Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Editorial
Journal of Diabetes: Ushering in Volume 10: 糖尿病杂志:开启第十卷
- Pages: 4-5
- First Published: 22 September 2017
News
Editors' Recommendations
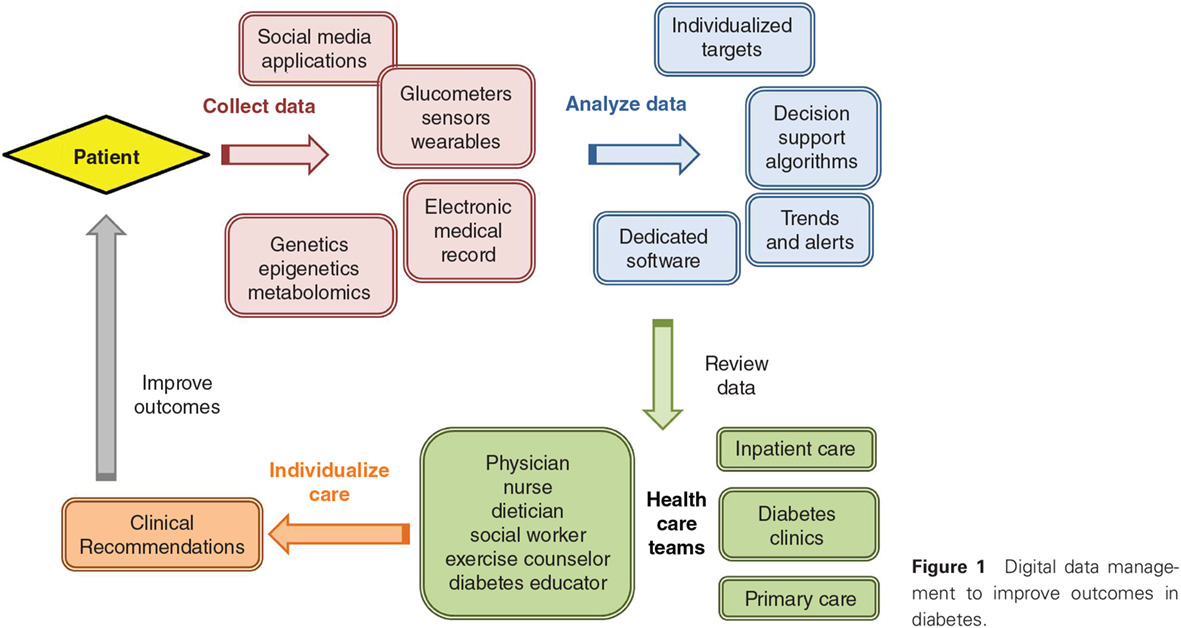
Digital health technology and diabetes management: 数字化医疗技术与糖尿病管理
- Pages: 10-17
- First Published: 05 September 2017
Highlights
- Digital therapy is gaining a pivotal role in the care of patients with diabetes at all levels of disease.
- Thousands of mobile apps are available for enhancing patient motivation, disease management and data provision, presentation, and analysis.
- Data management systems will handle the multitude of data generated daily by patients’ insulin and glucose monitors and other wearables, and decision support systems may, in future, incorporate all data to provide timely and relevant clinical recommendations.
- Future challenges include aspects of data filtering, access, privacy, and regulation.
Original Articles
Salivary gland hypofunction in KK-Ay type 2 diabetic mice: KK-Ay 2型糖尿病小鼠唾液腺功能减退
- Pages: 18-27
- First Published: 16 March 2017
- Saliva secretion from type 2 diabetic (T2D) mice decreased at the glandular level.
- Membrane proteins critical for fluid secretion are preserved in T2D mice.
- Decreased calcium signaling is the key for diabetes-induced hypofunction of salivary glands.
THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN RETRACTED
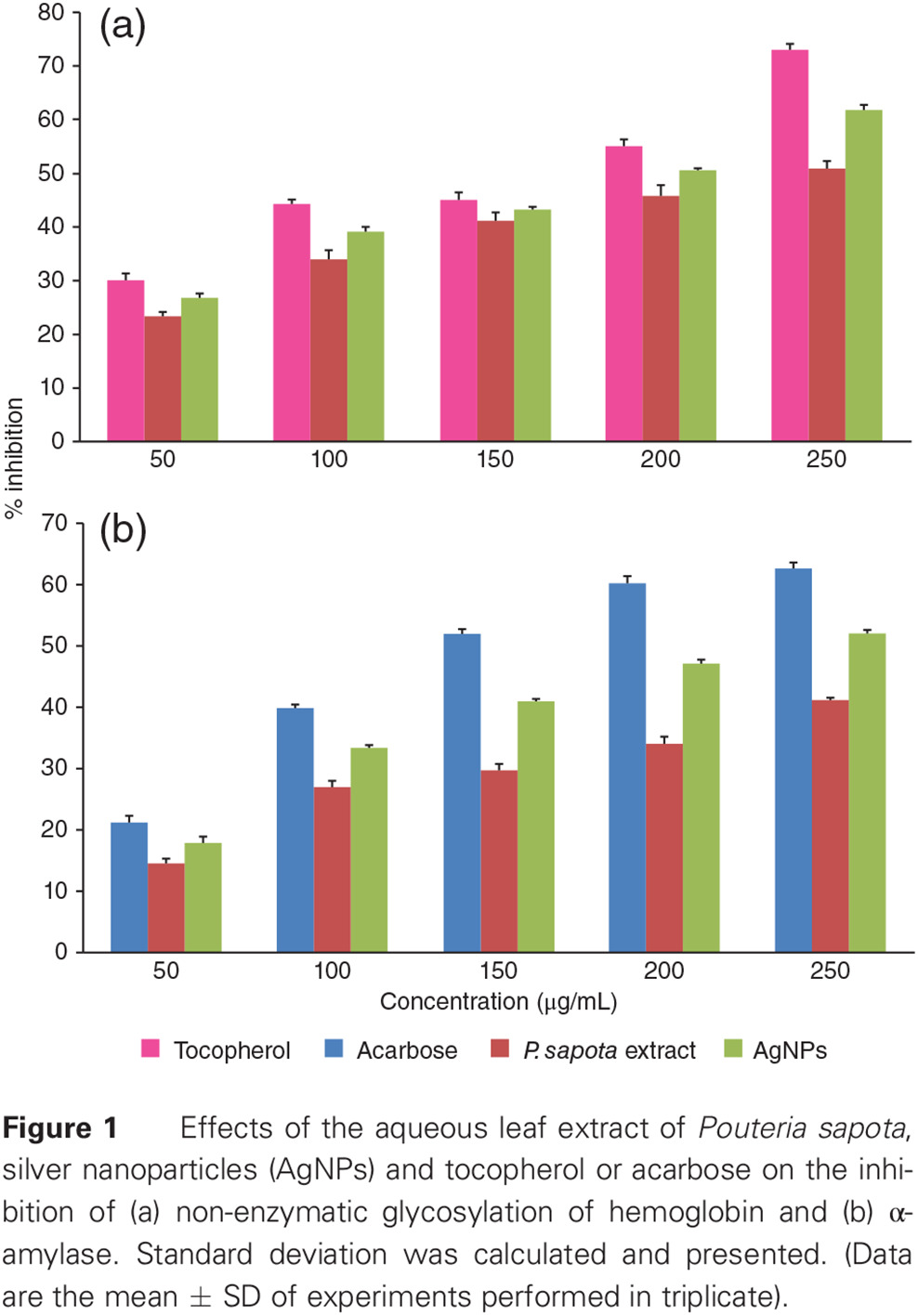
Retracted: Evaluation of antidiabetic activity of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles using Pouteria sapota in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: 在链脲霉素-诱导的糖尿病大鼠中评估使用山榄果生物合成的银纳米粒子的降糖活性
- Pages: 28-42
- First Published: 21 March 2017
Highlights
- The aqueous leaf extract of P. sapota and biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles play an important role in regulating glucose metabolism.
- Determining the role of P. sapota leaf extract in regulating glucose metabolism will provide new insights into the treatment of diabetes, as well as the role of silver nanoparticles in curbing the disease.
Original Articles
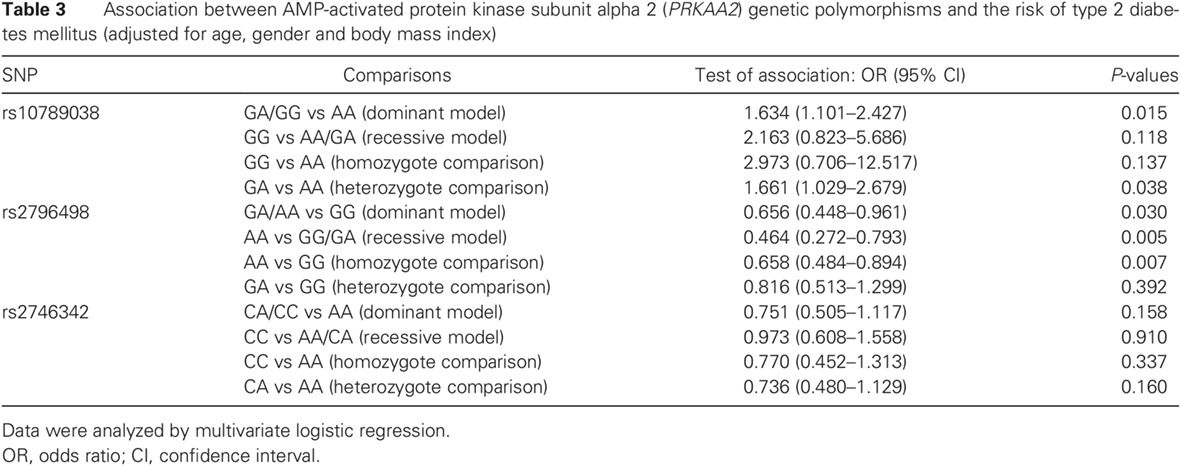
Effect of AMP-activated protein kinase subunit alpha 2 (PRKAA2) genetic polymorphisms on susceptibility to type 2 diabetes mellitus and diabetic nephropathy in a Chinese population: PRKAA2基因多态性对中国人群易感2型糖尿病和糖尿病肾病的影响研究
- Pages: 43-49
- First Published: 21 March 2017
Highlights
- The PRKAA2 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) rs10789038 and rs2796498 were found to be associated with susceptibility to type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
- These two SNPs seem to interact with the rs2746342 SNP of PRKAA2 to affect the development of T2DM.
- The present study is the first to find a significant association between rs2796498 and the incidence of diabetic nephropathy in the Chinese Han population.
Recovered insulin production after thiamine administration in permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus with a novel solute carrier family 19 member 2 (SLC19A2) mutation: 硫胺素治疗可恢复溶质载体家族19成员2(SLC19A2)基因突变所致的永久性新生儿糖尿病患儿的胰岛素分泌
- Pages: 50-58
- First Published: 30 March 2017
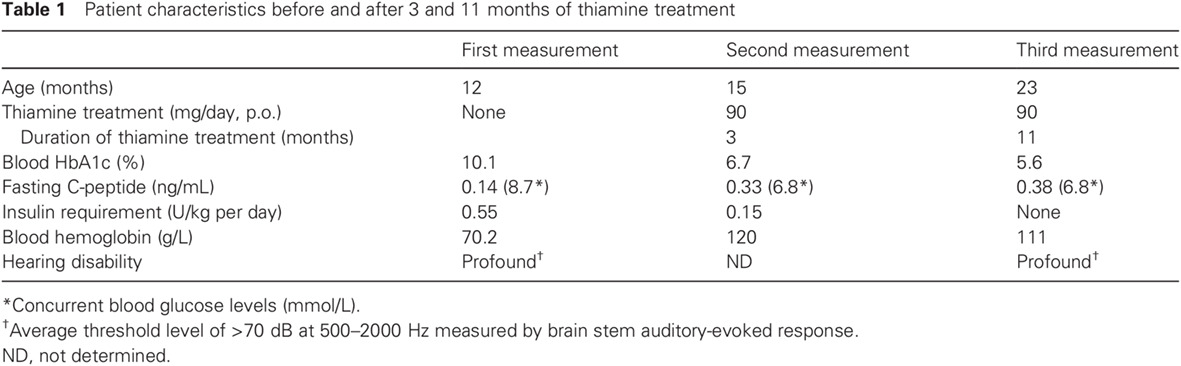
Highlights
- A novel SLC19A2 mutation (c.848G>A; p.W283X), inherited as segmental uniparental isodisomy, was identified in a patient with permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus (PNDM).
- The insulin insufficiency in this patient with SLC19A2 deficiency was corrected by thiamine supplementation.
- A differential diagnosis of SLC19A2 deficiency should be considered for children with PNDM accompanied by anemia or hearing defects to allow for early treatment.
Interactions between general and central obesity in predicting gestational diabetes mellitus in Chinese pregnant women: A prospective population-based study in Tianjin, China: 单纯性肥胖和中心性肥胖在预测中国孕妇妊娠糖尿病中的交互作用:一个中国天津前瞻性人群队列研究
- Pages: 59-67
- First Published: 06 April 2017
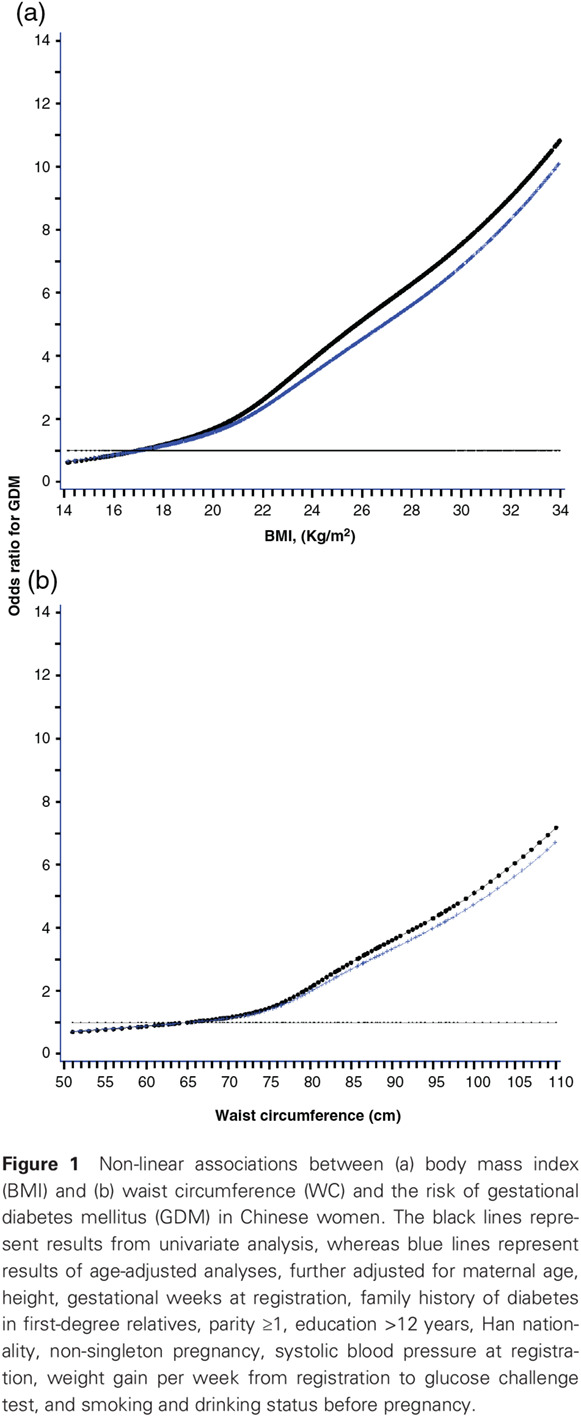
Highlights
- In a cohort of 17 803 Chinese pregnant women from Tianjin, China, body mass index (BMI) between ≥22.5 and <24.0 kg/m2 and waist circumference between ≥78.5 and <85.0 cm measured up to 12 weeks gestation were independently associated with increased risks of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM).
- The presence of BMI ≥22.5 kg/m2 and waist circumference ≥78.5 cm interacted to further increase the risk of GDM.
Effectiveness of vildagliptin as add-on to metformin monotherapy among uncontrolled type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in a real-world setting: 在一个真实世界环境中二甲双胍单药治疗后未控制的2型糖尿病患者加用维格列汀治疗的疗效
- Pages: 68-72
- First Published: 18 April 2017
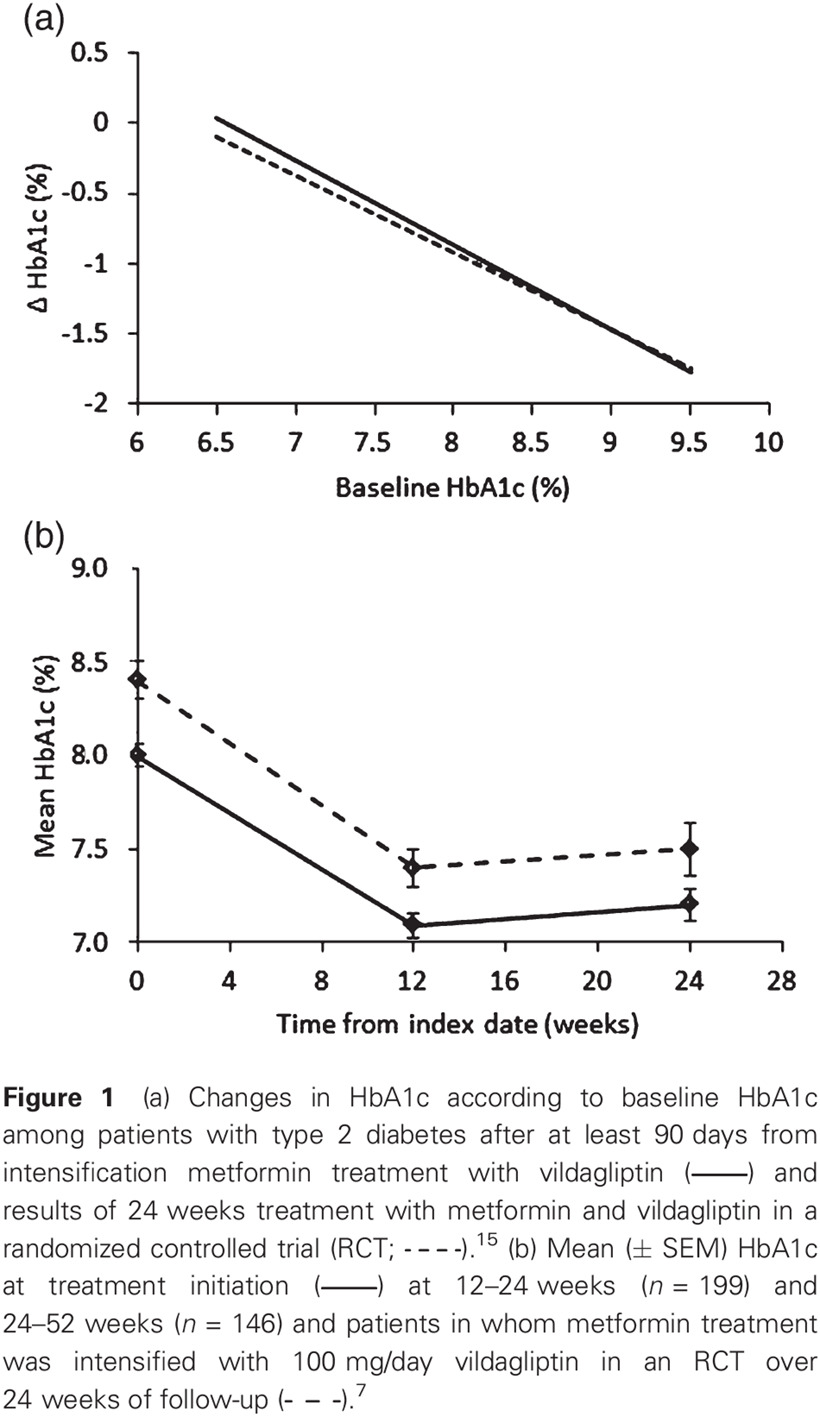
Highlights
- Add-on therapy with vildagliptin to a metformin monotherapy regimen in uncontrolled type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients is associated with a significant improvement in glycemic control, with no apparent increase in body weight.
- The real-world efficacy of vildagliptin as an add-on therapy to metformin is similar to that calculated in randomized controlled trials.
Effects of different aerobic exercise frequencies on streptozotocin–nicotinamide-induced type 2 diabetic rats: Continuous versus short bouts and weekend warrior exercises: 不同有氧运动频率对链脲霉素-烟酰胺诱导的2型糖尿病大鼠的影响:持续运动与短时间运动以及周末运动的对照研究
- Pages: 73-84
- First Published: 20 April 2017
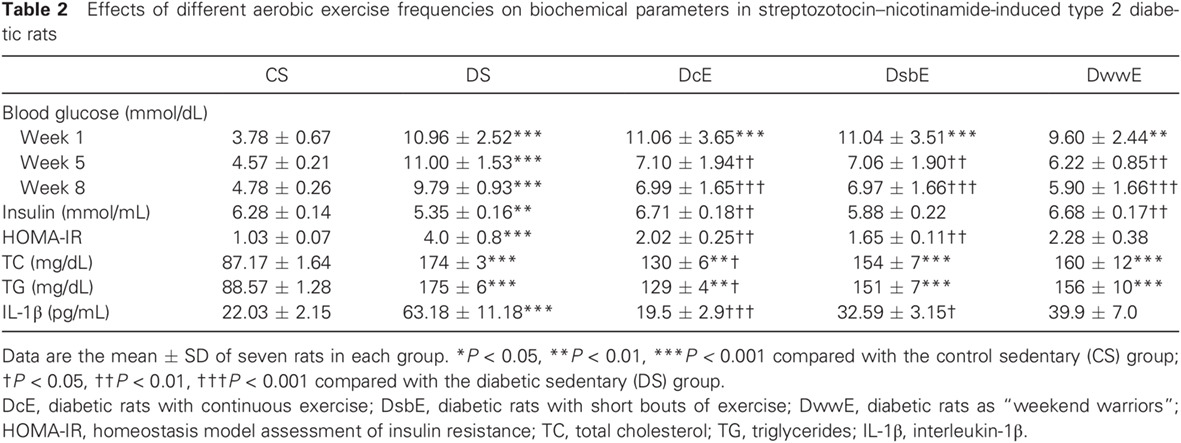
Highlights
- The findings of the present study suggest that different aerobic exercise frequencies improve diabetes markers and skeletal muscle damage in streptozotocin–nicotinamide-induced type 2 diabetes mellitus rats.
- The outcomes of different exercise modalities did not differ significantly from each other, provided that the total duration of the exercise remained constant.