Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER IMAGE
Cover Image
- Page: i
- First Published: 08 August 2023
Cover illustration: Lymph node fine needle aspiration smear showing a polymorphous population of dispersed lymphoid cells represented by small lymphocytes and follicular centre cells including nucleolated immunoblasts (Diff-Quick stain 430x), from the Review Article COVID-19 post-vaccination lymphadenopathy: A review of the use of fi ne needle aspiration cytology by Alessandro Caputo et al., pp. 423–432, https://doi.org/10.1111/cyt.13221 and Bar chart showing the percentage of cytology cases co-reported before and during the pandemic, from the Review Article International survey of cytopathology training during the pandemic: Water under the bridge? by Nataliya Piletska et al., pp. 433–441, https://doi.org/10.1111/cyt.13262.
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
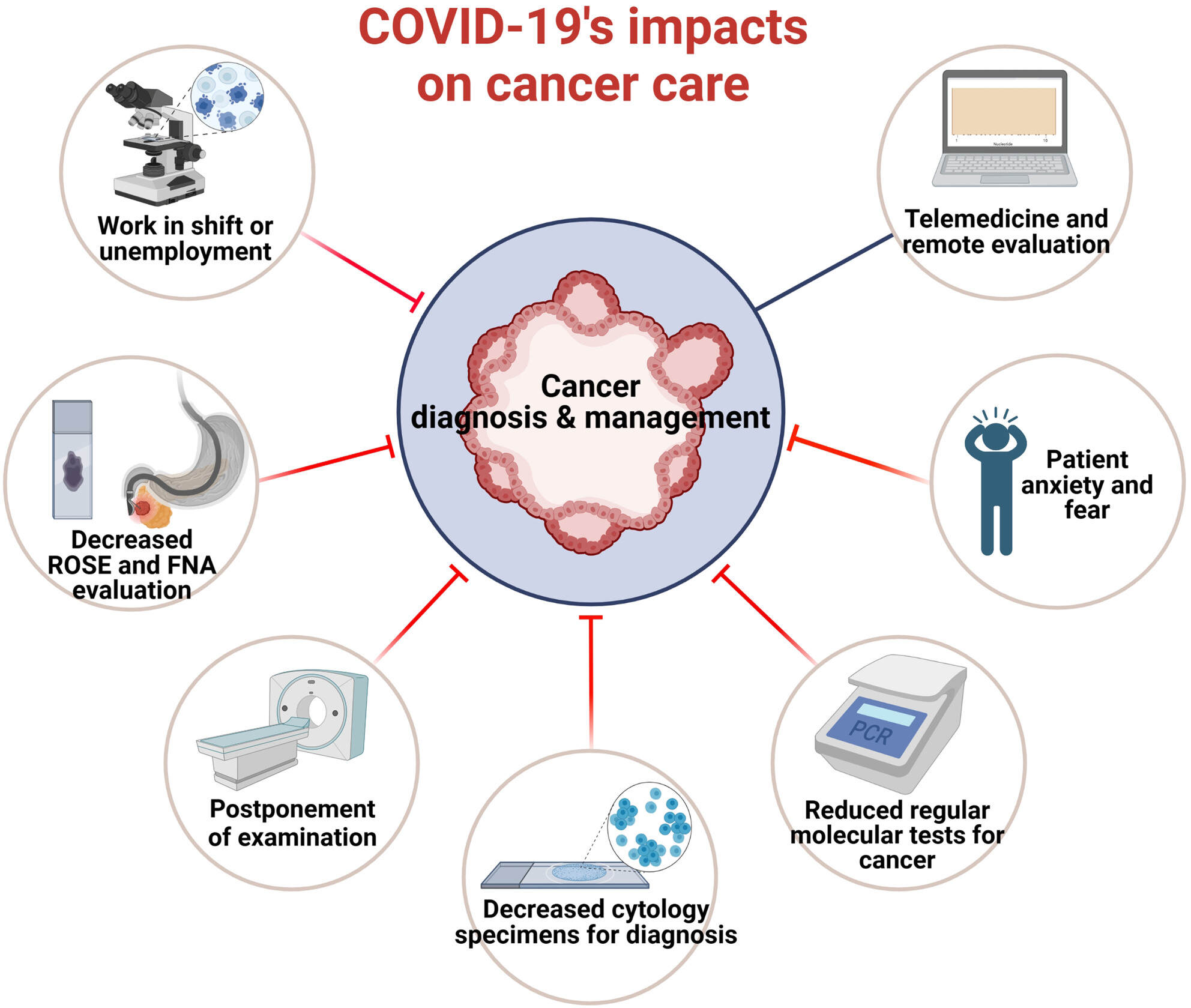
COVID-19 and cytopathology: The many faces of the pandemic's impact 3 years on
- Pages: 404-405
- First Published: 19 June 2023
This Special Issue aims to highlight some of the aspects that are inherent to the persisting impact of COVID-19 on cytopathology practice.
REVIEW
The COVID-19 pandemic has impeded cytopathology practices and hindered cancer screening and management
- Pages: 406-416
- First Published: 18 June 2023
EDITORIAL
Trends in the practice of molecular cytopathology in response to the COVID pandemic
- Pages: 417-418
- First Published: 09 June 2023

In the recent pandemic emergency caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), most activities in many areas of medicine have undergone a remarkable reduction. The health emergency has underlined the evolving role of cytopathology that is increasingly playing a remarkable role in providing oncologists and other physicians with timely information on personalised modern treatment of cancer diagnosed by cytological means.
REVIEWS
Digital diagnostic cytopathology: Has the pandemic brought us closer?
- Pages: 419-422
- First Published: 31 January 2023
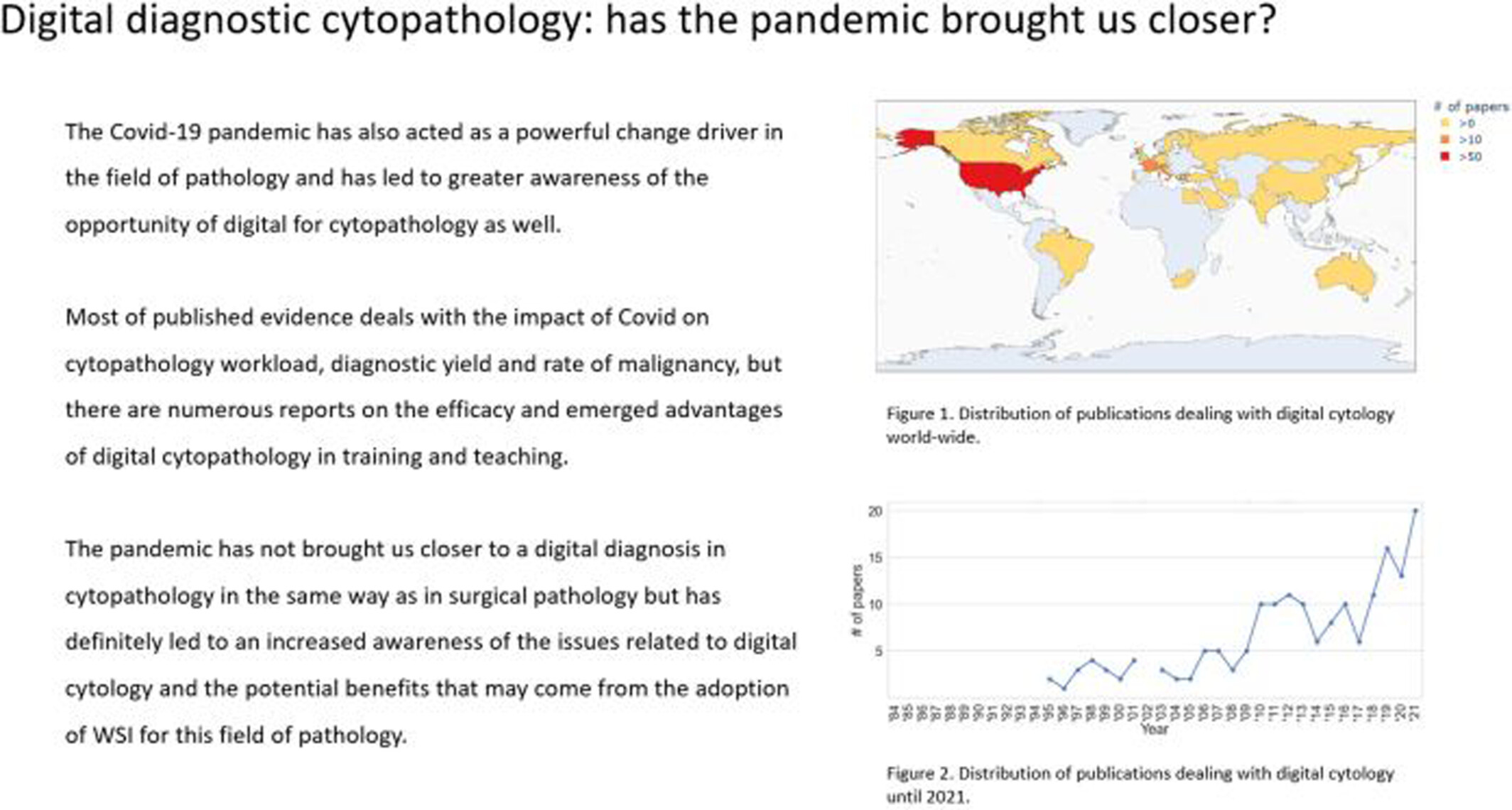
The COVID-19 pandemic has acted as a powerful change driver in the field of pathology and has led to greater awareness of the possibility of digital for cytopathology. Most of the published evidence for the impact of COVID on cytopathology deals with the workload, diagnostic yield, and rate of malignancy, but there are numerous reports on the efficacy and emerging advantages of digital cytopathology in training and teaching. The pandemic has not brought us closer to a digital diagnosis in cytopathology in the same way as in surgical pathology, but has definitely led to an increased awareness of the issues related to digital cytology and the potential benefits that may come from the adoption of whole slide imaging for this field of pathology.
COVID-19 post-vaccination lymphadenopathy: A review of the use of fine needle aspiration cytology
- Pages: 423-432
- First Published: 18 February 2023
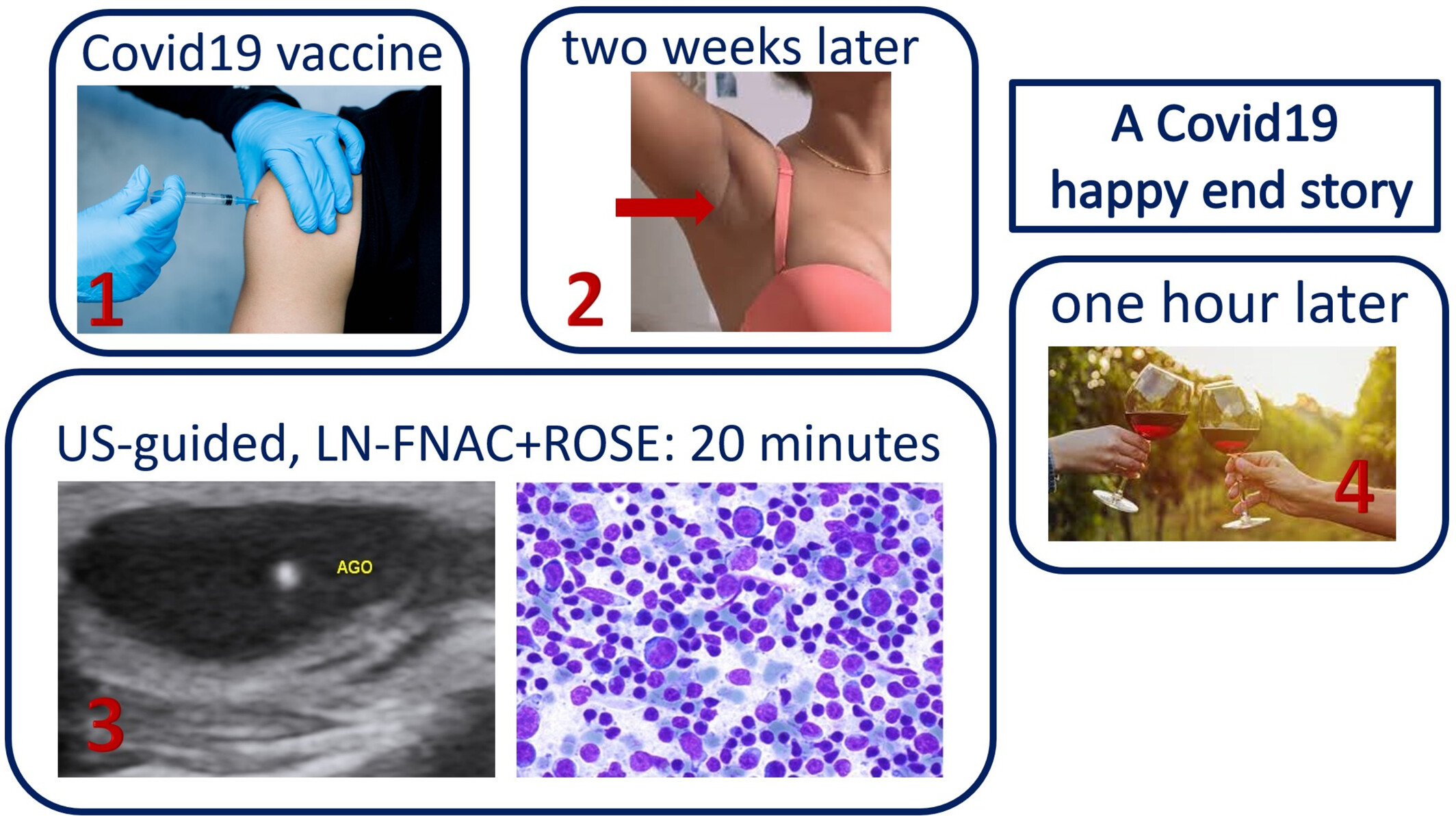
Lymph node (LN) Fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) has been used to diagnose single cases or small series of C19-LAP. All the cytological diagnoses were confirmed by follow-up or excisional biopsy. The high diagnostic value of LN-FNAC was extremely useful during the pandemic and may be precious when CNB or histological excisions are difficult to perform as it happened during Covid lockdowns.
International survey of cytopathology training during the pandemic: Water under the bridge?
- Pages: 433-441
- First Published: 28 June 2023
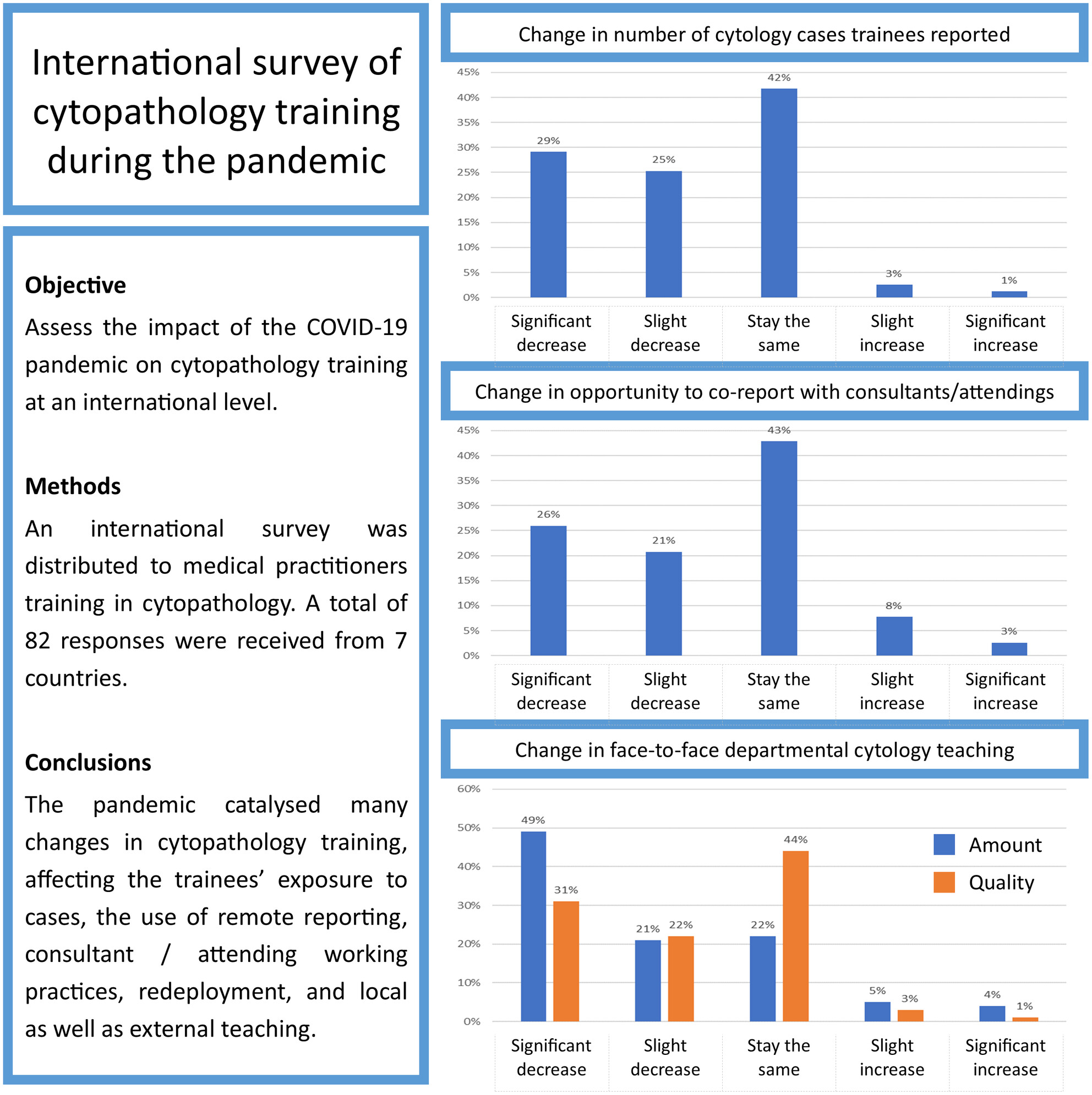
Assessment of the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on cytopathology training at an international level. An international survey was distributed to medical practitioners training in cytopathology. A total of 82 responses were received from seven countries. The pandemic catalysed many changes in cytopathology training, affecting the trainees’ exposure to cases, the use of remote reporting, consultant/attending working practices, redeployment, and local as well as external teaching.
The detrimental consequences of two consecutive disasters impacting cytopathology in Ukraine: COVID followed by the war
- Pages: 442-449
- First Published: 15 April 2023
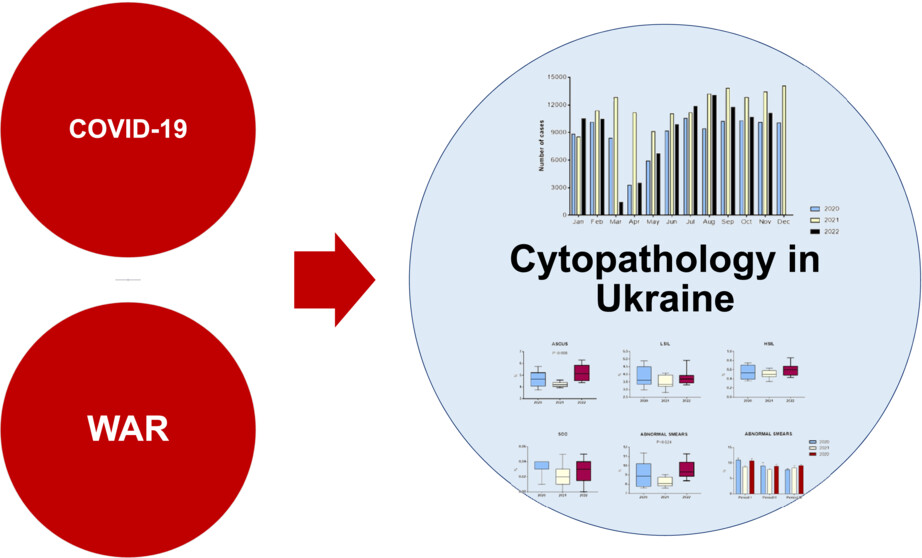
This paper elucidates the effect of two consecutive disasters—the COVID-19 pandemic followed by the war—on cytopathology practice in Ukraine. The impact of war on the numbers and geographic distribution of samples, on workload and laboratory performance indicators, as well as the rate of abnormal cytological samples are discussed.
Will we ever be the same again? The mental health impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on health care staff and institutions
- Pages: 450-455
- First Published: 02 May 2023
The added burdens of the COVID-19 pandemic have put extra stressors on the health system and its most precious resource—its workers. COVID-19 has lifted the lid on the extent of poor mental health and burnout in health care workers, including those working in cytology. Whilst working life is unlikely to return to pre-pandemic practices, the health care system now has an opportunity to reform its staff well-being practices by adhering to the principles that protect health care workers' mental health and mitigate burnout.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
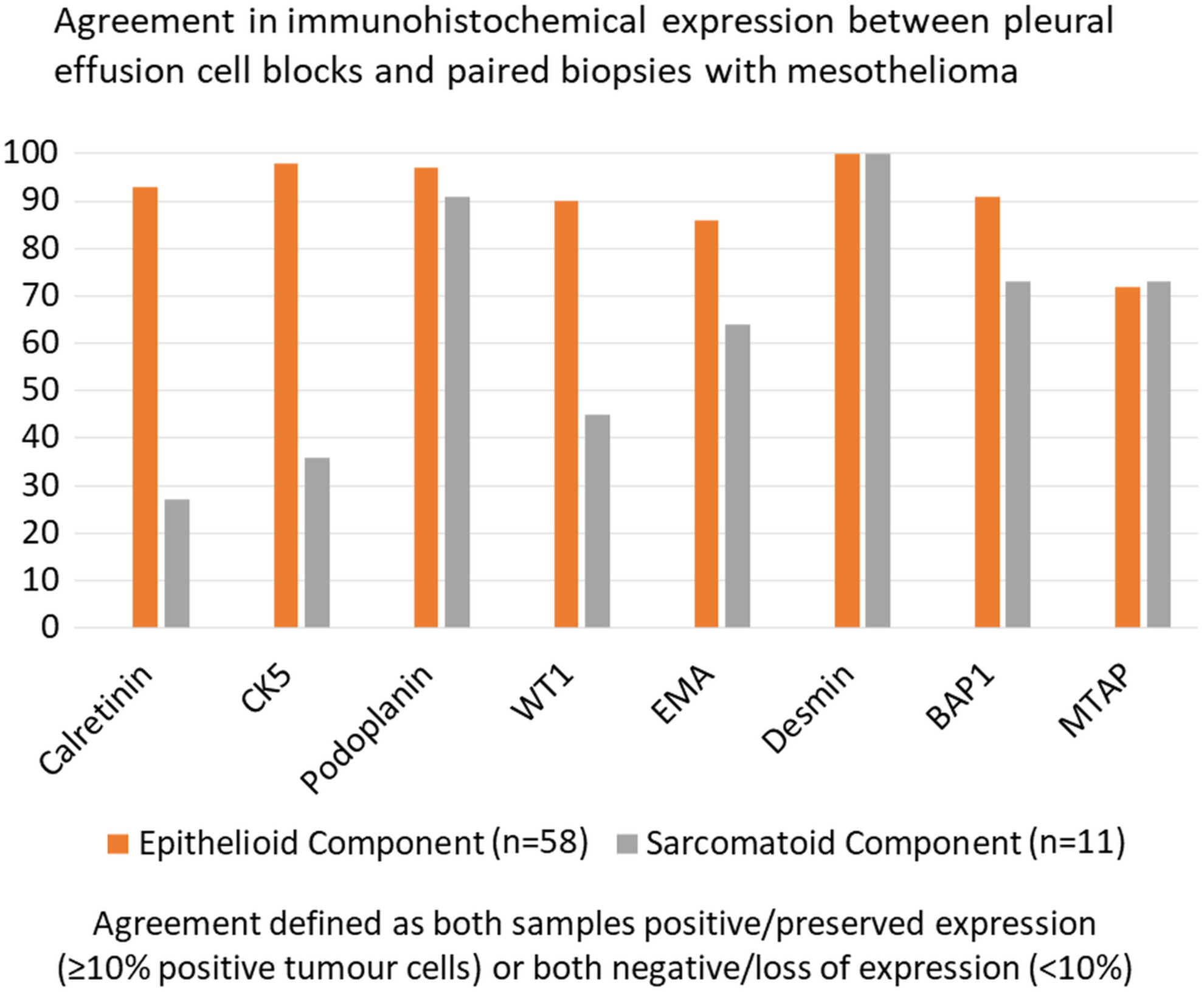
Comparison of immunohistochemical mesothelial biomarkers in paired biopsies and effusion cytology cell blocks from pleural mesothelioma
- Pages: 456-465
- First Published: 19 June 2023
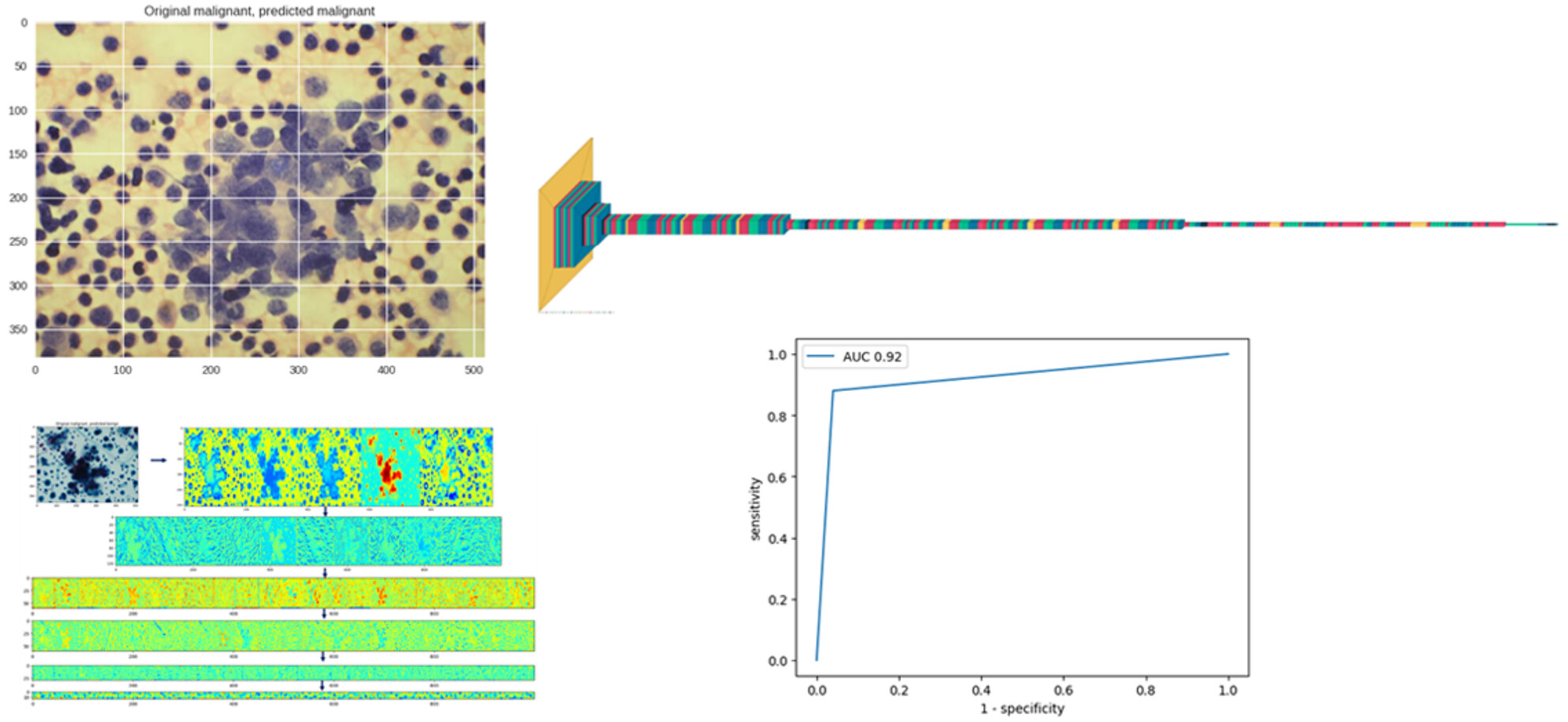
Using a deep learning neural network for the identification of malignant cells in effusion cytology material
- Pages: 466-471
- First Published: 23 June 2023
Fine needle aspiration cytopathology of pleomorphic dermal sarcoma
- Pages: 472-478
- First Published: 19 May 2023
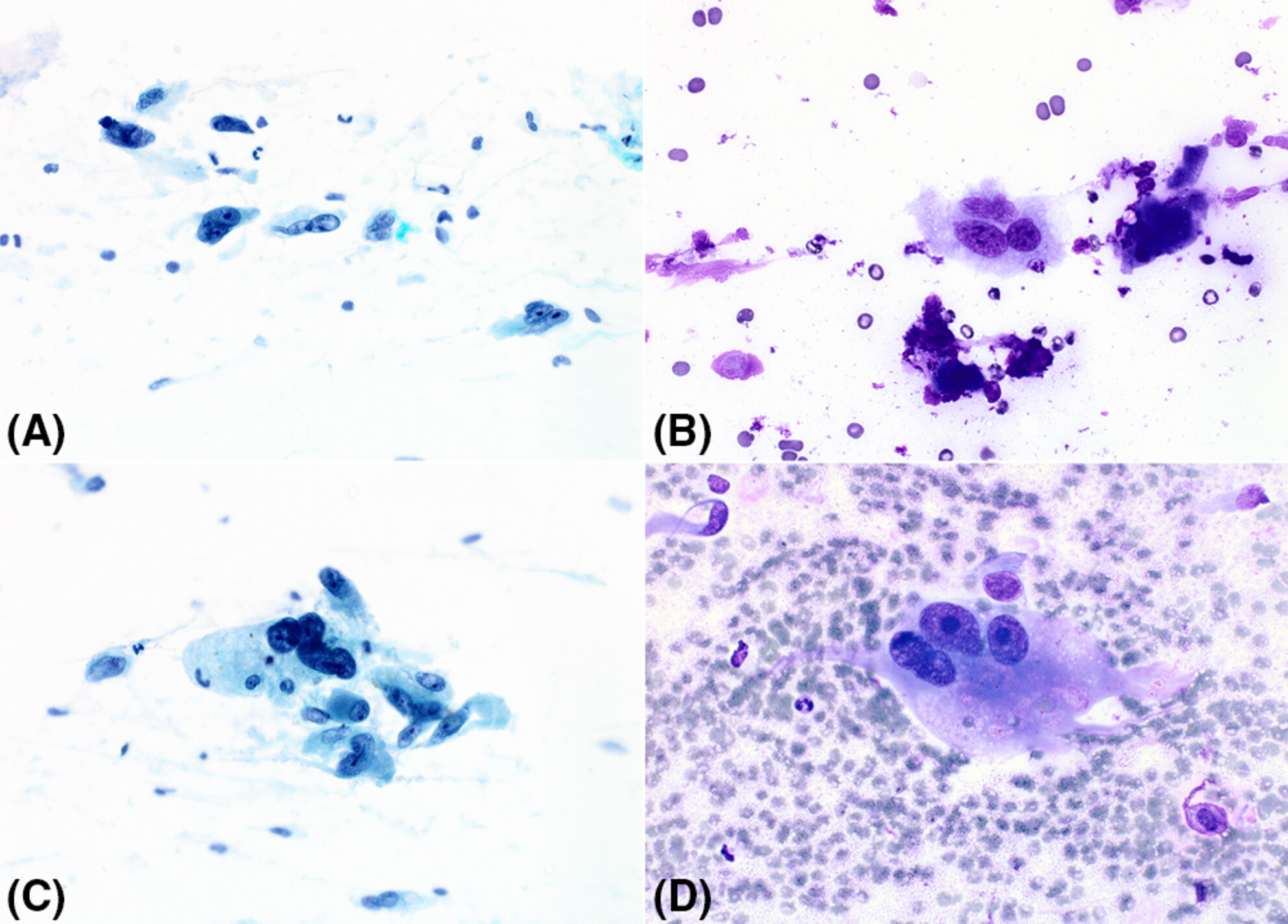
Reports of the fine needle aspiration (FNA) cytopathology of pleomorphic dermal sarcoma (PDS) are rare with this being the only series on the subject to date. FNA biopsy smears consist of a mixture of large spindle, epithelioid, and bizarre pleomorphic cells. Distinguishing PDS from atypical fibroxanthoma (AFX) is not possible using FNA biopsy.
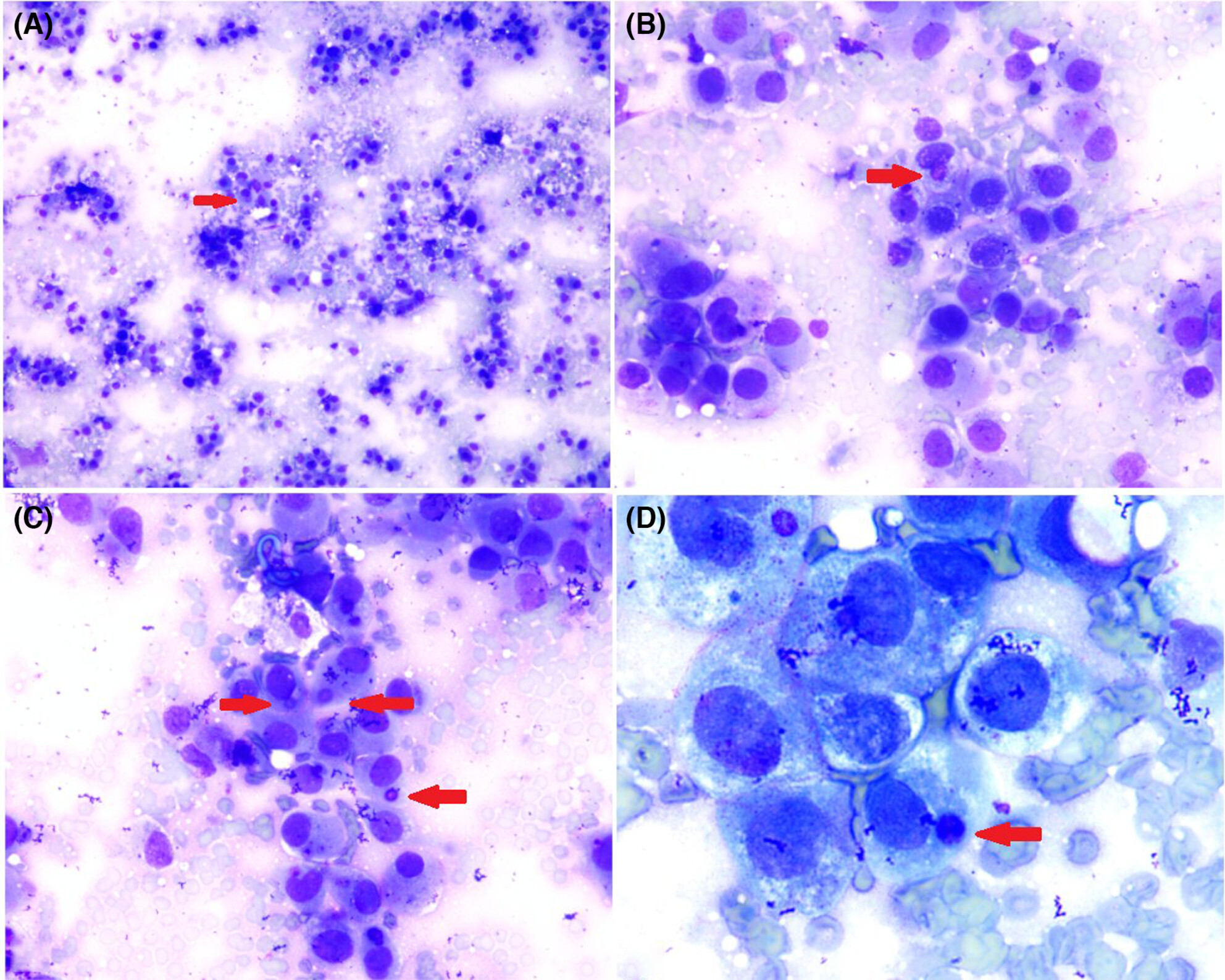
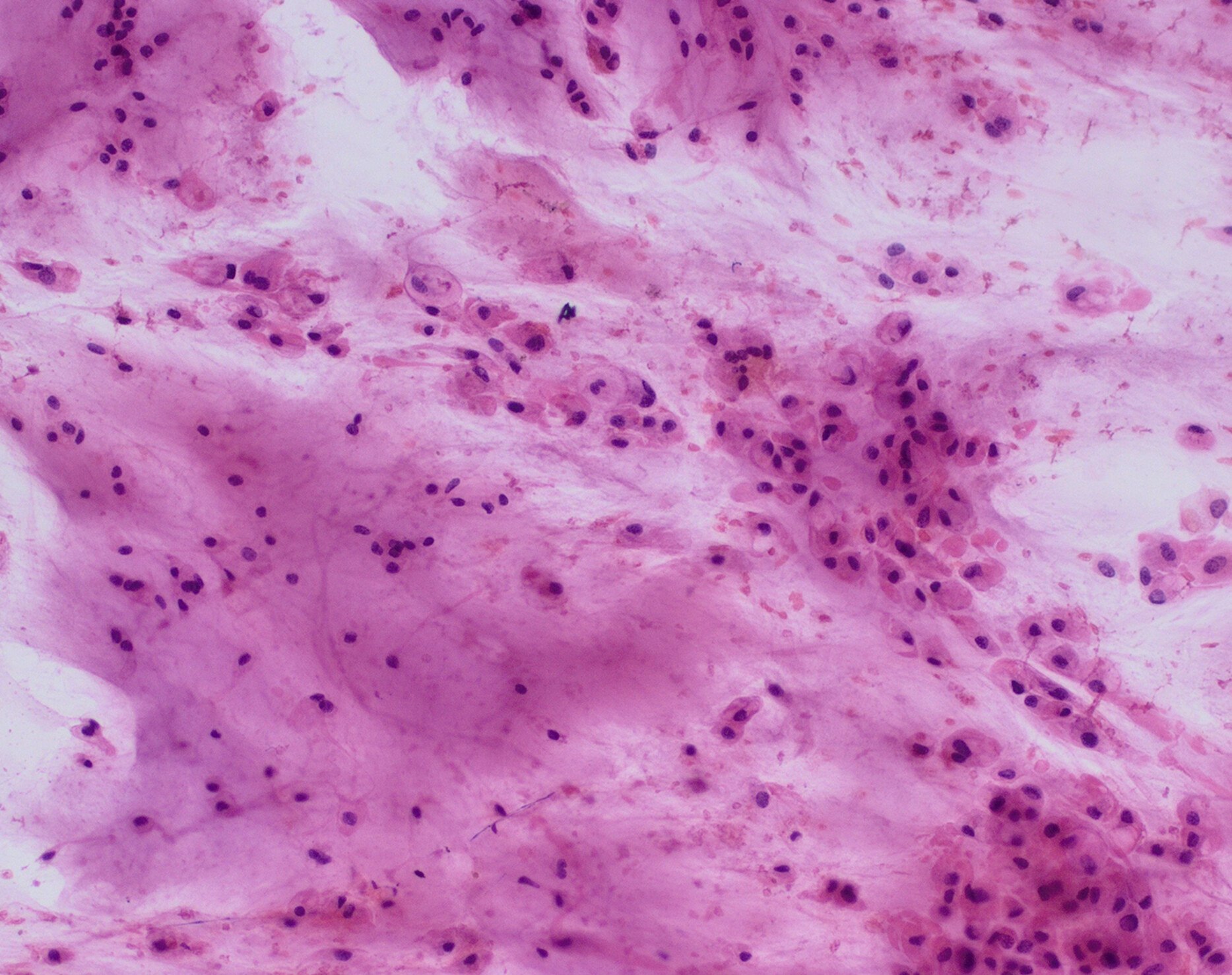
Cytomorphology of paediatric hepatocellular carcinoma: A useful diagnostic adjunct
- Pages: 479-488
- First Published: 26 June 2023
Photomicrograph highlighting the cytomorphological features of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in a child showing trabecular architecture with peripheral and central sinusoidal endothelial cell wrapping. The cells are relatively monomorphic and have abundant cytoplasm. Intranuclear inclusion (arrow) is seen. Cytomorphological features of HCC are well known in adults and are not different from those in paediatric age. But it needs to be differentiated from hepatoblastoma which is much more common in the paediatric age group. The present study highlights that these tumours share some cytomorphological features. But since they have different clinical implications and management, a meticulous cytomorphological evaluation with clinico-radiological correlation can be a useful tool for correct diagnosis prior to planning treatment.
CASE REPORT
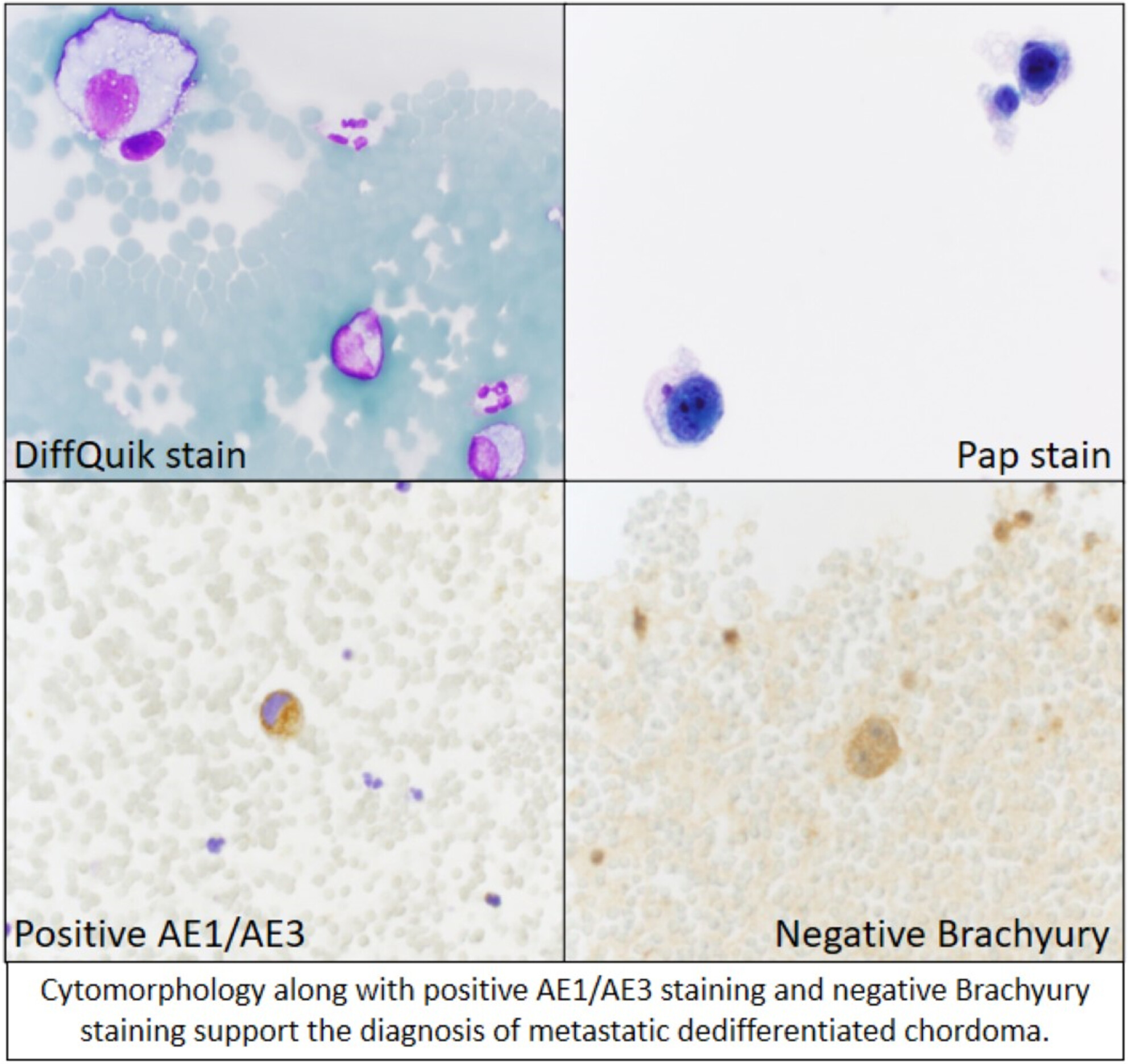
Cytomorphology of a unique case of dedifferentiated chordoma involving a pleural effusion specimen
- Pages: 489-492
- First Published: 26 June 2023
EDITORIAL
SCAN case studies
- Page: 493
- First Published: 23 July 2023
SCAN case study. A case study involving a urine sample is presented, which is intended to highlight the role cytology plays in the overall diagnostic process. Included in the study is a wide-ranging clinical scenario, the cytological impression together with the histological correlation, the immediate treatment, the follow-up and the prognosis for the patient concerned.
SCAN
From haematuria to nephroureterectomy via urine cytology—A case study
- Pages: 494-496
- First Published: 23 July 2023
Upper urinary tract urothelial carcinomas (UTUCs) are uncommon, accounting for only 5%-10% of urothelial carcinomas. Radical nephroureterectomy with bladder cuff excision is the standard treatment of high-risk UTUC. Therefore, accurate preoperative diagnosis, including the use of urine cytology, is essential for appropriate patient management. This case study details a patient's pathway from haematuria to nephroureterectomy.
ENIGMA PORTAL
Granulomatous thyroiditis—A rare case and the diagnostic approach
- Pages: 497-499
- First Published: 21 May 2023
The presence of well-formed granulomas, multinucleated giant cells containing colloid, and degenerative changes in thyroid follicular epithelium are the key diagnostic features of granulomatous (subacute, de Quervain's) thyroiditis. Fine needle aspiration cytology is a confirmatory test that is helpful in cases without any clinical suspicion and to exclude differential diagnoses.
Cytological assessment of a thyroid mass
- Pages: 500-502
- First Published: 28 June 2023
This case highlights an uncommon diagnosis encountered in thyroid fine needle aspiration, highlighting differentials based on the clinical features and how cytomorphology can distinguish these.
IMAGES IN CYTOLOGY
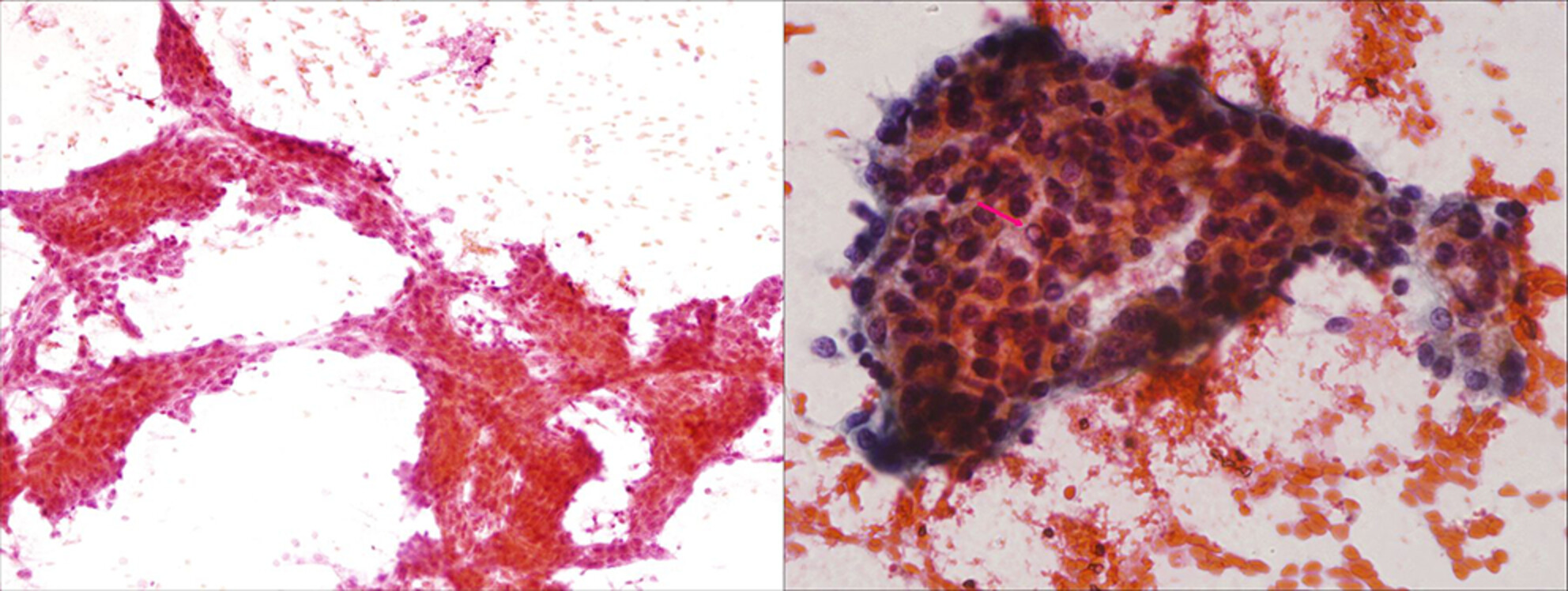
Squash smear and fine needle aspiration features of conventional chordoma
- Pages: 503-506
- First Published: 24 February 2023
A proper intraoperative or preoperative diagnosis of conventional chordoma is crucial for appropriate surgical management because incomplete excision reduces the likelihood of progression-free survival and overall survival. The article presents the characteristic cytological features (including an abundant myxochondroid stroma and cells with large vacuoles) and specific immunohistochemical staining results (nuclear brachyury positivity and co-expression of epithelial markers and S100) that make cytology an effective tool for the diagnosis of this entity.
Cytological findings in a central nervous system demyelinating disease
- Pages: 507-509
- First Published: 05 May 2023
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy is an infectious disease caused by JC polyomavirus. A case of a patient with neurological deterioration due to this disease is presented with its intraoperative cytological diagnosis.
CORRESPONDENCE
Lymphocytic emperipolesis in breast carcinoma on cytology smears—A curious finding!
- Pages: 510-511
- First Published: 19 June 2023