Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
IN THIS ISSUE
In this issue: Volume 114, Issue 11, November 2023
- Pages: 4131-4133
- First Published: 10 November 2023
REVIEW ARTICLES
Adipocyte regulation of cancer stem cells
- Pages: 4134-4144
- First Published: 25 August 2023
High-dose rate endorectal brachytherapy for rectal cancer: A state-of-the-art review
- Pages: 4145-4156
- First Published: 13 September 2023
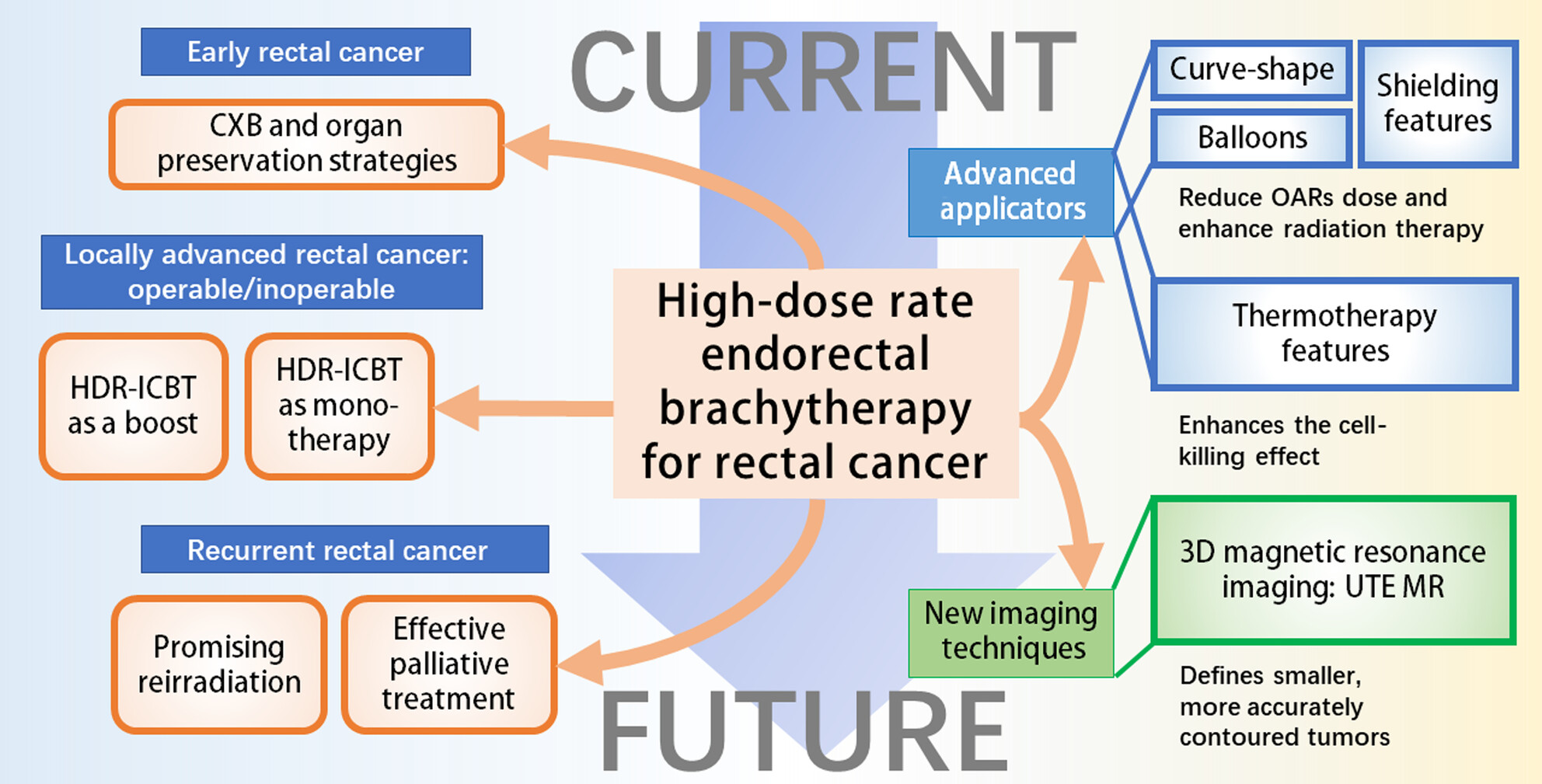
This review describes the use of HDREBT in rectal cancer radiotherapy, which delivers high doses of radiation directly to the tumor, protects normal tissue, and improves clinical complete remission rates. The article summarizes recent advances in HDREBT applicators and imaging techniques in rectal cancer, as well as the available evidence on the efficacy, safety, and feasibility of HDREBT as a neoadjuvant, radical, or palliative treatment option in patients with all stages of rectal cancer. The technique helps to achieve organ preservation and improve quality of life in patients with all stages of rectal cancer, but the impact on long-term survival is unclear and requires further study.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Basic and Clinical Immunology
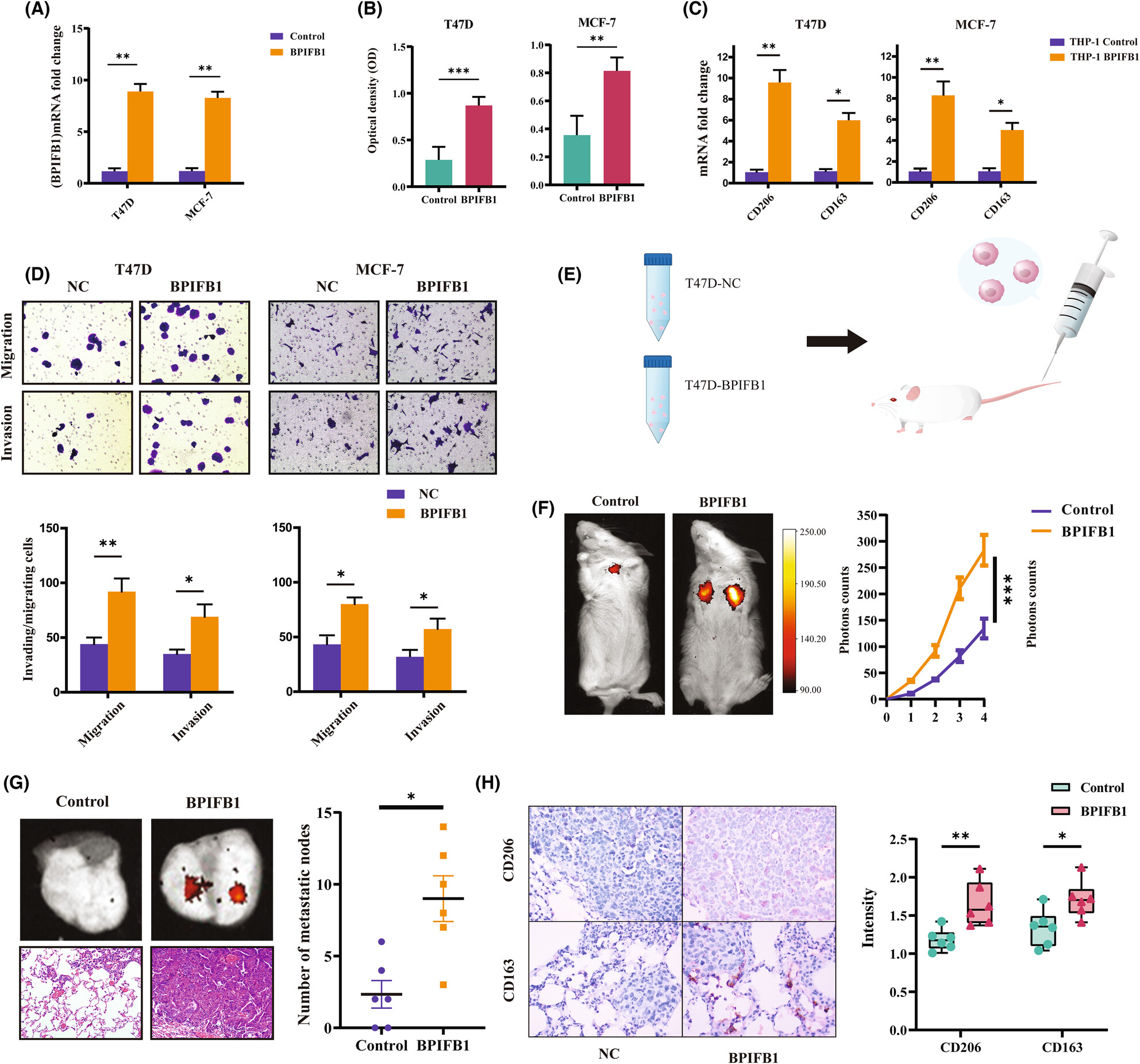
BPIFB1 promotes metastasis of hormone receptor-positive breast cancer via inducing macrophage M2-like polarization
- Pages: 4157-4171
- First Published: 13 September 2023
T cell receptor gene-modified allogeneic T cells with siRNA for endogenous T cell receptor induce efficient tumor regression without graft-versus-host disease
- Pages: 4172-4183
- First Published: 07 September 2023
Combination of PARP inhibitor and CDK4/6 inhibitor modulates cGAS/STING-dependent therapy-induced senescence and provides “one-two punch” opportunity with anti-PD-L1 therapy in colorectal cancer
- Pages: 4184-4201
- First Published: 13 September 2023
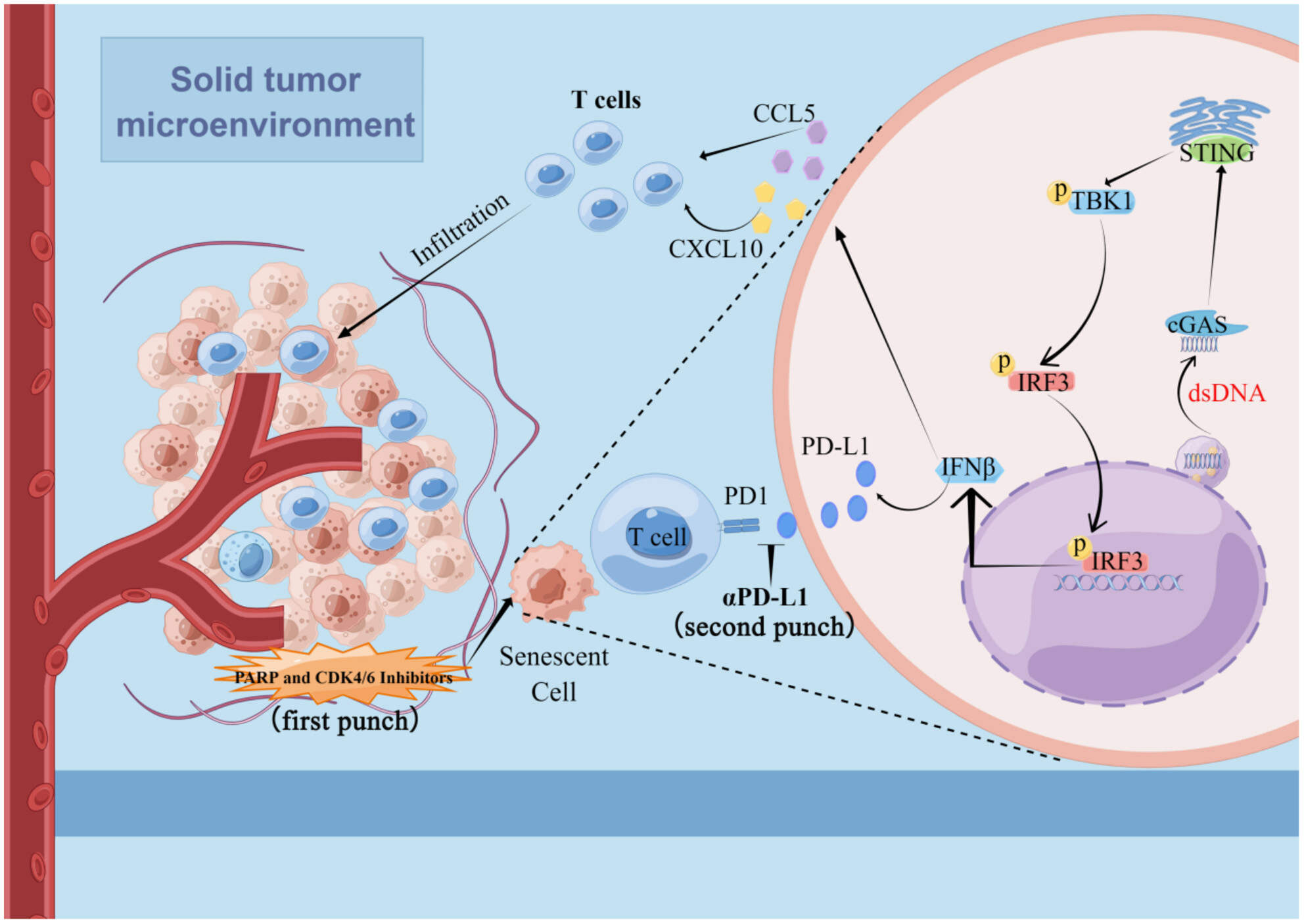
Talazoparib and palbociclib combination triggers therapy-induced senescence and activates antitumor immunity, which strengthens the anticancer effect of immune checkpoint blockade treatment in colorectal cancer. Characterization of senescence-associated secretory phenotype components reveals type I IFN-related mediators, which are amplified by cGAS/STING signaling.
Carcinogenesis
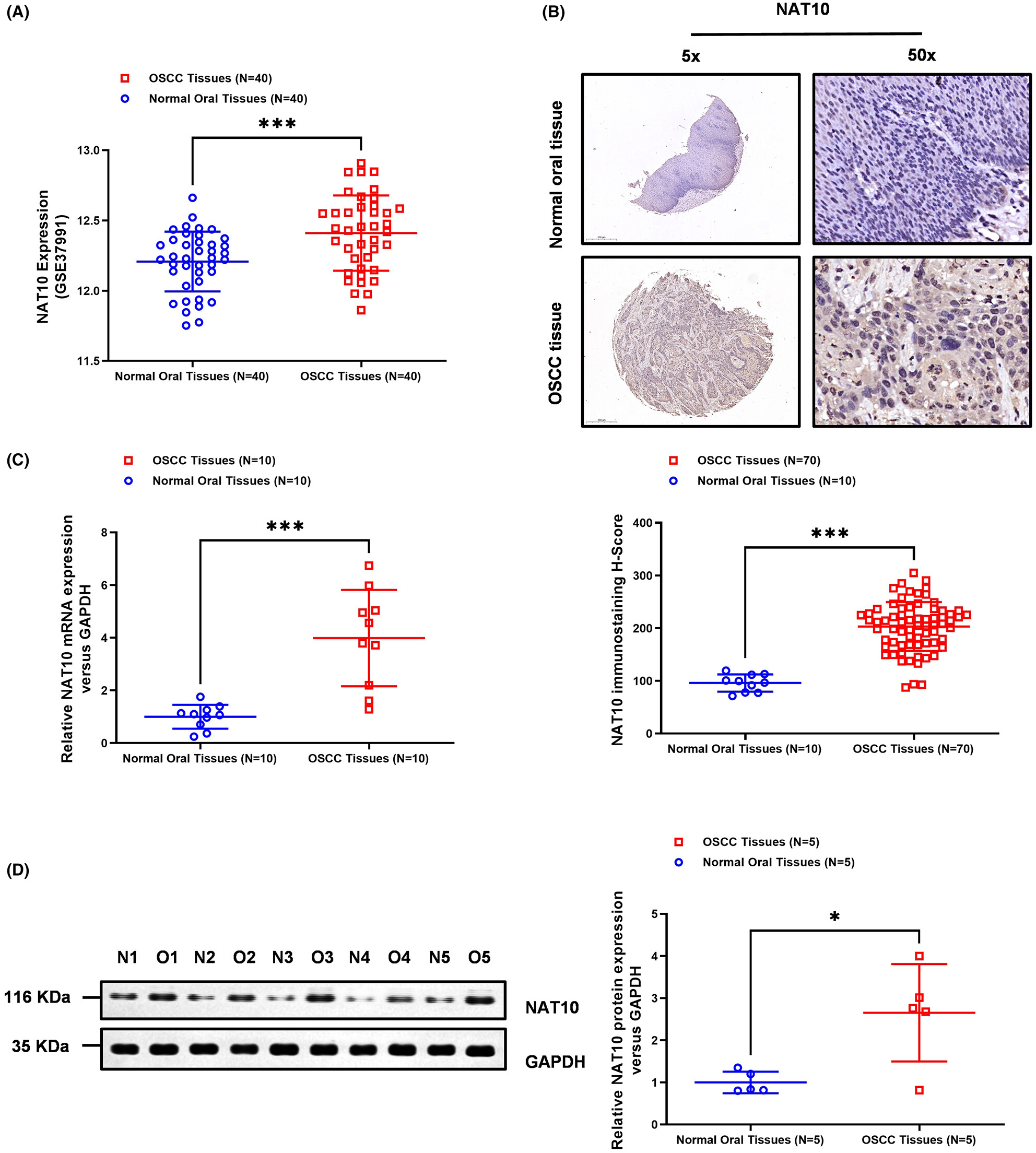
N-acetyltransferase 10 promotes the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma through N4-acetylcytidine RNA acetylation of MMP1 mRNA
- Pages: 4202-4215
- First Published: 13 September 2023
Development of novel tracers for sentinel node identification in cervical cancer
- Pages: 4216-4224
- First Published: 30 August 2023
B7H3 increases ferroptosis resistance by inhibiting cholesterol metabolism in colorectal cancer
- Pages: 4225-4236
- First Published: 03 September 2023
ZNF500 abolishes breast cancer proliferation and sensitizes chemotherapy by stabilizing P53 via competing with MDM2
- Pages: 4237-4251
- First Published: 12 September 2023
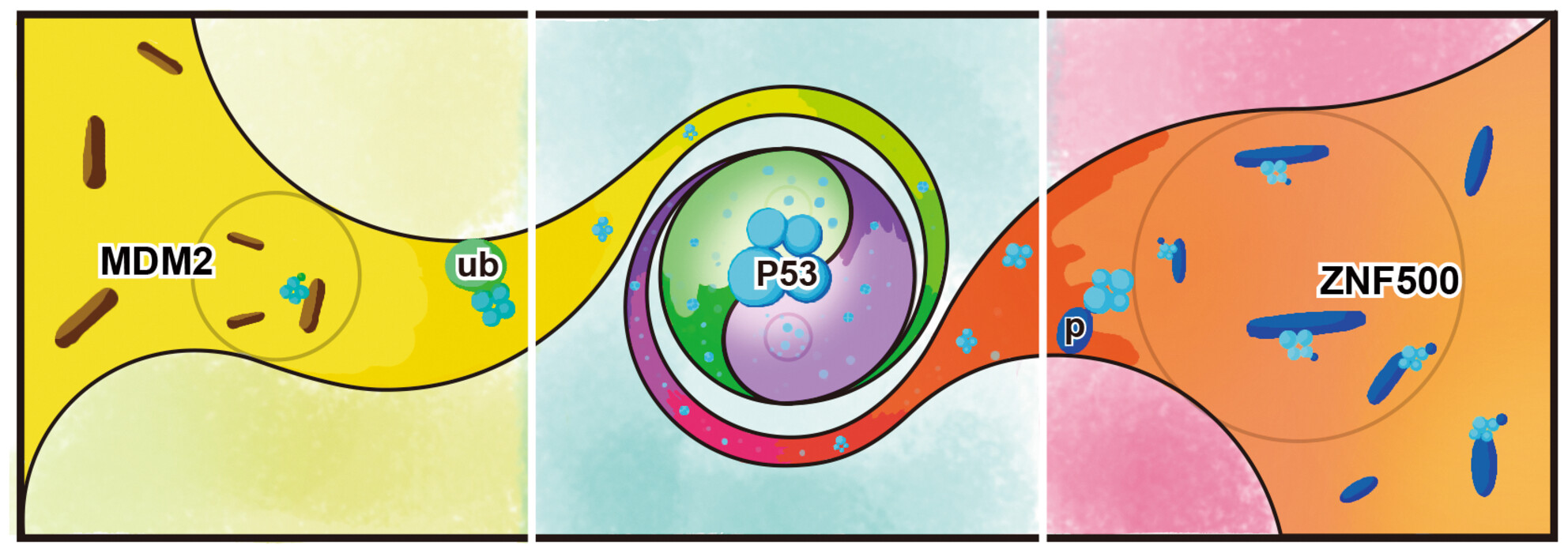
ZNF500 is elevated in breast cancer, whose expression significantly negatively correlated with advanced TNM stage, positive lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis. ZNF500 binds to the C-terminal domain of P53 directly via its C2H2 domain, which may block the interaction between MDM2 and P53, thus stabilizing P53. Overexpression of ZNF500 accelerated DNA damage and sensitized chemotherapy treatment, which was confirmed in human breast cancer with neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Exosomal miR-222-3p contributes to castration-resistant prostate cancer by activating mTOR signaling
- Pages: 4252-4269
- First Published: 06 September 2023
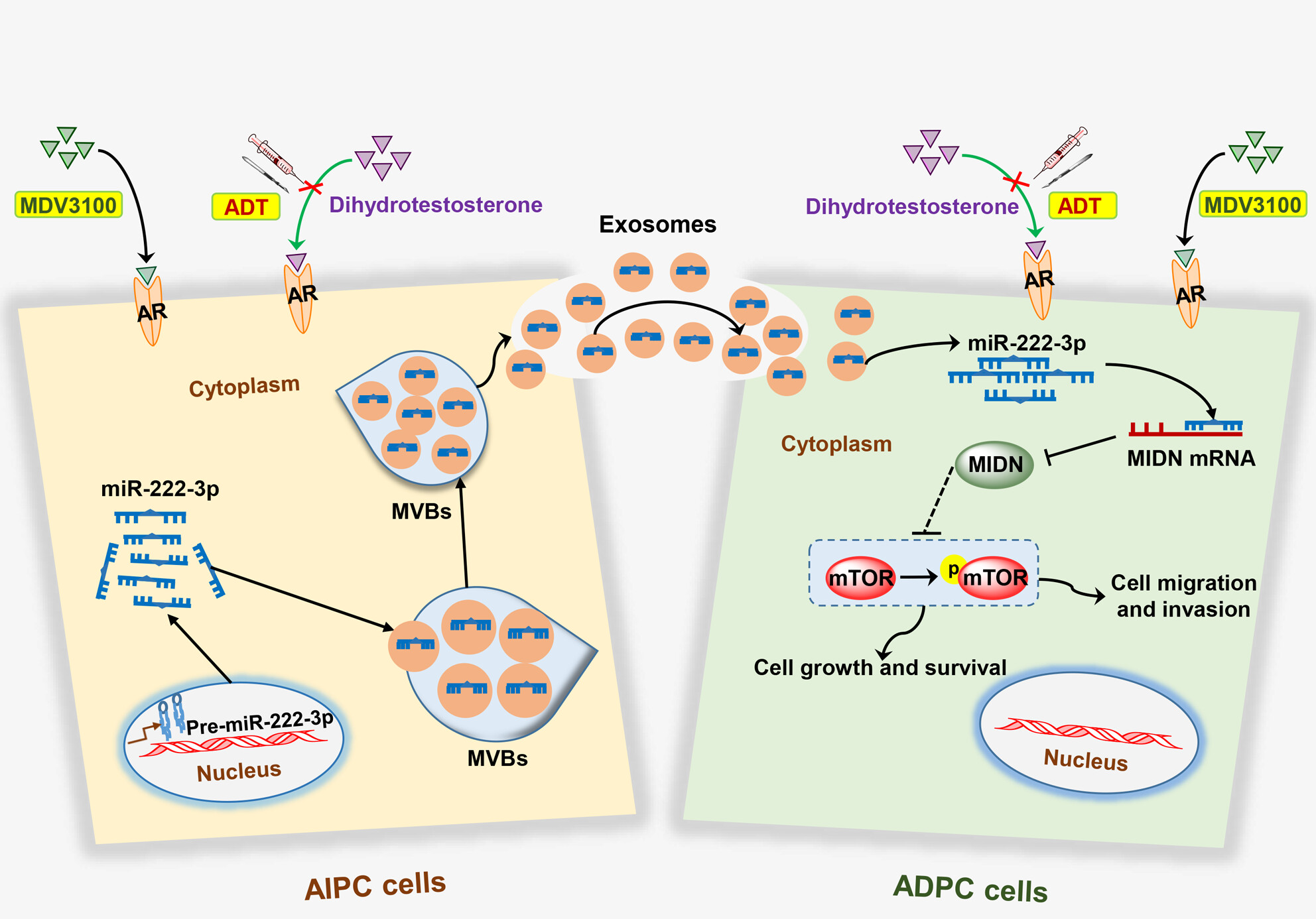
We found that Exos released by AIPC cells could acclimate ADPC cells to progressing to more aggressive cell types through the paracrine signaling system. Exos-miR-222-3p promoted ADPC cells transformed to AIPC-like cells, at least in part, by activating the mTOR signaling pathway by targeting MIDN. The current work underscores the great therapeutic potential of targeting Exo miRNAs, either as a single agent or in combination with the AR pathway inhibitors in the treatment of CRPC.
Branched-chain keto-acid dehydrogenase kinase regulates vascular permeability and angiogenesis to facilitate tumor metastasis in renal cell carcinoma
- Pages: 4270-4285
- First Published: 16 September 2023
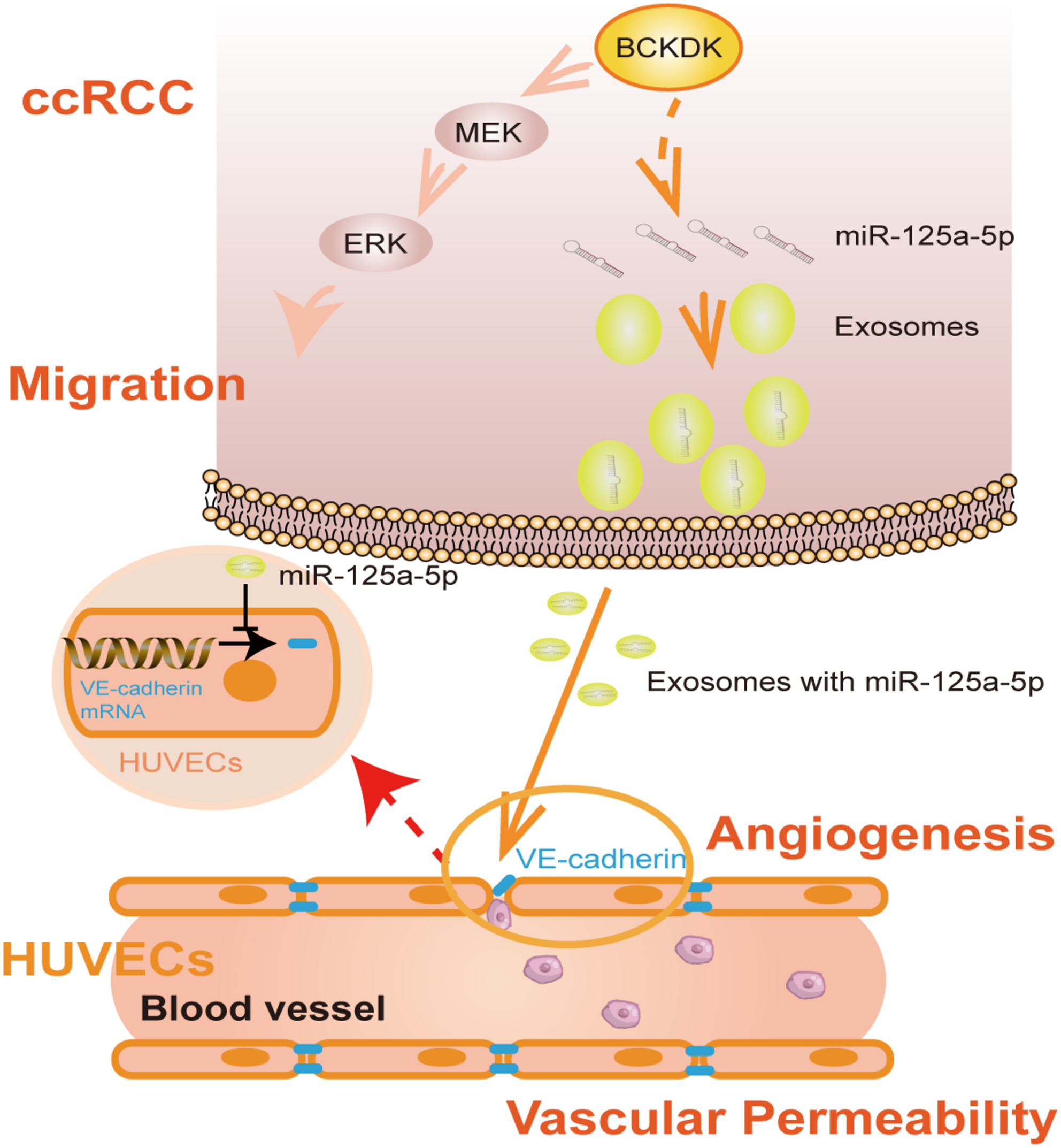
On the one hand, BCKDK can directly affect RCC metastasis by regulating the MEK-ERK signal. On the other hand, the new BCKDK/Exosomal miR-125a-5p/VE-cadherin signal axis provides a new understanding of RCC angiogenesis, markers, and potential therapeutic targets for anti-angiogenesis therapy of advanced RCC.
Collagen XVII regulates tumor growth in pancreatic cancer through interaction with the tumor microenvironment
- Pages: 4286-4298
- First Published: 08 September 2023
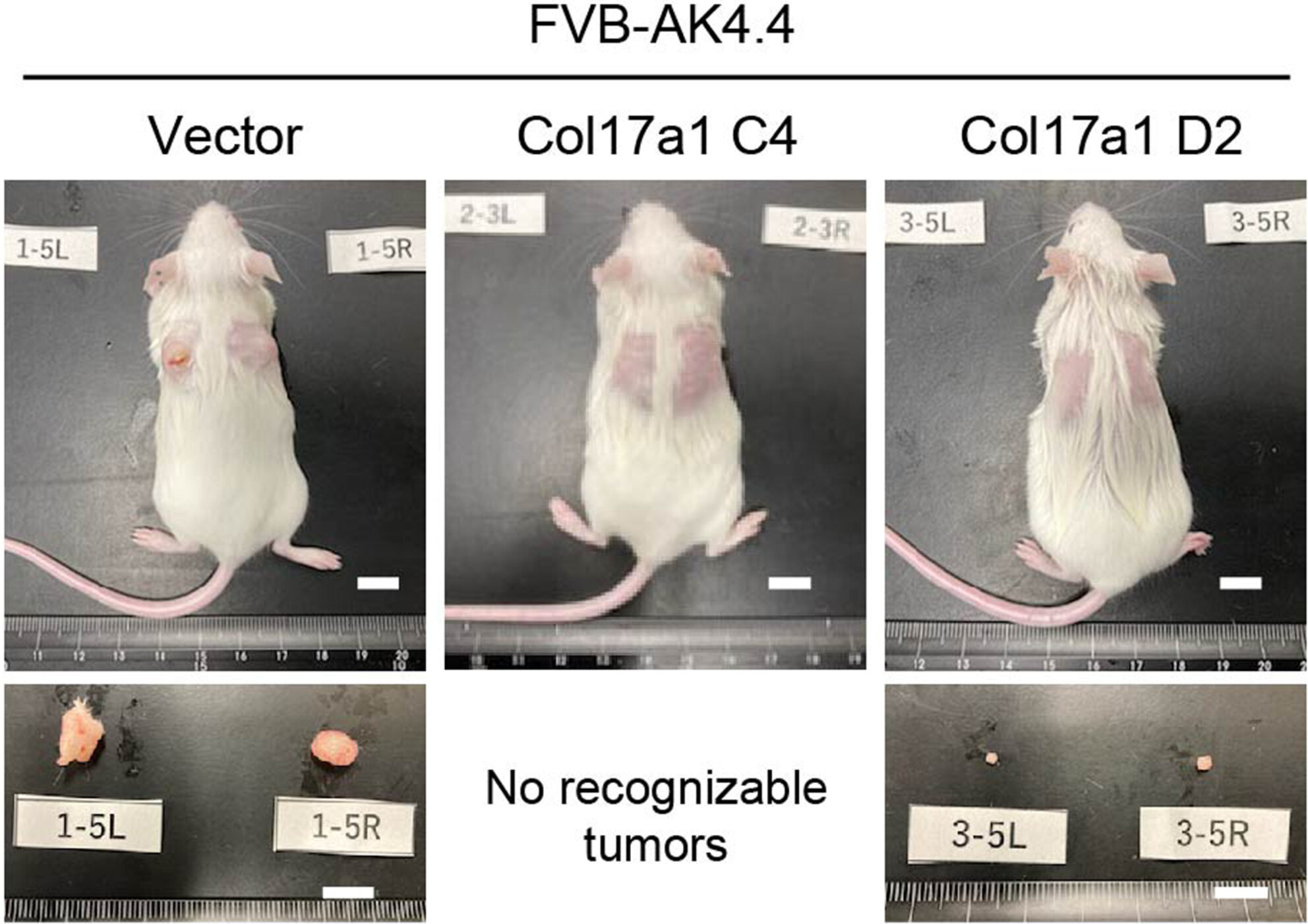
COL17A1 promoted or suppressed the tumorigenicity of KPC and AK4.4 cells, respectively, in vivo without affecting their proliferation in vitro. Tumor tissues exhibited distinct gene expression profiles including Wnt signaling and Hippo signaling between C57BL/6-KPC and FVB-AK4.4 models. COL17A1 promotes or suppresses cancer progression in a manner dependent on the interaction of tumor cells with the tumor microenvironment.
YTHDF2 promotes gallbladder cancer progression and gemcitabine resistance via m6A-dependent DAPK3 degradation
- Pages: 4299-4313
- First Published: 12 September 2023
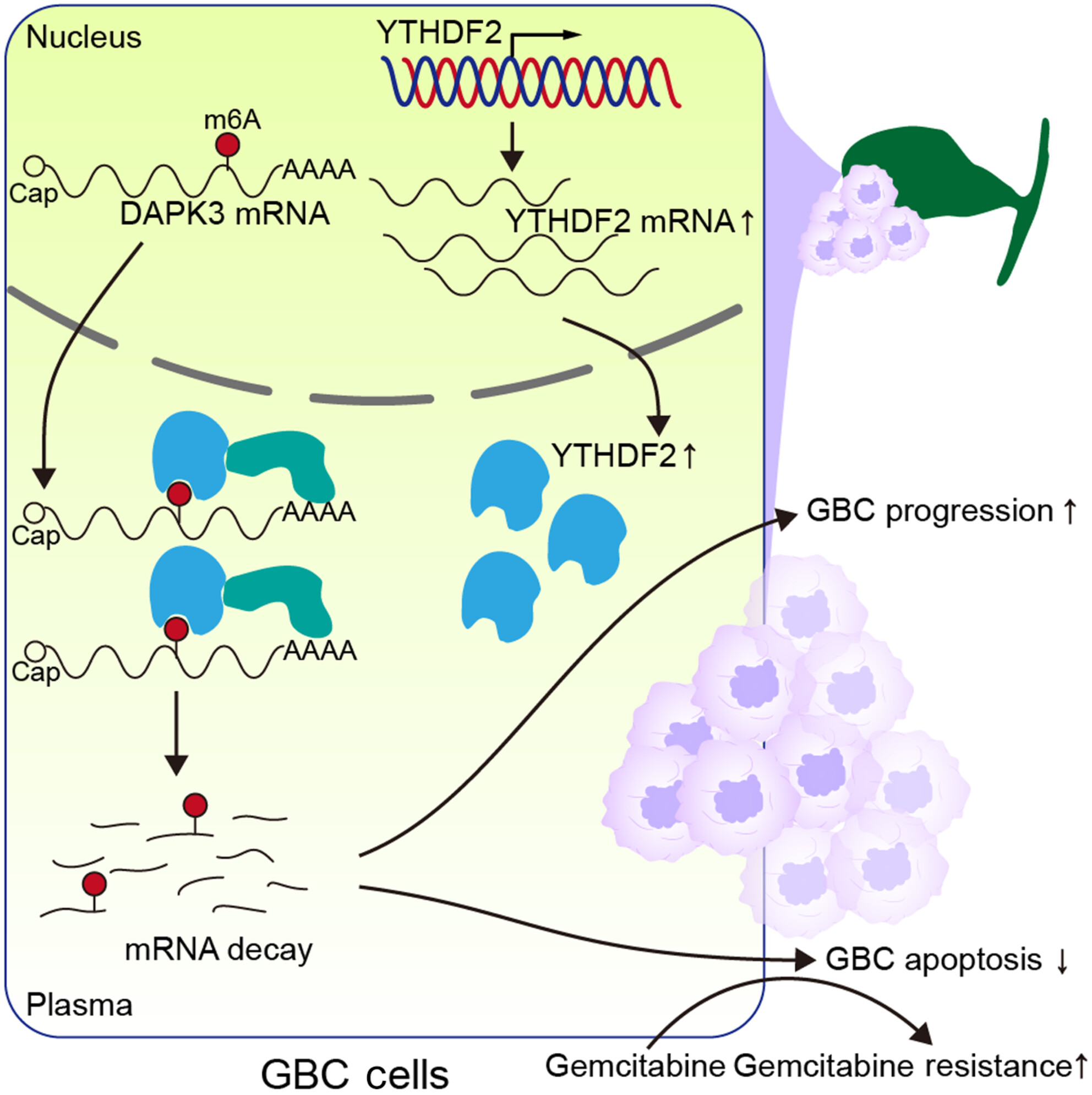
Our study reveals the essential role of YTHDF2 in gallbladder cancer (GBC). YTHDF2 was identified as the most significantly upregulated m6A-related gene in GBC and increases the mRNA degradation of the tumor suppressor DAPK3 in an m6A-dependent way, which promotes GBC progression and reduces its response to gemcitabine. These findings highlight an m6A-dependent molecular mechanism of GBC progression and provide new insights into the development of effective therapeutic approaches for GBC.
LINC01305 recruits basonuclin 1 to act on G-protein pathway suppressor 1 to promote esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- Pages: 4314-4328
- First Published: 13 September 2023
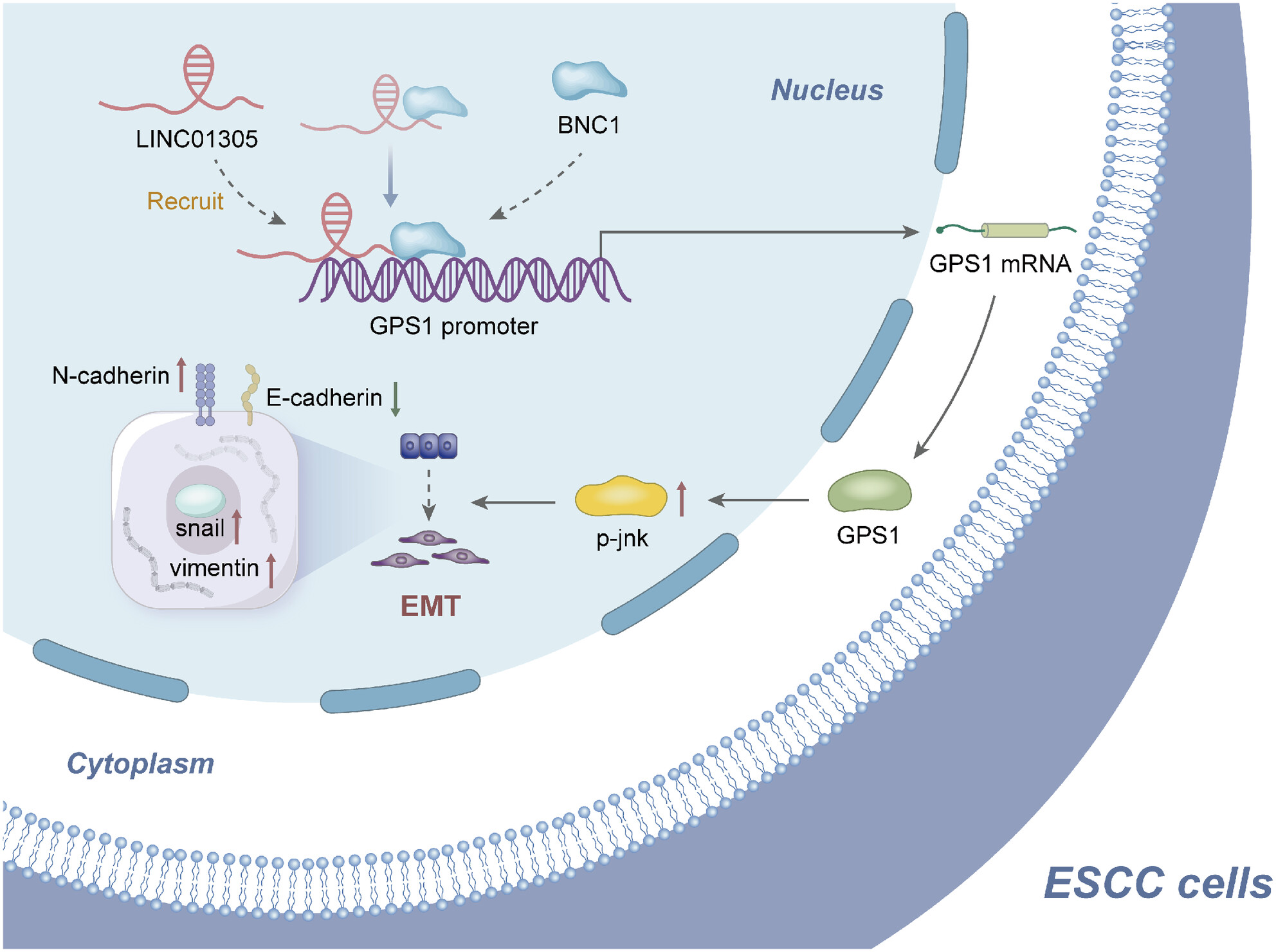
We screened the transcription factor basonuclin 1 (BNC1) to be highly expressed in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) by transcriptome sequencing of clinical samples and found that silencing BNC1 inhibited the malignant proliferation and metastasis ability of ESCC in vitro and in vivo. Furthermore, other experiments such as RNA immunoprecipitation, RNA pull-down, and ChIP sequencing revealed and verified the molecular mechanism by which LINC01305 recruits BNC1 to act on the GPS1 promoter to promote JNK phosphorylation and then mediate the epithelial–mesenchymal transition process of ESCC. Finally, clinical analysis revealed that BNC1 expression was elevated in moderately and poorly differentiated and lymph node metastatic ESCC tissues, which has the potential as a clinical diagnostic marker and targeted therapy.
Genomic gain/methylation modification/hsa-miR-132-3p increases RRS1 overexpression in liver hepatocellular carcinoma
- Pages: 4329-4342
- First Published: 13 September 2023
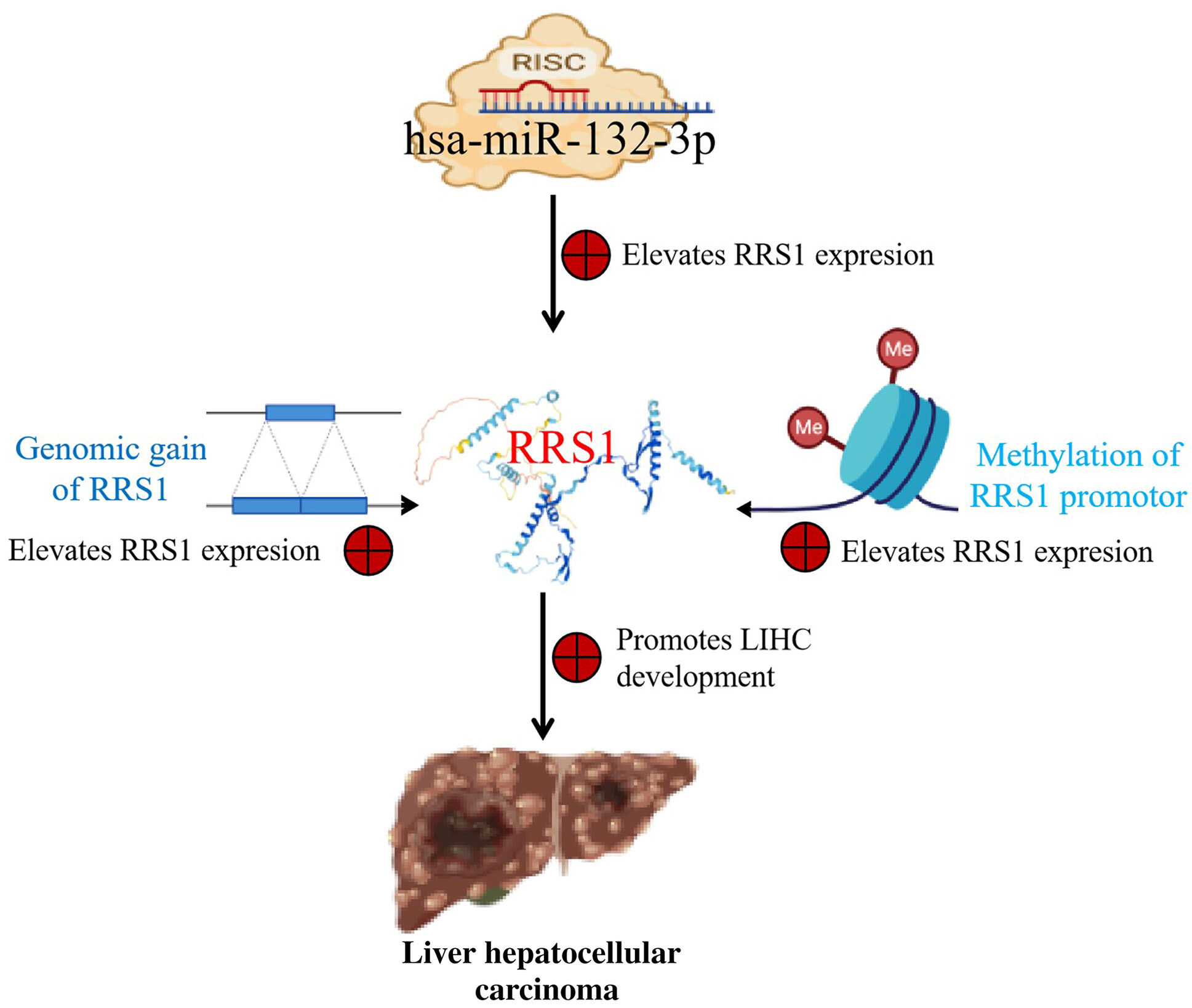
Low methylation of ribosome biogenesis regulator 1 homolog (RRS1) promoter and its genomic gain may elevate RRS1 expression and predict poor prognosis for liver hepatocellular carcinoma (LIHC). Increased hsa-miR-132-3p expression may elevate RRS1 expression and result in poor prognosis for LIHC. Hsa-miR-132-3p inhibition can decrease RRS1 expression and the development of liver tumor cell lines.
Cell, Molecular, and Stem Cell Biology
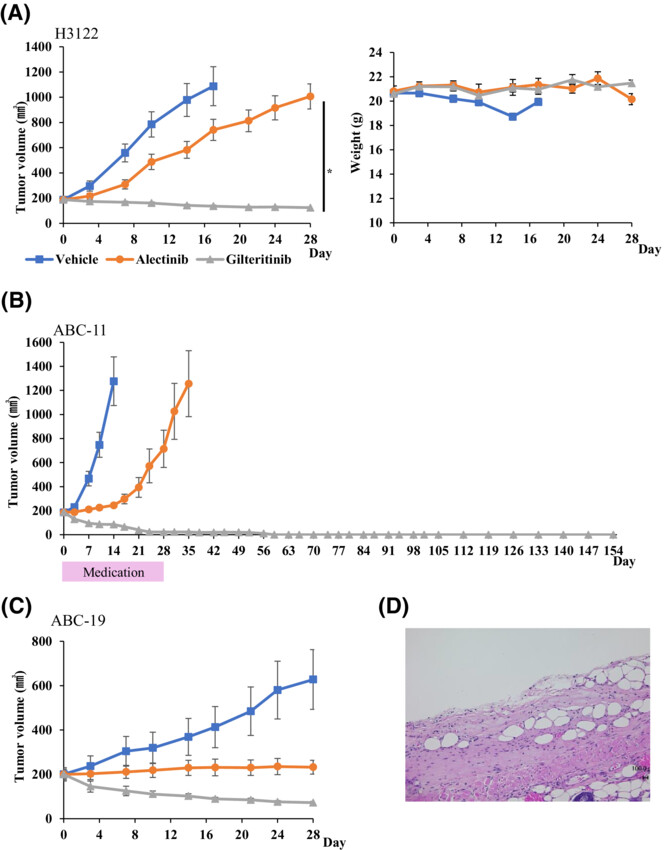
Efficacy of gilteritinib in comparison with alectinib for the treatment of ALK-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 4343-4354
- First Published: 15 September 2023
Distinct functions between ferrous and ferric iron in lung cancer cell growth
- Pages: 4355-4364
- First Published: 08 September 2023
Cholesterol biogenesis is a PTEN-dependent actionable node for the treatment of endocrine therapy-refractory cancers
- Pages: 4365-4375
- First Published: 14 September 2023
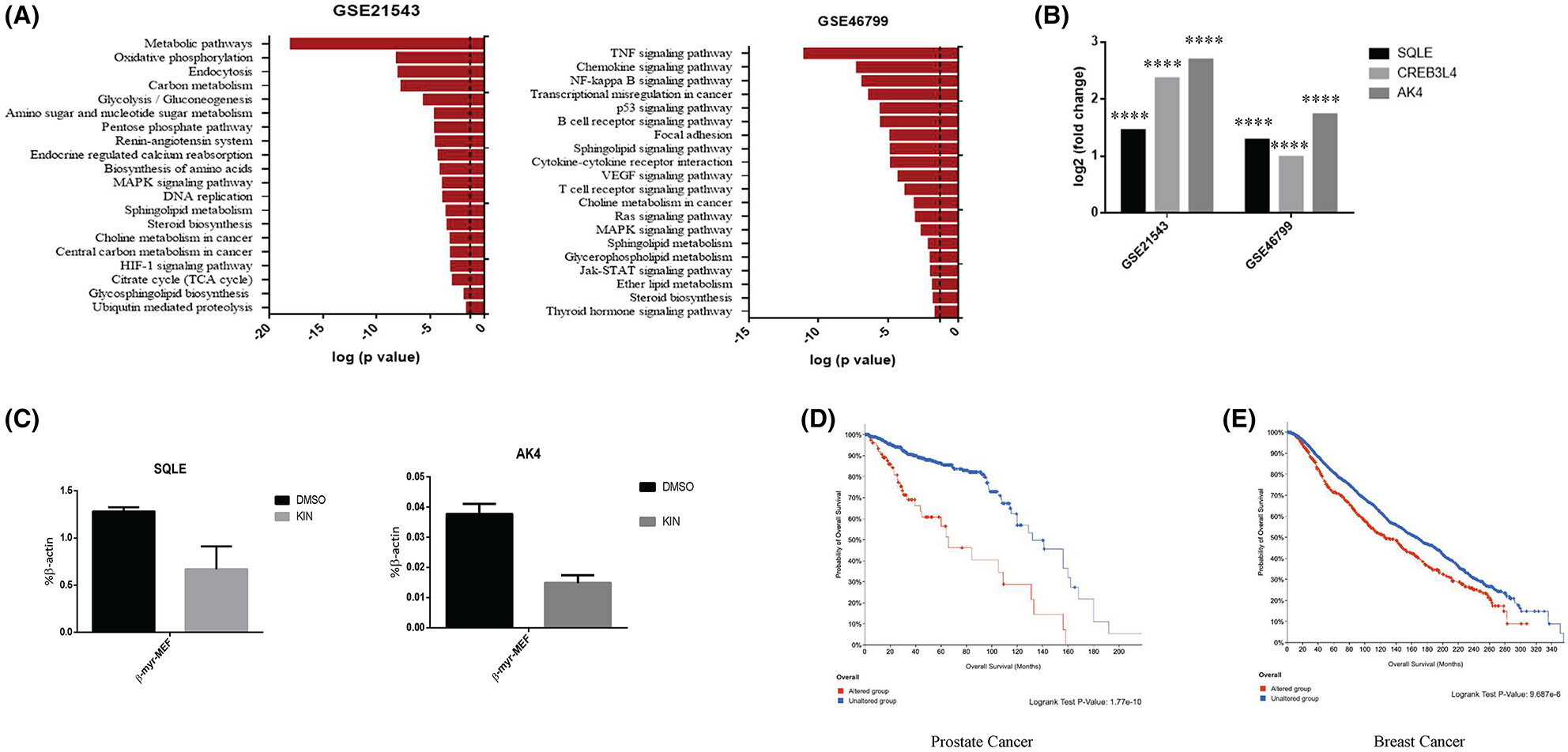
In this study, we found that PI3K activation upregulated metabolic pathways that fine-tuned the cholesterol and steroid biogenesis. According to our data, the cholesterol synthesis pathway could constitute a metabolic vulnerability for PTEN-deficient cancers, and we speculate that this strategy has the potential to treat endocrine therapy-refractory breast and prostate cancers.
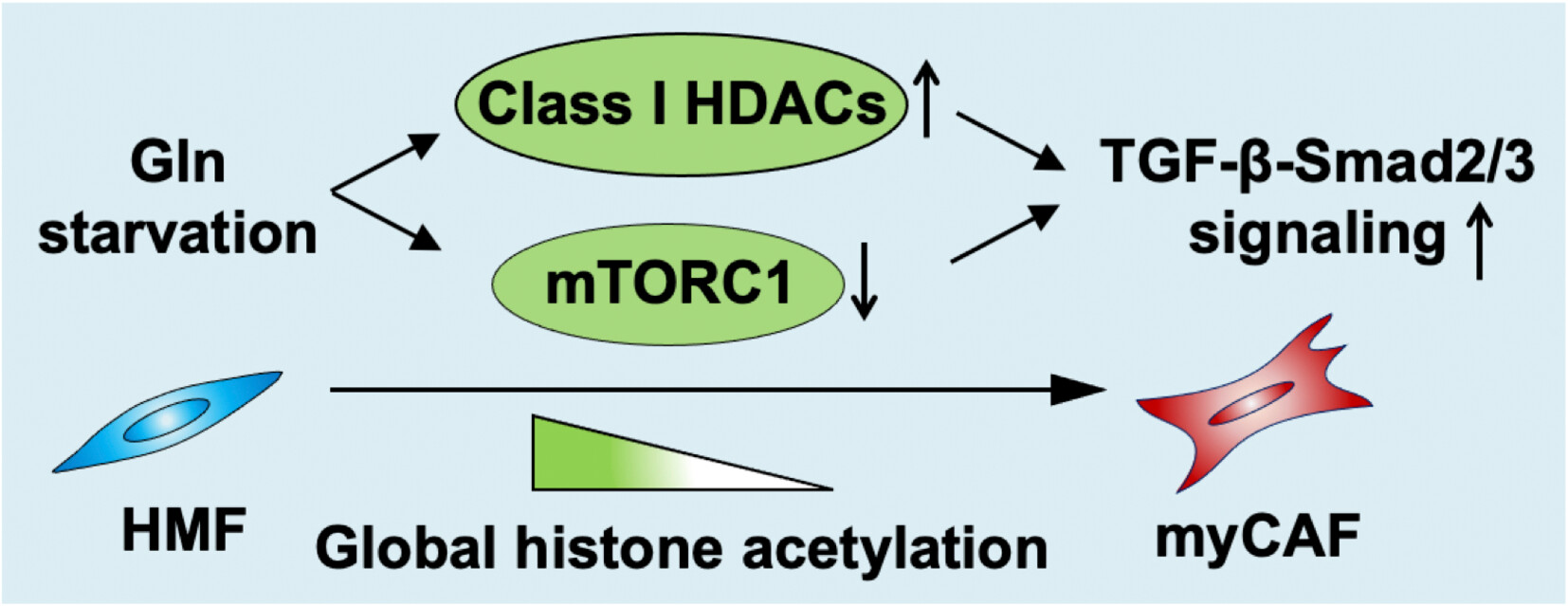
Glutamine deficiency drives transforming growth factor-β signaling activation that gives rise to myofibroblastic carcinoma-associated fibroblasts
- Pages: 4376-4387
- First Published: 14 September 2023
Increased mitochondria are responsible for the acquisition of gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer cell lines
- Pages: 4388-4400
- First Published: 12 September 2023
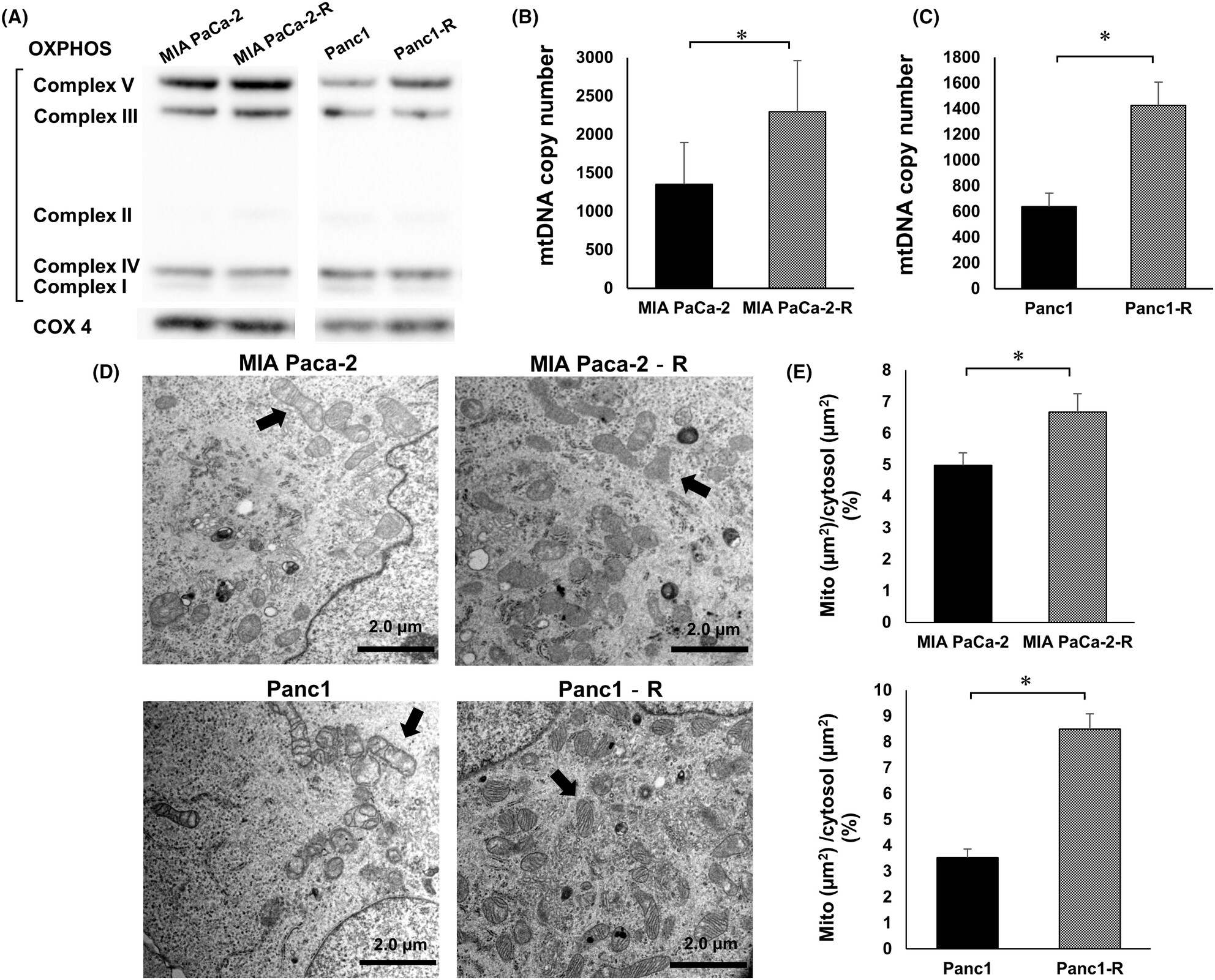
Mitochondria were increased in acquired GEM-resistant pancreatic cancer cell lines, which induced oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) and upregulation of BCL2 and BCL-xL anti-apoptotic proteins. As a result of OXPHOS, the AMP/ATP ratio and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activity were decreased, which activated the heat shock factor 1 (HSF1)–heat shock protein (HSP) pathway to promote environmental stress tolerance.
Clinical Research
Suitability of respiratory endoscopy for sampling malignant thoracic tumors for comprehensive genomic profiling
- Pages: 4401-4412
- First Published: 21 September 2023
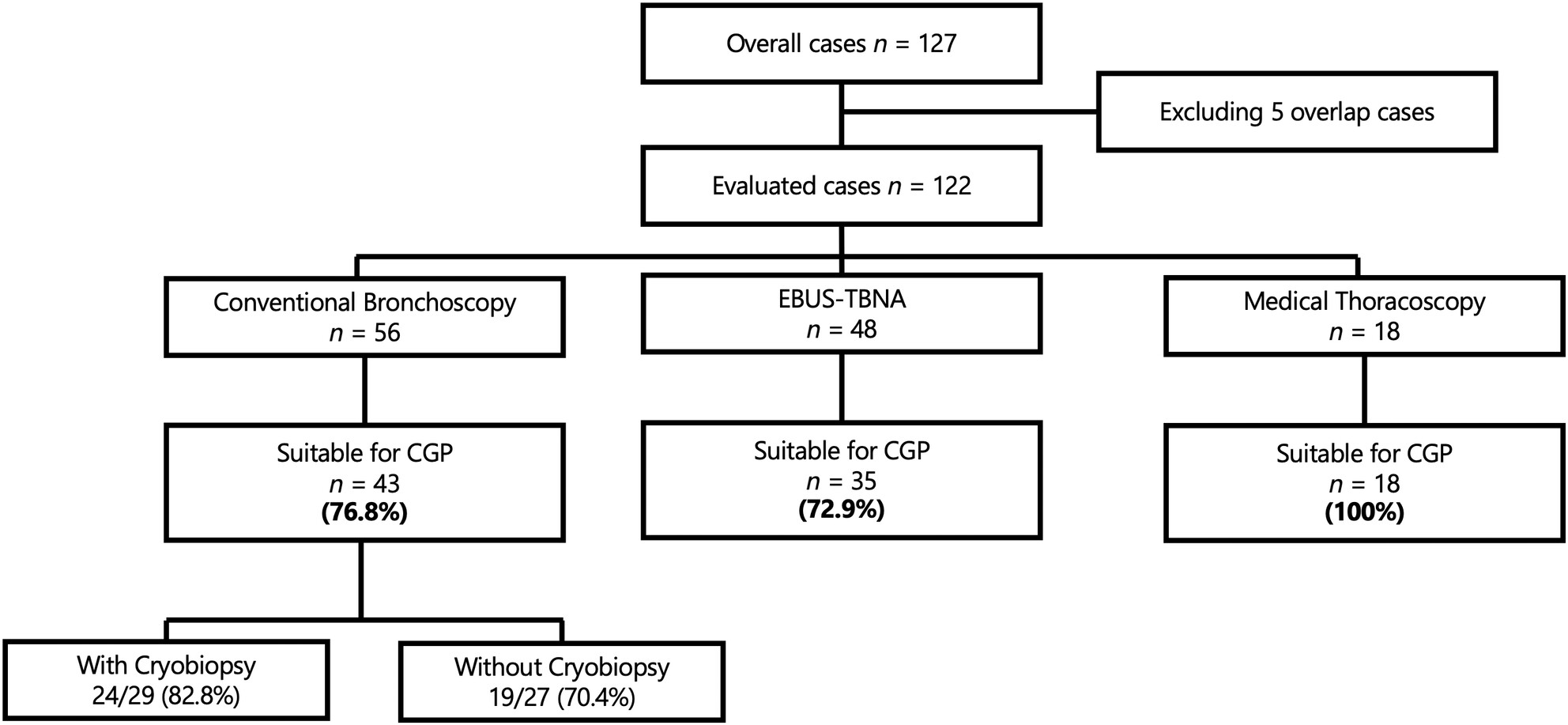
The findings of this study demonstrate that specimens obtained through respiratory endoscopy are suitable for comprehensive genome profiling in the population including primary intrathoracic tumors and thoracic metastases of extrathoracic origin. In particular, medical thoracoscopy and conventional bronchoscopy involving cryobiopsy have proven to be useful, with suitability rates of 100% (18/18 cases) and 82.8% (24/29 cases), respectively.
Drug Discovery and Delivery
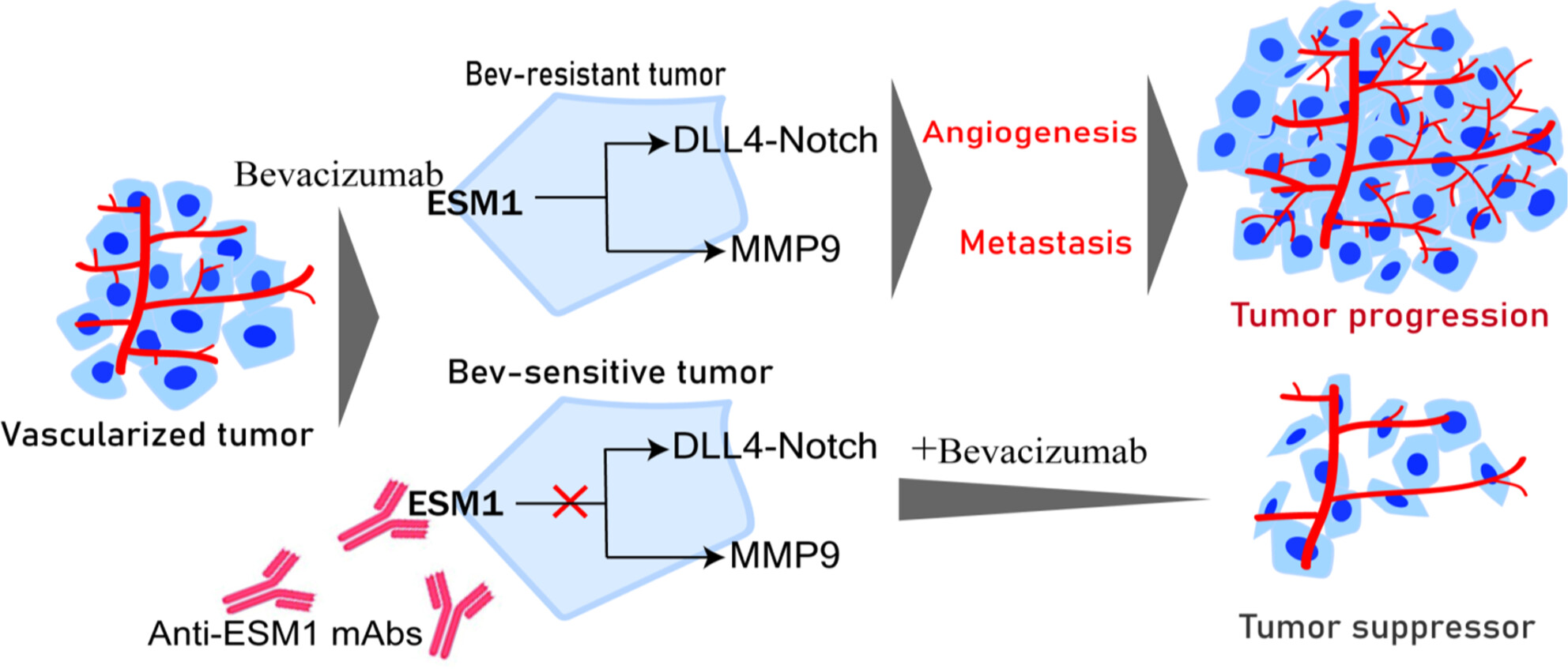
Novel specific anti-ESM1 antibodies overcome tumor bevacizumab resistance by suppressing angiogenesis and metastasis
- Pages: 4413-4425
- First Published: 16 September 2023
Epidemiology and Prevention
Human papillomavirus vaccine impact on invasive cervical cancer in Japan: Preliminary results from cancer statistics and the MINT study
- Pages: 4426-4432
- First Published: 08 September 2023
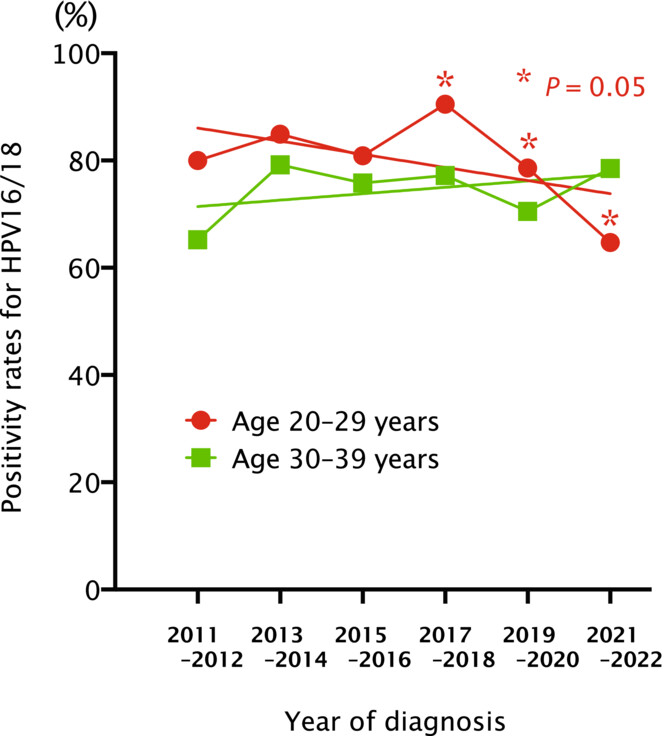
Using data from nationwide cancer registries, we showed the declining trends in newly diagnosed cervical cancer cases among Japanese women aged 20–29 years after the introduction of the HPV vaccination program; no similar trend was observed for older age groups. In addition, attribution of vaccine types HPV16 and HPV18 to invasive cervical cancer was reduced only among young women aged 20–29 years. This is the first report to suggest population-level effects of HPV vaccination on invasive cervical cancer in Japan.
Association between adherence to Eat-Lancet diet and incidence and mortality of lung cancer: A prospective cohort study
- Pages: 4433-4444
- First Published: 31 August 2023
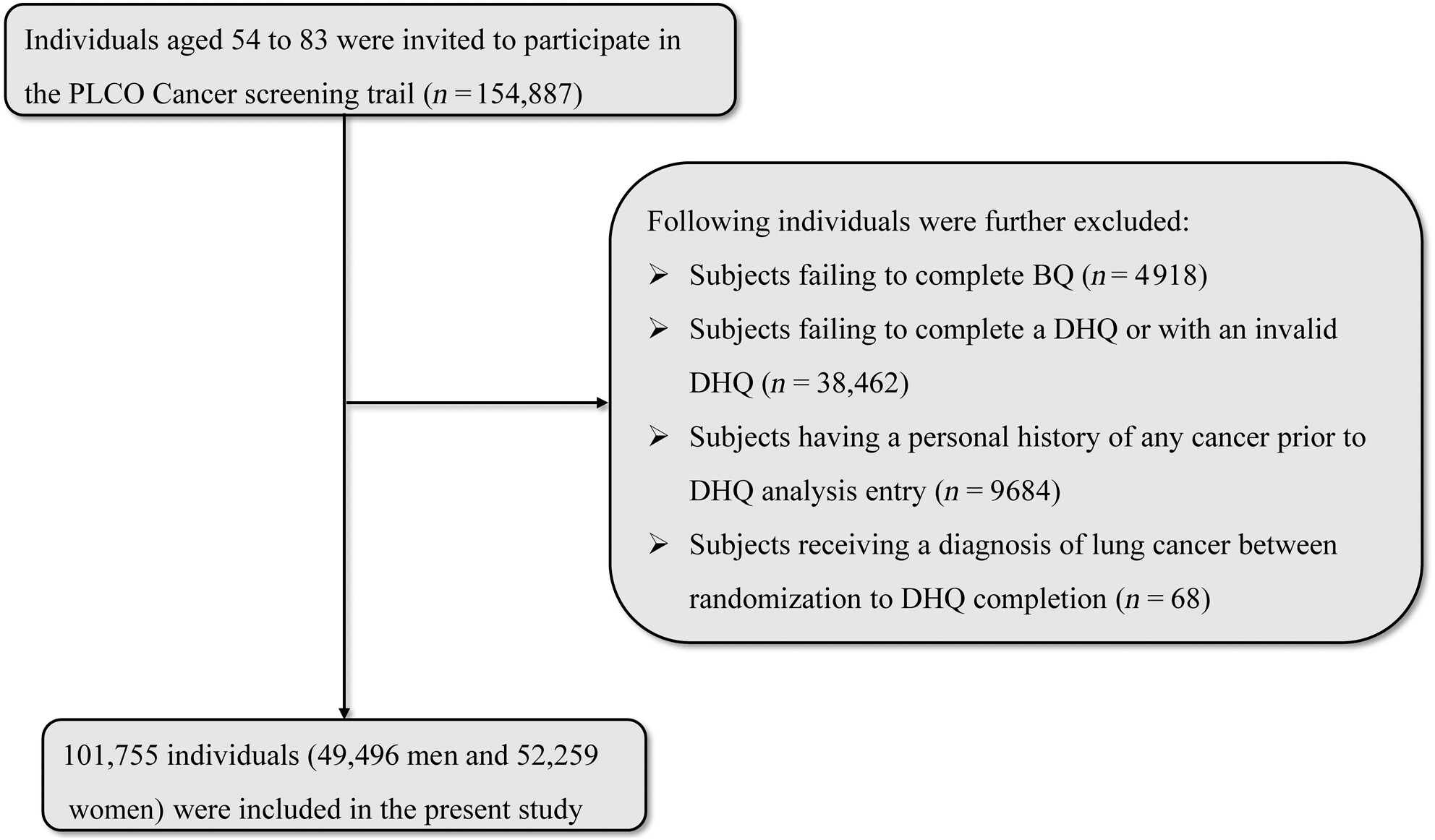
Adhering to the Eat-Lancet diet (ELD) is linked to reduced risk of chronic diseases and mortality, but its relationship with lung cancer incidence and mortality remains uncertain. Here, the authors addressed this gap through a prospective study on 101,755 PLCO trial adults in the USA. The results suggested that higher ELD score was associated with a reduced risk of 27% in lung cancer incidence and 26% in lung cancer mortality, particularly in non–small-cell lung cancer.
Genetics, Genomics and Proteomics
Upregulated SPAG6 correlates with increased STAT1 and is associated with reduced sensitivity of interferon-α response in BCR::ABL1 negative myeloproliferative neoplasms
- Pages: 4445-4458
- First Published: 08 September 2023
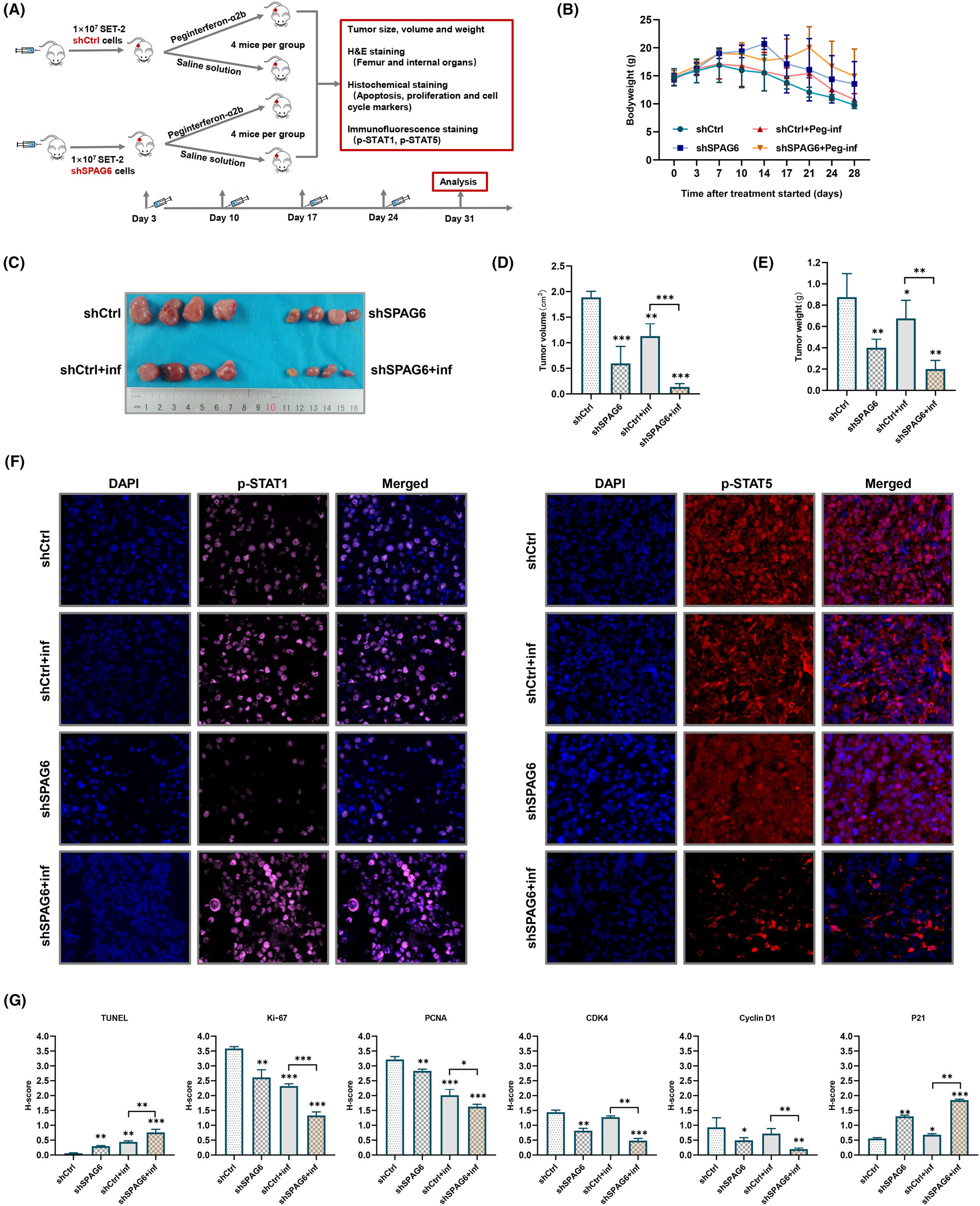
We clarified for the first time that sperm-associated antigen 6 (SPAG6) is significantly upregulated in myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN)-derived leukemia cells and regulated by signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1), showing pro-oncogenic activity. Downregulation of SPAG6 could impair autocrine function of inflammatory cytokines, reduce reactivation of the JAK-STAT pathway, and sensitize interferon-α response through enhancing the induction level of STAT1 in MPN.
Pathology
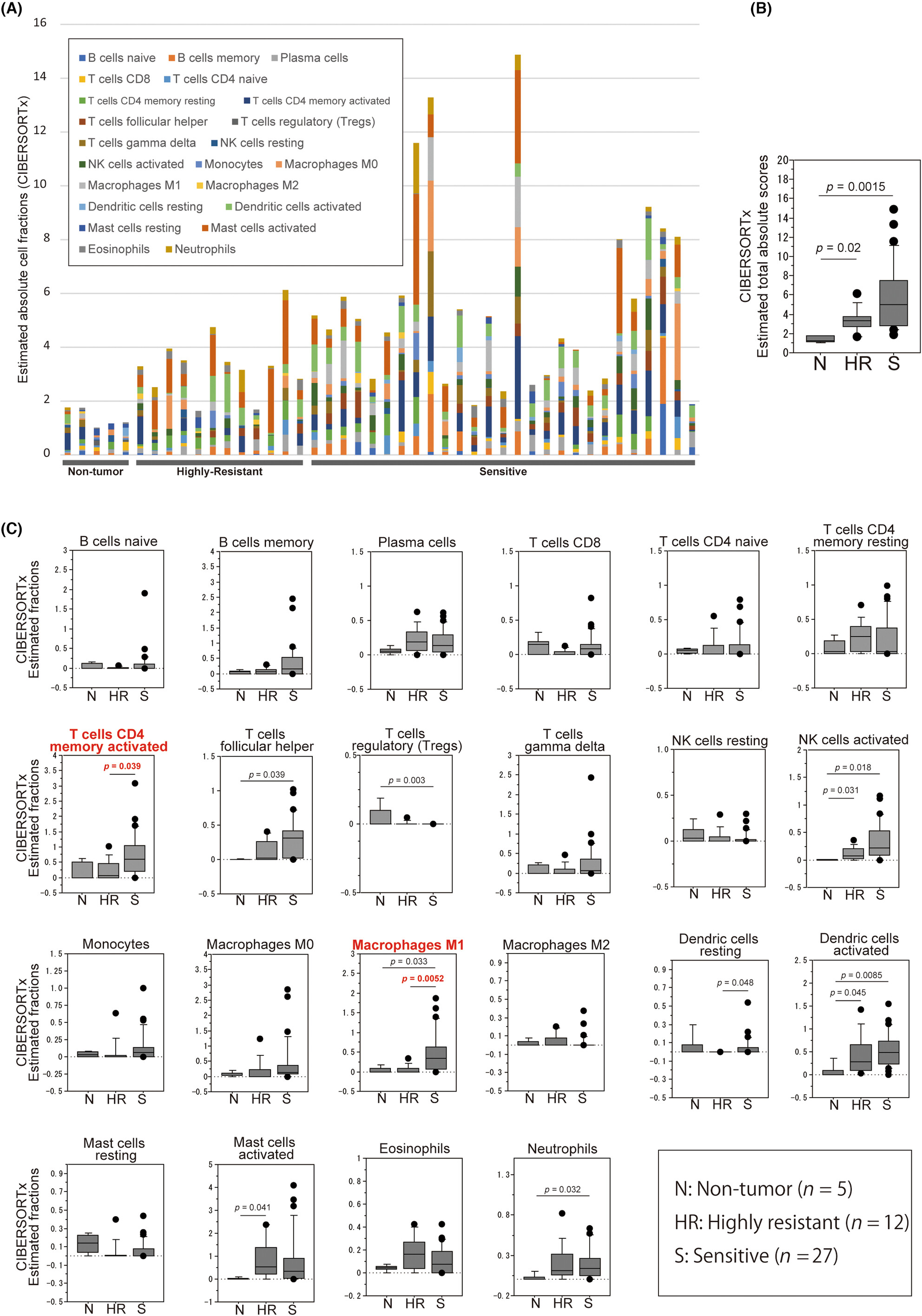
Association of immune-related expression profile with sensitivity to chemotherapy in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- Pages: 4459-4474
- First Published: 15 September 2023
CORRECTION
Correction to Circular RNA hsa_circ_001895 serves as a sponge of microRNA-296-5p to promote clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression by regulating SOX12
- Page: 4475
- First Published: 02 October 2023