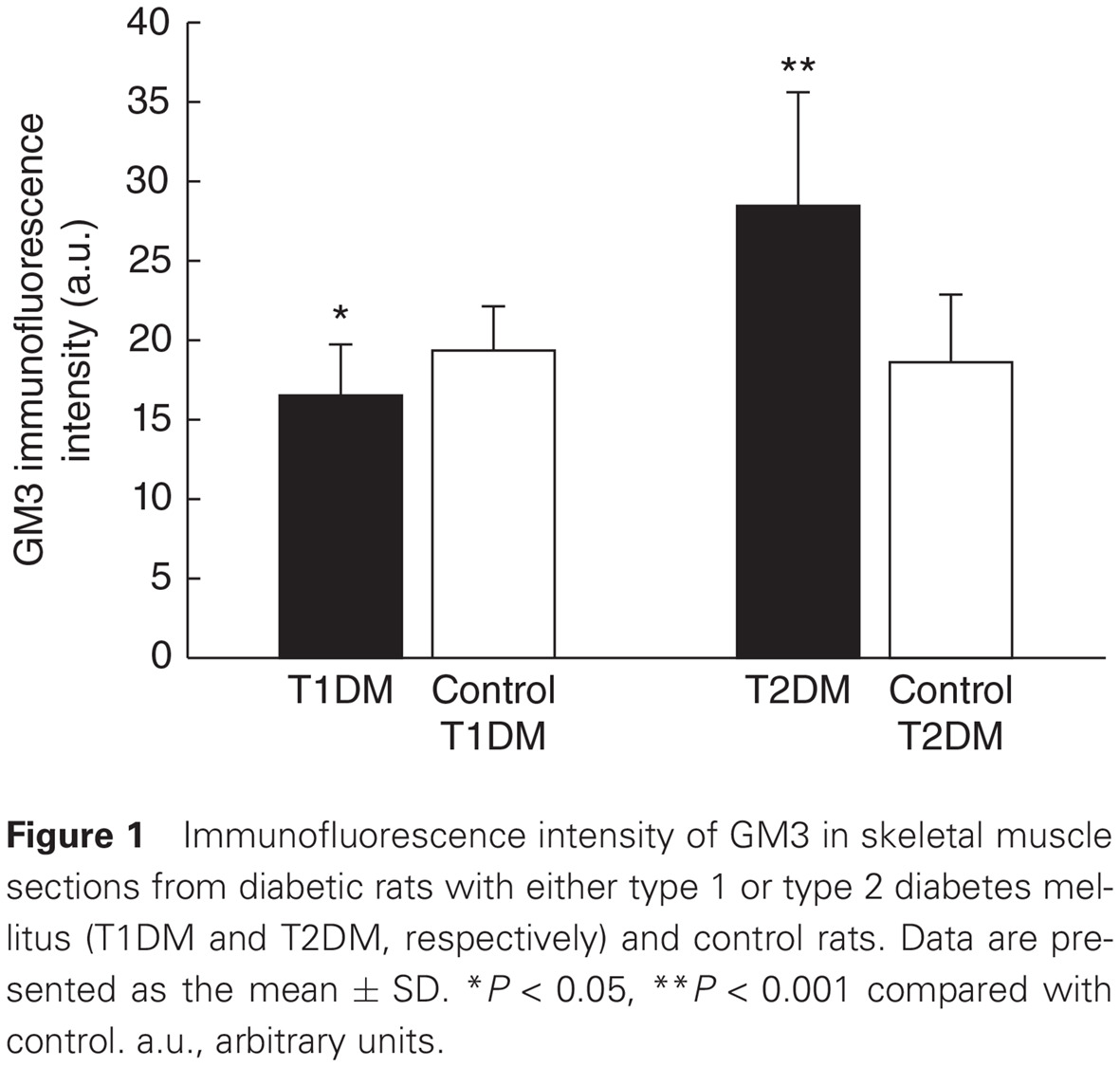
Highlights
- Skeletal muscles play an important role in insulin-stimulated glucose uptake, whereas gangliosides, such as GM3, attenuate insulin receptor signaling, thus contributing to the development of insulin resistance.
- Ganglioside GM3 muscle content was significantly higher in rats with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and significantly lower in rats with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) compared with control groups.
- Expression of GM3 precursors was significantly higher in T2DM rats, whereas ceramide expression was significantly lower in T1DM rats compared with controls.
Assessment of factors determining an HbA1c concentration ≤7.5% in patients with type 1 diabetes: 评估决定1型糖尿病患者HbA1c≤7.5%的因素
- Pages: 140-147
- First Published: 22 May 2017
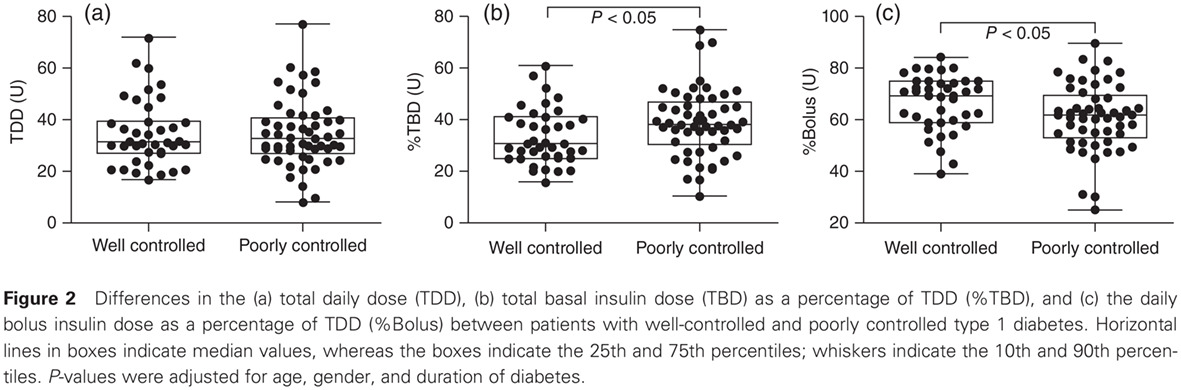
Highlights
- Appropriate insulin dose required for maintaining good glycemic control were assessed in patients with type 1 diabetes.
- Glycemic control did not depend on the total daily insulin dose; rather, the ratio of basal: bolus insulin is important.
- To achieve an HbA1c concentration ≤7.5%, the total daily insulin dose (TDD) should be based on body weight, and the total basal insulin dose as a percentage of TDD should be set at 30% in the Japanese population.
Diabetes and cardiometabolic risk factors in Cambodia: Results from two screening studies: 柬埔寨糖尿病与心血管代谢的危险因素:来自两项筛查研究的结果
- Pages: 148-157
- First Published: 22 May 2017
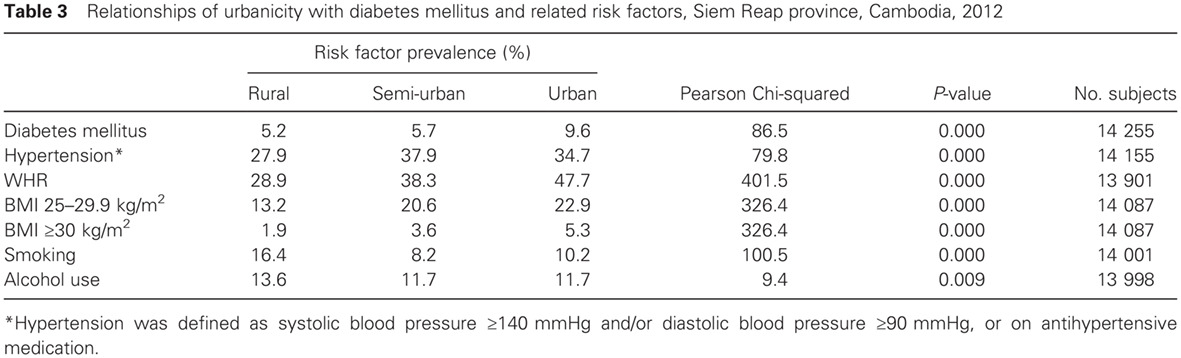
Highlights
- This paper consolidates research from two different studies in Cambodia illuminating contemporary prevalence rates of diabetes, glucose intolerance, and other non-communicable conditions associated with diabetes.
- Rates of obesity, elevated waist:hip ratio, hypertension, and diabetes were higher in urban than rural areas, with semi-urban areas experiencing intermediate rates for some factors.
- Rates of diabetes in Cambodia may be expected to rise as development continues and urban areas expand. An urgent public health response is needed to address non-communicable diseases in Cambodia.
β-Cell function in postmenopausal women with isolated post-challenge hyperglycemia: 单纯餐后高血糖绝经后妇女的β细胞功能
- Pages: 158-165
- First Published: 22 May 2017
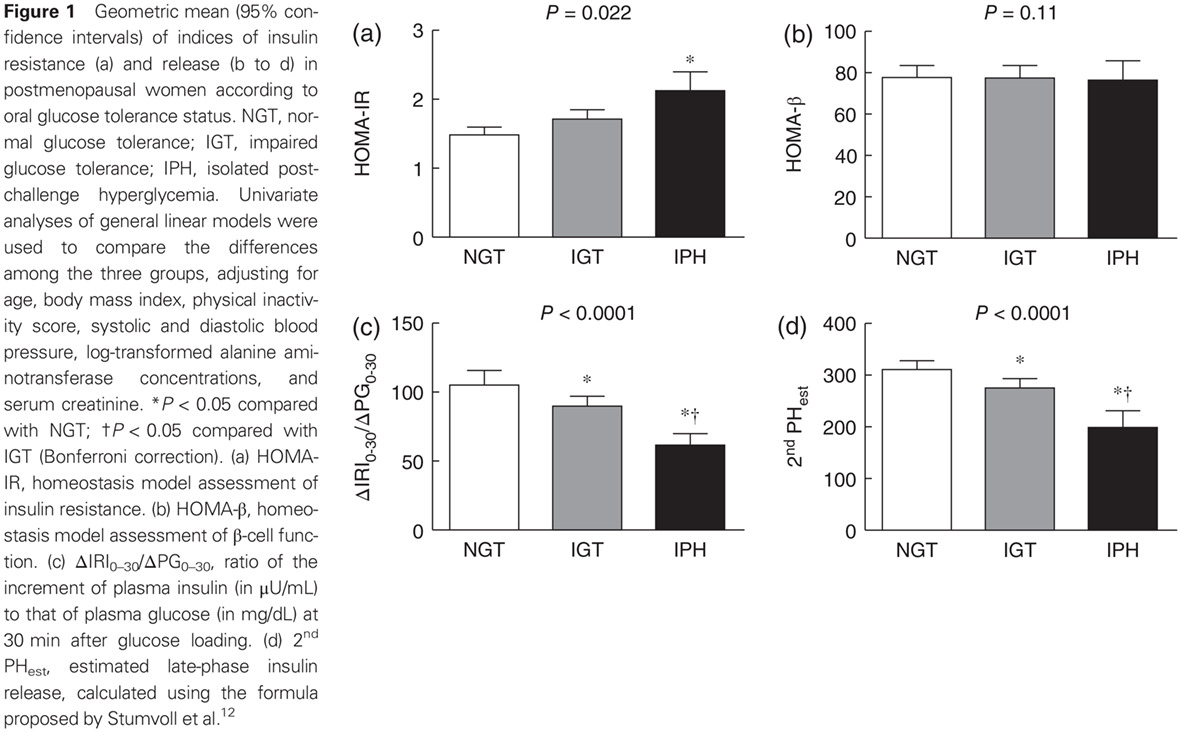
Highlights
- Isolated post-challenge hyperglycemia (IPH) is a common feature in women after menopause.
- Across the spectrum of glucose tolerance, there were significant decreases in early and late-phase insulin release as metabolic status shifted from normal glucose tolerance to impaired glucose tolerance to IPH in the present study.
- Disturbance in β-cell function seems to be an important factor associated with early diabetes mellitus in postmenopausal women.
Protective role of physical activity on type 2 diabetes: Analysis of effect modification by race–ethnicity: 体力活动对2型糖尿病的保护作用:根据人种-种族修正的效果分析
- Pages: 166-178
- First Published: 24 May 2017
Highlights
- There is a significant and similar risk reduction associated with physical activity across race–ethnicity with the exception of non-Hispanic Blacks.
- There are several physiological mechanisms that may explain this finding that require further exploration in the context of physical activity.
Rapid Publication
Indoor renovation and diabetes mellitus: Evidence from a cohort study: 室内装修与糖尿病:来自一项队列研究的证据
- Pages: 179-181
- First Published: 15 December 2017
Highlights
- Household or workplace renovations increase 2hPG levels and diabetes risk
- Stratified analysis by age, gender, BMI, and hypertension showed that the differences in each subgroup were not significant.