Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Front Cover
Front Cover: The Ability of Streptococcus thermophilus BT01 to Modulate Urease Activity in Healthy Subjects’ Fecal Samples Depends on the Biomass Production Process
- First Published: 22 March 2023

Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2023, 67, 202200529
Production conditions play a role in determining the probiotic properties of Streptococcus thermophilus. During the manufacturing process of the probiotic S. thermophilus BT01, the use of an appropriate cryoprotectant led to a significant reduction in fecal urease activity in healthy subjects during a randomized controlled crossover study. This is reported by Anđela Martinović, Marco Chittaro, Diego Mora, and Stefania Arioli in article number 2200529.
Editorial Board
Research Articles
The Ability of Streptococcus thermophilus BT01 to Modulate Urease Activity in Healthy Subjects’ Fecal Samples Depends on the Biomass Production Process
- First Published: 27 January 2023

Streptococcus thermophilus BT01 was freeze-dried with cryoprotectant A (Cryo-A) or B (Cryo-B). The two formulations, which differed in the level of urease activity, were administered to healthy subjects in a randomized crossover study, without affecting the recovery of S. thermophilus in fecal samples. However, the Cryo-A treated biomass was effective in causing a significant decrease in fecal urease activity.
Rice Bran Lipidome Identifies Novel Phospholipids, Glycolipids, and Oxylipins with Roles in Lipid Metabolism of Hypercholesterolemic Children
- First Published: 03 December 2022
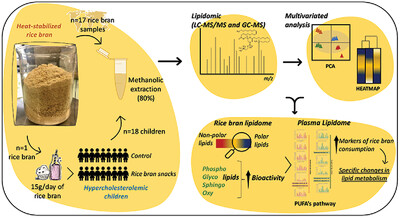
A global set of rice bran (RB) from 17 varieties and agro-environmental conditions is studied to advance the valorization of RB as a supplement for human nutrition. To do so, a lipidomic study of this RB set and the analysis of plasma lipidome of infants supplemented with one type of RB are conducted.
Effect of the Emulsifier Used in Dunaliella salina-Based Nanoemulsions Formulation on the β-Carotene Absorption and Metabolism in Rats
- First Published: 28 January 2023
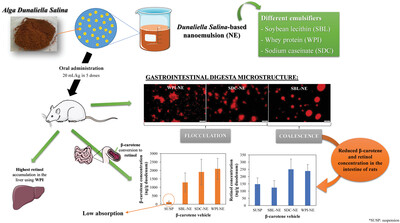
Nanoemulsions containing β-carotene from alga Dunaliella salina and different emulsifiers are orally administered to rats. β-Carotene absorption and retinol bioavailability is greatly increased using nanoemulsions in comparison to the control suspension, being protein nanoemulsions the most effective. Protein-based nanoemulsions present aggregation while soybean lecithin nanoemulsion presents coalescence in the gastrointestinal tract, which affects β-carotene absorption and its conversion to retinol.
The Impact of Zinc on Manganese Bioavailability and Cytotoxicity in HepG2 Cells
- First Published: 22 January 2023
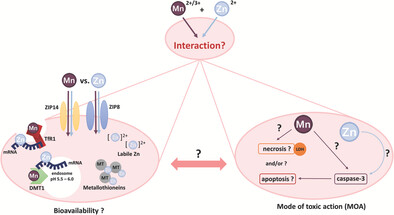
Interactions between manganese (Mn) and zinc (Zn) are rarely studied even though they share similar transport systems. Therefore, this study aims to elucidate the role of Zn on Mn bioavailability including homeostasis and cytotoxicity in HepG2 cells. Data suggest protective mechanisms against Mn-induced cytotoxicity due to decreased Mn bioavailability in HepG2 cells after combinational incubation of Mn and Zn.
Dietary Application of the Microalga Lobosphaera incisa P127 Reduces Severity of Intestinal Inflammation, Modulates Gut-Associated Gene Expression, and Microbiome in the Zebrafish Model of IBD
- First Published: 22 January 2023
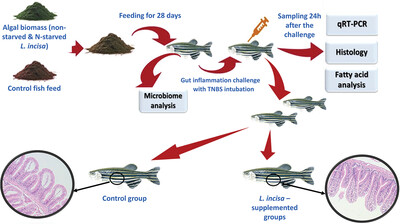
Microalgae are potent producers of biomolecules with health-beneficial properties. We investigated the immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory potential of the mutant strain P127 of the microalga Lobosphaera incisa, which accumulates a rare long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid dihomo-ɣ-linolenic acid, in a zebrafish model of IBD. Microalgae-supplemented diets alleviated chemically induced colitis, signifying the potential of microalgae in treating inflammatory gut conditions and diseases.
Luteolin Protects Against Obese Sarcopenia in Mice with High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity by Ameliorating Inflammation and Protein Degradation in Muscles
- First Published: 28 January 2023
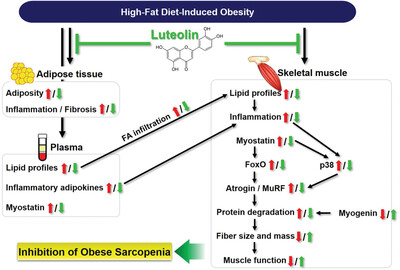
Luteolin (LU) has antiobesity and antiinflammatory activities in adipose tissue, plasma, and skeletal muscle. LU inhibits fatty acid infiltration into the muscle and muscle inflammation. As a result, LU exerts suppressive effects on muscle protein degradation. The above effects of LU ultimately improve muscle mass and function. LU may be a useful dietary ingredient to prevent obese sarcopenia.
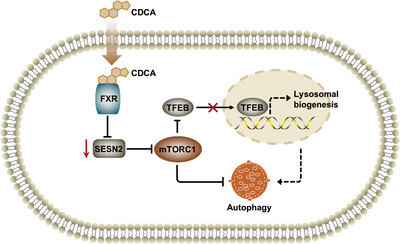
Farnesoid X Receptor (FXR) Regulates mTORC1 Signaling and Autophagy by Inhibiting SESN2 Expression
- First Published: 30 January 2023
Molecular Mechanisms Associated with Protecting IEC-6 Cells from Acrylamide-Induced Tight Junction Damage by Ganoderma atrum Polysaccharide
- First Published: 24 December 2022
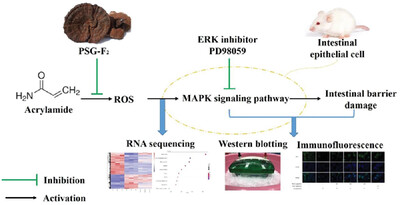
In this study, the protective mechanism of Ganodema atrum polysaccharide (PSG-F2) on acrylamide (AA)-induced IEC-6 cell damage based on RNA sequencing is further explored. Numerous genes involved in MAPK pathway are significantly changed. Thus, MAPK/ERK pathway-related and tight junction proteins are detected and verified, uncovering the molecular mechanisms involve in the protective effects of PSG-F2 against AA-induced intestinal barrier damage.