Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
2020
Increased antiviral response in circulating lymphocytes from hypogammaglobulinemia patients
- First Published: 13 June 2020
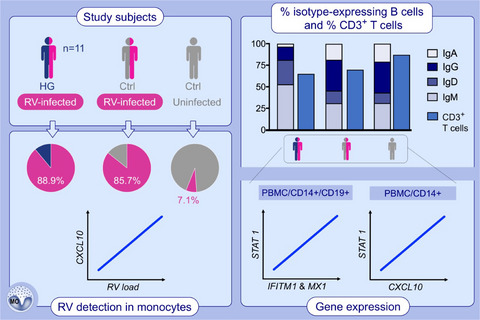
HG patients have increased levels of CD3 + T cells, IgM + and IgG + memory B cells and reduced number of IgA + and IgG + memory B cells compared to infected healthy controls. Expression of transcription factor STAT1 correlates to downstream antiviral genes and inflammatory cytokine CXCL10 in several blood cell types from healthy and infected individuals. RV-infection leads to increased peripheral CD14 + monocyte number in the blood and RV RNA can be detected in CD14 + monocytes from infected control subjects and HG patients. Abbreviations: CXCL10, C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 10; HG, hypogammaglobulinemia; IFITM1, interferon-induced transmembrane protein 1; MX1, interferon--induced GTP-binding protein Mx1; PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cells; RV, rhinovirus; STAT1, signal transducer and activator of transcription 1
A compendium answering 150 questions on COVID-19 and SARS-CoV-2
- First Published: 14 June 2020
Algorithms in allergen immunotherapy in allergic rhinoconjunctivitis
- First Published: 12 March 2020
Vitamin D supplementation in pregnancy does not prevent school-age asthma
- First Published: 26 April 2020
Novel tobacco products including electronic cigarette and heated tobacco products increase risk of allergic rhinitis and asthma in adolescents: Analysis of Korean youth survey
- First Published: 31 January 2020
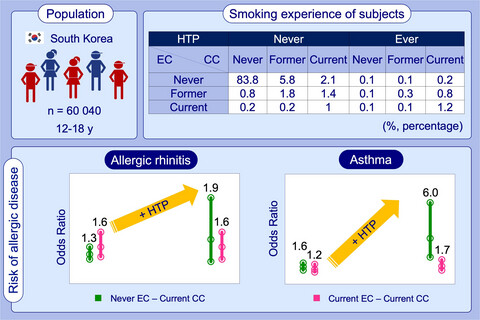
Among Korean adolescents aged from 12 to 18 years old, 6.7% and 2.7% currently use conventional cigarettes and electronic cigarettes, respectively and 2.9% ever used heated tobacco products. The use of conventional cigarette, electronic cigarette, and heated tobacco product, respectively and in combination increases the risk of allergic rhinitis and asthma in Korean adolescents. The use of heated tobacco product especially enhances the impact of conventional cigarettes on allergic rhinitis and asthma.
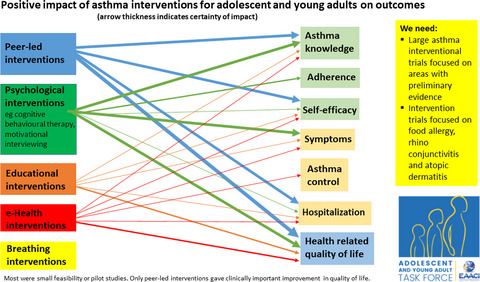
The effectiveness of interventions to improve self-management for adolescents and young adults with allergic conditions: A systematic review
- First Published: 11 March 2020
Impaired control of the contact system in hereditary angioedema with normal C1-inhibitor
- First Published: 20 December 2019
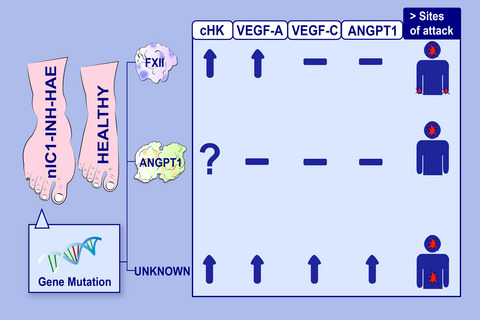
cHK levels in nl-C1-INH-HAE patients are higher than controls in absence of protease inhibitors. Pathogenesis of nl-C1-INH-HAE moves through an unbalanced control of kallikrein activity, with bradykinin as most likely mediator. VEGFs and Ang1 seem to participate in the pathophysiology of U-HAE increasing the basal vascular permeability. Frequency of angioedema location during attacks differ in the FXII-HAE, ANGPT1-HAE and U-HAE cohorts. Abreviations: angiopoietin 1; ANGP1-HAE, hereditary angioedema due to mutations in angiopoietin 1; cHK, cleaved high molecular weight kininogen; FXII-HAE, hereditary angioedema due to mutation in factor XII; nl-C1-INH-HAE, hereditary angioedema with normal C1-INH activity; U-HAE, hereditary angioedema of unknown origin; VEGFs, vascular endothelial growth factors
Genetic variants associated with T cell–mediated cutaneous adverse drug reactions: A PRISMA-compliant systematic review—An EAACI position paper
- First Published: 03 January 2020
Towards a more precise diagnosis of hypersensitivity to beta-lactams — an EAACI position paper
- First Published: 21 November 2019
Intranasal nanoemulsion vaccine confers long-lasting immunomodulation and sustained unresponsiveness in a murine model of milk allergy
- First Published: 26 September 2019
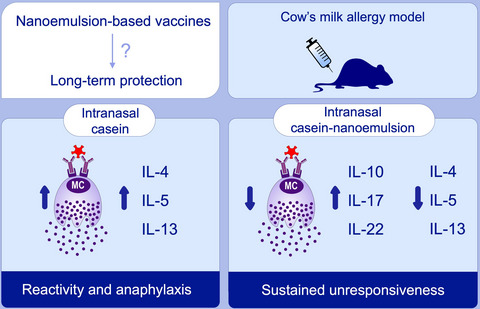
This study evaluates the ability of an intranasal nanoemulsion-based vaccine to induce long-term modulation of allergic reactions in a mouse model of cow's milk allergy. Intranasal immunization with nanoemulsion adjuvant suppresses Th2 responses and anaphylaxis. The sustained unresponsiveness of at least 16 weeks after vaccination suggests that the nanoemulsion vaccine alters the allergic phenotype.
Acid sphingomyelinase regulates TH2 cytokine release and bronchial asthma
- First Published: 08 September 2019
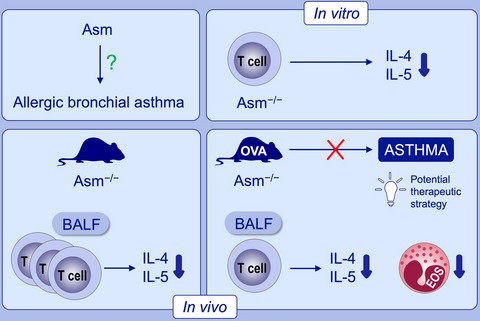
This study investigated the role of acid sphingomyelinase (Asm) in allergic bronchial asthma. Asm deficiency resulted in reduced TH2 cytokine release both in vitro and in vivo. In the ovalbumin model, ASM−/− mice were protected from bronchial asthma, showed decreased production of TH2 cytokines and lower number of eosinophils.
Abbreviations: Asm, acid sphingomyelinase; BALF, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid; OVA, ovalbumin
Colony-stimulating factor 1 and its receptor are new potential therapeutic targets for allergic asthma
- First Published: 06 August 2019
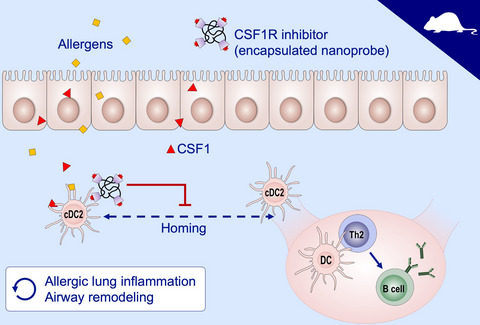
Genetic manipulation or pharmacological inhibition of the CSF1-CSF1R signaling pathway suppresses allergen sensitization and lowers the production of allergen-specific serum IgE. Inhibition of the CSF1-CSF1R pathway reverses established chronic allergic inflammation and airway remodeling. Intranasal delivery of CSF1R inhibitor carrying nanoprobes has efficacy and shows favorable pharmacokinetics without significant adverse effects. CSF1, colony stimulating factor 1
Drug-induced IgG-neutrophil-mediated anaphylaxis in humans: Uncovered!
- First Published: 17 November 2019
The role of mobile health technologies in allergy care: An EAACI position paper
- First Published: 22 June 2019