Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Editorial Board
Overview
Contents
Editorial
Highlights
Review
Relevance of the Second Harmonic Generation to Characterize Crystalline Samples
- Pages: 971-983
- First Published: 08 May 2015
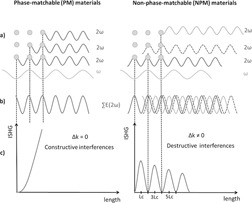
The application of second harmonic generation-based techniques to characterize crystalline samples is presented. Several examples are detailed for chemical purity, structural purity and polymorphism studies, with particular relevance to the pharmaceutical industry where crystalline active pharmaceutical ingredients are often made of a single enantiomer and are therefore non-centrosymmetric.
Research Articles
Generation of Crystalline Microcontainers of Salicylic Acid
- Pages: 984-990
- First Published: 08 April 2015

The formation of liquid inclusions in crystals could offer the option to generate microcontainer systems by means of controlled crystallization. Crystals containing large inclusions are necessary in order to fill them with another substance. Optimization of the inclusion sizes of salicylic acid crystals by means of antisolvent crystallization is investigated.
Production of High-Tensile-Strength Paracetamol Tablets Using the Freeze-Casting Process
- Pages: 991-998
- First Published: 06 May 2015

Low tensile strength limits the applicability of freeze-casted tablets in industrial production. Modified starch may serve as a binder for solid particles of the active pharmaceutical ingredient enhancing the mechanical strength of produced tablets. Freeze-casted paracetamol tablets are able to compete with commercial compressed tablets in terms of disintegration time and tensile strength.
Crystallization of Terutroban Sodium Salt Hydrate from the Deliquescent State
- Pages: 999-1005
- First Published: 08 April 2015
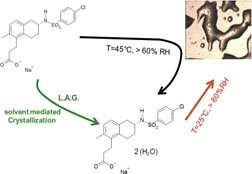
Besides studies on the crystallization processes of active pharmaceutical ingredients, stability studies at varying temperature and relative humidity are required. With Terutroban sodium salt as an example, the appearance of a hydrate (initially undesired) during storage is rationalized and its improvements in terms of stability are demonstrated.
Isomer Treatment by Additive Application in the Liquid Stage as Known from Industrial Crystallization
- Pages: 1006-1010
- First Published: 24 April 2015
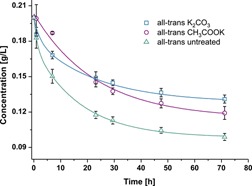
The principle of additive usage in crystallization was exploited to enhance the stability of dissolved all-trans astaxanthin (AXT), which is in high demand for feed supplementation. A variety of substances/factors triggers the isomerization and/or degradation of AXT. Application of an additive in solution provides the AXT-employing industries with a tool to improve their production economics.
Growth Rate Dispersion at the Single-Crystal Level
- Pages: 1011-1016
- First Published: 27 April 2015
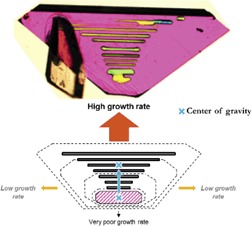
Crystal growth rate dispersion of ammonium perchlorate crystallized by evaporation of an aqueous solution at room temperature is evidenced by considering some Friedel pairs of faces. The relationship between the formation of inclusions and a high growth rate of crystal faces is highlighted. Considering the locations of the inclusions, the results demonstrate a high heterogeneity of crystal growth rates, from which the history of crystal growth can be retraced.
Protein Composite Materials by Crystallization: Product and Process Design
- Pages: 1017-1021
- First Published: 29 April 2015
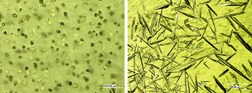
Product and process design approaches to control and optimize the properties of novel protein composite materials produced by reactive extrusion are presented. It was found that the control of crystalline structures within the protein material in conjunction with enzymatic cross-linking leads to advanced and application-oriented properties.
Growth and Dissolution Kinetics of A and B Polymorphs of L-Histidine
- Pages: 1022-1028
- First Published: 29 April 2015
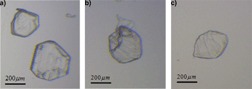
The essential amino acid L-histidine has shown to exhibit polymorphism and it exists in the solid phase as a stable polymorph A and a metastable polymorph B. The kinetics of growth and dissolution of the polymorphs which contribute to the rate of transformation between the polymorphs are investigated. The results indicate that the transformation is a growth-controlled process.
Dynamic Search Algorithm of Solubility in a Salt-Water System Based on the Solubility Product
- Pages: 1029-1034
- First Published: 29 April 2015

A dynamic search algorithm is introduced to predict the solubility based on equilibrium equations and solubility product in salt-water systems. A comparison between the calculated results of the algorithm and the experimental solubility data proves the high accuracy and efficiency of this algorithm. It exhibits great potential for low-salt system dissolution equilibrium calculations.
Correlation between Thermal Properties and Chemical Composition of Palm Oil Top Olein Fractions
- Pages: 1035-1041
- First Published: 29 April 2015
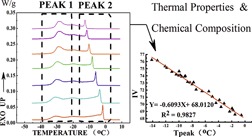
In the palm oil industry, the iodine value is normally determined by a titration method that uses toxic solvents. An innovative method is proposed to quickly determine the iodine value of oil samples. This approach can provide statistically similar results to those given by traditional official procedures, with the advantages of being extremely rapid and environmentally friendly.
Solubility Characteristics and Crystallization Behavior of Oxalic Acid in the Presence of Sulfuric Acid
- Pages: 1042-1046
- First Published: 06 May 2015

For effective recovery of oxalic acid from acidic wastewater by crystallization, oxalic acid solubility was investigated and found to be influenced by sulfuric acid concentration. Based on the solubility data, cooling crystallization of oxalic acid in sulfuric acid aqueous solution was conducted. Columnar-type crystals of oxalic acid precipitated in sub-mm size.
Non-Equimolar Discrete Phases Formed in the System of Malic Acid Enantiomers
- Pages: 1047-1052
- First Published: 06 May 2015
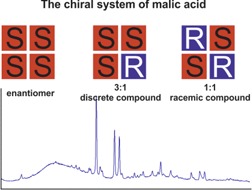
Non-equimolar discrete compounds formed by malic acid S- and R-enantiomers in ratios 3:1 and 1:3 are investigated by means of X-ray powder diffraction. The corresponding S3R and SR3 compounds are found to be stable or metastable phases in dependence on synthesis conditions. The phases are characterized and discussed with regard to their identity and crystallochemical nature.
Polymorphism, Size and Shape Control of Calcium Carbonate Crystals in the Presence of a Polyelectrolyte
- Pages: 1053-1058
- First Published: 06 May 2015
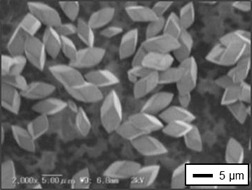
The effects of polyelectrolyte addition during reactive crystallization on the characteristics of calcium carbonate crystals were investigated. The supersaturation state, the material feed order, and the polyelectrolyte type and concentration were found to have great influence on the polymorphism, particle size and shape, and the crystal number of calcium carbonate.
Inline Monitoring of Taltirelin Crystallization in Batch Cooling Mode Using Raman Spectroscopy
- Pages: 1059-1067
- First Published: 26 May 2015
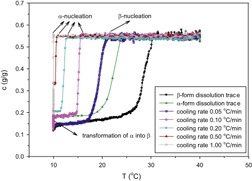
In cooling crystallization, supersaturation can be controlled by the cooling rate. Profiles of concentration are helpful for understanding polymorphic crystallization. At a low cooling rate, the α-form of taltirelin is nucleated and then transformed to the β-form. The α-form is formed at a high cooling rate, while the β-form is generated at a very slow cooling rate.
Effect of Seeding and pH Conditions on the Size and Shape of Au Nanoparticles in Reduction Crystallization
- Pages: 1068-1072
- First Published: 11 May 2015
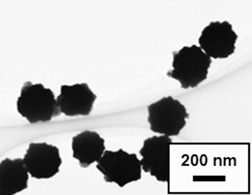
A simple method is suggested to control the sizes and shapes of nano/submicron-sized Au particles by reduction without additive to inhibit agglomeration. The mechanism of particle growth was analyzed by TEM-monitoring the crystallization process. The mean particle diameters of the Au particles were controlled at 6–650 nm by seeding or using pH-controlled ascorbic acid solutions.
Formation of Salicylic Acid/4,4′-Dipyridyl Cocrystals Based on the Ternary Phase Diagram
- Pages: 1073-1080
- First Published: 26 May 2015

Physical properties of active pharmaceutical ingredients can be tuned by pharmaceutical cocrystals without changing the chemical identity. The solubility behavior of salicylic acid/4,4′-dipyridyl (SAA/4,4′-dipy) cocrystals is investigated in an ethanol solvent to improve the fundamentals of the formation mechanisms, solution behavior, and solid-state properties of these cocrystals.
Size Control of Atorvastatin Calcium Particles Based on Spherical Agglomeration
- Pages: 1081-1087
- First Published: 26 May 2015
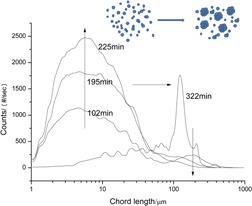
Spherical agglomeration is an effective method to improve the flowability and compressibility of Atorvastation calcium particles. A polymorph transformation occurred during the antisolvent precipitation and agglomeration process. The final size distribution of the particles is controllable by adjusting the amount of bridging liquid and stirring speed.
Communication
Saccharose Inversion and Metastable Zone
- Pages: 1088-1091
- First Published: 06 May 2015
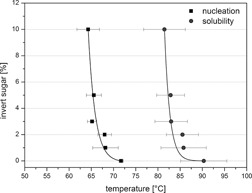
To control the crystallization of sugar such as saccharose in foods, knowledge of the position of the process in the phase diagram, and of the metastable zone in particular, is needed. The exposure time to citric acid and the amount of acid are shown to lead to an increased saccharose inversion. The metastable zone shifts to lower temperatures, but does not change in its width during inversion.
Overview
Overview Contents: Chemie Ingenieur Technik 6/2015
- Page: 1095
- First Published: 26 May 2015










