Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Editorial
News
American Association of Diabetes Educators 2017
- Pages: 1054-1057
- First Published: 18 August 2017
Editors' Recommendations
Predictors of type 1 diabetes mellitus outcomes in young adults after transition from pediatric care: 从儿童卫生保健系统过渡而来的年轻成人发生1型糖尿病结果的预测因子
- Pages: 1058-1064
- First Published: 08 February 2017

Highlights
- Several predictors of type 1 diabetes outcomes in young adults after transition from pediatric care have been investigated separately in different studies and in various study participants; the present study assessed these predictors and outcomes in the same individuals.
- The present study shows that poor glycemic control and hospitalization for hyperglycemia track from before to after transition.
- Having less education and the presence of comorbidities increase the risk of poor outcomes in young adults with type 1 diabetes.
Original Articles
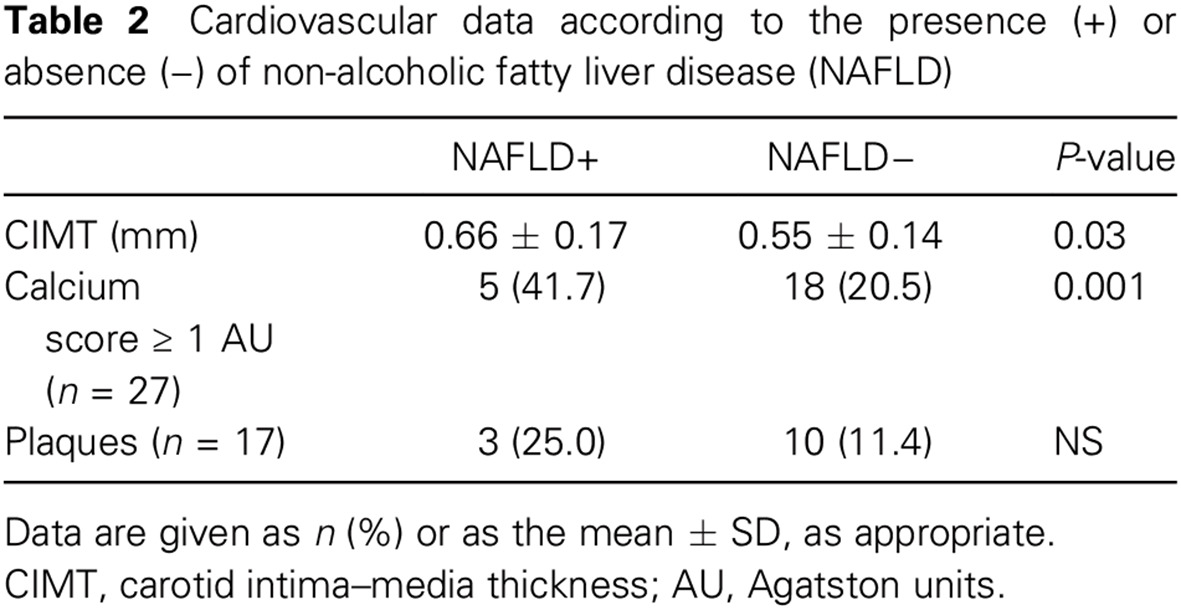
Low prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with type 1 diabetes is associated with decreased subclinical cardiovascular disease: 在1型糖尿病患者中非酒精性脂肪性肝病的患病率较低与亚临床心血管疾病较少相关
- Pages: 1065-1072
- First Published: 20 February 2017
Highlights
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has been associated with cardiovascular disease.
- Mediterranean type 1 diabetes (T1D) patients have a low prevalence of NAFLD, and T1D patients exhibit a low prevalence of subclinical atherosclerosis.
- The present study supports the relationship between NAFLD and subclinical cardiovascular disease even in a Mediterranean area.
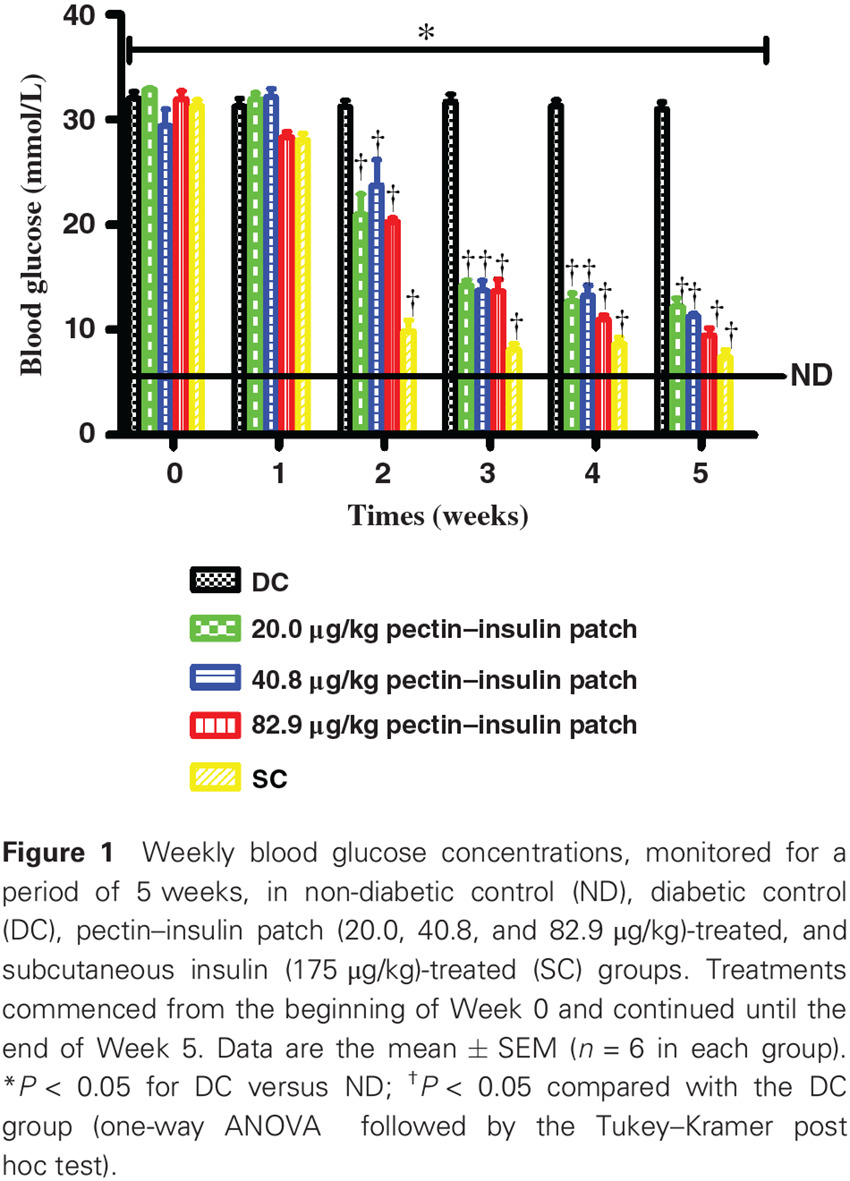
Cardioprotective effects of pectin–insulin patch in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: 果胶-胰岛素贴片对链脲霉素诱导的糖尿病大鼠心脏的保护作用
- Pages: 1073-1081
- First Published: 20 February 2017
Highlights
- Application of the transdermal pectin–insulin patch provides glycemic and hemodynamic control that attenuates the cardiac hypertrophy and cardiac inflammatory markers in diabetes.
- The observations in this study further reflect on cardiovascular hazards associated with subcutaneously administered insulin.
- Accordingly, the overall results of the study suggest that the pectin–insulin patch may be an alternative therapeutic approach in the management of diabetes.
Economic and social impact of diabetes mellitus in a low-income country: A case-control study in Sudan: 在低收入国家中糖尿病的经济与社会影响:在苏丹进行的一项病例对照研究
- Pages: 1082-1090
- First Published: 22 February 2017
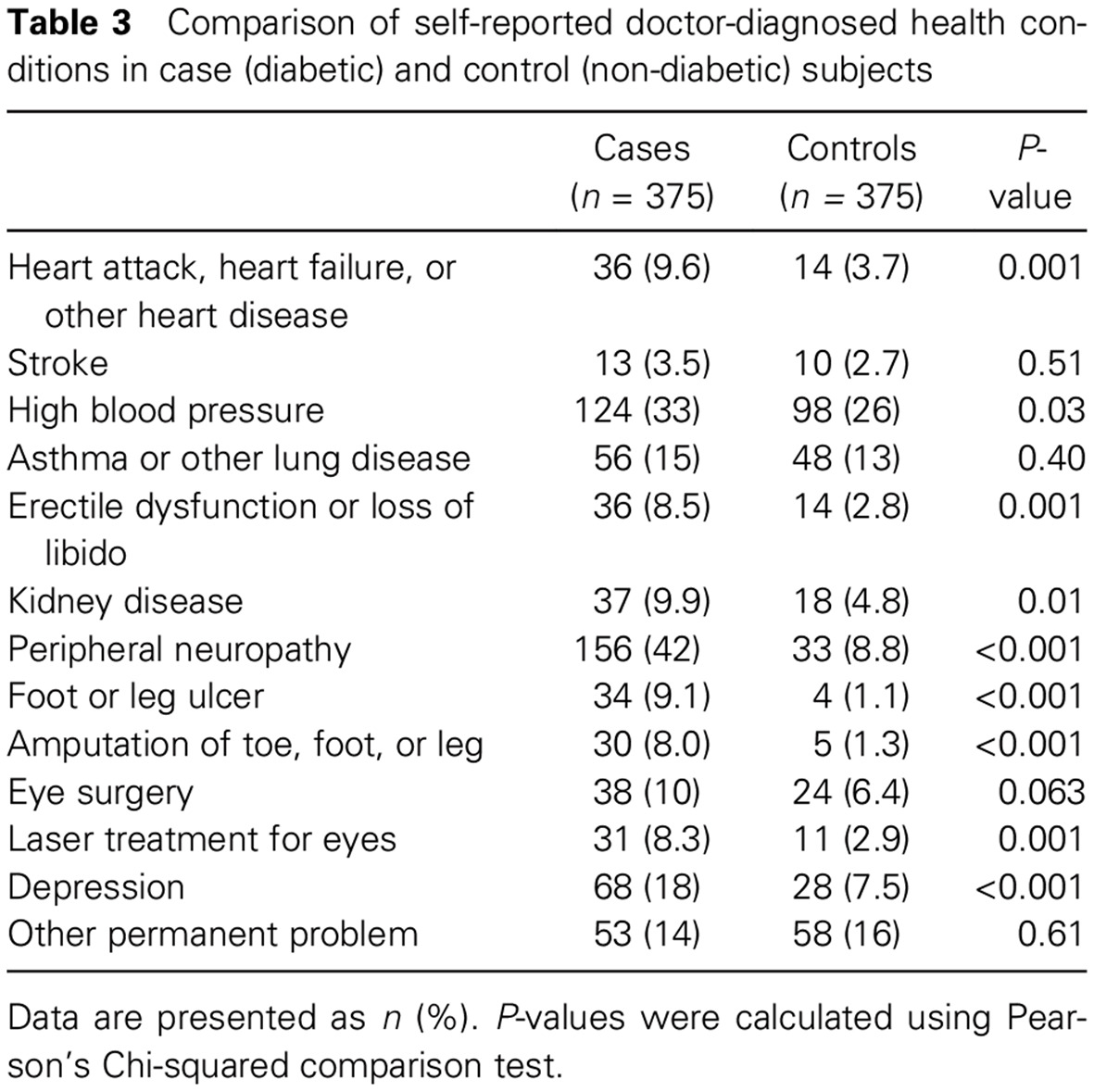
Highlights
- People with diabetes in Sudan have significantly more medical service and medication expenses compared with those without diabetes.
- Participants in the present study with diabetes had more comorbid diseases and experienced more negative effects related to ability to work, grow food, and achieve education.
- The study findings increase awareness of this costly and preventable disease among policy makers and clinicians, and support increased allocation of resources for diabetes prevention and control.
- The findings can be used to develop programs and policies for improved, cost-effective strategies by creating innovative models of alternative funding, such as national health insurance and cost-effective health care delivery.
Factors of primary and secondary sulfonylurea failure in type 2 diabetic subjects: 2型糖尿病患者原发性和继发性磺脲类药物失效的预测因素
- Pages: 1091-1099
- First Published: 24 February 2017

Highlights
- Using longitudinal data on 747 patients treated with sulfonylurea (SU) from a Phase 3 clinical trial in patients with type 2 diabetes, we found that patients with good glycemic control and higher β-cell reserve at entry are more likely to experience primary SU failure, but less likely to experience secondary SU failure.
- By combining baseline basal disposition index with initial response at the first month of treatment, we can get quick information about the long-term efficacy of SU treatment.
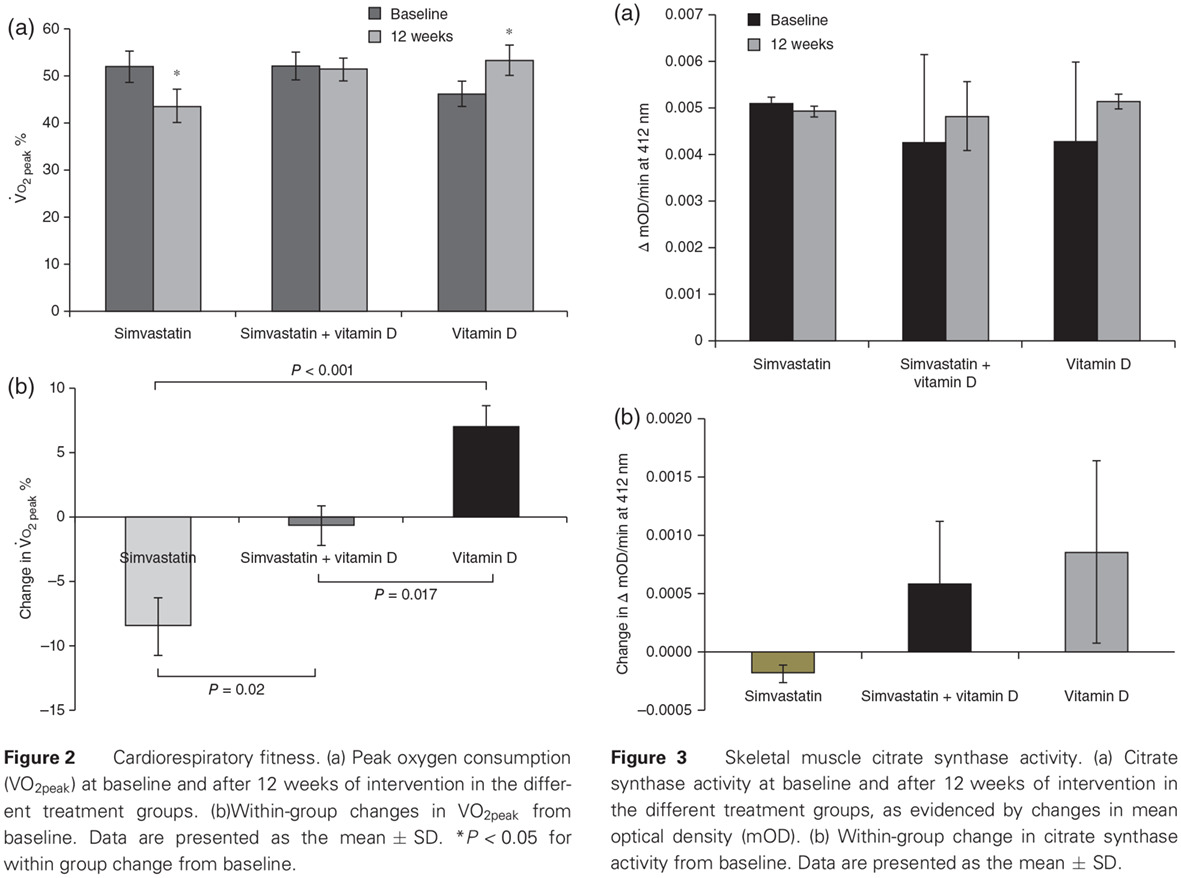
Vitamin D supplementation improves simvastatin-mediated decline in exercise performance: A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study : 补充维生素D治疗可以改善辛伐他汀介导的运动功能下降:一项随机双盲安慰剂对照研究
- Pages: 1100-1106
- First Published: 24 February 2017
Effects of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes patients with moderate to severe chronic kidney disease: Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials using unadjusted data: DPP-4抑制剂在2型糖尿病伴中至重度慢性肾脏病患者中的作用:利用随机对照研究中未校正数据的meta分析
- Pages: 1107-1117
- First Published: 07 March 2017
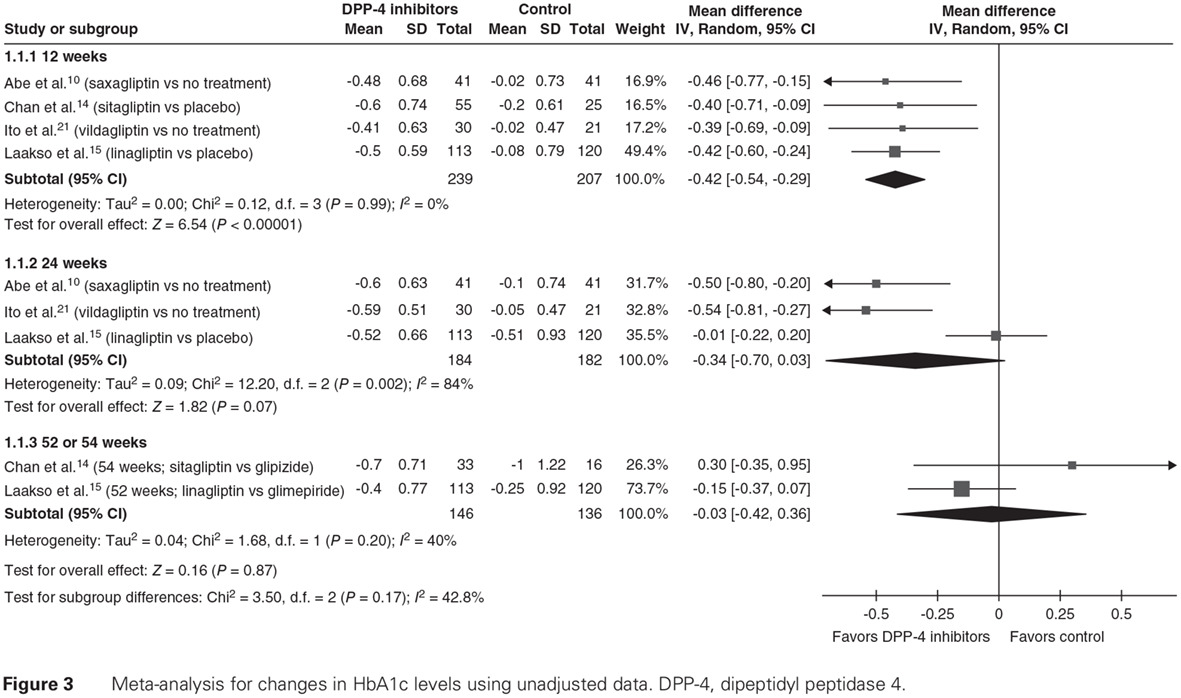
Highlights
- Dipeptidyl peptidase (DPP)-4 inhibitors significantly improved HbA1c levels at 12 weeks in both non-dialysis and dialysis patients, compared with 24 weeks in dialysis patients.
- Mean HbA1c changes induced by DPP-4 inhibitors were equivalent to those induced by sulfonylureas at 52 or 54 weeks.
- However, DPP-4 inhibitors induced fewer symptomatic hypoglycemic events than sulfonylureas at 52 or 54 weeks.
Letter to the Editor
Health and economic burden of diabetes in Bangladesh: Priorities for attention and control: 糖尿病对孟加拉国造成的健康与经济负担:需要关注和控制的优先事项
- Pages: 1118-1119
- First Published: 27 July 2017
Research Letter
Relationship between alanine aminotransferase levels and type 2 diabetes mellitus in the general Chinese population: 在普通中国人群中丙氨酸氨基转移酶水平与2型糖尿病之间的关系
- Pages: 1120-1123
- First Published: 10 August 2017
Highlights
- The present large-scale study of rural participants aged ≥35 years in the general Chinese population showed that the prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) increased with increments in alanine aminotransferase (ALT) concentrations and that increased ALT concentrations were significantly associated with the risk of T2DM.
- Concentrations of ALT >40 U/L were significantly associated with the increased prevalence of T2DM in addition to hypertriglyceridemia and hypertension.