Editor-in-Chief: Prisca-Maryla Henheik
The European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology is an innovative resource for lipids and oils research.
With a major focus on health-related topics with applied aspects, the journal also addresses food science and technology, biomedical science including clinical and pre-clinical research, nutrition, animal science, plant and microbial lipids, (bio)chemistry, oleochemistry, biotechnology, processing, physical chemistry, and analytics including lipidomics.
Journal Metrics
- 4CiteScore
- 1.8Journal Impact Factor
- 32%Acceptance rate
- 21 days Submission to first decision
On the Cover
Articles
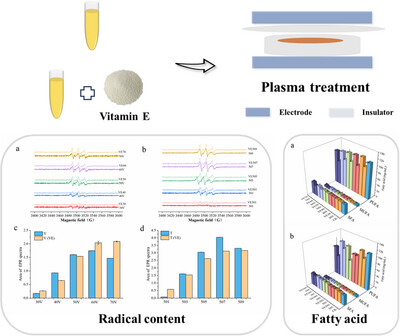
Effect of Treatment Voltage and Duration of Cold Plasma on the Oxidation Stability of Herring Oil and the Use of Vitamin E as Antioxidant
- 18 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
Lipid Nanoparticles as an Effective Strategy for Protecting Bioactive Compounds in Passion Fruit Seed Oil
- 18 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
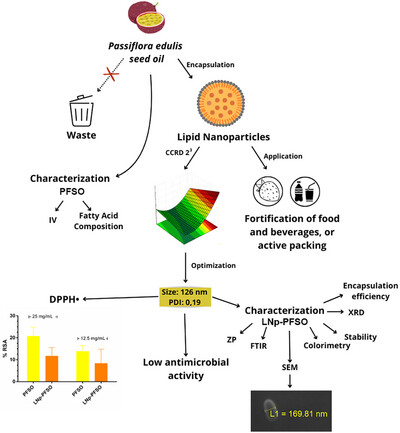
This schematic illustrates the encapsulation of Passiflora edulis seed oil (PFSO) into lipid nanoparticles (LNP-PFSO), transforming waste into value. The nanoparticles, optimized for size (126 nm, PDI: 0.19), were characterized (SEM, FTIR, XRD) and tested for antimicrobial and antioxidant activities, with applications in food fortification or active packaging.
Establishment of Oyster‐Water‐Soluble Protein–EGCG–Linseed Oil‐Emulsion System and Its Lipid Oxidation Stability During Storage and In Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion
- 13 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
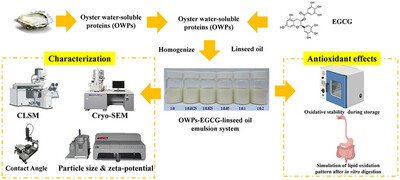
An oyster-derived oyster-water-soluble protein (OWP)–(−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) complex was used to form the OWP–EGCG linseed oil-emulsion system, whereas its characterization properties and antioxidant effects against lipid and protein oxidation during storage and in vitro digestion were investigated.
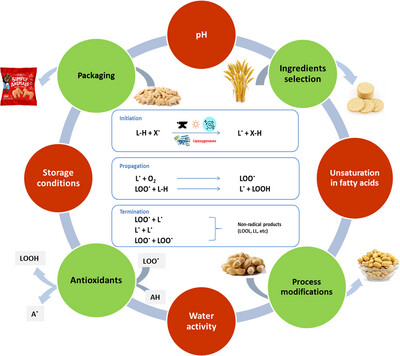
Mechanisms, Causes, and Solutions: A Comprehensive Review of Lipid Oxidation in Low‐Moisture Packaged Snacks
- 7 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
Measuring Bending Rigidity and Compression Resistance in Pickering Layers
- 30 June 2025
Graphical Abstract
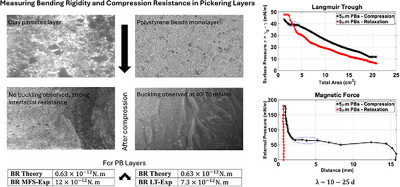
This graphical abstract presents the mechanical response of Pickering layers of polystyrene beads (PBs) and clay particles (CPs) under compression. PBs exhibit buckling at 40–70 mN/m, whereas CPs show no buckling. Experimental force–compression curves highlight distinct deformation behaviors, and deviations in bending rigidity emphasize interparticle interactions in layer stability. 2
The following is a list of the most cited articles based on citations published in the last three years, according to CrossRef.
The use of natural and synthetic phospholipids as pharmaceutical excipients†
- 1088-1107
- 25 August 2014
Graphical Abstract
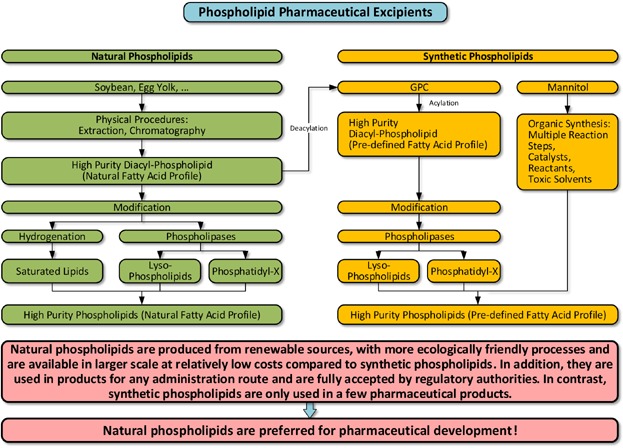
For selection of phospholipid excipients for pharmaceutical formulations, natural phospholipids are preferred compared to synthetic phospholipids because they are available at large scale with reproducible quality at lower costs of goods. They are well accepted by regulatory authorities and are produced using less chemicals and solvents at higher yields. In order to avoid scale up problems during pharmaceutical development and production, natural phospholipid excipients instead of synthetic phospholipids should be selected whenever possible.
Lipids of oleaginous yeasts. Part I: Biochemistry of single cell oil production
- 1031-1051
- 11 May 2011
Fatty acid profiles of 80 vegetable oils with regard to their nutritional potential
- 710-732
- 16 July 2007
Latest news
Recent issues
- Volume 127, Issue 7
Special Issue: Fats and Oils as Renewable Feedstock for the Chemical Industry
July 2025Guest Editor(s):
Jürgen Metzger, Ursula Biermann, Thomas Seidensticker - Volume 127, Issue 6June 2025
- Volume 127, Issue 5May 2025
- Volume 127, Issue 4April 2025