Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
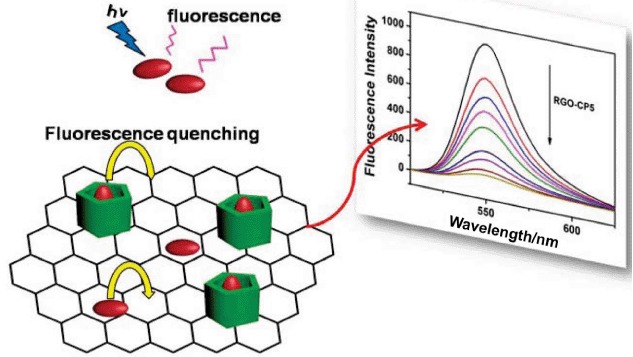
Cover Picture: Carboxylatopillarene-Modified Reduced Graphene Oxides with High Water Dispersibility for Fluorescent Dye Sensing (Chin. J. Chem. 1/2015)
- Page: 1
- First Published: 19 January 2015

The cover picture shows the synthesis of carboxylatopillar[5]arene-modified reduced graphene nanosheets (RGO-CP5) capable of molecular recognition. They exhibited much better water-dispersibility and enhanced fluorescence-quenching property as compared with native RGO, which can be used to detect analytes. More details are discussed in the article by Yang et al. on page 125–130.
Editorial
Contents
Account
Hybrid Liquid Crystals from the Self-Assembly of Surfactant-Encapsulated Polyoxometalate Complexes
- Pages: 15-23
- First Published: 08 October 2014
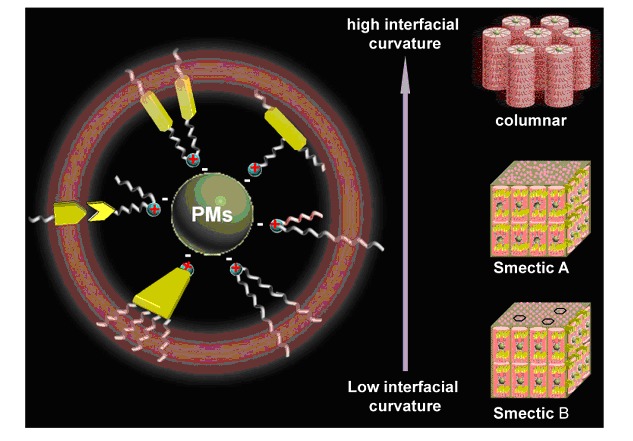
Nano-hybrid liquid crystals were designed and synthesized through attaching cationic surfactants on the surface of anionic polyoxometalate nano-clusters via ionic self-assembly strategy. We demonstrate the primary relationship between the nature of components and the liquid crystalline property. Emphases will be placed on the phase transition temperature and the self-assembly structures.
Reviews
Site-specific Analysis of Amyloid Assemblies by Using Scanning Tunneling Microscopy
- Pages: 24-34
- First Published: 05 December 2014
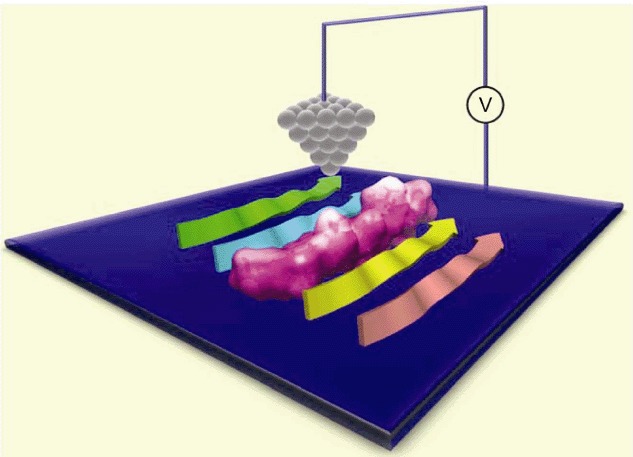
Assembly structures of amyloid peptides at liquid-solid interface can be visualized by scanning tunneling microscopy with site-specific resolution. The STM analysis can provide valuable information on the folding mechanism of amyloid peptides. This review highlights the application of STM on site-specific analysis of amyloid peptides.
Recent Advances in Near-Infrared Absorption Nanomaterials as Photoacoustic Contrast Agents for Biomedical Imaging
- Pages: 35-52
- First Published: 03 November 2014
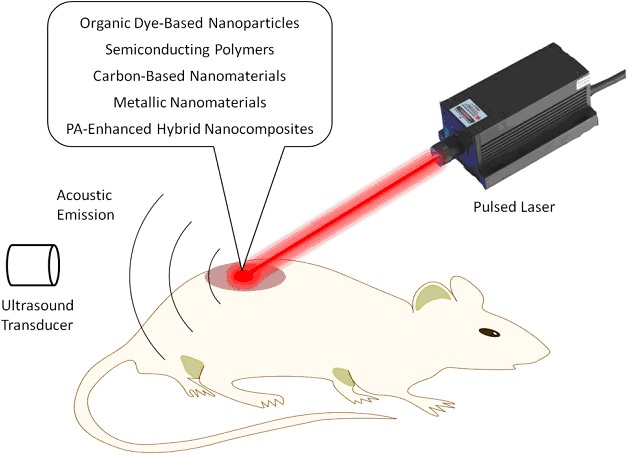
Photoacoustic imaging (PAI) is an emerging whole-body imaging modality offering high spatial resolution, deep penetration and high contrast in vivo. Signals for PAI are generated from contrast agents, where the pulsed laser-generated optical energy is transferred to acoustic emissions and detected by an ultrasound transducer. A great deal of research over the past ten years has shown that near-infrared absorption nanomaterials such as organic dye-based nanoparticles, semiconducting polymers, carbon-based nanomaterials, metallic nanomaterials and PA-enhanced hybrid nanocomposites are promising PA contrast agents, which can increase imaging resolution, contrast and even depth of detection.
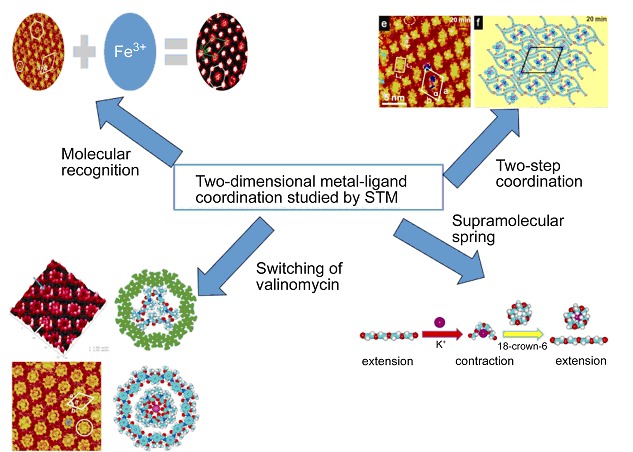
Two-dimensional (2D) Supramolecular Coordination at Liquid/Solid Interfaces Studied by Scanning Tunneling Microscopy
- Pages: 53-58
- First Published: 03 November 2014
Smart Supramolecular Nanosystems for Bioimaging and Drug Delivery
- Pages: 59-70
- First Published: 05 December 2014
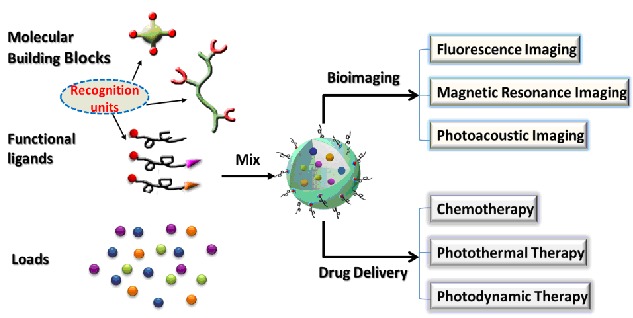
The application of smart supramolecular nanosystems in biomedicine increases rapidly and offers promising prospects for disease diagnostics and therapeutics. Supramolecular nanosystems such as liposomes, micelles, organic nanoaggregates and metallic nanostructures etc. have been widely explored as diagnostic/therapeutic tools. Here, we review the recent advances in supramolecular nanosystems with different built-in reporters, e.g., fluorescent, magnetic and photoacoustic signals for bioimaging. In addition, the substantial progress of supramolecular nanosystems as drug delivery carriers for cancer therapy, including chemotherapy, photothermal and photodynamic therapies is also summarized.
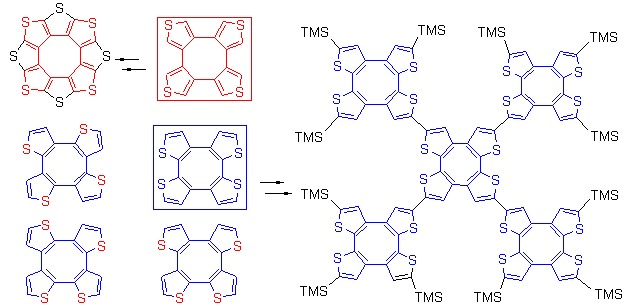
Recent Progress in the Synthesis and Application of Saddle-shaped Cyclooctatetrathiophenes and Their Derivatives
- Pages: 71-78
- First Published: 09 December 2014
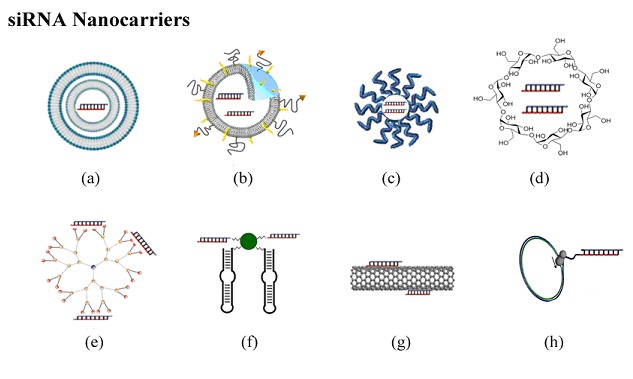
Supramolecular Assembly Models of siRNA Delivery Systems
- Pages: 79-89
- First Published: 09 December 2014
Communications
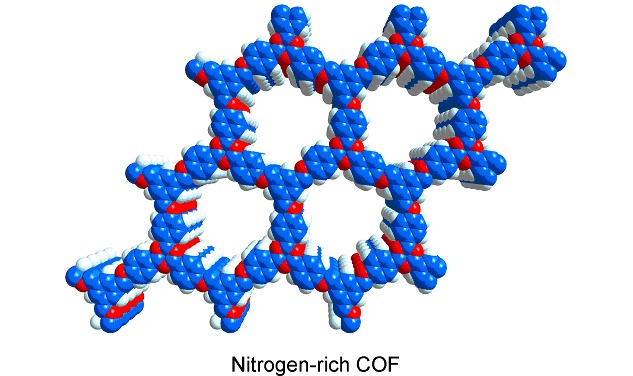
Synthesis of Microporous Nitrogen-Rich Covalent-Organic Framework and Its Application in CO2 Capture
- Pages: 90-94
- First Published: 03 November 2014
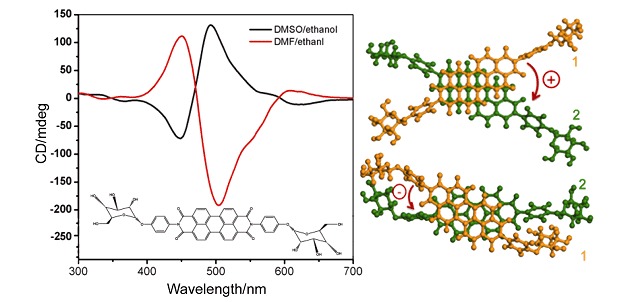
Modulating the Helicity of Sugar-Substituted Perylene Diimide Self-assemblies by Solvent Polarilities
- Pages: 95-100
- First Published: 13 June 2014
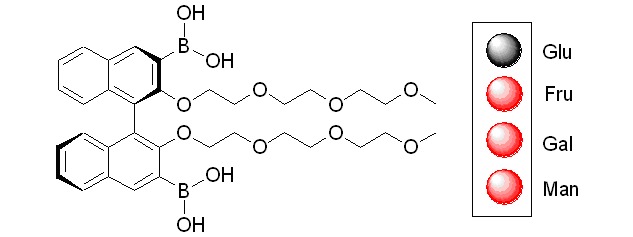
A BINOL Based Fluorescence Sensor for Distinction of D-Glucose
- Pages: 101-106
- First Published: 05 June 2014
Controllable Fabrication of Various Supramolecular Nanostructures Based on Nonamphiphilic Azobenzene Derivatives and Pillar[6]arene
- Pages: 107-111
- First Published: 08 October 2014
![Controllable Fabrication of Various Supramolecular Nanostructures Based on Nonamphiphilic Azobenzene Derivatives and Pillar[6]arene](/cms/asset/c93e7d6b-178d-4563-9365-23c39b6d9818/mcontent.jpg)
Various novel types of supramolecular nanostructures formed by nonamphiphilic azobenzene derivatives, G1 or G2 have been successful fabricated, where G2 is structurally similar with G1 but an extra phenoxy group is connected with the azobenzene motif. Micellar structures can be obtained from the self-assembly of G1, which further transformed to large-sized spindle structures; while nanorods can be initially formed by G2, which will gradually aggregate to form layered structures with much larger size. Moreover, it is found that upon addition of WP6, which can form inclusion-complex with G1 or G2, separately, the nonamphiphilic G1 and G2 thus converse to supramolecular amphiphiles WP6⊃G1 and WP6⊃G2, respectively. Consequently, both of the above WP6⊃G1 and WP6⊃G2 complexes can further assemble to form supramolecular binary vesicles, which will gradually transform to nanotubes (WP6⊃G1) or well-ordered nanosheets (WP6⊃G2).
Full Papers
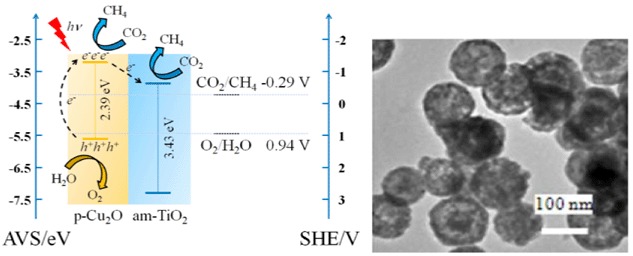
Visible-Light Photocatalytic Conversion of Carbon Dioxide into Methane Using Cu2O/TiO2 Hollow Nanospheres
- Pages: 112-118
- First Published: 15 September 2014
Sonochemical Synthesis of Graphene Oxide-Wrapped Gold Nanoparticles Hybrid Materials: Visible Light Photocatalytic Activity
- Pages: 119-124
- First Published: 25 August 2014
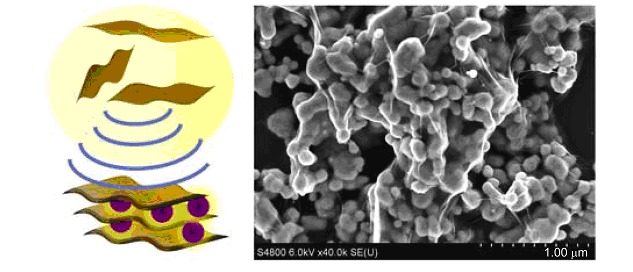
Graphene oxide (GO)-wrapped gold nanoparticles (Au NPs) hybrid materials are constructed via one-pot sonochemical synthesis and self-assembly, using ethylene glycol as the reducing agent. The obtained materials possess enhanced photocatalytic activity under visible light irradiation, owing to the synergistic effect of the two components in the hybrid materials.
Carboxylatopillarene-Modified Reduced Graphene Oxides with High Water Dispersibility for Fluorescent Dye Sensing
- Pages: 125-130
- First Published: 05 June 2014
Benzimidazole-Linked Porous Polymers: Synthesis and Gas Sorption Properties
- Pages: 131-136
- First Published: 07 November 2014
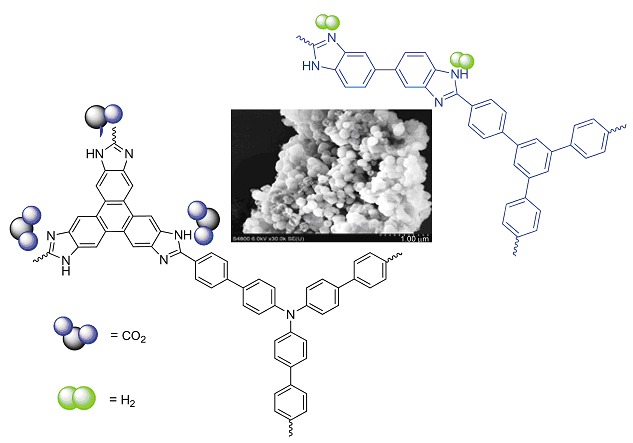
A series of benzimidazole-linked porous polymers are obtained in one-pot synthesis without employing any catalyst or template. The polymers possess Brunauer-Emmett-Teller specific surface area value over 600 m2·g−1, showing hydrogen storage (up to 1.6 wt%, at 77 K and 1×105 Pa) and carbon dioxide capture (up to 12.6 wt%, at 273 K and 1×105 Pa) properties.
Self-Assembly of Schiff Base Organogelator with Enhanced Fluorescence Emission
- Pages: 137-140
- First Published: 07 November 2014
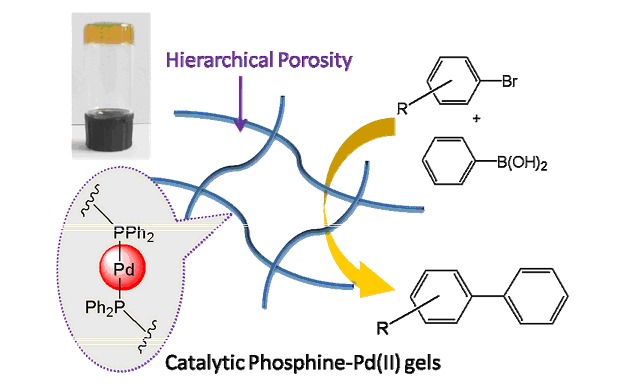
Coordination-Driven Terpyridyl Phosphine Pd(II) Gels
- Pages: 141-146
- First Published: 07 November 2014
A Rapid Synthesis of High Aspect Ratio Silver Nanowires for High-Performance Transparent Electrodes
- Pages: 147-151
- First Published: 07 November 2014

Silver nanowires with high aspect ratio and high purity were prepared via a rapid, simple and cost-effective polyol method. The aspect ratios of the silver nanowires were as high as ca. 1000 (average length 40 µm and some even as long as 80 µm, diameter 50–100 nm) via optimizing the reaction conditions. Transparent electrodes with superior optoelectronic performances (optical transmittance of 90%, sheet resistance of 23.2 Ω/□ and optical transmittance of 87%, sheet resistance of 19.7 Ω/□) comparable to commercial ITO were fabricated via spin coating the resulting silver nanowires onto the glass substrates. The high optoelectronic performances and the all-solution process of the as-prepared transparent electrodes render them rather promising for applications in cost-effective large-area optoelectronic devices.
Note
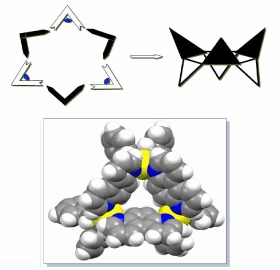
Self-Assembly of Chiral Nano-bowl from Chiral Pd-complex Building Corners and 4,7-Phenanthroline Linkers
- Pages: 152-155
- First Published: 04 April 2014