Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
IN THIS ISSUE
In this issue: Volume 114, Issue 12, December 2023
- Pages: 4481-4483
- First Published: 22 November 2023
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Peripheral blood inflammatory biomarkers dynamics reflect treatment response and predict prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer patients with neoadjuvant immunotherapy
- Pages: 4484-4498
- First Published: 20 September 2023
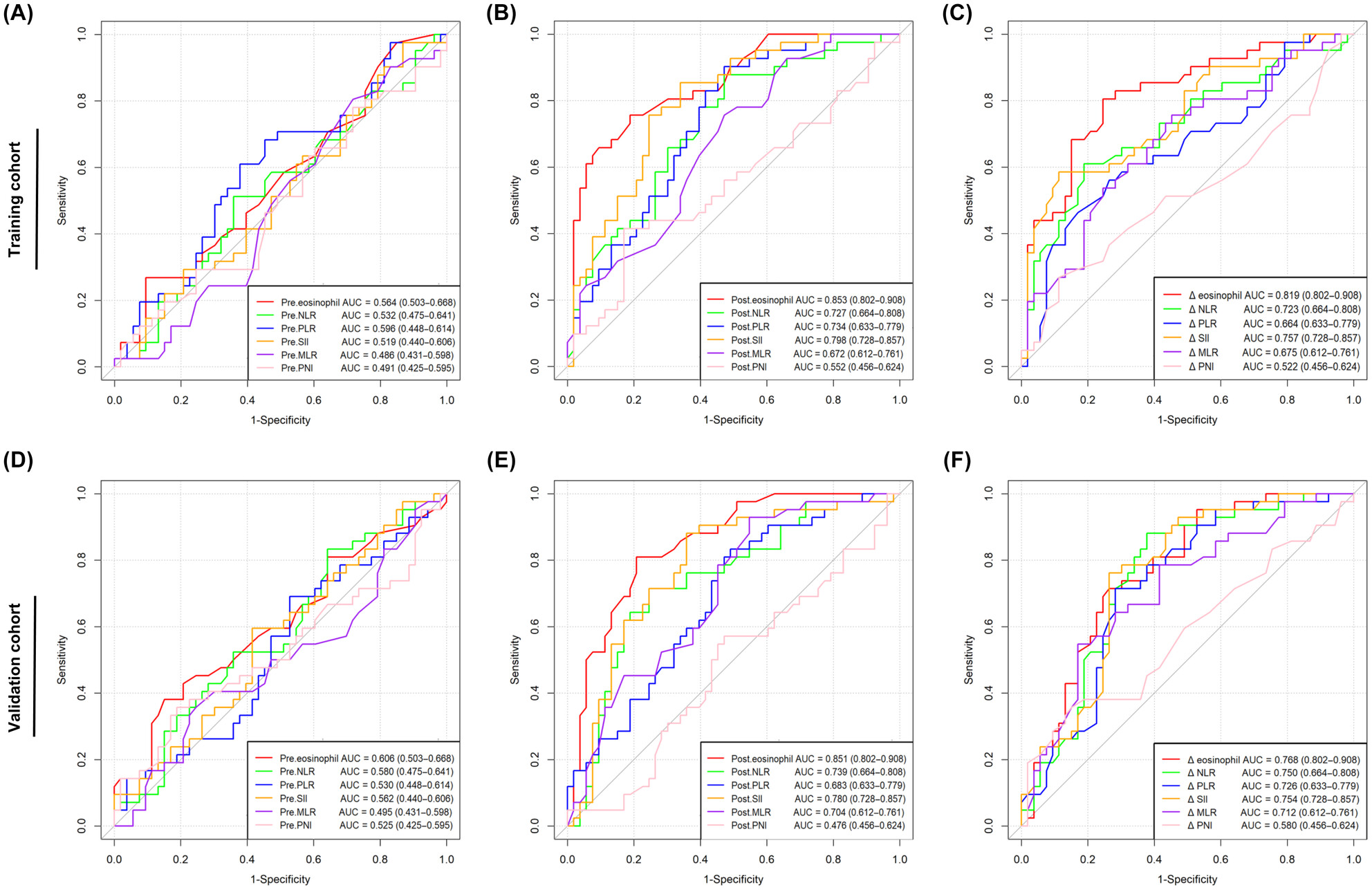
Post-treatment eosinophil fraction, SII, mGPS, and ΔSII could independently predict MPR in patients treated with neoadjuvant immunotherapy in both cohorts. Furthermore, high post-treatment NLR, PLR, SII, mGPS, ΔNLR, and ΔSII were significantly correlated with poor overall survival and event-free survival of patients. We aim to construct a comprehensive predictive model by integrating these non-invasive and easily accessible peripheral blood biomarkers to design new strategies for treating NSCLC patients undergoing neoadjuvant immunotherapy.
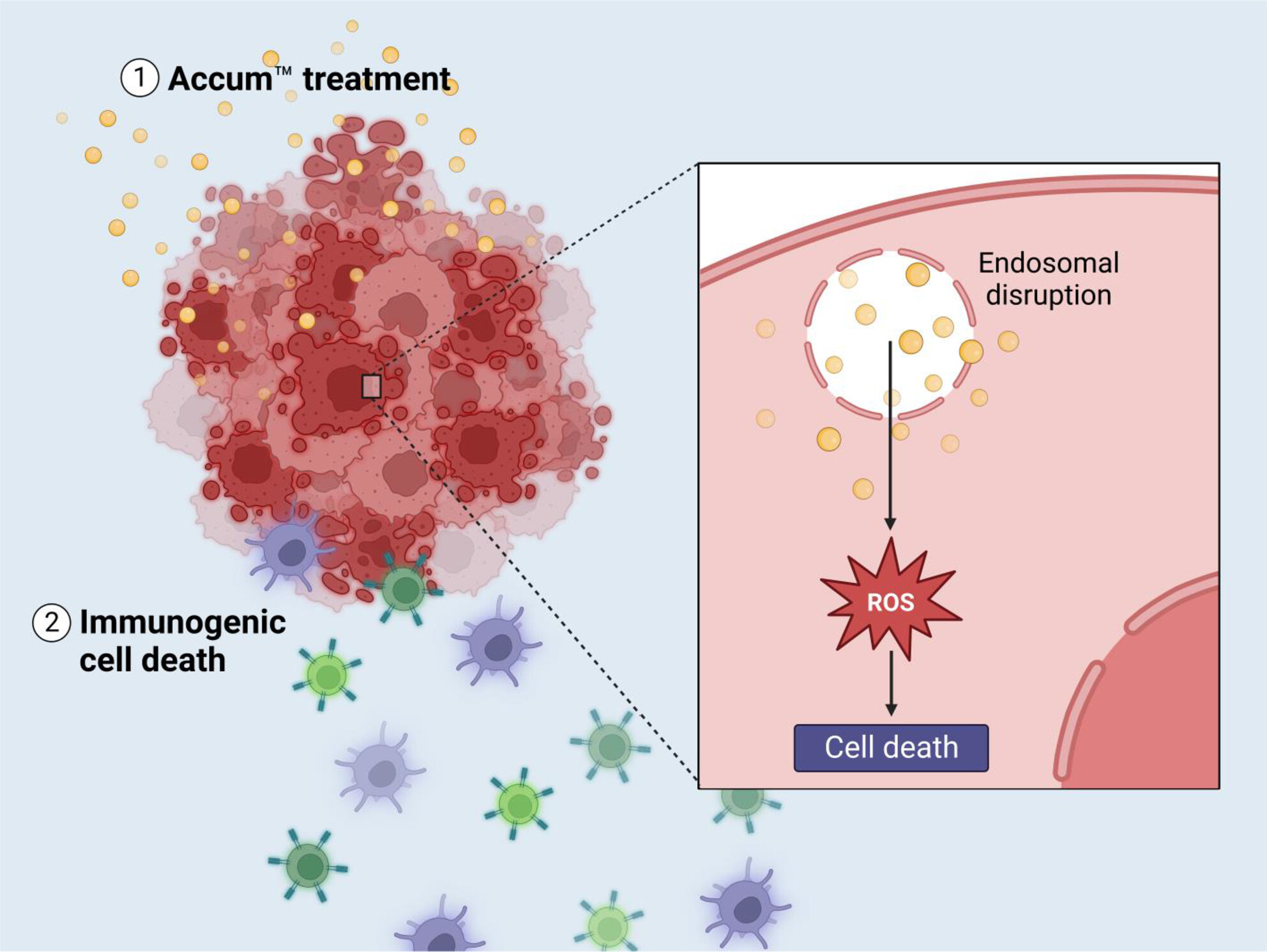
Intratumoral administration of unconjugated Accum™ impairs the growth of pre-established solid lymphoma tumors
- Pages: 4499-4510
- First Published: 29 September 2023
Eribulin is an immune potentiator in breast cancer that upregulates human leukocyte antigen class I expression via the induction of NOD-like receptor family CARD domain-containing 5
- Pages: 4511-4520
- First Published: 22 November 2023
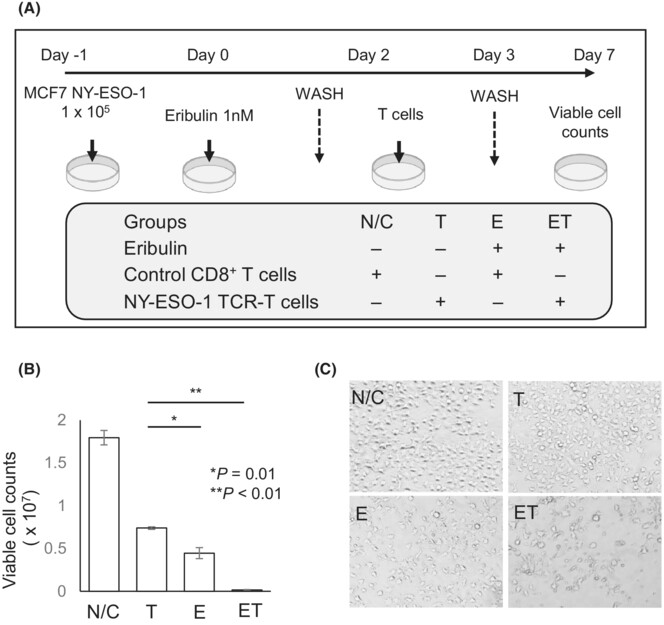
Eribulin inhibits microtubule polymerization and has been approved for recurrent metastatic breast cancer. Eribulin enhanced recognition by Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) by increasing the expression of human leukocyte antigen (HLA) class 1 via the HLA class 1 transactivator neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio family CARD domain-containing 5, thus eribulin can be used as an immunopotentiator.
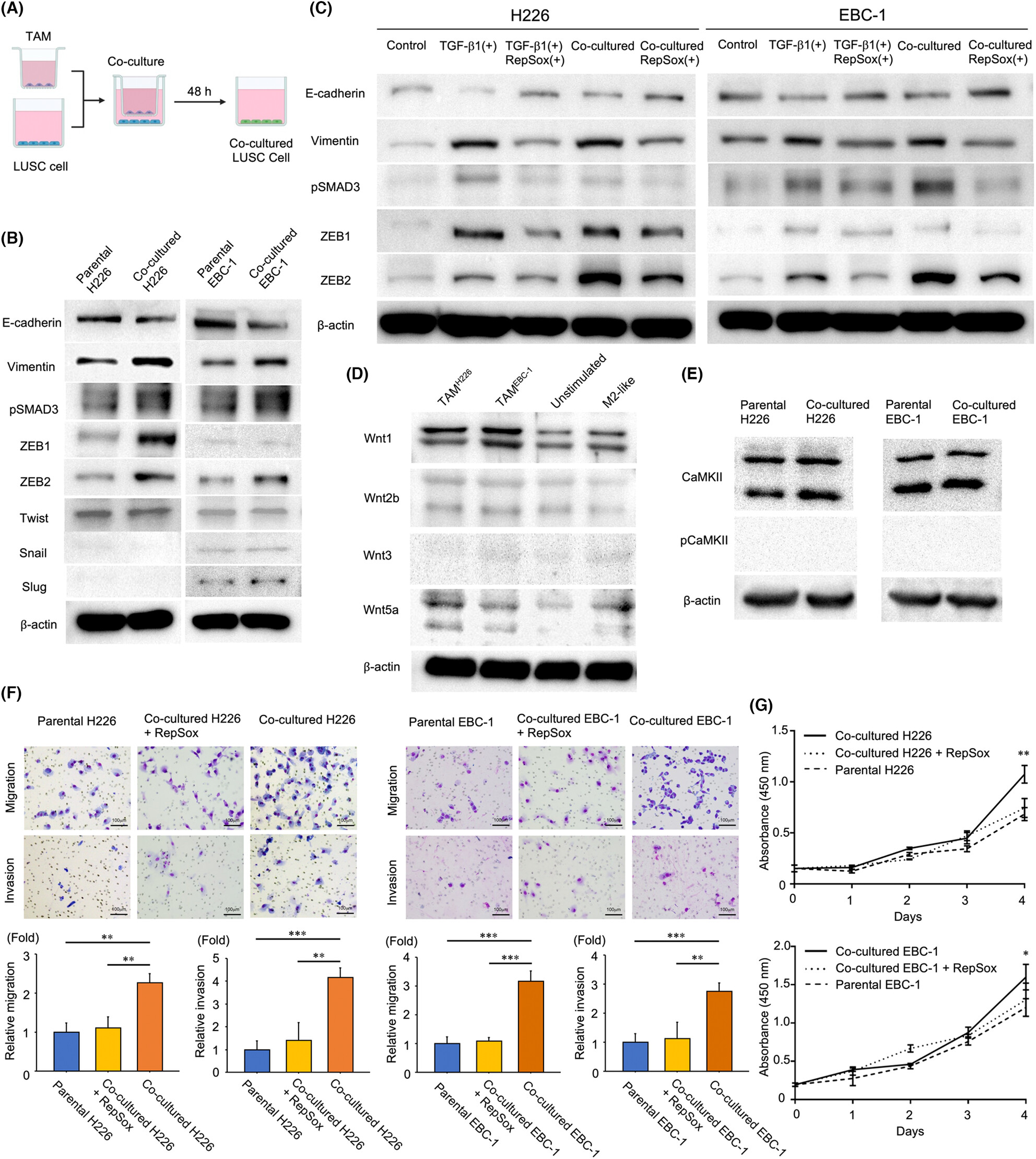
M2-like tumor-associated macrophages promote epithelial–mesenchymal transition through the transforming growth factor β/Smad/zinc finger e-box binding homeobox pathway with increased metastatic potential and tumor cell proliferation in lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Pages: 4521-4534
- First Published: 08 October 2023
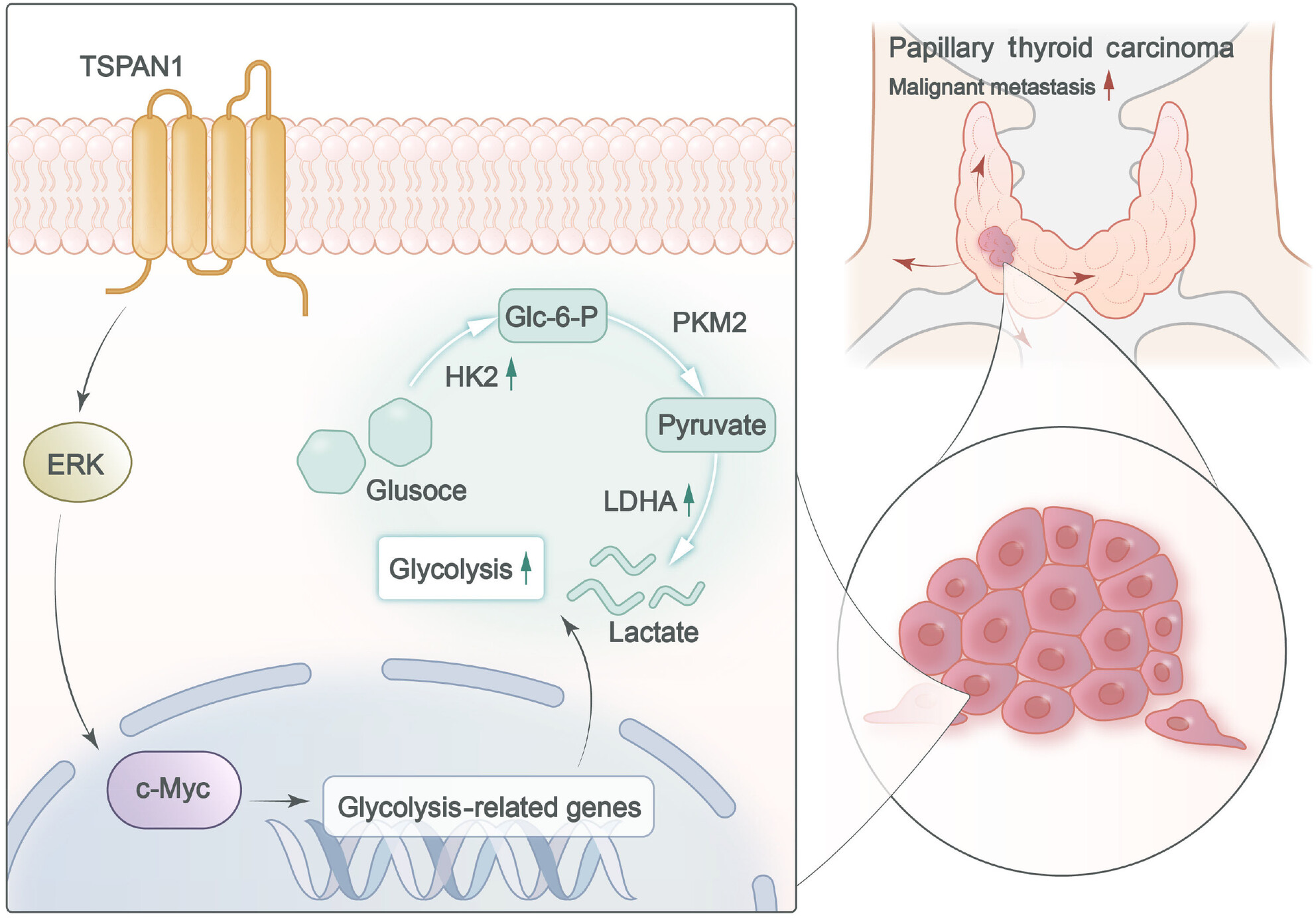
Tetraspanin 1 regulates papillary thyroid tumor growth and metastasis through c-Myc-mediated glycolysis
- Pages: 4535-4547
- First Published: 26 September 2023
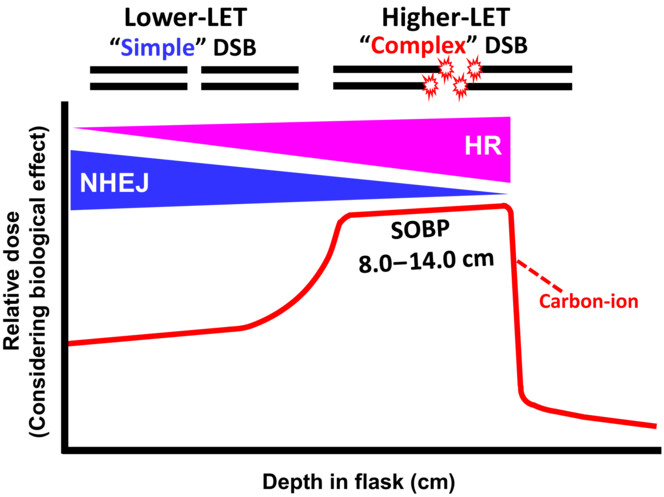
The impact of DNA double-strand break repair pathways throughout the carbon ion spread-out Bragg peak beam
- Pages: 4548-4557
- First Published: 03 October 2023
DYRK2 promotes chemosensitivity via p53-mediated apoptosis after DNA damage in colorectal cancer
- Pages: 4558-4570
- First Published: 30 September 2023
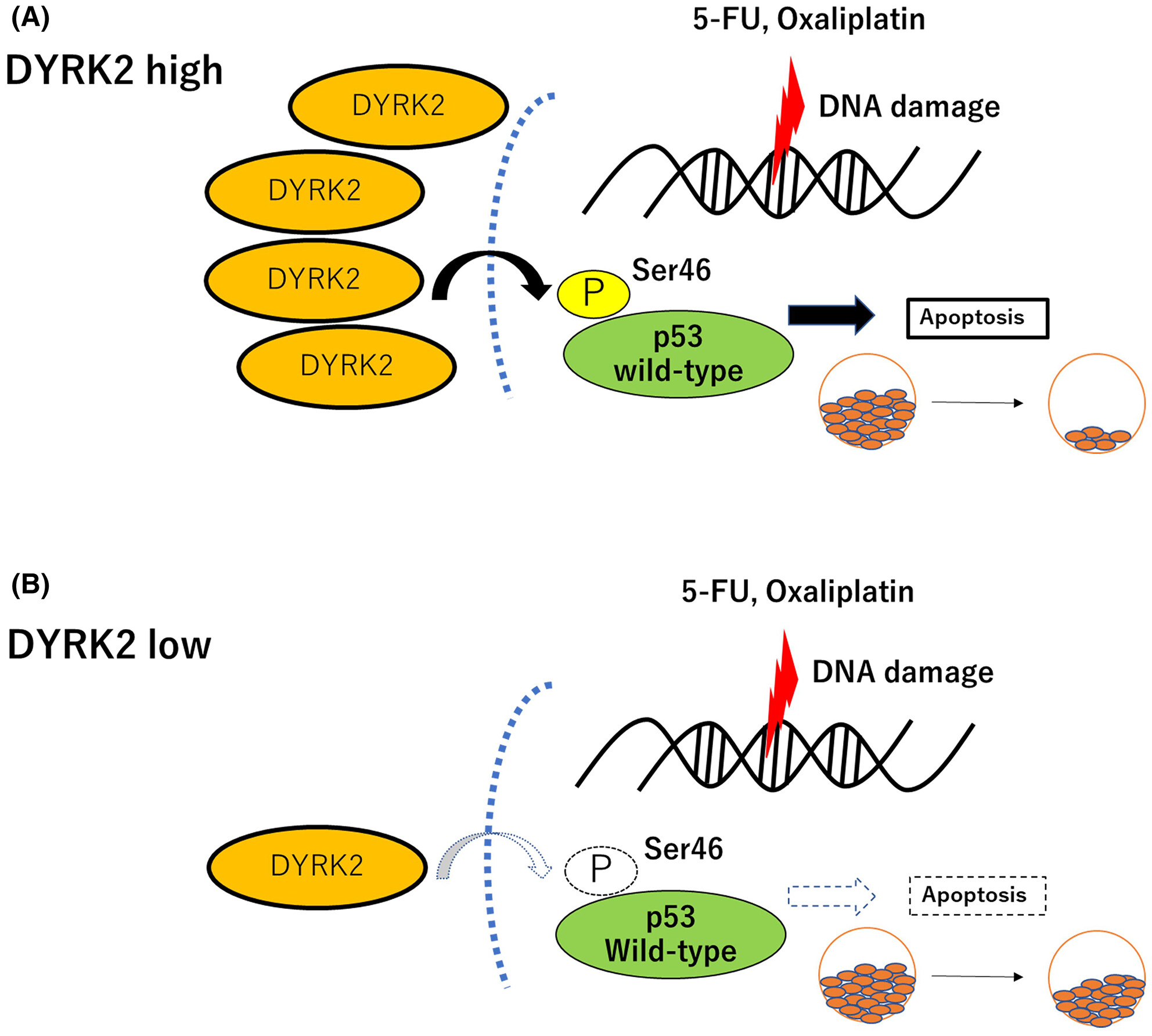
We show the strong relationship between DYRK2 expression and chemosensitivity after DNA damage in p53 wild-type, but not in p53 mutated, colorectal cancer cells. Our findings provide the importance of routine preoperative measurement of p53 status and DYRK2 expression that may help to predict chemosensitivity in patients undergoing 5-fluorouracil- and oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy for colorectal cancer.
Dual role of autotaxin as novel biomarker and therapeutic target in pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms
- Pages: 4571-4582
- First Published: 28 September 2023
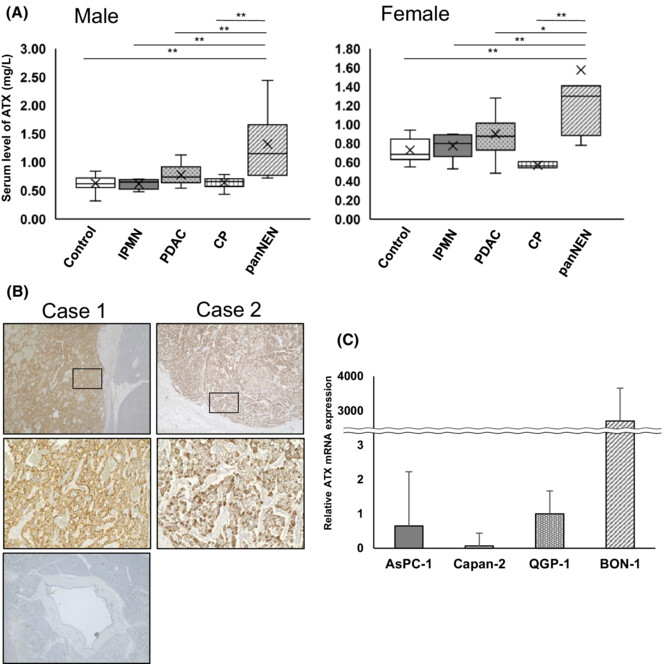
Autotaxin (ATX), which is a secreted autocrine motility factor involved in the production of a lipid mediator, was highly expressed in pancreatic endocrine neoplasm (panNEN). The mRNA expression of mRNA in panNEN cell lines was higher than in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cell lines. The serum level of ATX in panNEN patients was higher than in patients with other pancreatic diseases, and in immunohistochemical analysis of panNEN, tumor cells were stained strongly by ATX.
HOXD8 suppresses renal cell carcinoma growth by upregulating SHMT1 expression
- Pages: 4583-4595
- First Published: 26 September 2023
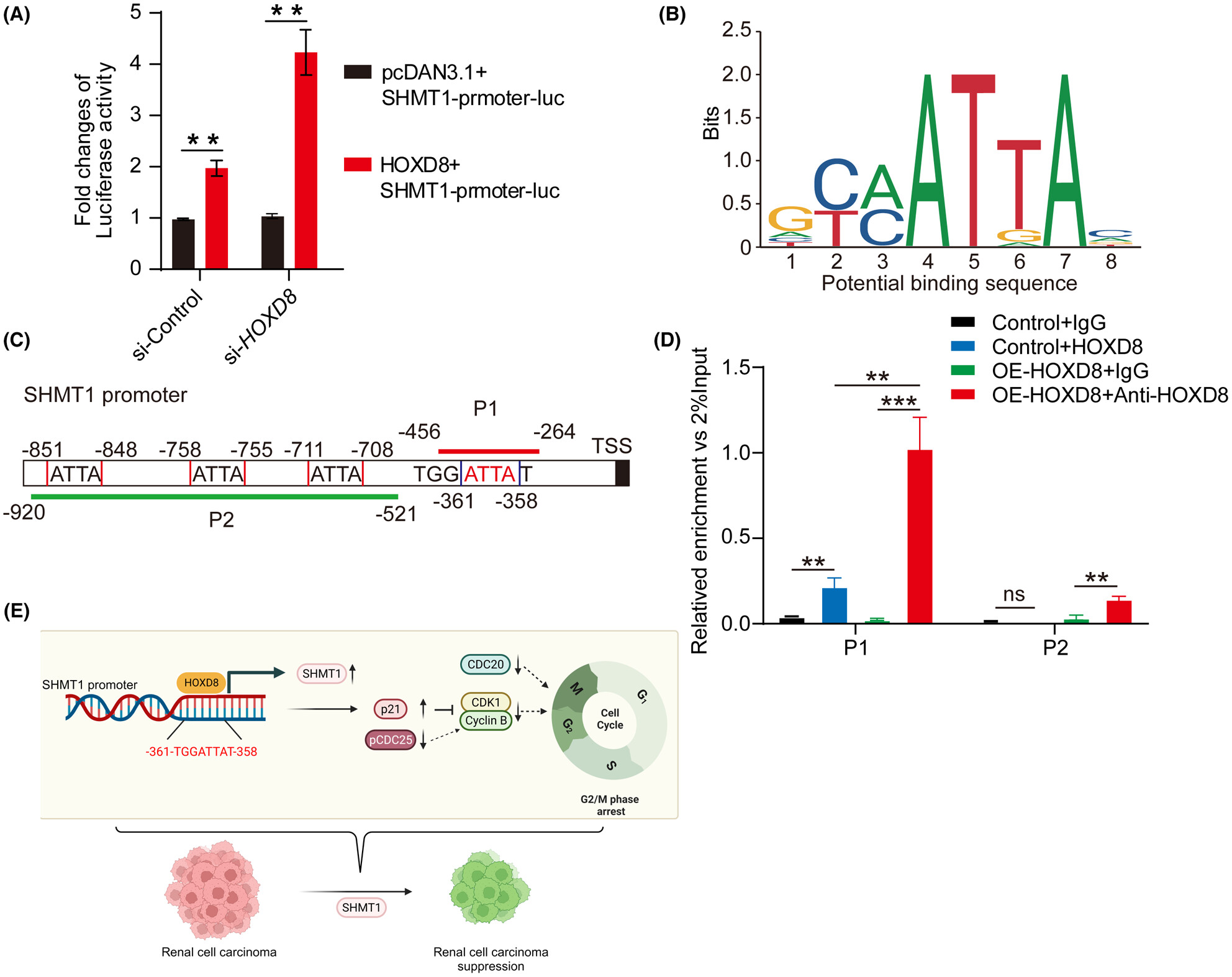
Serine hydroxymethyltransferase (SHMT)1 functions as a tumor suppressor in renal cell carcinoma (RCC). The transcription factor homeobox D8 (HOXD8) can promote SHMT1 expression and suppress RCC cell proliferation and migration, which provides new mechanisms of SHMT1 in RCC tumor growth and might be used as a potential therapeutic target candidate for clinical treatment.
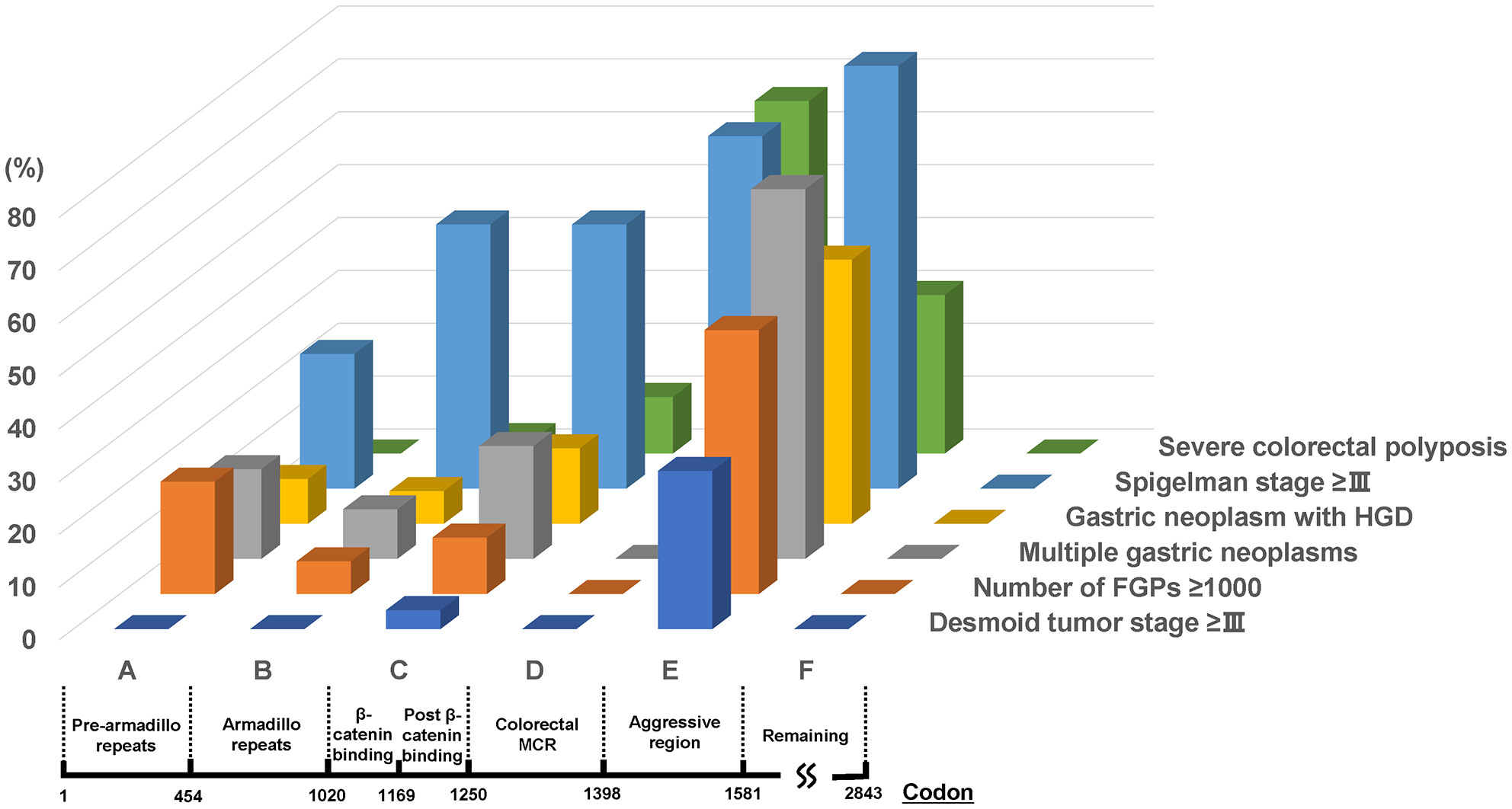
Genotype–phenotype correlation for extracolonic aggressive phenotypes in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis
- Pages: 4596-4606
- First Published: 05 October 2023
Noninvasive diagnosis of pulmonary nodules using a circulating tsRNA-based nomogram
- Pages: 4607-4621
- First Published: 28 September 2023
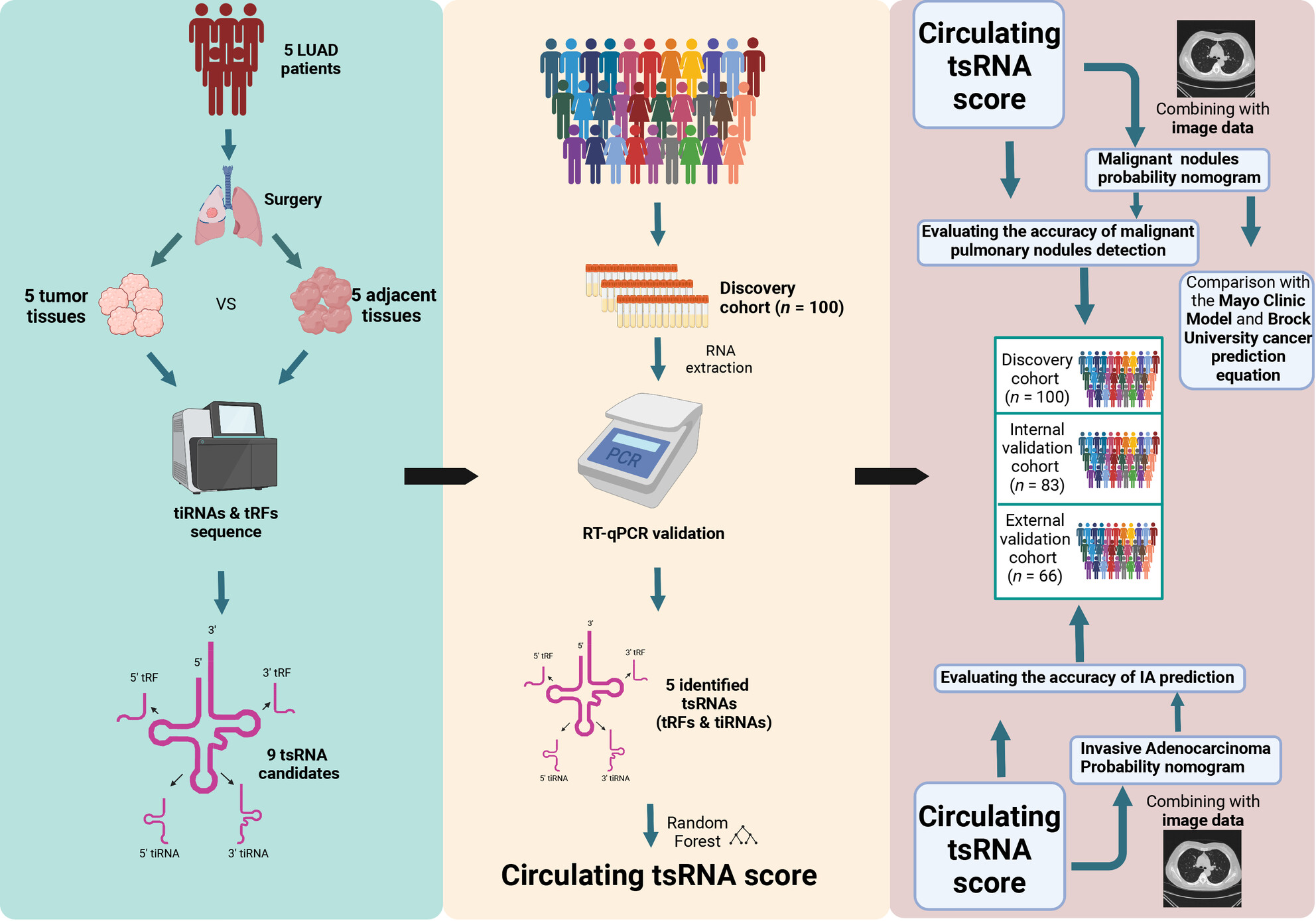
Low-dose computed tomography screening resulted in high detection rates of pulmonary nodules, which warranted invasive diagnostic procedures with high risk. We show that combining novel tsRNAs biomarkers in liquid biopsy with computed tomography information provides improved diagnostic accuracy. The model achieved robust accuracy in internal and external validation cohorts. In addition, this model provided fair results in discriminating invasive nodules from noninvasive nodules.
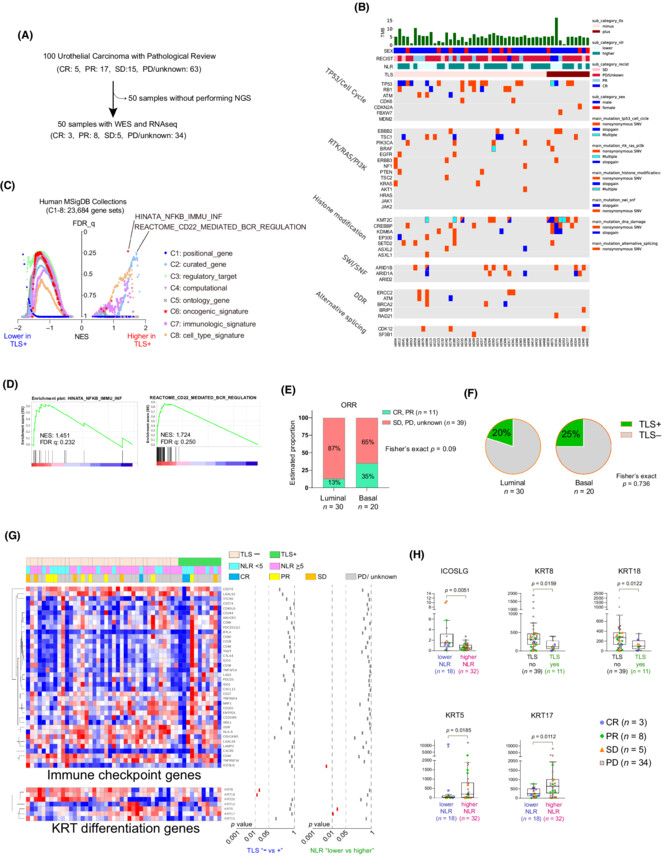
Tertiary lymphoid structure and neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio coordinately predict outcome of pembrolizumab
- Pages: 4622-4631
- First Published: 26 September 2023
Prognostic impact of cancer genomic profile testing for advanced or metastatic solid tumors in clinical practice
- Pages: 4632-4642
- First Published: 19 October 2023
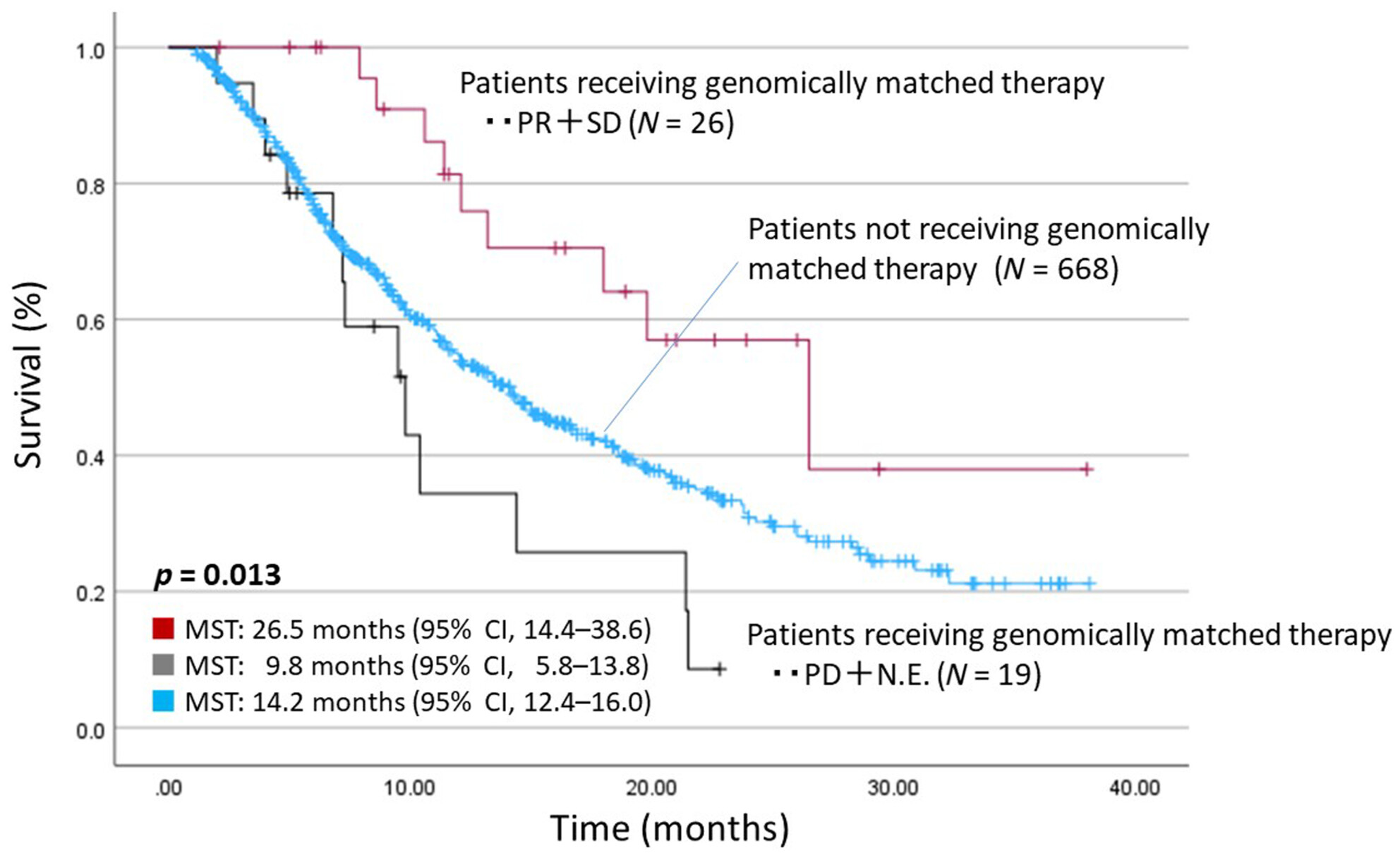
We herein first reported the prognostic impact according to the effect of genomically matched therapy after CGP testing for advanced or metastatic solid tumors in clinical practice under the Japanese national health insurance system. Although 40.0% of patients were recommended for treatment based on their gene mutations in our molecular tumor board review after CGP testing, only approximately 6.3% received this treatment. However, when treatment based on gene mutations was initiated and partial response or stable disease treatment effects were achieved, OS was significantly prolonged.
Subcutaneous epcoritamab monotherapy in Japanese adults with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- Pages: 4643-4653
- First Published: 03 November 2023
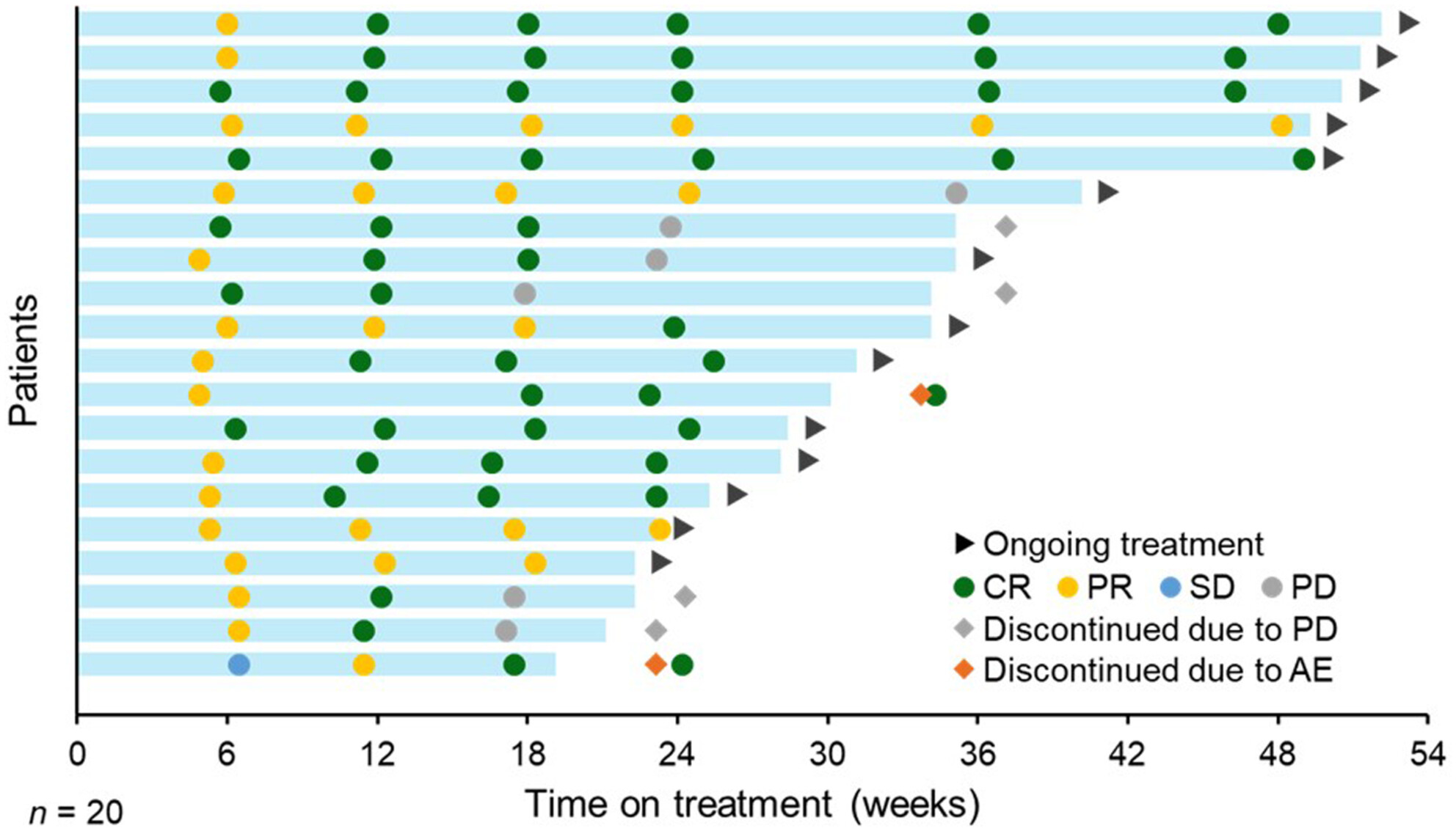
The EPCORE NHL-3 phase I/II trial is evaluating the efficacy and safety of epcoritamab subcutaneous monotherapy in Japanese patients with relapsed or refractory (R/R) CD20+ B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma previously treated with two or more lines of therapy. At a median follow-up of 8.4 months, overall response and complete response rates by independent review committee in the diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) expansion cohort (treated with epcoritamab 48 mg s.c.) were 55.6% and 44.4%, respectively, and the median duration of response, duration of complete response, and overall survival were not reached at the time of data cutoff; the safety profile was manageable. Results support the ongoing clinical evaluation of epcoritamab in Japanese patients with R/R DLBCL and in earlier treatment lines.
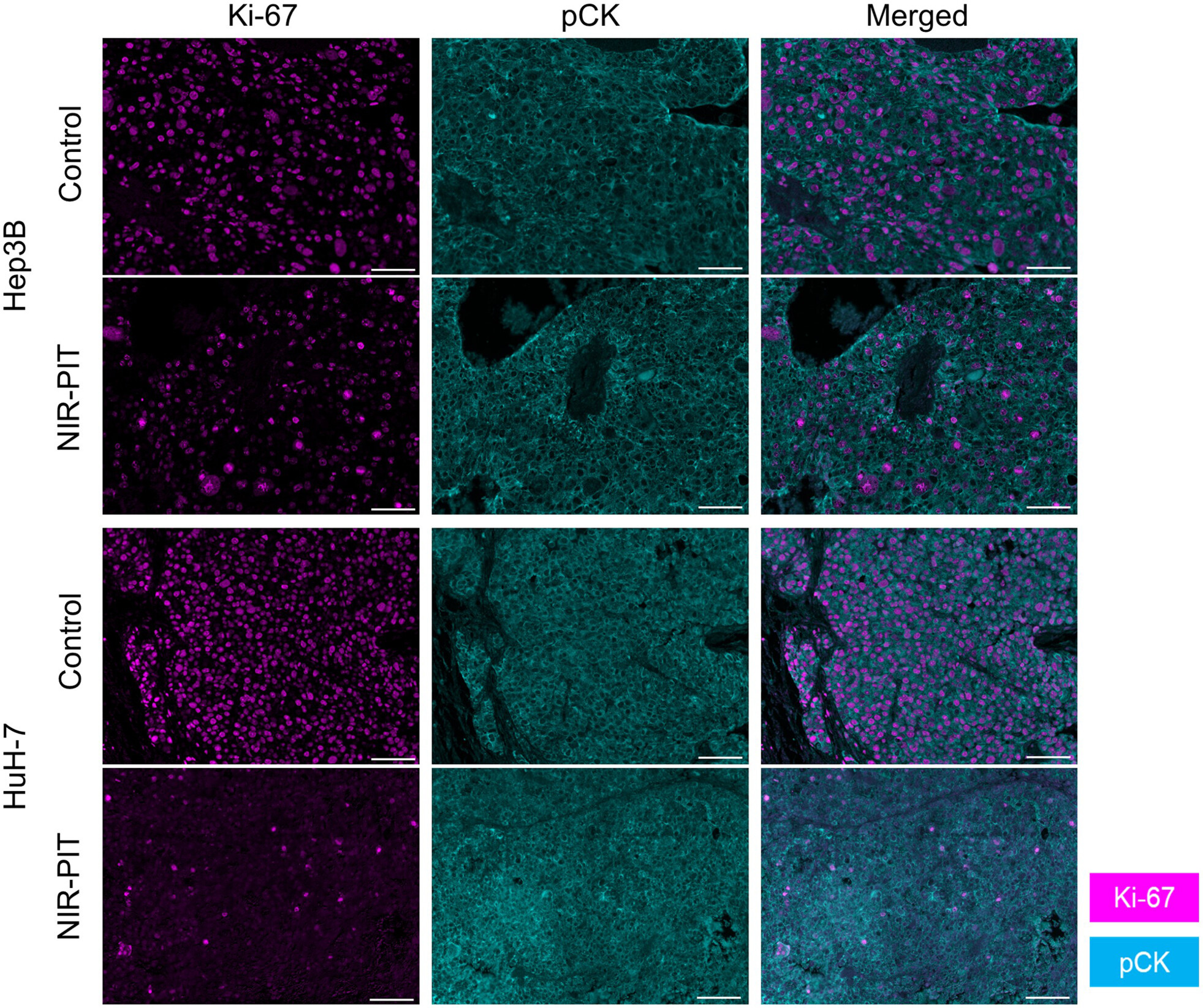
Near-infrared photoimmunotherapy in the models of hepatocellular carcinomas using cetuximab-IR700
- Pages: 4654-4663
- First Published: 10 October 2023
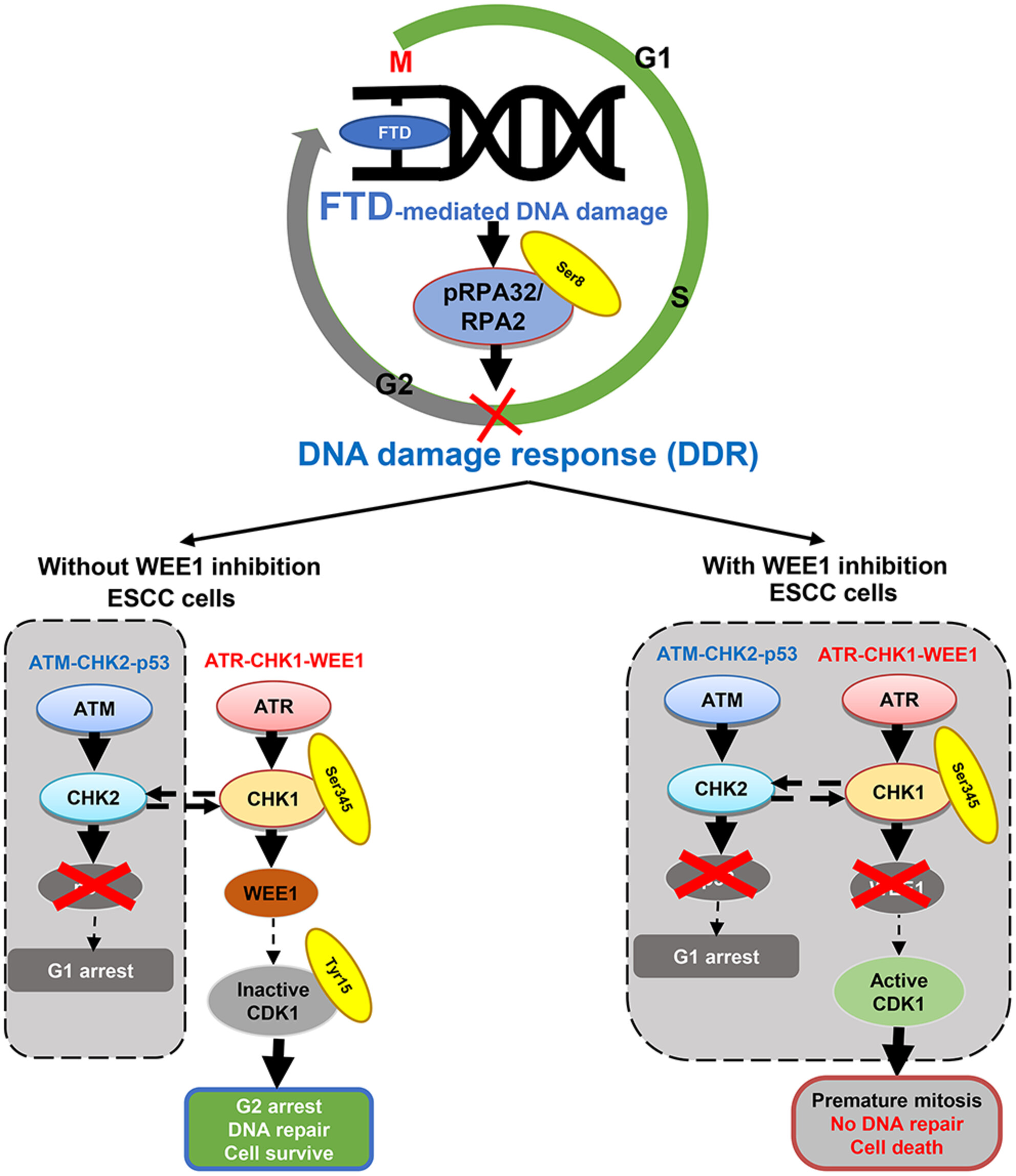
Combination therapy with WEE1 inhibition and trifluridine/tipiracil against esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- Pages: 4664-4676
- First Published: 19 September 2023
Head-to-head comparison of three chelates reveals DOTAGA promising for 225Ac labeling of anti-FZD10 antibody OTSA101
- Pages: 4677-4690
- First Published: 02 October 2023
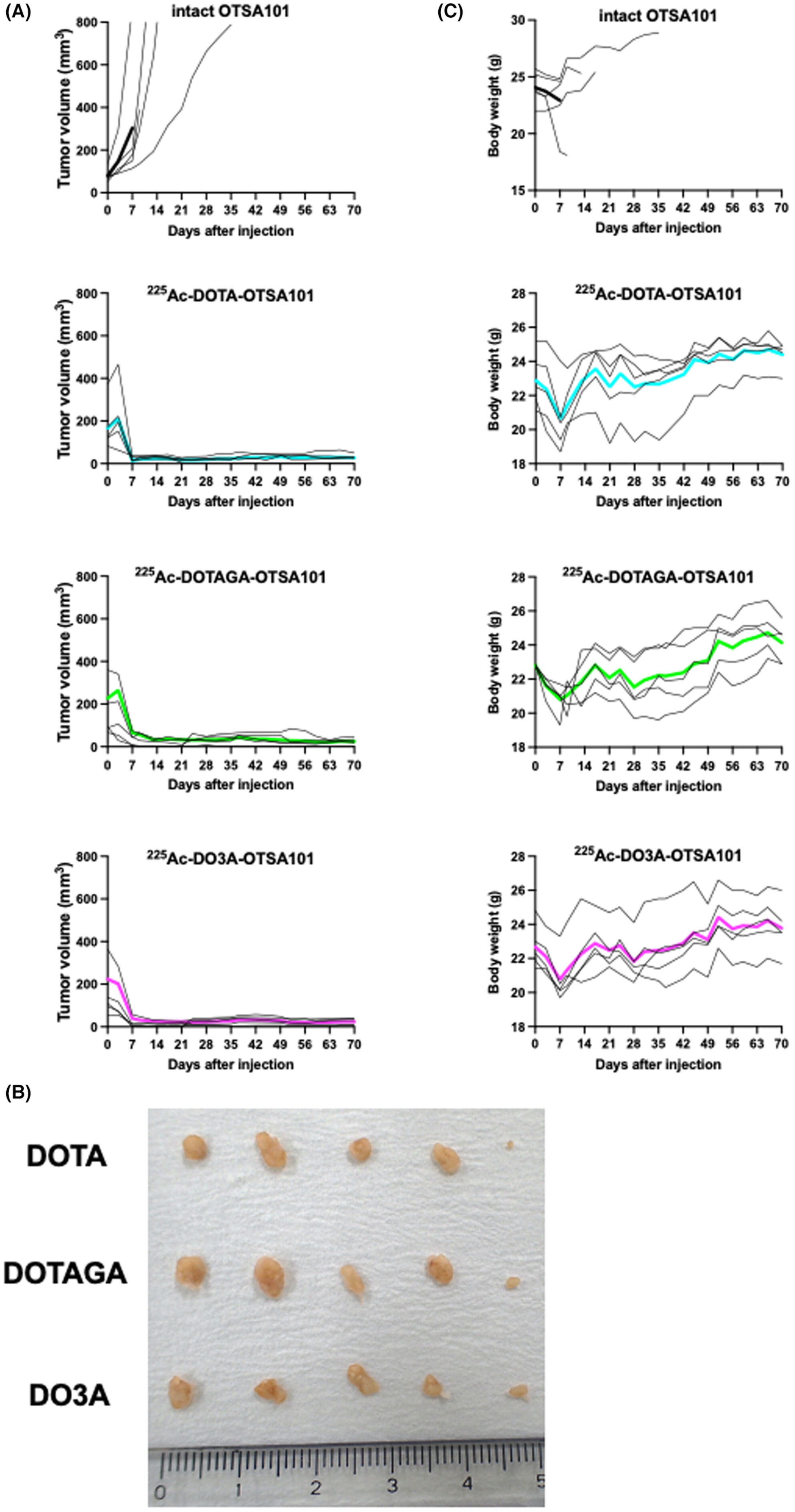
A direct comparison of three bifunctional chelates, p-SCN-Bn-DOTA, p-SCN-Bn-DOTAGA, and DO3A-NHS-ester demonstrated that DOTAGA would be the most promising chelate to produce 225Ac-labeled OTSA101 with high binding affinity and high labeling efficiency and to provide high absorbed doses to tumors and limited ones to bone marrow.
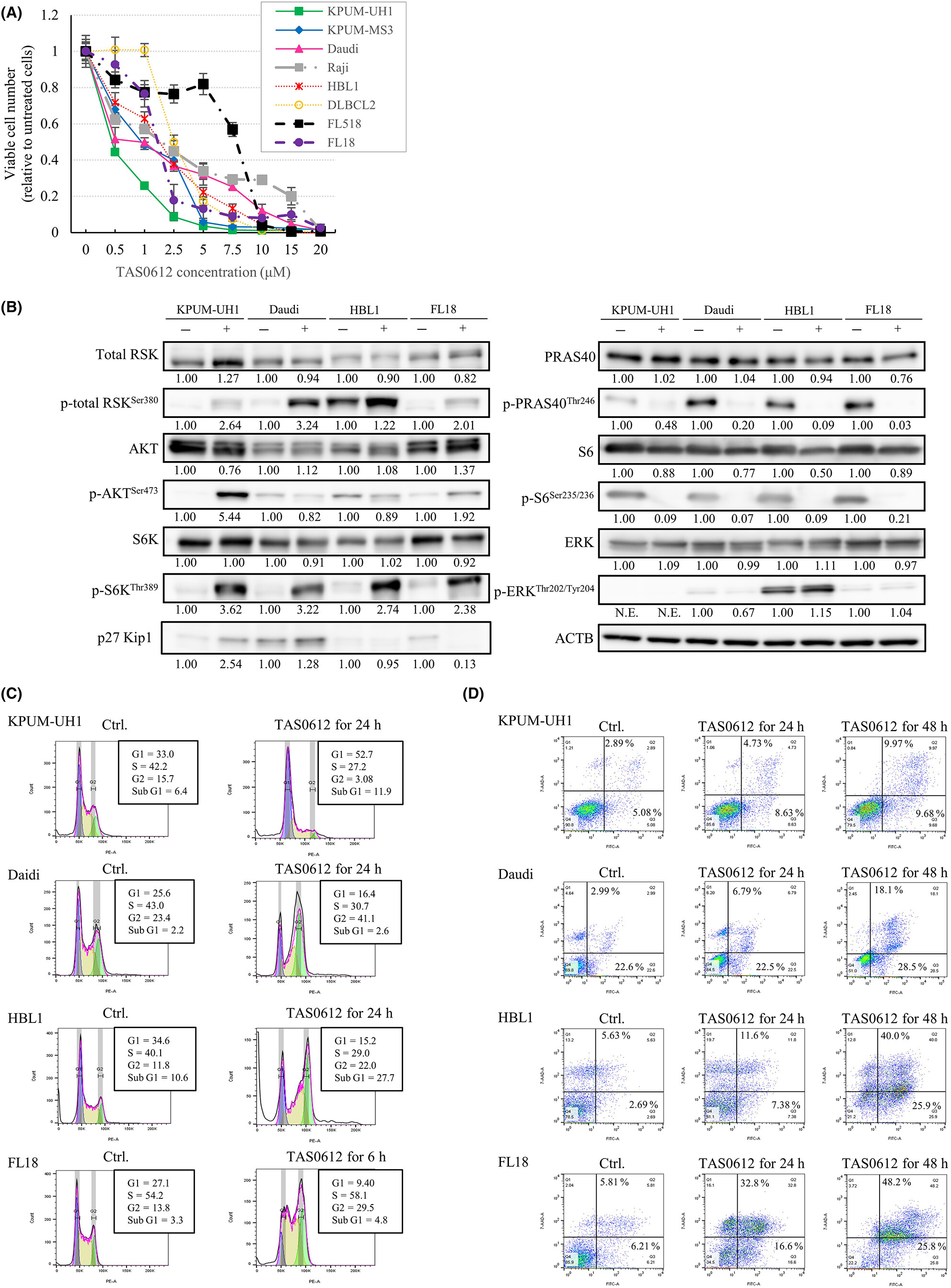
Triple targeting of RSK, AKT, and S6K as pivotal downstream effectors of PDPK1 by TAS0612 in B-cell lymphomas
- Pages: 4691-4705
- First Published: 15 October 2023
Evaluating the effect of childhood sunburn on the risk of cutaneous melanoma through Mendelian randomization
- Pages: 4706-4716
- First Published: 26 September 2023
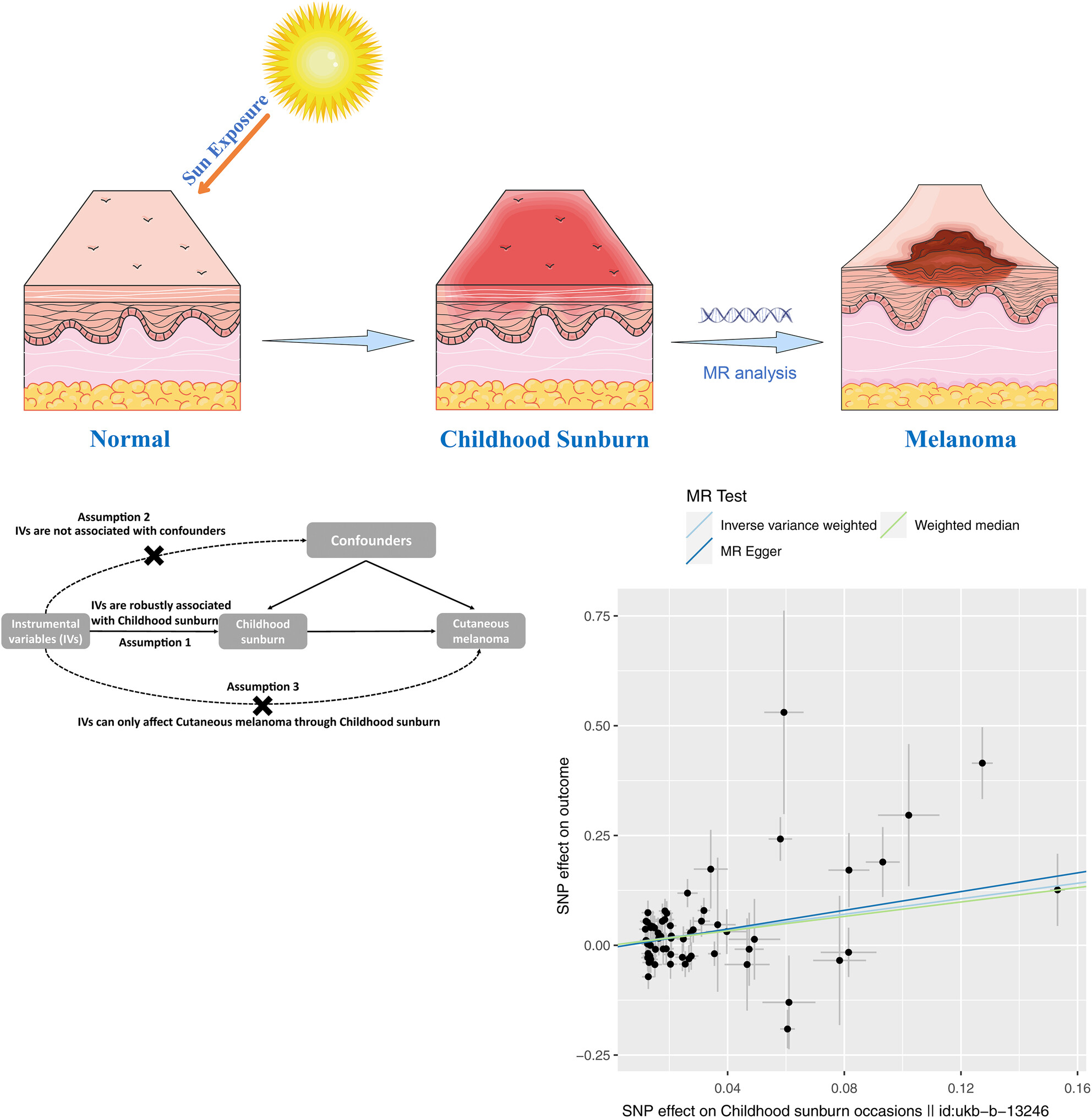
This article explores the potential causal relationship between childhood sunburn and the risk of melanoma through a Mendelian randomization design. The results suggest a positive correlation between genetically predicted childhood sunburn and the risk of melanoma. Therefore, this study provides potential evidence linking childhood sunburn to melanoma and suggests that individuals with a history of childhood sunburn should be more vigilant in preventing melanoma.
Gut microbiome as a biomarker for predicting early recurrence of HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma
- Pages: 4717-4731
- First Published: 01 October 2023
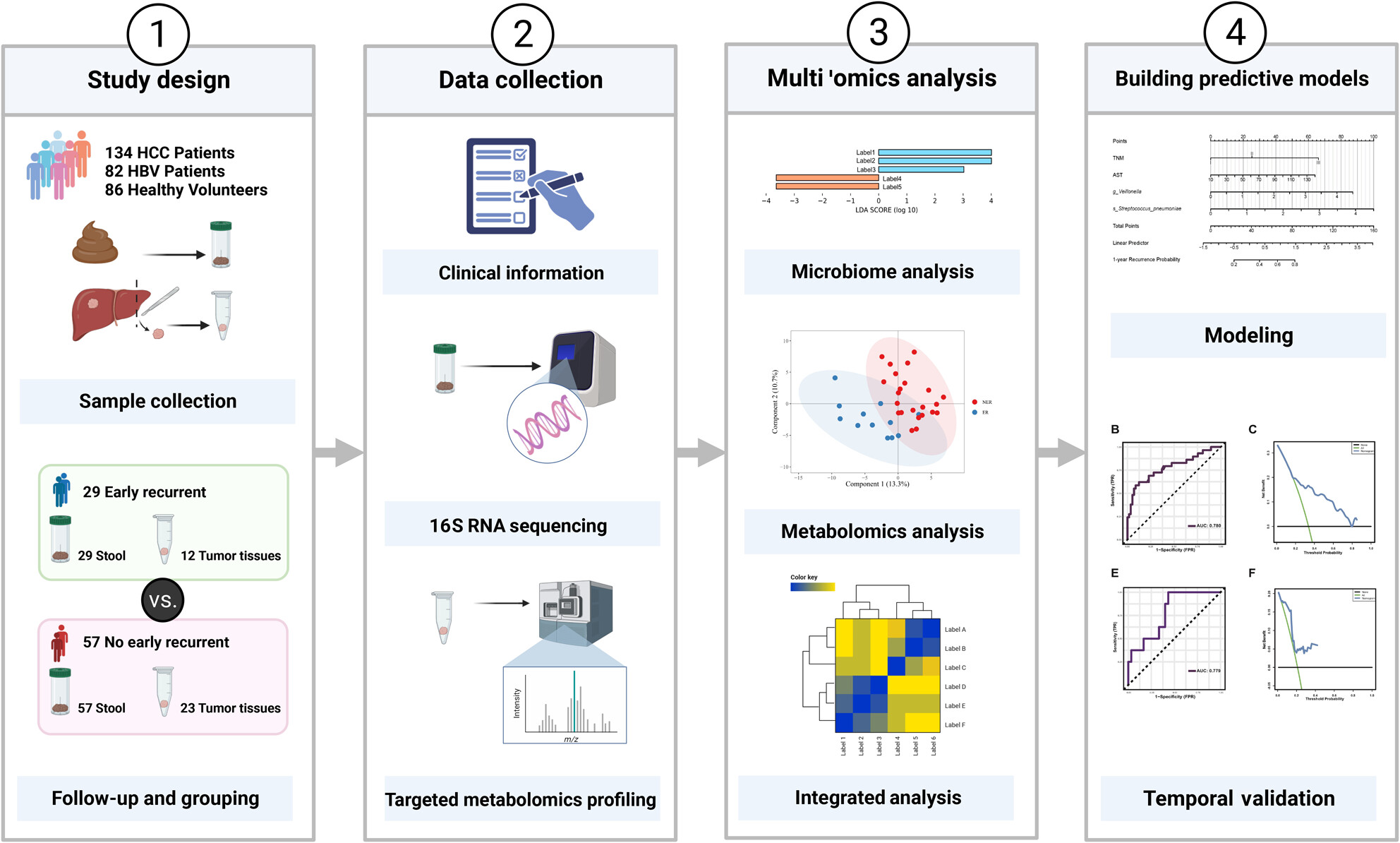
The study aimed to investigate the gut microbiome as a biomarker for predicting the early recurrence of HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and explore the gut microbial–liver-metabolite axis. The research found that specific microbial species and metabolites were associated with the early recurrence of HCC and proposed a prediction model based on the gut microbiome. The study highlights the potential of gut microbes as effective biomarkers and provides insights into the potential mechanism by which gut microbes promote the early recurrence of HCC.
Single-cell transcriptomic analysis of gingivo-buccal oral cancer reveals two dominant cellular programs
- Pages: 4732-4746
- First Published: 04 October 2023
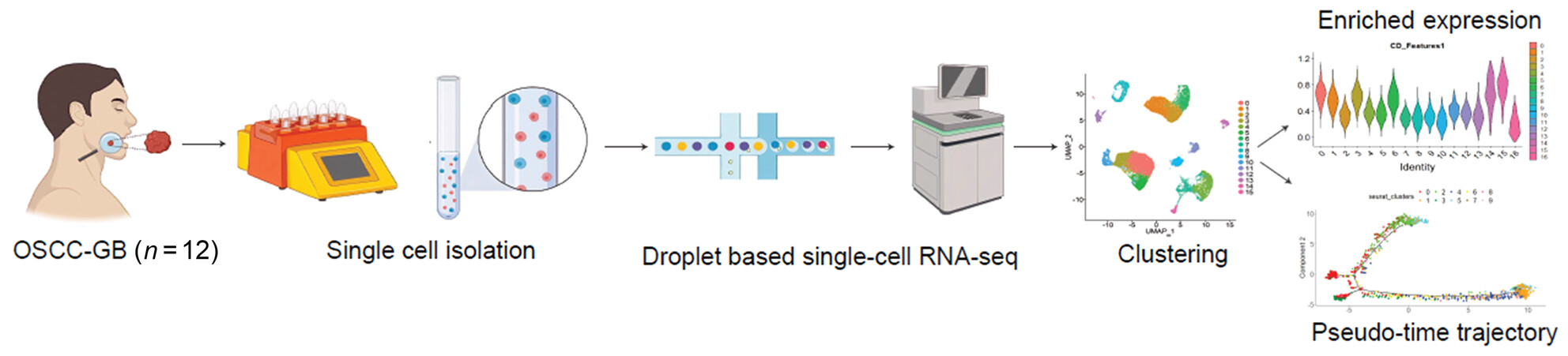
This is the first report of intratumor cellular heterogeneity at the single-cell level in gingivo-buccal oral cancer (OSCC-GB). Some unique malignant cell types were found when a precancerous lesion, oral submucous fibrosis, was concomitantly present with frank cancer (OSCC-GB). Malignant cell populations shared between tumors exhibited partial epithelial–mesenchymal transition or were enriched with fetal cell-type signatures. Double negative PLCG2+ T cells and intermediate M1–M2 macrophage polarization were also detected.
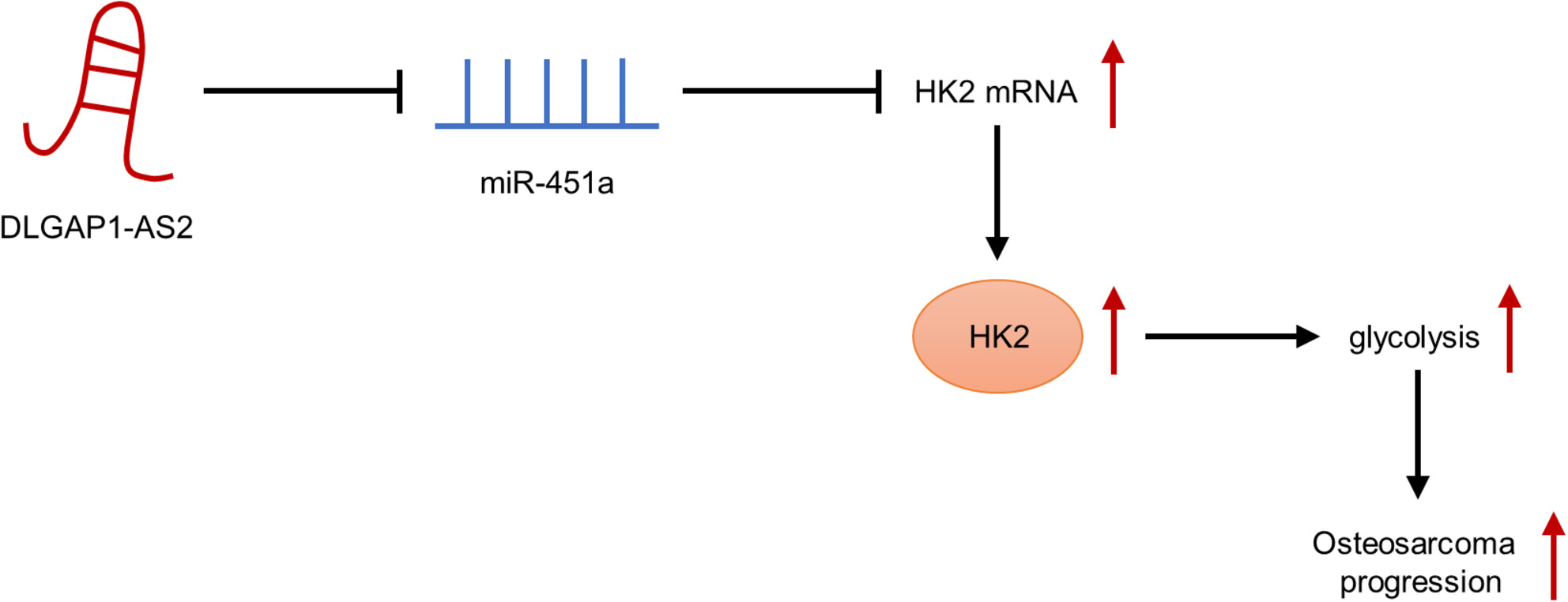
The knockdown of lncRNA DLGAP1-AS2 suppresses osteosarcoma progression by inhibiting aerobic glycolysis via the miR-451a/HK2 axis
- Pages: 4747-4762
- First Published: 10 October 2023
REPORT
EpCAM and APN expression in combination with γ-H2AX as biomarkers for detecting hepatocarcinogens in rats
- Pages: 4763-4769
- First Published: 19 October 2023
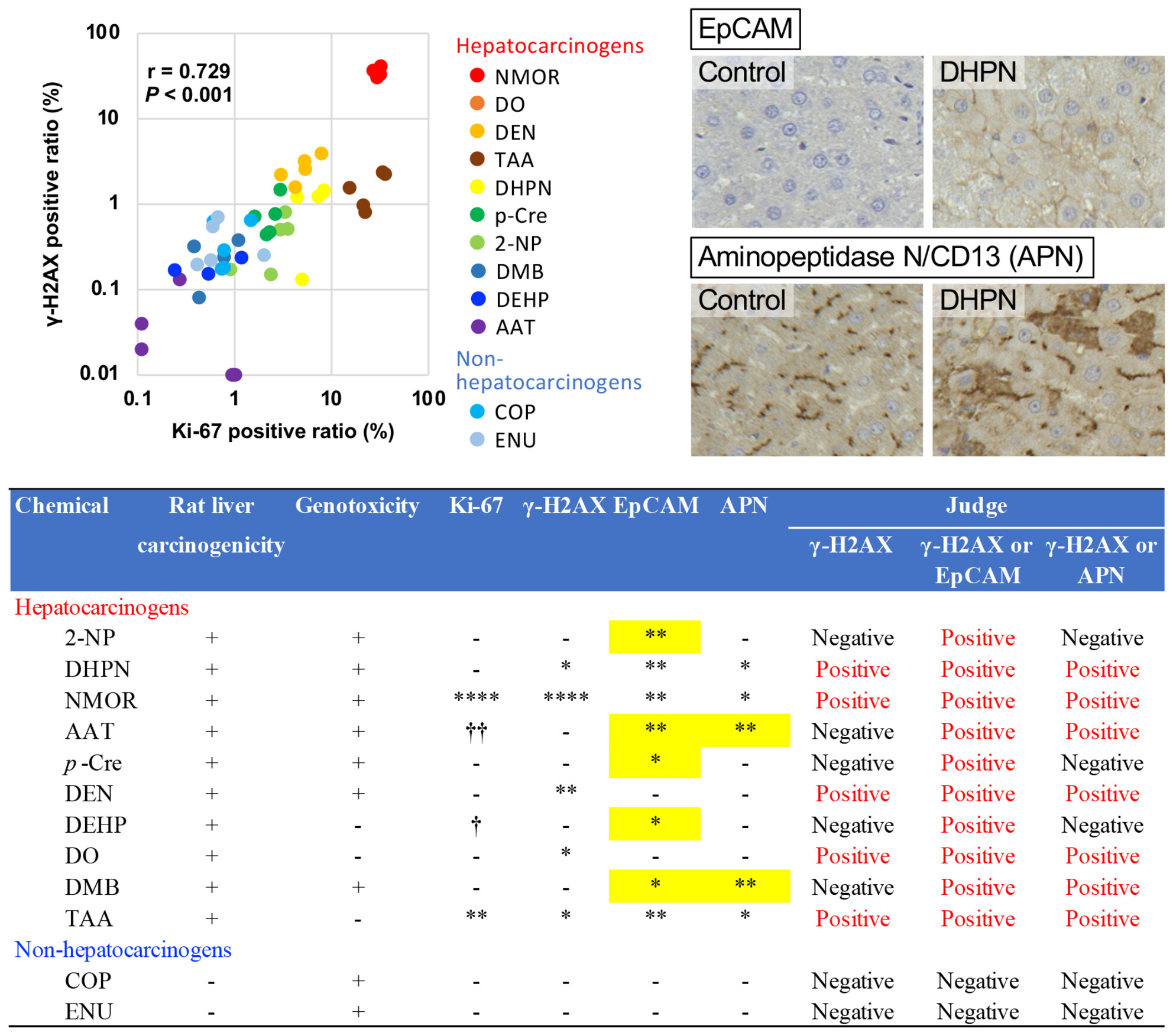
The phosphorylated form of histone H2AX (γ-H2AX) was a reliable biomarker for detecting bladder carcinogens in rats. However, it was not effective for hepatocarcinogens that did not stimulate hepatocyte proliferation. Increases in epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM/CD326)- and aminopeptidase N (APN/CD13)-positive hepatocytes were observed in rat hepatocytes exposed to various hepatocarcinogens, suggesting the potential of EpCAM and APN as complementary biomarkers with γ-H2AX for detecting chemical hepatocarcinogenicity.
LIST OF REVIEWERS
CORRECTION
Correction to Brigatinib in Japanese patients with ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: Final results of the phase 2 J-ALTA trial
- Pages: 4776-4777
- First Published: 10 December 2023