Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Picture: Chem. Eng. Technol. 1/2019
- Page: 1
- First Published: 18 December 2018

Oil refinery plant. Copyright: RonFullHD@Getti Images
Editorial Board
Editorial Board: Chem. Eng. Technol. 1/2019
- Page: 2
- First Published: 18 December 2018
Overview
Overview Contents: Chem. Eng. Technol. 1/2019
- Page: 3
- First Published: 18 December 2018
Highlights
Reviews
Cavitation in Diesel Fuel Injector Nozzles and its Influence on Atomization and Spray
- Pages: 6-29
- First Published: 21 September 2018
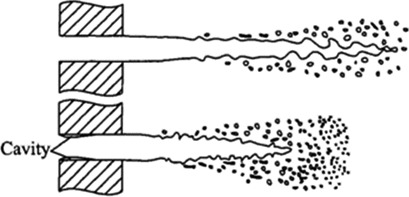
Fuel injector nozzles for liquid atomization and spray generation are a critical part of diesel engines. The internal cavitating flow has a predominant effect on fuel spray behavior, combustion performance, and pollutant emissions. Recent studies on the formation mechanism of cavitation and characterization of the cavitating flow from both experimental and computational viewpoints are reviewed.
Facile CO2 Separation in Composite Membranes
- Pages: 30-44
- First Published: 31 July 2018
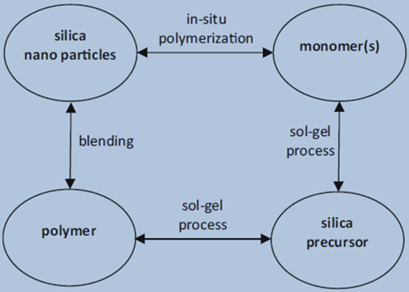
Membrane technology is considered as an efficient, environmentally friendly, and inexpensive technology for CO2 separation. Various approaches to improve membrane performance are reviewed with the focus on permeability and selectivity parameters. Polymer-inorganic nanocomposite membranes, metal organic frameworks, and ionic liquid mixed-matrix membranes are also discussed and evaluated.
Research Articles
SO2 Removal from Gas Streams by Ammonia Scrubbing: Process Optimization by Response Surface Methodology
- Pages: 45-52
- First Published: 21 September 2018
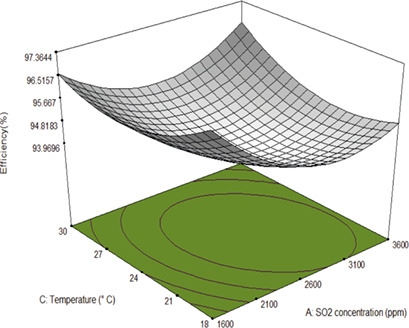
The SO2 content reduction in an incinerator by ammonia scrubbing was investigated by a systematic experimental design based on response surface methodology with central composite design. The developed model predicts the degree of desulfurization of ammonia wet flow gas disulfurization reactors, with the ammonia concentration having the most significant influence on the process efficiency.
Transient Simulation of Hollow-Fiber Membrane Filtration with Nonuniform Permeability Distribution
- Pages: 53-64
- First Published: 21 September 2018
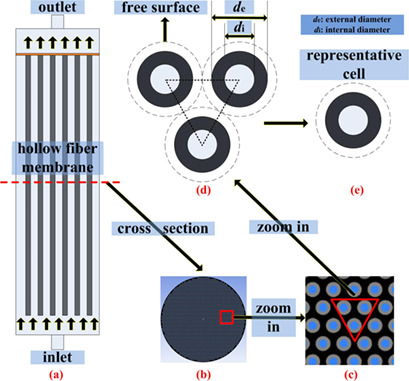
Despite its great significance, membrane engineering receives less attention than the membrane materials. Herein, the focus is on evaluating the time-dependent filtration process in hollow-fiber membranes (HFM) with various kinds of nonuniform permeability distributions. New understanding of fluid flow and fouling behavior in the HFM system is proposed.
Polyvinyl Butyral/Modified SiO2 Nanoparticle Membrane for Gasoline Desulfurization by Pervaporation
- Pages: 65-72
- First Published: 28 September 2018

PVB/SiO2 membranes were prepared using a coupling agent to covalently link inorganic SiO2 particles and organic PVB polymers. Crosslinking improves the compatibility between the inorganic and organic phases and avoids the generation of membrane defects. The composite membranes displayed superior performance for the removal of organosulfur compounds from fluid catalytic cracking gasoline.
Techno-Economic Analysis of a Coal Staged Conversion Polygeneration System for Power and Chemicals Production
- Pages: 73-88
- First Published: 28 September 2018
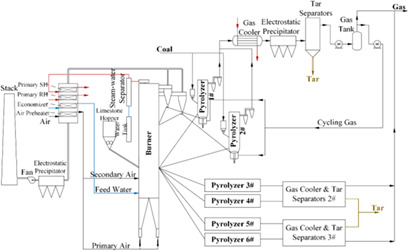
A coal staged conversion polygeneration plant for the coproduction of coal gas, tar, and electricity power, integrated with wastewater biochemical treatment after phenol-ammonia recovery, is proposed and simulated. Appropriate models for the proposed system are assessed. Such kind of plant exhibits practical and economic advantages, with excellent values of system energy and exergy efficiency.
Statistical Optimization of the Biodiesel Production Process Using a Magnetic Core-Mesoporous Shell KOH/Fe3O4@γ-Al2O3 Nanocatalyst
- Pages: 89-99
- First Published: 28 September 2018
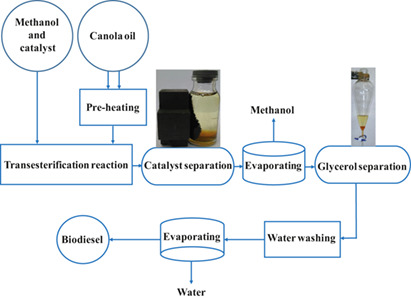
Transesterification of vegetable oils is the most common method to produce biodiesel. A heterogeneous magnetic core-mesoporous shell KOH/Fe3O4@γ-Al2O3 nanocatalyst was synthesized and successfully applied for biodiesel production from canola oil. The main parameters influencing the catalyst performance were optimized by response surface methodology based on the Box-Behnken design.
Effect of Reynolds Number on Laminar Mixing in an Annular Tube Combining Two Crossed Secondary Flows
- Pages: 100-108
- First Published: 02 October 2018
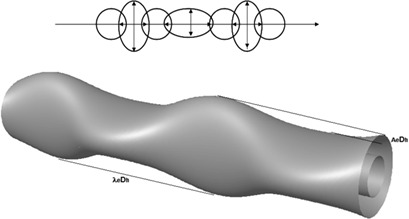
Generating chaotic behavior in laminar flow by geometrical modification is relevant to process intensification. Two passive intensification methods were applied to an annular laminar flow and numerically studied. Geometrical perturbations of the walls improve mixing at all investigated Reynolds numbers Re, and increased mixing above a threshold Re value is due to to chaotic advection in the flow.
Process Design and Operating Strategies for a Continuous Vaporization System for Purifying Organic Hole-Transport Materials
- Pages: 109-118
- First Published: 02 October 2018
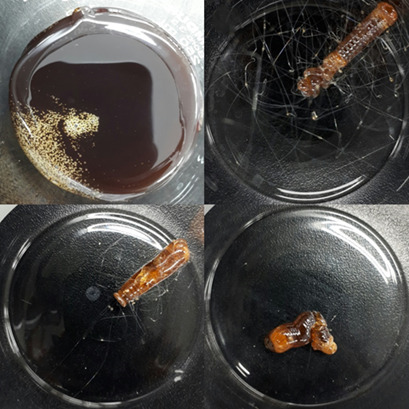

To purify organic hole-transport materials, the vacuum sublimation/vaporization method is commonly used; however, it has process inefficiency problems, such as limited production and laborious post-treatment procedures. Therefore, a design upgrade from a batch to a continuous process is proposed to increase the production rate, and operating strategies are suggested.
3D Mixing Dynamics in T-Jet Mixers
- Pages: 119-128
- First Published: 02 October 2018
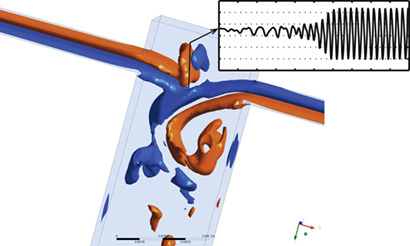
Fully resolved flow dynamics in T-jet mixers are obtained from 3D computational fluid dynamics simulations, particularly those on chaotic flow regimes that are characterized by a vortex issuing from the jet impingement point. The design and operational conditions to promote the chaotic flow regime are analyzed, and mixing scales and dynamics are assessed.
Syngas Methanation over Spray-Granulated Ni/Al2O3 Catalyst in a Laboratory Transport-Bed Reactor
- Pages: 129-136
- First Published: 02 October 2018
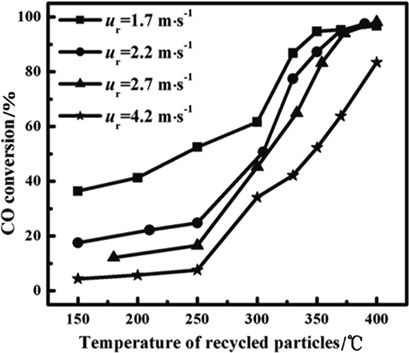
The CO conversion in a laboratory transport-bed reactor was tested to experimentally characterize syngas methanation to verify the feasibility of transport-bed methanation. The CO conversion was found to be very high. The results of this study indicate the high heat-transfer efficiency of particle recycling and the superiority of transport-bed methanation over other techniques.
Thermodynamic Modeling of the Use of Alkane Mixtures as Working Fluids in Absorption Cycles
- Pages: 137-147
- First Published: 10 October 2018
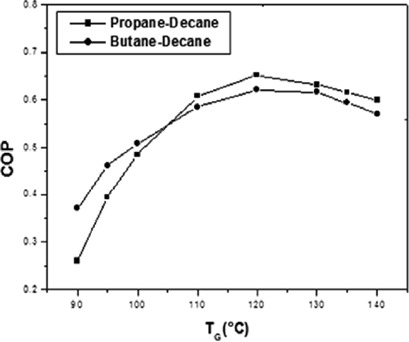
The data quality of the vapor-liquid phase equilibria (VLE) and of the calculated enthalpies of the different vapor and liquid streams in a refrigeration absorption machine depends on the activity-fugacity coefficient model combination used. As the UNIFAC-Peng-Robinson combination reproduced the VLE data reasonably well, it should be applied for these refrigeration systems operating with alkanes.
Viscosity Reduction of Heavy Oil during Slurry-Phase Hydrocracking
- Pages: 148-155
- First Published: 17 October 2018
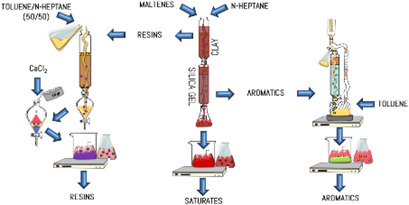
The changes in the properties of maltenes from upgraded oils during the slurry-phase hydrocracking of heavy crude oils using ore catalysts are mainly due to the increase of the saturates (S) and aromatics (A) fractions by means of the reduction of the resins (R) and asphaltenes fractions and the increase in the H/C ratio of all SAR fractions.
Amoxicillin Extraction from Aqueous Solution by Emulsion Liquid Membranes Using Response Surface Methodology
- Pages: 156-166
- First Published: 18 October 2018
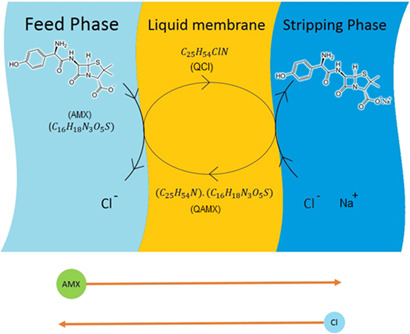
The antibiotic amoxicillin is hardly decomposed and difficult to remove from aquatic solutions. An innovative method of amoxicillin extraction using emulsion liquid membranes is proposed. The effects of process parameters on extraction using response surface methodology were evaluated. Under optimized conditions, an extraction yield of 99.8 % was achieved using the emulsion liquid membrane process.
Hydrotreating Model Comparison of Raw Castor Oil and its Methyl Esters for Biofuel Production
- Pages: 167-173
- First Published: 18 October 2018
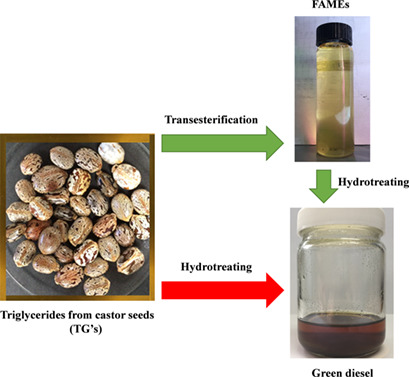
Some advantages of hydrotreating fatty acid methyl esters from castor oil seeds instead of their triglycerides are elucidated. Benefits and disadvantages of processing raw vegetable oils or their respective fatty acid methyl esters are investigated. The technical feasibility of employing methyl esters as hydrotreating feedstock for biofuel production such as green gasoline and diesel is highlighted.
Producing Fatty Acid Methyl Esters from Free Fatty Acids with Ionic Liquids as Catalyst
- Pages: 174-181
- First Published: 18 October 2018
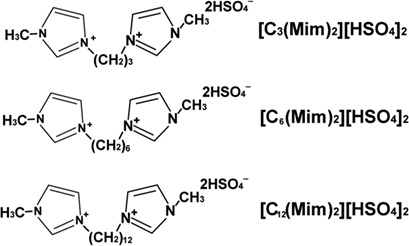
Brønsted acidic imidazole dicationic ionic liquids have great potential for application as green catalyst for producing fatty acid methyl esters from long-chain free fatty acids. They efficiently catalyze transesteri-fication reactions under mild reaction conditions while causing less corrosion on the reaction equipment. Three such catalysts with different length of alkyl chains were prepared and tested.
Optimization and Exergy Analysis of Natural Gas Liquid Recovery Processes for the Maximization of Plant Profits
- Pages: 182-195
- First Published: 18 October 2018
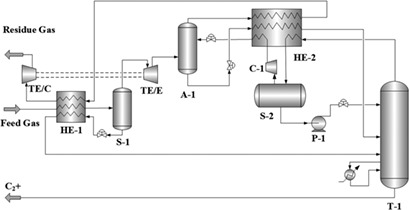
Existing plants for natural gas processing have low propane recovery rates due to inefficient refrigeration. To maximize plant profits, the efficient high-pressure absorber (HPA) process was chosen, analyzed, and further optimized. After optimization, the propane recovery rate of the NGL plant increased to 98.8 %.
Selective Removal of H2S from Gas Streams with High CO2 Concentration Using Hollow-Fiber Membrane Contractors
- Pages: 196-208
- First Published: 23 October 2018
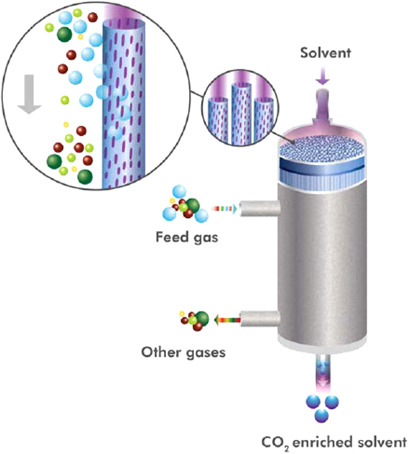
Selective and simultaneous removal of H2S and CO2 from CH4 by hollow-fiber hydrophobic membrane contactors is introduced. The removal performances of H2S and CO2 using an aqueous methyldiethanolamine solution were much higher than those reported for conventional packed towers. The membrane contactor is a highly efficient tool for removal of almost all H2S in the presence of a large CO2 content.
Asymptotic Properties of a Probabilistic-Statistical Model of Particle Classification in Hydrocyclones
- Pages: 209-214
- First Published: 26 October 2018
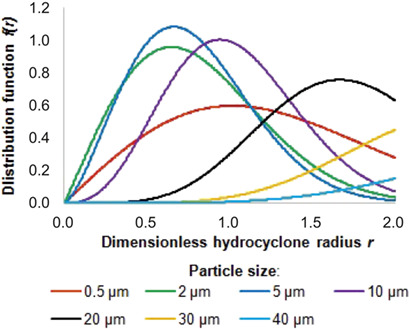
Responding to modern chemical engineering requirements, the peculiarities of practical implementation of a probabilistic-statistical model for a particle classification process of liquid-solid polydisperse systems in small hydrocyclones were evaluated. Stationary solutions of the Fokker-Planck-Kolmogorov kinetic equation were achieved for the considered separation process within reasonable assumptions.
Structure and Performance of Poly(vinylidene chloride-co-vinyl chloride) Porous Membranes with Different Additives
- Pages: 215-224
- First Published: 26 October 2018
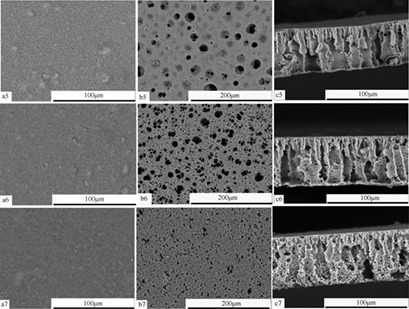
The issue of pore structure changes and antifouling performance of membranes was addressed by adding water-soluble and water-insoluble additives. Poly(vinylidene chloride-co-vinyl chloride) porous membranes with different contents of water-soluble polyethylene glycol and water-insoluble silicon dioxide hydrophilic nanoparticles were prepared by non-solvent-induced phase separation and tested.
Carbon Dioxide Absorption into Stirred Emulsions of n-Alkanes
- Pages: 225-231
- First Published: 26 October 2018
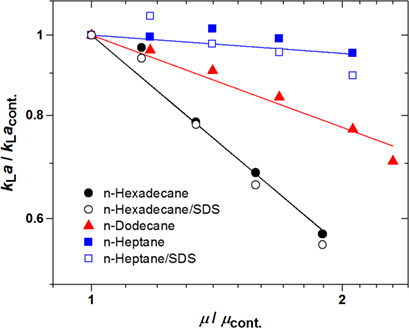
The effects of three organic liquids (n-heptane, n-dodecane, and n-hexadecane) and an anionic surfactant (SDS) on the absorption of CO2 into n-alkane/water emulsions was studied in a stirred tank. Except for n-heptane without SDS, kLa for CO2 decreased with increasing oil fraction for all oil/water emulsions, in correlation with the emulsion viscosity.
Kinetic Model of Two-Phase Epoxidation with Ionic Liquids as Micellar Catalysts
- Pages: 232-240
- First Published: 30 October 2018
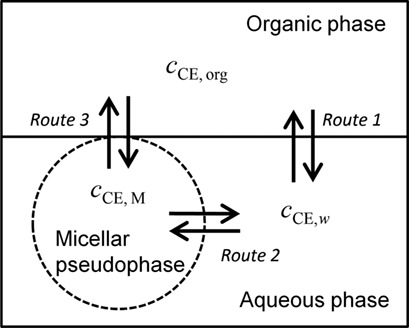
Imidazolium perrhenate ionic liquids form micelles in aqueous H2O2 and thus act as micellar catalysts in epoxidation of cyclooctene. Key parameters such as the critical micelle concentration are determined from kinetic experiments in a batch reactor. The kinetic description is based on an adapted enzyme-kinetic model, taking into account the micellar nature of the active species.
Gas Chromatographic Enantioseparation of Fluorinated Anesthetics: Single-Column Performance and Scale-up Estimation
- Pages: 241-251
- First Published: 06 November 2018
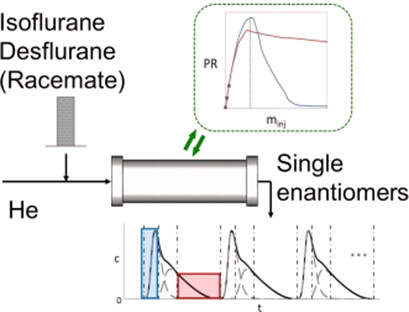
Separation of enantiomers of fluorinated anesthetic gases was investigated in gas-chromatographic columns employing a selector based on γ-cyclodextrin. The batch process with repetitive injections was theoretically analyzed to define the conditions that provide maximal productivity and high purity. The designed process can produce enough single enantiomers needed for further medical tests.
Communications
Rapid Hydrogen Peroxide Decomposition Using a Microreactor
- Pages: 252-256
- First Published: 02 October 2018
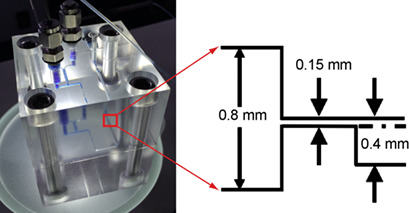
A rapid catalytic decomposition process of H2O2 in a microchannel is proposed. Different from traditional reactors, the microreactor with strengthened heat and mass transfer accelerated the decomposition process to less than ten seconds, yet still retaining high conversion. Remarkable catalyst passivation was observed and a series of catalysts were compared in terms of the conversion rate.
Treatment of Volatile Organic Compounds with a Pt/Co3O4-CeO2 Catalyst
- Pages: 257-260
- First Published: 30 October 2018
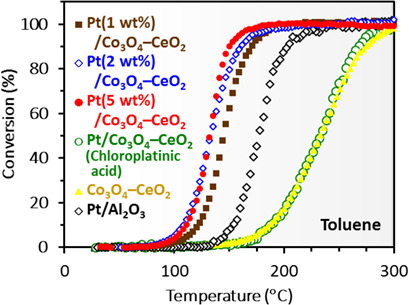
Platinum was directly supported on a Co3O4-CeO2 catalyst. Using chloroplatinic acid, the platinum cohered, not improving the catalytic activity. When the platinum was supported using platinum colloid coated with dispersant, high-dispersion support of the platinum on the Co3O4-CeO2 surface was achieved, and toluene, ethyl acetate, and isopropyl alcohol could be oxidized at less than 250 °C.










