Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Front Cover
Front Cover: A Synbiotic Ameliorates Con A-Induced Autoimmune Hepatitis in Mice through Modulation of Gut Microbiota and Immune Imbalance
- First Published: 09 April 2023

Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2023, 67, 202200428
The intestinal flora of AIH mice is disordered, the intestinal barrier is destroyed, LPS migrates to liver and activates the TLR4/NF-κB inflammatory pathway leading to liver injury. Gavage of Pro, Pre and Syn reverse this state. Postbiotics inhibit LPS-induced activation of TLR4/NF-κB pathway and reduce inflammatory factors in vitro. This is reported by Weiping Fan and co-workers in article number 2200428.
Editorial Board
Reviews
Are Phosphatidylcholine and Lysophosphatidylcholine Body Levels Potentially Reliable Biomarkers in Obesity? A Review of Human Studies
- First Published: 27 January 2023
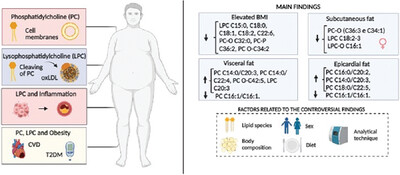
Phosphatidylcholine (PC) is the major component of cell membranes and lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) - a lipid class derived by the cleavage of PC - is the main component of oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL) that can lead to cardiovascular disease (CVD) and type 2 diabetes (T2DM). Controversial results are found on the associations of PC and LPC with obesity, which dependent on several factors.
A Review on Dietary Flavonoids as Modulators of the Tumor Microenvironment
- First Published: 25 January 2023
Research Articles
A Synbiotic Ameliorates Con A-Induced Autoimmune Hepatitis in Mice through Modulation of Gut Microbiota and Immune Imbalance
- First Published: 28 January 2023
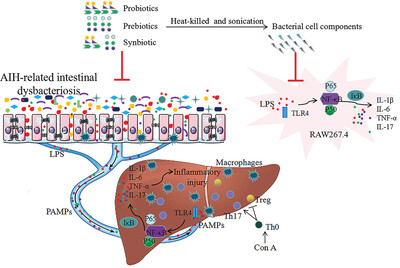
Protective mechanisms of probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotic against the AIH. The probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotic restore immune imbalance, intestinal flora, and intestinal barrier to inhibit bacteria and LPS transfer to the liver as well as inhibit the activation of the TLR4/NF-κB pathway and the production of inflammatory factors in the liver.
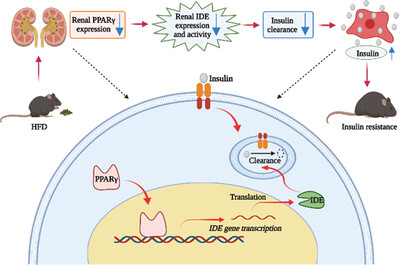
Long-Term High-Fat Diet Decreases Renal Insulin-Degrading Enzyme Expression and Function by Inhibiting the PPARγ Pathway
- First Published: 01 February 2023
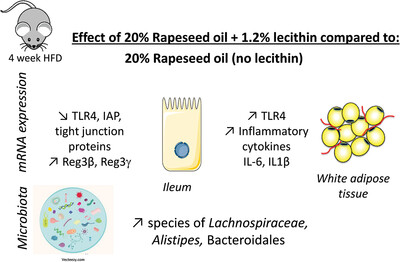
Soy Lecithin in High-Fat Diets Exerts Dual Effects on Adipose Tissue Versus Ileum
- First Published: 28 January 2023
Oxidative Stress Mediated by N6-Methyladenosine Methylation Contributes to High-Fat Diet Induced Male Reproductive Dysfunction
- First Published: 03 February 2023
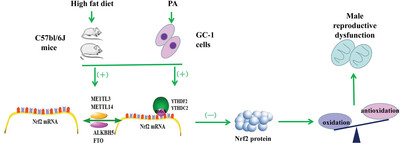
N6-methyladenosine Co-Immunoprecipitation quantitative polymerase chain reaction results show that the enrichment of m6A-modified Nrf2 mRNA and the levels of m6A regulatory proteins METTL3, METTL14, YTHDC2, and YTHDDF2 increase significantly in the DIO group and DIO-R group compared to the control group. Oxidative stress mediated by methylation of m6A may contribute to high fat diet-induced reproductive dysfunction in murine testicular tissue.
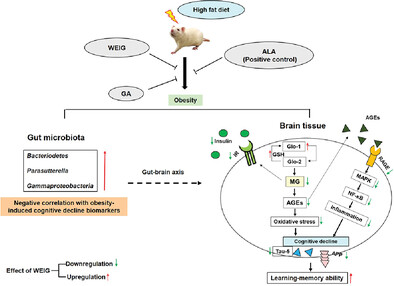
Preventive Effect of Indian Gooseberry (Phyllanthus emblica L.) Fruit Extract on Cognitive Decline in High-Fat Diet (HFD)-Fed Rats
- First Published: 04 February 2023
Diet Supplementation of Luteolin before Fatty Liver Formation Improves Hepatic Steatosis in Obese Mice by Inhibiting Visceral Adipose Tissue Lipolysis
- First Published: 09 February 2023

Long-term high-fat diet induces visceral adipose tissue lipolysis and liver ectopic lipid deposition. 5-HT-induced adipocyte lipolysis is essential for the development of obesity-related complications. Diet luteolin supplementation before fatty liver formation improves hepatic steatosis in obese mice by inhibiting visceral adipose tissue lipolysis. Mechanistically, luteolin inhibits 5-HT-induced lipolysis, Ca2+-PKG cascade, and SIRT1/FoxO1/AMPKα signaling through competitively binding to 5-HT receptor HTR2B.