Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Review Article
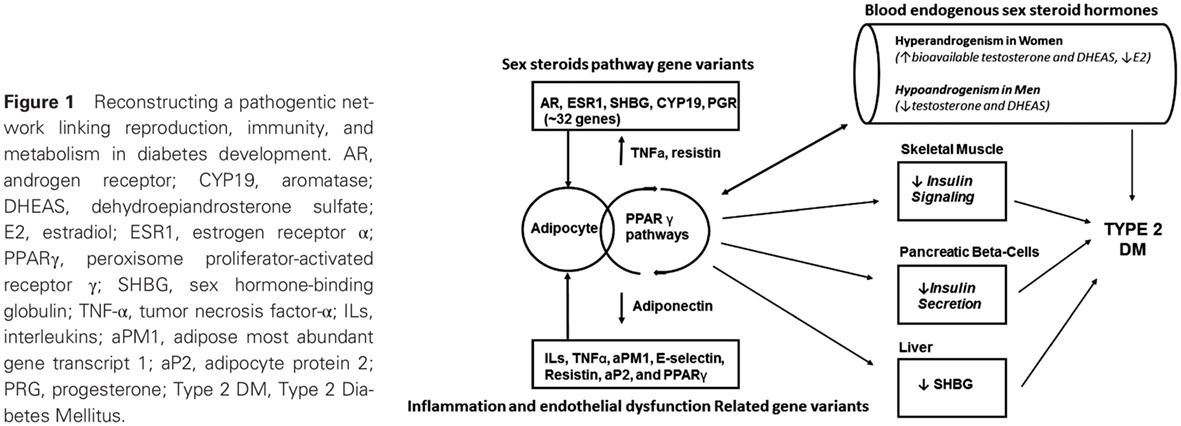
Sex differences, endogenous sex-hormone hormones, sex-hormone binding globulin, and exogenous disruptors in diabetes and related metabolic outcomes: 性别差异、内源性性激素、性激素结合球蛋白以及外源性干扰因子对糖尿病及其相关代谢结果的影响
- Pages: 428-441
- First Published: 19 December 2016
Highlights
- Sex steroids and sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) play a fundamental role in the pathogenesis of cardiometabolic disorders in men and women.
- Increasing evidence suggests that many endocrine-disrupting compounds and phytochemicals can modulate sex-hormone biology and exert adverse health effects through binding sex hormone receptors and interfering with signaling pathways.
- Therefore, research focus on sex differences for the fundamental roles of sex hormones, SHBG, and their environmental disruptors in cardiometabolic health is crucial.
Original Articles
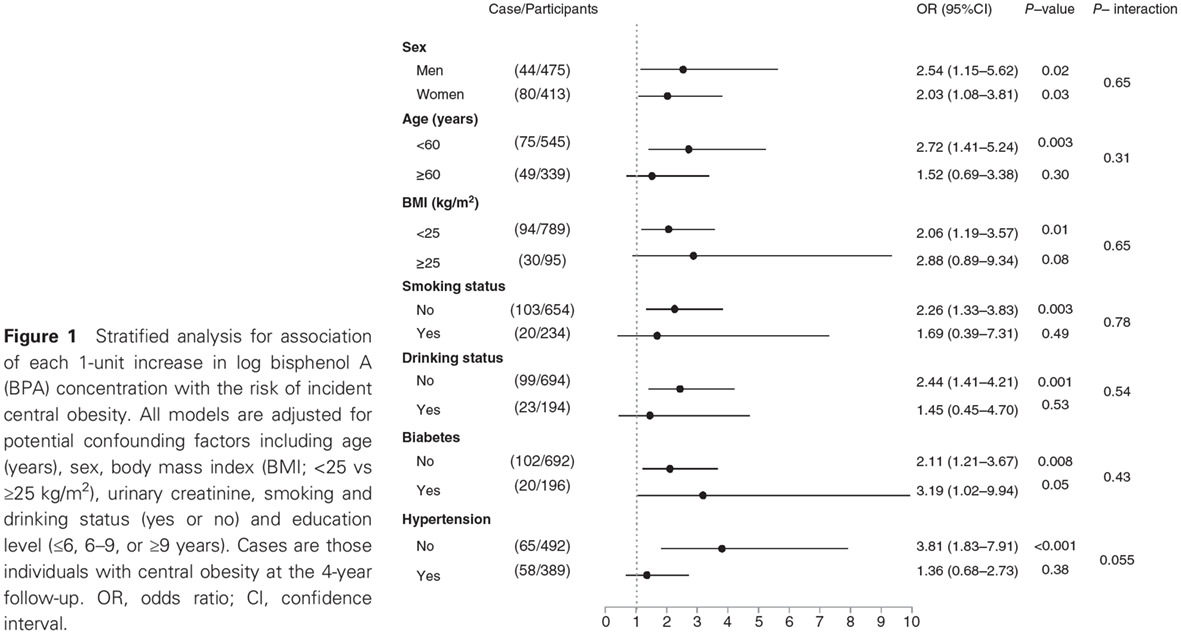
Urinary bisphenol A concentration and the risk of central obesity in Chinese adults: A prospective study: 尿双酚A浓度与中心性肥胖的发生风险:一项前瞻性研究
- Pages: 442-448
- First Published: 18 January 2017
Highlights
- Higher urinary bisphenol A (BPA) concentrations were positively and independently associated with a higher risk of incident central obesity in Chinese adults.
- A significant association has been reported between the prevalence of central obesity and urinary BPA in a Chinese population. The present study adds novel evidence of a prospective association between urinary BPA and risk of central obesity.
Differential sex effects of systolic blood pressure and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol on type 2 diabetes: Life course data from the Bogalusa Heart Study: 收缩压与低密度脂蛋白胆固醇的不同性别差异对2型糖尿病的影响:来自博加卢萨心血管研究的生命历程数据
- Pages: 449-457
- First Published: 27 February 2017

Highlights
- From childhood to adulthood, an increase in low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) imposes a differentially greater risk for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) for females versus males.
- Conversely, an increase in systolic blood pressure over the life course greatly increases males’ risk of T2DM, but has no effect in females.
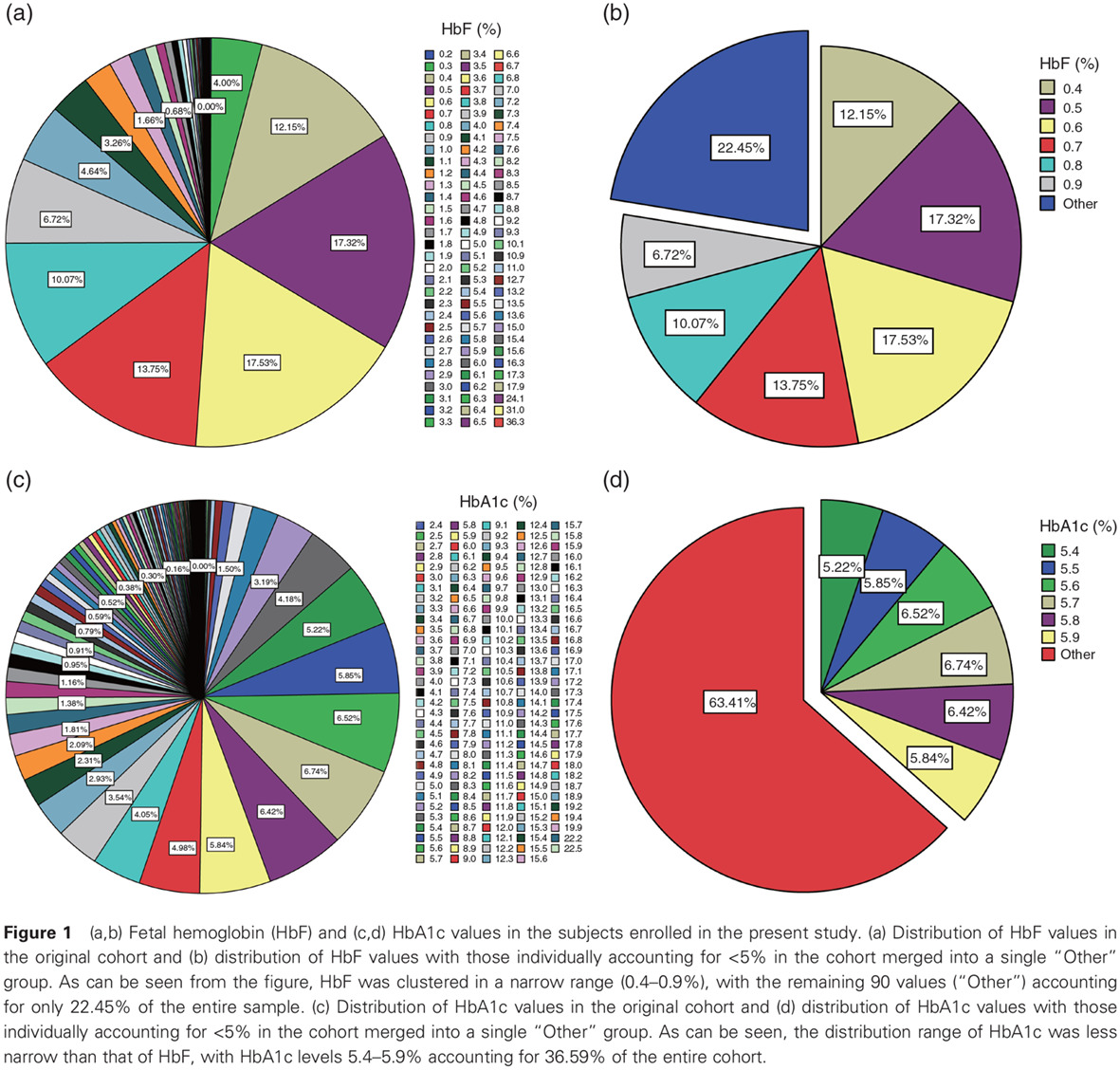
Sex and age discrepancy of HbA1c and fetal hemoglobin determined by HPLC in a large Chinese Han population: 利用HPLC法测定大样本量中国汉族人群糖化血红蛋白与胎儿血红蛋白的性别和年龄差异
- Pages: 458-466
- First Published: 02 March 2017
Highlights
- The present study found that HbA1c was positively associated with age, whereas fetal hemoglobin (HbF) was negatively associated with age.
- Male subjects had higher HbA1c levels in the 20–59 years age group and lower HbA1c levels in the 60–79 years age group compared with females.
- Sex and age should be considered in the clinical interpretation of HbA1c values.
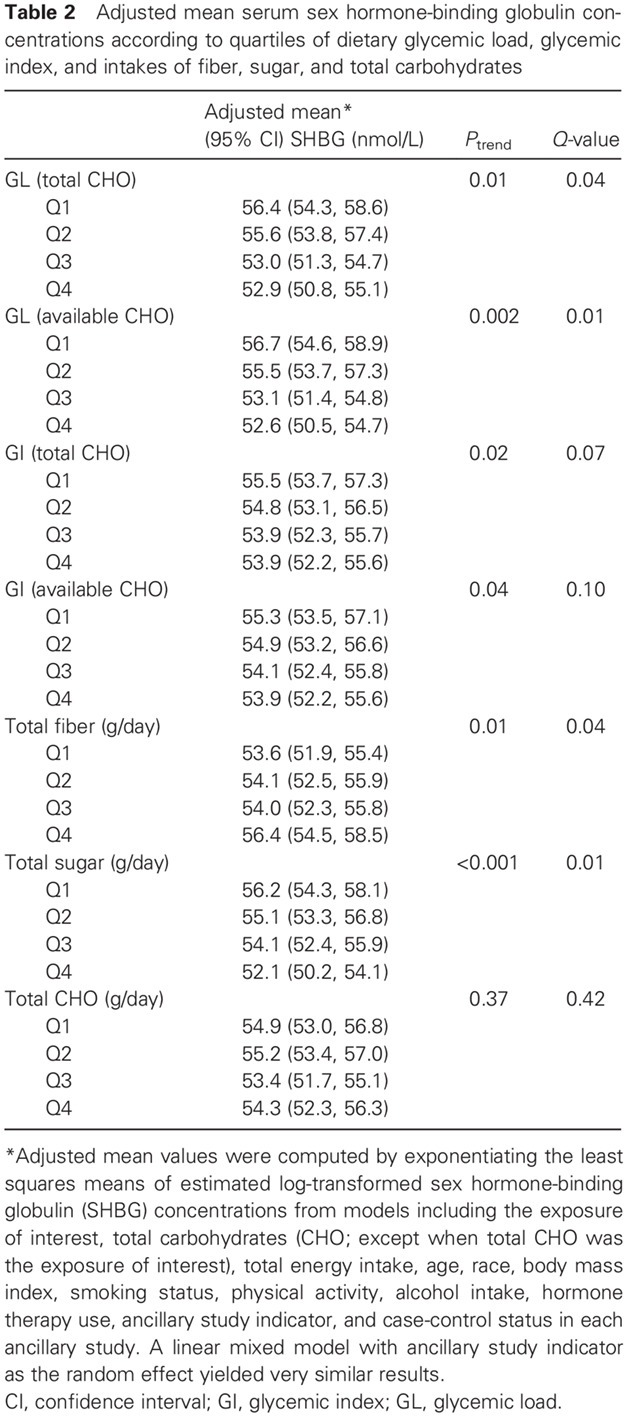
Relationship between dietary carbohydrates intake and circulating sex hormone-binding globulin levels in postmenopausal women: 在绝经后妇女中膳食碳水化合物摄入量与血液循环中性激素结合球蛋白水平的关系
- Pages: 467-477
- First Published: 17 March 2017
Highlights
- This large study of postmenopausal women with comprehensive assessment of diet and serum sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) levels indicated that low glycemic load (GL) or glycemic index (GI) and low sugar, but high dietary fiber, were associated with elevated levels of circulating SHBG.
- The findings support the notion that SHBG may be affected by dietary GL, GI, sugar, and fiber, and may also be an important mediator by which various dietary carbohydrates influence the risk of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and hormone-dependent cancers.
Serum adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein levels are associated with peripheral arterial disease in women, but not men, with type 2 diabetes mellitus: 血清脂肪细胞型脂肪酸结合蛋白水平与女性而不是男性2型糖尿病患者的外周动脉疾病相关
- Pages: 478-486
- First Published: 17 March 2017
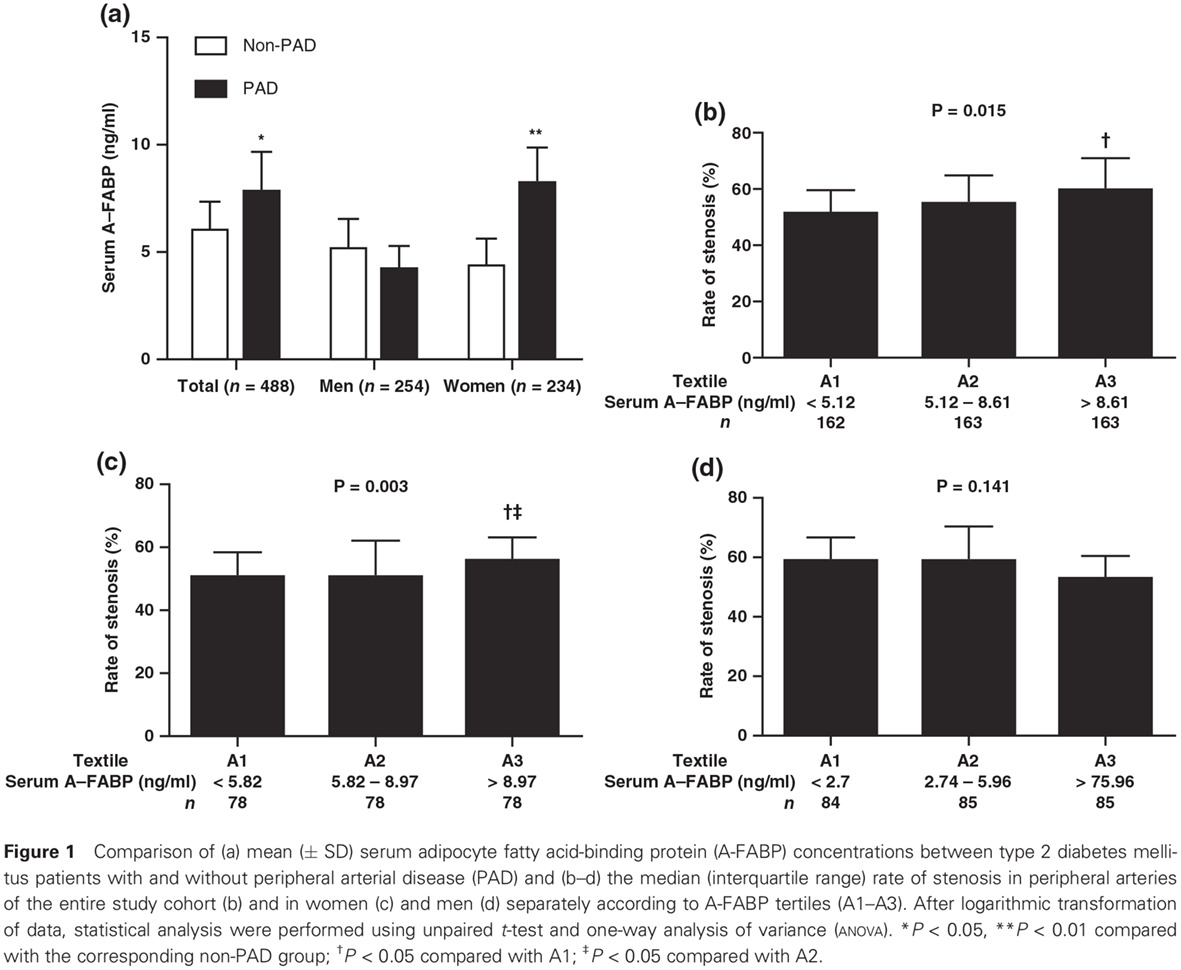
Highlights
- Adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein (A-FABP) levels are increased in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients with peripheral arterial disease (PAD).
- Higher A-FABP levels are associated with PAD only in female, and male, patients with T2DM.
- Higher A-FABP levels in female T2DM patients tend to explain the elimination of the “female advantage” regarding the risk of cardiovascular disease with diabetes.
Plasma concentrations of lipids during pregnancy and the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: A longitudinal study: 妊娠期间的血脂浓度与妊娠糖尿病风险:一项纵向研究
- Pages: 487-495
- First Published: 24 April 2017
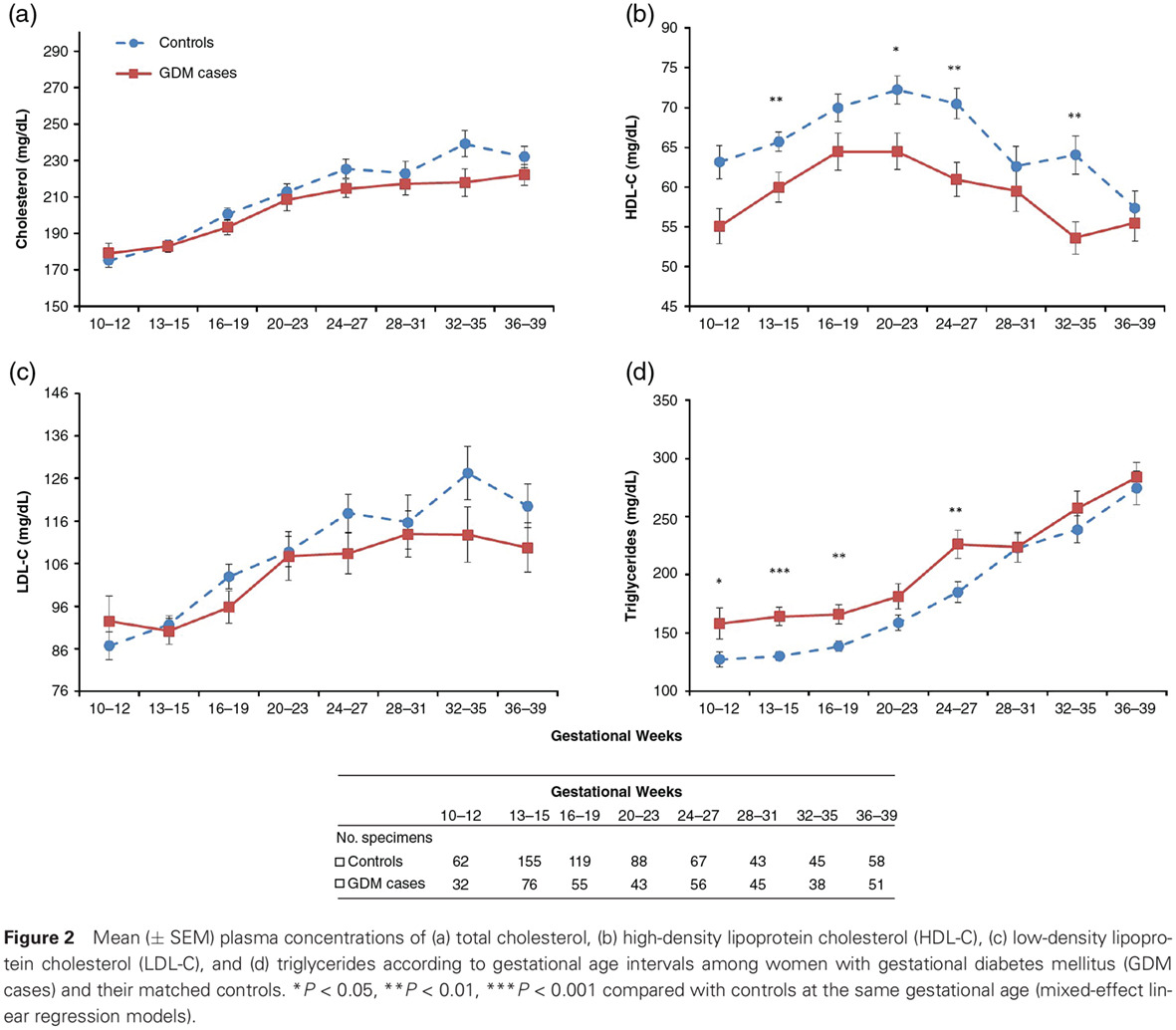
Highlights
- Higher concentrations of triglycerides and lower concentrations of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in early and mid-pregnancy are significantly related to a greater risk of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM).
- Total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol concentrations during pregnancy were not associated with risk of GDM.
- This study is based on longitudinal assessments of plasma lipid concentrations across pregnancy in a multiracial/multi-ethnic pregnancy cohort, which is uniquely suited to address temporal associations of plasma lipids in early and mid-pregnancy with the development of subsequent GDM.
Sex differences in cardiovascular risk profiles of ischemic stroke patients with diabetes in the Greater Cincinnati/Northern Kentucky Stroke Study: 在大辛辛那提/北肯塔基脑卒中研究中合并糖尿病的缺血性脑卒中患者心血管危险因素的性别差异
- Pages: 496-501
- First Published: 18 May 2017
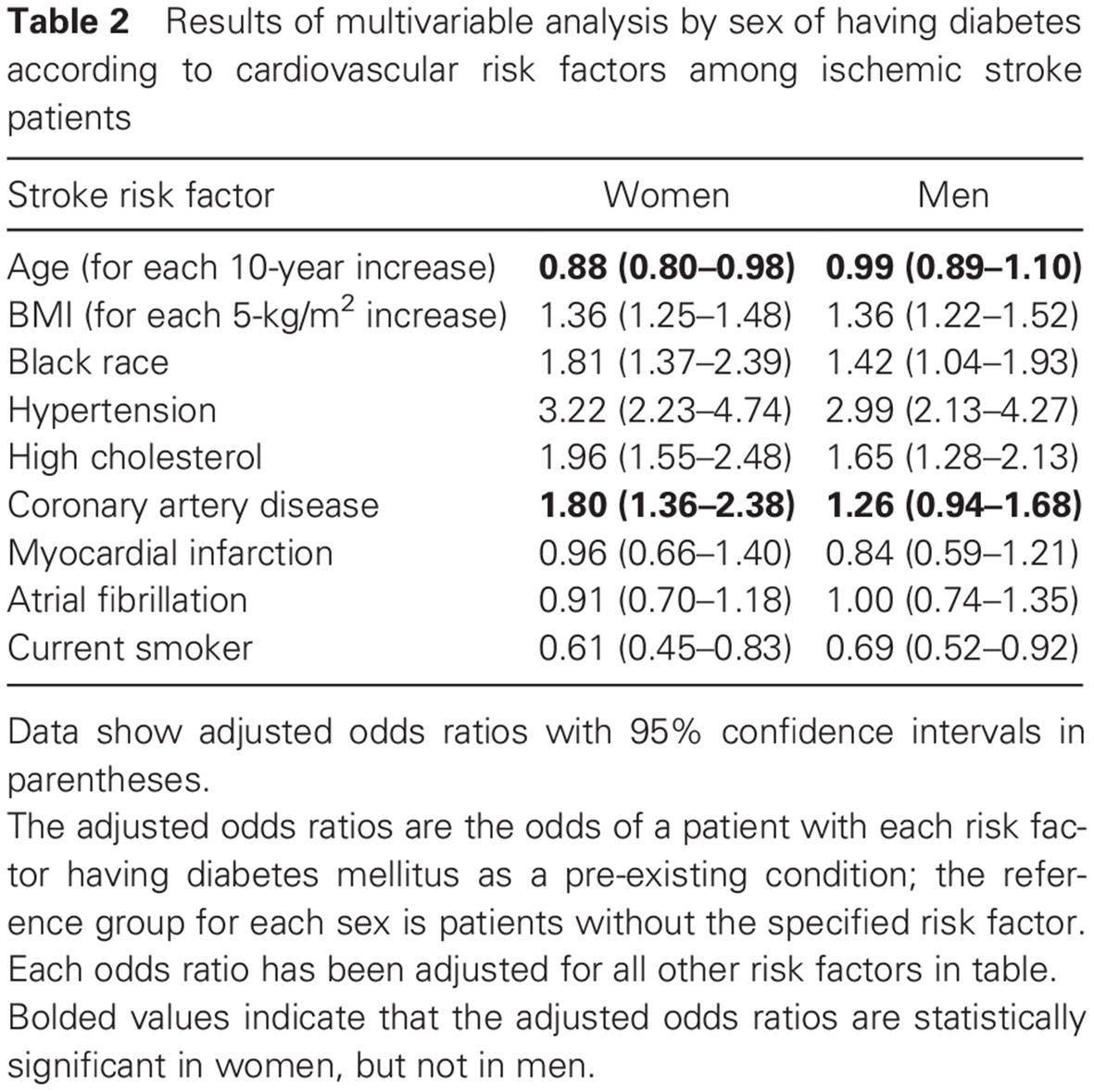
Highlights
- Among patients with incident ischemic stroke in the Greater Cincinnati Northern Kentucky Stroke Study, younger women and women with coronary artery disease (CAD) were more likely to have diabetes, whereas these associations were not significant for men.
- Our findings suggest that there is a sex-specific association between younger age and incident strokes in women with diabetes. Consequently, women with diabetes may benefit from more aggressive risk factor control.
Relationships of sex hormone levels with leukocyte telomere length in Black, Hispanic, and Asian/Pacific Islander postmenopausal women: 在黑种人、西班牙裔以及亚裔/太平洋岛民绝经后妇女中性激素水平与白细胞端粒长度的关系
- Pages: 502-511
- First Published: 13 June 2017
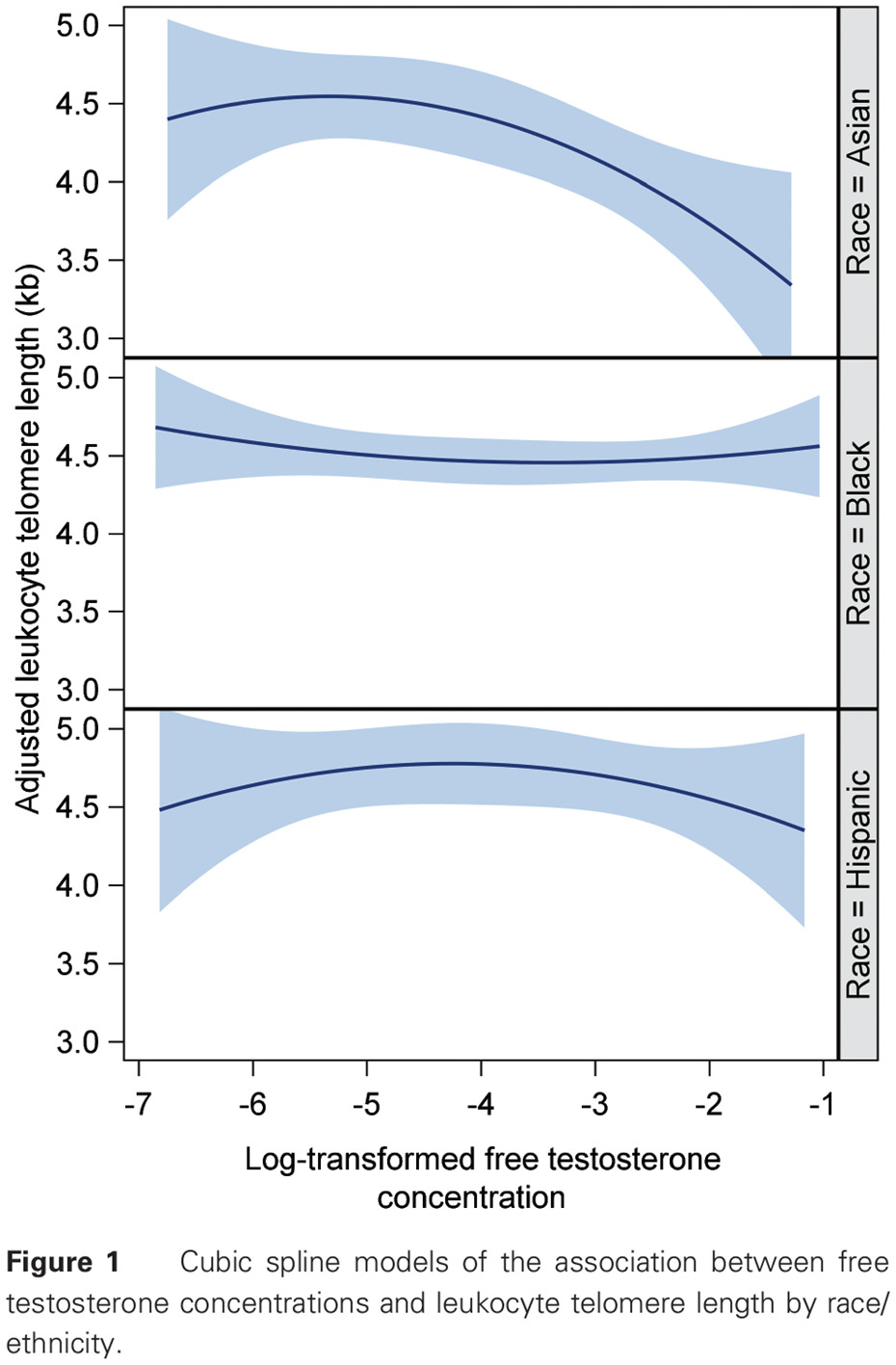
Highlights
- This study elucidates the potential roles of sex hormones in biological aging, and identified that total and free testosterone levels were inversely associated with telomere length in Asian/Pacific Islander women but not in Black and Hispanic women.
- The findings of the present study suggest that Asian/Pacific Islander women may be susceptible to the potential detrimental effects of high testosterone levels on biologic aging.
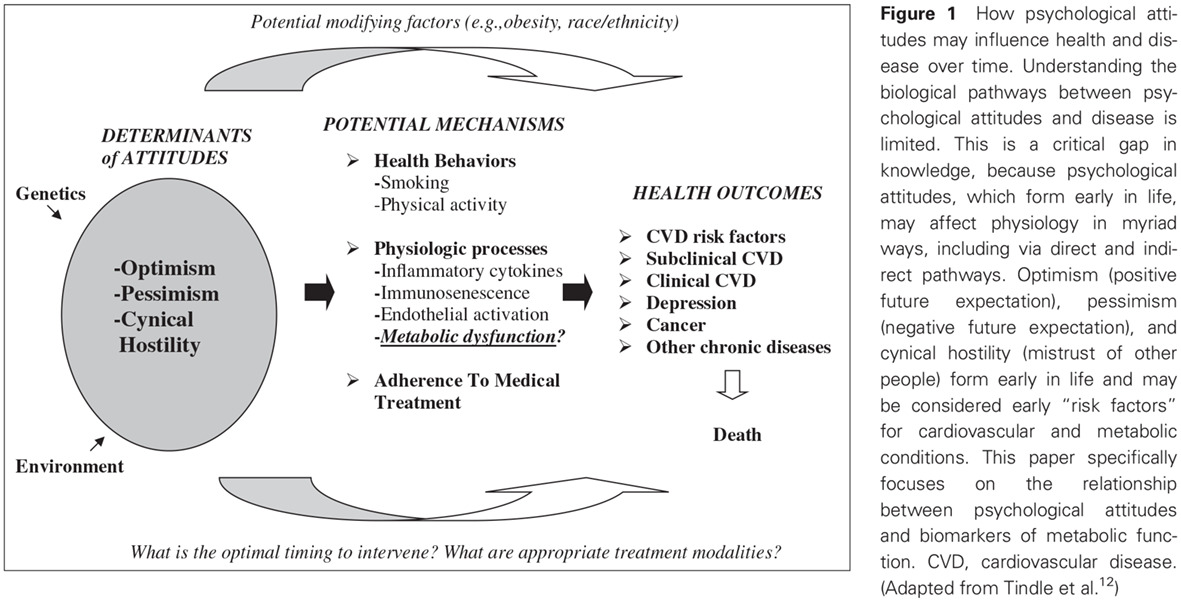
Optimism, pessimism, cynical hostility, and biomarkers of metabolic function in the Women's Health Initiative: 妇女健康倡议研究中的乐观情绪、悲观情绪、愤世嫉俗型敌意与代谢功能生物标志物
- Pages: 512-523
- First Published: 13 July 2017
Highlights
- In postmenopausal women, higher levels of pessimism were related to worse metabolic function.
- For each additional point on the pessimism scale, a woman's fasting insulin level was 1.2% higher, holding other health-related factors constant, while scoring 1 SD higher was associated with almost 3% higher insulin levels.
- Future research should address whether interventions to modify pessimistic attitudes could potentially reduce a woman's risk of diabetes and/or cardiovascular disease.
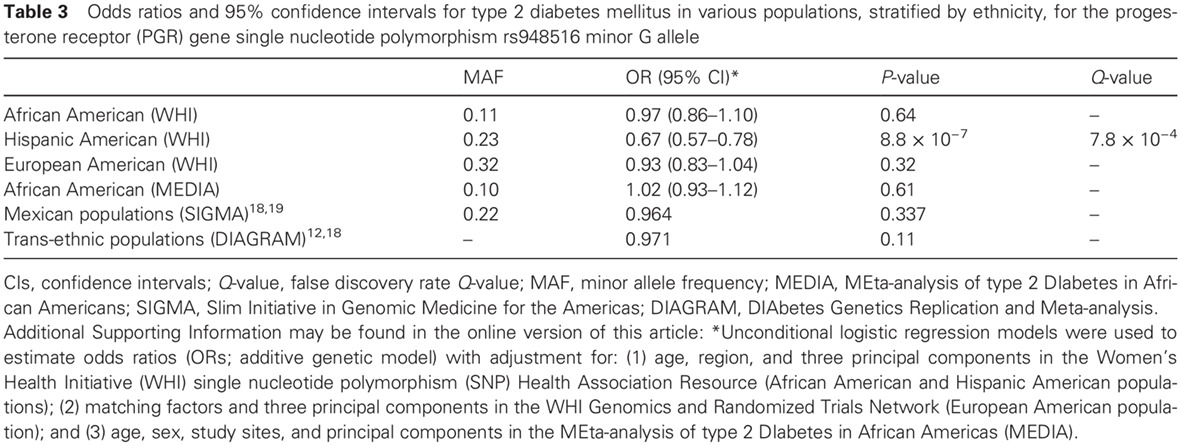
Genetic variants in sex hormone pathways and the risk of type 2 diabetes among African American, Hispanic American, and European American postmenopausal women in the US: 在非裔美国、西班牙裔美国以及在欧裔美国绝经后妇女中性激素途径的遗传变异与2型糖尿病风险
- Pages: 524-533
- First Published: 08 February 2018
Highlights
- In investigating the role of genetic variations in sex hormone pathways and the risk of diabetes, this study found a significant signal in the progesterone receptor (PGR) gene in Hispanic American women. However, this finding was not replicated in other populations.
- The data suggest the need for further studies, especially sex-specific analyses, to confirm the findings of the present study and clarify the role of sex hormone pathways in type 2 diabetes mellitus.









