Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
Issue Information
- Pages: 373-375
- First Published: 15 April 2016

Cover of this issue. Uptake of extracellar vesicles by endothelial cell. See also Fujita, Y., et al. (pages 385–390 of this issue).
IN THIS ISSUE
REVIEW ARTICLES
Dysregulation of protein methyltransferases in human cancer: An emerging target class for anticancer therapy
- Pages: 377-384
- First Published: 11 January 2016
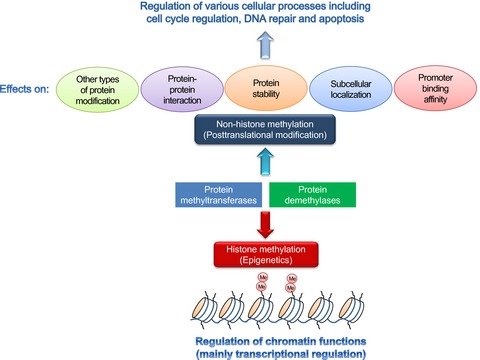
Although protein methylation was found around a half-century ago, biological and physiological functions of protein methylation remained unknown for a long time. In the 21st century, we and other researchers characterized a number of protein methyltransferases and elucidated their functions, in particular focusing on their epigenetic regulation through histone methylation. Now, protein methyltransferases are attracting considerable attention as new targets for development of anticancer therapy.
Extracellular vesicle transfer of cancer pathogenic components
- Pages: 385-390
- First Published: 21 January 2016
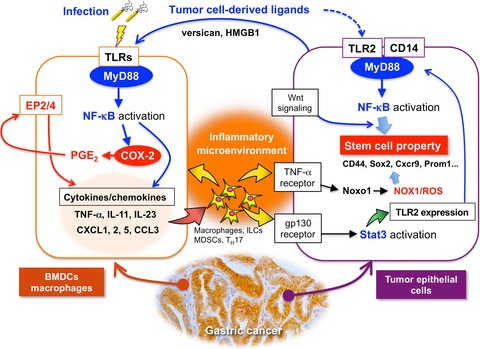
Inflammation in gastric cancer: Interplay of the COX-2/prostaglandin E2 and Toll-like receptor/MyD88 pathways
- Pages: 391-397
- First Published: 01 February 2016
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
BASIC AND CLINICAL IMMUNOLOGY
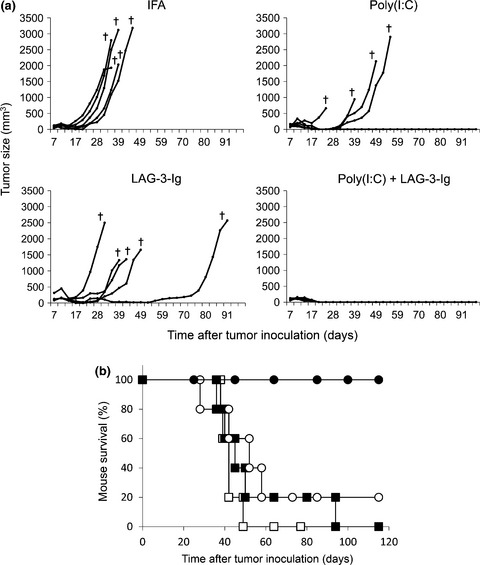
Combined adjuvants of poly(I:C) plus LAG-3-Ig improve antitumor effects of tumor-specific T cells, preventing their exhaustion
- Pages: 398-406
- First Published: 15 April 2016
CARCINOGENESIS
Elevated hepatocyte growth factor expression as an autocrine c-Met activation mechanism in acquired resistance to sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma cells
- Pages: 407-416
- First Published: 20 January 2016
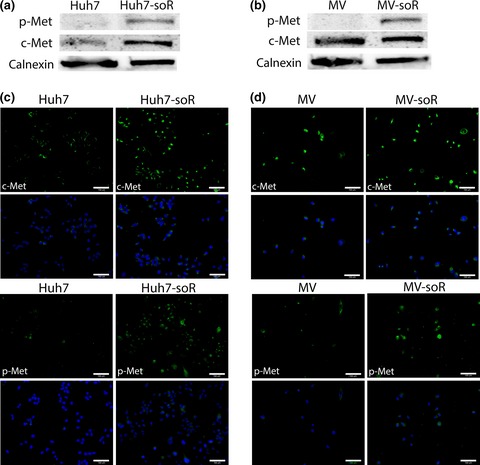
In this study, we demonstrate that long-term sorafenib treatment induces autocrine HGF secretion and activates c-Met signaling. Moreover, our findings suggest that dual inhibition of HGF and c-Met kinase in the resistant cells is more potent to restore sorafenib sensitivity than single inhibitions alone. Our data is the first demonstration of autocrine HGF/c-Met signaling in sorafenib resistant HCC cells and provide a novel strategy for the design of second-line treatments after sorafenib failure.
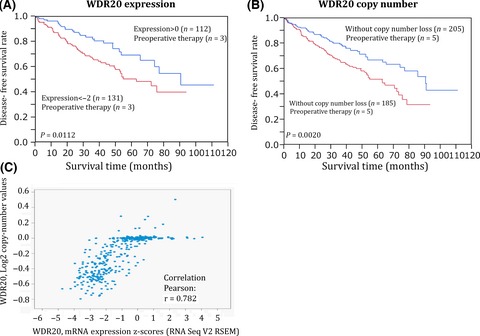
Downregulation of WDR20 due to loss of 14q is involved in the malignant transformation of clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- Pages: 417-423
- First Published: 20 January 2016
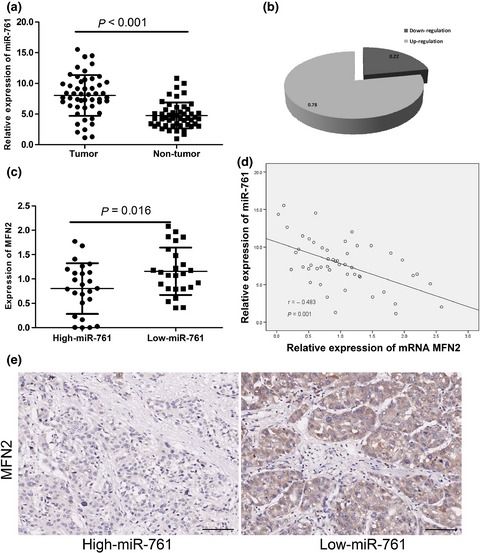
MicroRNA-761 is upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and regulates tumorigenesis by targeting Mitofusin-2
- Pages: 424-432
- First Published: 04 February 2016
CELL, MOLECULAR, AND STEM CELL BIOLOGY
ADAM23 is downregulated in side population and suppresses lung metastasis of lung carcinoma cells
- Pages: 433-443
- First Published: 22 January 2016
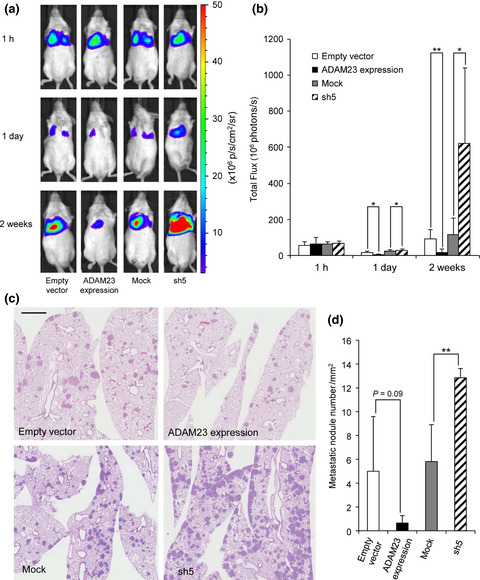
Lung metastasis after intravascular injection of A549 lung adenocarcinoma cells with different ADAM23 expression levels into NOD/SCID mice was determined by bioluminescence imaging and histological examination of the whole lungs. As shown in this figure, the metastasis was inhibited at two weeks in the mouse group received ADAM23-overexpressing cells and enhanced in that of ADAM23-knockdown cells.
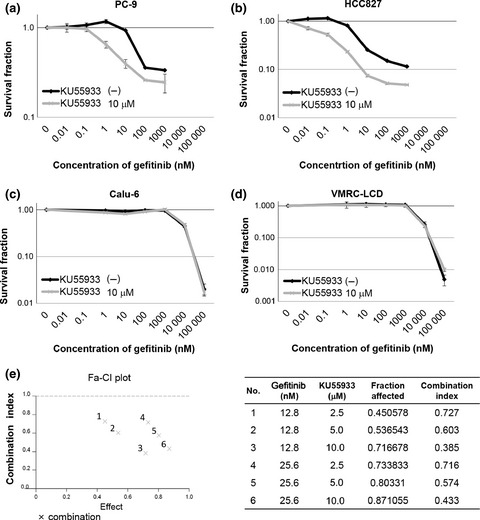
Enhanced gefitinib-induced repression of the epidermal growth factor receptor pathway by ataxia telangiectasia-mutated kinase inhibition in non-small-cell lung cancer cells
- Pages: 444-451
- First Published: 30 January 2016
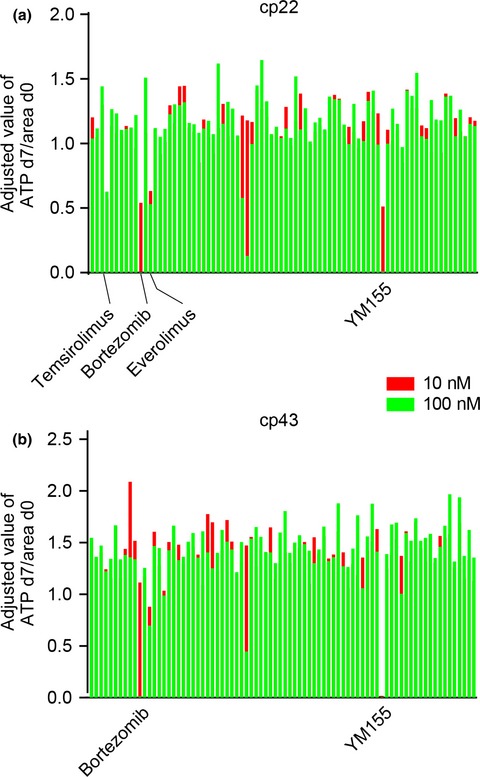
Drug screening and grouping by sensitivity with a panel of primary cultured cancer spheroids derived from endometrial cancer
- Pages: 452-460
- First Published: 30 January 2016
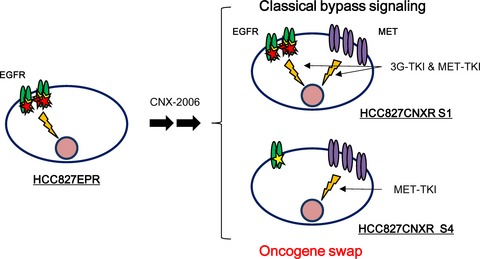
Oncogene swap as a novel mechanism of acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor in lung cancer
- Pages: 461-468
- First Published: 04 February 2016
CLINICAL RESEARCH
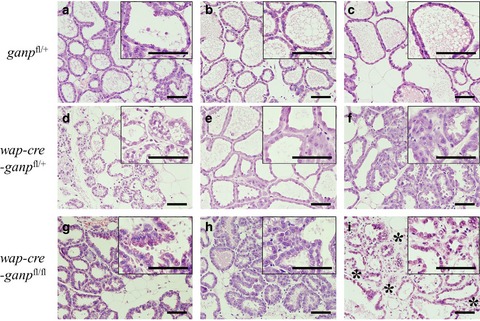
GANP protein encoded on human chromosome 21/mouse chromosome 10 is associated with resistance to mammary tumor development
- Pages: 469-477
- First Published: 09 January 2016
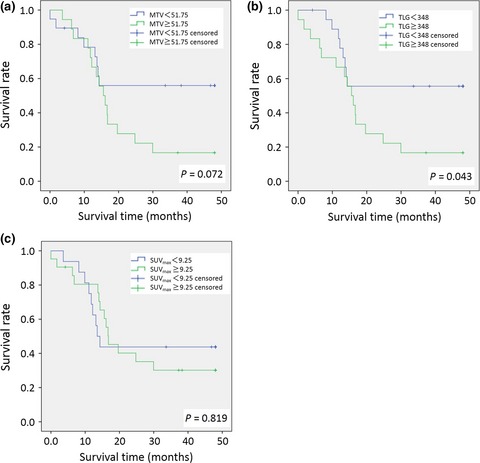
Metabolic tumor burden predicts prognosis of ovarian cancer patients who receive platinum-based adjuvant chemotherapy
- Pages: 478-485
- First Published: 20 January 2016
Nimotuzumab plus paclitaxel and cisplatin as the first line treatment for advanced esophageal squamous cell cancer: A single centre prospective phase II trial
- Pages: 486-490
- First Published: 21 January 2016
Fibroblast growth factor receptor-1 protein expression is associated with prognosis in estrogen receptor-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor-2-negative primary breast cancer
- Pages: 491-498
- First Published: 23 January 2016
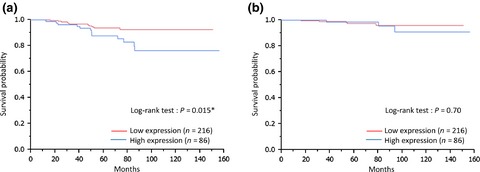
This is the first study to analyze gene copy number aberration, mRNA expression, and protein expression of FGFR1, and the correlation of each parameter with breast cancer characteristics. The expression level of FGFR1 protein may be an independent prognostic factor in terms of relapse free survival for ER-positive/HER2-negative primary breast cancer patients.
Preclinical and first-in-human phase I studies of KW-2450, an oral tyrosine kinase inhibitor with insulin-like growth factor receptor-1/insulin receptor selectivity
- Pages: 499-506
- First Published: 06 February 2016
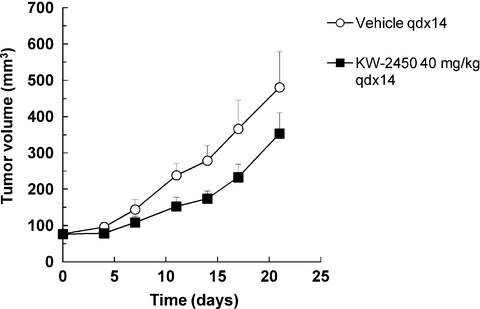
We summarize pre-clinical studies and the first-in-human study of KW-2450, an oral tyrosine kinase inhibitor with insulin-like growth factor receptor-1 and insulin receptor inhibitory activity. Single-agent KW-2450 was associated with modest antitumor activity in heavily pre-treated patients with solid tumors and is being further investigated in combination therapy with lapatinib/letrozole in patients with HER2-postive metastatic breast cancer.
DRUG DISCOVERY AND DELIVERY
Metformin inhibits the prometastatic effect of sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma by upregulating the expression of TIP30
- Pages: 507-513
- First Published: 11 January 2016
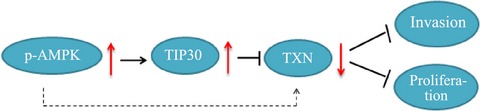
Our study is conducted to evaluate whether the combination of sorafenib and metformin is sufficient to revert the expression of TIP30, by which reducing the lung metastasis and improving the survival simultaneously. Our data show that the combination of sorafenib and metformin inhibits proliferation and invasion in vitro, prolongs the median survival and reduces lung metastasis of HCC in vivo. This effect is closely associated with the up-regulation of TIP30, partly through activating AMPK.
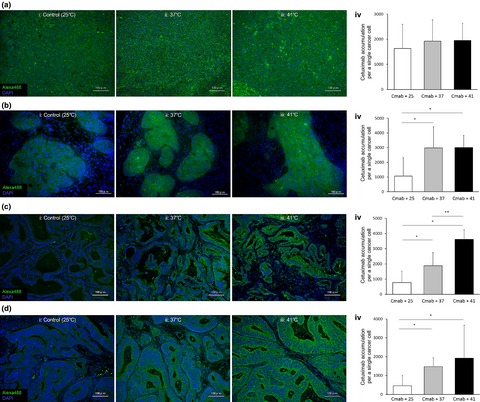
Cetuximab delivery and antitumor effects are enhanced by mild hyperthermia in a xenograft mouse model of pancreatic cancer
- Pages: 514-520
- First Published: 19 January 2016
EPIDEMIOLOGY AND PREVENTION
Burden of cancer associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Japan, 2010–2030
- Pages: 521-527
- First Published: 01 February 2016
This study provides the first comprehensive evidence on the current and future burden of cancer associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Between 2010 and 2030, the incident cancer cases associated with type 2 diabetes were found to increase constantly over time, particularly in liver, pancreas and colon in Japan. Given the prolonged life expectancy in Japan, increase in people living with type 2 diabetes and subsequent cancer will be a public health issue in the years to come.
GENETICS, GENOMICS, AND PROTEOMICS
Exome-wide single-base substitutions in tissues and derived cell lines of the constitutive Fhit knockout mouse
- Pages: 528-535
- First Published: 19 January 2016
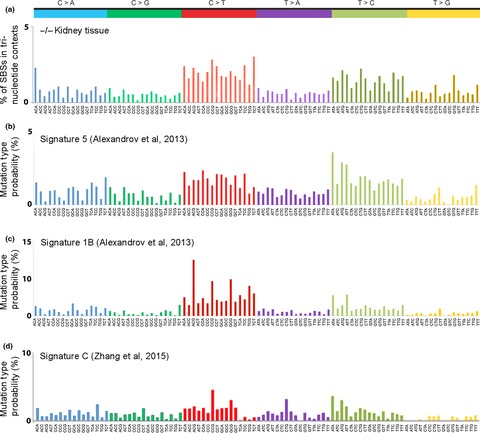
Due to absence of Fhit genome caretaker function, Fhit knockout mouse cells develop aneuploidy, allele copy number losses and −/− tissues develop >1000 single-base substitutions in the 2% of the genome included in exomes. The mutation signature is characterized by increased C>T and T>C mutations, similar to the “age at diagnosis” signature identified in human cancers. The increase in T>C mutations in −/− exomes may be due to thymidine triphosphate imbalance, resulting from decreased expression of Thymidine Kinase 1 in Fhit-deficient cells.
PATHOLOGY
Significant intratumoral heterogeneity of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 status in gastric cancer: A comparative study of immunohistochemistry, FISH, and dual-color in situ hybridization
- Pages: 536-542
- First Published: 11 January 2016
This study demonstrated that HER2 assessment in biopsy tissues may predict the HER2 status of the whole tumor by IHC, FISH, and DISH. However, some cases of discordance may occur because of intratumoral HER2 heterogeneity in gastric cancers. In cases of intratumoral heterogeneity, more accurate HER2 assessment can be achieved by analysis of whole sections and by using a combination of IHC and DISH, if possible.
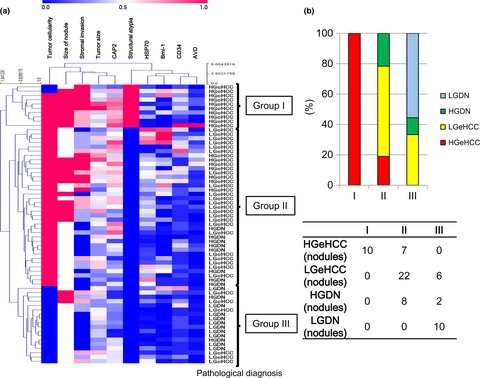
Early hepatocellular carcinoma with high-grade atypia in small vaguely nodular lesions
- Pages: 543-550
- First Published: 21 January 2016
REPORT
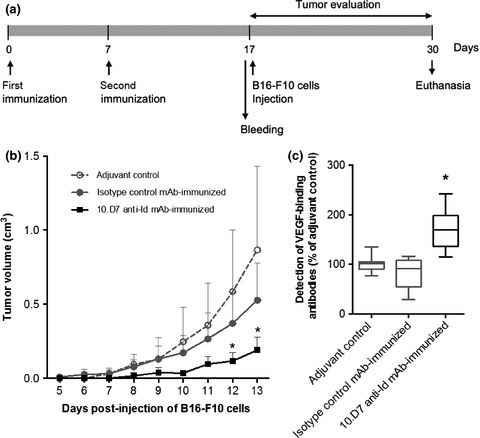
Anti-bevacizumab idiotype antibody vaccination is effective in inducing vascular endothelial growth factor-binding response, impairing tumor outgrowth
- Pages: 551-555
- First Published: 15 April 2016
MEETING REPORT
UICC International Session: What are the implications of sharing the concept of Universal Health Coverage for cancer in Asia?
- Pages: 556-563
- First Published: 15 April 2016
The Japan National Committee for the Union for International Cancer Control (UICC) and UICC-Asia Regional Office (ARO) organized an international session as part of the official program of the 74th Annual Meeting of the Japanese Cancer Association to discuss the topic “What are the implications of sharing the concept of Universal Health Coverage for cancer in Asia?” The presenters and participants discussed the growing cost of cancer in the Asian region and the challenges that this poses to the establishment and deployment of UHC in the countries of Asia, all of which face budgetary and other systemic constraints in tackling and controlling cancer in the region.