Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Editorial Board
Overview
Contents
Highlights
Amendment
Impact of Surfactant Addition on Oxygen Mass Transfer in a Bubble Column
- Pages: 571-573
- First Published: 25 March 2015
Editorial
CHISA 2014 – Worldwide Chemical Engineers Meet in the Heart of Europe
- Page: 574
- First Published: 25 March 2015
Research Articles
Multiscale Discrete Supercomputing – A Game Changer for Process Simulation?
- Pages: 575-584
- First Published: 11 March 2015
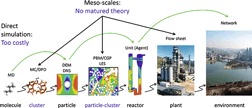
Virtual process engineering is a long-cherished dream of process engineering but its high standard for accuracy, capability, and efficiency was far beyond traditional simulation approaches. A systematic co-design of the physical model, numerical software, and computer hardware enables high-resolution interactive simulation of pilot-scale reactors or direct numerical simulation of microreactors.
Predicting Permeate Fluxes and Rejection Rates in Reverse Osmosis and Tight-Nanofiltration Processes
- Pages: 585-594
- First Published: 25 March 2015
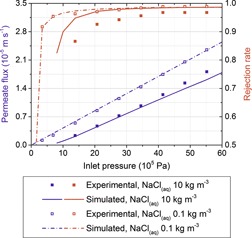
Averaged models are commonly used in reverse osmosis and nanofiltration despite their non-predictive nature. A predictive model is proposed combining mass and momentum conservation in the fluid phase coupled to the solution-diffusion model for membrane transport. Its main outputs are both rejection rates and permeate fluxes for plate-and-frame and spiral-wound membrane modules.
Flocculation Using Polyacrylamide Polymers for Fresh Microalgae
- Pages: 595-601
- First Published: 10 March 2015
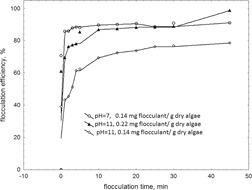
Microalgae may represent a promising future feedstock for biofuels or biogas production. The effect of high-molecular-weight cationic polyacrylamide flocculants with different cationicity on the flocculation of fresh microalgae cultures was evaluated. The efficiency of flocculation was found to be a function of the charge density of the polymeric flocculants.
Influence of Design Parameters on Hydrodynamics and Heat Transfer of a Modularized Millireactor
- Pages: 602-608
- First Published: 22 December 2014
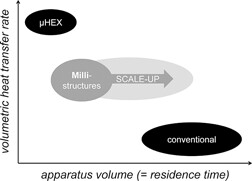
Reactors on a milli-scale open the possibility to develop modular equipment that allows for flexible production. An apparatus with rectangular product channels and mixing elements for process intensification is investigated in terms of hydrodynamics and heat transfer. The apparatus performs competitively with established reactor concepts and is, thus, an alternative for modular production units.
Application of a Semi-Mechanistic Model for Cracking Unit Balance
- Pages: 609-618
- First Published: 06 March 2015

To date, no study is published using a mechanistic model for simulating an entire steam-cracking unit for balance purposes. A steam-cracking kinetic model developed for industrial utilization by a combination of mechanistic and empirical approach was optimized to fit data obtained by process-scale experiments. Modeling results were compared to experimental data and process balance results.
Comparative Analysis of Different Control Strategies for a Train of Cryogenic 13C Separation Columns
- Pages: 619-631
- First Published: 23 February 2015
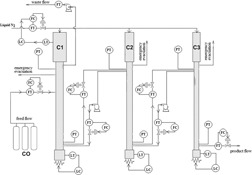
Enrichment of substances with 13C isotopes can be achieved by cryogenic distillation of CO. Three control strategies were designed for an experimental train of three cryogenic 13C isotope separation columns, with subsequent performance analysis. The novelty of the approach resides in the detailed step-by-step tuning procedure of the controllers and the comparative closed-loop performance analysis.
Group Contribution Methods for Estimation of Ionic Liquid Heat Capacities: Critical Evaluation and Extension
- Pages: 632-644
- First Published: 24 February 2015
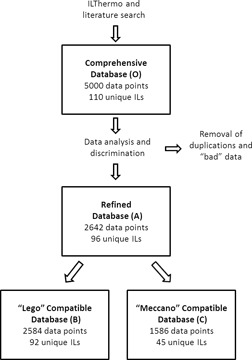
An extensive database of ionic liquid heat capacity data as a function of temperature was compiled and applied to evaluate two different group contribution method approaches named Meccano and Lego. The latter was found to be superior due to its balance between accuracy and range of applicability and was further extended to make it applicable to all ionic liquids evaluated.
Predictive Models for Thermal Behavior of Chemicals with Quantitative Structure-Property Relationships
- Pages: 645-650
- First Published: 23 February 2015

Chemicals involved in a process should be thoroughly characterized in order to properly design and implement appropriate safety measures. Experiments demanding resources could be lightened through predictive simulations. Application of predictive quantitative structure-property relationship to differential scanning calorimetry data offers early estimations of chemicals' thermal stability.
Green Diesel from Hydrotreated Vegetable Oil Process Design Study
- Pages: 651-657
- First Published: 24 February 2015
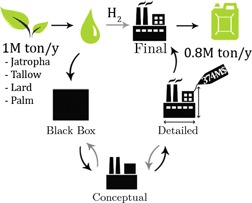
The process of hydrotreating vegetable oils is a promising alternative to the production of conventional biodiesel, because it can be integrated into existing refining infrastructure. The process flexibility with respect to the type of feedstock as well as the controllability of the product mix of jet fuel and diesel was included in this detailed design study, covering all aspects of process plant design.
LTA/Poly(1-trimethylsilyl-1-propyne) Mixed-Matrix Membranes for High-Temperature CO2/N2 Separation
- Pages: 658-666
- First Published: 04 March 2015
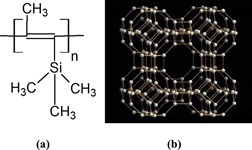
Membrane gas separation is a simple and energy-conservative technology for post-combustion carbon capture. Here, mixed-matrix membranes were prepared using the highly permeable poly(1-trimethylsilyl-1-propyne) polymer and small-pore LTA-type zeolites by the solution casting method and the performance of the mixed-matrix membranes was adjusted to the modified Maxwell model.
Application of Sorbents for Industrial Waste Water Purification
- Pages: 667-674
- First Published: 23 February 2015
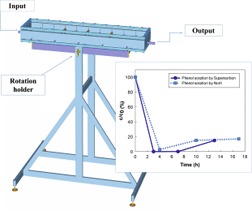
Underground coal gasification (UCG) still bears the risk of groundwater contamination. Post-processing UCG water was decontaminated via the sorption technique from a variety of organic and inorganic contaminants. The activated carbons Supersorbon and Norit and the nanoiron Nanofer revealed the highest efficiency in laboratory as well as in pilot plant sorption experiments.
An Innovative Approach for Adsorption Column Modeling
- Pages: 675-682
- First Published: 23 February 2015
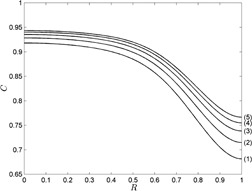
Modeling of adsorption processes in column apparatuses is difficult because the finding of the velocity distributions in the phases and the interphase surface is practically impossible. An innovative approach for physical and chemical adsorption modeling in such apparatuses is proposed and methods for model equation solutions and parameter identification are described.
Adsorption Processes for the Synthesis of Catalytically Active Metal Nanoparticles in Polymeric Matrices
- Pages: 683-689
- First Published: 04 March 2015
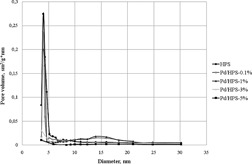
The main problem of metal-containing nanoparticel synthesis is to stabilize and provide control over their shape, particle size, and monodispersity and it is necessary to take into account the interaction between precursor and carrier. Here, the influence of the content of a hydrophilic Pd(II) compound on the adsorption and the formation of nanoparticles in a polymer matrix was studied.
Modeling of a Slurry Bubble Column Reactor for the Production of Biofuels via the Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis
- Pages: 690-700
- First Published: 05 March 2015
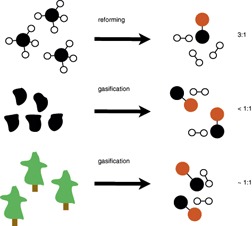
Biomass is a renewable feedstock candidate for the production of liquid fuels via the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. A multifluid population balance model developed for the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis in a slurry bubble column reactor is applied to five different synthesis gas compositions representing biomass, coal, and natural gas. The effect of CO2 in biomass synthesis gas is also investigated.
Influence of the Sparger Type and Added Alcohol on the Gas Holdup of an External-Loop Airlift Reactor
- Pages: 701-708
- First Published: 24 February 2015
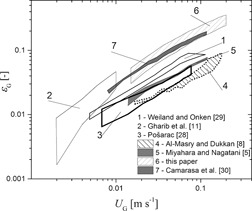
The effects of alcohol and three different gas spargers on the gas holdup in external-loop airlift reactors were studied. The sinter plate turned out to be the most efficient sparger. Small amounts of common aliphatic alcohols increased the gas holdup due to their coalescence-inhibiting nature. The proposed artificial neural network has the potential to predict the gas holdup in airlift reactors.
Communications
Bed Pressure Drop in a Draft-Tube Conical Spouted Bed for Thermal Treatment of Wastes
- Pages: 709-714
- First Published: 05 March 2015
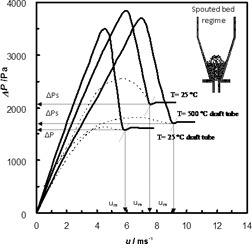
Conical spouted beds are used in applications handling coarse solids considered non-fluidizable because of the vigorous cyclic movement of the particles. Here, the hydrodynamics of conical spouted beds consisting of coarse waste particles was improved by insertion of a nonporous draft tube in the bed enhancing its stability and reducing the required pumping energy.
Stability of Three-Phase Water-Particle-Oil Systems
- Pages: 715-720
- First Published: 10 March 2015

Successful oil agglomeration depends mainly on the surface properties of the particles to be agglomerated. The problem of stability measurement and possible explanations for instability in a three-phase system were addressed. Stability determination along with zeta potential measurements allowed explaining destabilization phenomena in water-particle-oil systems.
Robust Multiobjective Optimization Applied to Optimal Control Problems Using Differential Evolution
- Pages: 721-726
- First Published: 04 March 2015
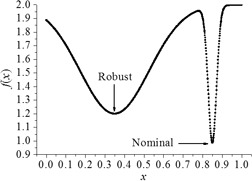
Multiobjective optimization differential evolution associated with the mean effective concept is applied to solve optimal control problems considering the robustness effect. The results obtained with applications in two chemical systems prove that the proposed algorithm represents an interesting alternative for the treatment of robust optimization problems.
Research Articles
Flashpoint Prediction for Binary Mixtures of Alcohols with Water in Order to Improve their Safety
- Pages: 727-733
- First Published: 06 March 2015

The flashpoint is a key factor influencing the safety behavior of flammable liquids. Simple dimensionless experimental formulae based on rational reciprocal and polynomial functions are described for correlating flashpoint data of binary mixtures. The model can be applied to assess fire and explosion hazards and to develop inherently safer designs for corresponding chemical processes.
Mixing Performance of a Curved-Ribbon Impeller during Blending of Food Powders
- Pages: 734-740
- First Published: 25 March 2015
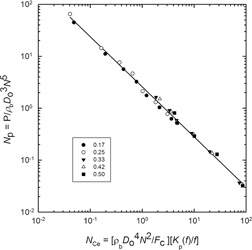
Mixing of particulate solids is a very important process in the food industry. The mixing time and power to reach certain homogeneity during blending of corn starch and icing sugar with a horizontal segmented curved-ribbon impeller was determined. The relationship between the power number and the effective cohesion number describes the impeller performance and can serve as an engineering tool in process design.
Retraction
Retraction: Effects of the Operating Conditions and Geometry Parameter on the Filtration Performance of the Fibrous Filter
- Page: 741
- First Published: 02 March 2015
Overview
Overview Contents: Chemie Ingenieur Technik 4/2015
- Page: 743
- First Published: 25 March 2015










