Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
40th Anniversary Celebration of The Institute of Polymer Chemistry at Nankai University
- First Published: 06 December 2023

Front Cover: This special issue is dedicated to celebrating 40th Anniversary of the Institute of Polymer Chemistry at Nankai University. In the guest editorial article 2300597, Wangqing Zhang, Yang Liu, and co-workers discuss the scientific focuses and research directions as well as highlight the achievements of the Institute of Polymer Chemistry at Nankai University for the last 40 years.
Inside Front Cover
Semiconducting Polymers for Cancer Immunotherapy
- First Published: 06 December 2023

Inside Front Cover: In article 2300496, Ji Qi, Dan Ding, and co-workers summarize the recent advancements in semiconducting polymer (SP)-based nanomedicines for enhanced tumor immunotherapy. The cancer immunotherapies enabled by SPs with the photothermal, photodynamic, or sonodynamic functions are highlighted in detail, which can not only kill tumors directly but also evoke immunogenic cell death of cancer cells for immunotherapy. Additionally, the constructions of combination immunotherapeutic nanoplatforms, in which immunomodulatory agents can further be released from SP NPs to boost immunotherapeutic action, are also introduced.
Back Cover
Synergistic Approaches in the Design and Applications of UCST Polymers
- First Published: 06 December 2023

Back Cover: In article 2300261, Chuanzhuang Zhao, X. X. Zhu, and co-workers summarize the synergistic approaches in the design and applications of thermoresponsive polymers with upper critical solution temperature (UCST) in aqueous systems. Synergy of hydrogen bonding with other types of physical interactions not only enables precise control of the responsive behavior, but also leads to emergence of novel functions of UCST polymers.
Masthead
Guest Editorial
40th Anniversary Celebration of The Institute of Polymer Chemistry at Nankai University
- First Published: 06 December 2023
Reviews
Semiconducting Polymers for Cancer Immunotherapy
- First Published: 15 September 2023
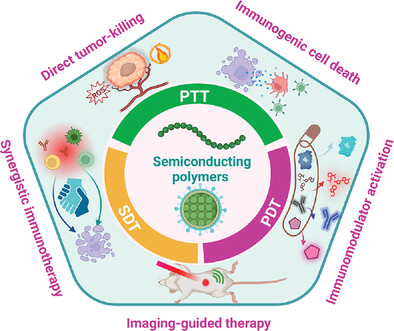
Herein, the recent advancements in semiconducting polymer-based nanomedicines are summarized for enhanced tumor immunotherapy. The cancer immunotherapies enabled by semiconducting polymers with the photothermal, photodynamic, or sonodynamic functions are highlighted in detail, with a particular focus on the construction of combination immunotherapy and activatable nanoplatforms to boost the outcomes of cancer immunotherapy.
Synergistic Approaches in the Design and Applications of UCST Polymers
- First Published: 21 July 2023
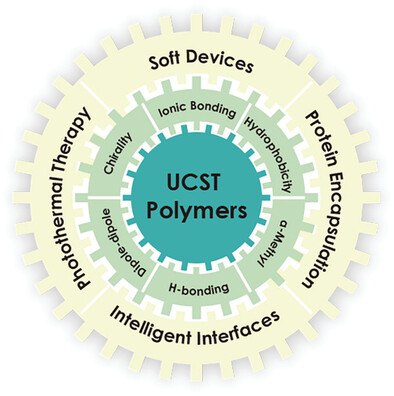
This review highlights the synergistic design strategy for upper critical solution temperature (UCST) polymers by the combination of hydrogen bonding with other molecular interactions in their structures. Potential applications are summarized for the new functional materials made by combining their UCST and other types of stimuli-responsiveness.
Tailoring the Architecture of Molecular Bottlebrushes via Click Grafting-Onto Strategy
- First Published: 25 August 2023
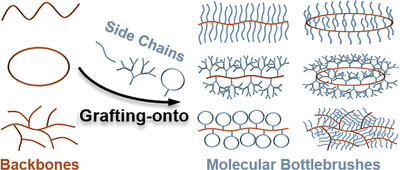
Molecular bottlebrush (MBB) represents an important type of unimolecular nanomaterial, and the topological structure of backbones and side chains in MBBs can also significantly affect their chemical and physical properties. In this mini-review, the recent progress on tailor of well-defined MBBs with diverse architectures using grafting-onto strategy combined with controlled polymerization technique are briefly summarized.
Molecular Structure and Properties of Sulfur-Containing High Refractive Index Polymer Optical Materials
- First Published: 26 August 2023
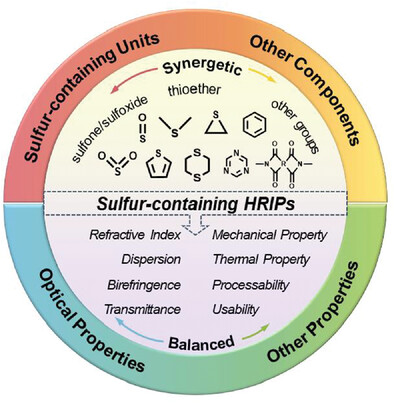
The development of high-performance optical materials is inseparable from the research of high refractive index polymers (HRIPs). In this review, the existing research work of sulfur-containing HRIPs and the structure–property relationship between their molecular structure and different properties are summarized. The significance of synergistic effect in the synthesis of HRIPs is proposed and the future research of HRIPs is prospected.
Research Articles
A Versatile Assembly Approach toward Multifunctional Supramolecular Poly(Ionic Liquid) Nanoporous Membranes in Water
- First Published: 30 May 2023

A facile yet versatile conceptual approach to co-assembly of water molecules, small additives, and poly(ionic liquid) into hydrogen-bonding assembled supramolecular functional polyelectrolyte nanoporous membranes with controllable manner in terms of pore architectures, mechanical properties, and functional attributes is established.
Self-Assembly and In Situ Quaternization of Triblock Bottlebrush Block Copolymers via Organized Spontaneous Emulsification for Effective Loading of DNA
- First Published: 16 May 2023
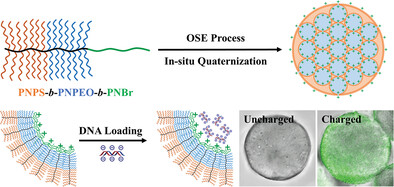
Porous spheres with quaternary ammonium cations are obtained through self-assembly of and in situ quaternization of triblock bottlebrush block copolymers within an ordered water-in-oil-in-water multiple emulsion system. The obtained spheres show high performances in loading and encapsulation of DNA macromolecules for many potential applications such as information storage.
Deciphering the Effects of Molecular Dipole Moments on the Photovoltaic Performance of Organic Solar Cells
- First Published: 25 May 2023
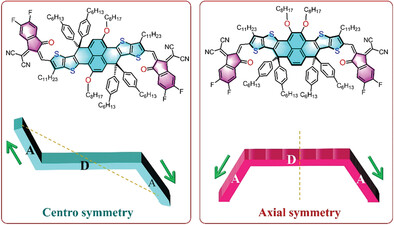
The effects of the molecular dipole on organic photovoltaic properties are systematically investigated by comparing two isomeric small molecule acceptors (axisymmetric ANDT-2F and centrosymmetric CNDT-2F). Interestingly, axisymmetric ANDT-2F with a larger dipole moment can improve exciton dissociation and charge generation efficiencies due to the strong intramolecular charge transfer effect, resulting in the higher photovoltaic performance of devices.
Twistocaloric Modeling of Elastomer Fibers and Experimental Validation
- First Published: 21 June 2023
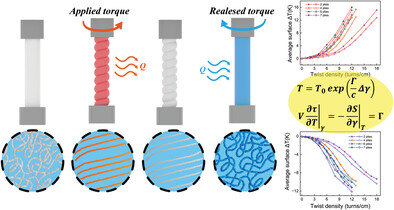
The twistocaloric model is established to capture the relationship between twist density and temperature variation of natural rubber fibers and thermoplastic elastomer yarns. An experimental setup consisting torsion actuator and torque sensor coupled with a temperature measurement system is built to validate the model. The experimental characterization of the twistocaloric effect is consistent with the theoretical predictions.
Arginine Methylation Regulates Self-Assembly of Peptides
- First Published: 18 July 2023
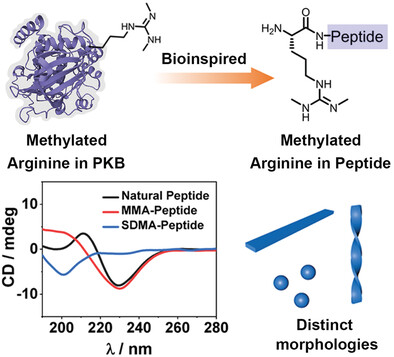
Inspired by arginine methylation in natural proteins, this study aims to incorporate methylated arginine into short peptides and explore arginine methylation as a toolkit for regulating self-assembly of short peptides. Therefore, mono-methylated, symmetrically dimethylated, or asymmetrically methylated arginine is rationally incorporated into bola-amphiphilic peptides, which exhibits distinct conformation and assemble into different nanostructures associate with peptide sequences.
High Cycle-Life Twistocaloric Cooling of Poly-p-Phenylene Benzodioxole Fibers
- First Published: 12 August 2023
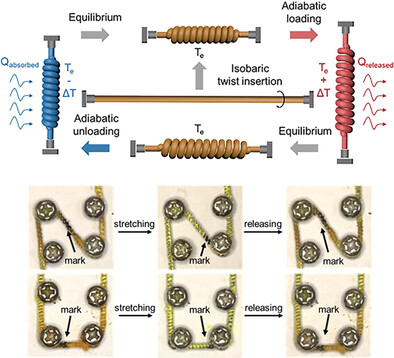
Elasto- and twistocaloric cooling of PBO fibers are studied, and the cooling temperatures are reached −0.4 and −1.3 K for fiber stretching and twisting, respectively. A self-coiled PBO fiber could achieve maximum cooling of −3.7 K upon stretching by 35% strain with an exceptionally high cycle life of 200 000 times.
Engineering Nanotrap Hydrogel for Immune Modulation in Wound Healing
- First Published: 02 August 2023
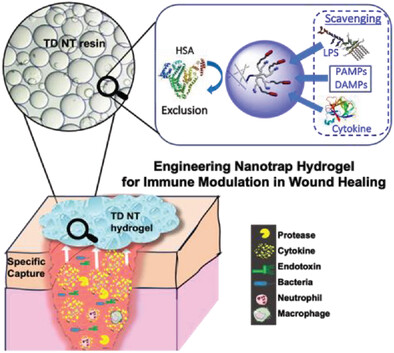
Telodendrimer (TD) nanotrap (NT) conjugated hydrogel resins are engineered for optimal immune modulation to treat the prolonged inflammation in chronic wounds. The bio-scavenging property is closely related with the density, valency, and swelling properties of TD NT hydrogel resins. The optimized resins demonstrate effective in vitro and in vivo cytokine attenuation and inflammation control without any cytotoxicity.
Dual-Cross-Linked Chitosan-Based Antibacterial Hydrogels with Tough and Adhesive Properties for Wound Dressing
- First Published: 11 August 2023
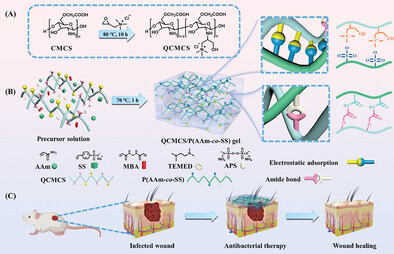
A kind of chitosan-based hydrogels with integrated functionalities are facilely prepared by solution polymerization of acrylamide and sodium p-styrene sulfonate in the presence of quaternized carboxymethyl chitosan. The optimized QCMCS/P(AAm-co-SS) hydrogel exhibits tough mechanical properties and moderate tissue adhesion. Moreover, biological evaluation in vitro and in vivo illustrated that as-prepared hydrogel possesses satisfactory biocompatibility, hemocompatibility, and excellent antibacterial ability.
Enhancing the Molecular Order and Vertical Component Distribution of the P3HT/O-IDTBR System during Layer-by-Layer Processing
- First Published: 16 August 2023
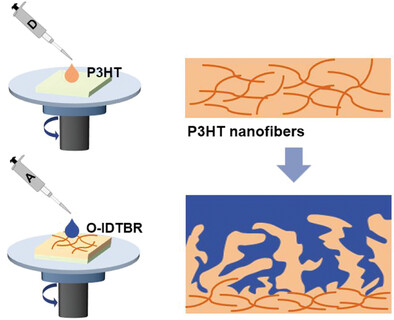
In sequential spin-coated P3HT/O-IDTBR film, UV irradiation and solution aging induce the formation of dense P3HT nanofibers. During LbL processing, P3HT nanofibers restrict the deep penetration of O-IDTBR into P3HT matrix. This leads to enhanced molecular order and enlarged vertical phase separation in the resulting film, boosting the PCE of the devices from 6.70 ± 0.12% to 7.71 ± 0.10%.
Self-Assembly of Glycolipid Epimers: Their Supramolecular Morphology Control and Immunoactivation Function
- First Published: 26 July 2023
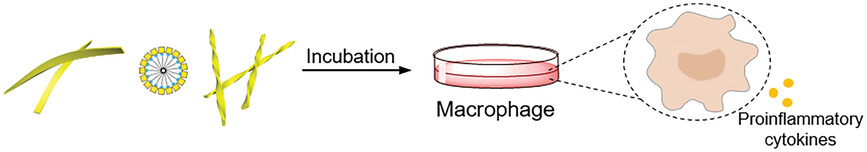
In this study, the stereoisomeric glycolipid amphiphiles based on GalNAc are synthesized, and they self-assemble into diverse structures such as ribbons and micelles in the aqueous solution due to distinct carbohydrate-carbohydrate interactions resulting from stereoisomerism. These glycocalyx-mimicking supramolecular materials constructed by glycolipid epimers can provoke the activation of macrophages and dendritic cells in vitro.
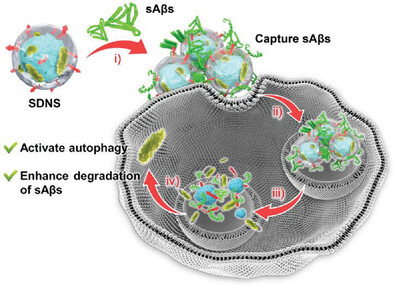
Self-Destructive Nanoscavengers Capture and Clear Neurotoxic Soluble β-Amyloid Aggregates
- First Published: 03 August 2023
Bacteria-Targeting Nanosilver-Based Antibacterial Drugs for Efficient Treatment of Drug-Resistant Bacterial-Infected Keratitis
- First Published: 06 September 2023
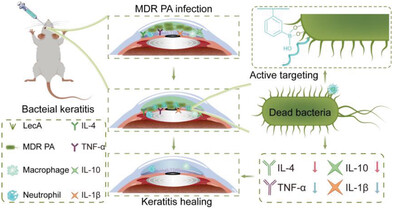
Bacteria-targeting nanosilver-based antibacterial drugs efficaciously penetrate intraocular tissue, protract ocular surface drug retention via precise pathogenic bacteria targeting, and demonstrate potent capabilities in eradicating drug-resistant bacteria and inhibiting bacterial growth. In a rat keratitis model, the application of nanoformulation not only enhanced bacterial clearance and corneal transparency but also attenuated inflammatory cell infiltration, thereby expediting corneal healing, suggesting potential for clinical translation.
B─N Covalent Bond-Based Nonfullerene Electron Acceptors for Efficient Organic Solar Cells
- First Published: 05 October 2023
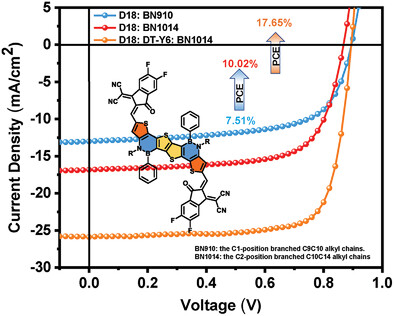
Two nonfullerene small-molecule acceptors featuring B─N covalent bonds, BN910 and BN1014, are designed and synthesized for binary and ternary organic solar cells. Their intermolecular aggregation and packing behaviors are fine-tuned by adjusting branching alkyl chains on nitrogen atoms. Consequently, a promising power conversion efficiency of 17.65% can be realized for D18:DT-Y6:BN1014-based ternary devices.
A Bioartificial Pancreas with “Immune Stealth” and Continuous Oxygen Supply for Islet Transplantation
- First Published: 06 September 2023
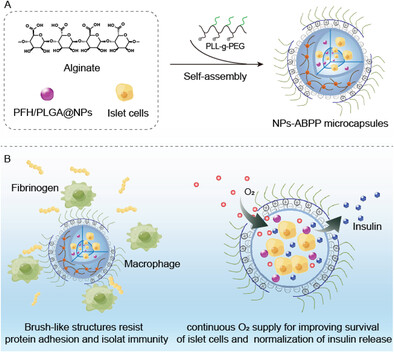
A bioartificial pancreas is constructed, which incorporates the “stealth effect” and the high oxygen-carrying performance. Polycationic poly(l-lysine)-grafted-PEG coating on the surface of microcapsules forms a brush-like structure that resists fibrinogen adhesion and isolates immunity. Perfluorohexane/poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)@nanoparticles act as O2 carriers leading to continuous O2 supply for islet cells and normalization of insulin release.
Type I Collagen-Adhesive and ROS-Scavenging Nanoreactors Enhanced Retinal Ganglion Cell Survival in an Experimental Optic Nerve Crush Model
- First Published: 04 September 2023
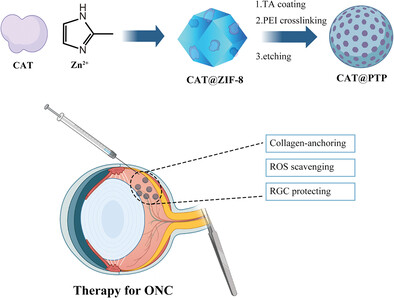
This study demonstrates the preservation of retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) through intravitreal injection of tannin (TA)-based nanoreactors loaded with catalase (CAT). The type I collagen-adhesive CAT@PTP nanoreactor adheres to the retina via collagen and effectively scavenges reactive oxygen species (ROS).
Conjugated Polymers from Direct Arylation Polycondensation of 3,4-Difluorothiophene-Substituted Aryls: Synthesis and Properties
- First Published: 28 August 2023
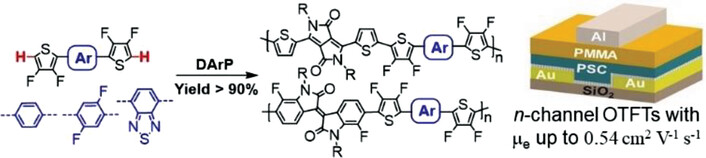
Three C─H monomers Ph-2FTh, 2FPh-2FTh, and BTz-2FTh with 3,4-difluorothiophene as terminal units and phenyl, 2,5-difluorophenyl and benzothiadiazole as central units are synthesized for direct arylation polycondensation to diketopyrrolopyrrole- and isoindigo-based high-mobility conjugated polymers. n-Channel organic thin-film transistors with electron mobility up to 0.54 cm2 V−1 s−1 are fabricated based on the resulting polymers.
Reconstituting Low-Density Lipoprotein with NIR-Absorbing Organic Photothermal Agents for Targeted Killing of Cancer Cells
- First Published: 11 August 2023
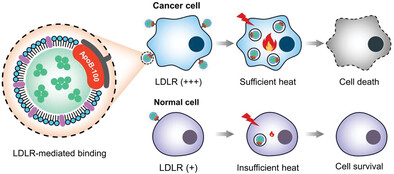
In this work, the lipophilic core of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) is reconstituted with a near-infrared (NIR)-absorbing organic photothermal agent. By virtue of the tumor-targeting capability of LDL, the reconstituted LDL particles can selectively kill LDL receptor-overexpressed cancer cells over normal cells via photothermal heating upon NIR irradiation, holding great promise in tumor eradication in vivo.
Structure Influence of Amine-Containing Additives on the Solution State and Out-of-Plane Conductivity of PEDOT:PSS for Efficient Organic Solar Cells
- First Published: 19 July 2023
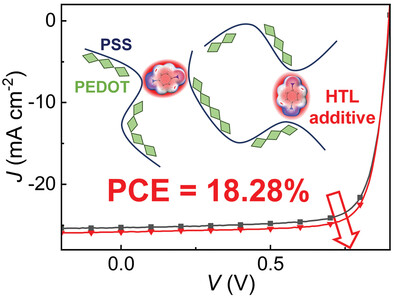
The molecular structure effect of phenylenediamine additives for PEDOT:PSS hole transporting layer is investigated for organic solar cells. The additives are found to influence solution states and increase the out-of-plane conductivities of the PEDOT:PSS layers that improved the power conversion efficiency of the devices to 18.28%.
A Polymer Acceptor with Grafted Small Molecule Acceptor Unit for Efficient All Polymer Organic Solar Cells
- First Published: 13 September 2023
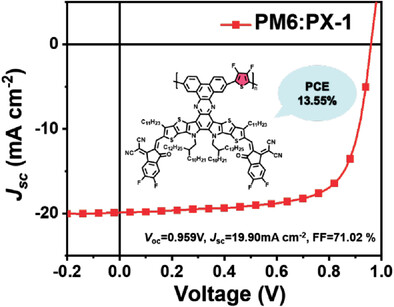
A polymer acceptor, named PX-1, is designed and synthesized using a polymerization strategy with grafted small molecule acceptors. This design approach allows for the freedom of end groups while maintaining efficient terminal packing, enhancing π–π interactions, and facilitating charge transport. All-polymer organic solar cells based on PM6: PX-1 demonstrate a promising efficiency of 13.55%.
Conjugation Length-Dependent Raman Scattering Intensity of Conjugated Polymers
- First Published: 15 September 2023
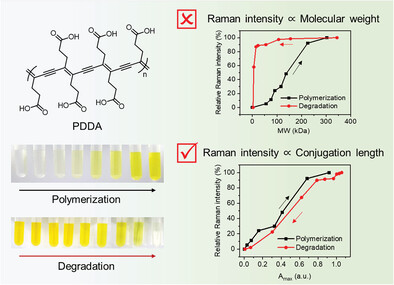
The structure–Raman activity relationship of the conjugated polymers is crucial for developing ideal Raman probes. Based on a series of water-soluble polydiacetylenes (poly(deca-4,6-diynedioic acid), PDDA) with different molecular weights (MWs) through controlled polymerization and degradation, the conjugation length dependence of polydiacetylene Raman signal is revealed, which will guide the future design of conjugated polymers for Raman imaging applications.
Polymer–Protein Nanovaccine Synthesized via Reactive Self-Assembly with Potential Application in Cancer Immunotherapy: Physicochemical and Biological Characterization In Vitro and In Vivo
- First Published: 14 September 2023
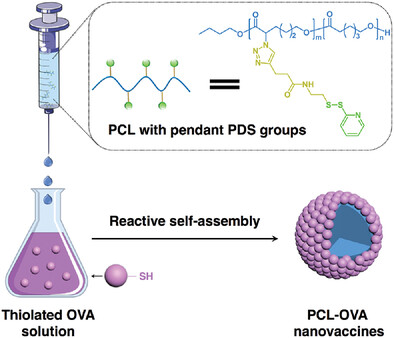
Reactive self-assembly is used to prepare covalently conjugated poly(ε-caprolactone)-ovalbumin (PCL-OVA) nanovaccines of high antigen loading. Compared to free OVA, the nanovaccines are superior in enhancing antigen uptake by bone marrow-derived dendritic cells (BMDCs), promoting BMDC maturation and antigen presentation, persisting at the injection site and draining lymph nodes, activating Th1 and Th2 immunity, and ultimately, resisting tumor challenge in mice.