Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Ultrathin Ultralow-Platinum Catalyst Coated Membrane for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells (Small 21/2023)
- First Published: 24 May 2023

Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells
In article number 2207155, Huiyuan Liu, Yujiang Song, and co-workers construct ultrathin ultralow-Pt integrated catalyst coated membrane by proton-initiated regioselective nucleation and growth of Pt/Pd catalyst layer on membrane. The highly active ultrathin catalyst layer greatly facilitates mass transfer and enhances the peak mass specific power density up to 59.9 W mgPt, Cathode−1 for proton exchange membrane fuel cell. [Correction added on 10th of August, after first online publication: the front cover image was updated.]
Inside Front Cover
Precision Delivery of Dual Immune Inhibitors Loaded Nanomodulator to Reverse Immune Suppression for Combinational Photothermal-Immunotherapy (Small 21/2023)
- First Published: 24 May 2023

Combinational Photothermal-Immunotherapy
In article number 2206441, Longjiang Zhang, Peng Huang, Zhongqiu Wang, and co-workers load dual-immune inhibitors nanomodulators for combinational photothermal-immunotherapy through regulating abnormal enzymatic metabolism of IDO, blocking PD-L1/PD-1 and CD47/SIRPα to reverse immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment, and prevent tumor growth and re-challenge.
Inside Back Cover
Re-Dispersion of Platinum From CNTs Substrate to α-MoC1 - x to Boost the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction (Small 21/2023)
- First Published: 24 May 2023

Hydrogen Evolution Reaction
In article number 2207146, Rui Gao, Chuan Shi, and co-workers present Pt atoms to redisperse on α-MoC1−x substrate from carbon nanotubes, which creates dual active interfaces of Pt species dispersed over carbon nanotubes and α-MoC1−x. Benefiting from the strong electronic interaction between the Pt atom and α-MoC1−x, the utilization efficiency of the Pt atom is evidently enhanced, providing practical solutions to enhance platinum dispersion, and thereby enhancing the catalytic activity in hydrogen production.
Back Cover
A Dual-Responsive Artificial Skin for Tactile and Touchless Interfaces (Small 21/2023)
- First Published: 24 May 2023

Tactile and Touchless Artificial Skins
In article number 2206830, Yifan Wang and co-workers present a dual-responsive artificial skin, which reacts to both pre-contact events and tactile pressure levels. Overlooked valuable information encoded in the proximal inputs from environments can be explored. Versatile human–machine interfaces (HMIs) for tactile and touchless interactions are achieved. Moreover, the proof-of-concept application for materials classification is successfully demonstrated in an entirely touchless mode.
Masthead
Correction
Reviews
Advanced Composite Solid Electrolytes for Lithium Batteries: Filler Dimensional Design and Ion Path Optimization
- First Published: 26 February 2023
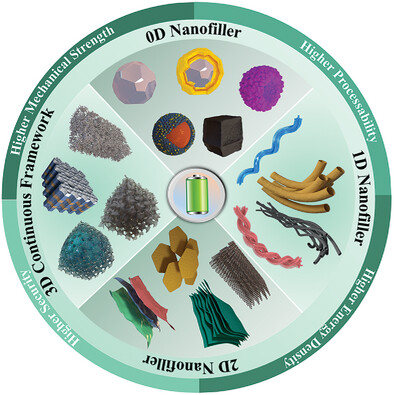
Different dimensional-shaped nanomaterials have played a prominent role in influencing the ionic conductivity of composite solid electrolytes for lithium batteries in recent studies. Some of the designs have achieved an excellent room-temperature ionic conductivity of 10–4 S cm–1. The dimensional designs for composite solid electrolytes should be further studied to contribute to the evolution of all-solid-state lithium batteries.
Platinum Drug-Incorporating Polymeric Nanosystems for Precise Cancer Therapy
- First Published: 26 February 2023
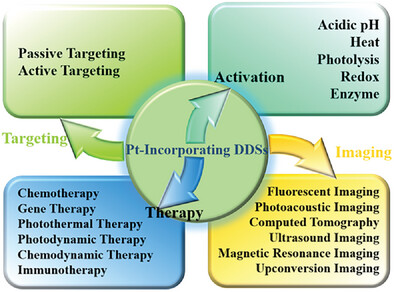
This article introduces the design and fabrication of various polymeric drug delivery systems including dendrimer, polymer-drug conjugate, polymeric micelle, liposome and polymersome, hydrogel, and polymer–inorganic hybrid for the precise delivery of platinum drugs with an emphasis on multi-modal synergistic cancer treatment and imaging-guided Pt-based cancer therapy.
Gold Nanomaterials-Implemented CRISPR-Cas Systems for Biosensing
- First Published: 25 February 2023
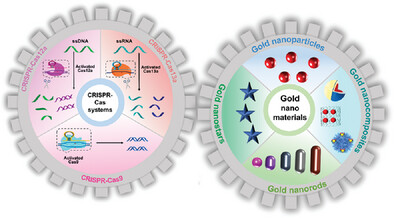
This review outlines the recent advances in the development of biosensors based on gold nanomaterials and clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)-Cas systems including CRISPR-Cas9, CRISPR-Cas12a, and CRISPR-Cas13a. The working mechanism, the sensing performance, and the prospect of gold nanomaterials-implemented CRISPR-Cas biosensors are highlighted and discussed.
Frontispiece
Co-Assembly of Carbon Nanotube Porins into Biomimetic Peptoid Membranes (Small 21/2023)
- First Published: 24 May 2023
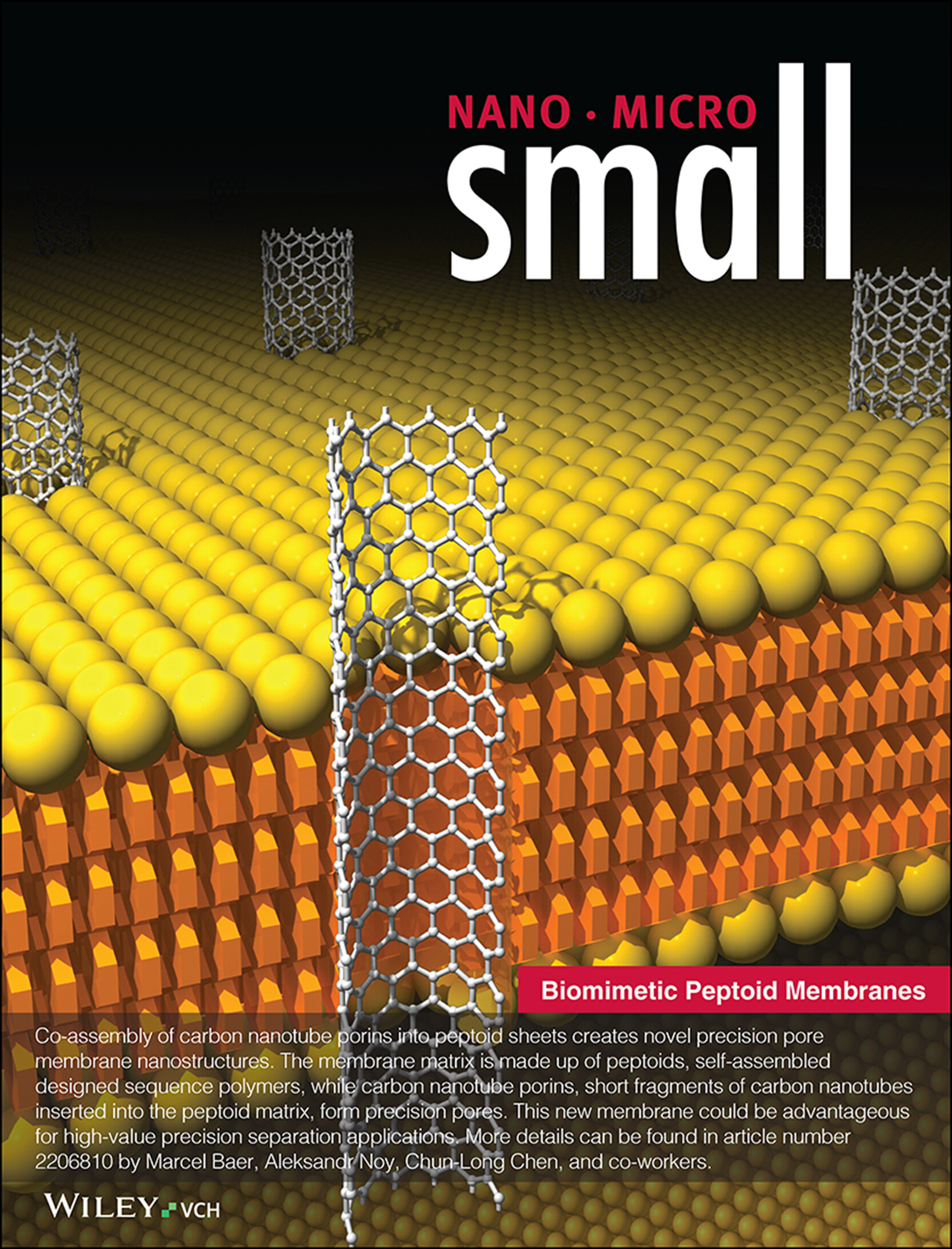
Biomimetic Peptoid Membranes
Co-assembly of carbon nanotube porins into peptoid sheets creates novel precision pore membrane nanostructures. The membrane matrix is made up of peptoids, self-assembled designed sequence polymers, while carbon nanotube porins, short fragments of carbon nanotubes inserted into the peptoid matrix, form precision pores. This new membrane could be advantageous for high-value precision separation applications. More details can be found in article number 2206810 by Marcel Baer, Aleksandr Noy, Chun-Long Chen, and co-workers.
Research Articles
Co-Assembly of Carbon Nanotube Porins into Biomimetic Peptoid Membranes
- First Published: 21 February 2023
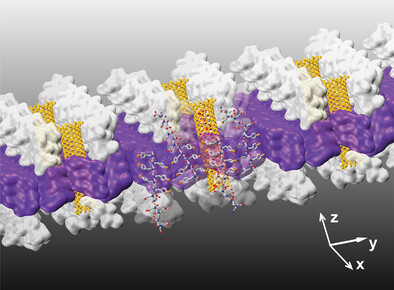
This work demonstrates the feasibility of engineering artificial membranes by co-assembling highly-programmable 2D peptoid sheets, with superior crystallinity and robustness, and CNTPs, with highly-efficient transport properties based on tunable pore sizes. This novel-engineered biomimetic membrane opens potential applications in precision separation, ranging from water purification to biopharmaceutical production.
Frontispiece
Dynamic Pluronic F127 Crosslinking Enhancement of Biopolymeric Nanocomposites for Piezo-Triboelectric Single-Hybrid Nanogenerators and Self-Powered Sensors (Small 21/2023)
- First Published: 24 May 2023

Biopolymeric Nanocomposites
In article number 2207384, Qufu Wei, Pengfei Lv, and co-workers report on biopolymeric composites for triboelectric nanogenerators (TENGs), piezoelectric nanogenerators (PENGs), and hybrid formats with outstanding mechanical and electrical properties. The designed composites are poling-responsive, outperform many reported biopolymer formats in voltage, currents, and power outputs. The materials demonstrate impressive energy storage capabilities, seamlessly interface with commercial microcontrollers, and power light-emitting diodes (LEDs). The devices and their functionalities advance the development of fully biopolymeric nanogenerators.
Research Articles
Dynamic Pluronic F127 Crosslinking Enhancement of Biopolymeric Nanocomposites for Piezo-Triboelectric Single-Hybrid Nanogenerators and Self-Powered Sensors
- First Published: 03 February 2023
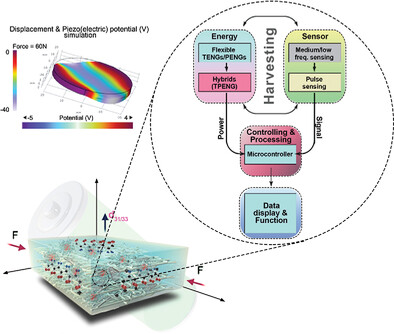
Dynamically robust biopolymeric nanocomposite triboelectric nanogenerators/piezoelectric nanogenerators/hybrid devices with excellent mechanical and electrical properties are designed based on biocompatible BaTiO3 and multiwalled carbon nanotubes crosslinked within a bacterial cellulose matrix by Pluronic F127. The electrical output performance of the composites is exceptionally high compared to other platforms with a sustainability approach that seamlessly interface with commercial microcontroller systems for operation as sensor switches and control units.
Frontispiece
Self-Sacrificing Template Synthesis of Carbon Nanosheets Assembled Hollow Spheres with Abundant Active Fe–N4O1 Moieties for Electrocatalytic Oxygen Reduction (Small 21/2023)
- First Published: 24 May 2023

Electrocatalytic Oxygen Reduction
In article number 2207991, Cheng-Yan Xu and co-workers develop a self-sacrificing strategy to encapsulate single-atom Fe-N4O1 species into carbon hollow spheres assembled by ultrathin nanosheets Fe1–N–C hollow microspheres (Fe1/N-HCMs). Such highly open architecture is supposed to be an ideal platform to isolate and fully expose single metal atoms. Benifiting from the highly open architecture and abundant Fe-N4O1 active sites, the Fe1/N-HCMs exhibit excellent oxygen reduction performance.
Research Articles
Self-Sacrificing Template Synthesis of Carbon Nanosheets Assembled Hollow Spheres with Abundant Active Fe–N4O1 Moieties for Electrocatalytic Oxygen Reduction
- First Published: 26 February 2023
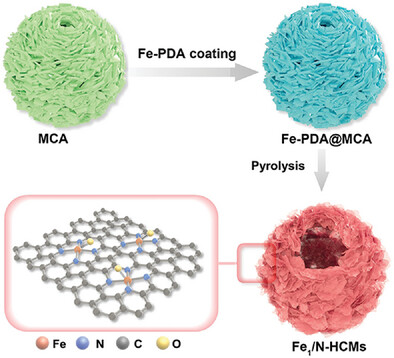
A self-sacrificing template strategy is developed to fabricate 2 nm-thick nanosheets assembled Fe1–N–C hollow microspheres (Fe1/N-HCMs) with highly open porous architecture, which is supposed to fully expose the catalytic active sites to boost the oxygen reduction reaction. Unlike the general Fe–N4 configuration in most reported Fe1–N–C catalysts, the active sites in Fe1/N-HCMs have been identified as Fe–N4O1 configuration.
Ultrathin Ultralow-Platinum Catalyst Coated Membrane for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells
- First Published: 25 February 2023
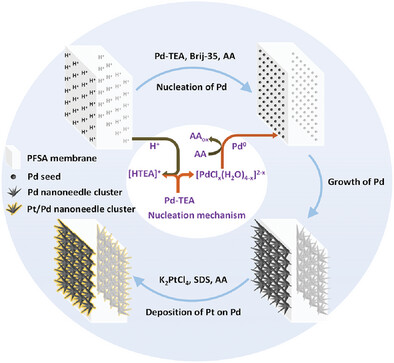
Ultrathin ultralow-Pt catalyst coated membrane (UUCCM) is fabricated by proton-initiated regioselective nucleation and growth of Pd nanoneedle clusters on membrane, followed by dense deposition of Pt nanoparticles on Pd. The single cell of the UUCCM demonstrates a remarkable activity of 59.9 W mgPt,Cathode−1, primarily arising from Pt/Pd interfacial strain, shortened mass transfer length, and optimal water management.
Precision Delivery of Dual Immune Inhibitors Loaded Nanomodulator to Reverse Immune Suppression for Combinational Photothermal-Immunotherapy
- First Published: 17 February 2023
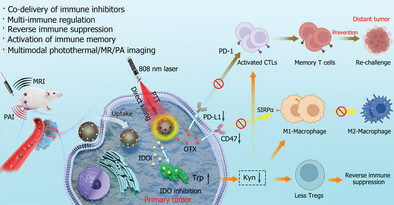
The co-delivery of dual-immune inhibitors, such as Indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase (IDO) inhibitor (IDOi, NLG919) and bromodomain extra-terminal inhibitor (OTX015) by mesoporous polydopamine nanoparticles is developed for combinational photothermal-immunotherapy through regulating abnormal enzymatic metabolism of IDO, blocking PD-L1/PD-1 and CD47/SIRPα to reverse immune suppressive tumor microenvironment, and preventing tumor growth and re-challenge.
Re-Dispersion of Platinum From CNTs Substrate to α-MoC1 - x to Boost the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction
- First Published: 11 February 2023
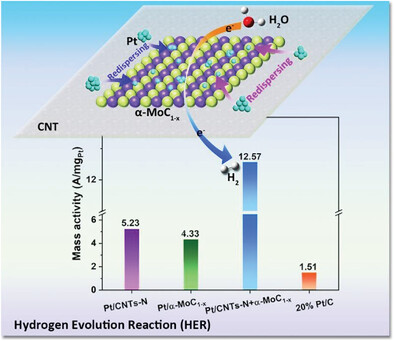
Pt/CNTs-N + α-MoC1 - x catalyst exhibits superior activity toward HER in both acidic and alkaline media. Thermo-activation treatment enables partial Pt atoms to redisperse on α-MoC1 - x substrate from carbon nanotubes. Dual active interfaces of Pt species dispersed over carbon nanotubes and α-MoC1 - x were formed. The strong electronic interaction between the Pt atom and α-MoC1 - x enhanced the utilization efficiency of the Pt atom.
A Dual-Responsive Artificial Skin for Tactile and Touchless Interfaces
- First Published: 26 January 2023
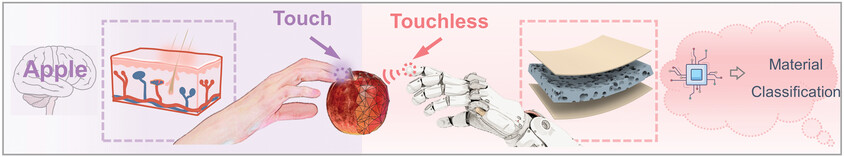
A dual-responsive artificial skin is present, for reacting to both pre-contact events and external pressure levels from environments. Versatile human–machine interfaces for tactile and touchless interactions are then demonstrated. Besides, overlooked valuable information encoded in the proximal inputs are explored. The proof-of-concept application for materials classification is successfully demonstrated in an entirely touchless mode.
Wetting-Enabled Three-Dimensional Interfacial Polymerization (WET-DIP) for Bioinspired Anti-Dehydration Hydrogels
- First Published: 20 February 2023
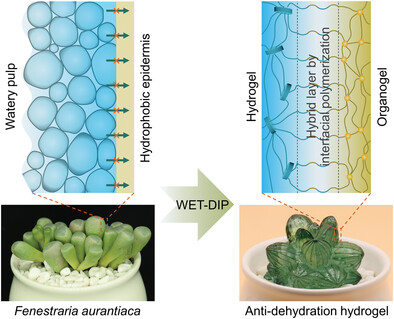
Inspired by the succulent Fenestraria aurantiaca with excellent anti-dehydration capacity, a wetting-enabled three-dimensional interfacial polymerization strategy is developed for organogel-sealed anti-dehydration hydrogels. The anti-dehydration hydrogels can be molded to various 3D shapes due to the wetting and fluidity of liquid precursors on 3D hydrophobic-oleophilic surfaces. Strain sensors based on anti-dehydration hydrogels exhibit long-term stability for finger gesture perception.
Pressure Regulating Self-Trapped States toward Remarkable Emission Enhancement of Zero-Dimensional Lead-Free Halides Nanocrystals
- First Published: 20 February 2023
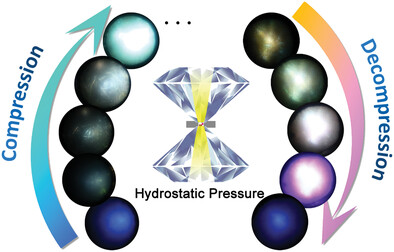
A stark enhancement of STE emission upon compression in a 0D lead-free inorganic metal halide Cs3Cu2I5 NCs is achieved. Moreover, in the process of decompression, a white light and a strong purple light emission is observed, in which the very bright purple light is able to be maintained at near-ambient pressure.
Spin-Wave Optics in YIG Realized by Ion-Beam Irradiation
- First Published: 21 February 2023
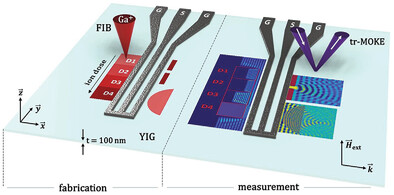
Direct focused-ion-beam writing is presented as an enabling technology for realizing functional spin-wave devices of high complexity, demonstrated by optically inspired designs. By experimentally showing flavors of reflective, refractive, and diffractive components (lenses, gratings, Fourier-domain processors), this technology is envisioned as the gateway to building magnonic computing devices that rival their optical counterparts in their complexity and computational power.
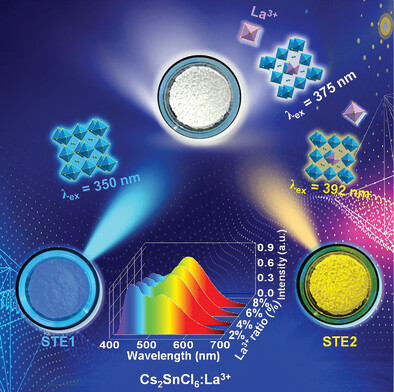
Precise Hue Control in a Single-Component White-Light Emitting Perovskite Cs2SnCl6 through Defect Engineering Based on La3+ Doping
- First Published: 22 February 2023
Dual Active Sites of Oversaturated Fe-N5 and Fe2O3 Nanoparticles for Accelerating Redox Kinetics of Polysulfides
- First Published: 23 February 2023
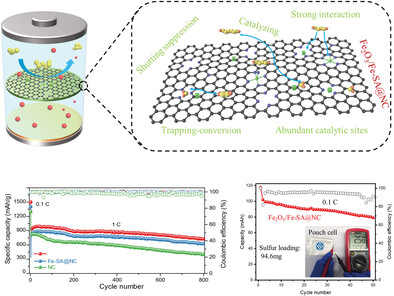
A novel cooperative catalytic with dual active sites (oversaturated Fe-N5 and Fe2O3 nanocrystals) are co-embedded in nitrogen-doped hollow carbon spheres (Fe2O3/Fe-SA@NC) is designed. The dual active sites synchronically enhance conversion ability of polysulfides. Consequently, the Li–S battery exhibits a high capacity retention of 78% after 800 cycles at 1 C and good performance at 0.1 C for pouch cell.
Ultrastretchable MXene Microsupercapacitors
- First Published: 23 February 2023
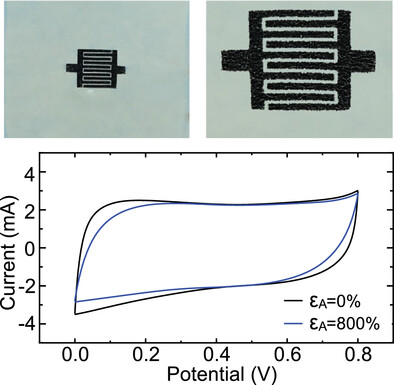
A stretchable microsupercapacitor utilizes crumpled MXene electrodes to achieve high specific area capacitance and ultrahigh stretchability of up to 800% area strain. Stable charging–discharging capability is well retained under both static and dynamic tensile loadings. A self-powered light-emitting diode array illustrates the practical application of integrated microsupercapacitors as the soft energy source for stretchable electronics.
Engineering the First Coordination Shell of Single Zn Atoms via Molecular Design Strategy toward High-Performance Sodium-Ion Hybrid Capacitors
- First Published: 23 February 2023
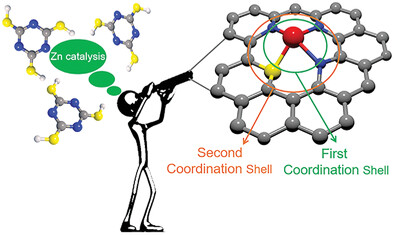
A molecular design strategy is developed for regulating the first coordination shell of single Zn atoms in carbon. Thanks to the high-density Zn–N3S moieties, the as-prepared carbon shows ultrahigh reactivity and efficient electron/ion transfer capability, which enables fascinating performance for sodium-ion hybrid capacitors.
Revealing the Kinetic Balance between Proton-Feeding and Hydrogenation in CO2 Electroreduction
- First Published: 23 February 2023
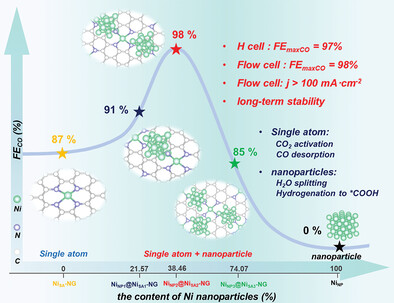
It is reported that the kinetic balance between proton-feeding and hydrogenation in CO2 electroreduction by fine-tuning the content of Ni single atom sites and Ni nanoparticles (denoted as NiNPx@NiSAy-NG (x,y = 1,2,3)). As a result, CO Faraday efficiency of 98% at −0.58 V (vs. RHE) and the current density of −264 mA cm−2 at −0.98 V (vs. RHE) can be achieved in NiNP2@NiSA-NG.
Chloride Adsorbates Enhance the Photocarrier Separation and Promote the Bio-Syngas Evolution
- First Published: 23 February 2023
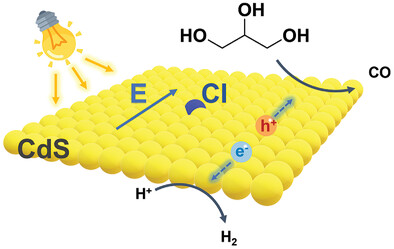
A method to increase the photocatalytic syngas production from biomass reforming reaction is established. Chloride, adsorbed on the surface of CdS, can increase the internal electric field, and enhance the charge separation and migration. The catalyst contributes an 11-fold enhanced photocatalytic syngas evolution from glycerol. The study offers a convenient strategy to prohibit surface holes and electrons recombination.
A Universal Room-Temperature 3D Printing Approach Towards porous MOF Based Dendrites Inhibition Hybrid Solid-State Electrolytes
- First Published: 23 February 2023
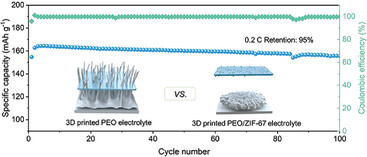
In this work, a universal room-temperature 3D printing strategy toward PEO/MOF (ZIF-67, MOF-74, UIO-66, ZIF-8) hybrid solid-state electrolyte is first proposed. The 3D-printed PEO/ZIF-67 hybrid solid-state electrolyte displays excellent dendrite inhibition, enhanced ionic conductivities, and improved electrochemical performances.
A Laser-Processed Carbon-Titanium Carbide Heterostructure Electrode for High-Frequency Micro-Supercapacitors
- First Published: 23 February 2023
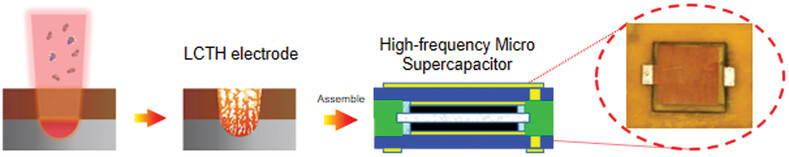
The authors present a laser-induced fabrication method for engineering a unique carbon-titanium carbide heterostructure electrode. Its featured macropores of the carbon nanofoam layer and mesopores of the underlying high polarity titanium carbide layer enable the assembled symmetric supercapacitor excellent frequency response and high areal specific energy density.
Nanoparticles Targeted to Fibroblast Activation Protein Outperform PSMA for MRI Delineation of Primary Prostate Tumors
- First Published: 25 February 2023

The binding of fibroblast activation protein (FAP)-targeting iron oxide nanoparticles within the complex tumor microenvironment. FAP is overexpressed in tumor stromal components such as cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) and vasculature cells, adding to its suitability as a target for the imaging of solid tumors for the guidance of focal therapies such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) guided-radiotherapy.
Pseudo-Elasticity and Variable Electro-Conductivity Mediated by Size-Dependent Deformation Twinning in Molybdenum Nanocrystals
- First Published: 24 February 2023
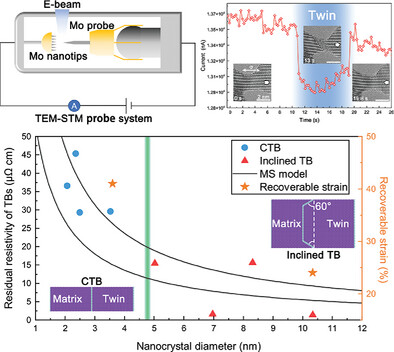
The reversible twinning-mediated pseudo-elasticity and variable electro-conductivity in Mo nanocrystals are shown by in situ tension and current measurement. Coherent and inclined twin boundary (TB) twinning mechanisms are uncovered in nanocrystals with smaller and larger diameters, respectively. The effects of size and TB types on the electrical conductivity are also quantified based on the experimental measurements and calculations.
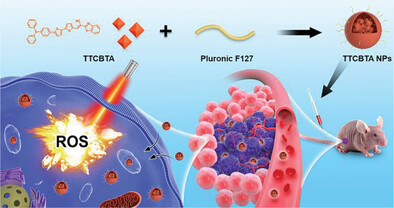
Engineered Organic Nanorockets with Light-Driven Ultrafast Transportability for Antitumor Therapy
- First Published: 25 February 2023
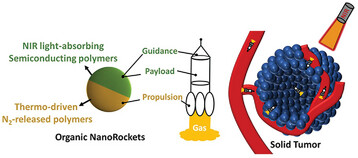
Engineered organic nanorockets are powered by photoactivated organic kinetic systems through a two-stage light-to-heat-to-chemical energy transition for a stable ultrafast (≈300 µm s−1) self-propulsion in the liquid media. The programmable navigation allows a high permeability against physiological barriers for elevating accumulation and deep penetration at the tumor site, thereby significantly enhancing the antitumor efficacy of the nanomedicines.
Interplay of Depletion Forces and Biomolecular Recognition in the Hierarchical Assembly of Supramolecular Tubes
- First Published: 25 February 2023

A crowding agent, poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG), invokes depletion forces that act on synthetic supramolecular tubes pushing them into hierarchically assembled bundles. Biotin groups on the surface of the tubes enable cross-linking via biotin–streptavidin interactions. The interplay of depletion forces and biomolecular recognition provides a new strategy for building hierarchically organized supramolecular architectures.
Physiologically-Based Kinetic Modeling of Intravenously Administered Gold (Au) Nanoparticles
- First Published: 24 February 2023
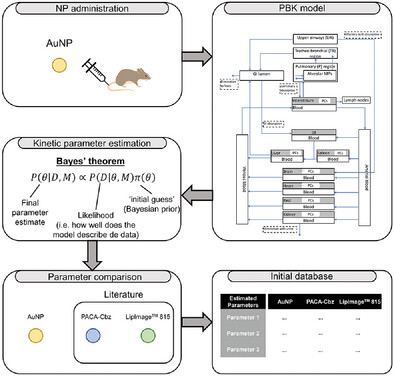
Physiologically-based kinetic (PBK) model parameters are estimated for gold nanoparticles (NPs) in rats. These parameters are complemented with previously published PBK parameters of two other NPs (i.e., LipImage 815 and poly(alkyl cyanoacrylate) loaded with cabazitaxel) to create an initial database of PBK parameters. This database may help in quantifying a relation between NP characteristics and PBK parameter values.
Boosting the Reversible, High-Rate Na+ Storage Capability of the Hard Carbon Anode Via the Synergistic Structural Tailoring and Controlled Presodiation
- First Published: 26 February 2023
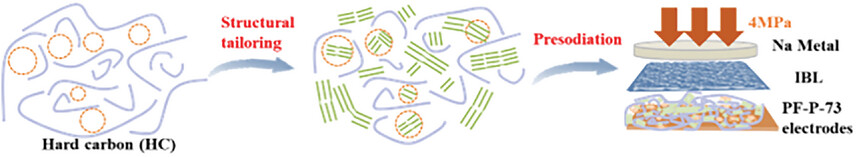
A multiscale modification strategy of hard carbon (HC) is proposed by exquisitely tuning the microstructure on the particle level as well as supplementing extra Na+ reservoir for the electrode through an insulation-buffer-layer assisted presodiation therapy. The coulombic efficiency of HC anode is precisely controlled till the close-to-unit value and Na+ diffusivity is drastically enhanced by two orders of magnitude at the low-potential region.
Synthesizing Cr-Based Two-Dimensional Conjugated Metal-Organic Framework Through On-Surface Substitution Reaction
- First Published: 26 February 2023
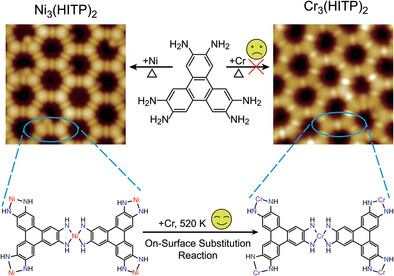
As revealed by low-temperature scanning tunneling microscopy and spectroscopy, single-layer Cr3(HITP)2 (HITP=2,3,6,7,10,11-hexaiminotriphenylene) conjugated metal-organic frameworks (c-MOFs) have been synthesized by substituting Cr for Ni atoms in Ni3(HITP)2 templates on Au(111) substrate under ultrahigh vacuum conditions. This work demonstrates a new on-surface synthesis strategy to prepare high-quality early-transition-metal-based c-MOFs.
A Combination of Bio-Orthogonal Supramolecular Clicking and Proximity Chemical Tagging as a Supramolecular Tool for Discovery of Putative Proteins Associated with Laminopathic Disease
- First Published: 26 February 2023
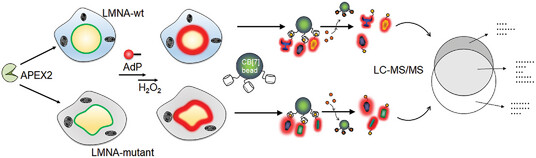
A new proteomics approach by a combined use of proximity-dependent chemical tagging and bio-orthogonal noncovalent click chemistry provides detection of altered proteomic environment upon nuclear protein mutations and allows to discover putative proteins associated with a nuclear protein mutation-linked disease.
Investigation of the Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production of Semiconductor Nanocrystal-Based Hydrogels
- First Published: 24 February 2023
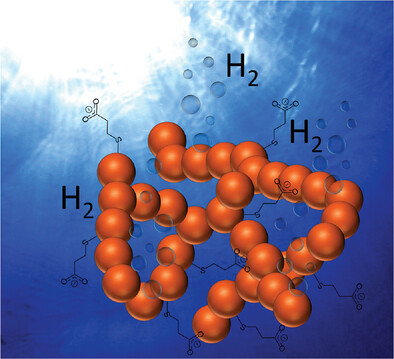
Gel structures based on nanocrystals (NCs) exhibit an interesting morphology with high porosity and good surface accessibility, which combines the physicochemical properties of NCs with the size of bulk material. Due to these properties, nanocrystal-based gel structures show a fivefold higher hydrogen evolution response in photocatalytic studies than their colloidal non-gelated nanocrystal counterparts.
The Precision Defect Engineering with Nonmetallic Element Refilling Strategy in g-C3N4 for Enhanced Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production
- First Published: 25 February 2023
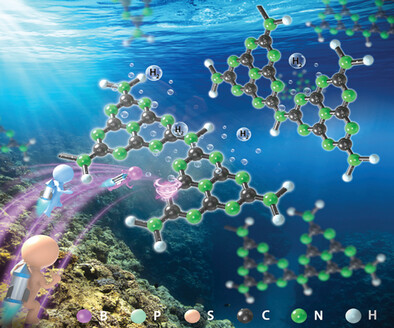
A defect-induced heteroatom refilling strategy is used here to synthesize heteroatoms introduced in carbon nitride by precisely controlling the “introduction” sites on efficient N1 sites. The refilling of B, P, and S has stronger H2O adsorption and dissociation capacity than traditional doping, which makes it an optimal H2 production path.
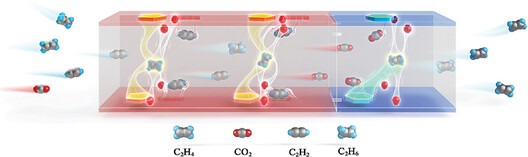
Customizing Metal-Organic Frameworks by Lego-Brick Strategy for One-Step Purification of Ethylene from a Quaternary Gas Mixture
- First Published: 26 February 2023
Coupling Hydrazine Oxidation with Seawater Electrolysis for Energy-Saving Hydrogen Production over Bifunctional CoNC Nanoarray Electrocatalysts
- First Published: 25 February 2023
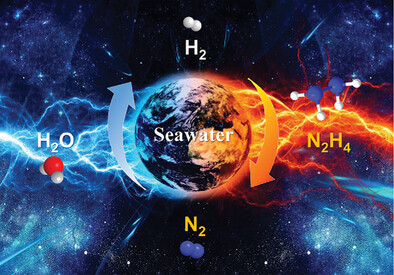
The construction of bifunctional cobalt/nitrogen-codoped carbon (CoNC) nanosheet arrays on carbon cloth (CC) as both cathode and anode to drive a hydrazine assisted seawater electrolysis system for H2 production is reported, which only needs an ultra-low cell voltage of 0.557 V and electricity consumption of 1.22 kW h per cubic meter of H2 at 200 mA cm−2.
Dual-Conductive CoSe2@TiSe2-C Heterostructures Promoting Overall Sulfur Redox Kinetics under High Sulfur Loading and Lean Electrolyte
- First Published: 26 February 2023
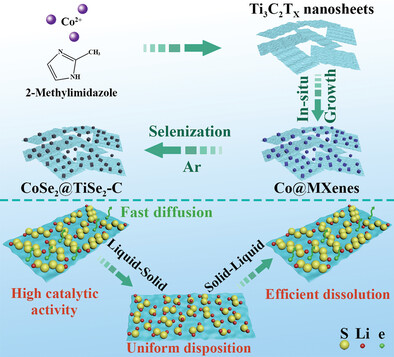
Cobalt selenide (CoSe2) polyhedrons anchored on few-layer TiSe2-C nanosheets derived from Ti3C2Tx MXenes (CoSe2@TiSe2-C) are constructed. The dual-conductive CoSe2@TiSe2-C heterostructures can accelerate the conversion reaction from liquid lithium polysulfides to solid Li2S and promote Li2S dissociation process through high conductivity and lowered reaction energy barriers for promoting overall sulfur redox kinetics under high sulfur loadings and lean electrolyte.
High-Energy Aqueous Magnesium Ion Batteries with Capacity-Compensation Evolved from Dynamic Copper Ion Redox
- First Published: 25 February 2023
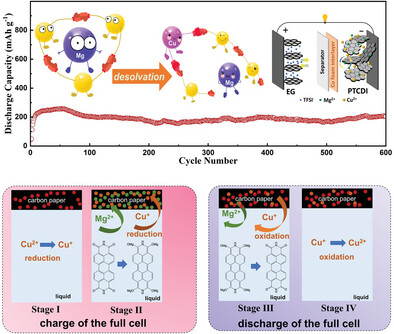
The assembled magnesium ion batteries using expanded graphite cathode coupled with 3,4,9,10-perylenetetracarboxylic diimide anode in a hybrid aqueous/organic electrolyte achieve an ultra-high capacity. The introduction of Cu foam interlayer offers effective capacity-compensation by means of the dynamic redox of copper ions, the weakened solvation of Mg2+ cations, and the enhanced electronic conductivity of anode.
Regulation of Interfacial Lattice Oxygen Activity by Full-Surface Modification Engineering towards Long Cycling Stability for Co-Free Li-Rich Mn-Based Cathode
- First Published: 26 February 2023
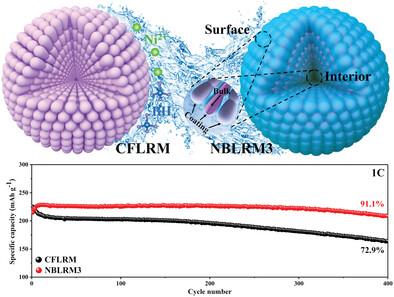
An efficient method to regulate the surface structure of Co-free Li-rich cathode materials is proposed by simply adjusting the distribution state of the boron nickel complexes coating layer. The full-surface coating layer plays the role of sharing voltage, protective layer, and passivation of surface lattice oxygen. As a result, the comprehensive electrochemical properties are enhanced effectively.
Transferring and Retaining of Different Polyaniline Nanofeatures via Electrophoretic Deposition for Enhanced Sensing Performance
- First Published: 24 February 2023
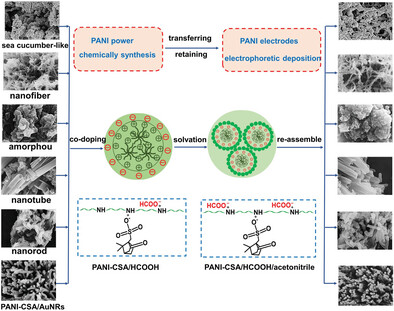
Camphorsulfonic acid doped polyaniline (PANI-CSA) displays a morphology memory effect, and five different nanofeatures (sea cucumber-like, nanofiber, amorphous, nanotube, and nanorod) have been successfully transferred onto indium tin oxide substrate via electrophoretic deposition without involving a dedoping process with ammonia solution. This method is also applicable to transfer PANI/gold nanorod composites which exhibits excellent sensing performance.
Electromagnetic Response of Multistage-Helical Nano-Micro Conducting Polymer Structures and their Enhanced Attenuation Mechanism of Multiscale-Chiral Synergistic Effect
- First Published: 26 February 2023
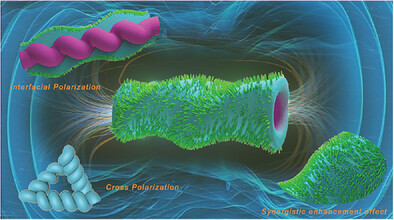
In this work, the conducting polymer-based composites with controllable multiscale chiral morphology are successfully prepared via in situ polymerization with broadband and efficient microwave absorption performance. Multiscale-chiral structure electromagnetic simulation models are established to reveal related electromagnetic response characteristics. The multiscale-chiral synergistic effect and broadband absorption mechanism are discussed in term of experiment and theory.
Ultrasound-Activatable g-C3N4-Anchored Titania Heterojunction as an Intracellular Redox Homeostasis Perturbator for Augmented Oncotherapy
- First Published: 26 February 2023
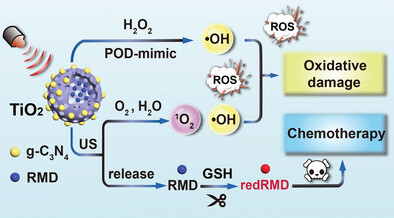
A facilely designed TCR reactor is developed by the encapsulation of GSH-reducible RMD into TiO2@g-C3N4 heterojunction, which serves as an intracellular redox homeostasis perturbator for augmented oncotherapy. This study provides useful insights into promoting the therapeutic performance of TiO2-based sonosensitizers by optimizing the semiconductor heterostructures.
Injectable Conductive Hydrogels with Tunable Degradability as Novel Implantable Bioelectrodes
- First Published: 24 February 2023
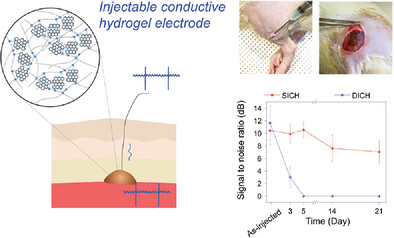
The injectable conductive hydrogel electrodes, composed of functionalized poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) polymers and Pluronic-coated reduced graphene oxide, exhibit good electrical conductivity, softness, cell and tissue compatibility, and tunable degradability in vivo. These injectable conductive hydrogels displaying different degradation profiles are useful for implantable bioelectrodes.
Overcoming Non-Specific Interactions for Efficient Encapsulation of Doxorubicin in Ferritin Nanocages for Targeted Drug Delivery
- First Published: 07 February 2023
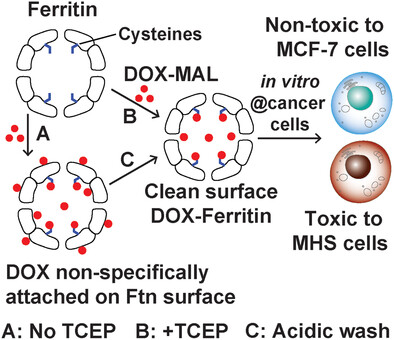
The presence of TCEP during the encapsulation of DOX in Ftn reduces the non-specific interaction between DOX and Ftn. Similar results can be achieved by washing with acidic solution. Finally, in vitro cell experiments shows that the resulting DOX-Ftn variants are non-toxic to MCF-7 cancer cells, but toxic to MHS cancer cells.
A Versatile Theranostic Nanoplatform with Aggregation-Induced Emission Properties: Fluorescence Monitoring, Cellular Organelle Targeting, and Image-Guided Photodynamic Therapy
- First Published: 17 February 2023
Spark Discharge Doping—Achieving Unprecedented Control over Aggregate Fraction and Backbone Ordering in Poly(3-hexylthiophene) Solutions
- First Published: 02 March 2023
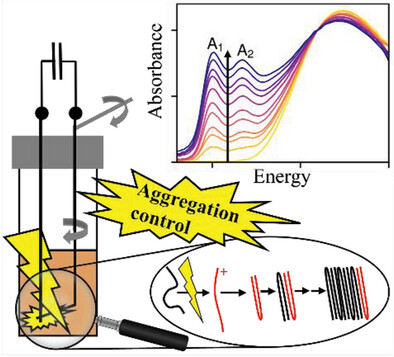
This work introduces a novel solution treatment utilizing spark discharges to enable a highly controlled aggregation of semiconducting polymers. The aggregate fraction and the quality of the polymer backbone order can be finely tuned over exceptionally broad ranges by choosing appropriate parameters for this current-induced doping treatment.
A Metabolic Driven Bio-Responsive Hydrogel Loading Psoralen for Therapy of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- First Published: 04 March 2023
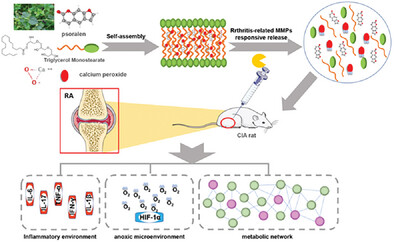
The psoralen- and calcium peroxide-loaded tripolycerol monostearate (TGMS) hydrogel (psoralen gel) is developed to administer via intra-articular injection for rheumatoid arthritis treatment by regulating inflammatory environment, anoxic microenvironment, and metabolic network, and metabolomic analysis used further proves the efficacy of hydrogel as a sustained-release carrier.
Electrochemical Oxidation to Fabricate Micro-Nano-Scale Surface Wrinkling of Liquid Metals
- First Published: 03 March 2023
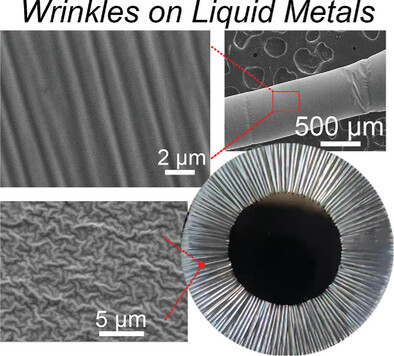
A generalized method to fabricate multi-scale and diverse-dimensional oxide wrinkles on liquid metal surfaces by an electrochemical anodization mechanism is reported. By altering the distribution of growth stress, changing the substrate geometry, or tuning the surface tension, various wrinkle morphologies of different scales can be generated, such as striped, labyrinthine, and radial wrinkles.
Mussel-Inspired, Underwater Self-Healing Ionoelastomers Based on α-Lipoic Acid for Iontronics
- First Published: 03 March 2023
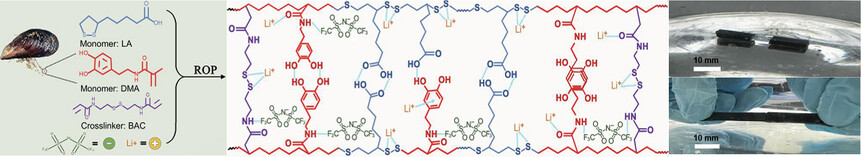
A molecular design strategy is devised to generate α-lipoic acid-derived ion-conductive elastomers which show unprecedented, prolonged, superfast self-healing underwater, universal adhesion, sensing capability, and flame retardancy. These unusual characteristics stem synergistically from the maximized availability of dynamic disulfide bonds and high-density diverse noncovalent interactions in combination involving carboxylic groups, catechols and associated hydrogen bonds and π–π stacking, and others.
Bi-Functional Co/Al Modified 1T-MoS2/rGO Catalyst for Enhanced Uranium Extraction and Hydrogen Evolution Reaction in Seawater
- First Published: 04 March 2023
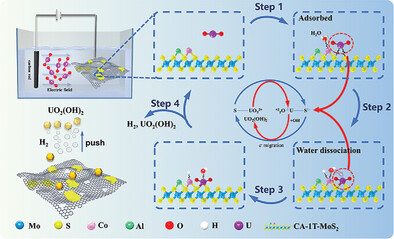
A bi-functional Co/Al modified 1T-MoS2/rGO catalyst is developed. The catalyst exhibits high hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) performance and uranium extraction capability in seawater and without a post-treatment process, showing good reusability and easy recovery of uranium-containing products. This work provides a new strategy for the design and preparation of bi-functional catalysts with high HER performance and uranium extraction and recovery capabilities in seawater.
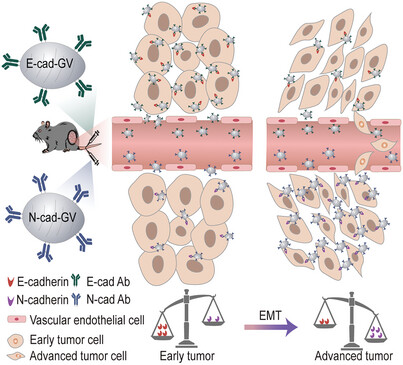
Ultrasound Molecular Imaging of Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition for Evaluating Tumor Metastatic Potential via Targeted Biosynthetic Gas Vesicles
- First Published: 03 March 2023
Lithiophilic Magnetic Host Facilitates Target-Deposited Lithium for Practical Lithium-Metal Batteries
- First Published: 03 March 2023
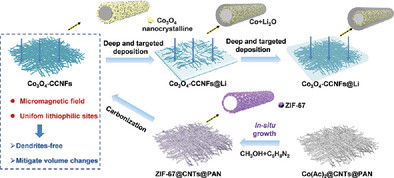
A lithiophilic-magnetic host (Co3O4-CCNFs) is prepared by in situ anchoring of homogeneous Co3O4 nanocrystal onto carbon nanofibers composite matrix. The Co3O4-CCNFs can endow a targeted Li deposition behavior throughout the whole 3D matrix, thus, facilitating the formation of compact Li anode by inducing a micromagnetic field. Benefiting from the elaborate design, lithium-metal batteries assembled with Co3O4-CCNFs deliver remarkably improved performance.