Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EAACI POSITION PAPER
Granulocytes and mast cells in AllergoOncology—Bridging allergy to cancer: An EAACI position paper
- Pages: 2319-2345
- First Published: 22 July 2024
REVIEW ARTICLE
The impact of exposure to tobacco smoke and e-cigarettes on asthma-related outcomes: Systematic review informing the EAACI guidelines on environmental science for allergic diseases and asthma
- Pages: 2346-2365
- First Published: 23 May 2024
Integrating multi-omics approaches in deciphering atopic dermatitis pathogenesis and future therapeutic directions
- Pages: 2366-2379
- First Published: 04 June 2024
Pyroptosis, gasdermins and allergic diseases
- Pages: 2380-2395
- First Published: 14 July 2024
Disease modification in chronic spontaneous urticaria
- Pages: 2396-2413
- First Published: 24 July 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Asthma and Lower Airway Disease
Immunoglobulin free light chains in severe asthma patient: Could they be a new biomarker?
- Pages: 2414-2422
- First Published: 29 February 2024
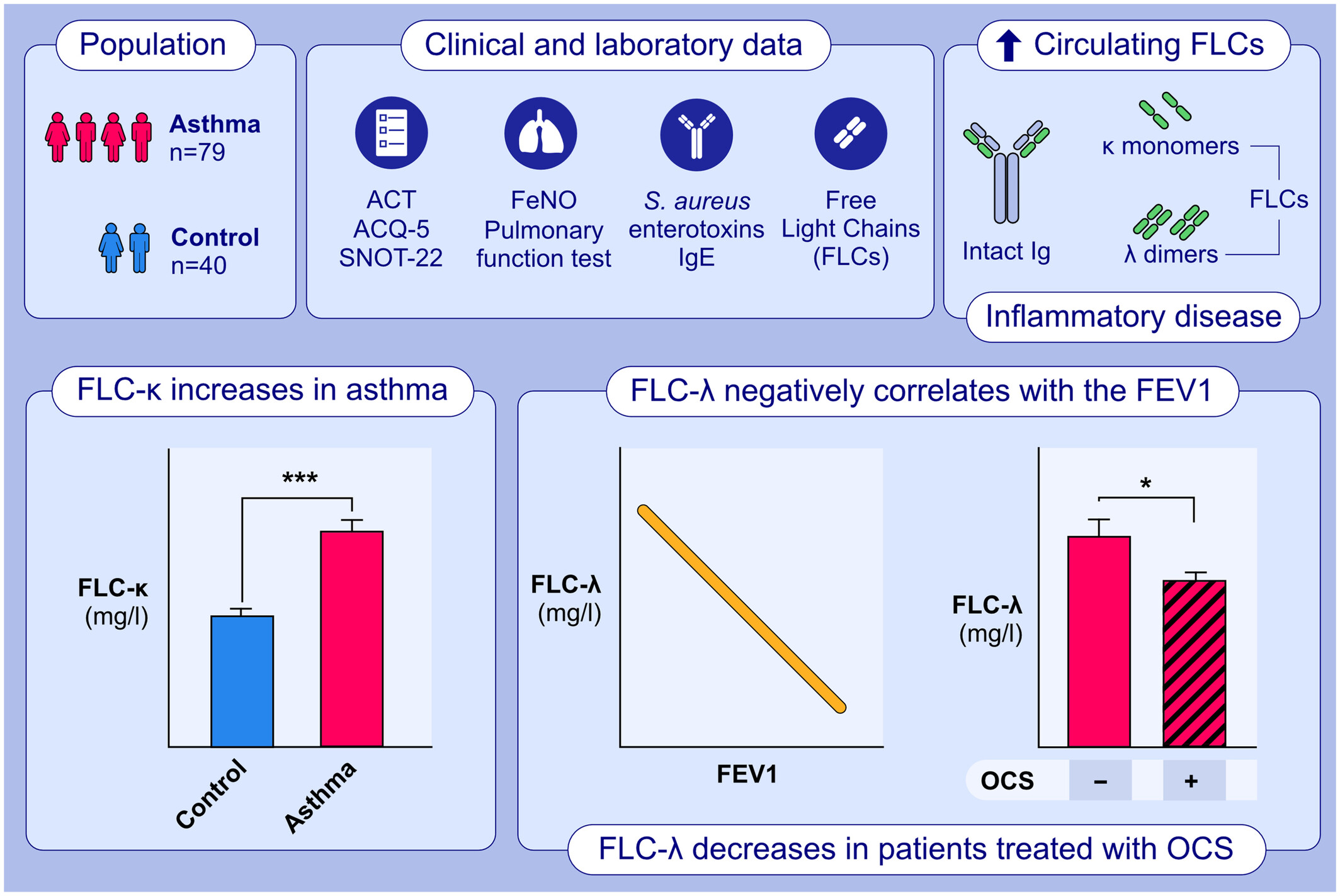
This study aimed to describe clinical and laboratory.characteristics of a population of patients with asthma and to investigate the potential role of FLCs as quantitative and objective serum biomarkers.FLC-κ levels were significantly increased in the asthmatic population, compared to the control group.FLC-λ levels displayed a significant negative correlation with the FEV1 value and were significantly decreased in patients treated with OCS.Abbreviations: ACT, Asthma Control Test; ACQ-5, Asthma Control Questionnaire 5; FeNo, Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide; FEV1; forced expiratory volume in the first second; FLC, free light chain; Ig, immunoglobulin; OCS, oral corticosteroids; SNOT-22, Sino-nasal Outcome Test 22.
Atopic Dermatitis, Urticaria and Skin Disease
Lin−CD117+CD34+FcεRI+ progenitor cells are increased in chronic spontaneous urticaria and predict clinical responsiveness to anti-IgE therapy
- Pages: 2423-2434
- First Published: 17 April 2024
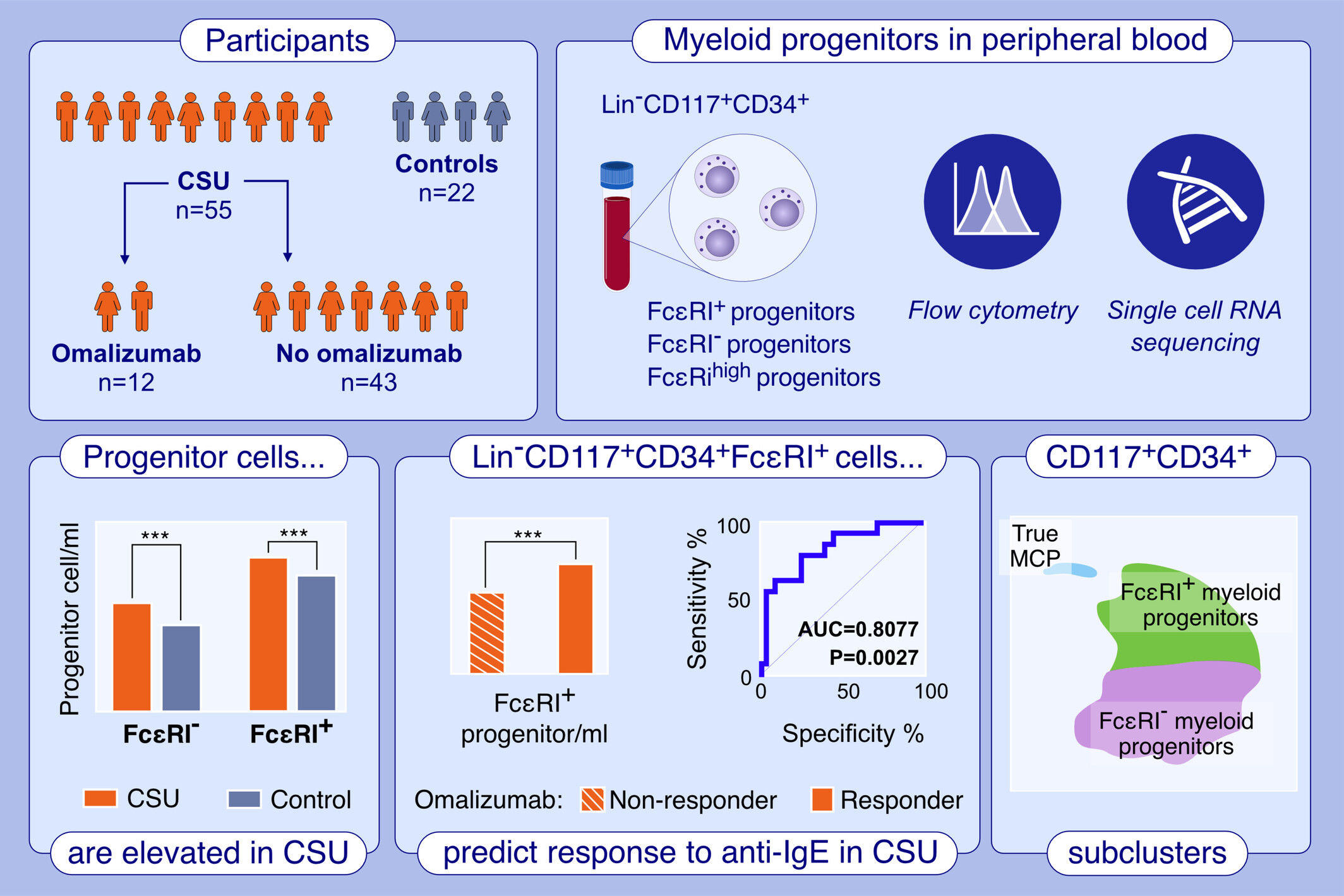
Patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) have higher numbers of CD117+ CD34+FcεRI+ progenitors in peripheral blood. Higher numbers of CD117+CD34+FcεRI+ progenitors are associated with a more rapid response to anti-immunoglobulin E therapy in CSU patients. Single-cell RNA sequencing shows the CD117+CD34+ cells contain mast cell precursors but also related immature FcεRI− and FcεRI+ progenitors.Abbreviations: AUC, area under the curve; CSU, chronic spontaneous urticaria, IgE, immunoglobulin E.
In chronic spontaneous urticaria, increased Galectin-9 expression on basophils and eosinophils is linked to high disease activity, endotype-specific markers, and response to omalizumab treatment
- Pages: 2435-2447
- First Published: 18 July 2024
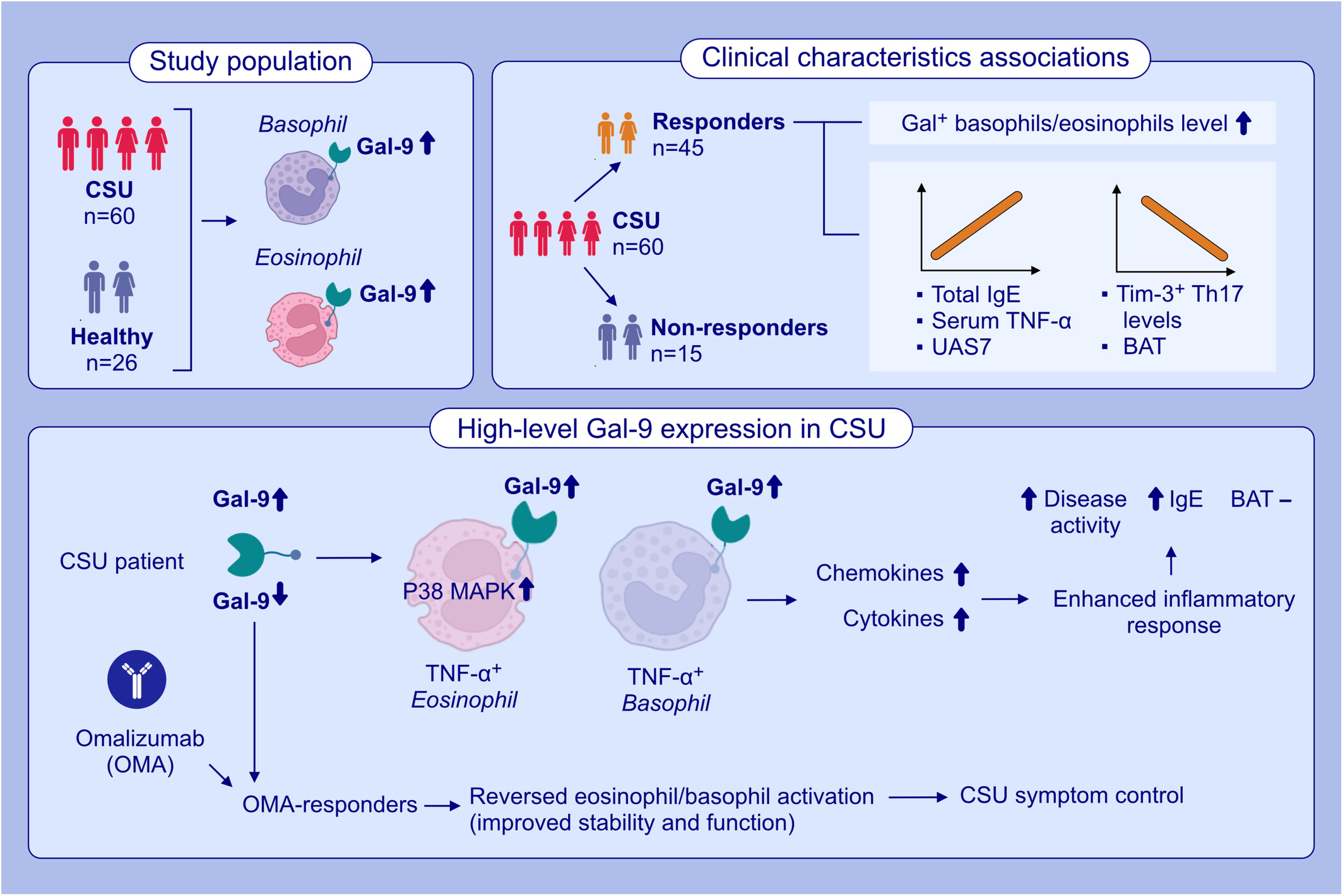
Increased levels of circulating Gal-9+ eosinophils and Gal-9+ basophils in CSU lined to high disease activity, markers of non-autoimmune CSU, and good response to omalizumab treatment. Elevated serum TNF-α levels led to an increase in Gal-9 expression in CSU patients. The rates of Gal-9+ eosinophils and basophils were negatively linked to levels of TIM-3+ TH17 cells, suggesting that Gal-9 via TIM-3 protect CSU patients from type IIb autoimmunity.Abbreviations: BAT, basophil activation test; CSU, chronic spontaneous urticaria; Gal-9, Galectin-9; IgE, immunoglobulin E; OMA, omalizumab; TIM-3, T cell immunoglobulin-and mucin-domain-containing molecule-3 (Gal-9 ligand); TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
Characterization of omalizumab updosing patterns and predictive factors in chronic spontaneous urticaria: A prospective multicentric observational study
- Pages: 2448-2457
- First Published: 26 July 2024
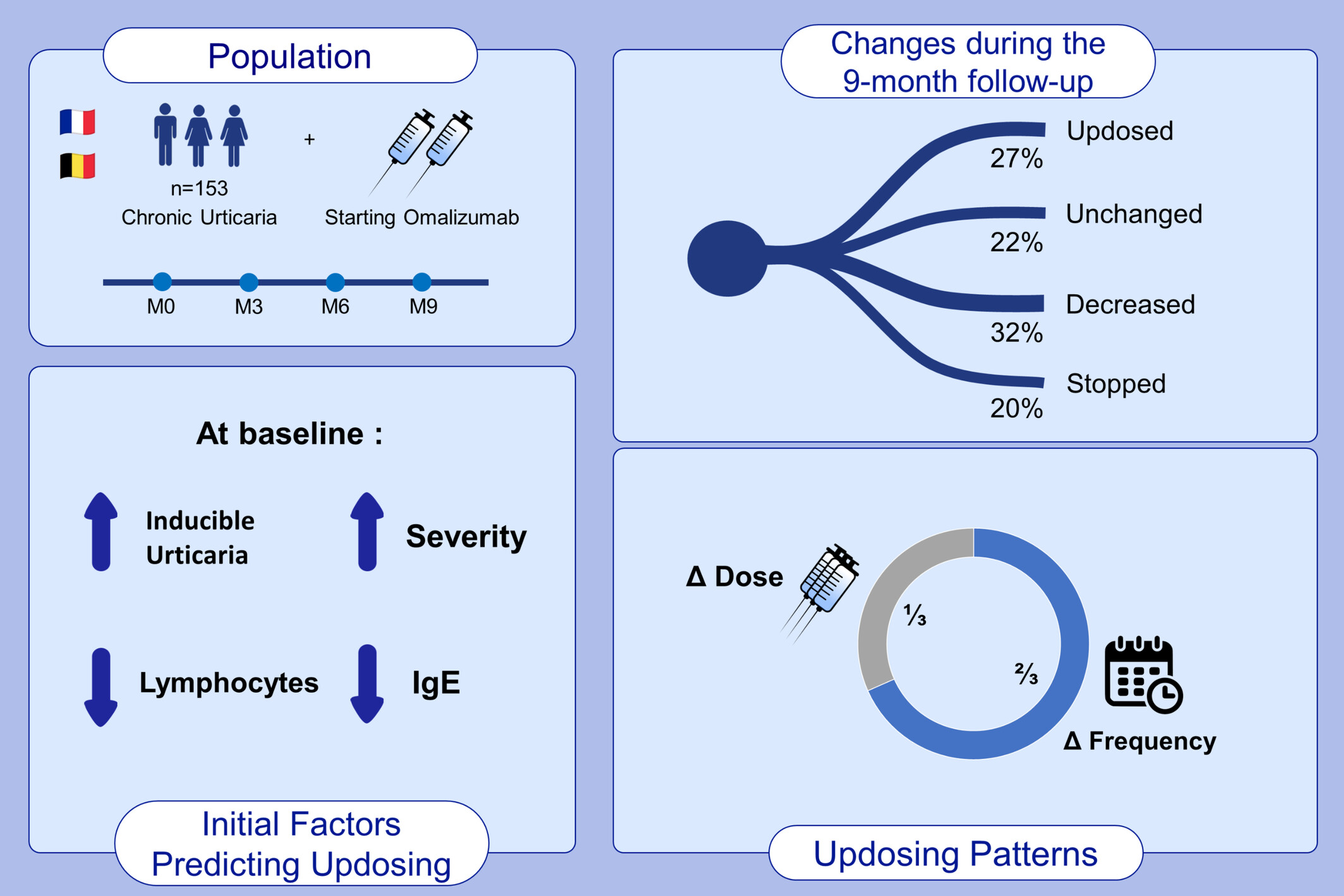
We conducted a prospective, multicentric, observational study, including 153 patients diagnosed with chonic urticaria and starting omalizumab. Twenty percent of patients at M3 were updosed, and 27% during the 9-month follow-up. Practitioners mainly chose to increase the frequency of injections (66%). At baseline, the updosed patients were more likely, to have inducible urticaria, severe urticaria, lower IgE and lymphocyte count.
Drug Allergy, Insect Sting Allergy, and Anaphylaxis
High burden of clonal mast cell disorders and hereditary α-tryptasemia in patients who need Hymenoptera venom immunotherapy
- Pages: 2458-2469
- First Published: 13 March 2024
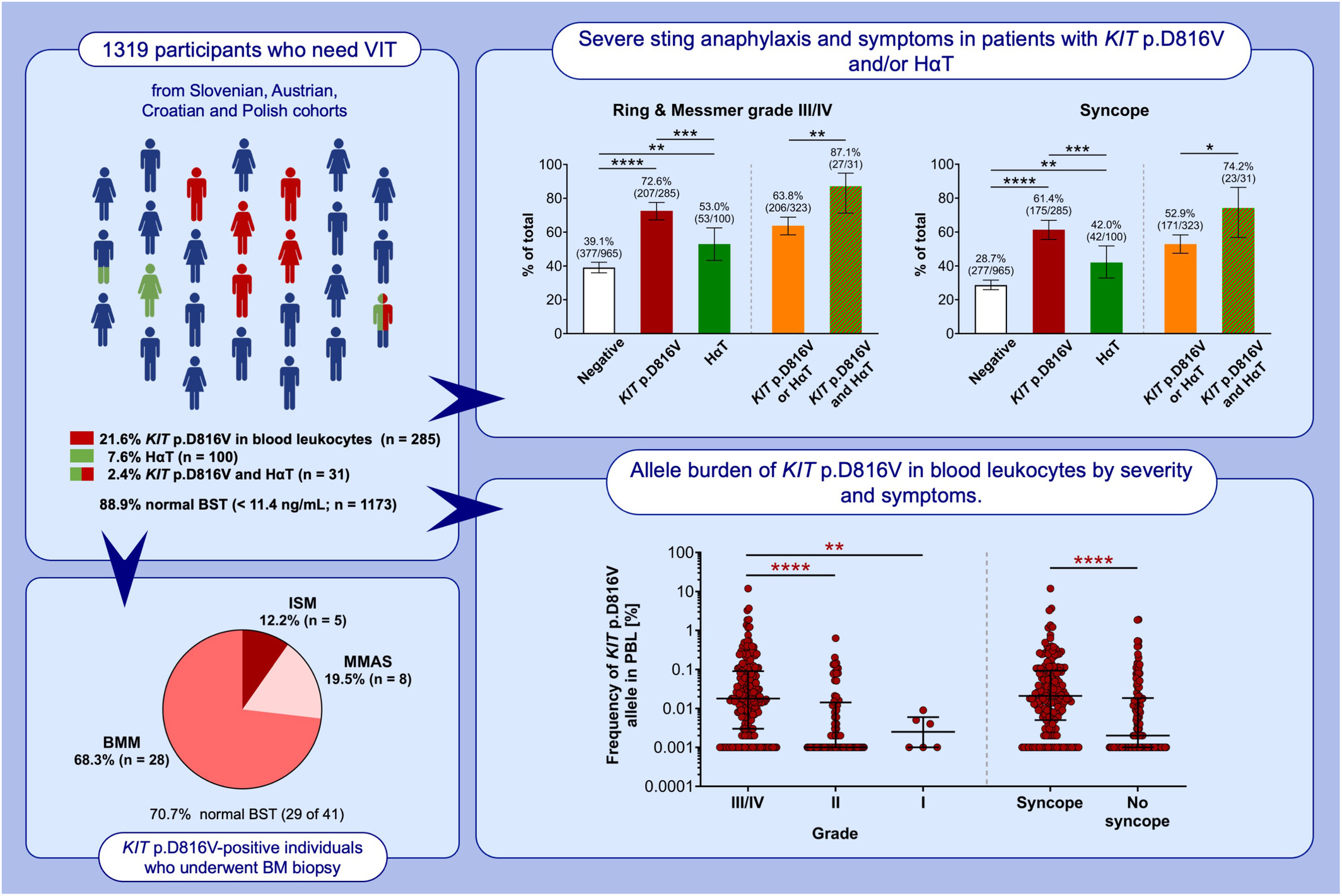
In this multicenter study, we have demonstrated that clonal mast cell disease and HαT are more prevalent among individuals who need VIT; one or both was found in 27% of individuals overall. Both diagnoses were highly concentrated among individuals with severe anaphylaxis. Higher KIT p.D816V allelic burden was associated with more severe reactions. Abbreviations: BMM, bone marrow mastocytosis; BST, basal serum tryptase; HαT, hereditary alpha tryptasemia; ISM, indolent systemic mastocytosis; MMAS, monoclonal mast cell activation syndrome; PBL, peripheral blood leukocytes; VIT, venom immunotherapy.
Prevalence of hypersensitivity reactions in various forms of mastocytosis: A pilot study of 2485 adult patients with mastocytosis collected in the ECNM registry
- Pages: 2470-2481
- First Published: 23 April 2024
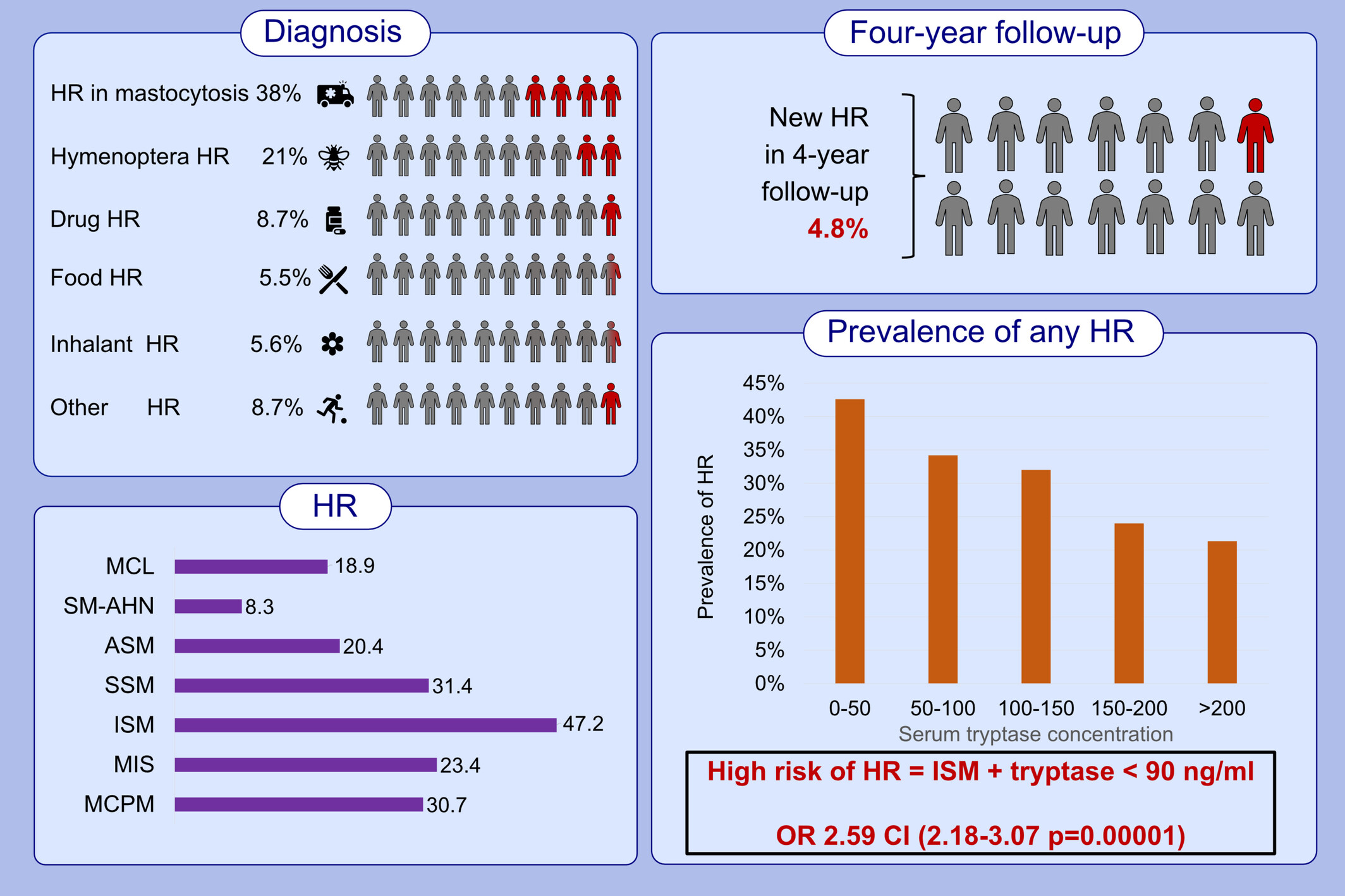
HR are mainly triggered by Hymenoptera venoms in patients with CM and ISM and by drugs in patients with advSM. Tryptase levels <90 ng/mL, mast cell bone marrow infiltration <15%, and WHO category ISM are predictors of HR. New HR occur in 4.8% of all patients within 4 years.Abbreviations: advSM, advanced systemic mastocytosis; ASM, aggressive systemic mastocytosis; CI, confidence interval; HR, hypersensitivity reaction; ISM, indolent systemic mastocytosis; MCL, mast cell leukemia; MCPM, maculopapular cutaneous mastocytosis; MIS, mastocytosis in the skin; OR, odds ratio; SM-AHN, systemic mastocytosis with associated hematological neoplasm; SSM, smoldering systemic mastocytosis; WHO, World Health Organization.
Autoimmunity and Clinical Immunology
Differential decline of SARS-CoV-2-specific antibody levels, innate and adaptive immune cells, and shift of Th1/inflammatory to Th2 serum cytokine levels long after first COVID-19
- Pages: 2482-2501
- First Published: 14 July 2024
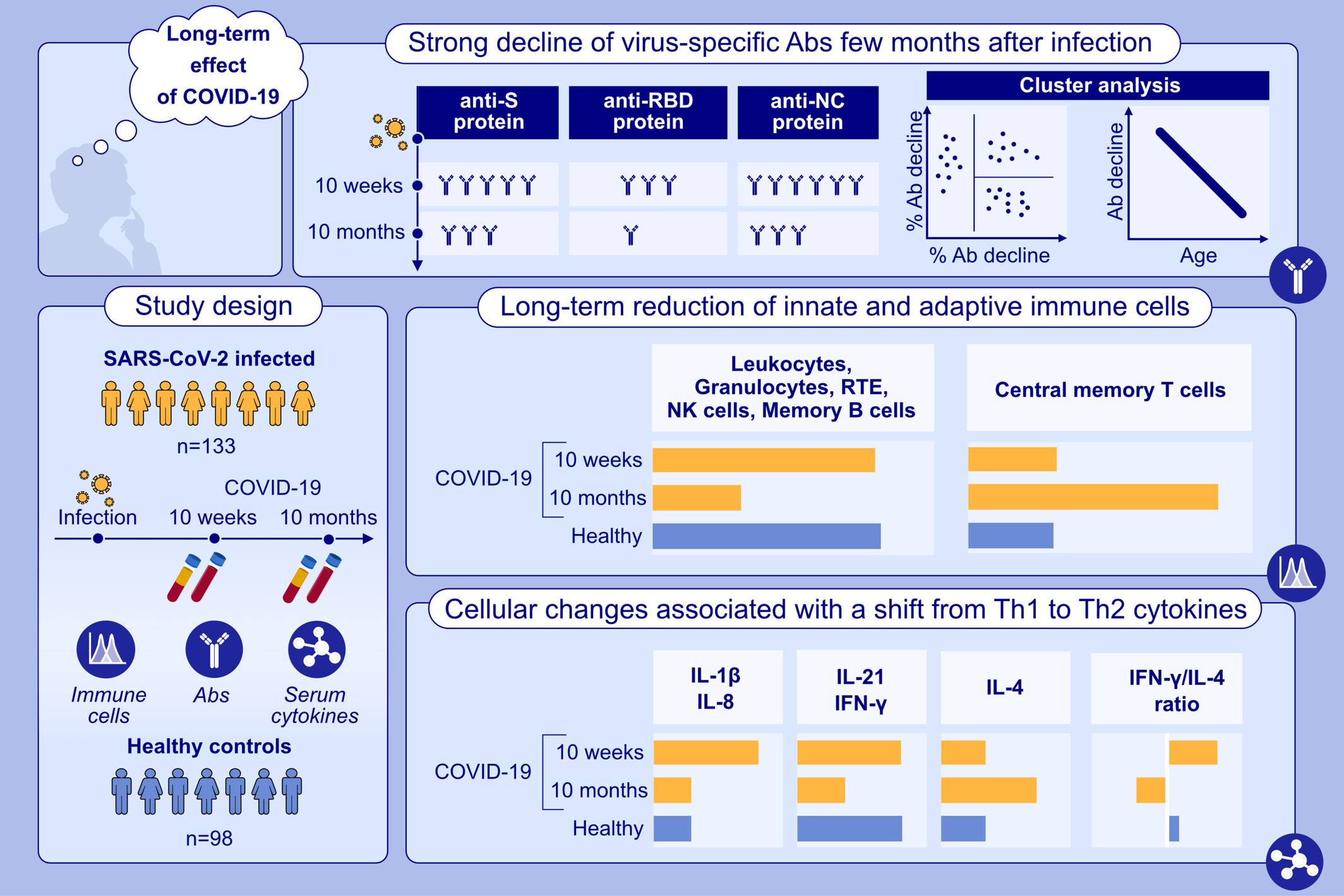
COVID-19 leads to a sustained reduction of immune cells of the myeloid and lymphoid cell lineages even 10 months after the first infection. Ten months after the first infection, S- and RBD-specific IgG responses declined below the detection limit in almost 18% and in more than 80% in subjects, respectively. Anti-NC antibodies remained positive in all subjects 10 m after the first infection. A shift towards a Th2 cytokine pattern in serum accompanied by an inversion of the IFN-γ/IL-4-ratio was found between the time point 10 weeks and 10 months after infection.Abbreviations: CD, cluster of differentiation; COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019; IL, interleukin; IFN, interferon; NC, nucleocapsid protein; NK, natural killer; RBD, receptor binding domain; RTE, recent thymic emigrants; S, spike protein; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
Elucidating allergic reaction mechanisms in response to SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination in adults
- Pages: 2502-2523
- First Published: 20 July 2024
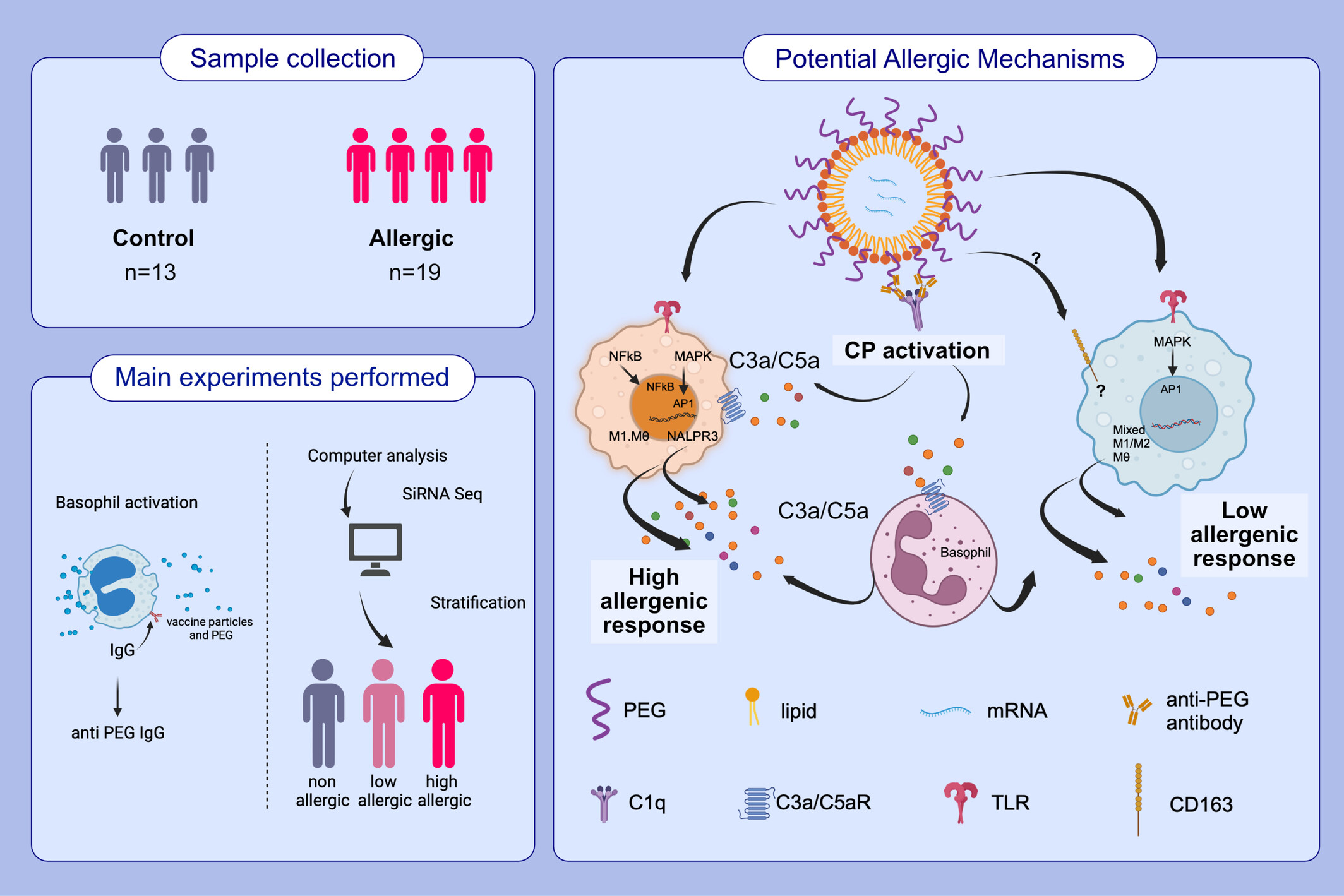
We analyze some of the mechanisms underlying allergic reactions to COVID-19 mRNA vaccines. After performing hemolysis, indirect basophil activation, and single-cell multiome assays, we elucidated certain allergic reaction mechanisms. We found anti-PEG IgG correlates with vaccine-mediated complement activation and that epigenetic modulation of mononuclear phagocytes could influence vaccine reaction manifestations.Abbreviations: AP-1, activator protein 1; C1q, complement component 1q; C3, complement component 3; COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019; CP, classical pathway; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer; NLRP3, nucleotide-binding domain, leucine-rich–containing family, pyrin domain–containing-3; PEG, polyethylene glycol; siRNA seq, small interfering RNA sequencing; TLR, Toll-like receptor.
LETTER
Mast cell chymase suppresses functional parameters in primary human airway smooth muscle cells
- Pages: 2524-2527
- First Published: 26 February 2024
Blood basophils and asthma among participants from CONSTANCES, the French population-based cohort
- Pages: 2527-2531
- First Published: 29 February 2024
Mast cell activation identified through urine mediators
- Pages: 2531-2533
- First Published: 26 March 2024
Prior respiratory syncytial viral infection contributes to severe COVID-19 illness: A nationwide cohort study
- Pages: 2534-2537
- First Published: 05 April 2024
Lipopolysaccharides in combination with amoxicillin increases basophil activation test sensitivity to amoxicillin IgE-mediated hypersensitivity
- Pages: 2537-2542
- First Published: 27 April 2024
Clinical applicability of AI-based prognosis prediction for a rare ocular surface disease
- Pages: 2542-2543
- First Published: 25 April 2024
Mouse IgE clone SPE-7 can contain functional mouse IgG
- Pages: 2544-2547
- First Published: 06 May 2024
Plasma proteomics analysis of patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria reveals significant associations with key disease characteristics but not with response to omalizumab treatment
- Pages: 2547-2550
- First Published: 26 May 2024
Benralizumab reduces blood basophil percentage and activation in vitro without eliciting degranulation
- Pages: 2551-2553
- First Published: 06 June 2024
Predicting relapse in chronic spontaneous urticaria: A retrospective cohort study evaluating omalizumab withdrawal regimens
- Pages: 2554-2557
- First Published: 24 June 2024
MMP9 and CCL18 associate with chronic urticaria while type I, IV, and VI collagens change with omalizumab treatment
- Pages: 2558-2561
- First Published: 02 July 2024
Mast cell responses in a mouse model of food allergy are regulated via a ST2/IL-4 axis
- Pages: 2561-2564
- First Published: 24 July 2024
NEWS & VIEWS
Recent Patents and Major Discoveries
Recent patents in allergy and immunology: The interleukin-2 receptor pathway agonist rezpegaldesleukin (REZPEG) for the rescue of regulatory T cells in chronic inflammatory and autoimmune diseases
- Pages: 2565-2566
- First Published: 16 August 2024
Algorithms in Allergy and Clinical Immunology
An algorithm for the diagnosis, pathogenesis and treatment of chronic spontaneous urticaria, 2024 update
- Pages: 2567-2569
- First Published: 01 April 2024
An algorithm for the management of radiocontrast media hypersensitivity, 2024 update
- Pages: 2570-2572
- First Published: 18 June 2024
An algorithm for the diagnosis and treatment of chronic inducible urticaria, 2024 update
- Pages: 2573-2576
- First Published: 26 July 2024
Groundbreaking Discoveries in Clinical and Basic Science
CD8+ T-cell efficiency is affected by the form of membrane lipids in lipid rafts
- Pages: 2577-2579
- First Published: 25 May 2024
CORRESPONDENCE
Reply to Correspondence to “Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis with atopic, nonatopic, and sans asthma—factor analysis”
- Pages: 2580-2582
- First Published: 21 February 2024






