Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cellular Behaviors of Human Dermal Fibroblasts on Pyrolytically Stripped Carbon Nanofiber's Surface
- First Published: 12 March 2025

Front Cover: When used as a scaffold, the electroconductive, pyrolytically stripped carbon nanofiber (cCNF) supports cell attachment and spreading of skin fibroblasts (nHDF). When the scaffold's surface is planar, it develops cell-cell communication and demonstrates cell proliferation like a non-woven electrospun nanofiber mat. The cell proliferation profile of cCNF using nHDF is similar to that of a reference electrospun nanofiber mat, polycaprolactone. More details can be found in article 2400603 by Minseok Kwak, Dong-Wook Han, and co-workers.
Issue Information
Review
The Application of Biomaterial-Based Spinal Cord Tissue Engineering
- First Published: 29 October 2024
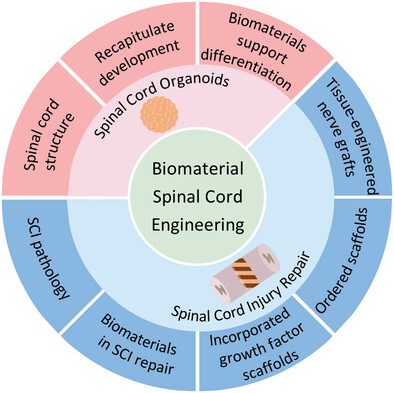
This review summarizes the contribution of biomaterials to the spinal cord organoids progression and discusses strategies for biomaterial-based spinal cord engineering in spinal cord injury (SCI) therapy. These achievements underscore the transformative potential of biomaterials to recapitulate spinal cord development, improve treatment options for SCI treatments, and accelerate future clinical applications.
Advances in Adhesive Materials for Oral and Maxillofacial Soft Tissue Diseases
- First Published: 26 November 2024
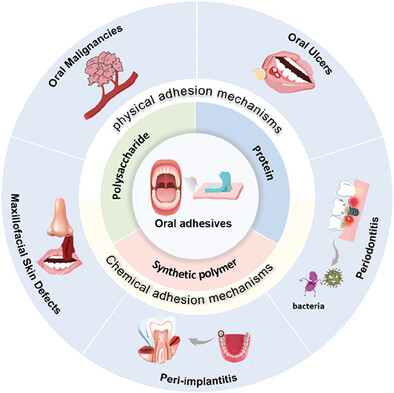
Adhesive materials are highly effective in addressing the moist and dynamic microenvironments, making them a viable solution for oral cavity wound repair. This review aims to highlight the design strategies and summarize the latest advancements in adhesives specifically tailored for oral and maxillofacial soft tissue diseases, with the objective of inspiring innovative developments in oral adhesive technology.
Research Article
Cellular Behaviors of Human Dermal Fibroblasts on Pyrolytically Stripped Carbon Nanofiber's Surface
- First Published: 27 January 2025
Sustained Drug Release from Dual-Responsive Hydrogels for Local Cancer Chemo–Photothermal Therapy
- First Published: 20 November 2024
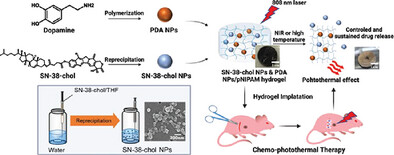
A novel dual-responsive hydrogel system is designed for the delivery of nanomedicines, focusing on drug release and the local antitumor efficacy of SN-38-cholesterol nanoparticles and polydopamine NPs/poly(n-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogels. By combining the thermosensitive properties of pNIPAM with the near-infrared responsiveness of PDA NPs, the hydrogel aims to enhance on-demand drug release.
Electrospinning of Cellulose Benzyl Carbamates for Enantioselective Membrane Filtration
- First Published: 27 November 2024
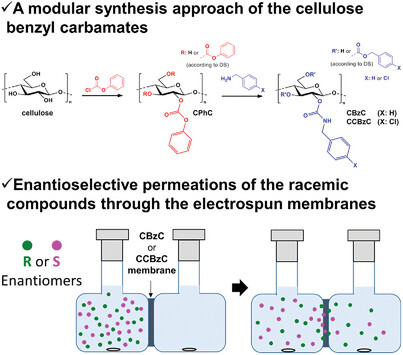
Aromatic cellulose derivatives, namely cellulose benzyl carbamate (CBzC) and cellulose 4-chlorobenzyl carbamate (CCBzC), are synthesized as a new type of polysaccharide-based chiral selectors (CSs) by a modular synthesis approach. These CSs are electrospun for the first time to form self-standing nanofibrous membranes. Their enantioselective permeation properties are investigated experimentally by liquid–liquid permeations and theoretically by molecular docking simulations.
In Situ Forming Injectable Gelatin-Based Antibacterial Bioadhesives for Preventing Postoperative Leakage and Abdominal Adhesions
- First Published: 08 November 2024
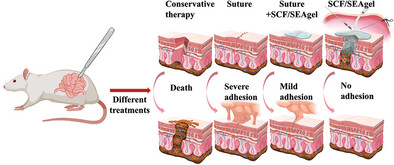
In this work, Bi-PEG-succinimidyl succinate (PEG-NHS), amino-gelatin (Agel), and cefoperazone-sulbactam (SCF) are combined to formulate a multifunctional bioadhesive (SCF/SEAgel) for the leakage sealing after intestinal surgery. SCF/SEAgel exhibits remarkable sealing capacities with good antibacterial properties. Meanwhile, it demonstrates effective prevention of post-operative tissue adhesion.
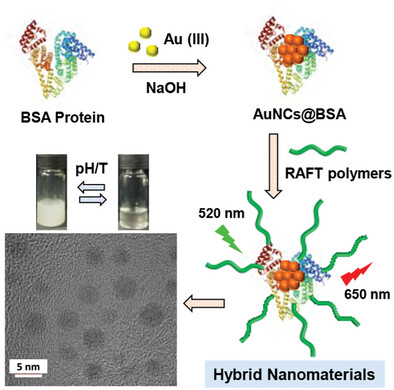
Engineering RAFT Polymers to the Protein-capped Gold Nanoclusters for Developing Fluorescent Polymeric Nanoconjugates
- First Published: 11 December 2024
Exploring Morphological and Molecular Properties of Different Adipose Cell Models: Monolayer, Spheroids, Gellan Gum-Based Hydrogels, and Explants
- First Published: 25 October 2024
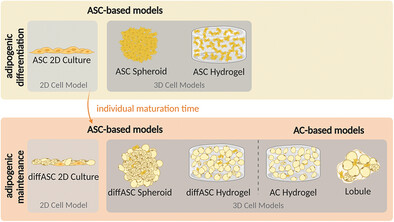
During adipogenesis and after 3 weeks of maintenance, white adipose cell models based on differentiated adipose-derived stem cells or mature adipocytes are investigated. Adipocyte characteristics are analyzed in spheroids, 3D gellan gum hydrogels, explanted lobules, and 2D cultures. Clear advantages of each model emerged: strong differentiation in 2D cultures, self-assembly in spheroids, long-term stability in hydrogels, and mature phenotype in hydrogels and lobules.
Nanoscale Liposomes Co-Loaded with Irinotecan Hydrochloride and Thalidomide for Colorectal Cancer Synergistic Therapy
- First Published: 20 December 2024
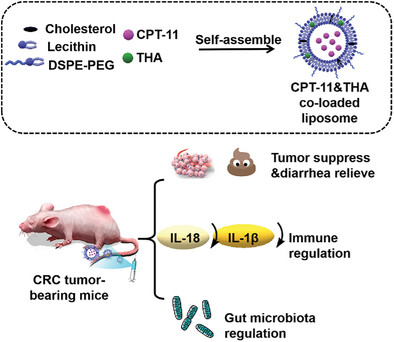
Thalidomide (THA) in combination with Irinotecan hydrochloride (CPT-11) is expected to alleviate the diarrheal effects brought by CPT-11. For this purpose, CPT-11 and THA co-loaded liposomes constructed in this manuscript can treat CRC tumors while alleviate the side effects. Moreover, the co-loaded liposomes could reduce IL-10 and IL-1β levels and regulate gut microbiota.
Polymeric Microneedles for Transdermal Delivery of Human Placental Tissue for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis
- First Published: 20 December 2024
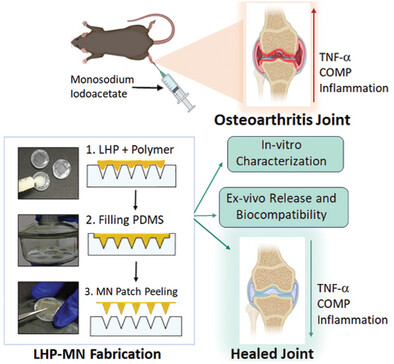
Formulated and evaluated lyophilized human placental tissue (LHP)-loaded, third-generation transdermal delivery system (LHP-polymeric microneedles) capable of penetrating the skin in a non-invasive manner. The therapeutic efficacy of the biologic, LHP for osteoarthritis (OA) treatment is proved through in vitro and in vivo studies, thereby validating its therapeutic potential.
PROTAC and Molecular Glue Degraders of the Oncogenic RNA Binding Protein Lin28
- First Published: 22 November 2024
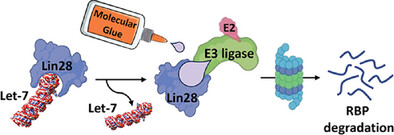
This study explores innovative approaches to degrade the Lin28, pivotal in cancer progression. Utilizing molecular glue (MG) and proteolysis-targeting chimera (PROTAC) strategies, significant inhibition of cancer cell migration and oncogene expression are demonstrated. These findings reveal effective targeting of Lin28, restoring let-7 function and presenting a promising therapeutic avenue.
A Natural Eumelanin-Assisted Pullulan/Chitosan Hydrogel for the Management of Diabetic Oral Ulcers
- First Published: 27 November 2024
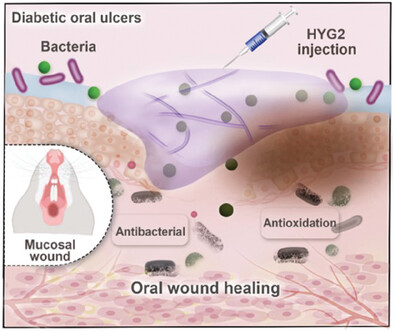
A natural eumelanin-assisted pullulan/chitosan hydrogel (HYG2) is developed for managing diabetic oral ulcers. The hydrogel combines oxidized pullulan, quaternized chitosan, and eumelanin nanoparticles to provide antibacterial, antioxidative, and pro-angiogenic effects. This multifunctional system aims to accelerate wound healing by reducing inflammation, managing oxidative stress, and supporting tissue regeneration, showing promising results in diabetic ulcer models.
A Comparative Study between Thiol-Ene and Acrylate Photocrosslinkable Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel Inks for Digital Light Processing
- First Published: 31 December 2024
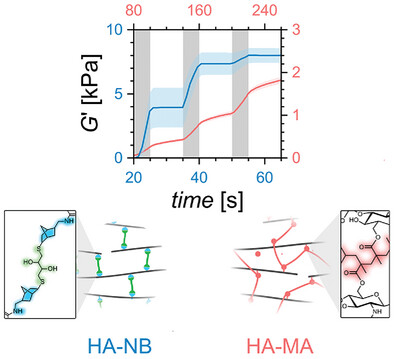
Hyaluronic acid (HA) inks functionalized with norbornene, allyl ether, or methacrylate groups are compared regarding stability, photocrosslinking kinetics, and mechanical properties. Rheology experiments demonstrate up to 4.7-times faster photocrosslinking for thiol-ene HA and higher temporal control in network formation. Using digital light processing, norbornene functionalized HA polymerized with a dithiol crosslinker is printed with 100 µm resolution within 2 s.